Intercepting 3I/ATLAS at Its Closest Approach to Jupiter with the Juno Spacecraft
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Orbit Calculation
3. Future Opportunities
- 1.
- The time available from application of the initial V to reach and intercept the target, 3I/ATLAS.
- 2.
- The precise perijove of Juno, since the lower this value, the greater the kick which can be delivered from the Oberth effect using the same magnitude V.
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Seligman, D.Z.; Micheli, M.; Farnocchia, D.; Denneau, L.; Noonan, J.W.; Hsieh, H.H.; Santana-Ros, T.; Tonry, J.; Auchettl, K.; Conversi, L.; et al. Discovery and Preliminary Characterization of a Third Interstellar Object: 3I/ATLAS. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2507.02757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loeb, A. 3I/ATLAS is Smaller or Rarer than It Looks. Res. Notes AAS 2025, 9, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolin, B.T.; Belyakov, M.; Fremling, C.; Graham, M.J.; Abdelaziz, A.M.; Elhosseiny, E.; Gray, C.L.; Ingebretsen, C.; Jewett, G.; Karpov, S.; et al. Interstellar comet 3I/ATLAS: Discovery and physical description. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2507.05252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Candal, A.; Rizos, J.L.; Lara, L.M.; Santos-Sanz, P.; Gutierrez, P.J.; Ortiz, J.L.; Morales, N. X-SHOOTER Spectrum of Comet C/2025 N1: Insights into a Distant Interstellar Visitor. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2507.07312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opitom, C.; Snodgrass, C.; Jehin, E.; Bannister, M.T.; Bufanda, E.; Deam, S.E.; Dorsey, R.; Ferrais, M.; Hmiddouch, S.; Knight, M.M.; et al. Snapshot of a new interstellar comet: 3I/ATLAS has a red and featureless spectrum. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2507.05226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandler, C.O.; Bernardinelli, P.H.; Jurić, M.; Singh, D.; Hsieh, H.H.; Sullivan, I.; Jones, R.L.; Kurlander, J.A.; Vavilov, D.; Eggl, S.; et al. NSF-DOE Vera C. Rubin Observatory Observations of Interstellar Comet 3I/ATLAS (C/2025 N1). arXiv, 2025; arXiv:2507.13409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belyakov, M.; Fremling, C.; Graham, M.J.; Bolin, B.T.; Kilic, M.; Jewett, G.; Lisse, C.M.; Ingebretsen, C.; Davis, M.R.; Wong, I. Palomar and Apache Point Spectrophotometry of Interstellar Comet 3I/ATLAS. Res. Notes Am. Astron. Soc. 2025, 9, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flekkøy, E.G.; Luu, J.; Toussaint, R. The interstellar object’Oumuamua as a fractal dust aggregate. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2019, 885, L41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seligman, D.; Laughlin, G. Evidence that 1I/2017 U1 (Oumuamua) was composed of molecular hydrogen ice. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2005.12932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, A.P.; Desch, S.J. 1I/‘Oumuamua as an N 2 Ice Fragment of an exo-Pluto Surface: I. Size and Compositional Constraints. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2021, 126, e2020JE006706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desch, S.J.; Jackson, A.P. 1I/‘Oumuamua as an N 2 Ice Fragment of an Exo-Pluto Surface II: Generation of N 2 Ice Fragments and the Origin of ‘Oumuamua. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2021, 126, e2020JE006807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bialy, S.; Loeb, A. Could Solar Radiation Pressure Explain ‘Oumuamua’s Peculiar Acceleration? Astrophys. J. Lett. 2018, 868, L1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymond, S.N.; Armitage, P.J.; Veras, D. Interstellar Object ’Oumuamua as an Extinct Fragment of an Ejected Cometary Planetesimal. Astrophys. J. 2018, 856, L7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jewitt, D.; Luu, J. Initial Characterization of Interstellar Comet 2I/2019 Q4 (Borisov). Astrophys. J. Lett. 2019, 886, L29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- i4is. Initiative for Interstellar Studies, UK Non-Profit Company, 27/29 South Lambeth Road, London SW8 1SZ, UK, 2025. Available online: https://i4is. (accessed on 14 September 2025).
- Hein, A.M.; Perakis, N.; Eubanks, T.M.; Hibberd, A.; Crowl, A.; Hayward, K.; Kennedy, R.G.; Osborne, R. Project Lyra: Sending a spacecraft to 1I/’Oumuamua (former A/2017 U1), the interstellar asteroid. Acta Astronaut. 2019, 161, 552–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hein, A.M.; Eubanks, T.M.; Lingam, M.; Hibberd, A.; Fries, D.; Schneider, J.; Kervella, P.; Kennedy, R.; Perakis, N.; Dachwald, B. Interstellar Now! Missions to Explore Nearby Interstellar Objects. Adv. Space Res. 2022, 69, 402–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hibberd, A.; Hein, A.M.; Eubanks, T.M. Project Lyra: Catching 1I/’Oumuamua-Mission opportunities after 2024. Acta Astronaut. 2020, 170, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hibberd, A.; Hein, A.M. Project Lyra: Catching 1I/’Oumuamua-Using Nuclear Thermal Rockets. Acta Astronaut. 2021, 179, 594–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hibberd, A. Project Lyra: Another possible trajectory to 1I/’Oumuamua. Acta Astronaut. 2023, 211, 431–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hibberd, A. Project Lyra: The Way to Go and the Launcher to Get There. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.03065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seligman, D.; Laughlin, G. The Feasibility and Benefits of In Situ Exploration of ‘Oumuamua-like Objects. Astron. J. 2018, 155, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hibberd, A.; Perakis, N.; Hein, A.M. Sending a spacecraft to interstellar comet 2I/Borisov. Acta Astronaut. 2021, 189, 584–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaginuma, A.; Frincke, T.; Seligman, D.Z.; Mandt, K.; DellaGiustina, D.N.; Peña-Asensio, E.; Taylor, A.G.; Nolan, M.C. The Feasibility of a Spacecraft Flyby with the Third Interstellar Object 3I/ATLAS from Earth or Mars. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2507.15755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eubanks, T.M.; Bills, B.G.; Hibberd, A.; Blase, W.P.; Hein, A.M.; III, R.G.K.; Coffinet, A.; Schneider, J.; Kervella, P.; de Olea Ballester, C.G. 3I/ATLAS (C/2025 N1): Direct Spacecraft Exploration of a Possible Relic of Planetary Formation at “Cosmic Noon”. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2508.15768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, B.A.; Paris, S.W. Spacecraft trajectory optimization using direct transcription and nonlinear programming. Spacecr. Trajectory Optim. 2010, 29, 37. [Google Scholar]
- Jezewski, D.J. Primer Vector Theory and Applications; NASA Technical report; NASA: Washington, DC, USA, 1975; NASA TR-454. [CrossRef]
- Cage, P.; Kroo, I.; Braun, R. Interplanetary trajectory optimization using a genetic algorithm. In Proceedings of the Astrodynamics Conference, Scottsdale, AZ, USA, 1–3 August 1994; p. 3773. [Google Scholar]
- Hibberd, A. Github repository for OITS. 2017. Open Source Software Repository 10 July 2025. Available online: https://github.com/AdamHibberd/Optimum_Interplanetary_Trajectory. (accessed on 14 September 2025).
- Hibberd, A. Intermediate Points for Missions to Interstellar Objects Using Optimum Interplanetary Trajectory Software. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2205.10220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Digabel, S. Algorithm 909: NOMAD: Nonlinear optimization with the MADS algorithm. ACM Trans. Math. Softw. (TOMS) 2011, 37, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlueter, M.; Egea, J.; Banga, J. Extended Ant Colony Optimization for non-convex Mixed Integer Nonlinear Programming. Comput. Oper. Res. 2009, 36, 2217–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlueter, M.; Gerdts, M. The Oracle Penalty Method. J. Glob. Optim. 2010, 47, 293–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlueter, M.; Erb, S.; Gerdts, M.; Kemble, S.; Ruckmann, J. MIDACO on MINLP Space Applications. Adv. Space Res. 2013, 51, 1116–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NAIF. Planetary Data System Navigation Node, 10 July 2025. NASA JPL. Available online: https://naif.jpl.nasa.gov/naif/about.html (accessed on 14 September 2025).
- Blanco, P.R.; Mungan, C.E. High-speed escape from a circular orbit. Am. J. Phys. 2021, 89, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bate, R.R.; Mueller, D.D.; White, J.E. Fundamentals of Astrodynamics; Dover Publications: New York, NY, USA, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- NASA. Juno Launch Press Kit. 2011. Available online: https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/news/press_kits/JunoLaunch.pdf (accessed on 14 September 2025).
- Rein, H.; Liu, S.F. REBOUND: An open-source multi-purpose N-body code for collisional dynamics. Astron. Astrophys. 2012, 537, A128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rein, H.; Spiegel, D.S. IAS15: A fast, adaptive, high-order integrator for gravitational dynamics, accurate to machine precision over a billion orbits. Mon. Notes R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 446, 1424–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
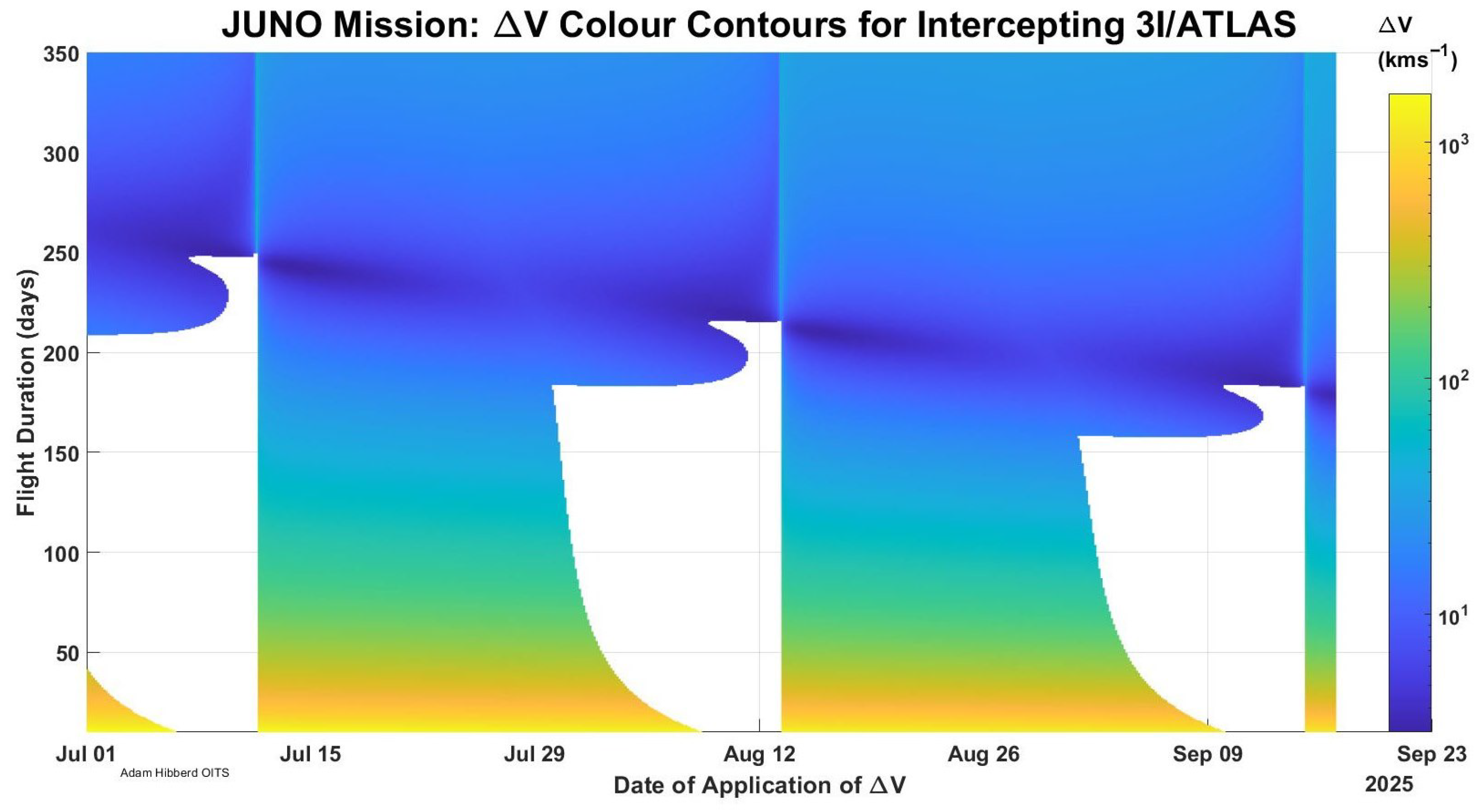
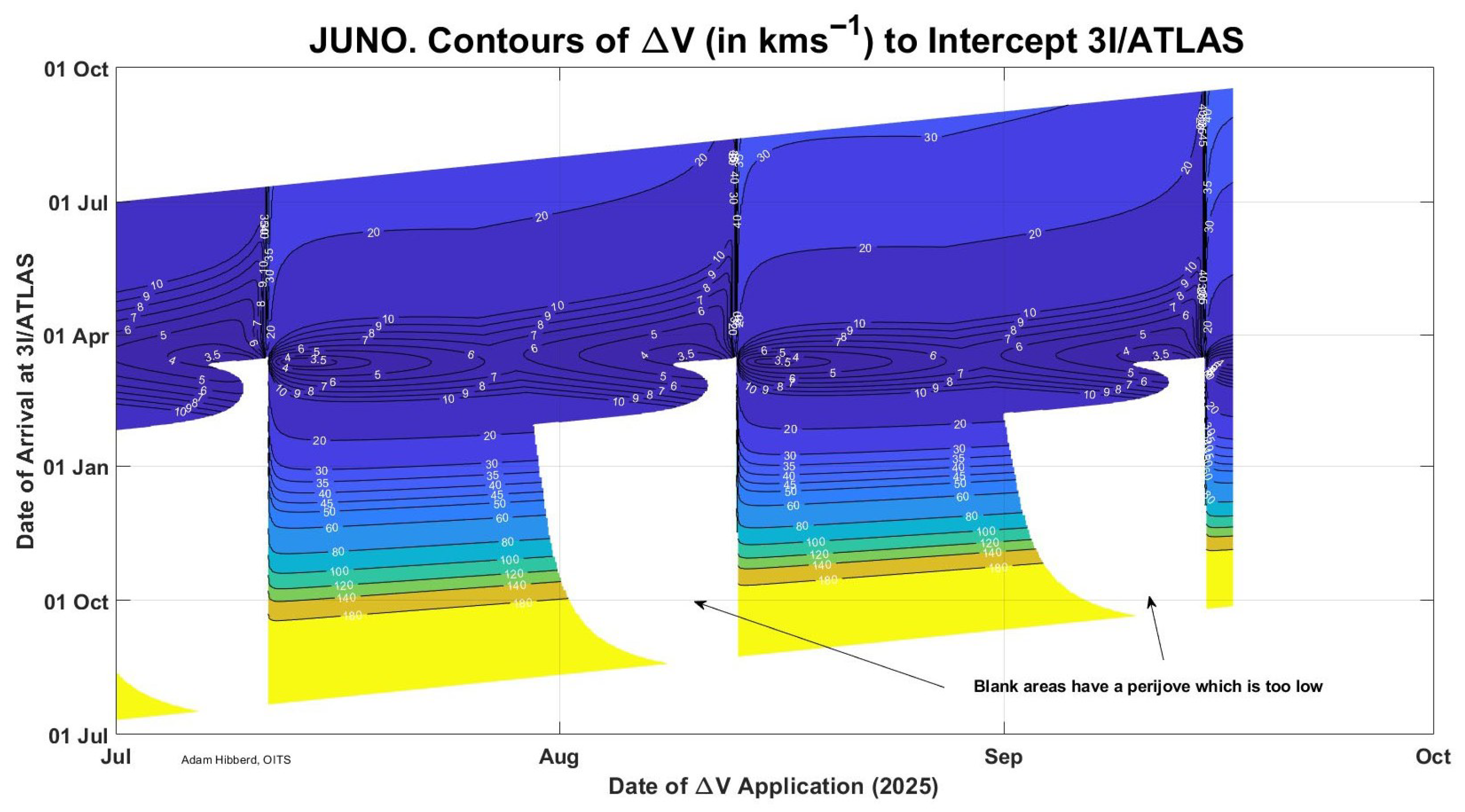
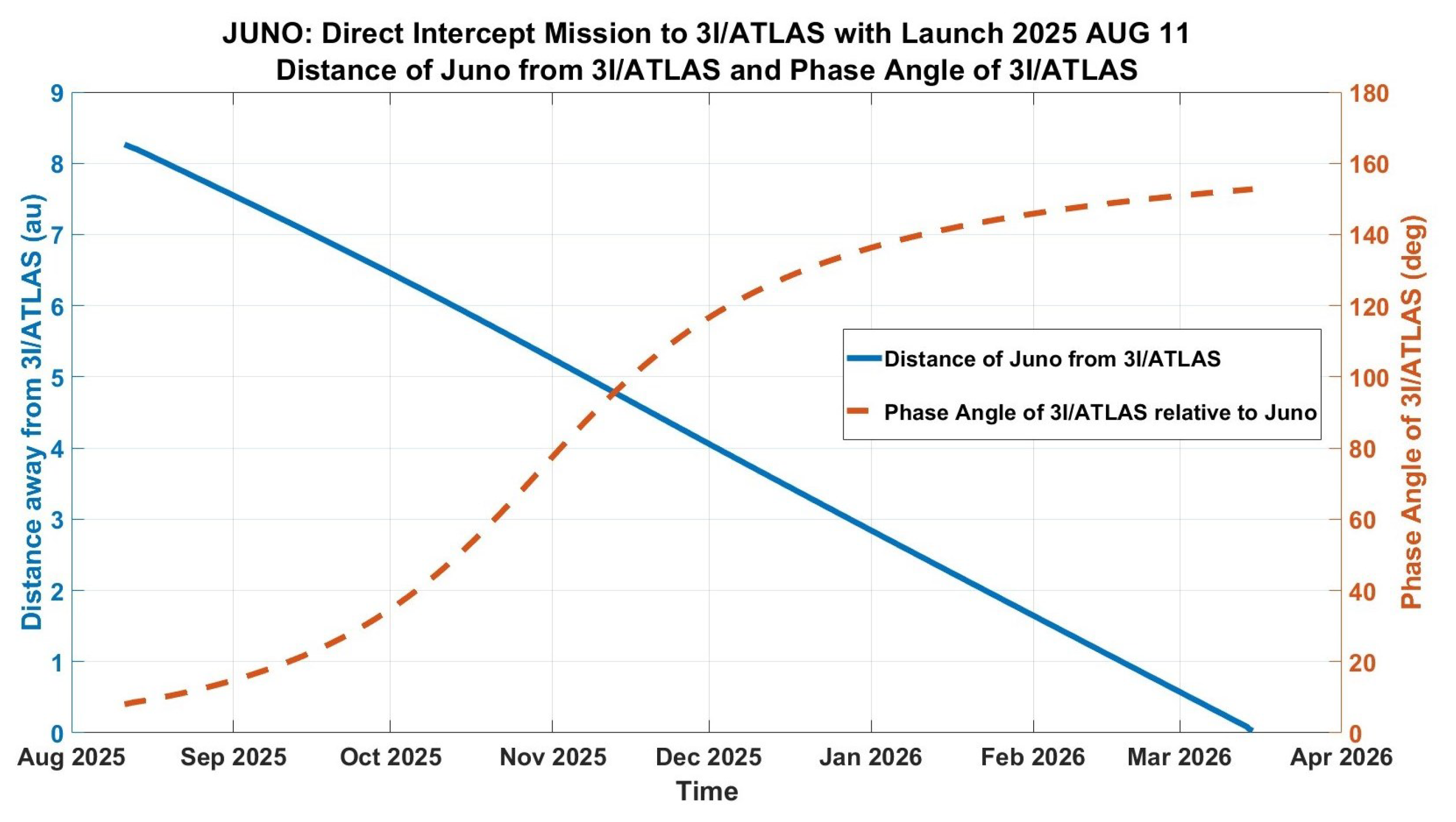

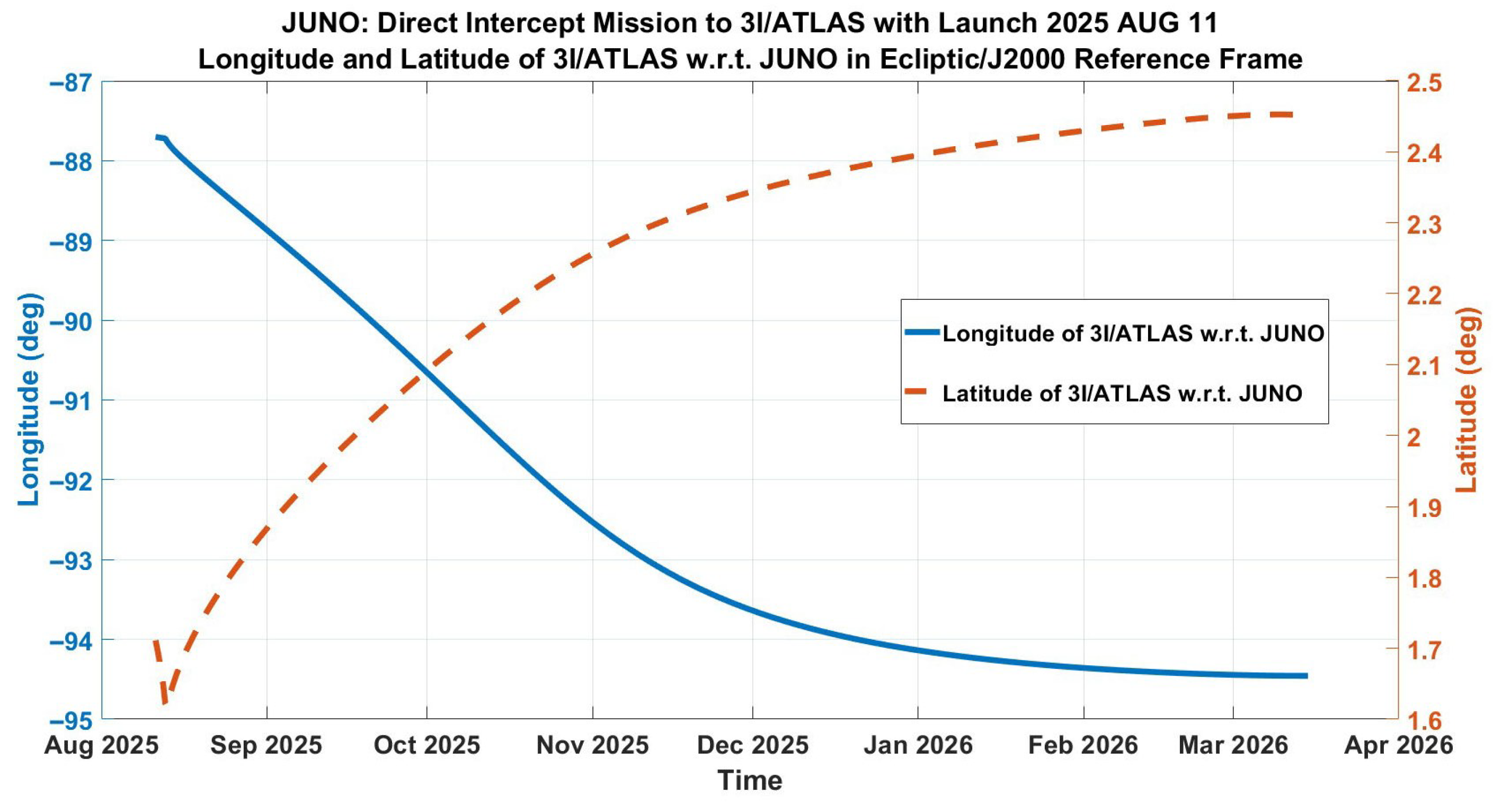
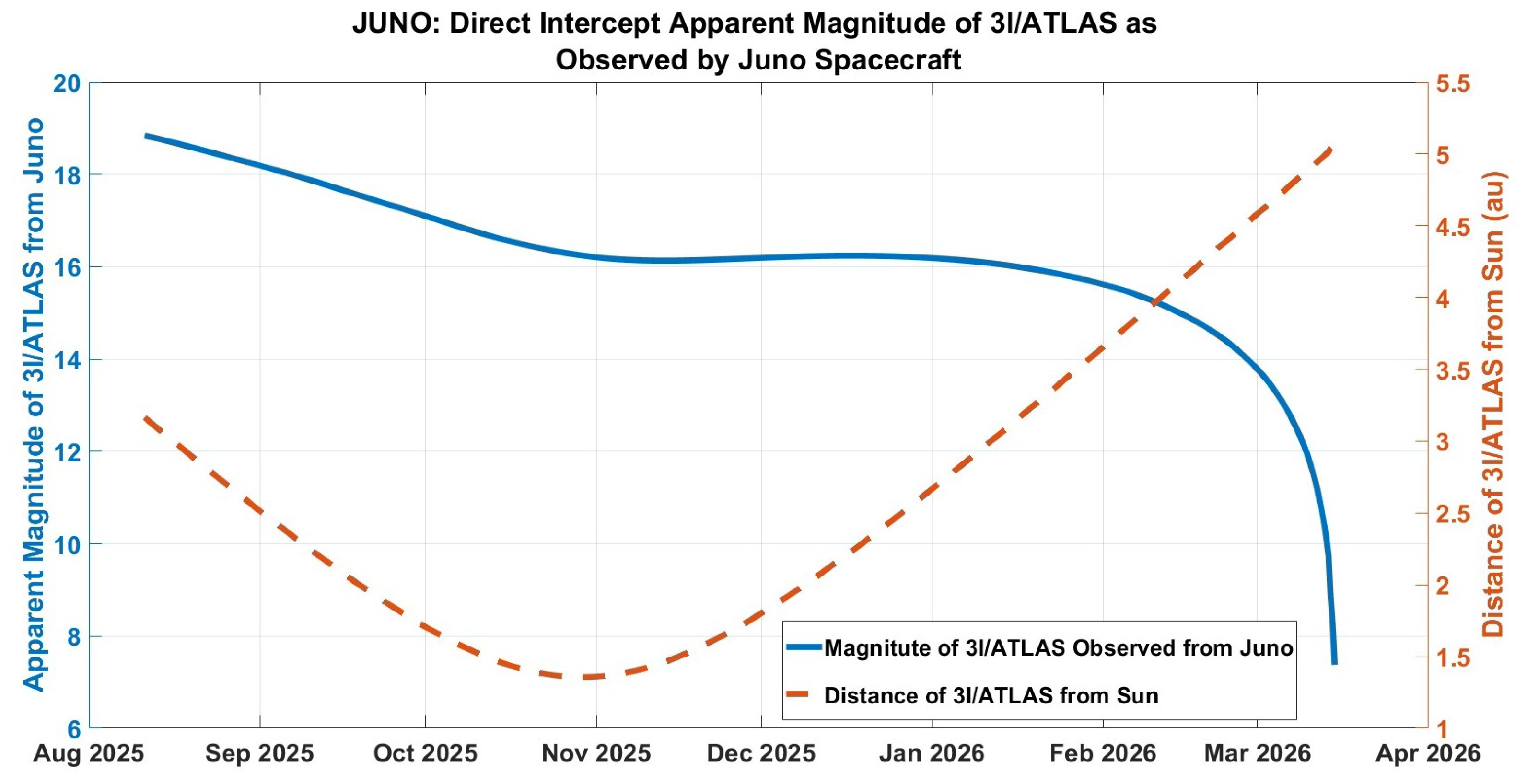

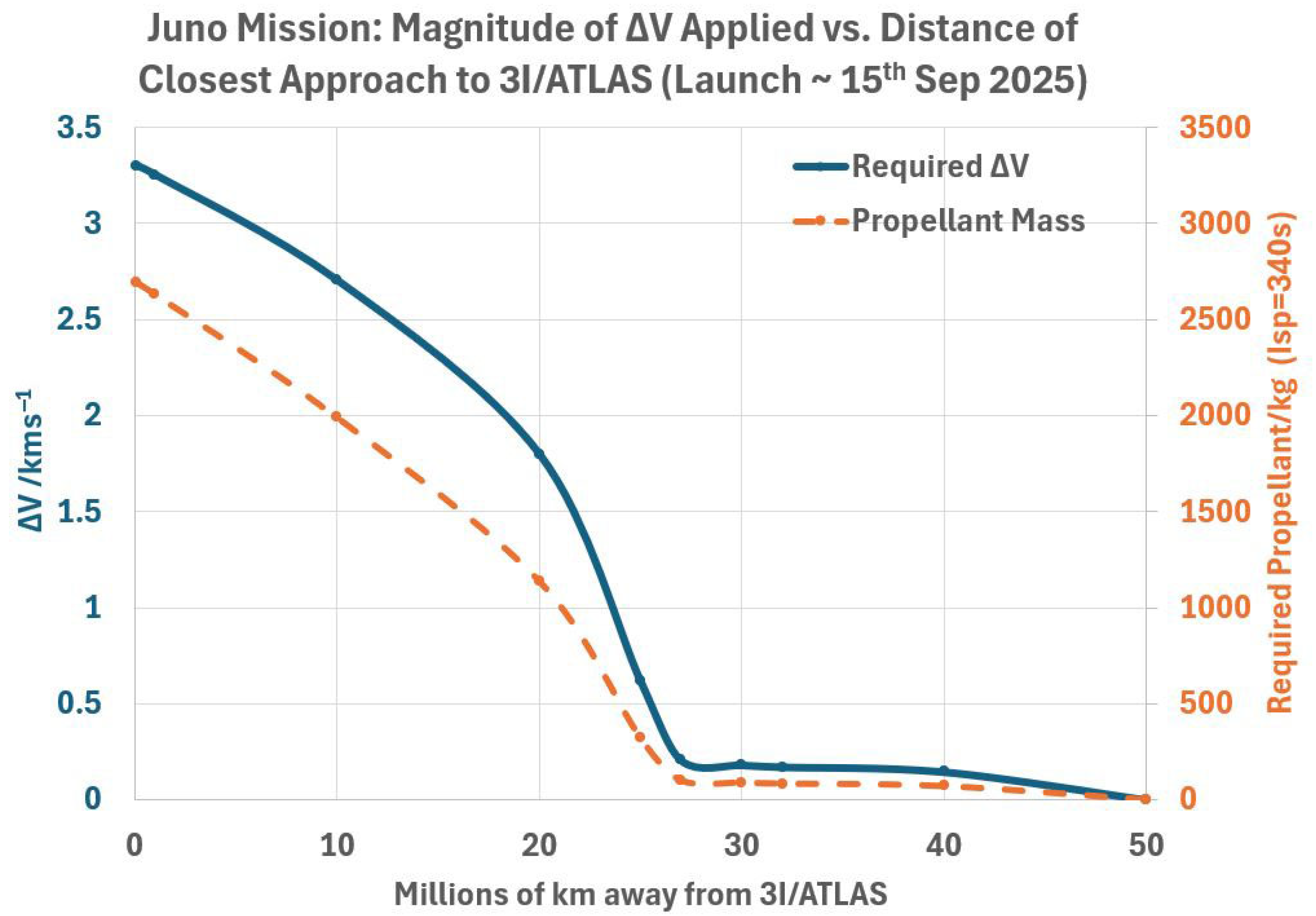

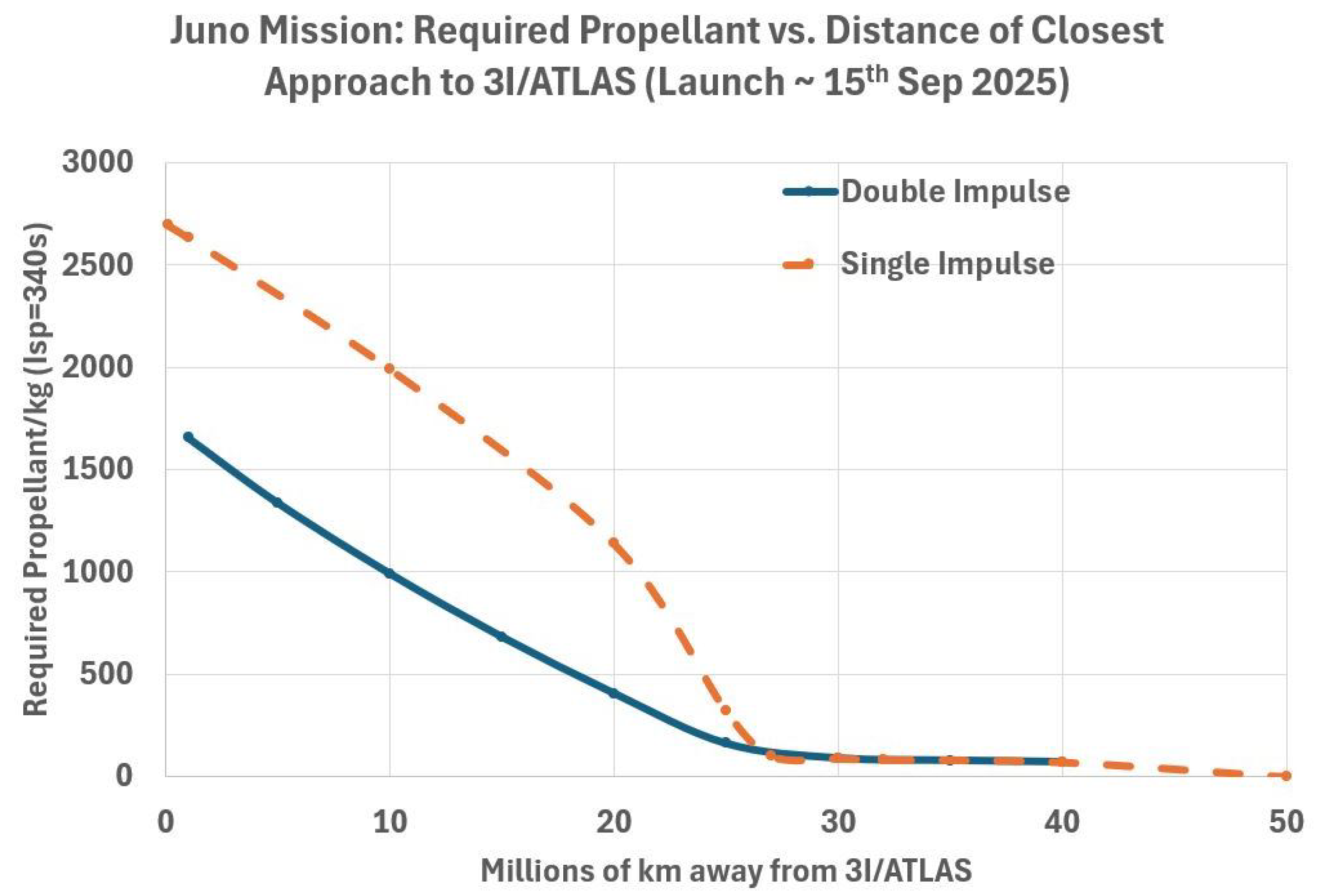

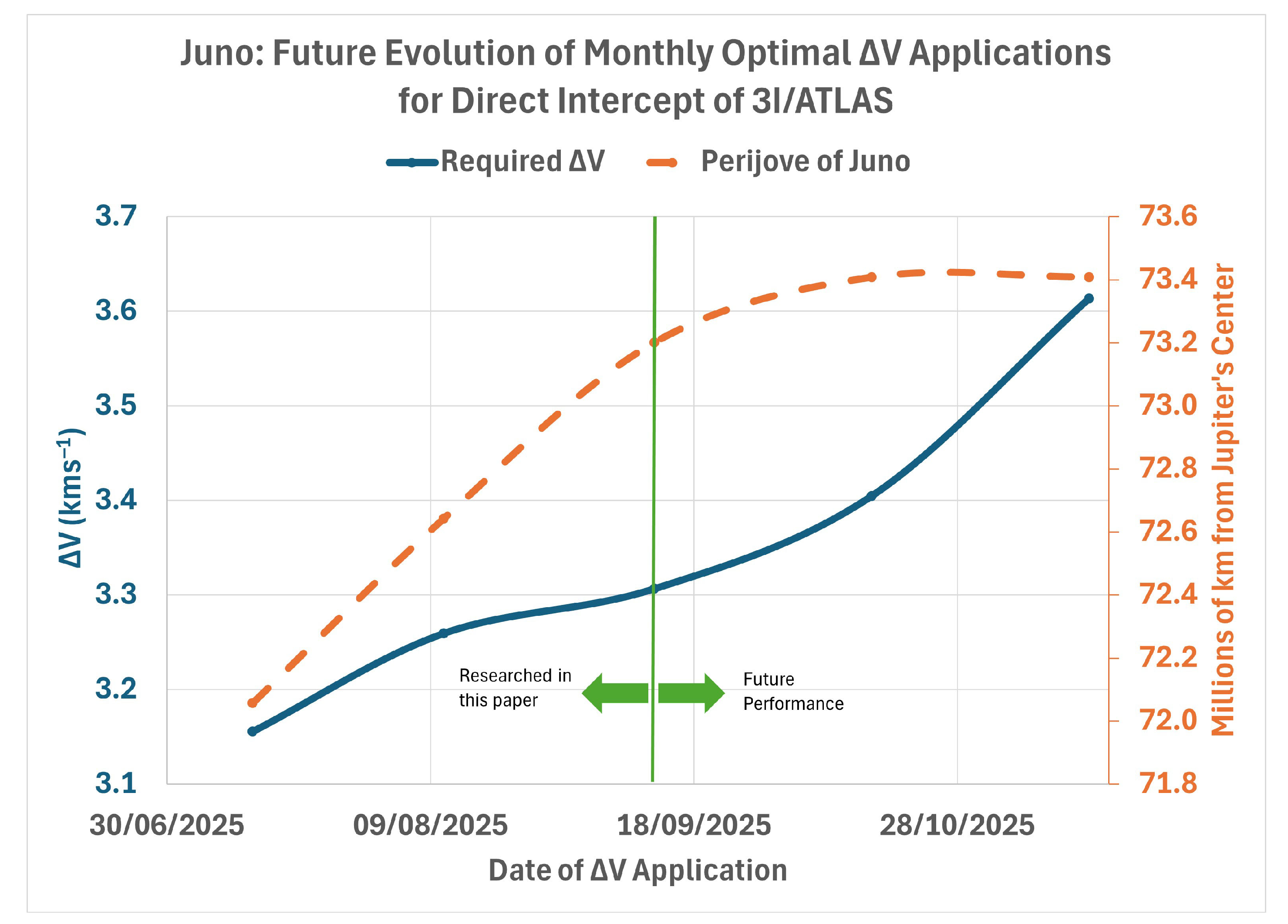
| Number | Event | Time | Arrival Speed | Departure Speed | V | Distance from Jupiter | Perijove Alt. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m/s | m/s | m/s | km | km | |||
| 1 | Juno | 2025 AUG 11 03:19:36 | 0 | 3259.3 | 3259.3 | 2,303,610 | 63,276 |
| 2 | 3I/ATLAS | 2026 MAR 16 01:32:30 | 66,129.2 | 66,129.2 | 0 | 53,392,590 | 63,276 |
| Contingency Margin | 490 (15%) | ||||||
| Total V | 3749.3 |
| Number | Event | Time | Arrival Speed | Departure Speed | V | Distance from Jupiter | Perijove Alt. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m/s | m/s | m/s | km | km | |||
| 1 | Juno | 2025 SEP 12 22:29:49 | 0 | 3306.5 | 3306.5 | 2,235,639 | 60,390 |
| 2 | 3I/ATLAS | 2026 MAR 16 11:45:48 | 66,068.9 | 66,068.9 | 0 | 53,331,939 | 60,390 |
| Contingency Margin | 500 (15%) | ||||||
| Total V | 3806.5 |
| Number | Event | Time | Arrival Speed | Departure Speed | V | Distance from Jupiter | Perijove Alt. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m/s | m/s | m/s | km | km | |||
| 1 | Juno | 2025 SEP 09 22:40:01 | 0 | 2157.4 | 2157.4 | 3,863,491 | |
| 2 | 2.68 Jupiter Radii | 2025 SEP 14 18:37:14 | 35,881.8 | 36,388.6 | 518.1 | 191,595 | 120,103 |
| 3 | 3I/ATLAS | 2026 MAR 14 12:51:04 | 66,536.8 | 66,536.8 | 0 | 54,576,427 | 88,660 |
| Contingency Margin | 400 (15%) | ||||||
| Total V | 3075.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Loeb, A.; Hibberd, A.; Crowl, A. Intercepting 3I/ATLAS at Its Closest Approach to Jupiter with the Juno Spacecraft. Aerospace 2025, 12, 851. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace12090851
Loeb A, Hibberd A, Crowl A. Intercepting 3I/ATLAS at Its Closest Approach to Jupiter with the Juno Spacecraft. Aerospace. 2025; 12(9):851. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace12090851
Chicago/Turabian StyleLoeb, Abraham, Adam Hibberd, and Adam Crowl. 2025. "Intercepting 3I/ATLAS at Its Closest Approach to Jupiter with the Juno Spacecraft" Aerospace 12, no. 9: 851. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace12090851
APA StyleLoeb, A., Hibberd, A., & Crowl, A. (2025). Intercepting 3I/ATLAS at Its Closest Approach to Jupiter with the Juno Spacecraft. Aerospace, 12(9), 851. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace12090851







