Spray Characteristics of Alternative Aviation Fuel Blends
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Brief Description of Tested Fuels—Evaluation of Physical Properties
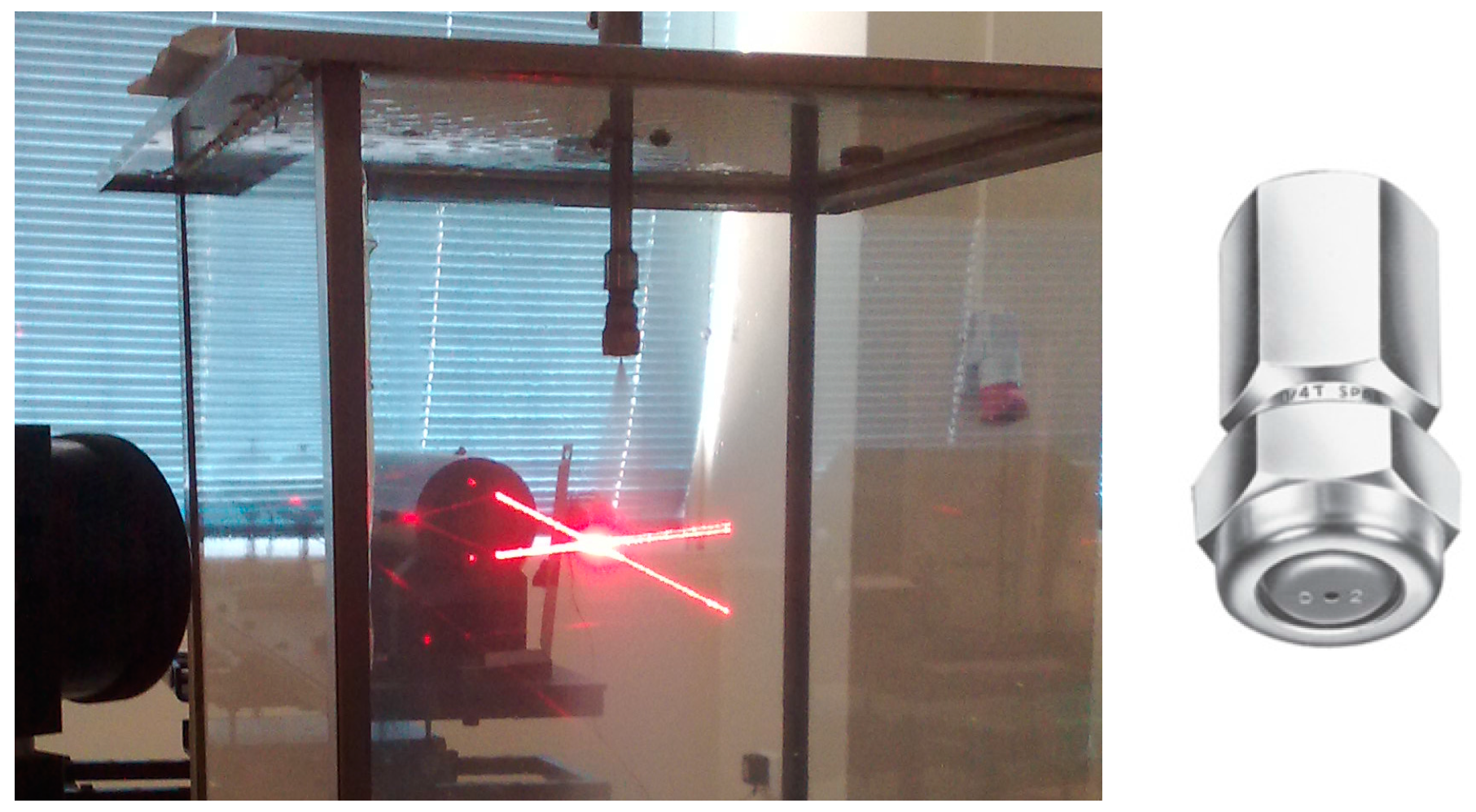
2.2. Experimental Facility
2.3. Measuring Technique
2.4. Experimental Conditions
3. Results and Discussion
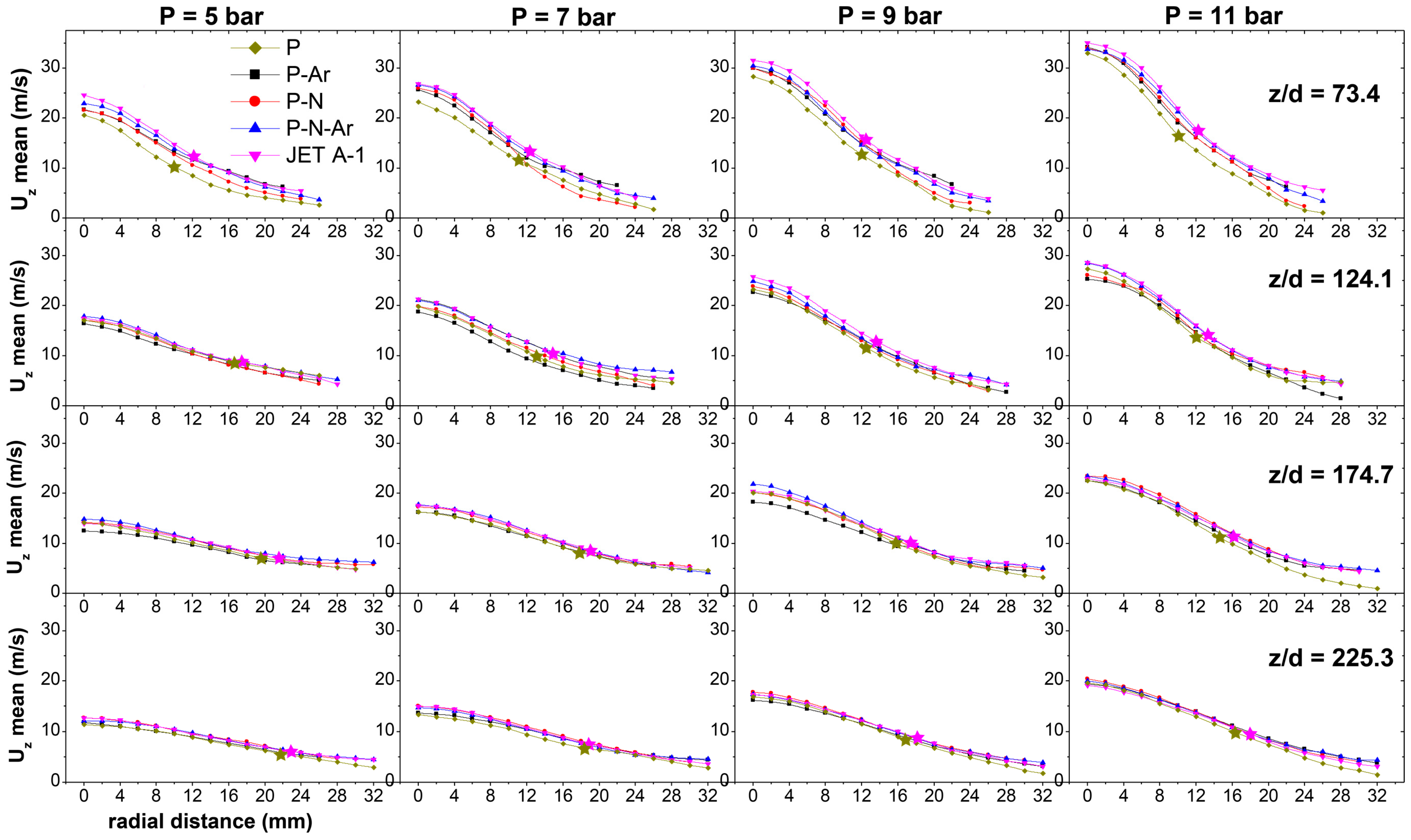
3.1. Axial Droplet Velocity
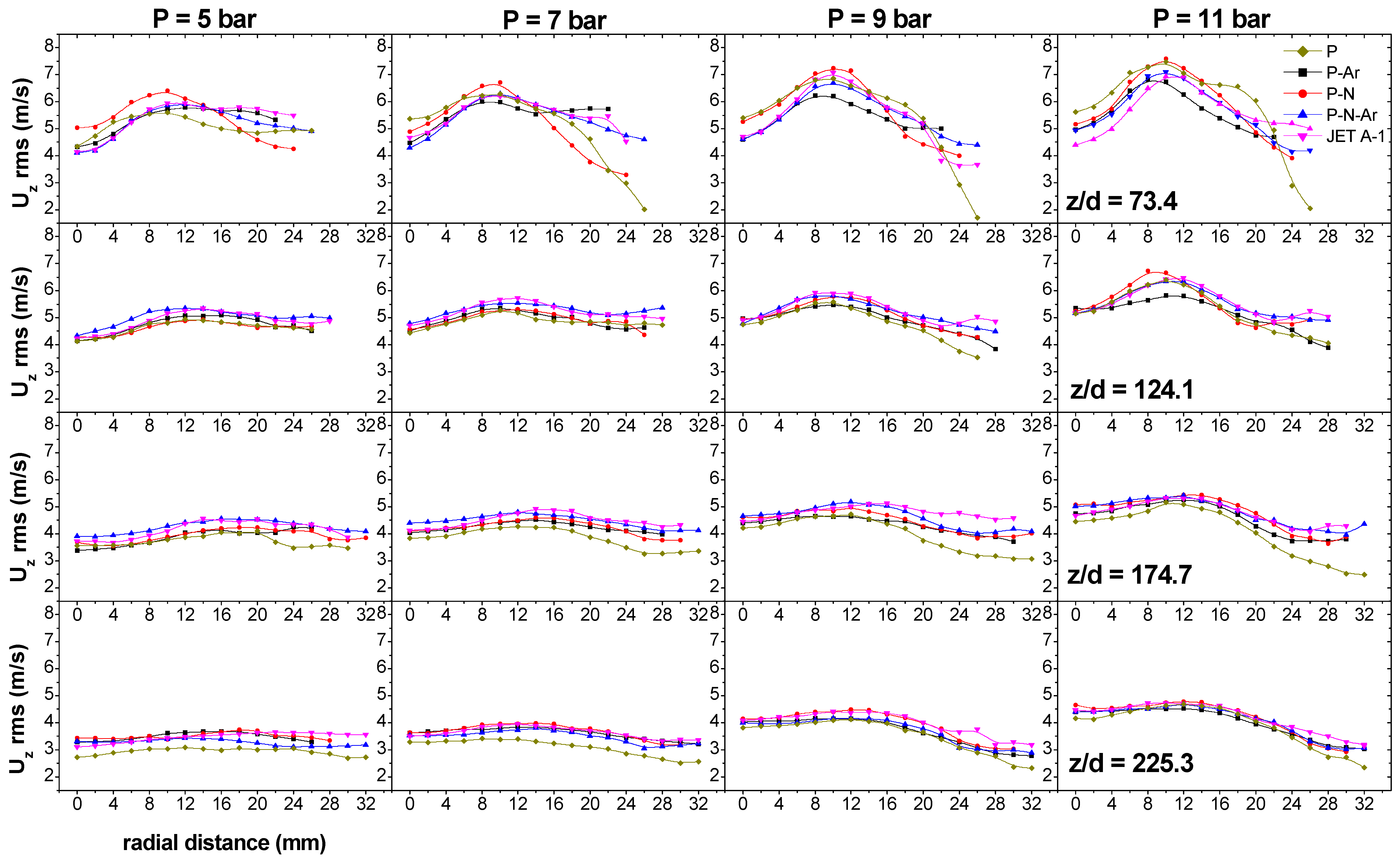
3.2. Axial Rms Velocity
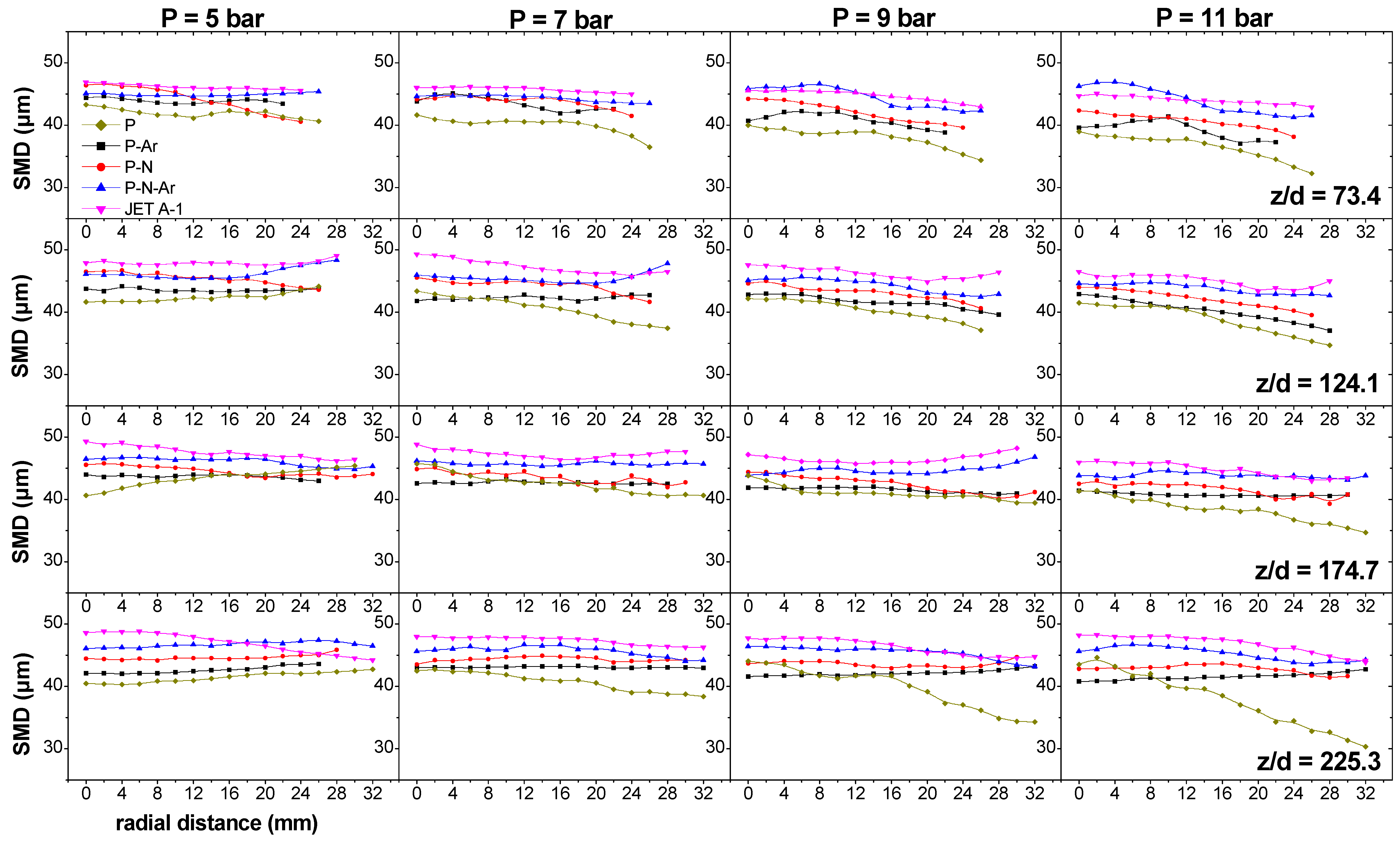
3.3. Sauter Mean Droplet Diameters
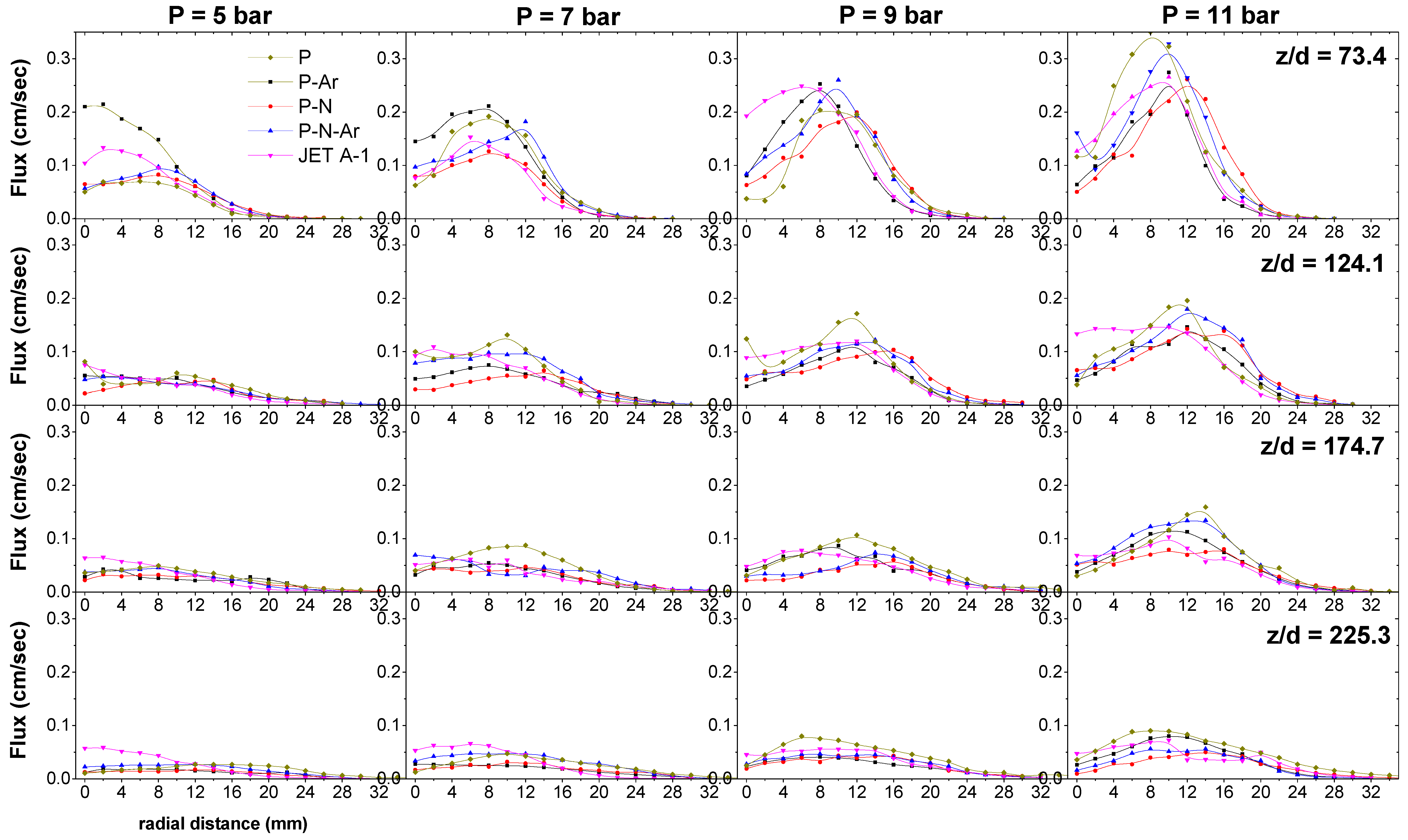
3.4. Volumetric Flux
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schafer, A.W. The Prospects for Biofuels in Aviation, in Biofuels for Aviation—Feedstocks, Technology and Implementation; Chuck, C.J., Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2016; pp. 3–16. [Google Scholar]
- SWAFEA Final Report. Sustainable Way for Alternative Fuels and Energy in Aviation. 2011. Available online: http://www.icao.int/environmental-protection/GFAAF/Documents/SW_WP9_D.9.1%20Final%20report_released%20July2011.pdf (accessed on 11 December 2016).
- Blakey, S.; Rye, L.; Wilson, C.W. Aviation gas turbine alternative fuels: A review. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2011, 33, 2863–2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurice, L.Q.; Lander, H.; Edwards, T.; Harrison, W.E. Advanced aviation fuels: A look ahead via a historical perspective. Fuel 2001, 80, 747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gökalp, I.; Lebas, E. Alternative fuels for industrial gas turbines (AFTUR). Appl. Therm. Eng. 2004, 24, 1655–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IATA 2010 Report on Alternative Fuels; Ref. No: 9709-03; International Air Transport Association: Montreal–Geneva, 2010; ISBN 978-92-9233-491-8. Available online: http://www.iata.org/publications/Documents/IATA%202010%20Report%20on%20Alternative%20Fuels.pdf (accessed on 11 December 2016).
- Chevron Alternative Jet Fuels—A Supplement to Chevron’s Aviation Fuels Technical Review. 2006. Available online: https://www.cgabusinessdesk.com/document/5719_Aviation_Addendum._webpdf.pdf (accessed on 11 December 2016).
- El Banhawy, Y.; Whitelaw, J.H. Experimental study of the interaction between a fuel spray and surrounding combustion air. Combust. Flame 1981, 42, 253–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chigier, N.A.; McCreath, C.G.; Makepeace, R.W. Dynamics of droplets in burning and isothermal kerosene sprays. Combust. Flame 1974, 23, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrad, T.; Bibik, A.; Shcherbik, D.; Lubarsky, E.; Zinn, B.T. Feasibility of intermittent active control of combustion instabilities in liquid fuelled combustors using a smart fuel injector. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2007, 31, 2223–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckstein, J.; Freitag, E.; Hirsch, C.; Sattelmayer, T.R.; von der Bank, T.; Schilling, J. Forced low–frequency spray characteristics of a generic airblast swirl diffusion burner. Eng. Gas Turbines Power 2005, 127, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carl, M.; Behrendt, T.; Frodermann, M.; Heinze, J.; Hassa, C.; Meier, U.; Wolff-Gassmann, D.; Hohmann, S.; Zarzalis, N. Experimental and numerical investigation of a planar combustor sector at realistic operating conditions. J. Eng. Gas Turbines Power 2001, 123, 810–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardalupas, Y.; Taylor, A.M.K.P.; Whitelaw, J.H. Velocity and size characteristics of liquid–fuelled flames stabilized by a swirl burner. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A 1990, 428, 129–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardalupas, Y.; Liu, C.H.; Whitelaw, J.H. Experiments with disk stabilized kerosene–fuelled flames. Combust. Sci. Technol. 1994, 97, 157–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reitz, R.D. Modeling atomization processes in high-pressure vaporizing sprays. At. Spray Technol. 1987, 3, 309–337. [Google Scholar]
- Reitz, R.D.; Bracco, F.V. Mechanism of atomization of a liquid jet. Phys. Fluids 1982, 25, 1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, A.H. Basic processes in atomization. In Atomization and Sprays, 2nd ed.; Taylor & Francis, Hemisphere Publishing Corporation: New York, NY, USA, 1989; pp. 37–59. [Google Scholar]
- Sornek, R.J.; Dobashi, R.; Hirano, T. Effect of turbulence on vaporization, mixing, and combustion of liquid-fuel sprays. Combust. Flame 2000, 120, 479–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannaiyan, K.; Sadr, R. Effect of fuel properties on spray characteristics of alternative. At. Spray 2014, 24, 575–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakumar, D.; Vankeswaram, S.K.; Sakthikumar, R.; Raghunandan, B.N. Analysis on the atomization characteristics of aviation biofuel discharging from simplex swirl atomizer. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2015, 72, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charalampous, G.; Hardalupas, Y. How do liquid fuel physical properties affect liquid jet development in atomisers. Phys. Fluids 2016, 28, 102106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feddema, R.T. Effect of aviation fuel type and fuel injection conditions on the spray characteristics of pressure swirl and hybrid air blast fuel injectors. Master’s Thesis, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Buschhagen, T.; Zhang, R.Z.; Naik, S.V.; Slabaugh, C.D.; Meyer, S.E.; Gore, J.P.; Lucht, R.P. Effect of aviation fuel type and fuel injection conditions on non-reacting spray characteristics of hybrid air blast fuel injector. In Proceedings of the 54th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting, AIAA SciTech Forum, San Diego, CA, USA, 4-8 January 2016. AIAA 2016-1154. [Google Scholar]
- Keramiotis, C.; Zannis, G.; Skevis, G.; Founti, M.A. Performance investigation of Fischer-Tropsch kerosene blends in a laboratory-scale premixed flame burner. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2013, 44, 868–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vukadinovic, V.; Habisreuther, P.; Zarzalis, N. Experimental study on combustion characteristics of conventional and alternative liquid fuels. J. Eng. Gas Turbines Power 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rye, L.; Wilson, C. The influence of alternative fuel composition on gas turbine ignition performance. Fuel 2012, 96, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tropea, C.; Xu, T.-H.; Onofri, F.; Grehan, G.; Haugen, P.; Stieglmeier, M. Dual-mode phase-Doppler anemometer. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 1996, 13, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tropea, C.; Yarin, A.L.; Foss, J.F. Velocity Vorticity and Mach Number in Handbook of Experimental Fluid Mechanics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 296–309. [Google Scholar]
- Pitcher, G.; Wigley, G.; Saffman, M. Sensitivity of dropsize measurements by phase Doppler anemometry to refractive index changes in combusting fuel sprays. In Applications of Laser Techniques to Fluid Mechanics; Adrian, R.J., Durao, D., Durst, F., Maeda, M., Whitelaw, J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1991; pp. 227–247. [Google Scholar]
- Panidis, T.; Sommerfeld, M. The Locus of Centres Method for LDA and PDA Measurements, Developments in Laser Techniques and Fluid Mechanics; Adrian, R.J., Durao, D., Durst, F., Heitor, M.V., Maeda, M., Whitelaw, J.H., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1997; pp. 203–220. [Google Scholar]
- Hardalupas, Y.; Taylor, A.M.K.P.; Whitelaw, J.H. Mass Flux, Mass Fraction and Concentration of Liquid Fuel in a Swirl—Stabilized Flame. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 1994, 20, 233–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widmann, J.F.; Presser, C.; Leigh, S.D. Improving phase Doppler volume flux measurements in low data rate applications. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2001, 12, 1180–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saffman, M. Automatic calibration of LDA measurement volume size. Appl. Opt. 1987, 26, 2592–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tate, R.W. Some problems associated with the accurate representation of droplet size distributions. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Liquid Atomic and Spray Systems, Madison, WI, USA, 20–24 June 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Handbook of Aviation Fuel Properties. CRC Report No. 635. 2004. Available online: www.dtic.mil/dtic/tr/fulltext/u2/a429439.pdf (accessed on 27 February 2017).
- Ghosh, P. Colloid and Interface Science; PHI Learning: New Delhi, India, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM D341-03 Standard Test Method for Viscosity-Temperature Charts for Liquid Petroleum Products. 2004. Available online: www.astm.org/Standards/D341.htm (accessed on 11 December 2016).
- Mayhew, E.; Mitsingas, C.M.; McGann, B.; Hendershott, T.; Stouffer, S.; Wrzesinski, P.; Caswell, A.W.; Lee, T. Spray characteristics and flame structure of Jet A and alternative jet fuels. In Proceedings of the 55th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting, AIAA SciTech Forum, AIAA 2017-0148, Grapevine, TX, USA, 9–13 January 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.F.; Lefebvre, A.H. Influence of fuel temperature on atomization performance of pressure-swirl atomizers. J. Propuls. Power 1988, 4, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Blend | Compound Content | Molecular Formulae |
|---|---|---|
| P (GTL) | Paraffins (99%) | C10.14H22.25 |
| P–Ar | Paraffins (80%) + Aromatics (20%) | C10.08H20.35 |
| P–N | Paraffins (60%) + Naphthenes (40%) | C12.18H25.28 |
| P–N–Ar | Paraffins (50%) + Naphthenes (30%) + Aromatics (20%) | C11.48H22.18 |
| Blend | Fuel Density (15 °C) | Kinematic Viscosity | Surface Tension (22 °C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ρ (kg/m3) | ν (cSt) | σ (mN m−1) | |
| Jet A-1 | 821.0 | 0.99 ± 0.04 at 24.95 °C | 29.84 ± 0.06 |
| P | 737.6 | 1.01 ± 0.04 at 25.02 °C | 26.28 ± 0.05 |
| P–Ar | 768.7 | 0.98 ± 0.04 at 25.04 °C | 27.43 ± 0.04 |
| P–N | 787.9 | 1.13 ± 0.04 at 20.61 °C | 28.87 ± 0.05 |
| P–N–Ar | 805.4 | 1.15 ± 0.04 at 22.75 °C | 29.43 ± 0.02 |
| Component | Type | |
|---|---|---|
| Laser | Source | He–Ne |
| Wavelength | 632.8 nm | |
| Power | 20 mW | |
| Transmitting Optics | Focal length | 250 mm |
| Frequency shift | 40 MHz | |
| Receiving Optics | Model | PDA 57X10 |
| Focal length | 310 mm | |
| Receiving Angle | 67° to forward | |
| Blend | Fuel Density | Kinematic Viscosity | Surface Tension | Exit Non-Dimensional Numbers at 11 Bars | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ρ (kg/m3) | ν (cSt) | σ (mN m−1) | Re | We | Oh | |
| Jet A-1 | 803.1 | 0.81 | 28.45 | 4.83 × 104 | 5.42 × 104 | 4.82 × 10−3 |
| P | 719.7 | 0.82 | 24.89 | 4.38 × 104 | 4.74 × 104 | 4.97 × 10−3 |
| P–Ar | 750.8 | 0.80 | 26.04 | 4.97 × 104 | 5.77 × 104 | 4.83 × 10−3 |
| P–N | 770.0 | 0.86 | 27.48 | 4.51 × 104 | 5.31 × 104 | 5.10 × 10−3 |
| P–N–Ar | 787.5 | 0.90 | 28.04 | 4.04 × 104 | 4.68 × 104 | 5.35 × 10−3 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vouros, A.P.; Vouros, A.P.; Panidis, T. Spray Characteristics of Alternative Aviation Fuel Blends. Aerospace 2017, 4, 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace4020018
Vouros AP, Vouros AP, Panidis T. Spray Characteristics of Alternative Aviation Fuel Blends. Aerospace. 2017; 4(2):18. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace4020018
Chicago/Turabian StyleVouros, Andreas P., Alexandros P. Vouros, and Thrassos Panidis. 2017. "Spray Characteristics of Alternative Aviation Fuel Blends" Aerospace 4, no. 2: 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace4020018
APA StyleVouros, A. P., Vouros, A. P., & Panidis, T. (2017). Spray Characteristics of Alternative Aviation Fuel Blends. Aerospace, 4(2), 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace4020018






