Abstract
Free and open-source hardware (FOSH) development has been shown to increase innovation and reduce economic costs. This article reviews the opportunity to use FOSH as a sanction to undercut imports and exports from a target criminal country. A formal methodology is presented for selecting strategic national investments in FOSH development to improve both national security and global safety. In this methodology, first the target country that is threatening national security or safety is identified. Next, the top imports from the target country as well as potentially other importing countries (allies) are quantified. Hardware is identified that could undercut imports/exports from the target country. Finally, methods to support the FOSH development are enumerated to support production in a commons-based peer production strategy. To demonstrate how this theoretical method works in practice, it is applied as a case study to a current criminal military aggressor nation, who is also a fossil-fuel exporter. The results show that there are numerous existing FOSH and opportunities to develop new FOSH for energy conservation and renewable energy to reduce fossil-fuel-energy demand. Widespread deployment would reduce the concomitant pollution, human health impacts, and environmental desecration as well as cut financing of military operations.
1. Introduction
Free and open-source software (FOSS) is released under a license that allows anyone to use, copy, study, and change it, and the source code is openly shared so that people are encouraged to voluntarily improve the design in exchange for requiring adaptations to be re-shared with the same license [1]. This gift economy [2] results in rapid innovation [3,4] and using FOSS licenses has been widely [5] and repeatedly [6] successful [7]. FOSS has become a dominant form of technical development in the software industry and now 90% of cloud servers [8] run open-source operating systems (this includes most internet companies such as Facebook, Twitter, Yahoo, Google and Amazon) as do 90% of the Fortune Global 500 (e.g., including less-tech-focused companies such as Wal-Mart and McDonalds) [9]. Similarly, 100% of supercomputers [10], over 84% of the global smartphone market [11] and more than 80% of the internet of things (IOT) market [12] also use FOSS.
The same open-source development paradigm [13,14] has started to democratize [15] manufacturing of physical products [16]. This is known as free and open-source hardware (FOSH). The Open Source Hardware Association defines open-source hardware [17] as:
Hardware whose design is made publicly available so that anyone can study, modify, distribute, make, and sell the design or hardware based on that design. The hardware’s source, the design from which it is made, is available in the preferred format for making modifications to it. Ideally, open source hardware uses readily-available components and materials, standard processes, open infrastructure, unrestricted content, and open-source design tools to maximize the ability of individuals to make and use hardware. Open source hardware gives people the freedom to control their technology while sharing knowledge and encouraging commerce through the open exchange of designs.
Open hardware uses viral licenses (e.g., CERN [18]) that demand if users make modifications, they must share their improvements with the global community [19]. FOSH is demonstrating rapid innovation [20,21,22] and is approximately 15 years behind FOSS in terms of technical development [23]. Both technologies have followed an exponential rate of growth in the peer-reviewed literature [23].
One of the core strengths of FOSH is the ability to replicate the hardware from digital designs [24,25] that themselves can be customized [26] with FOSS [27]. Digital fabrication of open-source designs enables wealth growth [28,29,30] and helps even the poor access high-value products such as state-of-the-art equipment [31]. It is well known that open hardware can create opportunities for distributed manufacturing that radically undercut commercial products [32,33,34,35,36]. For scientific hardware, for example, researchers can expect to save approximately 87% compared to proprietary products [37]. The savings are strongest when a form of distributed manufacturing is used (e.g., the open-source self-replicating rapid prototyper (or RepRap) [38,39,40,41] dramatically reduces additive manufacturing costs [42] and increases the number of 3D printing designs exponentially [43] that now number in the millions). The literature shows that low-cost open-source 3D printers can even reduce costs for mass-manufactured consumer goods, on average by 90–99% [43,44].
These savings can be scaled to the national level by investing in the development of new open-source software [45] and hardware of strategic interest to a specific country [46]. In the analysis completed in Finland, one of the secondary advantages is that imported products could be offset by manufacturing products internally from open-source designs [46]. This advantage can be leveraged to act in the same way as a sanction if applied to undercut imports from a specific country and technology sector to increase national security and global safety. Although FOSH is becoming well known, the strategic development of it to meet national goals outside of scientific research has not been explored.
This article reviews this opportunity by formalizing a methodology for selecting strategic national investments in open hardware development to improve national security and global safety. In the methodology, first the target criminal country that is threatening national security is identified. Next, the top imports from the target criminal country as well as potentially other importing countries (allies) are quantified. Then, hardware is identified that could undercut those imports as well as potentially other strategic exports from the target criminal country. Finally, methods to support the FOSH development are enumerated. The FOSH are designed in a way that facilitates distributed manufacturing from digital designs using local materials and tools. Thus, in addition to sanctions or instead of sanctions, supporting FOSH development can undercut the export market for the target criminal countries. To demonstrate how this theoretical method works in practice, it is applied as a case study to a current military aggressor nation. It is classified as a fossil-fuel exporter. Thus, how the development of energy conservation and renewable energy-based open hardware could reduce fossil-fuel-energy demand and the concomitant pollution, human health impacts, environmental desecration as well as financing of military operations is discussed.
2. Methods
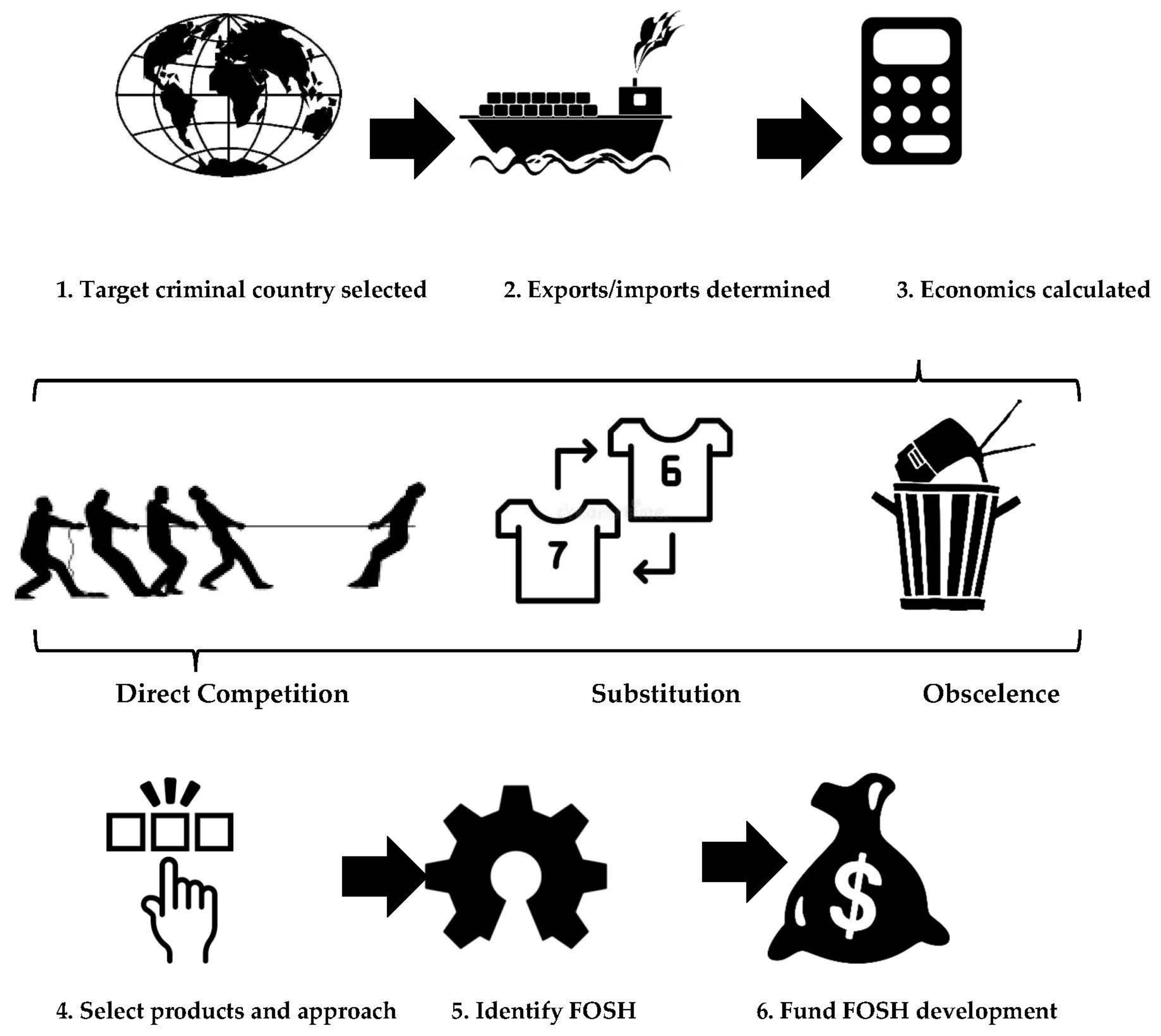
The method used to determine strategic investments in open hardware is summarized in Figure 1.
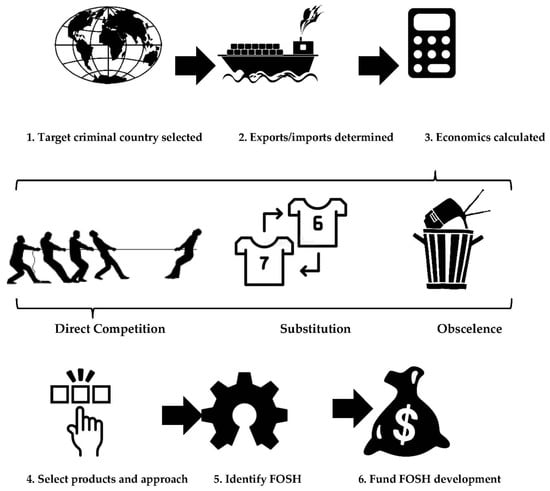
Figure 1.
Flow diagram of method to determine strategic investments in open hardware.
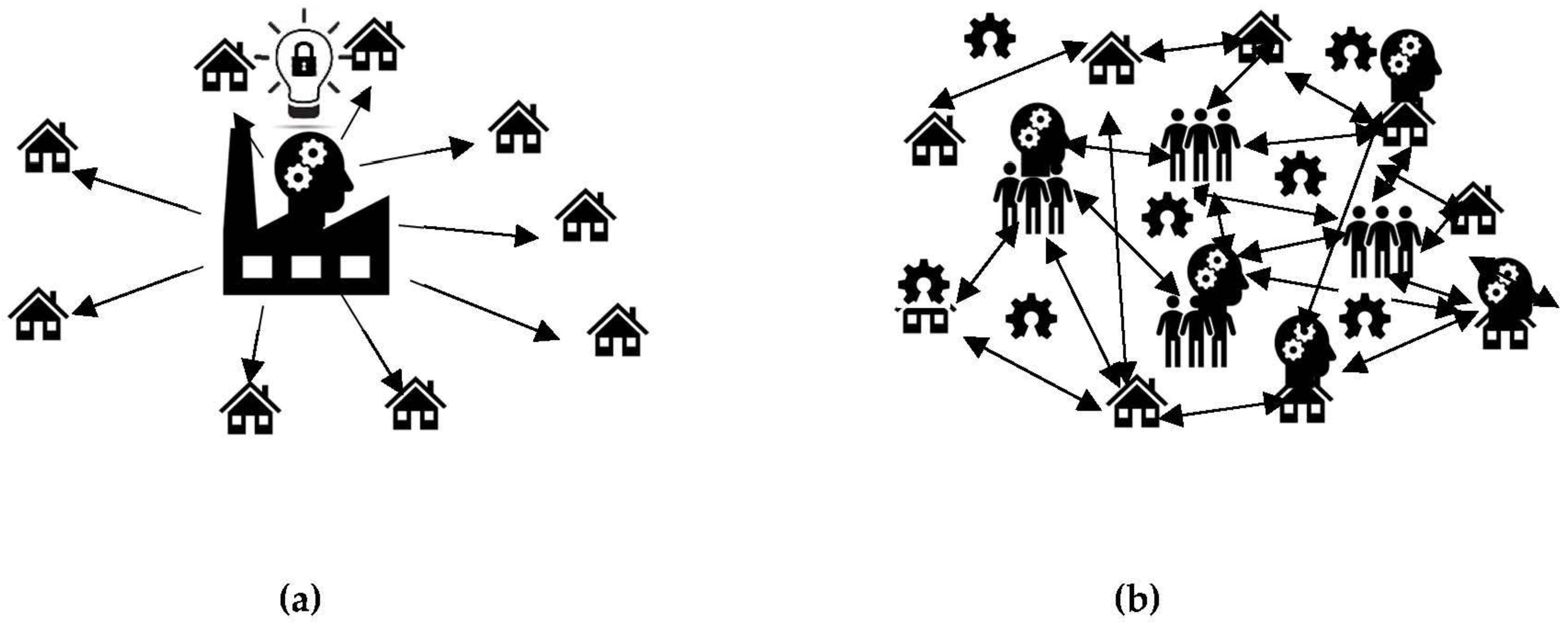
As shown in Figure 1, first, the target criminal country is identified for disruption with strategic investment in FOSH. The target criminal country can be a political rival, an enemy or a country threatening the stability or safety of a region or the world. Next, both the major exports for the target criminal country are identified from public data as well as the imports to the country doing the analysis are identified. These imports and exports are quantified in economic terms for specific products. Then, the highest-value exports (and/or imports) are evaluated for the technical capacity to be disrupted by innovation. This can be determined using three approaches. First, direct competition is producing the same product at lower costs. For example, a USD $20,000 potentiostat/galvanostat for characterizing thin-film batteries can be replaced with a USD $100 open-source model [47]. With such opportunities, products can be directly open sourced to undercut the existing market for the product. Second, substitution is replacing a product with a different one that serves the same function. For example, a study of a single open hardware toy repository found that users were offsetting USD $60 million purchases per year by 3D printing 100 FOSH toy designs rather than purchasing similar proprietary toys [48]. For toys that were functionally equivalent, the most common savings fell by 40–90%, which represents savings expected for open-source design replications of low-value products. Third, elimination of the demand for an existing product by producing a new product that makes the need for the target product obsolete. For example, Wikipedia, an open-source digital encyclopedia running on open-source Wikimedia software, made the 244-year-old paper-based Encyclopedia Britannica obsolete and it is no longer produced [49]. Wikipedia did this by creating enormous laterally scaled value, as for example, the images on Wikimedia alone have been valued at more than USD $28.9 billion [50]. Wikipedia has essentially eliminated the market for hard-copy encyclopedias. Finally, after the target products and innovations are selected, specific open hardware is identified to reach the goal of reducing or eliminating the export of the products from the target criminal nation. Imports into one’s own nation are likely the easiest to offset, but open hardware can be used to out innovate and thus reduce costs or increase functionality faster than the target criminal country’s existing system (or companies within it) can innovate on its own. In addition to the imports into one’s own nation, these same sources can determine other countries (allies) that are importing goods from the target criminal nation. These allies could form alliances to open hardware and leverage digital technologies [51] to use the do-it-together (DIT) methodology [52] to accomplish more than possible by going alone [53]. Since the industrial revolution, a conventional centralize manufacturing model has held sway (Figure 2a), where all intellectual property is held by an organization that manufactures products and ships it to consumers. DIT consists of participatory design and collaborative production (e.g., global design and home or local manufacturing), as shown in Figure 2b. As can be seen in Figure 2, rather than have the design ideas only come from large companies, communities and individuals can assist in developing open-source designs and then community organizations (e.g., fablabs, makerspaces as well as small- and medium-sized businesses) can manufacture the products locally. DIT encourages local production in a commons-based peer production strategy. Such social manufacturing generates positive externalities for all the involved stakeholders including customers, professionals and the local producers [54]. DIT is well suited for small-scale production on local sites, offering significant potential for new businesses and employment as DIT can provide competitive advantages while limiting costs and risks associated with innovation [55]. These imports, which can be converted to distributed local production, need to be quantified and hardware is identified that could undercut those imports. Thus, in addition to sanctions (or instead of sanctions), supporting FOSH development can undercut the market for the target countries by enabling distributed manufacturing of products that reduce or eliminate exported products from a targeted criminal nation.
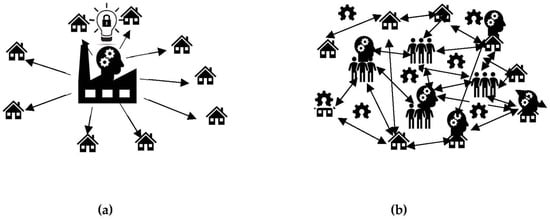
Figure 2.
(a) Conventional centralized and proprietary manufacturing model and (b) the decentralized open-source hardware model (design and share globally, while manufacturing locally).
3. Case Study
In order to illustrate this method, Russia was selected as an example country (step 1) for the case study. Russia, a country of 142 million citizens, has a gross domestic product per capita of $26,500 [56]. Russia also possesses thousands of nuclear weapons [57] and has continued to reproduce existing nuclear warhead designs even as it has reduced stockpiles [58]. Thus, Russia still controls enough nuclear weapons to be past the rational limit (e.g., where using them would hurt Russians even in the best-case scenario by aggravating food shortages) and worse, plunge the world into nuclear winter single handedly, which would result in mass starvation throughout the world [59]. Despite its inflated military, Russia is an otherwise developing country, where the average wage is only 51,100 Russian rubles per month or USD $7284/year [60] (e.g., the average Russia is below the poverty line in the U.S.). Note, these figures were taken prior to the 2022 sanctions. Russia, however, is described as an energy superpower due only to its fossil-fuel reserves [61]. Russia has the largest natural gas reserves in the world (followed by Iran) [62]. Still lamenting the loss of the USSR, Russian leadership has ambitions to expand its control over regions near it [63]. This was most clearly seen by several recent acts of aggression towards its neighboring countries that came in the form of invasions. First in 2008 the Russo–Georgian War, the European Court of Human Rights ruled that Russia maintained direct control over Abkhazia and South Ossetia [64] and was responsible for grave human rights abuses [65]. In 2014, Russia invaded and annexed Crimea [66,67]; the UN General Assembly condemned the occupation of the Autonomous Republic of Crimea and part of the territory of Ukraine [68]. Finally, most recently, Russia is the clear illegal aggressor in the 2022 full-scale invasion of Ukraine [69]. A full-scale war with Russia would be catastrophic even if nuclear war is prevented, so the U.S. and allies have retaliated with a long and growing list of sanctions [70,71]. The sanctions are meant to apply economic pressure on Russia to stop aggression, the destabilization of Europe and the rest of the world; but even as these sanctions are in place, they do not permanently disable the economic engine that makes Russia’s threat to global safety a reality: exporting fossil fuels. Not only do fossil-fuel sales finance Russia’s military [72], but fossil-fuel pollution is destabilizing the global climate, with severe impacts of climate change [73]. These risks include forcing 1/3 of global food production outside of a safe climate space [74] and creating human health risks [75]; and climate change also threatens the global economy [76].
4. Results
4.1. Case Study Risks from Exports
To complete steps 2 and 3, the top Russian exports are identified—(1) crude petroleum (USD $123B), (2) refined petroleum (USD $66.2B), (3) petroleum gas (USD $26.3B), and (4) coal briquettes (USD $17.6B) [77]. All of the top exports from Russia are fossil fuels, which is a serious threat to global safety if combusted, resulting in greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions and concomitant climate change [78,79]. Such human-caused global climate destabilization is established with a 95% confidence [80] as are the overwhelmingly detrimental repercussions on the environment as well as human social systems [81]. The impacts of burning Russia’s fossil-fuel exports resulting in further climate change include
- (1)
- Increased global temperatures and heat waves, which are already responsible for thousands of human deaths [82,83,84];
- (2)
- Increased crop failures throughout the world [85,86], which aggravates global hunger and starvation [87,88,89];
- (3)
- Increased electric grid failures and intermittent power outages [90,91];
- (4)
- Increased droughts [92,93,94];
- (5)
- Increased number and severity of forest fires [95,96,97];
- (6)
- Increased sea level rise, which submerges low-lying coastal areas and increases shoreline erosion [98,99];
- (7)
- Increased saltwater intrusion [99,100], which can threaten drinking water supplies [101];
- (8)
- Increased storm damage to coast lines and increased flood risks [102,103,104,105,106].
4.2. Case Study FOSH Targets
4.2.1. FOSH for Electric Vehicles
For step 4, the profit centers of Russia’s fossil-fuel industry will be targeted systematically with open hardware (step 5). As the first two profit centers for Russia focus on both crude and refined petroleum, targeted investments in open-source development revolve around those that antiquate the internal combustion engine that burns gasoline or diesel fuel. Any hardware that reduces the need for gas-based automobiles could be of some help (e.g., improved public transportation and equipment for telecommuting). Currently, however, electric vehicles (EV) offer the best potential for elimination of fossil-fuel-based land transport and are already gaining in market share [107], having more than doubled in 2021 [108]. Despite this growth, there are still several technical challenges to overcome [109] to reduce EV costs (and their batteries [110]) to accelerate the obsolesce of the use of oil for internal combustion engines altogether.
There is already some FOSH development revolving around EVs. Support for open-source development to support EV charging stations [111] exists. In addition, Tesla unlocked its EV patents [112]. Shortly after, Ford also announced opening its portfolio of previously patented EV technologies in an effort to accelerate industry-wide development [113]. Open-source battery management has been developed [114]. FOSH has also been developed for in situ monitoring of Li-ion cells [115], a maintenance tool for light-electric-vehicle batteries [116] and research has been performed on a line of open-source all-iron batteries [117,118].
Further open-source development of batteries and electronics could all be expected to reduce the capital and operating costs of EVs, helping to expand the diffusion of the technology and for eliminating oil for transportation. In addition, there is an opportunity for distributed manufacturing of EV components and potentially entire vehicles in high-population-density regions.
4.2.2. FOSH for Energy Conservation
The third profit center is petroleum gas or natural gas, which is primarily used to heat buildings in Europe although it is also burned to generate electric power. There are several areas that could benefit from open-source development that would reduce natural gas use for heating and some are already underway. Open hardware that is part of the internet of things (IOT) [119,120] is used for low-energy-consumption devices [121], monitoring power quality and energy savings [122]. There are numerous FOSH methods that have been developed for power monitoring [123,124,125,126], and smart meters [127,128,129] including those for institutional buildings (i.e., schools) [130]. FOSH is also used to improve energy efficiency and demand response [131] as well as smart converters [132] and microgrid communications [133]. There are also opportunities to develop open-source smart sockets, programmable thermostats, and high-efficiency LED lighting.
Related to conservation, development of open-source technologies could also take the form of those that help improve energy efficiency for physical testing such as an open-source blower door [134] to help identify air leaks in buildings. This technology could enable library-check out style of the device to help retrofit homes in an area. Other devices in this class would be thermal imaging cameras to detect improper insulation or faulty windows. Similarly, reducing heat loss can also be reduced with insulation. So open-source development could reduce the cost of insulation by providing the tools to turn local materials into insulating materials. The clearest opportunity would be the machinery at the fablab scale [135,136] to convert newspaper and fire retardant into cellulose insulation [137]. However, it should be pointed out that the costs of all of the types of insulation may benefit from open-source distributed manufacturing such as FOSH methods to make fibers [138].
4.2.3. FOSH for Heat Pumps
With the invasion of the Ukraine, the EU has already unveiled a strategy to eliminate their dependence on Russian natural gas [139]. Energy conservation, however, is not going to be enough to do it and the other approach is to electrify heating to not only cut down on natural gas, but to eliminate its use (and thus the demand for natural gas from Russia) all together. One promising upcoming technology to do this is heat pumps—both ground source and air source. Heat pump systems are often uneconomic unless coupled with solar power for offsetting natural gas or propane fuels [140,141]. Open-source development for a heat pump is already underway [142]. Future work could focus on FOSH for local fabrication of heat exchangers, pumps, motors, and piping. Ground source heat pumps would benefit from open hardware development of bore hole drilling units, such as an open-source ecology tractor [143] attachment.
4.2.4. FOSH for Renewable Energy
The fourth profit center for Russia is exporting coal, which is most commonly combusted for electricity. It should be pointed out here that even if EV scaling eliminates internal combustion engine-based vehicles and heat pumps offset the need for burning natural gas for heat, to completely eliminate the need for fossil fuels from Russia, electricity from other sources must be generated. According to the International Energy Agency, wind and solar are the fastest-growing sources of energy [144]. Choi et al. developed a renewable energy monitoring system [145], which is a start towards FOSH development in the renewable energy space. Although there are now FOSH-based hardware in the loop simulators for wind turbine testing [146] and there is some potential for open-source small wind turbines [147], there is less of an opportunity for small-scale distributed production with wind than solar.
Solar photovoltaic (PV) is particularly promising because it is more geographically diverse—available to most of humanity and growing rapidly [148,149]. PV is sustainable [150], a net energy producer [151] with an excellent ecological balance sheet [152,153]. The capital costs for PV are dropping rapidly (60% in the last decade) [154,155,156,157]. Because of this, already large-scale PV is generally the lowest-cost option for generating electricity [158]. Despite the lifetime economic benefits of PV, capital costs are the primary barrier to faster deployment, in the developing [159] and developed nations [160]. There are several approaches to reducing upfront PV costs including small-scale do it yourself (DIY) [161], which can cut more than half of the cost by eliminating most labor and soft costs.
The majority of PV system cost declines were caused by the $/W declines in the cost of PV modules, but racking, electronics, and wiring have seen far lower rates of cost decline [162]. PV costs can be more manageable if broken in small components that can be purchased over time, rather than all at once. For example, plug-and-play solar, where PV modules are connected with microinverters directly to the household circuits by consumers is technically possible [163,164,165,166,167], but regulations have stalled scaling of the technology in much of the world even though it allows the poor to enter the PV market [168]. There are currently no FOSH based microinverters, which is a large opportunity to reduce solar costs. Such microinverters would need to be developed for all of the world’s standard voltages.
Secondly, racking is focused proprietary and costly designs, and racking costs dominate the cost of small PV systems [161]. There are, however, FOSH designs that substantially reduce racking costs for low-tilt-angle ground mounts, which result in 85% and 92% savings from proprietary alternatives [169], large-scale ground mounts with low-concentration reflectors [170], tensegrity structures (saved up to 77%) [171], and small-scale agrivoltaic cold frames [172]. For buildings, there are also FOSH designs for flat roofs that save over 80% [173], RV rooftops mounts [174], and post-market module retrofits for building integrated PV [175]. In addition to fixed mounts, FOSH solar trackers [176,177,178] and dual axis trackers [179] have been developed. Far more work is needed to develop the lowest-cost FOSH designs for PV racks based on the availability of materials locally for all parts of the world so that all communities can take advantage of these generally >75% savings.
Research into improving the PV industry can also benefit from open-source design [180]. Currently, no PV manufacturer is able to use all the known improvements to device performance and opportunities exist for opening up patents in the PV space similar to what Tesla and Ford have done for EVs. Open-source is mature, however, in part of the PV technical ecosystem: software. There is already extensive open-source software to assist in PV system design including PVLib [181,182] and the National Renewable Energy Lab’s Systems Advisory Model (SAM) [183,184] as well as a module emulator [185] and FOSS for modeling advanced inverters [186]. FOSS has also been developed to determine the PV potential in urban areas [187] or over entire regions with open-source geographic information system software [188].
In addition, the Open Source Outdoors Testing Facility provides open access data on PV systems in northern environments [189] and could be replicated in other parts of the world. Any outdoor testing facility can reduce capital cost for monitoring using open-source systems for real time measurement of the sunlight incident angle [190], for UV–Vis-NIR radiation measurements [191] and radiation shields for environmental sensors [192]. Modules can be tested on site or in the lab with a solar simulator using an open-source IV curve tracer for solar [193]. There is also considerable FOSH developed for monitoring PV systems including data logging [194] and those for monitoring PV device performance [195], in situ monitoring of smart PV modules [196], system monitoring [197], monitoring PV plants [198], and remote monitoring [199,200]. FOSH has also been developed to monitor PV integrated into microgrid [201,202], agrivoltaic weather stations [203] and smart monitoring [204]. All of these solar-related FOSH can be further improved to be completely digitally manufactured so that communities could locally manufacture as much of the system as possible from local materials.
5. Discussion
5.1. Countries Positioned to Use the FOSH Model
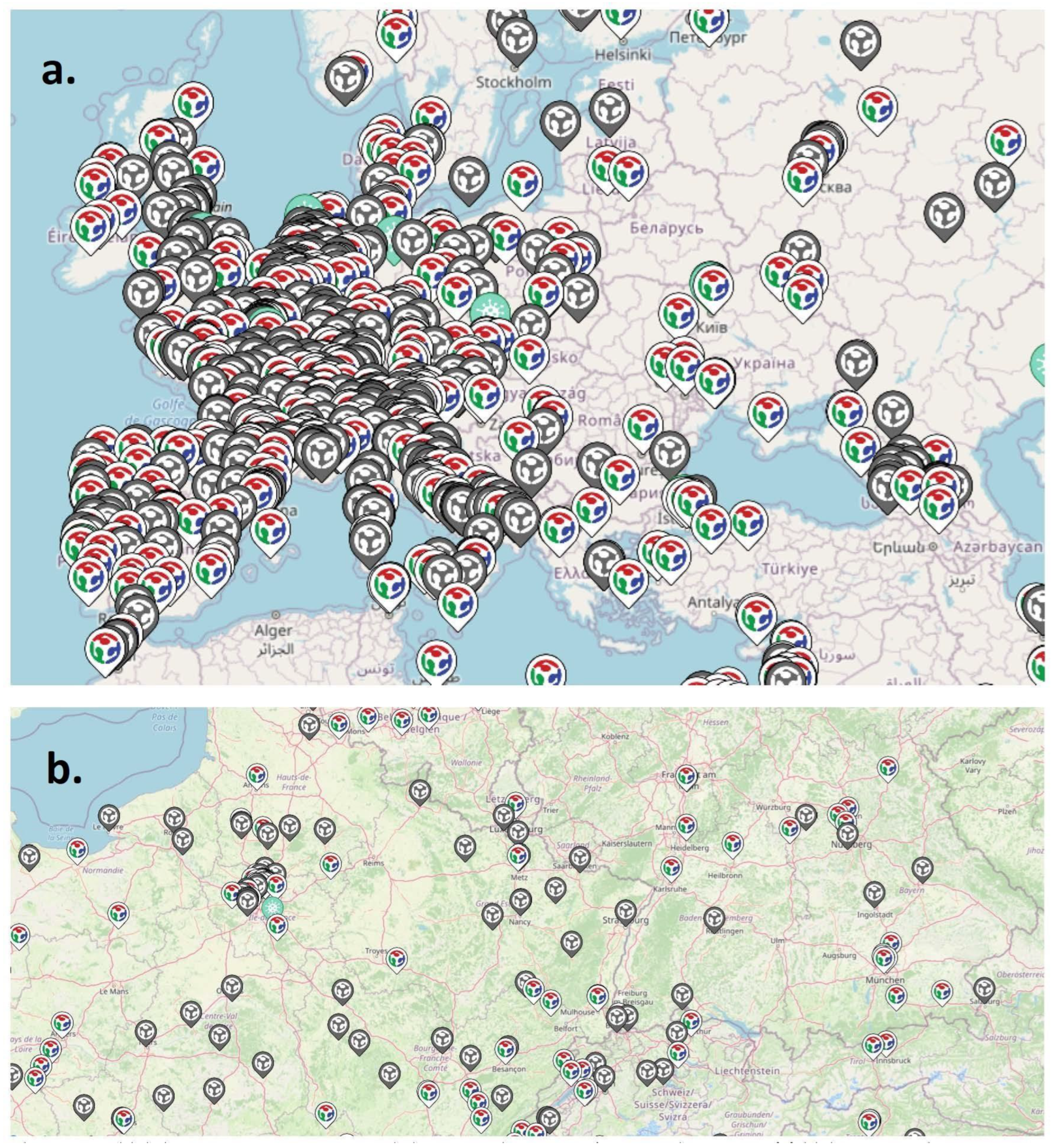
Russia primarily exports to the EU (USD $188), China (USD $58.1B), the Netherlands (USD $41.7B), Belarus (USD $20.5B), Germany (USD $18.9B), and Italy (USD $16.7B) [205]. Thus, these countries are in the best position to spearhead the FOSH development recommended from the results of this study. Europe is particularly well endowed with fablabs and makerspaces as shown in Figure 3 [206]. Thus, they are well prepared to follow a distributed manufacturing (e.g., DIT) model to fabricate EVs, energy conservation equipment and renewable energy such as PV FOSH. In addition, China is already a major open-source technology proponent [207]. China, for example, developed the open-source Kylin operating system, and by 2019, a NeoKylin variant was compatible with more than 4000 software and hardware products and ships pre-installed on most computers sold in China [208]. Combined, Kylin and Neokylin dominate the domestic Chinese market with over 90% of the operating system market share in the government sector [209]. In addition, China is already the leading manufacturer of solar photovoltaics modules, and thus appears well positioned to benefit from FOSH development of peripheral technologies (e.g., racking and electronics) that would increase the size of their market throughout the world faster than it is already increasing.
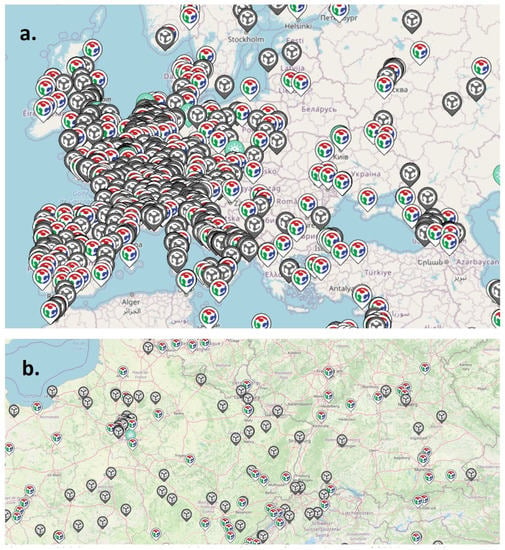
Figure 3.
Fablab locations (a) throughout Europe and (b) zoomed-in view showing clustering of fablabs in population centers [205].
5.2. Target Response
If a wave of FOSH was developed that made energy conservation, heat pumps, EVs and PV extremely inexpensive to manufacture locally, and countries that import Russia’s goods adopted the ‘design global—manufacture local’ system, Russia’s current fossil-fuel-export model would be made obsolete. If Russia attempted to maintain business as usual, it would be economically devastating. As this would be a distributed method of resistance and any retaliation would be against customers, such retaliation would be futile. Instead of maintaining the status quo as an aggressor nation and fossil-fuel exporter, Russia has the opportunity to lift its own citizens out of poverty [210] by leveraging the FOSH funded by external countries to manufacture fossil-fuel-conserving products to meet their own domestic demand and help transition them to a sustainable more diversified economy. This would not only help improve climate stability, but it would also directly improve domestic economic security and thus the perceived need for militarization and aggression.
5.3. Funding National Strategic FOSH Development
There are several ways the open hardware development identified in Section 4 could be funded. First, federal governments can use standard calls for proposals (CFPs) specifically requiring open-source licensing of the FOSH technologies listed. Already, for example, the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) is investing USD $20 million in the Pathways to Enable Open-Source Ecosystems (POSE) program [211]. The NSF aims to “harness the power of open-source development for the creation of new technology solutions to problems of national and societal importance” [211]. Prior work has shown that open-source investment should result in an extremely high return on investment (ROI) in FOSH [29]. The funding would work as normal university or industry grants/contracts, with the exception that rather than fund researchers and allow them to gain a monopoly on the intellectual property, instead there would be an open-source license agreement mandate. In this way, the researchers are still funded, but the benefits of the research accrue to society more directly. Surveys indicate that the vast majority of faculty would be amenable to open-source development as they would accept an open-source-endowed chair requiring them to open source all of their work [212]. Additionally, national and international funding agencies may wish to sponsor challenges or contests such as the XPRIZE to promote development of FOSH toward specific technical goals by offering “bounties”, scholarships, tax breaks, national park passes, lottery entries, awards or even citizenship. The latter rewarding of innovators of citizenship could be a particularly strong incentive to innovate given the current demand in some countries.
In addition to funding and incentivizing FOSH development, governments can also use their purchasing power to accelerate the adoption of FOSH developed in the national interest. This can be achieved by having purchasing policy preferences for open-source technologies. This would include prioritizing funding for open-source technologies over purchasing proprietary commercial products. The government could also make bulk purchases of materials or provide tax breaks for those manufacturing or purchasing FOSH that supports the national interests. Lastly, national governments have the opportunity of creating a free online database of tested, vetted, and validated FOSH to further national interests. It could act as an equivalent to a digital twin model being used in industry [213]. The database would include the bill of materials (BOMs), digital designs files (e.g., CAD), instructions for assembly and operation, and raw source code for all software and firmware. In order to vet designs, governments could provide funding to universities, companies, and/or utilize technical staff at government labs. Already, the U.S. National Institute of Health maintains an open design database called the 3D Print Exchange [214] and the United Nations is evaluating starting an open hardware database for appropriate technology to meet its sustainable development goals [215].
6. Conclusions
This article has reviewed the opportunity to take advantage of the innovation acceleration and economic savings provided by open-source design coupled to distributed manufacturing by formalizing a methodology for selecting strategic national investments in open hardware development to improve national security and global safety. The method was explained in detail, along with a summary of ways to support the FOSH development. For this method to work and scale, FOSH are designed in a way that facilitates distributed manufacturing from digital designs and then made using local materials and tools. Thus, in addition to sanctions or instead of sanctions, nations now have the option of supporting FOSH development to undercut the export market for target criminal countries.
Some of the largest current threats to humanity come from both acts of military aggression and climate destabilization. As the case study results in this review show, by investing in FOSH development of technologies for energy conservation, EVs, heat pumps and renewable energy technologies, nations of good will have the opportunity to radically reduce costs and thus accelerate the diffusion of these technologies that can move humanity towards a sustainable state. With freely available open-source designs of these technologies able to be manufactured locally, as for example in makerspaces and fablabs, the adoption of these technologies can play a strategic role in economically limiting criminal fossil-fuel states, while also helping to limit the negative impacts of global warming.
Funding
This research was supported by the Thompson Endowment.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
References
- Lakhani, K.R.; von Hippel, E. How Open Source Software Works: “Free” User-to-User Assistance. In Produktentwicklung Mit Virtuellen Communities: Kundenwünsche Erfahren und Innovationen Realisieren; Herstatt, C., Sander, J.G., Eds.; Gabler Verlag: Wiesbaden, Germany, 2004; pp. 303–339. ISBN 978-3-322-84540-5. [Google Scholar]
- Zeitlyn, D. Gift Economies in the Development of Open Source Software: Anthropological Reflections. Res. Policy 2003, 32, 1287–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymond, E. The Cathedral and the Bazaar. Know Technol. Pol. 1999, 12, 23–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herstatt, C.; Ehls, D. Open Source Innovation: The Phenomenon, Participant’s Behaviour, Business Implications; Routledge: London, UK, 2015; ISBN 978-1-317-62425-7. [Google Scholar]
- Comino, S.; Manenti, F.M.; Parisi, M.L. From Planning to Mature: On the Success of Open Source Projects. Res. Policy 2007, 36, 1575–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-Y.T.; Kim, H.-W.; Gupta, S. Measuring Open Source Software Success. Omega 2009, 37, 426–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, S. The Success of Open Source; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2004; ISBN 978-0-674-01292-9. [Google Scholar]
- Hiteshdawda. Realising the Value of Cloud Computing with Linux. Available online: https://www.rackspace.com/en-gb/blog/realising-the-value-of-cloud-computing-with-linux (accessed on 24 February 2022).
- Parloff, R. How Linux Conquered the Fortune 500|Fortune. Available online: https://fortune.com/2013/05/06/how-linux-conquered-the-fortune-500/ (accessed on 24 February 2022).
- Vaughan-Nichols, S. Supercomputers: All Linux, All the Time. Available online: https://www.zdnet.com/article/supercomputers-all-linux-all-the-time/ (accessed on 24 February 2022).
- IDC—Smartphone Market Share. Available online: https://www.idc.com/promo/smartphone-market-share (accessed on 24 February 2022).
- Eclipse. IoT Developer Survey 2019 Results. Available online: https://iot.eclipse.org/community/resources/iot-surveys/assets/iot-developer-survey-2019.pdf (accessed on 24 February 2022).
- Gal, M.S. Viral Open Source: Competition vs. Synergy. J. Compet. Law Econ. 2012, 8, 469–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hausberg, J.P.; Spaeth, S. Why Makers Make What They Make: Motivations to Contribute to Open Source Hardware Development. RD Manag. 2020, 50, 75–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, A. Democratizing production through open source knowledge: From open software to open hardware. Media Cult. Soc. 2012, 34, 691–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spaeth, S.; Hausberg, P. Can Open Source Hardware Disrupt Manufacturing Industries? The Role of Platforms and Trust in the Rise of 3D Printing. In The Decentralized and Networked Future of Value Creation: 3D Printing and Its Implications for Society, Industry, and Sustainable Development; Ferdinand, J.-P., Petschow, U., Dickel, S., Eds.; Progress in IS; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 59–73. ISBN 978-3-319-31686-4. [Google Scholar]
- Open Hardware Definition (English). Available online: https://www.oshwa.org/definition/ (accessed on 20 September 2021).
- Cern Ohl Version 2 Wiki Projects/CERN Open Hardware Licence. Available online: https://ohwr.org/project/cernohl/wikis/Documents/CERN-OHL-version-2 (accessed on 24 February 2022).
- Gibb, A. Building Open Source Hardware: DIY Manufacturing for Hackers and Makers; Pearson Education: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Yip, M.C.; Forsslund, J. Spurring Innovation in Spatial Haptics: How Open-Source Hardware Can Turn Creativity Loose. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2017, 24, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosemagen, S.; Liboiron, M.; Molloy, J. Gathering for Open Science Hardware 2016. J. Open Hardw. 2017, 1, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsing, P.-Y. Sustainable Innovation for Open Hardware and Open Science -Lessons from The Hardware Hacker. J. Open Hardw. 2018, 2, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, J.M. Sponsored Libre Research Agreements to Create Free and Open Source Software and Hardware. Inventions 2018, 3, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, P. Tools for Public Participation in Science: Design and Dissemination of Open-Science Hardware. In Proceedings of the 2019 on Creativity and Cognition, San Diego, CA, USA, 13 June 2019; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA; pp. 697–701. [Google Scholar]
- Pearce, J.M. Quantifying the Value of Open Source Hard Ware Development. Mod. Econ. 2015, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, K.F.; Peter, J.G. Open-Source Hardware Is a Low-Cost Alternative for Scientific Instrumentation and Research. Mod. Instrum. 2012, 2012, 18950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberloier, S.; Pearce, J.M. Open Source Low-Cost Power Monitoring System. HardwareX 2018, 4, e00044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, C. Build it. Share it. Profit. Can open source hardware work. Wired Magazine, 20 October 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Pearce, J.M. Return on Investment for Open Source Scientific Hardware Development. Sci. Public Policy 2016, 43, 192–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, J.M. Impacts of Open Source Hardware in Science and Engineering. The Bridge 2017, 47, 24–31. [Google Scholar]
- Harnett, C. Open Source Hardware for Instrumentation and Measurement. IEEE Instrum. Meas. Mag. 2011, 14, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, J.M. Building Research Equipment with Free, Open-Source Hardware. Science 2012, 337, 1303–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, J.M. Open-Source Lab: How to Build Your Own Hardware and Reduce Research Costs; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Chagas, A.M. Haves and have nots must find a better way: The case for open scientific hardware. PLoS Biol. 2018, 16, e3000014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibney, E. ‘Open-Hardware’ Pioneers Push for Low-Cost Lab Kit. Nature 2016, 531, 147–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearce, J.M. Cut Costs with Open-Source Hardware. Nature 2014, 505, 618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearce, J.M. Economic Savings for Scientific Free and Open Source Technology: A Review. HardwareX 2020, 8, e00139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sells, E.; Bailard, S.; Smith, Z.; Bowyer, A.; Olliver, V. RepRap: The Replicating Rapid Prototyper: Maximizing Customizability by Breeding the Means of Production. In Handbook of Research in Mass Customization and Personalization; World Scientific Publishing Company: Singapore, 2009; pp. 568–580. ISBN 978-981-4280-25-9. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, R.; Haufe, P.; Sells, E.; Iravani, P.; Olliver, V.; Palmer, C.; Bowyer, A. RepRap- The replicating rapid prototyper. Robotica 2011, 29, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kentzer, J.; Koch, B.; Thiim, M.; Jones, R.W.; Villumsen, E. An open source hardware-based mechatronics project: The replicating rapid 3-D printer. In Proceedings of the 2011 4th International Conference on Mechatronics (ICOM), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 17–19 May 2011; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Bowyer, A. 3D Printing and Humanity’s First Imperfect Replicator. 3D Print. Addit. Manuf. 2014, 1, 4–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rundle, G. A Revolution in the Making; Simon and Schuster: New York, NY, USA, 2014; ISBN 978-1-922213-48-8. [Google Scholar]
- Wittbrodt, B.T.; Glover, A.G.; Laureto, J.; Anzalone, G.C.; Oppliger, D.; Irwin, J.L.; Pearce, J.M. Life-cycle economic analysis of distributed manufacturing with open-source 3-D printers. Mechatronics 2013, 23, 713–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, E.E.; Pearce, J. Emergence of Home Manufacturing in the Developed World: Return on Investment for Open-Source 3-D Printers. Technologies 2017, 5, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, J.A. Government Open Source Policies. p. 66. Available online: https://openforumeurope.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/06/100416_Open_Source_Policies-1.pdf (accessed on 24 February 2022).
- Heikkinen, I.T.S.; Savin, H.; Partanen, J.; Seppälä, J.; Pearce, J.M. Towards National Policy for Open Source Hardware Research: The Case of Finland. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2020, 155, 119986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobbelaere, T.; Vereecken, P.M.; Detavernier, C. A USB-Controlled Potentiostat/Galvanostat for Thin-Film Battery Characterization. HardwareX 2017, 2, 34–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, E.E.; Kidd, R.W.; Pearce, J.M. Impact of DIY Home Manufacturing with 3D Printing on the Toy and Game Market. Technologies 2017, 5, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olanoff, D. The Internet Has Just Finally Killed The Encyclopedia. Available online: https://thenextweb.com/news/wikipedia-and-the-internet-just-killed-244-year-old-encyclopaedia-britannica (accessed on 24 February 2022).
- Erickson, K.; Perez, F.R.; Perez, J.R. What Is the Commons Worth? Estimating the Value of Wikimedia Imagery by Observing Downstream Use. In Proceedings of the 14th International Symposium on Open Collaboration, Paris, France, 22–24 August 2018; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Fauchart, E.; Bacache-Beauvallet, M.; Bourreau, M.; Moreau, F. Do-It-Yourself or Do-It-Together: How Digital Technologies Affect Creating Alone or with Others? Technovation 2021, 112, 102412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupont, L.; Kasmi, F.; Pearce, J.M.; Ortt, R.J. “Do-It-Together”: Towards the Factories of the Future. Cosmolocal Reader; José, M.R., Michel, B., Sharon, E., James, G.W., Eds.; Cosmo-local Reader; 2021; pp. 52–59. Available online: https://clreader.net/ (accessed on 24 February 2022).
- Mahajan, S.; Luo, C.-H.; Wu, D.-Y.; Chen, L.-J. From Do-It-Yourself (DIY) to Do-It-Together (DIT): Reflections on Designing a Citizen-Driven Air Quality Monitoring Framework in Taiwan. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 66, 102628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirscher, A.-L.; Niinimäki, K.; Joyner Armstrong, C.M. Social Manufacturing in the Fashion Sector: New Value Creation through Alternative Design Strategies? J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 4544–4554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullmann, S.; Guittard, C.; Schenk, E. Participative Creativity Serving Product Design in SMEs: A case study. J. Innov. Econ. Manag. 2015, 18, 79–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russia. The World Factbook; CIA: Washington, DC, USA, 2022. Available online: https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/russia (accessed on 24 February 2022).
- Kristensen, H.M.; Norris, R.S. Russian Nuclear Forces. Bull. At. Sci. 2016, 72, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, R.S.; Kristensen, H.M. Global Nuclear Weapons Inventories, 1945–2010. Bull. At. Sci. 2010, 66, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, J.M.; Denkenberger, D.C. A National Pragmatic Safety Limit for Nuclear Weapon Quantities. Safety 2018, 4, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russia: Average Nominal Wage per Month 2020. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1010660/russia-average-monthly-nominal-wage/ (accessed on 25 February 2022).
- Rutland, P. Russia as an Energy Superpower. New Political Econ. 2008, 13, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Natural Gas Reserves by Country 2020. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/265329/countries-with-the-largest-natural-gas-reserves/ (accessed on 25 February 2022).
- Putin Says He Moonlighted as Taxi Driver after Fall of Soviet Union. Available online: https://www.nbcnews.com/news/world/russia-s-putin-laments-soviet-collapse-says-he-moonlighted-taxi-n1285807 (accessed on 25 February 2022).
- Makszimov, V. Strasbourg Court Rules Russia Has “Direct Control” over Abkhazia, South Ossetia. Available online: https://www.euractiv.com/section/europe-s-east/news/strasbourg-court-rules-russia-has-direct-control-over-abkhazia-south-ossetia/ (accessed on 25 February 2022).
- European Court Finds Russia Guilty of Georgia Violations in 2008. Available online: https://www.euronews.com/2021/01/26/russia-guilty-of-violations-during-2008-war-with-georgia-says-europe-s-top-court (accessed on 25 February 2022).
- Mankoff, J. Russia’s Latest Land Grab: How Putin Won Crimea and Lost Ukraine. Foreign Aff. 2014, 93, 60. [Google Scholar]
- Treisman, D. Why Putin Took Crimea: The Gambler in the Kremlin. Foreign Aff. 2016, 95, 47. [Google Scholar]
- Resolutions Calling on Withdrawal of Forces from Crimea, Establishing Epidemic Preparedness International Day among Texts Adopted by General Assembly|Meetings Coverage and Press Releases. Available online: https://www.un.org/press/en/2020/ga12295.doc.htm (accessed on 25 February 2022).
- Putin Shatters Peace in Europe as Russia Invades Ukraine. Available online: https://www.aljazeera.com/news/2022/2/24/russia-putin-shatters-peace-europe-ukraine-invasion (accessed on 25 February 2022).
- Toh, M.; Ogura, J.; Humayun, H.; McGee, C.; Yee, I.; Cheung, E.; Fossum, S.; Kennedy, N. CNN The List of Global Sanctions on Russia for the War in Ukraine. Available online: https://www.cnn.com/2022/02/25/business/list-global-sanctions-russia-ukraine-war-intl-hnk/index.html (accessed on 25 February 2022).
- CNN, K.L. Biden Imposes Additional Sanctions on Russia: “Putin Chose This War”. Available online: https://www.cnn.com/2022/02/24/politics/joe-biden-ukraine-russia-sanctions/index.html (accessed on 25 February 2022).
- Henderson, J.; Mitrova, T. Implications of the Global Energy Transition on Russia. In The Geopolitics of the Global Energy Transition; Hafner, M., Tagliapietra, S., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Energy; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 93–114. ISBN 978-3-030-39066-2. [Google Scholar]
- Jamet, S.; Corfee-Morlot, J. Assessing the Impacts of Climate Change: A Literature Review; OECD: Paris, France, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Kummu, M.; Heino, M.; Taka, M.; Varis, O.; Viviroli, D. Climate Change Risks Pushing One-Third of Global Food Production Outside the Safe Climatic Space. One Earth 2021, 4, 720–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, S.; Ebi, K. Preventing and Mitigating Health Risks of Climate Change. Environ. Res. 2019, 174, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stern, N. Stern Review: The Economics of Climate Change; Government of the United Kingdom: London, UK, 2006.
- Russia (RUS) Exports, Imports, and Trade Partners|OEC -The Observatory of Economic Complexity. Available online: https://oec.world/en/profile/country/rus/ (accessed on 25 February 2022).
- Hansen, J.; Kharecha, P.; Sato, M.; Masson-Delmotte, V.; Ackerman, F.; Beerling, D.J.; Hearty, P.J.; Hoegh-Guldberg, O.; Hsu, S.-L.; Parmesan, C.; et al. Assessing “Dangerous Climate Change”: Required Reduction of Carbon Emissions to Protect Young People, Future Generations and Nature. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ripple, W.J.; Wolf, C.; Newsome, T.M.; Galetti, M.; Alamgir, M.; Crist, E.; Mahmoud, M.I.; Laurance, W.F. World Scientists’ Warning to Humanity: A Second Notice. BioScience 2017, 67, 1026–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachauri, R.K.; Allen, M.R.; Barros, V.R.; Broome, J.; Cramer, W.; Christ, R.; Church, J.A.; Clarke, L.; Dahe, Q.; Dasgupta, P.; et al. Climate Change 2014: Synthesis Report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Pachauri, R., Meyer, L., Eds.; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014; 151p, ISBN 978-92-9169-143-2. [Google Scholar]
- Moss, R.H.; Edmonds, J.A.; Hibbard, K.A.; Manning, M.R.; Rose, S.K.; Van Vuuren, D.P.; Carter, T.R.; Emori, S.; Kainuma, M.; Kram, T.; et al. The next generation of scenarios for climate change research and assessment. Nature 2010, 463, 747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhainaut, J.F.; Claessens, Y.E.; Ginsburg, C.; Riou, B. Unprecedented heat-related deaths during the 2003 heat wave in Paris: Consequences on emergency departments. Crit. Care 2003, 8, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poumadère, M.; Mays, C.; Le Mer, S.; Blong, R. The 2003 Heat Wave in France: Dangerous Climate Change Here and Now: The 2003 Heat Wave in France. Risk Anal. 2005, 25, 1483–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouillet, A.; Rey, G.; Laurent, F.; Pavillon, G.; Bellec, S.; Guihenneuc-Jouyaux, C.; Clavel, J.; Jougla, E.; Hémon, D. Excess mortality related to the August 2003 heat wave in France. Int. Arch. Occ. Env. Health 2006, 80, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amato, G.; Cecchi, L. Effects of climate change on environmental factors in respiratory allergic diseases. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2008, 38, 1264–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gislason, A.; Gorsky, G. (Eds.) Proceedings of the Joint ICES/CIESM Workshop to Compare Zooplankton Ecology and Methodologies between the Mediterranean and the North Atlantic (WKZEM); ICES, International Council for the Exploration of the Sea: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Parry, M.L.; Rosenzweig, C.; Iglesias, A.; Livermore, M.; Fischer, G. Effects of climate change on global food production under SRES emissions and socio-economic scenarios. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2004, 14, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parry, M.; Rosenzweig, C.; Livermore, M. Climate change, global food supply and risk of hunger. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society. Bio. Sci. 2005, 360, 2125–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidhuber, J.; Tubiello, F.N. Global food security under climate change. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 19703–19708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vine, E. Adaptation of California’s electricity sector to climate change. Clim. Chang. 2012, 111, 75–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Val, D.V.; Yurchenko, D.; Nogal, M.; O’Connor, A. Chapter Seven-Climate Change-Related Risks and Adaptation of Interdependent Infrastructure Systems. In Climate Adaptation Engineering; Bastidas-Arteaga, E., Stewar, M.G., Eds.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2019; pp. 207–242. ISBN 978-0-12-816782-3. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, A. Drought under global warming: A review. WIREs Clim. Chang. 2011, 2, 45–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diffenbaugh, N.S.; Swain, D.L.; Touma, D. Anthropogenic warming has increased drought risk in California. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 3931–3936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, M.E.; Gleick, P.H. Climate change and California drought in the 21st century. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 3858–3859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dale, V.H.; Joyce, L.A.; Mcnulty, S.; Neilson, R.P.; Ayres, M.P.; Flannigan, M.D.; Hanson, P.J.; Irland, L.C.; Lugo, A.E.; Peterson, C.J.; et al. Climate Change and Forest Disturbances. BioScience 2001, 51, 723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiro, B.D.; Stocks, B.J.; Alexander, M.E.; Flannigan, M.D.; Wotton, B.M. Fire, climate change, carbon and fuel management in the Canadian boreal forest. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2001, 10, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flannigan, M.; Stocks, B.; Turetsky, M.; Wotton, M. Impacts of climate change on fire activity and fire management in the circumboreal forest. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2009, 15, 549–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorhead, K.K.; Brinson, M.M. Response of Wetlands to Rising Sea Level in the Lower Coastal Plain of North Carolina. Ecol. App. 1995, 5, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frihy, O.E. The Nile delta-Alexandria coast: Vulnerability to sea-level rise, consequences and adaptation. Mitig. Adapt. Strateg. Glob. Chang. 2003, 8, 115–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobba, A.G. Numerical modelling of salt-water intrusion due to human activities and sea-level change in the Godavari Delta, India. Hydro. Sci. J. 2002, 47, S67–S80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, V.E.A. Fresh and Saline Groundwater Interaction in Coastal Aquifers: Is Our Technology Ready for the Problems Ahead? Hydrogeol. J. 2005, 13, 120–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholls, R.J.; Hoozemans, F.M.; Marchand, M. Increasing flood risk and wetland losses due to global sea-level rise: Regional and global analyses. Glob. Environ. Chang. 1999, 9, S69–S87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desantis, L.R.G.; Bhotika, S.; Williams, K.; Putz, F.E. Sea-level rise and drought interactions accelerate forest decline on the Gulf Coast of Florida, USA. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2007, 13, 2349–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, D.; Hunt, J.; Mason, P.; Wheater, H.; Wolf, P.; Poff, N.L. Ecological Response to and Management of Increased Flooding Caused by Climate Change. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2002, 360, 1497–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knox, J.C. Sensitivity of Modern and Holocene Floods to Climate Change. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2000, 19, 439–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnicer, J.; Coll, M.; Ninyerola, M.; Pons, X.; Sánchez, G.; Peñuelas, J. Widespread crown condition decline, food web disruption, and amplified tree mortality with increased climate change-type drought. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 1474–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Ou, X.; Yan, X.; Zhang, X. Electric Vehicle Market Penetration and Impacts on Energy Consumption and CO2 Emission in the Future: Beijing Case. Energies 2017, 10, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, F. Global Market Share of Electric Cars More than Doubled in 2021 as the EV Revolution Gains Steam. Electrek 2022. Available online: https://electrek.co/2022/02/02/global-market-share-of-electric-cars-more-than-doubled-2021/ (accessed on 24 February 2022).
- Sanguesa, J.A.; Torres-Sanz, V.; Garrido, P.; Martinez, F.J.; Marquez-Barja, J.M. A Review on Electric Vehicles: Technologies and Challenges. Smart Cities 2021, 4, 372–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Bae, C.; Denlinger, A.; Miller, T. Electric Vehicles Batteries: Requirements and Challenges. Joule 2020, 4, 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan-Nichols, S. EVerest: The Open Source Software Stack for EV Charging Infrastructure. Available online: https://www.zdnet.com/article/everest-the-open-source-software-stack-for-electric-vehicle-charging-infrastructure/ (accessed on 25 February 2022).
- All Our Patent Are Belong to You. Available online: https://www.tesla.com/blog/all-our-patent-are-belong-you (accessed on 25 February 2022).
- Ford Motor Company Announces Open Source Portfolio of EV Patents. Available online: http://greenlivingguy.com/2015/06/ford-motor-company-announces-open-source-portfolio-of-ev-patents/ (accessed on 27 February 2022).
- Sylvestrin, G.R.; Scherer, H.F.; Hideo Ando Junior, O. Hardware and Software Development of an Open Source Battery Management System. IEEE Lat. Am. Trans. 2021, 19, 1153–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, J.; Amietszajew, T.; McTurk, E.; Towers, D.P.; Greenwood, D.; Bhagat, R. Development and Evaluation of In-Situ Instrumentation for Cylindrical Li-Ion Cells Using Fibre Optic Sensors. HardwareX 2018, 3, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carloni, A.; Baronti, F.; Di Rienzo, R.; Roncella, R.; Saletti, R. An Open-Hardware and Low-Cost Maintenance Tool for Light-Electric-Vehicle Batteries. Energies 2021, 14, 4962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yensen, N.; Allen, P.B. Open Source All-Iron Battery for Renewable Energy Storage. HardwareX 2019, 6, e00072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koirala, D.; Yensen, N.; Allen, P.B. Open Source All-Iron Battery 2.0. HardwareX 2021, 9, e00171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loukatos, D.; Dimitriou, N.; Manolopoulos, I.; Kontovasilis, K.; Arvanitis, K.G. Revealing Characteristic IoT Behaviors by Performing Simple Energy Measurements via Open Hardware/Software Components. In Proceedings of the Sixth International Congress on Information and Communication Technology, London, UK, 25–26 February 2021; Yang, X.-S., Sherratt, S., Dey, N., Joshi, A., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 1045–1053. [Google Scholar]
- Raval, M.; Bhardwaj, S.; Aravelli, A.; Dofe, J.; Gohel, H. Smart Energy Optimization for Massive IoT Using Artificial Intelligence. Internet Things 2021, 13, 100354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, L.J.R.; Aponte, G.P.; Garcia, A.R. Internet of Things Applied in Healthcare Based on Open Hardware with Low-Energy Consumption. Healthc. Inform. Res. 2019, 25, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viciana, E.; Alcayde, A.; Montoya, F.G.; Baños, R.; Arrabal-Campos, F.M.; Manzano-Agugliaro, F. An Open Hardware Design for Internet of Things Power Quality and Energy Saving Solutions. Sensors 2019, 19, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makonin, S.; Popowich, F.; Moon, T.; Gill, B. Inspiring Energy Conservation through Open Source Power Monitoring and In-Home Display. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Power Energy Society General Meeting, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 21–25 July 2013; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Makonin, S.; Sung, W.; Dela Cruz, R.; Yarrow, B.; Gill, B.; Popowich, F.; Bajić, I.V. Inspiring Energy Conservation through Open Source Metering Hardware and Embedded Real-Time Load Disaggregation. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE PES Asia-Pacific Power and Energy Engineering Conference (APPEEC), Kowloon, Hong Kong, 8–11 December 2013; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Adamo, F.; Cavone, G.; Di Nisio, A.; Lanzolla, A.M.L.; Spadavecchia, M. A Proposal for an Open Source Energy Meter. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference (I2MTC), Minneapolis, MN, USA, 6–9 May 2013; pp. 488–492. [Google Scholar]
- Ferry, C.; Connolly, J. Open Source Power Quality Meter with Cloud Monitoring. In Proceedings of the 2020 31st Irish Signals and Systems Conference (ISSC), Letterkenny, Ireland, 11–12 June 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Klemenjak, C.; Egarter, D.; Elmenreich, W. YoMo: The Arduino-Based Smart Metering Board. Comput. Sci. Res. Dev. 2016, 31, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemenjak, C.; Jost, S.; Elmenreich, W. YoMoPie: A User-Oriented Energy Monitor to Enhance Energy Efficiency in Households. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Conference on Technologies for Sustainability (SusTech), Long Beach, CA, USA, 11–13 November 2018; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Jameel, H.; Farhan, H.K. Low-Cost Energy-Efficient Smart Monitoring System Using Open-Source Microcontrollers. IREACO 2016, 9, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pocero, L.; Amaxilatis, D.; Mylonas, G.; Chatzigiannakis, I. Open Source IoT Meter Devices for Smart and Energy-Efficient School Buildings. HardwareX 2017, 1, 54–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreou, G.T.; Chatzigeorgiou, I.M. Open Source Hardware and Software to Support Energy Efficiency and Demand Response in LV Installations. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Eindhoven PowerTech, Eindhoven, The Netherlands, 29 June 2015; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Merenda, M.; Iero, D.; Pangallo, G.; Falduto, P.; Adinolfi, G.; Merola, A.; Graditi, G.; Della Corte, F.G. Open-Source Hardware Platforms for Smart Converters with Cloud Connectivity. Electronics 2019, 8, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlakić, D.; Baghaee, H.R.; Nikolovski, S.; Vukobratović, M.; Balkić, Z. Conceptual Design of IoT-Based AMR Systems Based on IEC 61850 Microgrid Communication Configuration Using Open-Source Hardware/Software IED. Energies 2019, 12, 4281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A DIY Blower Door—Easy to Build—Easy to Use—Cheap. Available online: https://www.builditsolar.com/Projects/Conservation/BlowerDoor/BlowerDoor.htm (accessed on 25 February 2022).
- Walter-Herrmann, J.; Büching, C. FabLab: Of Machines, Makers and Inventors; Transcript Verlag: Bielefeld, Germany, 2014; ISBN 978-3-8394-2382-0. [Google Scholar]
- Redlich, T.; Buxbaum-Conradi, S.; Basmer-Birkenfeld, S.-V.; Moritz, M.; Krenz, P.; Osunyomi, B.D.; Wulfsberg, J.P.; Heubischl, S. OpenLabs—Open Source Microfactories Enhancing the FabLab Idea. In Proceedings of the 2016 49th Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences (HICSS), Kauai, HI, USA, 5–8 January 2016; pp. 707–715. [Google Scholar]
- Open Source Cellulose Insulation Manufacturing. Available online: https://www.appropedia.org/Open_source_cellulose_insulation_manufacturing (accessed on 25 February 2022).
- Domínguez, J.E.; Olivos, E.; Vázquez, C.; Rivera, J.M.; Hernández-Cortes, R.; González-Benito, J. Automated Low-Cost Device to Produce Sub-Micrometric Polymer Fibers Based on Blow Spun Method. HardwareX 2021, 10, e00218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E.U. Will Unveil a Strategy to Break Free from Russian Gas, after Decades of Dependence. Washington Post. Available online: https://www.washingtonpost.com/climate-environment/2022/02/23/russia-ukraine-eu-nordstream-strategy-energy/ (accessed on 24 February 2022).
- Pearce, J.M.; Sommerfeldt, N. Economics of Grid-Tied Solar Photovoltaic Systems Coupled to Heat Pumps: The Case of Northern Climates of the U.S. and Canada. Energies 2021, 14, 834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padovani, F.; Sommerfeldt, N.; Longobardi, F.; Pearce, J.M. Decarbonizing Rural Residential Buildings in Cold Climates: A Techno-Economic Analysis of Heating Electrification. Energy Build. 2021, 250, 111284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowntree, D. Arduino Powered Heat Pump Controller Helps Warm Your Toes. Hackaday 2021. Available online: https://hackaday.com/2021/09/08/arduino-powered-heat-pump-controller-helps-warm-your-toes/ (accessed on 24 February 2022).
- Thomson, C.C.; Jakubowski, M. Toward an Open Source Civilization: Innovations Case Narrative: Open Source Ecology. Innov. Technol. Gov. Glob. 2012, 7, 53–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renewable Electricity Growth Is Accelerating Faster than Ever Worldwide, Supporting the Emergence of the New Global Energy Economy—News. Available online: https://www.iea.org/news/renewable-electricity-growth-is-accelerating-faster-than-ever-worldwide-supporting-the-emergence-of-the-new-global-energy-economy (accessed on 25 February 2022).
- Choi, C.-S.; Jeong, J.-D.; Lee, I.-W.; Park, W.-K. LoRa Based Renewable Energy Monitoring System with Open IoT Platform. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Electronics, Information, and Communication (ICEIC), Honolulu, HI, USA, 24–27 January 2018; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Vidal, Y.; Acho, L.; Luo, N.; Tutiven, C. Hardware in the Loop Wind Turbine Simulator for Control System Testing. In Wind Turbine Control and Monitoring; Luo, N., Vidal, Y., Acho, L., Eds.; Advances in Industrial Control; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 449–466. ISBN 978-3-319-08413-8. [Google Scholar]
- Reinauer, T.; Hansen, U.E. Determinants of Adoption in Open-Source Hardware: A Review of Small Wind Turbines. Technovation 2021, 106, 102289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solar Industry Research Data. Available online: https://www.seia.org/solar-industry-research-data (accessed on 13 April 2020).
- Vaughan, A. Time to shine: Solar power is fastest-growing source of new energy. Guardian, 4 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Pearce, J.M. Photovoltaics—A Path to Sustainable Futures. Futures 2002, 34, 663–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, J.; Lau, A. Net Energy Analysis For Sustainable Energy Production From Silicon Based Solar Cells. In Proceedings of the American Society of Mechanical Engineers Solar 2002: Sunrise on the Reliable Energy Economy, Reno, NV, USA, 15–20 June 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Fthenakis, V.M.; Moskowitz, P.D. Photovoltaics: Environmental, health and safety issues and perspectives. Prog. Photovolt. Res. Appl. 2000, 8, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fthenakis, V.; Alsema, E. Photovoltaics energy payback times, greenhouse gas emissions and external costs: 2004–early 2005 status. Prog. Photovolt. Res. Appl. 2006, 14, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman, D.; Barbose, G.; Margolis, R.; Bolinger, M.; Chung, D.; Fu, R.; Seel, J.; Davidson, C.; Darghouth, N.; Wiser, R. Photovoltaic System Pricing Trends: Historical, Recent, and Near-Term Projections 2015 Edition; NREL: Golden, CO, USA, 2015.
- Barbose, G.L.; Darghouth, N.R.; LaCommare, K.H.; Millstein, D.; Rand, J. Tracking the Sun: Installed Price Trends for Distributed Photovoltaic Systems in the United States-2018 Edition; LBL: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2018.
- Barron, A.R. Cost reduction in the solar industry. Mater. Today 2015, 18, 2–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Matasci, S. Solar Panel Cost: Avg. Solar Panel Prices by State in 2019: EnergySage. Solar News, Energy Sage. 5 June 2019. Available online: news.energysage.com/how-much-does-the-average-solar-panel-installation-cost-in-the-u-s/ (accessed on 24 February 2022).
- Dudley, D. Renewable Energy Will Be Consistently Cheaper Than Fossil Fuels by 2020, Report Claims [WWW Document]. Forbes. 2019. Available online: https://www.forbes.com/sites/dominicdudley/2018/01/13/renewable-energy-cost-effective-fossil-fuels-2020/ (accessed on 13 April 2020).
- Minigrids in the Money. Available online: https://rmi.org/insight/minigrids-money/ (accessed on 25 February 2022).
- Alafita, T.; Pearce, J.M. Securitization of residential solar photovoltaic assets: Costs, risks and uncertainty. Energy Policy 2014, 67, 488–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grafman, L.; Pearce, J.M. To Catch the Sun; Humboldt University Press: Arcata, CA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Feldman, D.G.; Barbose, R.; Margolis, R.; Wiser, N.D.; Goodrich, A. Photovoltaic (PV) Pricing Trends: Historical, Recent, and Near-Term Projections, Sunshot; NREL: Golden, CO, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Renewables International. Photovoltaics after Grid Parity Plug-and-Play PV: The Controversy 2013. Renewables. 2013. Available online: http://www.renewablesinternational.net/plug-and-play-pv-the-controversy/150/452/72715/ (accessed on 18 December 2015).
- Mundada, A.S.; Nilsiam, Y.; Pearce, J.M. A review of technical requirements for plug-and-play solar photovoltaic microinverter systems in the United States. Sol. Energy 2016, 135, 455–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.T.A.; Norris, G.; Chattopadhyay, R.; Husain, I.; Bhattacharya, S. Autoinspection and Permitting with a PV Utility Interface (PUI) for Residential Plug-and-Play Solar Photovoltaic Unit. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2017, 53, 1337–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.T.A.; Husain, I.; Lubkeman, D. Power electronic components and system installation for plug-and-play residential solar PV. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 14–18 September 2014; pp. 3272–3278. [Google Scholar]
- Lundstrom, B.R. Plug and Play Solar Power: Simplifying the Integration of Solar Energy in Hybrid Applications; Cooperative Research and Development Final Report, CRADA Number CRD-13-523; National Renewable Energy Lab. (NREL): Golden, CO, USA, 2017.
- Mundada, A.S.; Prehoda, E.W.; Pearce, J.M. US market for solar photovoltaic plug-and-play systems. Renew. Energy 2017, 103, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittbrodt, B.; Pearce, J.M. 3-D Printing Solar Photovoltaic Racking in Developing World. Energy Sustain. Dev. 2017, 36, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollman, M.R.; Pearce, J.M. Geographic Potential of Shotcrete Photovoltaic Racking: Direct and Low-Concentration Cases. Sol. Energy 2021, 216, 386–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arefeen, S.; Dallas, T. Low-Cost Racking for Solar Photovoltaic Systems with Renewable Tensegrity Structures. Sol. Energy 2021, 224, 798–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, J.M. Parametric Open Source Cold-Frame Agrivoltaic Systems. Inventions 2021, 6, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittbrodt, B.T.; Pearce, J.M. Total U.S. Cost Evaluation of Low-Weight Tension-Based Photovoltaic Flat-Roof Mounted Racking. Sol. Energy 2015, 117, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittbrodt, B.; Laureto, J.; Tymrak, B.; Pearce, J.M. Distributed Manufacturing with 3-D Printing: A Case Study of Recreational Vehicle Solar Photovoltaic Mounting Systems. J. Frugal Innov. 2015, 1, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, J.M.; Meldrum, J.; Osborne, N. Design of Post-Consumer Modification of Standard Solar Modules to Form Large-Area Building-Integrated Photovoltaic Roof Slates. Designs 2017, 1, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motahhir, S.; EL Hammoumi, A.; EL Ghzizal, A.; Derouich, A. Open Hardware/Software Test Bench for Solar Tracker with Virtual Instrumentation. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2019, 31, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carballo, J.A.; Bonilla, J.; Roca, L.; Berenguel, M. New Low-Cost Solar Tracking System Based on Open Source Hardware for Educational Purposes. Sol. Energy 2018, 174, 826–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carballo, J.A.; Bonilla, J.; Berenguel, M.; Fernández-Reche, J.; García, G. New Approach for Solar Tracking Systems Based on Computer Vision, Low Cost Hardware and Deep Learning. Renew. Energy 2019, 133, 1158–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Uceda, F.J.; Ramirez-Faz, J.; Varo-Martinez, M.; Fernández-Ahumada, L.M. New Omnidirectional Sensor Based on Open-Source Software and Hardware for Tracking and Backtracking of Dual-Axis Solar Trackers in Photovoltaic Plants. Sensors 2021, 21, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buitenhuis, A.J.; Pearce, J.M. Open-Source Development of Solar Photovoltaic Technology. Energy Sustain. Dev. 2012, 16, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, J.S.; Holmgren, W.F.; Forbess, J.; Hansen, C.W. PVLIB: Open Source Photovoltaic Performance Modeling Functions for Matlab and Python. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 43rd Photovoltaic Specialists Conference, Portland, OR, USA, 5–10 June 2016; pp. 3425–3430. [Google Scholar]
- Andrews, R.W.; Stein, J.S.; Hansen, C.; Riley, D. Introduction to the Open Source PV LIB for Python Photovoltaic System Modelling Package. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE 40th Photovoltaic Specialist Conference, Denver, CO, USA, 8–13 June 2014; pp. 170–174. [Google Scholar]
- Freeman, J.M.; DiOrio, N.A.; Blair, N.J.; Neises, T.W.; Wagner, M.J.; Gilman, P.; Janzou, S. System Advisor Model (SAM) General Description (Version 2017.9.5); National Renewable Energy Lab. (NREL): Golden, CO, USA, 2018.
- SAM Open Source—System Advisor Model (SAM). Available online: https://sam.nrel.gov/about-sam/sam-open-source.html (accessed on 26 February 2022).
- Merenda, M.; Iero, D.; Carotenuto, R.; Della Corte, F.G. Simple and Low-Cost Photovoltaic Module Emulator. Electronics 2019, 8, 1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunderman, W.; Dugan, R.C.; Smith, J. Open Source Modeling of Advanced Inverter Functions for Solar Photovoltaic Installations. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE PES T D Conference and Exposition, Chicago, IL, USA, 14 April 2014; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Hofierka, J.; Kaňuk, J. Assessment of Photovoltaic Potential in Urban Areas Using Open-Source Solar Radiation Tools. Renew. Energy 2009, 34, 2206–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.T.; Pearce, J.M. Estimating Potential Photovoltaic Yield with r.Sun and the Open Source Geographical Resources Analysis Support System. Sol. Energy 2010, 84, 831–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, J.; Babasola, A.; Andrews, R. Open Solar Photovoltaic Systems Optimization. In Proceedings of the Open 2012: NCIIA 16th Annual Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 21–24 May 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Botero-Valencia, J.S.; Valencia-Aguirre, J.; Gonzalez-Montoya, D.; Ramos-Paja, C.A. A Low-Cost System for Real-Time Measuring of the Sunlight Incident Angle Using IoT. HardwareX 2022, 11, e00272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botero-Valencia, J.S.; Mejia-Herrera, M. Modular System for UV–Vis-NIR Radiation Measurement with Wireless Communication. HardwareX 2021, 10, e00236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botero-Valencia, J.S.; Mejia-Herrera, M.; Pearce, J.M. Design and Implementation of 3-D Printed Radiation Shields for Environmental Sensors. HardwareX 2022, 11, e00267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, I.; Portalo, J.M.; Calderón, A.J. Configurable IoT Open-Source Hardware and Software I-V Curve Tracer for Photovoltaic Generators. Sensors 2021, 21, 7650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, T.; Thakur, R. Design and Development of PV Solar Panel Data Logger. IJCSE 2019, 7, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montes-Romero, J.; Piliougine, M.; Muñoz, J.V.; Fernández, E.F.; De la Casa, J. Photovoltaic Device Performance Evaluation Using an Open-Hardware System and Standard Calibrated Laboratory Instruments. Energies 2017, 10, 1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papageorgas, P.; Piromalis, D.; Antonakoglou, K.; Vokas, G.; Tseles, D.; Arvanitis, K.G. Smart Solar Panels: In-Situ Monitoring of Photovoltaic Panels Based on Wired and Wireless Sensor Networks. Energy Procedia 2013, 36, 535–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charaabi, L. Open Monitoring System for Photovoltaic Solar Installations. In Proceedings of the 2020 6th IEEE International Energy Conference (ENERGYCon), Gammarth, Tunisia, 1 October 2020; pp. 1068–1071. [Google Scholar]
- De Arquer Fernández, P.; Fernández Fernández, M.Á.; Carús Candás, J.L.; Arboleya Arboleya, P. An IoT Open Source Platform for Photovoltaic Plants Supervision. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2021, 125, 106540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Vargas, A.; Fuentes, M.; García, M.V.; Muñoz-Rodríguez, F.J. Low-Cost Datalogger Intended for Remote Monitoring of Solar Photovoltaic Standalone Systems Based on ArduinoTM. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 19, 4308–4320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Vargas, A.; Fuentes, M.; Vivar, M. On the Application of IoT for Real-Time Monitoring of Small Stand-Alone PV Systems: Results from a New Smart Datalogger. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 7th World Conference on Photovoltaic Energy Conversion (WCPEC) (A Joint Conference of 45th IEEE PVSC, 28th PVSEC 34th EU PVSEC), Waikoloa, HI, USA, 10–15 June 2018; pp. 605–607. [Google Scholar]
- Portalo, J.M.; González, I.; Calderón, A.J. Monitoring System for Tracking a PV Generator in an Experimental Smart Microgrid: An Open-Source Solution. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González Pérez, I.; Calderón Godoy, A.J.; Portalo Calero, J.M.; Calderón Godoy, M. Monitoring Interfaces for Photovoltaic Systems and DC Microgrids: Brief Survey and Application Case; Universidade da Coruña, Servizo de Publicacións: A Coruña, Spain, 2021; pp. 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botero-Valencia, J.S.; Mejia-Herrera, M.; Pearce, J.M. Low Cost Climate Station for Smart Agriculture Applications with Photovoltaic Energy and Wireless Communication. HardwareX 2022, 11, e00296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadhim Abed, J. Smart Monitoring System of DC to DC Converter for Photovoltaic Application. IJPEDS 2018, 9, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russia Exports—January 2022 Data—1994-2021 Historical—February Forecast. Available online: https://tradingeconomics.com/russia/exports (accessed on 25 February 2022).
- Labs Map|FabLabs. Available online: https://www.fablabs.io/labs/map (accessed on 26 February 2022).
- China Bets on Open-Source Technologies to Boost Domestic Innovation. Available online: https://merics.org/en/short-analysis/china-bets-open-source-technologies-boost-domestic-innovation (accessed on 26 February 2022).
- Cimpanu, C. Two of China’s Largest Tech Firms Are Uniting to Create a New ‘Domestic OS’|ZDNet. 2019. Available online: https://www.zdnet.com/google-amp/article/two-of-chinas-largest-tech-firms-are-uniting-to-create-a-new-domestic-os (accessed on 24 February 2022).
- Winning Bid Software + Tianjin Kirin = the New Flagship of China’s Domestic Operating System-China Electronics. Available online: https://www.cec.com.cn/jtxw/2019/1209/8ac085cc6e112a0f016ee947c8ac00b5.html (accessed on 24 February 2022).
- One-Fifth Of Russians Live In Poverty, 36 Percent In “Risk Zone”, Study Finds. Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty 14:19:18Z. Available online: https://www.rferl.org/a/study-22-percent-of-russians-live-in-poverty-36-percent-in-risk-zone-/29613059.html (accessed on 24 February 2022).
- Pathways to Enable Open-Source Ecosystems (POSE). Available online: https://beta.nsf.gov/funding/opportunities/pathways-enable-open-source-ecosystems-pose (accessed on 26 February 2022).
- Pearce, J.; Pascaris, A.S.; Schelly, C. Professors Want to Share: Preliminary Survey Results on Establishing Open Source Endowed Professorships. Res. Sq. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierla, S.; Sorsamäki, L.; Azangoo, M.; Villberg, A.; Hytönen, E.; Vyatkin, V. Towards Semi-Automatic Generation of a Steady State Digital Twin of a Brownfield Process Plant. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coakley, M.F.; Hurt, D.E.; Weber, N.; Mtingwa, M.; Fincher, E.C.; Alekseyev, V.; Chen, D.T.; Yun, A.; Gizaw, M.; Swan, J.; et al. The NIH 3D Print Exchange: A Public Resource for Bioscientific and Biomedical 3D Prints. 3D Print. Addit. Manuf. 2014, 1, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNCTAD. Note on a Proposed United Nations Centralised Database of Open-Source Appropriate Technologies; UNCTAD: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021; Available online: https://unctad.org/webflyer/note-proposed-united-nations-centralised-database-open-source-appropriate-technologies (accessed on 24 February 2022).
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).