The Role of Game-Based Learning in Experiential Education: Tool Validation, Motivation Assessment, and Outcomes Evaluation among a Sample of Pharmacy Students
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Setting
2.2. Educational Setting and Procedures
2.3. Game-Based Learning Activities
2.4. Variables and Outcomes
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics of Students
3.2. Learning Outcomes
3.3. Active Learning Motivation Assessment Scale (ALMAS)
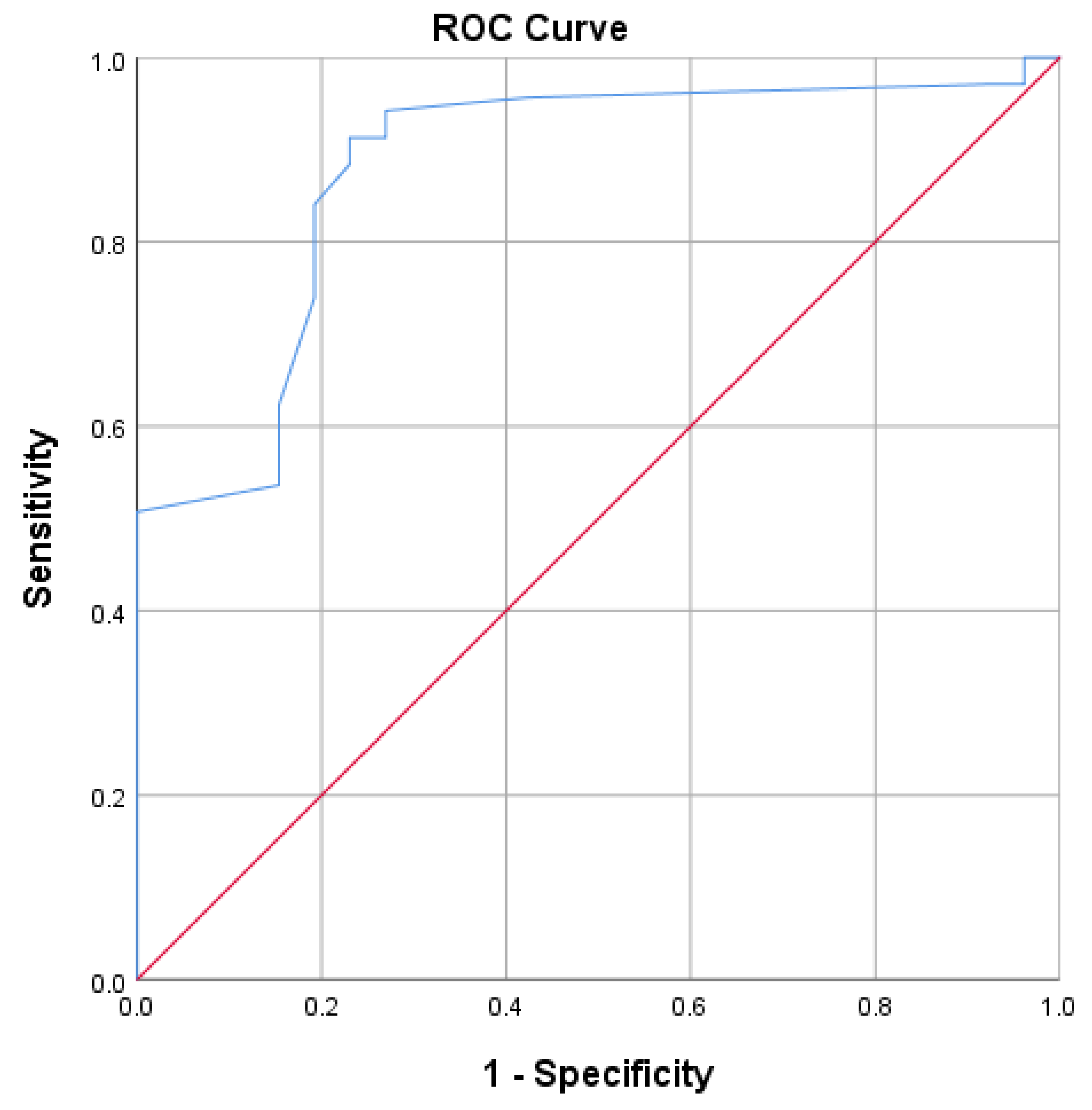
3.3.1. Factor Analysis
3.3.2. Reliability and Validity Measures
3.4. Motivation and Learning Outcomes
4. Discussion
Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Deterding, S.; Dixon, D.; Khaled, R.; Nacke, L. From Game Design Elements to Gamefulness: Defining “Gamification”. In Proceedings of the 15th International Academic MindTrek Conference: Envisioning Future Media Environments, Tampere, Finland, 28–30 September 2011; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 9–15. [Google Scholar]
- Sera, L.; Wheeler, E. Game on: The Gamification of the Pharmacy Classroom. Curr. Pharm. Teach. Learn. 2017, 9, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zichermann, G.; Cunningham, C. Gamification by Design: Implementing Game Mechanics in Web and Mobile Apps; O’Reilly Media, Inc.: Sebastopol, CA, USA, 2011; ISBN 978-1-4493-9767-8. [Google Scholar]
- Abdul Jabbar, A.I.; Felicia, P. Gameplay Engagement and Learning in Game-Based Learning: A Systematic Review. Rev. Educ. Res. 2015, 85, 740–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabricatore, C. Gameplay and game mechanics design: A key to quality in videogames. In Proceedings of the ENLACES (MINEDUC Chile)—OECD Expert Meeting on Videogames and Education, Santiago de Chile, Chile, 29–31 October 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Hull, D.C.; Williams, G.A.; Griffiths, M.D. Video Game Characteristics, Happiness and Flow as Predictors of Addiction among Video Game Players: A Pilot Study. J. Behav. Addict. 2013, 2, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brangier, E.; Marache-Francisco, C. Measure of the Lived and Functional Effects of Gamification: An Experimental Study in a Professional Context. In Proceedings of the Advances in Ergonomics in Design, San Diego, CA, USA, 16–20 July 2020; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 242–253. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.-H.; Liu, J.-H.; Shou, W.-C. How Competition in a Game-Based Science Learning Environment Influences Students’ Learning Achievement, Flow Experience, and Learning Behavioral Patterns. J. Educ. Technol. Soc. 2018, 21, 164–176. [Google Scholar]
- Taguchi, N. The Routledge Handbook of Second Language Acquisition and Pragmatics; Routledge: London, UK, 2019; ISBN 978-1-351-16406-1. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, S.; Hew, K.F.; Huang, B. Does Gamification Improve Student Learning Outcome? Evidence from a Meta-Analysis and Synthesis of Qualitative Data in Educational Contexts. Educ. Res. Rev. 2020, 30, 100322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltahir, M.E.; Alsalhi, N.R.; Al-Qatawneh, S.; AlQudah, H.A.; Jaradat, M. The Impact of Game-Based Learning (GBL) on Students’ Motivation, Engagement and Academic Performance on an Arabic Language Grammar Course in Higher Education. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2021, 26, 3251–3278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koivisto, J.; Hamari, J. The Rise of Motivational Information Systems: A Review of Gamification Research. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2019, 45, 191–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marín, B.; Frez, J.; Cruz-Lemus, J.; Genero, M. An Empirical Investigation on the Benefits of Gamification in Programming Courses. ACM Trans. Comput. Educ. 2018, 19, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sailer, M.; Homner, L. The Gamification of Learning: A Meta-Analysis. Educ. Psychol. Rev. 2020, 32, 77–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rachels, J.R.; Rockinson-Szapkiw, A.J. The Effects of a Mobile Gamification App on Elementary Students’ Spanish Achievement and Self-Efficacy. Comput. Assist. Lang. Learn. 2018, 31, 72–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De-Marcos, L.; Domínguez, A.; Saenz-de-Navarrete, J.; Pagés, C. An Empirical Study Comparing Gamification and Social Networking on E-Learning. Comput. Educ. 2014, 75, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Tlili, A.; Li, J.; Jiang, F.; Shi, G.; Yu, H.; Yang, J. How to Implement Game-Based Learning in a Smart Classroom? A Model Based on a Systematic Literature Review and Delphi Method. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 749837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zheng, X. Using Game-Based Learning to Support Learning Science: A Study with Middle School Students. Asia-Pac. Educ. Res. 2021, 30, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.-H.; Lu, B.-C. Towards the Successful Game-Based Learning: Detection and Feedback to Misconceptions Is the Key. Comput. Educ. 2021, 160, 104033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadolny, L.; Valai, A.; Cherrez, N.J.; Elrick, D.; Lovett, A.; Nowatzke, M. Examining the Characteristics of Game-Based Learning: A Content Analysis and Design Framework. Comput. Educ. 2020, 156, 103936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perini, S.; Luglietti, R.; Margoudi, M.; Oliveira, M.; Taisch, M. Learning and Motivational Effects of Digital Game-Based Learning (DGBL) for Manufacturing Education—The Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) Game. Comput. Ind. 2018, 102, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taub, M.; Sawyer, R.; Smith, A.; Rowe, J.; Azevedo, R.; Lester, J. The Agency Effect: The Impact of Student Agency on Learning, Emotions, and Problem-Solving Behaviors in a Game-Based Learning Environment. Comput. Educ. 2020, 147, 103781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.K.; Oyelere, S.S. Contextualized Mobile Game-Based Learning Application for Computing Education. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2021, 26, 2539–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batson, L.; Feinberg, S. Game Designs That Enhance Motivation and Learning for Teenagers. Electron. J. Integr. Technol. Educ. 2006, 5, 34–43. [Google Scholar]
- Kalogiannakis, M.; Papadakis, S.; Zourmpakis, A.-I. Gamification in Science Education. A Systematic Review of the Literature. Educ. Sci. 2021, 11, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagušt, T.; Botički, I.; So, H.-J. Examining Competitive, Collaborative and Adaptive Gamification in Young Learners’ Math Learning. Comput. Educ. 2018, 125, 444–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De-Marcos, L.; García-Cabot, A.; García, E. Towards the Social Gamification of E-Learning: A Practical Experiment. Int. J. Eng. Educ. 2017, 33, 66–73. [Google Scholar]
- Fuster-Guilló, A.; Pertegal-Felices, M.L.; Jimeno-Morenilla, A.; Azorín-López, J.; Rico-Soliveres, M.L.; Restrepo-Calle, F. Evaluating Impact on Motivation and Academic Performance of a Game-Based Learning Experience Using Kahoot. Front. Psychol. 2019, 10, 2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Unimed. Digihealth, Innovative Digital Skills & Teaching Methods 4 Effective Health Education in Lebanon & Syria. Available online: https://www.uni-med.net/progetti/digihealth/ (accessed on 6 June 2022).
- ACPE Standards. Available online: https://www.ahrq.gov/health-literacy/professional-training/pharmacy/app-2.html (accessed on 25 May 2022).
- Oestreich, J.H.; Guy, J.W. Game-Based Learning in Pharmacy Education. Pharm. J. Pharm. Educ. Pract. 2022, 10, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ee, R.W.X.; Yap, K.Z.; Yap, K.Y.-L. Herbopolis—A Mobile Serious Game to Educate Players on Herbal Medicines. Complement. Ther. Med. 2018, 39, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, J.; Bawab, N.; De Mooij, J.; Sutter Widmer, D.; Szilas, N.; De Vriese, C.; Bugnon, O. An Open Randomized Controlled Study Comparing an Online Text-Based Scenario and a Serious Game by Belgian and Swiss Pharmacy Students. Curr. Pharm. Teach. Learn. 2018, 10, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bindoff, I.; Ling, T.; Bereznicki, L.; Westbury, J.; Chalmers, L.; Peterson, G.; Ollington, R. A Computer Simulation of Community Pharmacy Practice for Educational Use. Am. J. Pharm. Educ. 2014, 78, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Korenoski, A.S.; Ginn, T.R.; Seybert, A.L. Use of an Immersive, Simulated Learning Game to Teach Pharmacy Students Clinical Concepts of Toxicology. Curr. Pharm. Teach. Learn. 2021, 13, 556–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalafalla, F.G.; Alqaysi, R. Blending Team-Based Learning and Game-Based Learning in Pharmacy Education. Curr. Pharm. Teach. Learn. 2021, 13, 992–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cain, J.; Piascik, P. Are Serious Games a Good Strategy for Pharmacy Education? Am. J. Pharm. Educ. 2015, 79, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thompson, M.; Kanmaz, T.; Cheryl, C.; Tanzer, K. Recommendations for Participation in Experiential Education Activities during a National, Regional or Local Crisis 2020. Available online: https://www.acpe-accredit.org/wp-content/uploads/Experiential-Education-ACPE-Proposal-Response-Final.pdf (accessed on 28 May 2022).
- Lucas, C.; Williams, K.; Tudball, J.; Walpola, R.L. Community, Hospital and Industry Preceptor Perceptions of Their Role in Experiential Placements- the Need for Standardization of Preceptor Responsibilities and Evaluations on Students. Curr. Pharm. Teach. Learn. 2018, 10, 1447–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilbur, K.; Wilby, K.J.; Pawluk, S. Pharmacy Preceptor Judgments of Student Performance and Behavior During Experiential Training. Am. J. Pharm. Educ. 2018, 82, 6451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mort, J.R.; Johnson, T.J.; Hedge, D.D. Impact of an Introductory Pharmacy Practice Experience on Students’ Performance in an Advanced Practice Experience. Am. J. Pharm. Educ. 2010, 74, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Al-Azar, M. AUB Study: Gamification Improves Active Learning and Class Engagement in Higher Education 2015. Available online: https://www.aub.edu.lb/communications/media/Documents/feb-15/gamification-highered-EN.pdf (accessed on 28 May 2022).
- Bangalee, V.; Oosthuizen, F.; Perumal-Pillay, V.A.; Suleman, F.; Walters, F. Pharmacy Students Experience with PharmacyPhlash—A Pilot Educational Board Game. Curr. Pharm. Teach. Learn. 2021, 13, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitman, A.C.; Tanzer, K.; Nemec, E.C. Gamifying the Memorization of Brand/Generic Drug Names. Curr. Pharm. Teach. Learn. 2019, 11, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legaki, N.-Z.; Xi, N.; Hamari, J.; Karpouzis, K.; Assimakopoulos, V. The Effect of Challenge-Based Gamification on Learning: An Experiment in the Context of Statistics Education. Int. J. Hum.-Comput. Stud. 2020, 144, 102496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akel, M.E.; Rahal, M.; Dabbous, M.; Mourad, N.; Dimassi, A.; Sakr, F. Experiential Education in Pharmacy Curriculum: The Lebanese International University Model. Pharmacy 2020, 9, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devine, P.S.; Darbishire, P.L. National Trends in IPPE Programs at US Schools of Pharmacy from 2008–2013. Am. J. Pharm. Educ. 2015, 79, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parinyarux, P.; Dhippayom, T.; Wongpoowarak, P.; Kitikannakorn, N. Development of Community Pharmacy Competencies. J. Pharm. Technol. 2022, 38, 875512252210813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Wangenheim, C.G.; Savi, R.; Borgatto, A.F. DELIVER!—An Educational Game for Teaching Earned Value Management in Computing Courses. Inf. Softw. Technol. 2012, 54, 286–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.S.; Tincher, L.; Odeng-Otu, E.; Herdman, M. An Educational Board Game to Assist PharmD Students in Learning Autonomic Nervous System Pharmacology. Am. J. Pharm. Educ. 2015, 79, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lam, J.T.; Gutierrez, M.A.; Goad, J.A.; Odessky, L.; Bock, J. Use of Virtual Games for Interactive Learning in a Pharmacy Curriculum. Curr. Pharm. Teach. Learn. 2019, 11, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.Y.; White, P.J.; Malone, D.T. Online Educational Games Improve the Learning of Cardiac Pharmacology in Undergraduate Pharmacy Teaching. Pharm. Educ. 2018, 18, 298–302. [Google Scholar]
- Tavakol, M.; Dennick, R. Making Sense of Cronbach’s Alpha. Int. J. Med. Educ. 2011, 2, 53–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, J. Using Game Format in Small Group Classes for Pharmacotherapeutics Case Studies. Am. J. Pharm. Educ. 2008, 72, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roche, V.; Alsharif, N.; Ogunbadeniyi, A. Reinforcing the Relevance of Chemistry to the Practice of Pharmacy Through the Who Wants to Be a Med Chem Millionaire? Learning Game. Am. J. Pharm. Educ. 2004, 68, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.; Lynch, L.M.J.; Macias-Moriarity, L.Z. Crossword Puzzles as a Tool to Enhance Learning about Anti-Ulcer Agents. Am. J. Pharm. Educ. 2010, 74, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neef, N.A.; Perrin, C.J.; Haberlin, A.T.; Rodrigues, L.C. Studying as Fun and Games: Effects on College Students’ Quiz Performance. J. Appl. Behav. Anal. 2011, 44, 897–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- da Rocha Seixas, L.; Gomes, A.S.; de Melo Filho, I.J. Effectiveness of Gamification in the Engagement of Students. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2016, 58, 48–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapp, K. The Gamification of Learning and Instruction: Game-Based Methods and Strategies for Training and Education; Pfeiffer: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2012; ISBN 978-1-118-09634-5. [Google Scholar]
- O’Donovan, S.; Gain, J.; Marais, P. A Case study in the gamification of a university-level games development course. In Proceedings of the SAICSIT ’13 South African Institute for Computer Scientists and Information Technologists Conference, East London, South Africa, 7–9 October 2013; p. 251. [Google Scholar]
| Variable | Total Sample N = 233 Mean (SD) or N (%) | Game-Based Learning Group N = 69 (29.6%) Mean (SD) or N (%) | Traditional Learning Group N = 164 (70.4%) Mean (SD) or N (%) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 23.16 (1.82) | 23.49 (2.05) | 23.02 (1.7) | 0.075 |
| Gender Male Female | 70 (30.0) 163 (70.0) | 17 (24.6) 52 (75.4) | 53 (32.3) 111 (67.7) | 0.243 |
| GPA | 3.14 (0.35) | 3.12 (0.40) | 3.14 (0.34) | 0.707 |
| Area of residence Beirut Bekaa Mount Lebanon North of Lebanon South of Lebanon | 84 (36.1) 50 (21.5) 32 (13.7) 26 (11.2) 41 (17.6) | 31 (44.9) 13 (18.8) 8 (11.6) 7 (10.1) 10 (14.5) | 53 (32.3) 37 (22.6) 24 (14.6) 19 (11.6) 31 (18.9) | 0.492 |
| Pre-game-based-learning averages Total average Averages of domains Foundational knowledge Pharmaceutical care Essentials for practice and care Approach to practice and care | 65.59 (18.86) 13.68 (4.15) 13.79 (4.15) 20.59 (6.62) 17.53 (7.07) | 66.86 (20.10) 13.27 (4.51) 13.73 (4.27) 19.23 (7.18) 20.64 (6.93) | 65.04 (18.34) 13.85 (4.0) 13.82 (4.11) 16.79 (6.91) 20.58 (6.50) | 0.513 0.347 0.875 0.019 0.950 |
| Class Average | Game-Based Learners | Traditional Learners | Mean Difference | 95% Confidence Interval | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | Lower | Upper | |||
| Total | 81.77 (9.81) | 74.62 (9.64) | 7.152 | 4.414 | 9.891 | <0.001 |
| Foundational knowledge | 17.41 (2.49) | 16.04 (2.60) | 1.369 | 0.644 | 2.095 | <0.001 |
| Pharmaceutical care | 15.22 (3.15) | 13.79 (3.26) | 1.431 | 0.519 | 2.343 | 0.002 |
| Essentials for practice and care | 23.90 (4.29) | 22.05 (4.24) | 1.85 | 0.647 | 3.052 | 0.03 |
| Approach to practice and care | 25.25 (4.50) | 22.74 (4.63) | 2.502 | 1.204 | 3.801 | <0.001 |
| Factor | Factor 1 Loading | Factor 2 Loading | Communalities |
|---|---|---|---|
| Beneficial for acquiring the desired knowledge more easily | 0.911 | 0.685 | |
| Beneficial for acquiring the intended learning outcomes | 0.886 | 0.790 | |
| Helped to learn course content | 0.886 | 0.762 | |
| Helped to connect ideas in new ways | 0.876 | 0.681 | |
| Helped to apply the course content | 0.831 | 0.797 | |
| Helped to develop confidence | 0.803 | 0.648 | |
| Enhanced learning experience and made it easier | 0.791 | 0.592 | |
| Helped to participate in course activities that enhanced learning | 0.765 | 0.756 | |
| Beneficial for incorporating additional information | 0.530 | 0.495 | |
| Greater attention to tasks | 0.963 | 0.671 | |
| Motivated learning the course material more than traditional | 0.878 | 0.708 | |
| Recommended to be part of the course | 0.641 | 0.584 | |
| Provided opportunity to practice and improve competencies | 0.604 | 0.743 | |
| Important supplement to this class | 0.534 | 0.723 | |
| Percentage of variances explained | 60.665% | 8.142% |
| Item | r * | p Value |
|---|---|---|
| Beneficial for acquiring the desired knowledge more easily | 0.833 | <0.001 |
| Beneficial for acquiring the intended learning outcomes | 0.908 | <0.001 |
| Helped to learn course content | 0.893 | <0.001 |
| Helped to connect ideas in new ways | 0.859 | <0.001 |
| Helped to apply the course content | 0.908 | <0.001 |
| Helped to develop confidence | 0.845 | <0.001 |
| Enhanced learning experience and made it easier | 0.829 | <0.001 |
| Helped to participate in course activities that enhanced learning | 0.914 | <0.001 |
| Beneficial for incorporating additional information | 0.812 | <0.001 |
| Greater attention to tasks | 0.653 | <0.001 |
| Motivated learning the course material more than traditional | 0.775 | <0.001 |
| Recommended to be part of the course | 0.813 | <0.001 |
| Provided opportunity to practice and improve competencies | 0.876 | <0.001 |
| Important supplement to this class | 0.886 | <0.001 |
| Variable | Beta | 95% Confidence Interval | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | |||
| ALMAS for game-based learning | 0.296 | 0.110 | 0.545 | 0.004 |
| Pre-game-based-learning total average | 0.029 | −0.087 | 0.118 | 0.767 |
| GPA | 0.332 | 3.147 | 15.322 | 0.003 |
| Age | −0.116 | −1.614 | 0.482 | 0.286 |
| Gender | −0.253 | −10.150 | −1.339 | 0.011 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dabbous, M.; Kawtharani, A.; Fahs, I.; Hallal, Z.; Shouman, D.; Akel, M.; Rahal, M.; Sakr, F. The Role of Game-Based Learning in Experiential Education: Tool Validation, Motivation Assessment, and Outcomes Evaluation among a Sample of Pharmacy Students. Educ. Sci. 2022, 12, 434. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci12070434
Dabbous M, Kawtharani A, Fahs I, Hallal Z, Shouman D, Akel M, Rahal M, Sakr F. The Role of Game-Based Learning in Experiential Education: Tool Validation, Motivation Assessment, and Outcomes Evaluation among a Sample of Pharmacy Students. Education Sciences. 2022; 12(7):434. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci12070434
Chicago/Turabian StyleDabbous, Mariam, Anwar Kawtharani, Iqbal Fahs, Zahraa Hallal, Dina Shouman, Marwan Akel, Mohamad Rahal, and Fouad Sakr. 2022. "The Role of Game-Based Learning in Experiential Education: Tool Validation, Motivation Assessment, and Outcomes Evaluation among a Sample of Pharmacy Students" Education Sciences 12, no. 7: 434. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci12070434
APA StyleDabbous, M., Kawtharani, A., Fahs, I., Hallal, Z., Shouman, D., Akel, M., Rahal, M., & Sakr, F. (2022). The Role of Game-Based Learning in Experiential Education: Tool Validation, Motivation Assessment, and Outcomes Evaluation among a Sample of Pharmacy Students. Education Sciences, 12(7), 434. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci12070434







