Antimicrobial Desensitization: A Review of Published Protocols
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Indications and Contraindications
2.1.1. Indications
2.1.2. Contraindications
2.2. Review of Antimicrobial Desensitization Protocols
2.2.1. β-Lactam Antimicrobials
Penicillins
Cephalosporins
Carbapenems
Monobactams
2.2.2. Non-β-Lactam Antimicrobials
Vancomycin
Daptomycin
Linezolid
Clindamycin
Macrolides
Aminoglycosides
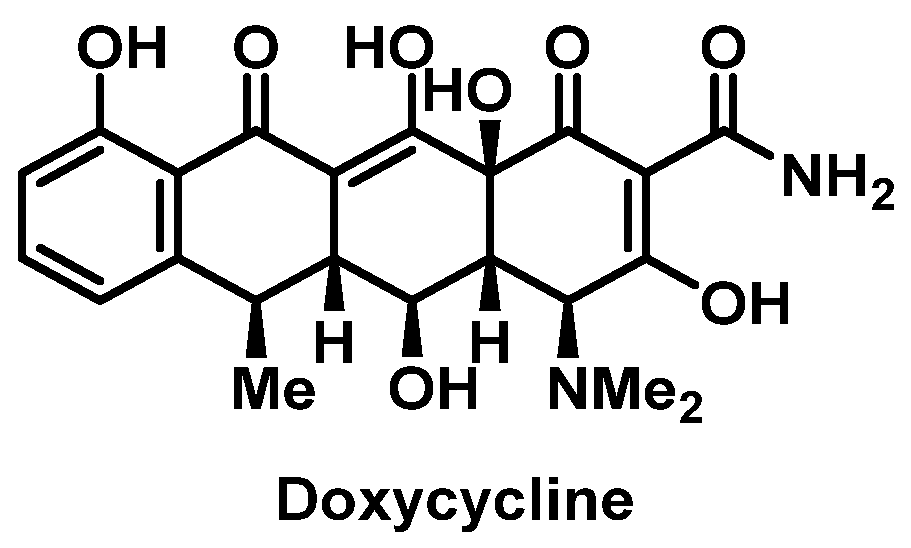
Tetracyclines
Sulfonamides
Metronidazole
Fluoroquinolones
2.2.3. Antifungals
Polyene Antifungals
Triazole Antifungals
Echinocandins
2.2.4. Antivirals
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Joint Task Force on Practice Parameters; American Academy of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology; American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology; Joint Council of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology. Drug allergy: An updated practice parameter. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2010, 105, 259–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trubiano, J.A.; Stone, C.A.; Grayson, L.M.; Urbancic, K.; Slavin, M.A.; Thursky, K.A.; Phillips, E.J. The Three C’s of Antibiotic Allergy—Classification, Cross-Reactivity and Collaboration. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2017, 5, 1532–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legendre, D.P.; Muzny, C.A.; Marshall, G.D.; Swiatlo, E. Antibiotic hypersensitivity reactions and approaches to desensitization. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2014, 58, 1140–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalle, J.; Ramos, M.C.; Jimenez, M.F.; Escobar, F.G.; Antonello, V.S. Oral Desensitization to Penicillin for the Treatment of Pregnant Women with Syphilis: A Successful Program. Rev. Bras. Ginecol. Obstet. 2018, 40, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wendel, G.D.; Stark, B.J.; Jamison, R.B.; Molina, R.D.; Sullivan, T.J. Penicillin Allergy and Desensitization in Serious Infections during Pregnancy. N. Engl. J. Med. 1985, 312, 1229–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siripassorn, K.; Ruxrungtham, K.; Manosuthi, W. Successful drug desensitization in patients with delayed-type allergic reactions to anti-tuberculosis drugs. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 68, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bobolea, I.; Del Pozo, V.; Sanz, V.; Cabañas, R.; Fiandor, A.; Alfonso-Carrillo, C.; Salcedo, M.Á.; Revuelto, R.H.; Quirce, S. Aspirin desensitization in aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease: New insights into the molecular mechanisms. Respir. Med. 2018, 143, 39–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fam, A.G.; Dunne, S.M.; Iazzetta, J.; Paton, T.W. Efficacy and safety of desensitization to allopurinol following cutaneous reactions. Arthritis Rheum. 2001, 44, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solensky, R. Drug desensitization. Immunol. Allergy Clin. N. Am. 2004, 24, 425–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solensky, R. Drug Hypersensitivity. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2006, 90, 233–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adkinson, N.F.; Bochner, B.S.; Burks, A.W.; Busse, W.W.; Holgate, S.T.; Lemanske, R.F.; O’Hehir, R.E.; Middleton, E. Middleton’s Allergy: Principles and Practice; Elsevier/Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Sobotka, A.K.; Dembo, M.; Goldstein, B.; Lichtenstein, L.M. Antigen-specific desensitization of human basophils. J. Immunol. 1979, 122, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shalit, M.; Levi-Schaffer, F. Challenge of mast cells with increasing amounts of antigen induces desensitization. Clin. Exp. Allergy 1995, 25, 896–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinman, R.M. Endocytosis and the recycling of plasma membrane. J. Cell Biol. 1983, 96, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castells, M. Drug Desensitization in Oncology: Chemotherapy Agents and Monoclonal Antibodies; Karger: Basel, Switzerland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Bonfanti, P.; Pusterla, L.; Parazzini, F.; Libanore, M.; Cagni, A.; Franzetti, M.; Faggion, I.; Landonio, S.; Quirino, T. The effectiveness of desensitization versus rechallenge treatment in HIV-positive patients with previous hypersensitivity to TMP-SMX: A randomized multicentric study. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2000, 54, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorman, S.K.; Zed, P.J.; Dhingra, V.K.; Ronco, J.J. Rapid Imipenem/Cilastatin Desensitization for Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter Pneumonia. Ann. Pharmacother. 2003, 37, 513–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gell, P.G.H.; Coombs, R.R.A. Clinical Aspects of Immunology; Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Brunton, L.L.; Knollmann, B.C.; Hilal-Dandan, R. Goodman & Gilman’s: The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, 13th ed.; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Cernadas, J.R.; Brockow, K.; Romano, A.; Aberer, W.; Torres, M.J.; Bircher, A.; Campi, P.; Sanz, M.L.; Castells, M.; Demoly, P.; et al. General considerations on rapid desensitization for drug hypersensitivity—A consensus statement. Allergy 2010, 65, 1357–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scherer, K.; Brockow, K.; Aberer, W.; Gooi, J.H.C.; Demoly, P.; Romano, A.; Schnyder, B.; Whitaker, P.; Cernadas, J.S.R.; Bircher, A.J. Desensitization in delayed drug hypersensitivity reactions—An EAACI position paper of the Drug Allergy Interest Group. Allergy 2013, 68, 844–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Workowski, K.A.; Bolan, G.A. Sexually Transmitted Diseases Treatment Guidelines, 2015. MMWR Recomm. Rep. 2015, 64, 1–137. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Simons, F.E.R. Anaphylaxis pathogenesis and treatment. Allergy 2011, 66, 31–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thong, B.Y.H.; Tan, T.C. Epidemiology and risk factors for drug allergy. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2011, 71, 684–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roujeau, J.C. Clinical heterogeneity of drug hypersensitivity. Toxicology 2005, 209, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douglas, R.; Spelman, D.; Czarny, D.; O’Hehir, R.E. Successful Desensitization of Two Patients Who Previously Developed Stevens-Johnson Syndrome While Receiving Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1997, 25, 1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruano, F.J.; Garcimartin, M.I.; De La Torre, M.V.; Blanca, M.; Canto, G. Desensitization of epoetin-α in a confirmed case of acute exanthematic pustulosis. Allergy 2009, 64, 1797–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joint Task Force on Practice Parameters, the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology, the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology, and the Joint Council of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology. Executive summary of disease management of drug hypersensitivity: A practice parameter. Ann. Allergy Asthma. Immunol. 1999, 83, 665–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruchalla, R.S.; Pirmohamed, M. Clinical practice. Antibiotic allergy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castells, M. Rapid desensitization for hypersensitivity reactions to medications. Immunol. Allergy Clin. N. Am. 2009, 29, 585–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yusin, J.; Klaustermeyer, W.; Simmons, C.; Baum, M. Desensitization in patients with beta-lactam drug allergy. Allergol. Immunopathol. 2013, 41, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Groot, H.; Mulder, W.M.C.; Terreehorst, I. Utility of desensitisation for allergy to antibiotics. Neth. J. Med. 2012, 70, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, A.; Fanning, L.; Chong, H.; Fernández, J.; Sloane, D.; Sancho-Serra, M.; Castells, M. Desensitization regimens for drug allergy: State of the art in the 21st century. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2011, 41, 1679–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, M.J.; Blanca, M.; Fernández, J.; Romano, A.; Weck, A.; Aberer, W.; Brockow, K.; Pichler, W.J.; Demoly, P.; Enda, F.; et al. Diagnosis of immediate allergic reactions to beta-lactam antibiotics. Allergy 2003, 58, 961–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousquet, P.J.; Co-Minh, H.; Arnoux, B.; Daures, J.; Demoly, P. Importance of mixture of minor determinants and benzylpenicilloyl poly-l-lysine skin testing in the diagnosis of β-lactam allergy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2005, 115, 1314–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pichichero, M.E. Cephalosporins can be prescribed safely for penicillin-allergic patients. J. Fam. Pract. 2006, 55, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sodhi, M.; Axtell, S.S.; Callahan, J.; Shekar, R. Is it safe to use carbapenems in patients with a history of allergy to penicillin? J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2004, 54, 1155–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frumin, J.; Gallagher, J.C. Allergic Cross-Sensitivity Between Penicillin, Carbapenem, and Monobactam Antibiotics: What are the Chances? Ann. Pharmacother. 2009, 43, 304–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanca, M.; Perez, E.; Garcia, J.; Miranda, A.; Fernandez, J.; Vega, J.M.; Terrados, S.; Avila, M.; Martin, A.; Suau, R. Anaphylaxis to amoxycillin but good tolerance for benzyl penicillin. In vivo and in vitro studies of specific IgE antibodies. Allergy 1988, 43, 508–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, J.M.; Blanca, M.; Garcia, J.J.; Carmona, M.J.; Miranda, A.; Perez-Estrada, M.; Fernandez, S.; Acebes, J.M.; Terrados, S. Immediate allergic reactions to amoxicillin. Allergy 1994, 49, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DePestel, D.D.; Benninger, M.S.; Danziger, L.; LaPlante, K.L.; May, C.; Luskin, A.; Pichichero, M.; Hadley, J.A. Cephalosporin use in treatment of patients with penicillin allergies. J. Am. Pharm. Assoc. 2008, 48, 530–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borish, L.; Tamir, R.; Rosenwasser, L.J. Intravenous desensitization to beta-lactam antibiotics. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1987, 80, 314–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legere, H.J., 3rd; Palis, R.I.; Rodriguez Bouza, T.; Uluer, A.Z.; Castells, M.C. A safe protocol for rapid desensitization in patients with cystic fibrosis and antibiotic hypersensitivity. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2009, 8, 418–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Win, P.H.; Brown, H.; Zankar, A.; Ballas, Z.K.; Hussain, I. Rapid intravenous cephalosporin desensitization. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2005, 116, 225–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yates, A.B. Management of Patients with a History of Allergy to Beta-Lactam Antibiotics. Am. J. Med. 2008, 121, 572–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solensky, R. Drug allergy: Desensitization and treatment of reactions to antibiotics and aspirin. Clin. Allergy Immunol. 2004, 18, 585–606. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Castells, M. Rapid desensitization of hypersensitivity reactions to chemotherapy agents. Curr. Drug Saf. 2006, 1, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castells, M.C.; Tennant, N.M.; Sloane, D.E.; Hsu, F.I.; Barrett, N.A.; Hong, D.I.; Laidlaw, T.M.; Legere, H.J.; Nallamshetty, S.N.; Palis, R.I.; et al. Hypersensitivity reactions to chemotherapy: Outcomes and safety of rapid desensitization in 413 cases. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2008, 122, 574–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castells, M. Rapid desensitization for hypersensitivity reactions to chemotherapy agents. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2006, 6, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burrows, J.A.; Toon, M.; Bell, S.C. Antibiotic desensitization in adults with cystic fibrosis. Respirology 2003, 8, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmar, J.S.; Nasser, S. Antibiotic allergy in cystic fibrosis. Thorax 2005, 60, 517–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelkar, P.S.; Li, J.T. Cephalosporin allergy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 345, 804–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madaan, A.; Li, J.T. Cephalosporin allergy. Immunol. Allergy Clin. N. Am. 2004, 24, 463–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirakian, R.; Leech, S.C.; Krishna, M.T.; Richter, A.G.; Huber, P.A.J.; Farooque, S.; Khan, N.; Pirmohamed, M.; Clark, A.T.; Nasser, S.M. Management of allergy to penicillins and other beta-lactams. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2015, 45, 300–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macy, E.; Romano, A.; Khan, D. Practical Management of Antibiotic Hypersensitivity in 2017. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2017, 5, 577–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papakonstantinou, G.; Bogner, J.R.; Hofmeister, F.; Hehlmann, R. Cefotaxime desensitization. Clin. Investig. 1993, 71, 165–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ghosal, S. Intravenous desensitization to ceftazidime in cystic fibrosis patients. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 1997, 39, 556–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Jones, J.M.; Richter, L.M.; Alonto, A.; Leedahl, D.D. Desensitization to ceftaroline in a patient with multiple medication hypersensitivity reactions. Am. J. Heal. Pharm. 2015, 72, 198–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxon, A.; Adelman, D.; Patel, A.; Hajdu, R.; Calandra, G. Imipenem cross-reactivity with penicillin in humans. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1988, 82, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, A.; Viola, M.; Guéant-Rodriguez, R.M.; Gaeta, F.; Pettinato, R.; Guéant, J.L. Imipenem in Patients with Immediate Hypersensitivity to Penicillins. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 2835–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, A.; Viola, M.; Guéant-Rodriguez, R.M.; Gaeta, F.; Valluzzi, R.; Guéant, J.L. Brief communication: Tolerability of meropenem in patients with IgE-mediated hypersensitivity to penicillins. Ann. Intern. Med. 2007, 146, 266–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, D.L.; Owens, R.C.; Zuckerman, J.B. Successful Meropenem Desensitization in a Patient with Cystic Fibrosis. Ann. Pharmacother. 2003, 37, 1424–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxon, A.; Beall, G.N.; Rohr, A.S.; Adelman, D.C. Immediate Hypersensitivity Reactions to Beta-Lactam Antibiotics. Ann. Intern. Med. 1987, 107, 204–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patriarca, G.; Schiavino, D.; Lombardo, C.; Altomonte, G.; Decinti, M.; Buonomo, A.; Nucera, E. Tolerability of Aztreonam in Patients with IgE-Mediated Hypersensitivity to Beta-Lactams. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2008, 21, 375–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buonomo, A.; Nucera, E.; De Pasquale, T.; Pecora, V.; Lombardo, C.; Sabato, V.; Colagiovanni, A.; Rizzi, A.; Aruanno, A.; Pascolini, L.; et al. Tolerability of Aztreonam in Patients with Cell-Mediated Allergy to β-Lactams. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2011, 155, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimiento, A.P.; Martínez, M.G.; Mena, A.M.; González, A.T.; Arranz, S.P.; Mosquera, M.R. Aztreonam and ceftazidime: Evidence of in vivo cross-allergenicity. Allergy 1998, 53, 624–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romano, A.; Gaeta, F.; Valluzzi, R.L.; Maggioletti, M.; Zaffiro, A.; Caruso, C.; Quaratino, D. IgE-mediated hypersensitivity to cephalosporins: Cross-reactivity and tolerability of alternative cephalosporins. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 136, 685–691.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwak, E.; Mainardi, T.; Canfield, S.; Miller, R.; DiMango, E. A Novel Desensitization Protocol for Inhaled Aztreonam. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 131, AB174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, T.L.; Ruffing, M.J.; Lamp, K.C.; Warbasse, L.H.; Rybak, M.J. Prospective Evaluation of Red Man Syndrome in Patients Receiving Vancomycin. J. Infect. Dis. 1993, 168, 773–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, M.R.; Mascola, J.R.; Oldfield, E.C., 3rd. Red man syndrome: Incidence, etiology, and prophylaxis. J. Infect. Dis. 1991, 164, 1180–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeShazo, R.D. Allergic reactions to drugs and biologic agents. JAMA 1997, 278, 1895–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minhas, J.S.; Wickner, P.G.; Long, A.A.; Banerji, A.; Blumenthal, K.G. Immune-mediated Reactions to Vancomycin: A Systematic Case Review and Analysis. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2016, 116, 544–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polk, R.E.; Israel, D.; Wang, J.; Venitz, J.; Miller, J.; Stotka, J. Vancomycin skin tests and prediction of “red man syndrome” in healthy volunteers. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1993, 37, 2139–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, T.J. Antigen-specific desensitization to prevent allergic reactions to drugs. Ann. Allergy 1994, 73, 375–377. [Google Scholar]
- Anne’, S.; Middleton, E., Jr.; Reisman, R.E. Vancomycin anaphylaxis and successful desensitization. Ann. Allergy 1994, 73, 402–404. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gould, I.M.; Miró, J.M.; Rybak, M.J. Daptomycin: The role of high-dose and combination therapy for Gram-positive infections. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2013, 42, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gisler, V.; Müller, S.; Müller, L.; Jörg-Walther, L.; Sendi, P. Acute Angioedema Triggered by Daptomycin. Infect. Dis. Ther. 2016, 5, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- CUBICIN (daptomycin) [package insert]. Whitehouse Station; Merck & Co., Inc.: Kenilworth, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Metz, G.M.; Thyagarajan, A. A Successful Protocol for Daptomycin Desensitization. Ann. Allergy Asthma. Immunol. 2008, 100, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahedi Bialvaei, A.; Rahbar, M.; Yousefi, M.; Asgharzadeh, M.; Samadi Kafil, H. Linezolid: A promising option in the treatment of Gram-positives. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2017, 72, 354–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagwell, A.D.; Stollings, J.L.; White, K.D.; Fadugba, O.O.; Choi, J.J. Linezolid Desensitization for a Patient with Multiple Medication Hypersensitivity Reactions. Ann. Pharmacother. 2013, 47, e30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cawley, M.J.; Lipka, O. Intravenous Linezolid Administered Orally: A Novel Desensitization Strategy. Pharmacother. J. Hum. Pharmacol. Drug Ther. 2006, 26, 563–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lammintausta, K.; Tokola, R.; Kalimo, K. Cutaneous adverse reactions to clindamycin: Results of skin tests and oral exposure. Br. J. Dermatol. 2002, 146, 643–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thong, B.Y.H. Update on the Management of Antibiotic Allergy. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2010, 2, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulloch, M.N.; Baccas, J.T.; Arnold, S. Clindamycin-induced hypersensitivity reaction. Infection 2016, 44, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lochmann, O.; Kohout, P.; Výmola, F. Anaphylactic shock following the administration of clindamycin. J. Hyg. Epidemiol. Microbiol. Immunol. 1977, 21, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chiou, C.S.; Lin, S.M.; Lin, S.P.; Chang, W.G.; Chan, K.H.; Ting, C.K. Clindamycin-induced Anaphylactic Shock during General Anesthesia. J. Chin. Med Assoc. 2006, 69, 549–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulewski, R.J.; Blyumin, M.; Kerdel, F.A. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis due to clindamycin. Dermatol. Online J. 2008, 14, 14. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Paquet, P.; Schaaf-Lafontaine, N.; Piérard, G.E. Toxic epidermal necrolysis following clindamycin treatment. Br. J. Dermatol. 1995, 132, 665–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Borges, M.; Thong, B.; Blanca, M.; Ensina, L.F.C.; González-Díaz, S.; Greenberger, P.A.; Jares, E.; Jee, Y.K.; Kase-Tanno, L.; Khan, D.; et al. Hypersensitivity reactions to non beta-lactam antimicrobial agents, a statement of the WAO special committee on drug allergy. World Allergy Organ. J. 2013, 6, 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Marcos, C.; Sopeña, B.; Luna, I.; González, R.; De La Fuente, J.; Vázquez, C.M. Clindamycin desensitization in an AIDS patient. AIDS 1995, 9, 1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín, J.A.; Alonso, M.D.; Navas, E.; Antela, A. Clindamycin desensitization in a patient with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Medicina Clínica 1992, 98, 478–479. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mazzei, T.; Mini, E.; Novelli, A.; Periti, P. Chemistry and mode of action of macrolides. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 1993, 31, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, L.; Mudd, L.; Baize, T.; Herzig, R. Cross-sensitivity reaction between tacrolimus and macrolide antibiotics. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2000, 25, 907–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florido Lopez, J.F.; Lopez Serrano, M.C.; Belchi Hernandez, J.; Estrada Rodriguez, J.L. Fixed eruption due to erythromycin. A case report. Allergy 1991, 46, 77–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brkljacić, N.; Gracin, S.; Prkacin, I.; Sabljar-Matovinović, M.; Mrzljak, A.; Nemet, Z. Stevens-Johnson syndrome as an unusual adverse effect of azithromycin. Acta Dermatovenerol. Croat. ADC 2006, 14, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Periti, P.; Periti, P.P.; Mazzei, T.; Mini, E.; Novelli, A. Adverse Effects of Macrolide Antibacterials. Drug Saf. 1993, 9, 346–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swamy, N.; Laurie, S.A.; Ruiz-Huidobro, E.; Khan, D.A. Successful Clarithromycin Desensitization in a Multiple Macrolide–Allergic Patient. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2010, 105, 489–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascual, C.; Crespo, J.F.; Quiralte, J.; Lopez, C.; Wheeler, G.; Martin-Esteban, M. In vitro detection of specific IgE antibodies to erythromycin. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1995, 95, 668–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, N.E.; Hodgkinson, M.; Dendle, C.; Korman, T.M. Report of oral clarithromycin desensitization. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2008, 66, 323–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liippo, J.; Lammintausta, K. Positive patch test reactions to gentamicin show sensitization to aminoglycosides from topical therapies, bone cements, and from systemic medication. Contact Dermat. 2008, 59, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, C.M.; Holden, C.R.; Gawkrodger, D.J. Contact allergy to topical medicaments becomes more common with advancing age: An age-stratified study. Contact Dermat. 2007, 56, 229–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, J.E.; Dolin, R.; Blaser, M.J.; Mandell, G.L.; Douglas, R.G. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett’s Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases; Elsevier/Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Bensaid, B.; Rozières, A.; Nosbaum, A.; Nicolas, J.F.; Bérard, F. Amikacin-induced drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms syndrome: Delayed skin test and ELISPOT assay results allow the identification of the culprit drug. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 130, 1413–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, A.; Viola, M.; Di Fonso, M.; Rosaria Perrone, M.; Gaeta, F.; Andriolo, M. Anaphylaxis to streptomycin. Allergy 2002, 57, 1087–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, S.; Wollina, U. Gentamicin-induced anaphylaxis. Allergy 2003, 58, 88–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vervloet, D.; Birnbaum, J.; Koeppel, M.C. Drug Allergy. 3rd ed., Editions de Conde, Paris. Available online: http://www.phadia.com/PageFiles/27357/Drug-Book-web.pdf (accessed on 9 August 2019).
- MacPherson, P. Sensitization to P.A.S., Streptomycin, and Isoniazid. BMJ 1957, 2, 505–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Russell, B. Desensitization to Streptomycin and P.A.S. BMJ 1953, 2, 1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Earl, H.S.; Sullivan, T.J. Acute desensitization of a patient with cystic fibrosis allergic to both beta-lactam and aminoglycoside antibiotics. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1987, 79, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogita, A.; Takada, K.; Kawana, S. Case of anaphylaxis due to tetracycline hydrochloride. J. Dermatol. 2011, 38, 597–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fellner, M.J.; Baer, R.L. Anaphylactic Reaction to Tetracycline in A Penicillin-Allergic Patient: Immunologic Studies. JAMA 1965, 192, 997–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okano, M.; Imai, S. Anaphylactoid symptoms due to oral minocycline. Acta Derm. Venereol. 1996, 76, 164. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jang, J.W.; Bae, Y.J.; Kim, Y.G.; Jin, Y.J.; Park, K.S.; Cho, Y.S.; Moon, H.B.; Kim, T.B. A Case of Anaphylaxis to Oral Minocycline. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2010, 25, 1231–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raeder, J.C. Anaphylactoid reaction caused by intravenous doxycycline during general anesthesia and beta-blockade treatment. Drug Intell. Clin. Pharm. 1984, 18, 481–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caplunik-Pratsch, A.L.; Potasman, I.; Kessel, A.; Paz, A. Doxycycline desensitization in chronic Q fever—A critical tool for the clinician. IDCases 2018, 11, 70–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, S.L.; Hudson, B.J. Rapid desensitization to doxycycline. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2013, 111, 73–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshizawa, S.; Yasuoka, A.; Kikuchi, Y.; Honda, M.; Gatanaga, H.; Tachikawa, N.; Hirabayashi, Y.; Oka, S. A 5-day course of oral desensitization to trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (T/S) in patients with human immunodeficiency virus type-1 infection who were previously intolerant to T./S. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2000, 85, 241–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyle, R.C.; Butterfield, J.H.; Volcheck, G.W.; Podjasek, J.C.; Rank, M.A.; Li, J.T.; Harish, A.; Poe, K.L.; Park, M.A. Successful Outpatient Graded Administration of Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole in Patients Without HIV and With a History of Sulfonamide Adverse Drug Reaction. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2014, 2, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taqi, S.A.; Zaki, S.A.; Nilofer, A.R.; Sami, L.B. Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole-induced Steven Johnson syndrome in an HIV-infected patient. Indian J. Pharmacol. 2012, 44, 533–535. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- El Benaye, J.; Nihal, B.; Hicham, J.; Mohamed, E. Seven hours for effective and safe desensitization in HIV-positive patients intolerant to cotrimoxazole. Pan. Afr. Med. J. 2014, 18, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patriarca, G.; Schiavino, D.; Buonomo, A.; Aruanno, A.; Altomonte, G.; Nucera, E. Desensitization to co-trimoxazole in a patient with fixed drug eruption. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2008, 18, 309–311. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kumar, N.; Sundriyal, D.; Walia, M.; Trisal, D. Metronidazole-induced fixed drug eruption. BMJ Case Rep. 2013, 2013, 325–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weart, C.W.; Hyman, L.C. Serum Sickness Associated with Metronidazole. South. Med J. 1983, 76, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazumdar, G.; Shome, K. Stevens-Johnson syndrome following use of metronidazole in a dental patient. Indian J. Pharmacol. 2014, 46, 121–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, T.A.; Dávila, I.; Moreno, E.; Laffond, E.; Macías, E.; Ruiz, A.; Lorente, F. Anaphylaxis due to metronidazole with positive skin prick test. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2008, 18, 138–139. [Google Scholar]
- Thami, G.P.; Kanwar, A.J. Fixed drug eruption due to metronidazole and tinidazole without cross-sensitivity to secnidazole. Dermatology 1998, 196, 368. [Google Scholar]
- Gendelman, S.R.; Pien, L.C.; Gutta, R.C.; Abouhassan, S.R. Modified oral metronidazole desensitization protocol. Allergy Rhinol. 2014, 5, e66–e69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helms, D.J.; Mosure, D.J.; Secor, W.E.; Workowski, K.A. Management of Trichomonas vaginalis in women with suspected metronidazole hypersensitivity. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2008, 198, 370.e1–370.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurohara, M.; Kwong, F.; Lebherz, T.; Klaustermeyer, W. Metronidazole hypersensitivity and oral desensitization. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1991, 88, 279–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannes, C.B.; Ziyadeh, N.; Seeger, J.D.; Tucker, E.; Reiter, C.; Faich, G. Incidence of allergic reactions associated with antibacterial use in a large, managed care organisation. Drug Saf. 2007, 30, 705–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Hu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Che, D.; Cao, J.; Wang, J.; Zhao, T.; Jia, Q.; Wang, N.; Zhang, T. Mast cell-mediated hypersensitivity to fluoroquinolone is MRGPRX2 dependent. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 70, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manfredi, M.; Severino, M.; Testi, S.; Macchia, D.; Ermini, G.; Pichler, W.J.; Campi, P. Detection of specific IgE to quinolones. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2004, 113, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdem, G.; Staat, M.A.; Connelly, B.L.; Assa’ad, A. Anaphylactic Reaction to Ciprofloxacin in A Toddler: Successful Desensitization. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 1999, 18, 563–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gea-Banacloche, J.C.; Metcalfe, D.D. Ciprofloxacin desensitization. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1996, 97, 1426–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lantner, R.R. Ciprofloxacin desensitization in a patient with cystic fibrosis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1995, 96, 1001–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, H.; Uruma, T.; Seita, I.; Chikasawa, Y.; Kikuchi, R.; Itoh, M.; Aoshiba, K.; Nakamura, H.; Oishi, T. Successful desensitization therapy involving fluoroquinolone for the treatment of a solitary tuberculoma: A case report and literature review. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 5, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benken, S.T.; Nyenhuis, S.M.; Dunne, S. Sequential rapid oral desensitization to rifampin and moxifloxacin for the treatment of active mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2017, 5, 195–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ensina, L.F.; Tanno, L.K.; Motta, A.A.; Kalil, J.; Giavina-Bianchi, P. Ketoconazole Allergy. Clinics (Sao Paulo) 2009, 64, 373–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Hamill, R.J. Amphotericin B Formulations: A Comparative Review of Efficacy and Toxicity. Drugs 2013, 73, 919–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolve, H.; Ahlke, E.; Fegeler, W.; Ritter, J.; Jürgens, H.; Groll, A.H. Safety, tolerance and outcome of treatment with liposomal amphotericin B in paediatric patients with cancer or undergoing haematopoietic stem cell transplantation. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2009, 64, 383–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shadur, B.; Trahair, T.N.; O’Brien, T.; Russell, S.J.; Ziegler, J.B. Desensitisation to liposomal amphotericin B. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2017, 5, 181–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, M.K.; Harris, C.; Shoham, S. Graded isavuconazole introduction in a patient with voriconazole allergy. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2017, 19, e12772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, A.; Chan, R.C. Lack of Allergic Cross-Reactivity between Fluconazole and Voriconazole. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 1715–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lash, D.B.; Jolliff, J.; Munoz, A.; Heidari, A. Cross-reactivity between voriconazole, fluconazole and itraconazole. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2016, 41, 566–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randolph, C.; Kaplan, C.; Fraser, B. Rapid Desensitization to Fluconazole (Diflucan). Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2008, 100, 616–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jariwala, S.; Vernon, N.; De Vos, G. A novel method of desensitization for fluconazole hypersensitivity in a patient with AIDS. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2011, 106, 542–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittleman, D.B.; Stapleton, J.; Casale, T.B. Casale Report of successful desensitization to itraconazole. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1994, 94, 270–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douglas, R.; Spelman, D.; Czarny, D.; O’Hehir, R. Desensitization to itraconazole. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1997, 99, 269. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jean, T.; Kwong, K. Successful desensitization of voriconazole in an immunosuppressed pediatric patient. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2015, 3, 637–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logsdon, S.L.; Lee, J.J.Y. Novel Echinocandin Desensitization in a Pediatric Patient with Hypersensitivity to Micafungin. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 131, AB166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeSimone, J.A.; Ojha, A.; Pathak, R.; Cohn, J. Successful Desensitization to Enfuvirtide after a Hypersensitivity Reaction in an HIV-1-Infected Man. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2004, 39, 110–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milpied-Homsi, B.; Moran, E.M.; Phillips, E.J. Antiviral Drug Allergy. Immunol. Allergy Clin. N. Am. 2014, 34, 645–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pichler, W.; Yawalkar, N.; Schmid, S.; Helbling, A. Pathogenesis of drug-induced exanthems. Allergy 2002, 57, 884–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, J.; Pichler, W.J.; Yerly, D. Delayed drug hypersensitivity: Models of T-cell stimulation. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2011, 71, 701–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pichler, W.J.; Beeler, A.; Keller, M.; Lerch, M.; Posadas, S.; Schmid, D.; Spanou, Z.; Zawodniak, A.; Gerber, B. Pharmacological Interaction of Drugs with Immune Receptors: The p-i Concept. Allergol. Int. 2006, 55, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostrov, D.A.; Grant, B.J.; Pompeu, Y.A.; Sidney, J.; Harndahl, M.; Southwood, S.; Oseroff, C.; Lu, S.; Jakoncic, J.; De Oliveira, C.A.F.; et al. Drug hypersensitivity caused by alteration of the MHC-presented self-peptide repertoire. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 9959–9964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunihastuti, E.; Widhani, A.; Karjadi, T.H. Drug hypersensitivity in human immunodeficiency virus-infected patient: Challenging diagnosis and management. Asia Pac. Allergy 2014, 4, 54–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Seki, J.T.; Ng, P.; Lam, W.; Cote, J.; Prica, A. Recurrent Body Rash Warranted Second Desensitization with Acyclovir in a Myeloma Patient: A Case Report. J. Clin. Med. Res. 2017, 9, 725–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kawsar, M.; Parkin, J.; Forster, G. Graded challenge in an aciclovir allergic patient. Sex. Transm. Infect. 2001, 77, 204–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snape, S.E.; Finch, R.G.; Venkatesan, P. Aciclovir desensitisation and rechallenge. BMJ Case Rep. 2011, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, R.E.; Wegmann, J.A.; Hartle, J.E.; Christopher, G.W. Successful oral acyclovir desensitization. Ann. Allergy 1993, 70, 386–388. [Google Scholar]
- Cernadas, J.R.; Carolino, F.; Carvalho, A.C.; Sarmento, A. A desensitization protocol to ganciclovir. Clin. Transl. Allergy 2014, 4, P60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Estrada, A.; Fernandez, J. Novel Valganciclovir Desensitization Protocol. Transplantation 2014, 98, 50–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Recommendations for Testing, Managing, and Treating Hepatitis C. Available online: http://www.hcvguidelines.org (accessed on 31 July 2019).
- Toker, O.; Tal, Y.; Daher, S.; Shalit, M. Ribavirin Desensitization in Chronic Hepatitis, C. Isr. Med. Assoc. J. IMAJ 2015, 17, 583–584. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ladd, A.M.; Martel-Laferriere, V.; Dieterich, D. Successful Desensitization to Ribavirin in a Patient with Chronic Hepatitis, C. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2012, 46, 716–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demoly, P.; Messaad, D.; Fabre, J.; Reynes, J.; Bousquet, J. Nevirapine-induced cutaneous hypersensitivity reactions and successful tolerance induction. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1999, 104, 504–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- New combination studied. AIDS Patient Care STDS 2000, 14, 169–170. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=10.1089%2F108729100317957 (accessed on 9 August 2019). [CrossRef]
- Phillips, E.J.; Kuriakose, B.; Knowles, S.R. Efavirenz-Induced Skin Eruption and Successful Desensitization. Ann. Pharmacother. 2002, 36, 430–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demoly, P.; Messaad, D.; Trylesinski, A.; Faucherre, V.; Fabre, J.; Reynes, J.; Delmas, C.; Dohin, E.; Godard, P.; Bousquet, J. Nelfinavir-induced urticaria and successful desensitization. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1998, 102, 875–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, P.E.; Sorensen, S.J.; Baker, W.H.; Cushing, H.E.; Abraham, P. Nelfinavir Desensitization. Ann. Pharmacother. 2001, 35, 553–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bravo, M.C.M.; Hermida, A.O.; Vilela, J.M.; Rodríguez, M.T.P.; Montenegro, M.J.G.; Villarroel, L.J.A.; Alvarez, C.M.; DaSilva, A.R.; Vázquez, C.M. Hypersensitivity reaction to darunavir and desensitization protocol. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2009, 19, 250–251. [Google Scholar]
- Duque, S.; Delapuente, J.; Rodríguez, F.; Fernandezpellon, L.; Maquiera, E.; Jerez, J. Zidovudine-related erythroderma and successful desensitization: A. case report. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1996, 98, 234–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiros-Roldan, E.; Tirelli, V.; Torti, C.; Sosta, E.; Tosoni, C.; Damiolini, E.; Carosi, G. Successful long-course after failure of short-course desensitization in a patient with severe hypersensitivity reaction to enfuvirtide. AIDS 2007, 21, 1388–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahar, E.; Moar, C.; Pollack, S. Successful desensitization of enfuvirtide-induced skin hypersensitivity reaction. AIDS 2005, 19, 451–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, E.S.; Passoni, L.F.C.; Sidi, L.C.; Andrade, H.B.; De Menezes, J.A. Successful desensitization of enfuvirtide after a first attempt failure. AIDS 2006, 20, 2130–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escaut, L.; Liotier, J.Y.; Albengres, E.; Cheminot, N.; Vittecoq, D. Abacavir rechallenge has to be avoided in case of hypersensitivity reaction. AIDS 1999, 13, 1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, B.J.; Earl, H.S.; Gross, G.N.; Lumry, W.R.; Goodman, E.L.; Sullivan, T.J. Acute and chronic desensitization of penicillin-allergic patients using oral penicillin. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1987, 79, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




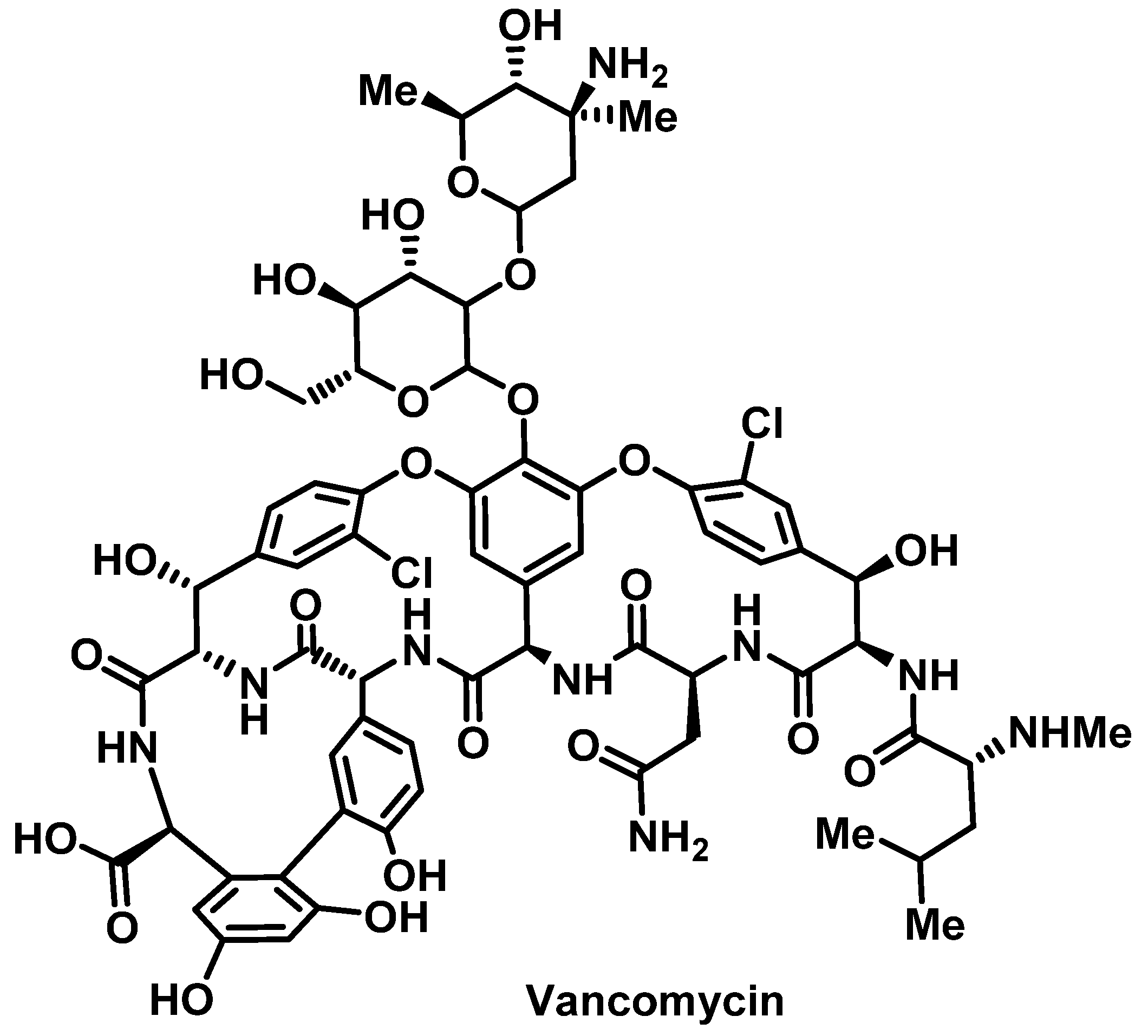
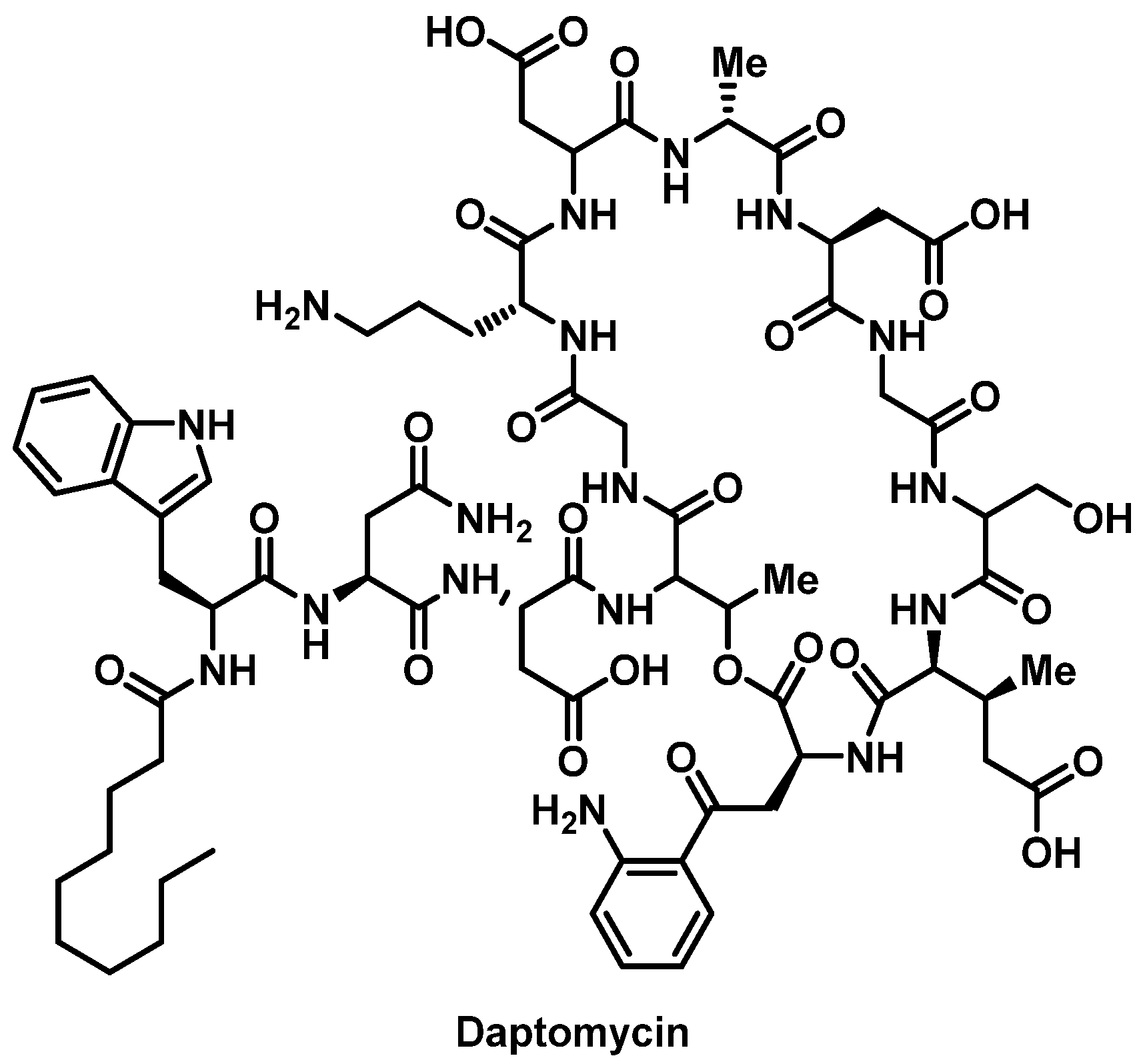
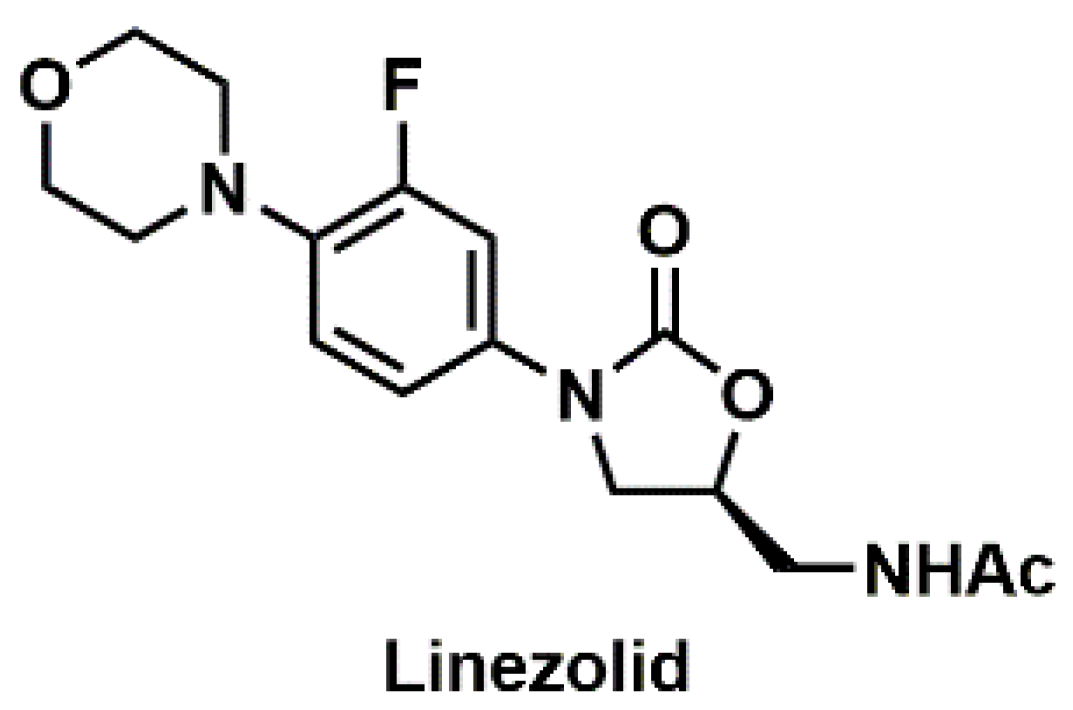











| Underlying Mechanism | Initial Dose | Protocol Duration | Potential Outcome | Duration of Induced Tolerance | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Immunologic IgE (desensitization) | Micrograms | Hours | Blunting the mast cell response | Temporary | β-lactam antibiotics |
| Immunologic non-IgE | Milligrams | Hours to days (e.g., 6 h to 10 days) | Unknown | Temporary | Delayed cutaneous reactions to SMX-TMP in HIV-infected patients |
| Pharmacologic | Milligrams | Hours to days (e.g., 2 h to 5 days) | Inhibition of tyrosine kinases and STAT6 resulting in IL-4 suppression | Temporary | Aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease (AERD) |
| Undefined | Micrograms to milligrams | Prolonged; days to weeks | Unknown | Temporary | Allopurinol-induced pruritic maculopapular rash |
| Indications | Relative Contraindications | Absolute Contraindications | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Immediate HSR | No safe and effective alternative is available Benefits > risks | Receiving β-blockers Previous severe anaphylactic reaction Chronic hepatic or renal disease | Severe asthma or COPD Hemodynamic instability Uncontrolled CVD |
| Delayed HSR | No safe and effective alternative is available Previous delayed drug reaction was not severe Benefits > risks | AGEP Chronic hepatic or renal disease Chronic severe cardiac disease Uncontrolled autoimmune disorders | SJS TEN DRESS Cutaneous/systemic vasculitis Extensive mucosal ulcers Autoimmune drug reactions Internal organ involvement Cytopenias |
| A | ||||
| Dose Number | Penicillin Concentration (Units/mL) | Amount (mL) | Dose (Units) | Cumulative Dose (Units) |
| 1 | 1000 | 0.1 | 100 | 100 |
| 2 | 1000 | 0.2 | 200 | 300 |
| 3 | 1000 | 0.4 | 400 | 700 |
| 4 | 1000 | 0.8 | 800 | 1500 |
| 5 | 1000 | 1.6 | 1600 | 3100 |
| 6 | 1000 | 3.2 | 3200 | 6300 |
| 7 | 1000 | 6.4 | 6400 | 12,700 |
| 8 | 10,000 | 1.2 | 12,000 | 24,700 |
| 9 | 10,000 | 2.4 | 24,000 | 48,700 |
| 10 | 10,000 | 4.8 | 48,000 | 96,700 |
| 11 | 80,000 | 1.0 | 80,000 | 176,700 |
| 12 | 80,000 | 2.0 | 160,000 | 336,700 |
| 13 | 80,000 | 4.0 | 320,000 | 656,700 |
| 14 | 80,000 | 8.0 | 640,000 | 1,296,700 |
| Interval between doses was 15–30 min, with a total time of 4–8 h. Observation before full parenteral therapeutic dose was 30 min. Each dose was diluted in 30 mL of water prior to oral administration. | ||||
| B | ||||
| Dose Number | Penicillin Concentration (mg/mL) | Amount (mL) | Dose (mg) | Cumulative Dose (mg) |
| 1 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 0.05 | 0.05 |
| 2 | 0.5 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.15 |
| 3 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.35 |
| 4 | 0.5 | 0.8 | 0.4 | 0.75 |
| 5 | 0.5 | 1.6 | 0.8 | 1.55 |
| 6 | 0.5 | 3.2 | 1.6 | 3.15 |
| 7 | 0.5 | 6.4 | 3.2 | 6.35 |
| 8 | 5.0 | 1.2 | 6.0 | 12.35 |
| 9 | 5.0 | 2.4 | 12.0 | 24.35 |
| 10 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 25.0 | 49.35 |
| 11 | 50 | 1.0 | 50.0 | 100.0 |
| 12 | 50 | 2.0 | 100.0 | 200.0 |
| 13 | 50 | 4.0 | 200.0 | 400.0 |
| 14 | 50 | 8.0 | 400.0 | 800.0 |
| Dose Number | Penicillin Concentration (mg/mL) | Infusion Rate (mL/h) | Dose (mg) | Cumulative Dose (mg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.01 | 6 | 0.015 | 0.015 |
| 2 | 0.01 | 12 | 0.03 | 0.045 |
| 3 | 0.01 | 24 | 0.06 | 0.105 |
| 4 | 0.01 | 50 | 0.125 | 0.23 |
| 5 | 0.1 | 10 | 0.25 | 0.48 |
| 6 | 0.1 | 20 | 0.5 | 1.0 |
| 7 | 0.1 | 40 | 1.0 | 2.0 |
| 8 | 0.1 | 80 | 2.0 | 4.0 |
| 9 | 0.1 | 160 | 4.0 | 8.0 |
| 10 | 10.0 | 3 | 7.5 | 15.0 |
| 11 | 10.0 | 6 | 15.0 | 30.0 |
| 12 | 10.0 | 12 | 30.0 | 60.0 |
| 13 | 10.0 | 25 | 62.5 | 123.0 |
| 14 | 10.0 | 50 | 125.0 | 250.0 |
| 15 | 10.0 | 100 | 250.0 | 500.0 |
| 16 | 10.0 | 200 | 500.0 | 1000.0 |
| A | ||||||
| Solution: | Total Volume | Concentration | Dose | |||
| Solution 1 | 100 mL | 0.100 mg/mL | 10 mg | |||
| Solution 2 | 100 mL | 1.00 mg/mL | 100 mg | |||
| Solution 3 | 100 mL | 10.00 mg/mL | 1000 mg | |||
| B | ||||||
| Step | Solution# | Rate (mL/hr) | Time (minutes) | Volume (mL) | Dose (mg) | Cumulative dose (mg) |
| 1 | 1 | 2 | 15 | 0.5 | 0.050 | 0.050 |
| 2 | 1 | 5 | 15 | 1.25 | 0.125 | 0.175 |
| 3 | 1 | 10 | 15 | 2.5 | 0.25 | 0.425 |
| 4 | 1 | 20 | 15 | 5 | 0.5 | 0.925 |
| 5 | 2 | 5 | 15 | 1.25 | 1.25 | 2.175 |
| 6 | 2 | 10 | 15 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 4.675 |
| 7 | 2 | 20 | 15 | 5 | 5 | 9.675 |
| 8 | 2 | 40 | 15 | 10 | 10 | 19.675 |
| 9 | 3 | 10 | 15 | 2.5 | 25 | 44.675 |
| 10 | 3 | 20 | 15 | 5 | 50 | 94.675 |
| 11 | 3 | 40 | 15 | 10 | 100 | 194.675 |
| 12 | 3 | 80 | 60.40 | 80.53 | 805.325 | 1000 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chastain, D.B.; Hutzley, V.J.; Parekh, J.; Alegro, J.V.G. Antimicrobial Desensitization: A Review of Published Protocols. Pharmacy 2019, 7, 112. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy7030112
Chastain DB, Hutzley VJ, Parekh J, Alegro JVG. Antimicrobial Desensitization: A Review of Published Protocols. Pharmacy. 2019; 7(3):112. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy7030112
Chicago/Turabian StyleChastain, Daniel B., Vanessa Johanna Hutzley, Jay Parekh, and Jason Val G. Alegro. 2019. "Antimicrobial Desensitization: A Review of Published Protocols" Pharmacy 7, no. 3: 112. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy7030112
APA StyleChastain, D. B., Hutzley, V. J., Parekh, J., & Alegro, J. V. G. (2019). Antimicrobial Desensitization: A Review of Published Protocols. Pharmacy, 7(3), 112. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy7030112




