In-Ear Electrode EEG for Practical SSVEP BCI
Abstract
1. Introduction
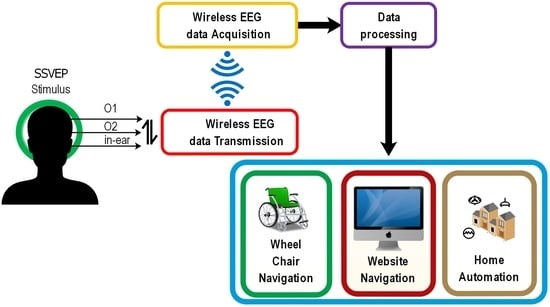
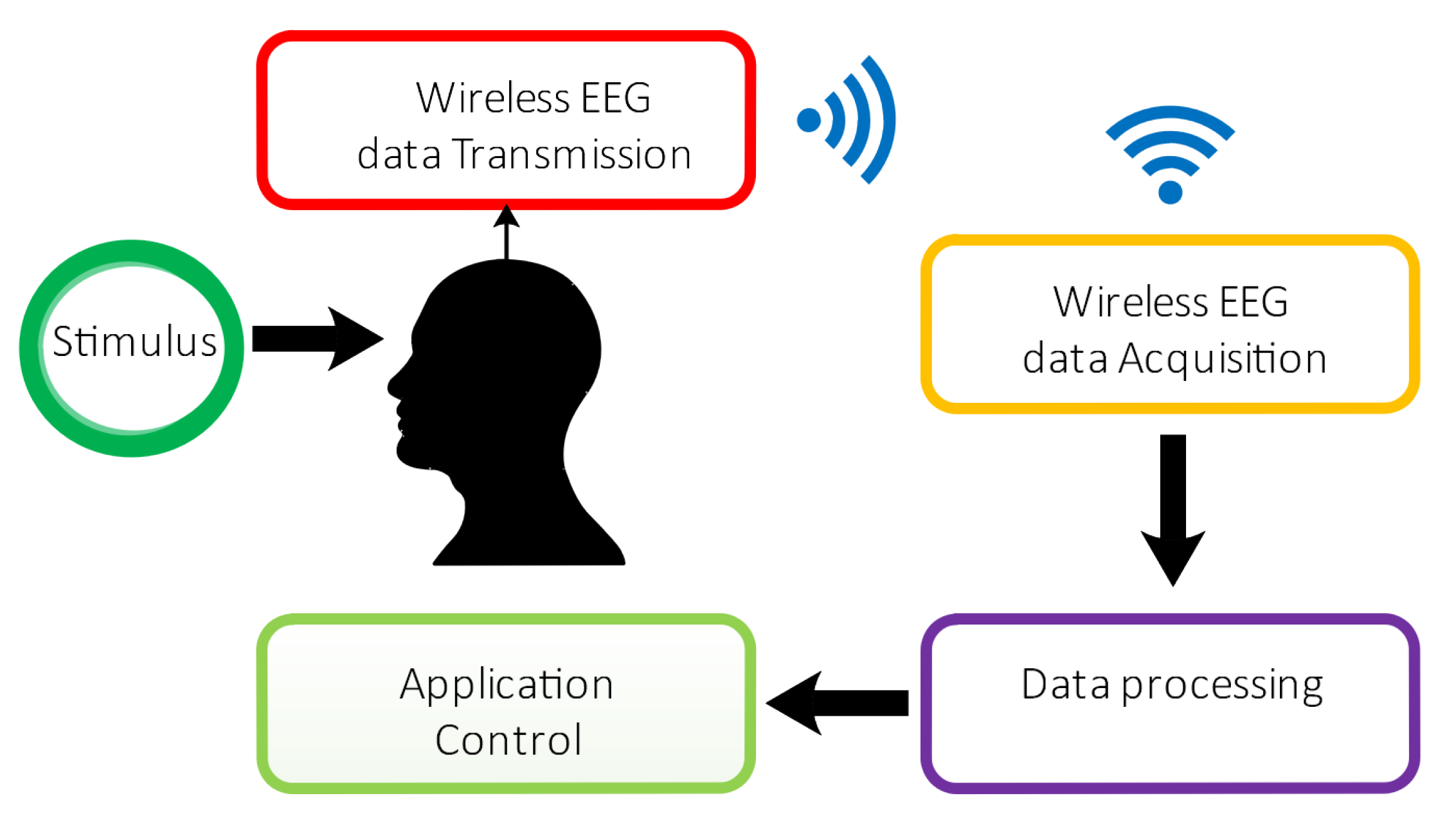
2. Methodology
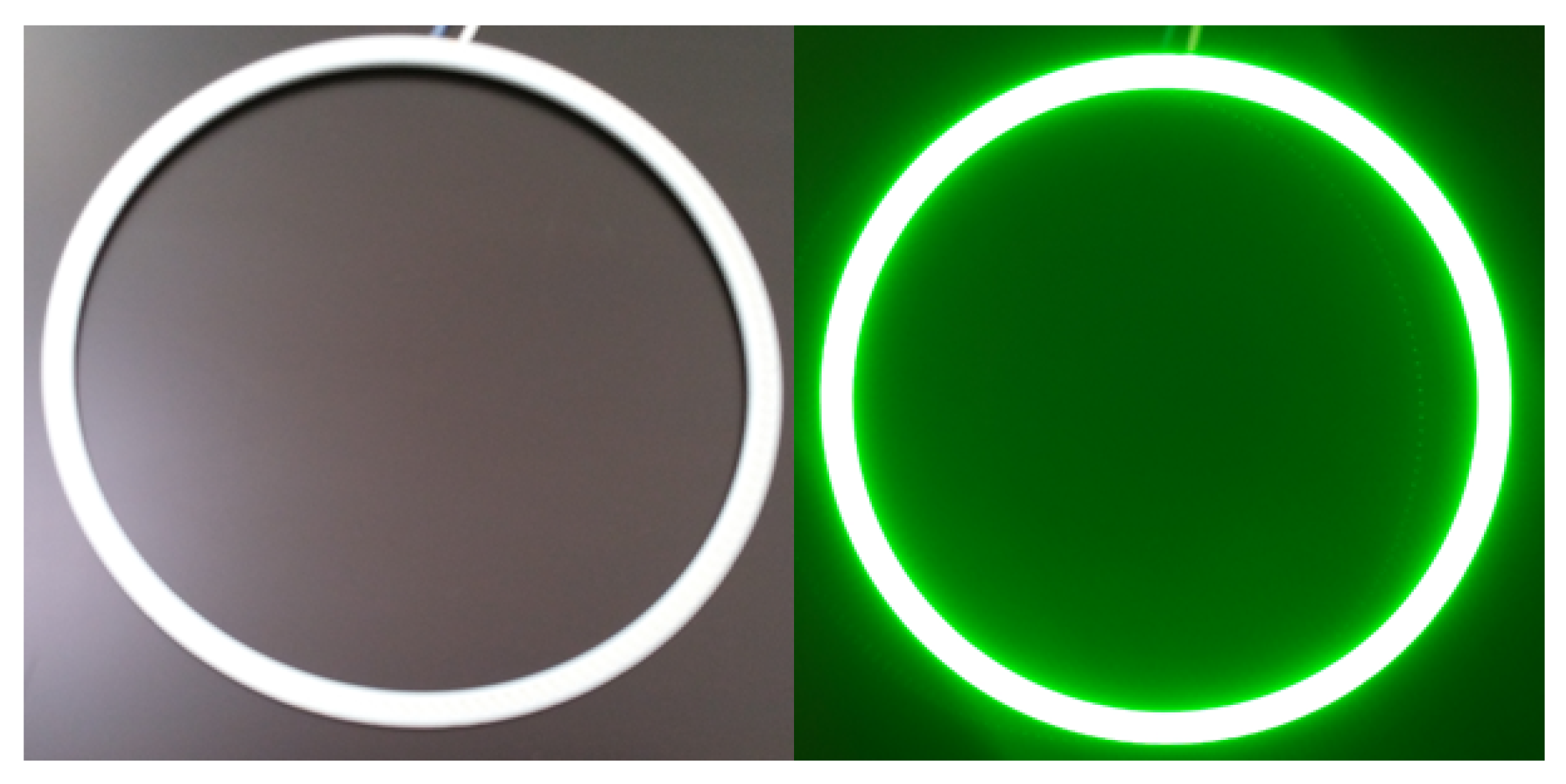
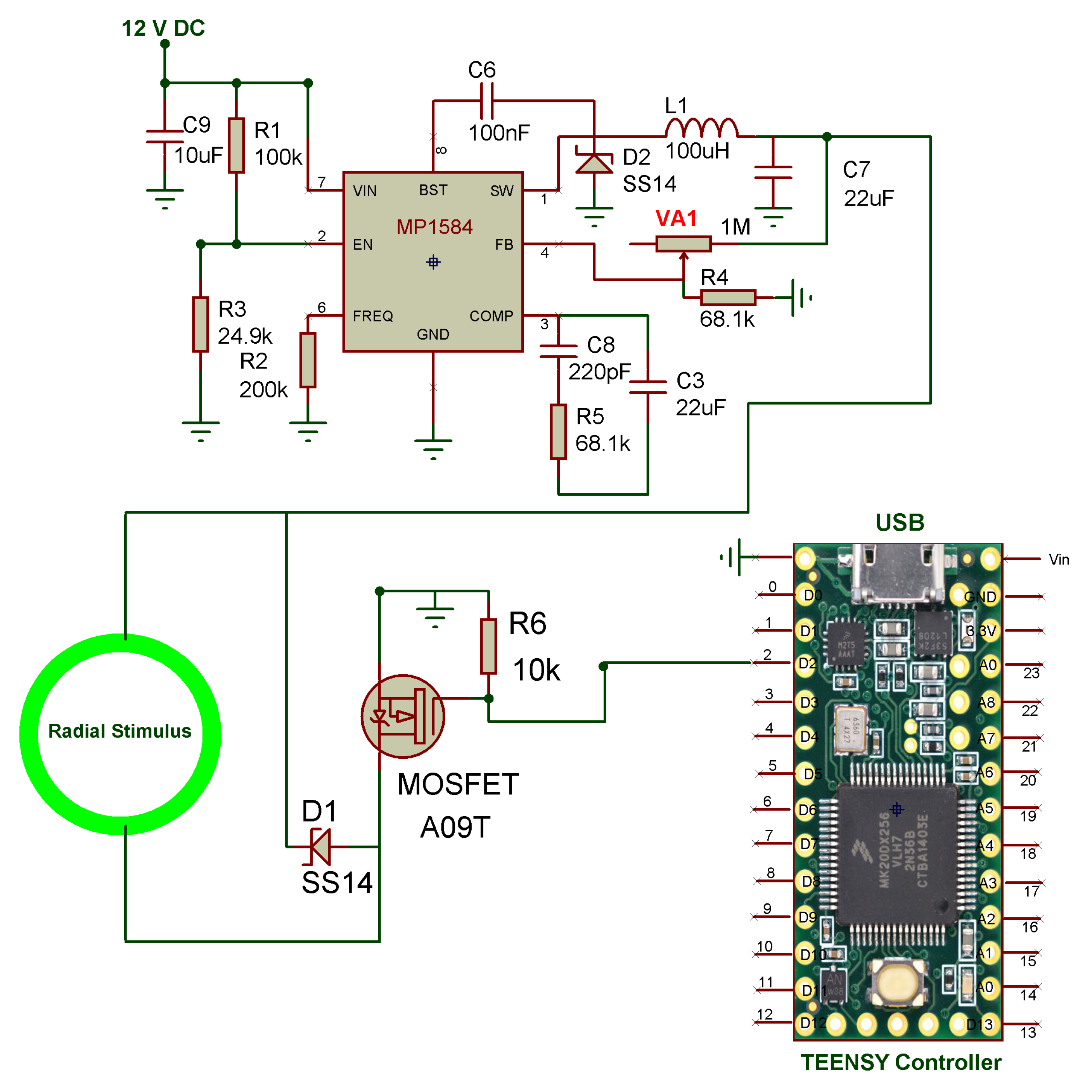
2.1. Hardware Design
2.2. Data Acquisition
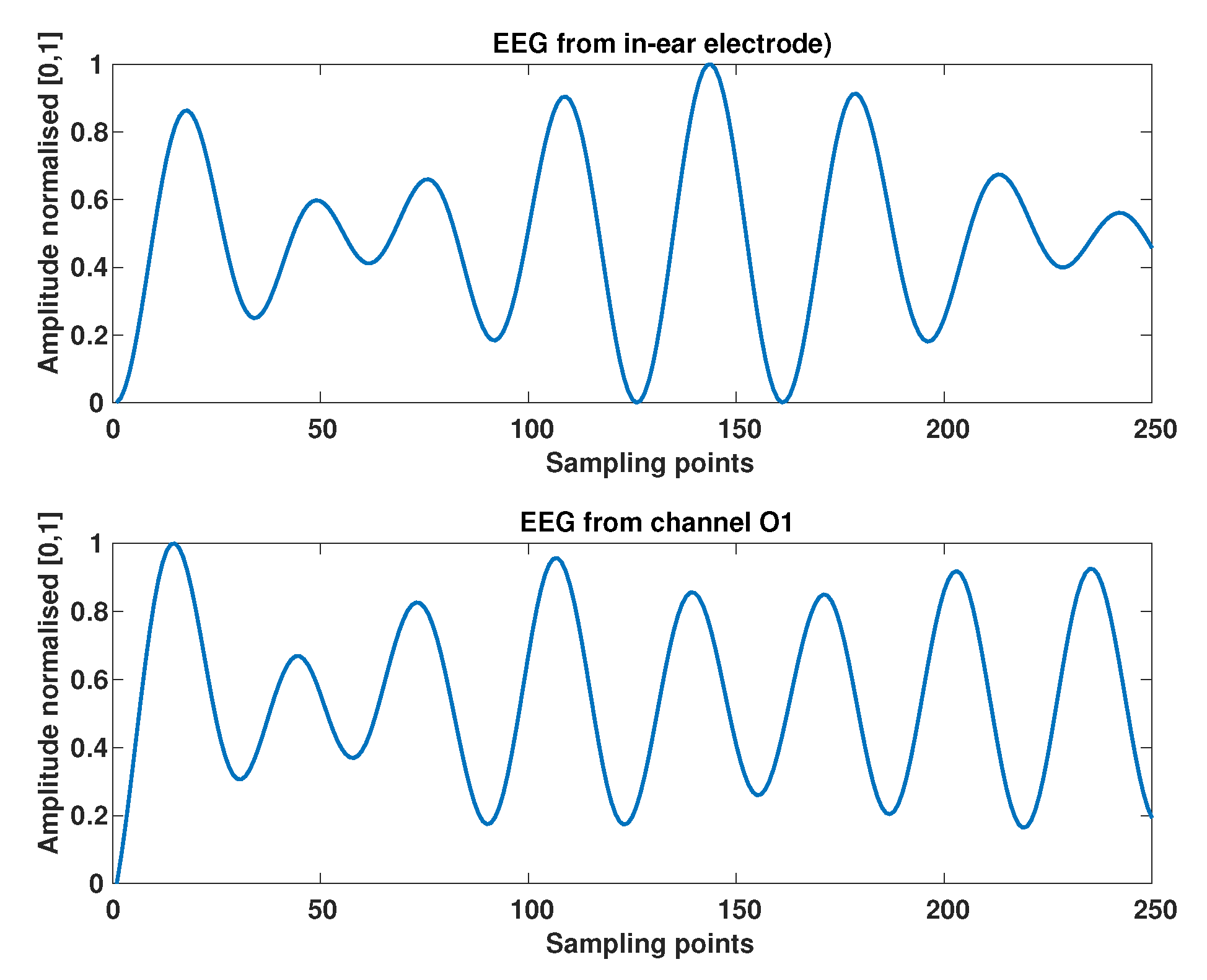
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liyanage, S.R.; Bhatt, C. Wearable electroencephalography technologies for brain–computer interfacing. In Wearable and Implantable Medical Devices; Dey, N., Ashour, A.S., James Fong, S., Bhatt, C., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; Volume 7, pp. 55–78. [Google Scholar]
- Cannard, C.; Brandmeyer, T.; Wahbeh, H.; Delorme, A. Self-health monitoring and wearable neurotechnologies. In Handbook of Clinical Neurology; Ramsey, N.F., Millán, J.d.R., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; Volume 168, pp. 207–232. [Google Scholar]
- Mudgal, S.K.; Sharma, S.K.; Chaturvedi, J.; Sharma, A. Brain computer interface advancement in neurosciences: Applications and issues. Interdiscip. Neurosurg. 2020, 20, 100694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, X.; Zhang, Z.; Guan, K.; Lu, Y.; Liu, G.; Zhang, T.; Niu, H. A hybrid BCI-controlled smart home system combining SSVEP and EMG for individuals with paralysis. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2020, 56, 101687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sintotskiy, G.; Hinrichs, H. In-ear-EEG—A portable platform for home monitoring. J. Med Eng. Technol. 2020, 44, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souders, L.; Sheehan, L. Demonstrating the Therapeutic Potential of Contralesional BCI Control for Motor Recovery in Chronic Stroke. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2019, 100, e61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira Júnior, W.G.; de Oliveira, J.M.; Munoz, R.; de Albuquerque, V.H.C. A proposal for Internet of Smart Home Things based on BCI system to aid patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neural Comput. Appl. 2020, 32, 11007–11017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erkan, E.; Akbaba, M. A study on performance increasing in SSVEP based BCI application. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2018, 21, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Bieger, J.; Garcia Molina, G.; Aarts, R.M. A Survey of Stimulation Methods Used in SSVEP-Based BCIs. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2010, 2010, 702357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouli, S.; Palaniappan, R.; Sillitoe, I.P.; Gan, J.Q. Performance analysis of multi-frequency SSVEP-BCI using clear and frosted colour LED stimuli. In Proceedings of the 13th IEEE International Conference on BioInformatics and BioEngineering, Chania, Greece, 10–13 November 2013; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Allison, B.Z.; McFarland, D.J.; Schalk, G.; Zheng, S.D.; Jackson, M.M.; Wolpaw, J.R. Towards an independent brain-computer interface using steady state visual evoked potentials. Clin. Neurophysiol. Off. J. Int. Fed. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2008, 119, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Middendorf, M.; McMillan, G.; Calhoun, G.; Jones, K.S. Brain-computer interfaces based on the steady-state visual-evoked response. IEEE Trans. Rehabil. Eng. 2000, 8, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Chen, Z.; Gao, S.; Gao, X. A high-ITR SSVEP-based BCI speller. Brain-Comput. Interfaces 2014, 1, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kappel, S.L.; Makeig, S.; Kidmose, P. Ear-EEG Forward Models: Improved Head-Models for Ear-EEG. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikkelsen, K.B.; Tabar, Y.R.; Kappel, S.L.; Christensen, C.B.; Toft, H.O.; Hemmsen, M.C.; Rank, M.L.; Otto, M.; Kidmose, P. Accurate whole-night sleep monitoring with dry-contact ear-EEG. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Athavipach, C.; Pan-ngum, S.; Israsena, P. A Wearable In-Ear EEG Device for Emotion Monitoring. Sensors 2019, 19, 4014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Floriano, A.; Diez, P.F.; Freire Bastos-Filho, T. Evaluating the influence of chromatic and luminance stimuli on SSVEPs from behind-the-ears and occipital areas. Sensors 2018, 18, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.I.; Han, C.H.; Choi, G.Y.; Shin, J.; Song, K.S.; Im, C.H.; Hwang, H.J. On the feasibility of using an ear-EEG to develop an endogenous brain-computer interface. Sensors 2018, 18, 2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikkelsen, K.B.; Kappel, S.L.; Mandic, D.P.; Kidmose, P. EEG Recorded from the Ear: Characterizing the Ear-EEG Method. Front. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouli, S.; Palaniappan, R. DIY hybrid SSVEP-P300 LED stimuli for BCI platform using EMOTIV EEG headset. HardwareX 2020, 8, e00113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuś, R.; Duszyk, A.; Milanowski, P.; Łabęcki, M.; Bierzyńska, M.; Radzikowska, Z.; Michalska, M.; Żygierewicz, J.; Suffczyński, P.; Durka, P.J. On the Quantification of SSVEP Frequency Responses in Human EEG in Realistic BCI Conditions. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e77536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouli, S.; Palaniappan, R. Radial photic stimulation for maximal EEG response for BCI applications. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Human System Interactions (HSI), Portsmouth, UK, 6–8 July 2016; pp. 362–367. [Google Scholar]

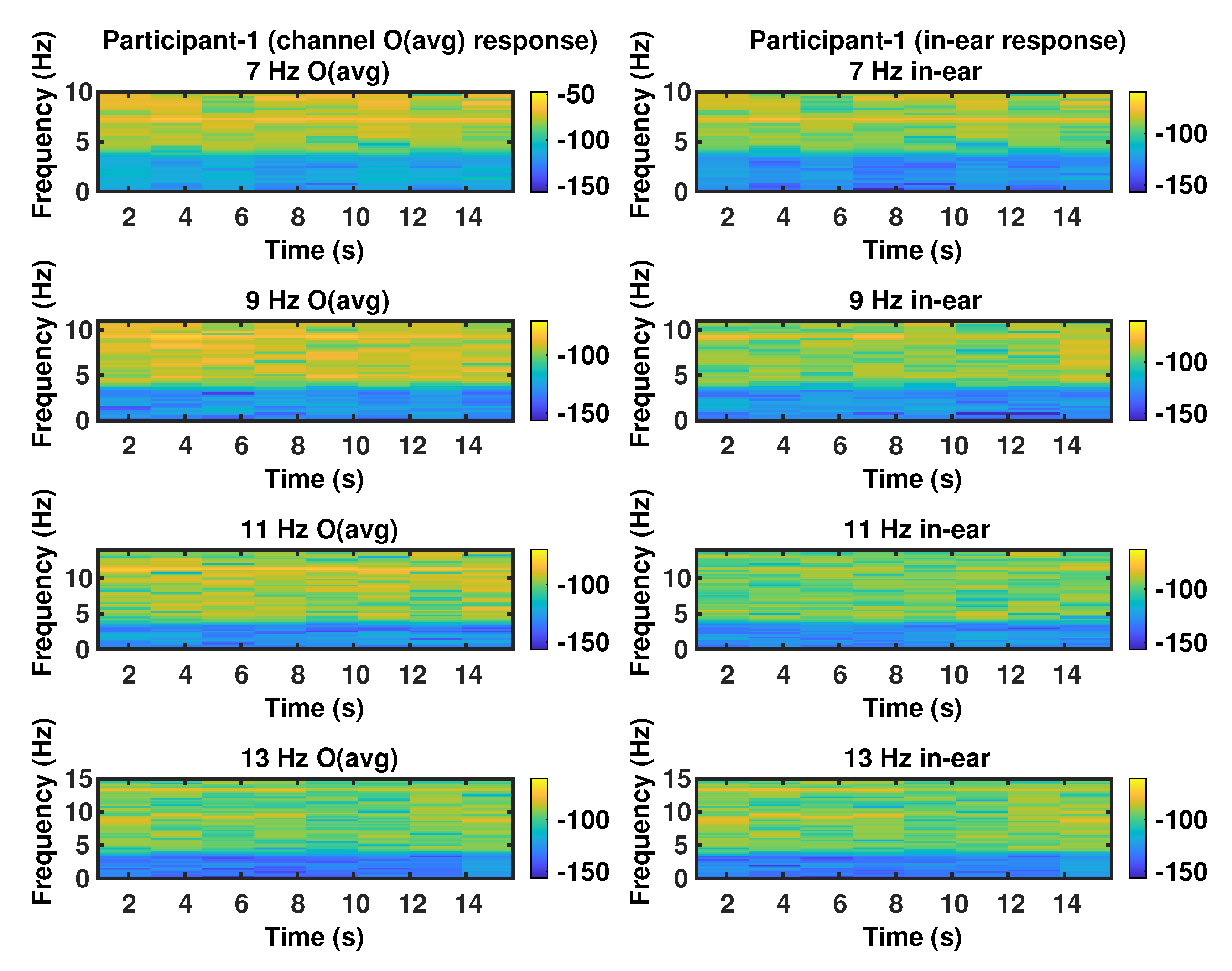

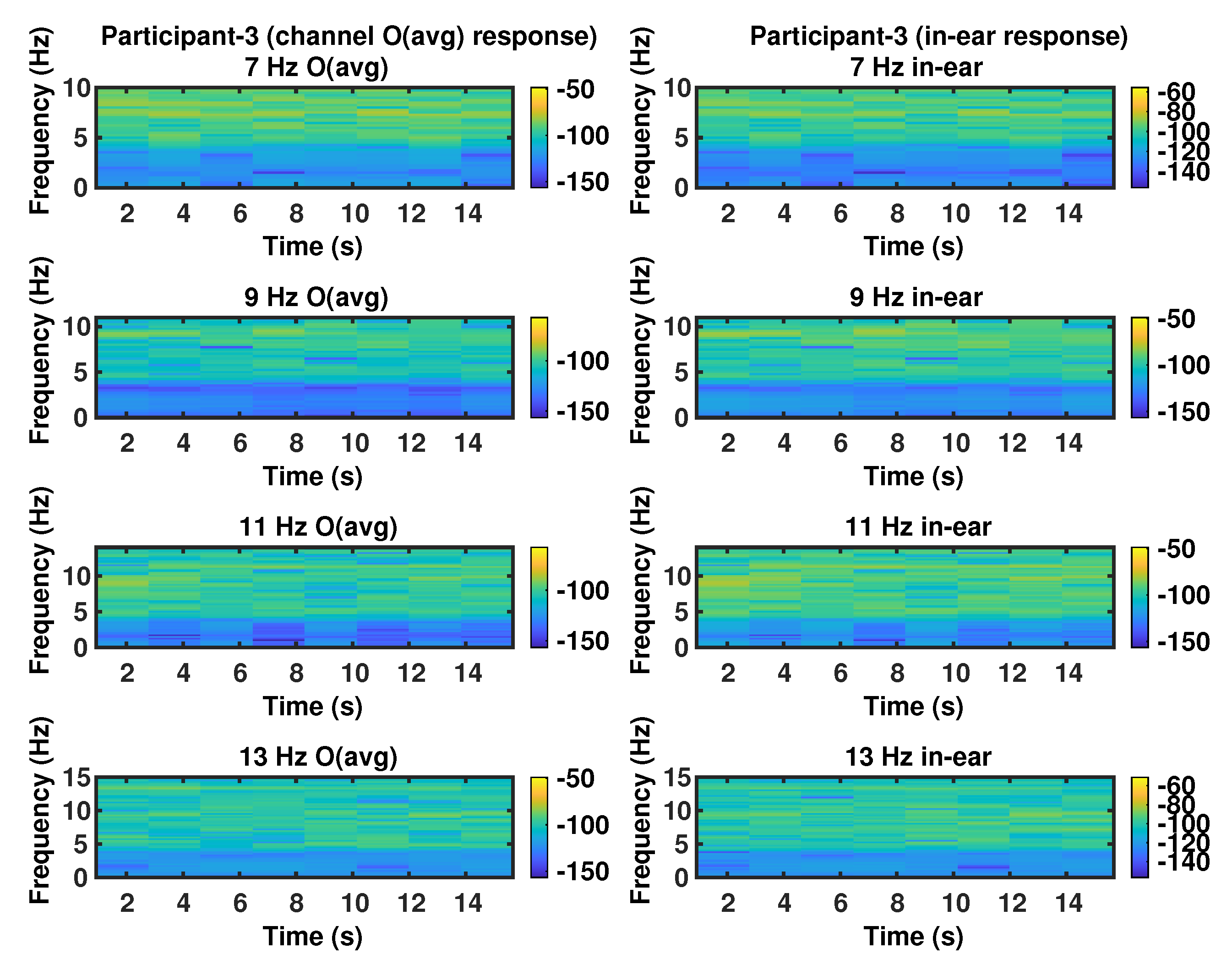
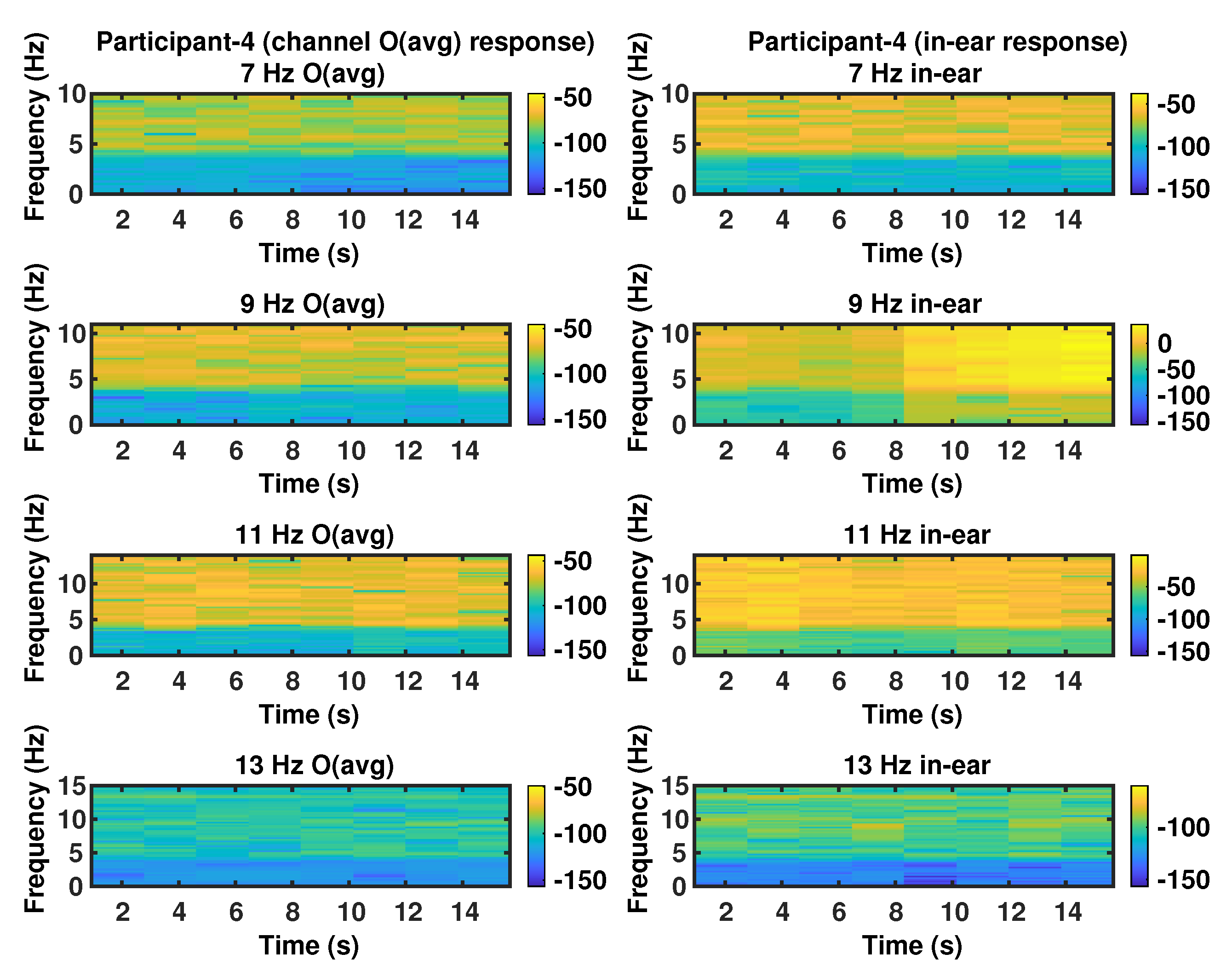


| Participant | Stimulus Flicker Frequency (Hz) | Peak Frequency (Hz) | SNR (dB) | Bandwidth (Hz) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O (Avg) | In-Ear | O (Avg) | In-Ear | O (Avg) | In-Ear | ||
| P1 | 7 | 7.10 | 7.10 | 0.02 | 7.51 | 0.46 | 0.10 |
| P2 | 7 | 7.10 | 7.10 | 8.57 | 12.63 | 0.10 | 0.14 |
| P3 | 7 | 7.10 | 7.42 | 3.92 | 27.84 | 0.10 | 0.14 |
| P4 | 7 | 7.10 | 7.10 | 1.19 | 4.20 | 0.21 | 0.28 |
| P5 | 7 | 7.10 | 7.42 | 3.75 | 8.57 | 0.10 | 0.17 |
| Avg ± Std | 7.1 ± 0 | 7.22 ± 0.17 | 3.49 ± 3.29 | 12.15 ± 9.27 | 0.19 ± 0.15 | 0.16 ± 0.06 | |
| P1 | 9 | 9.10 | 9.10 | 4.96 | 3.02 | 0.17 | 0.21 |
| P2 | 9 | 9.14 | 9.12 | 3.80 | 3.86 | 1.14 | 1.32 |
| P3 | 9 | 9.03 | 8.96 | 1.78 | 16.25 | 0.53 | 0.14 |
| P4 | 9 | 9.14 | 9.16 | 11.06 | 11.06 | 0.21 | 11.55 |
| P5 | 9 | 9.35 | 9.46 | 9.39 | 7.11 | 0.14 | 0.35 |
| Avg ± Std | 9.15 ± 0.11 | 9.16 ± 0.18 | 6.19 ± 3.89 | 8.26 ± 5.47 | 0.44 ± 0.42 | 2.71 ± 4.96 | |
| P1 | 11 | 11.03 | 11.10 | 3.69 | 0.14 | 0.14 | 0.21 |
| P2 | 11 | 11.10 | 11.11 | 6.06 | 0.59 | 0.28 | 0.10 |
| P3 | 11 | 11.11 | 11.10 | 5.56 | 0.72 | 0.29 | 0.43 |
| P4 | 11 | 11.10 | 10.56 | 1.89 | 1.87 | 0.35 | 0.21 |
| P5 | 11 | 11.25 | 11.45 | 1.68 | 5.40 | 0.18 | 0.11 |
| Avg ± Std | 11.11 ± 0.08 | 11.06 ± 0.31 | 1.62 ± 2.02 | 1.74 ± 2.14 | 0.24 ± 0.08 | 0.21 ± 0.13 | |
| P1 | 13 | 13.07 | 13.10 | 1.76 | 1.09 | 0.25 | 0.35 |
| P2 | 13 | 13.1 | 13.07 | 1.09 | 0.39 | 0.35 | 0.17 |
| P3 | 13 | 13.11 | 13.10 | 5.87 | 4.77 | 0.28 | 0.35 |
| P4 | 13 | 13.07 | 13.10 | 2.78 | 1.36 | 0.18 | 0.21 |
| P5 | 13 | 13.07 | 13.12 | 2.86 | 3.02 | 0.11 | 0.1 |
| Avg ± Std | 13.08 ± 0.01 | 13.09 ± 0.01 | 2.87 ± 1.83 | 2.12 ± 1.76 | 0.23 ± 0.09 | 0.23 ± 0.11 | |
| Stimulus Frequency (Hz) | Coefficient (r) | p-Value (p) |
|---|---|---|
| 7 Hz | 0.76 | 0.03 |
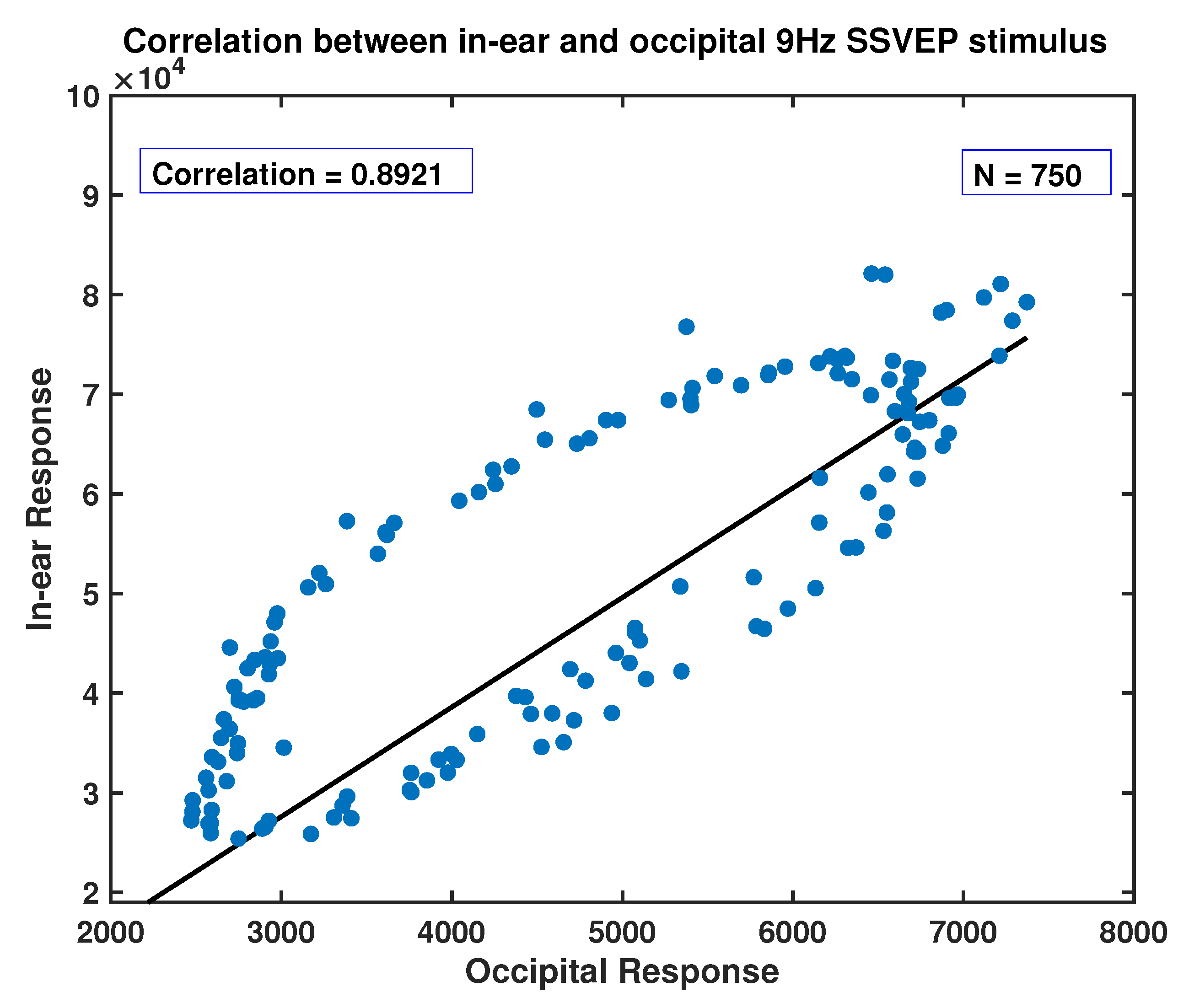
| 9 Hz | 0.89 | 0.03 |
| 11 Hz | 0.79 | 0.04 |
| 13 Hz | 0.85 | 0.04 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mouli, S.; Palaniappan, R.; Molefi, E.; McLoughlin, I. In-Ear Electrode EEG for Practical SSVEP BCI. Technologies 2020, 8, 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies8040063
Mouli S, Palaniappan R, Molefi E, McLoughlin I. In-Ear Electrode EEG for Practical SSVEP BCI. Technologies. 2020; 8(4):63. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies8040063
Chicago/Turabian StyleMouli, Surej, Ramaswamy Palaniappan, Emmanuel Molefi, and Ian McLoughlin. 2020. "In-Ear Electrode EEG for Practical SSVEP BCI" Technologies 8, no. 4: 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies8040063
APA StyleMouli, S., Palaniappan, R., Molefi, E., & McLoughlin, I. (2020). In-Ear Electrode EEG for Practical SSVEP BCI. Technologies, 8(4), 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies8040063