Abstract
The proliferation of CubeSats in Earth orbit has accelerated dramatically in recent years, with projections indicating continued growth in the coming decades. This review examines the evolution of CubeSat applications, from basic technology demonstrations to complex mission capabilities, including Earth observation, telecommunications, astronomical research, biological experimentation, and deep-space exploration. A notable shift has occurred over the past fifteen years, with CubeSats transitioning from standalone platforms to integrated nodes within larger constellations, particularly for Earth observation and telecommunications applications. We analyze the key enabling factors behind the CubeSat revolution, including decreased launch costs, miniaturized electronics, standardized components, and institutional support frameworks. Through the examination of significant past, current, and planned missions, this paper provides a comprehensive overview of CubeSat capabilities across diverse application domains. The review highlights how these miniaturized satellite platforms are democratizing access to space while enabling innovative scientific and commercial applications previously restricted to larger spacecraft.
1. Introduction
A satellite may be defined as any natural or artificial object that orbits a celestial body, such as a planet or a star. For the purposes of the present study, the term “satellite” refers exclusively to artificial satellites, unless explicitly specified otherwise. Satellites are placed into the desired orbits by launch vehicles and may be equipped with a variety of payloads (such as optical sensors, microwave sensors, antennas, telescopes, etc.) depending on the mission they are designed to accomplish [1]. Satellites are designed and manufactured in a variety of forms and dimensions, depending on their intended functions and mission requirements. It is, therefore, common practice to classify satellites according to their size, which is usually expressed in terms of mass. A common rule used for the classification of satellites in terms of mass is presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
A common satellite classification based on mass [2].
Currently, the vast majority of nanosatellites, as well as a considerable number of microsatellites, adhere to the CubeSat architecture. This architecture was first established in 1999 through the CubeSat project, a collaborative effort between Professor Jordi Puig-Suari at California Polytechnic State University and Professor Bob Twiggs of Stanford University’s Space Systems Development Laboratory. The term CubeSat defines a class of small-sized satellites that adopt a standard size and form factor, in which the base unit is defined as “U” corresponding to a cube with sides approximately 10 cm in length. In this context, a 1U CubeSat resembles a 10 cm × 10 cm × 10 cm cube with a maximum expected mass of up to 2 kg. Similarly, a 2U CubeSat has approximate dimensions of 10 cm × 10 cm × 20 cm and a maximum mass of 4 kg. CubeSats are equipped with four rigid aluminum rails on their corners which support the satellite during launch and aid in its eventual deployment, while some other CubeSats are supported by aluminum tabs located on only two of their corners [3]. Larger CubeSats such as 3U, 6U, 8U, 12U, and 16U can be constructed by repetitive addition of 1U building blocks as presented in Figure 1. Furthermore, smaller CubeSat form factors such as 0.25U are also possible and have been utilized, while larger ones, such as 24U and 27U have been proposed for future missions. Table 2 provides more accurate information on the typical maximum dimensions (at the rails) and maximum allowable weight of CubeSats based on their size; however, the exact values (especially the weight) ultimately depend entirely on the CubeSat dispenser that will be used. Furthermore, depending on the dispenser used, protrusions from the rail dimensions are commonly allowed on specific areas of the satellite.
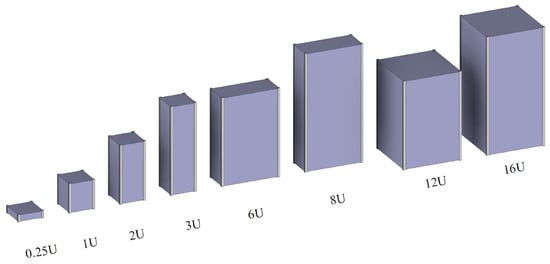
Figure 1.
An illustrative example of some commonly used CubeSat sizes.

Table 2.
Typical maximum allowable rail dimensions and weight of CubeSats based on their size.
There are two primary methods for deploying CubeSats into orbit. In the first method, CubeSats are carried by launch vehicles inside specifically designed containers called CubeSat dispensers (also commonly referred to as CubeSat deployers). These dispensers may carry one or more CubeSats simultaneously and, after orbital insertion, eject the satellites through spring mechanisms, deploying them into orbit. When deployed from rockets, CubeSats may serve as secondary payloads to the rocket launch’s primary payload or may be part of rideshare missions designed to place numerous CubeSats and other small satellites into specific orbits. Figure 2a illustrates the integration of CubeSat dispensers on the Evolved Expendable Launch Vehicle Secondary Payload Adapter (ESPA) of United Launch Alliance’s (Denver, CO, USA) (ULA) Atlas V 401 launch vehicle. These CubeSat dispensers were used for the deployment of four CubeSats launched as secondary payload to National Aeronautics and Space Administration’s (NASA) Landsat 9 Earth observation satellite [4]. Another common method of placing CubeSats into Earth orbit involves first transporting them to the International Space Station (ISS) as cargo during International Space Station (ISS) resupply missions. The CubeSats are then loaded into the Nanoracks CubeSat Deployer (NRCSD) or the JEM Small Satellite Orbital Deployer (J-SSOD) of the ISS’s Japanese Experiment Module (JEM) by the station crew and subsequently deployed into the same orbit as the ISS [5,6]. Figure 2b shows the moment of deployment of the University of Patras Satellite (UPSat) CubeSat from the NRCSD of the ISS.
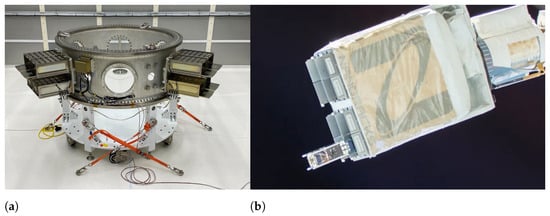
Figure 2.
(a) The integration of CubeSats to the Evolved Expendable Launch Vehicle Secondary Payload Adapter (ESPA) of United Launch Alliance’s (ULA) Atlas V launch vehicle as secondary payloads to National Aeronautics and Space Administration’s (NASA) Landsat-9 Earth observation satellite. Photo by NASA/Jerry Nagy [7]. (b) The 2U University of Patras Satellite (UPSat) CubeSat during its deployment from the International Space Station (ISS). “Cropped version of the original image. Credit: Libre Space Foundation. Copyright (2023), Creative Commons CC BY 4.0 license” [8].
Similar to their larger counterparts, the equipment carried by CubeSats can be classified into two distinct categories: the satellite bus and the satellite payload. The term bus refers to all the subsystems responsible for sustaining and supporting the satellite during its mission. Such subsystems include the satellite Structure (STRU), the communications subsystem (COMM), the attitude and orbit control subsystem (AOCS), the electrical power subsystem (EPS), the onboard data handling subsystem (OBDH), the telemetry, tracking, and command system (TT&C), and the thermal control subsystem (TCS). The term payload refers to the equipment that provides the mission capability or service that the satellite is intended for. For example, the payload of an Earth observation satellite could be an optical imaging sensor, whereas the payload of a communications satellite would consist of all the antennas, amplifiers, transceivers, and transponders that enable communication with the ground segment of the overall system [9]. As a typical example of a CubeSat subsystem layout, Figure 3 presents the subsystem diagram of the University of Patras Satellite (UPSat), a 2U CubeSat jointly developed by the University of Patras and Libre Space Foundation (Athens, Greece) for the study of the lower thermosphere as part of the QB50 mission.
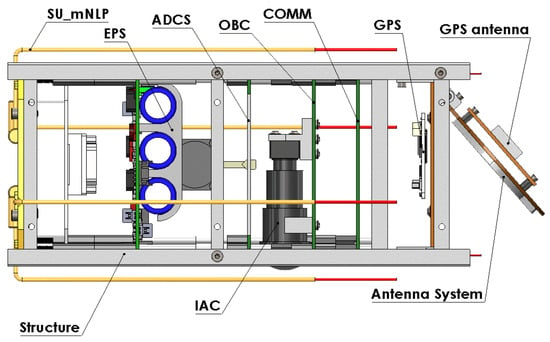
Figure 3.
An illustration of the subsystem layout of the CubeSat UPSat. “Adapted from Ampatzoglou and Kostopoulos, International Journal of Aerospace Engineering, 2018, Article ID 9724263, licensed under CC BY 4.0” [10].
Although the initial CubeSats were mostly custom-designed and custom-built platforms, their success over the past two decades has led to the establishment of numerous companies specializing in CubeSat manufacturing and integration. These companies provide a wide array of standardized and qualified Commercial-Off-The-Shelf (COTS) CubeSat platform solutions, complete with structural, electrical power, communications, attitude and orbit control, onboard data handling subsystems, as well as various payload solutions such as imagers, spectrometers, laser-optical communication terminals, radiofrequency amplifiers, antennas, etc. Notable examples of CubeSat manufacturing and integration companies include NanoAvionics (Vilnius, Lithuania), GomSpace (Aalborg, Denmark), ISISPACE (Delft, The Netherlands), EnduroSat (Sofia, Bulgaria), TERRAN ORBITAL (Irvine, CA, USA), AAC Clyde Space (Uppsala, Sweden), Spire Global (Vienna, VA, USA), and SPUTNIX LLC (Moscow, Russia). Moreover, manufacturers that specialize in satellite payload manufacturing such as antennas, imagers, and scientific instruments are also active in the domain of CubeSat payload manufacturing, with notable examples being Simera Sence (Leuven, Belgium), Thoth Technology (Deep River, ON, Canada), Triad RF Systems (East Brunswick, NJ, USA), Tesat-Spacecom GmbH (Backnang, Germany), Astrolight (Vilnius, Lithuania), etc. Among COTS CubeSat solutions, a high degree of versatility and modularity is a notable characteristic, as such products allow for easy subsystem reconfiguration and the integration of different subsystems and payloads on the main structural platform of the satellite, allowing for a variety of missions to be realized. Furthermore, the use of common structural architectures and communication standards also sometimes allows for the combination of systems COTS from different providers into a single satellite platform.
In recent years, some of the leaders of the aerospace industry, as well as several space agencies around the world, have acknowledged the utility of CubeSats as cost-effective solutions for space exploration and technology demonstration and have been incorporating them in several important missions. A notable example in that regard is the slate of ten CubeSats that were launched as secondary payloads of the Artemis I mission on 16 November 2021, which were developed through the collaboration of various institutions, companies, and space agencies, each tasked with performing important scientific missions and milestones [11], or NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS), which is a constellation of Earth science CubeSat platforms that perform weather-related atmospheric measurements [12]. NASA’s understanding of CubeSat utility is further demonstrated by the Planetary Science Deep Space SmallSat Studies (PSDS3) program, which aimed to accelerate the development of selected mission concepts utilizing CubeSats and other small-satellite platforms for space exploration [13].
It is evident that although the first CubeSats were mostly custom-made technology demonstration platforms, they have rapidly evolved into mature, mission-enabling systems capable of undertaking a wide range of space activities, including Earth observation, telecommunications, astronomical research, planetary exploration, and advanced technology validation. As their capabilities expand, CubeSats are increasingly being integrated into complex mission architectures involving autonomous formation flying and active debris mitigation [14,15]. This transformation reflects not only their growing technical maturity, but also the increasing scale and coordination demands of modern space operations, such as satellite constellations and deep-space navigation. Recent advances in autonomous control algorithms [16] and contactless manipulation techniques further position CubeSats as key enablers of future space sustainability, with the potential to serve as foundational elements of next-generation orbital infrastructures. The present work aims to provide a comprehensive overview of CubeSat success and the missions they undertake. The paper is structured as follows: Section 2 presents data on the rising number of CubeSats in orbit around the Earth, demonstrating their success in recent years, along with a discussion of the enabling factors that have led to this success and future prospects. Section 3 presents the use of CubeSats for Earth observation and Earth science missions. Section 4 discusses examples of telecommunication CubeSats, classified into radio communication and laser-optical communication categories. Section 5 presents examples of CubeSats used as astronomical observation platforms. Section 6 examines CubeSats used as platforms for the execution of chemical and biological experiments, while Section 7 explores examples of CubeSats serving as instruments for lunar, planetary, and asteroid exploration. Section 8 provides illustrative examples of past, present, and upcoming CubeSat missions serving as platforms for state-of-the-art technology demonstration. Finally, Section 9 discusses various observations made during the review and presents some conclusions that are derived from them.
It should be noted that this work does not aim to provide exhaustive documentation of every CubeSat mission conducted to date for each category. Instead, it seeks to offer illustrative examples that define the scope of missions currently achievable with CubeSat platforms.
2. The Success of CubeSats and Its Enabling Factors
As presented in Figure 4, in recent years, there has been a significant rise in the number of CubeSats in orbit around the Earth, a trend that is forecasted to continue for decades to come. This increase is largely attributed to several enabling factors, including the reduction of launch costs, the emergence of rideshare launch missions, the miniaturization and commercialization of space-grade electronic components, the existence of a large number of commercial CubeSat manufacturers, the standardization of structural and electronic components, and the involvement and support provided by space agencies through financial, programmatic, and technical assistance. These enabling factors are examined in detail in the following section.
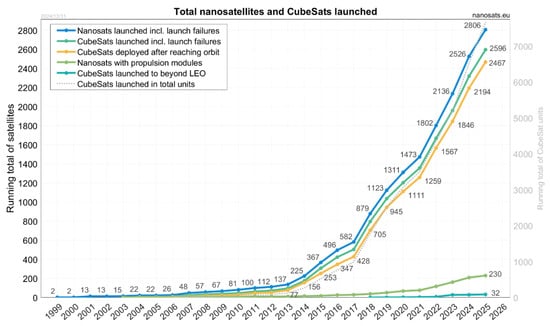
Figure 4.
The total number of CubeSat and other nanosatellite launches that have taken place in the period between 1998 and 2025. Data and illustration by Nanosats Database/Erik Kulu [17].
2.1. The Reduction of Launch Costs and Rideshare Opportunities
The first and perhaps one of the most significant factors enabling the proliferation of CubeSats is the considerable reduction in the cost of accessing space. This has been driven by the introduction into service of partially reusable orbital-class launch vehicles such as SpaceX’s (Hawthorne, CA, USA) Falcon 9 and Falcon Heavy, Blue Origin’s (Kent, WA, USA) New Glenn, and Rocket Lab’s (Long Beach, CA, USA) Electron rockets. These systems are designed to recover, refurbish, and reuse key components of the launch vehicle, which in turn lowers the cost associated with new space missions. This market pressure and competition between launch providers have further helped in lowering launch costs even more for expendable launch vehicles. The commissioning of fully reusable launch vehicles, such as SpaceX’s Starship, is expected to further decrease payload launch costs, expanding access to space even for institutions with limited financial resources. The impact of these cost reductions is evident when comparing the cost per kilogram of payload to low Earth orbit (LEO) for various launch vehicles, with reusable launch vehicles offering significantly lower prices than traditional expendable systems [18].
Another critical factor contributing to more affordable launch prices is the widespread adoption of rideshare launch missions. In such missions, two or more payloads from different clients share the same launch vehicle, thereby distributing the launch-associated costs [19]. While multiple-payload launches have existed since the early space age, only in recent decades have consistent efforts been made to fully exploit rideshare capabilities through standardized mechanical interfaces. According to NASA, payloads in rideshare missions are classified into three categories:
- Primary payload: The term primary payload refers to the satellite or other type of spacecraft for the launch of which the launch is procured. It is usually the largest and most expensive of the payloads and it is the one that usually dictates the launch profile, final orbit, as well as the integration procedures to a large degree. The primary payload is also the payload that usually separates first from the payload adapter of the launch vehicle.
- Secondary payload: The term secondary payload refers to satellites that are usually smaller in size compared to the primary payload and are parts of independent missions that have little to no impact on the primary payload.
- Tertiary payload: The term tertiary payload refers to very small satellites that in no way interfere with the mission primary payload.
Some notable examples of CubeSats launched as secondary payloads are the transporter missions by SpaceX. The first Transporter-1 mission in January 2021 set a record by launching 143 satellites, making it the largest rideshare mission to date [20]. As of 2026, several commercial providers, apart from SpaceX with its Falcon 9 rocket [21], such as Rocket Lab with the Electron rocket [22] and Arianespace (Évry-Courcouronnes n. Paris, France) with the Vega and Ariane 6 launch vehicles [23], offer dedicated rideshare services, allowing dozens or even hundreds of CubeSats to be launched in a single mission.
2.2. The Miniaturization of Electronics and the Emergence of COTS Solutions
Another prominent factor that has led to the exponential development of the small satellite market is the miniaturization of electronic components. Advances in microelectronics have enabled the integration of entire satellite subsystems into compact and lightweight modules. Today, processors, memory chips, optics, and batteries designed for commercial applications often meet the stringent quality requirements of space missions. This allows CubeSat developers to acquire and integrate COTS electronic equipment, significantly reducing costs compared to custom-built solutions [24,25]. Furthermore, a growing number of commercial companies specialize in CubeSat development, offering complete end-to-end solutions. Many CubeSat manufacturers provide fully designed and tested satellites, allowing organizations with limited space-related expertise to acquire and operate a small satellite [26]. A similar approach applies to ground stations, where organizations can either purchase infrastructure or lease services from existing providers, minimizing complexity and integration costs.
2.3. Standardization
A high degree of standardization has played a key role in the success of CubeSats. The 1U CubeSat form factor (10 cm × 10 cm × 10 cm) set by the CubeSat Design Specification (CDS) serves as a standardized building block, with variations such as 2U, 3U, and 6U configurations allowing for scalability [3,27]. This standardization extends to multiple aspects of CubeSat development, including structural components, electronic interfaces, and communication protocols. Key standardization aspects include the following:
- Structural Standardization: The Poly-PicoSatellite Orbital Deployer (P-POD) system, developed by Cal Poly San Luis Obispo and NASA, which allows CubeSats to be deployed safely and reliably into space [28]. This standardization ensures compatibility with a variety of launch vehicles, reducing integration complexity and costs. Figure 5a presents an example of the P-POD system.
- Electronic Standardization: While no strict electronic standard exists, the PC/104 form factor has emerged as the de facto industry standard for CubeSat avionics [29]. PC/104 components are designed to fit within the limited internal volume of CubeSats while maximizing available space. Their stack-through connectors facilitate the quick and easy assembly of complex electronic stacks that run the length of the satellite. An example of a typical PC/104 electronics board, such as the ones utilized in cubesat manufacturing, is given in Figure 5b.
- Battery Standardization: Similarly, in terms of battery storage, CubeSat designers commonly utilize COTS cylindrical 18650 batteries to create complete battery packs for the satellite’s EPS in a cost-effective manner. Common material choices used for the manufacturing of these batteries are Lithium-Ion (Li-Ion), Lithium-polymer (Li-pol), Lithium-Chloride (Li-Cl), Nickel-Cadmium (Ni-Cd), and Nickel-metal hydride (Ni-MH) [30].
- Communication Standardization: CubeSats utilize a range of established communication protocols, including the Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI), Controller Area Network Bus (CAN Bus), Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C), Universal Asynchronous Receiver-Transmitter (UART), SpaceWire, and Ethernet. These standard protocols enable seamless communication between onboard subsystems and ground stations, improving efficiency and interoperability.
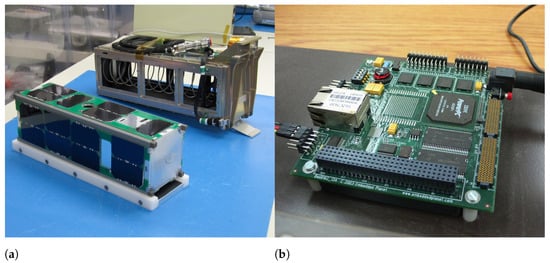
Figure 5.
(a) The Colorado Student Space Weather Experiment (CSSWE) CubeSat next to its Poly-PicoSatellite Orbital Deployer (P-POD) Dispenser. “Image by CSSWE at English Wikipedia. Creative Commons CC BY-SA 3.0 license” [31]. (b) An example of a PC/104 board. Cropped version of the original image by Vocaro at English Wikipedia [32].
2.4. Support from Space Agencies and Research Institutions
Space agencies, having understood the significance of CubeSats and the ability of such platforms to perform even more complex scientific missions for a fraction of the design, assembly, and integration cost of larger traditional satellite platforms, have launched design facilitation programs through which they select CubeSat mission proposals which then receive financial and technical support in order to materialize. One such notable example is NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative (CLSI), a program via which CubeSats built by US educational institutions and non-profit organizations are selected and provided with a free launch service. So far, more than 200 CubeSat missions from more than 100 different organizations have been selected through the CubeSat Launch Initiative [33]. In a similar manner, the European Space Agency (ESA), through the Fly Your Satellite program, allows university and other tertiary education student teams to develop and fly their CubeSat or PocketQube satellite. Through the Fly Your Satellite program, the selected student teams have access to training courses provided by ESA in order to improve the design of their satellite, access to the agency’s cleanroom laboratory and CubeSat test facilities for assembly, integration, and testing, and eventually, a satellite launch opportunity. Furthermore, after orbital insertion, ESA aids the selected teams during the satellite’s operational phase and will share mission data as well as technical or scientific results [34]. NASA has also offered the Small, Innovative Missions for PLanetary Exploration (SIMPLEx) [35] and Planetary Science Deep Space SmallSat Studies (PSDS3) [13] programs, through which planetary and other deep space exploration mission concepts utilizing CubeSat and other types of small spacecraft platforms were selected and received developmental funding.
Another example of a program that provides CubeSat manufacturers and operators with opportunities is the flight ticket initiative which has been established by the collaboration between the European Commission and ESA with the goal of providing European institutions and companies with the opportunity of launching their flight-ready satellite. These flight opportunities are awarded in a competitive manner and are aimed at satellite missions that have the goal of In-Orbit Demonstration (IOD) or In-Orbit Validation (IOV) of state-of-the-art technologies and operational concepts with applications in fields such as Earth observation, Positioning, Navigation and Timing (PNT), Space Situational Awareness (SSA), Satellite telecommunication technologies, as well as space science [36,37]. In a similar manner, the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) features the Innovative Satellite Technology Demonstration Program which is aimed at facilitating the development and launch of microsatellites and CubeSats, which are developed by research and educational institutions, as well as by commercial companies [38].
In Russia, the Space- initiative, part of the broader “Planet Sentinel” program and supported by the Innovation Promotion Fund, enables school and university students to develop CubeSats in collaboration with research institutions and commercial satellite developers. With more than 45 satellites launched and thousands of students engaged, Space- provides access to design resources, integration support, and opportunities for in-orbit experimentation, with missions such as UmKA-1 and Geoscan-Edelveis demonstrating its educational and technological impact [39]. In India, although the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) does not operate a named CubeSat initiative akin to CLSI or Fly Your Satellite, it has long supported student and academic CubeSat missions by offering launch services aboard its PSLV rockets. Successful examples include STUDSAT, Jugnu, SATHYABAMASAT, and INSPIRESat-1, developed by Indian universities and launched as secondary payloads. Moreover, through the establishment of IN-SPACe (Indian National Space Promotion and Authorization Center), ISRO now actively promotes private-sector and university participation in satellite development, providing technical guidance and facilitating integration and launch opportunities [40]. Up until now, China does not have a centralized CubeSat aid program like NASA’s CLSI, but the CNSA supports CubeSat development through university collaborations and international partnerships. Chinese universities like Harbin Institute of Technology and Tsinghua University frequently launch CubeSats, and projects such as ICUBE-Q show China’s commitment to educational and cooperative space missions [41].
2.5. A New Business Model
With the evolution of the CubeSat ecosystem and business models, the growth of the CubeSat industry has given rise to a dedicated ecosystem encompassing manufacturing, launch services, and operational support. Companies now specialize in CubeSat components, mission integration, and satellite operations, contributing to a thriving commercial sector. One emerging trend is Satellite-as-a-Service (SaaS), where companies provide fully managed CubeSat missions, covering design, manufacturing, launch, and operation. This allows organizations without in-house space expertise to deploy CubeSat missions tailored to their needs [42].
Since the first CubeSat was launched in 2003, their numbers have grown exponentially. By 2024, over 2500 CubeSats had been launched, with projections indicating that over 10,000 could be deployed within the next decade. CubeSats have evolved from simple educational tools into sophisticated platforms supporting diverse scientific, commercial, and exploratory missions. As their ecosystem continues to expand, CubeSats are expected to play an even more significant role in space exploration, further democratizing access to space and enabling groundbreaking applications in research, communications, and planetary exploration.
3. CubeSats as Earth Observation and Earth Science Platforms
Earth observation satellite missions can be defined as missions that have the objective of collecting data related to various aspects of the Earth, such as the condition of the Earth’s terrestrial surface, its bodies of water, its atmosphere, its magnetic field, etc. The data gathered by Earth observation satellite platforms are then analyzed in order to extract useful information which can be used for a multitude of purposes and applications including meteorology, climate change monitoring, environmental protection, precision agriculture, forestry and urban area monitoring, scientific research, local and regional planning, as well as civil protection through real-time natural disaster and wildfire monitoring [43]. Furthermore, the acquisition of Earth observation data has been of extreme importance for military intelligence applications since the dawn of the space age.
The present section is divided into two subsections. The first one covers the role of CubeSats in the field of traditional Earth remote sensing applications, with satellite missions dedicated to Earth imaging, atmospheric condition, and weather monitoring being discussed, while the second subsection is dedicated towards Earth science missions, a subcategory of Earth observation missions which are dedicated to the scientific study of the Earth as a system and the understanding of its processes and dynamics.
3.1. The Role of CubeSats in Earth Observation Missions
In general, the main sensory instruments that are utilized by all Earth observation satellites, regardless of size, can be classified into two main categories, optical sensors and microwave sensors. Optical sensors may include instruments operating in the visible (VIS) and/or infrared (IR) spectra or Light Detection And Ranging (LIDAR) equipment. Microwave sensors of Earth observation satellites, on the other hand, may include Synthetic Aperture Radars (SAR) and microwave radiometers [44]. Furthermore, Global Navigation Satellite System antennas and receivers can be utilized to collect information for the Earth’s surface, as well as its atmosphere [45]. In recent years, the miniaturization of electronics and remote sensing equipment has enabled the development of miniaturized versions of most of the aforementioned sensory instruments, which are now capable of fitting inside the limited volume that is available to CubeSat platforms and has thus allowed CubeSats to undertake an important and increasing role in Earth observation missions, supplementing the traditional large Earth observation platforms.
For Earth observation missions, the limited size and power generation capacity offered by CubeSat platforms presents a considerable hurdle that limits CubeSats to the utilization of mostly passive imaging instruments. More specifically, some of the most common sensory instruments found in Earth observation CubeSat missions include optical imagers and spectrometers operating in the visible, Near-Infrared (NIR), Short-Wave Infrared (SWIR), Medium-Wave Infrared (MWIR), Long-Wave Infrared (LWIR) or Far-Infrared (FIR) spectral bands. Imaging instruments operating in the visible and NIR spectra are commonly utilized in missions intended to capture photographs of the planet’s surface, reconnaissance applications, or for the identification of chemical compounds. Imagers and spectrometers operating in the longer-wavelength IR spectra, on the other hand (MWIR, LWIR, and FIR) are utilized in missions involving thermal energy emission monitoring, land, sea or atmospheric temperature mapping, night imaging, wildfire and volatile compound monitoring, as well as for mineral characterization. It must also be noted that multispectral and hyperspectral variants of imaging instruments such as cameras and spectrometers which simultaneously collect information from a large number of distinct spectral bands of the electromagnetic spectrum are also commonly found on Earth observation CubeSat missions. Such instruments are used in missions involving material, chemical pollutant, chlorophyll and microorganism detection, as well as volatile compound and moisture monitoring among others. Another type of instrument commonly found onboard Earth observation CubeSats are radiometers. Radiometers commonly operate in the IR and microwave regions of the electromagnetic spectrum and are used to perform atmosphere-related measurements such as temperature measurements, water vapor content and precipitation monitoring, as well as for the identification and monitoring of greenhouse gases. Furthermore, other types of passive microwave sensors such as scatterometers, altimeters, and Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) receivers are also commonly utilized by CubeSat platforms to collect reflected or occulted GNSS signals for missions that involve terrain mapping, altimetry, and atmospheric condition monitoring. Finally, some limited efforts to incorporate active microwave sensors, such as imaging microwave radars, on Earth observation CubeSat platforms are also underway [46,47]. Table 3 presents some commonly recognized wavelength boundaries among the distinct regions covered by the visible, IR bands, and microwave bands of the electromagnetic spectrum.

Table 3.
A comparison among the wavelength boundaries of the distinct regions of the visible, Infrared (IR), and microwave bands of the electromagnetic spectrum.
The high interest for the development of Earth observation CubeSat missions involving optical instruments over the years has facilitated the development of a multitude of COTS imaging solutions which are tailor-made for CubeSat missions. Among notable examples of COTS imaging solutions for the visible and NIR regions of the electromagnetic spectrum that are available as of 2025 are the Simera Sense (Leuven, Belgium) xScape50, xScape100, and xScape200 series of optical imagers which can provide a Ground Sampling Distance (GSD) of 30 m, 4.75 m, and 1.5 m, respectively, at an altitude of 500 km. These imagers are available in Red-Blue-Green (RGB), multispectral, and hyperspectral variants [48]. Other well-known COTS RGB, multispectral, and hyperspectral imaging solutions with considerable flight heritage for the visible and NIR spectrums include Dragonfly Aerospace’s (Stellenbosch, South Africa) Gecko, Mantis, Chameleon, Caiman, and Komodo, high performance camera systems which can each offer a GSD of 39 m, 16 m, 10 m, 3.25 m, and 1.5 m, respectively, at the same altitude of 500 km [49]. Furthermore, Dragonfly Aerospace also offers a version of the Chameleon imager which is capable of operating in the SWIR spectrum, offering a resolution of four spectral bands between 1000 nm and 1750 nm wavelengths and providing an 8.7 m GSD and an 11.2 km swath from a 500 km altitude [50]. Another example of an optical imaging sensor developed for CubeSat use is the SATLANTIS (Leioa-BILBAO, Spain) iSIM-90, a large high-resolution imaging instrument designed to be integrated with 12U and 16U CubeSat platforms. The iSIM90 is capable of operating in both visible, NIR, and SWIR spectral ranges simultaneously, providing a GSD of 2 m for visible and NIR wavelengths and a GSD of 5 m for SWIR from an altitude of 500 km [51]. Furthermore, Earth observation CubeSats can also be equipped with COTS IR spectrometers such as the Thothx (Deep River, ON, Canada) Argus 2000, which are capable of operating in the NIR and SWIR spectra, which can be utilized for Earth observation missions that include the study of atmospheric composition [52]. Apart from the use of COTS sensors, it is common for many Earth observation CubeSat missions to feature custom-made or in-house developed imagers and spectrometers as payload.
A notable recent Earth observation CubeSat mission combining Visible and Near-Infrared (VNIR) multispectral imaging and NIR spectrometry is FACSAT-2, which involves the launch of a 6U CubeSat platform that was co-developed by the Colombian Air Force and GomSpace. FACSAT-2 was tasked with the mission of performing multispectral imaging duties over the Colombian territory as well as obtaining data regarding greenhouse gas (such as CO2 and CH4) emissions. As its payload, FACSAT-2 was equipped with COTS optical instruments, namely the MultiScape100 (Simera Sense Europe BV, Leuven, Belgium) imager and the Argus 2000 (Thoth Technology Inc, Deep River, ON, Canada) spectrometer [53]. An example of a similar mission was the SATHYABAMASAT, a 2U CubeSat that was developed by Sathyabama University and ISRO under the mission of collecting data on the concentration and density of greenhouse gases such as water vapor and hydrogen fluoride CO2 and CH4, utilizing the Argus 1000 (Thoth Technology Inc, Deep River, ON, Canada) IR spectrometer as its mission-enabling payload [54,55]. Another similar example is the OrbiCraft-Zorkiy, a 6U Earth remote sensing spacecraft developed by the Russian company SPUTNIX LLC. For its mission, OrbiCraft-Zorkiy was equipped with a high-resolution imaging sensor capable of acquiring image data with a resolution of up to 6.6 m per pixel from LEO while the satellite was also equipped with two wide-angle cameras that were utilized for the purpose of visual observation and control of spacecraft’s systems. The primary goal of the mission revolved around the in-orbit demonstration and validation of the satellite’s primary imaging payload, as well as for a variety of its bus subsystems and a newly developed launch canister [56,57]. Notable examples of more capable Earth observation CubeSat platforms also developed by SPUTNIX LLC are the Zorkiy-2M series of 12U CubeSats. Each of the Zorkiy-2M CubeSats is equipped with an optical instrument capable of acquiring images with a resolution of approximately 2.75 m per pixel and a maximum swath of 14 km from orbital altitudes between 500 km and 600 km, which can operate at four spectral ranges, namely, red, green, blue, and NIR. Furthermore, along with their primary Earth observation payload, the Zorkiy-2M satellites are also equipped with an Automatic Identification System (AIS) which is used to provide naval vessels with safety-of-navigation services along the Northern Sea routes [58,59].
Another example of a recent optical-imaging Earth observation CubeSat mission is HORACIO, a 16U satellite manufactured by NanoAvionics which is equipped with the SATLANTIS (Leioa-BILBAO, Spain) iSIM-90 high resolution imager as its main payload, under the mission of acquiring Earth observation data that will be utilized for applications including coastal monitoring, border security, methane emissions quantification, infrastructure monitoring, and agriculture. HORACIO’s imaging payload enables simultaneous image acquisition in visible, NIR, as well as SWIR spectral ranges, with four bands dedicated towards the visible spectrum and six towards NIR and SWIR spectra. The satellite was placed in a Sun-synchronous orbit with an altitude between 520 km and 590 km. From there, it is expected to provide images with the best possible resolution of 2 m and a swath of 14 km [60]. One more example of a contemporary Earth observation mission involving CubeSat platforms in the imaging role is the case of the Advanced Nanosatellites Systems for Earth Observation Research (ANSER) which is overseen by the Spanish Institute of Aerospace Technology (INTA). This constellation comprises three 3U CubeSats which are equipped with Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor (CMOS) imaging photometers and are connected via inter-satellite communication links. These CubeSats fly in formation using fuel-free, aerodynamic orbital maneuvering techniques and are utilized for monitoring the water quality in reservoirs and swamps in the regions of Spain and Portugal by identifying the presence of chemical pollutants and microorganisms such as phytoplankton or algal blooms within the water [61,62,63].
Another example of an ongoing Earth observation CubeSat mission is the Repeater Arrangement & Disaster Early View (RANDEV) 3U CubeSat, which is developed and operated by the Aerospace Systems and Control Laboratory of the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology. This CubeSat is capable of capturing images with wavelengths between 350 nm and 900 nm (VNIR spectrum), supporting 58 individual spectral bands. The main mission of RANDEV is the observation of volcanoes, coastal areas, and cloud cover, and the extraction of data that would be used to identify potential hazards [64]. An example of a similar mission was the Forest Observation and Recognition Experimental Smallsat Thermal Detector-1 (FOREST-1), a 6U CubeSat created by the collaborative efforts of Spire Global, Inc. and OroraTech GmbH (Munich, Germany) which was equipped with the SAFIRE Gen-1 (OroraTech GmbH, Munich, Germany), a TIR sensory instrument capable of operating in both MWIR and LWIR spectral bands, providing a GSD of 250 m and a swath of 160 km. The SAFIRE Gen-1 sensor also incorporates an RGB camera. The main mission of FOREST-1 was to demonstrate the capability of wildfire detection and monitoring using its payload. Furthermore, using its payload, FOREST-1 was also capable of monitoring ground, sea surface, and urban area temperature distributions. The success of the FOREST-1 mission led to the development of FOREST-2, another 6U CubeSat by Spire, now equipped with OroraTech’s more capable SAFIRE Gen-2 TIR sensory instrument, which comprises two TIR cameras and an RGB camera. Compared to SAFIRE Gen-1, it features an improved detector offering three times more pixels and is capable of providing 200 m GSD and a 160 km swath; furthermore, it provides data in one MWIR and two separate LWIR bands [65,66,67,68].
An example of an upcoming Earth observation mission is the Field Imaging Nanosatellite for Crop residue Hyperspectral mapping (FINCH). FINCH is a 3U SWIR imaging CubeSat under development by the University of Toronto, which is going to undertake the mission of measuring CH4 column concentrations over landfills by using the atmospheric absorption features present between 1600 nm and 1680 nm wavelengths. For this mission, FINCH is going to be equipped with a custom-made hyperspectral spectrometer operating in the SWIR spectrum, called the FINCH Eye, as its main payload. The data collected by FINCH could help in the improvement of crop residue retention practices and the reduction in greenhouse gas emissions from the crop soil, thus aiding in precision agriculture operations [69]. Another example of an upcoming Earth observation mission is VULCAIN, a mission that will consist of two 12U CubeSats developed under the supervision of ESA by Politecnico di Milano and five more Italian space science and engineering entities. Their mission will primarily revolve around the performance of IR observations in volcanic areas to detect surface temperature changes due to volcanic activity and the Measurement of SO2 and ash emissions from active volcanoes in an effort to detect anomalies that could indicate changes in activity such as upcoming volcanic eruptions. For this mission, the two VULCAIN CubeSats will be equipped with a custom designed and built TIR imaging instrument developed by LEONARDO S.p.A. (Rome, Italy) and a COTS VNIR camera developed by Dragonfly Aerospace (Stellenbosch, South Africa). The two CubeSats are expected to orbit the Earth at a 400 km Sun-synchronous orbit, maintaining an along-track formation with a separation distance of 300 km using low-thrust electric propulsion [70,71].
So far, that present work has been limited in discussing examples of CubeSat missions comprising of single platforms or CubeSat constellation examples that are so far comprise only a few satellites. However, it must be noted that due to their low cost and their ability to manufacture, integrate, and launch fast and in large numbers, CubeSats represent excellent platforms for the formation of large Earth observation constellations that ensure short revisit times and continuous data flow. Such constellations are extremely useful for both civilian and military applications by providing institutions and other potential customers with continuous image data from the surface of the Earth, enabling near-real time monitoring of the planet’s surface and/or its weather conditions. This way, organizations, industries, governments, and militaries around the world can make timely, well-informed decisions.
Perhaps the most prominent and well-known example among existing and proposed commercial optical-imaging Earth observation CubeSat constellations is the Flock constellation, which comprises SuperDove CubeSats that are developed and operated by Planet Labs PBC (San Francisco, CA, USA). The 3U SuperDove CubeSats orbit the Earth at altitudes between 400 km and 550 km and are equipped with an eight-spectral-band VNIR imaging sensor each, providing optical imagery with resolutions between 3 m and 5 m, depending on the satellite’s orbital altitude. Since its establishment in 2010, Planet Labs has launched more than 500 imaging satellites into orbit (mainly CubeSats), making it the largest commercial Earth observation satellite operator in the world. The constellation of SuperDove CubeSats currently numbers around 200 operational satellites in orbit around the Earth [72,73,74]. Furthermore, the success of the FOREST-1 and FOREST-2 missions has facilitated the development of FOREST-3, an advanced 8U CubeSat featuring improvements over its two predecessors which was launched on 14 January 2025 [75], as well as an upcoming TIR imaging constellation of CubeSat platforms by OroraTech GmbH which will be tasked with the all-important mission of wildfire detection and monitoring. When complete, this constellation is expected to encompass approximately 100 satellites and offer a 30-min revisit time over an area of interest [76,77,78].
Another imaging method, which satellites and CubeSats, specifically, can utilize in the Earth observation role, is the mapping of the Earth’s surface through Global Navigation Satellite System Reflectometry (GNSS-R). The basic concept of GNSS-R (see Figure 6) is that a satellite equipped with a GNSS receiver will receive multiple versions of the signal coming from a GNSS satellite in Medium Earth Orbit (MEO). More specifically, it will receive the direct GNSS signal, as well as a multitude of signals reflected by the surface of the Earth, with the reflected GNSS signals being affected by parameters such as ground geometry, terrain roughness, moisture, etc. Thus, by using specifically designed GNSS antennas and receivers which are acting as passive bi-static radar systems, a satellite can receive these reflected GNSS signals from satellite navigation constellations such as the Global Positioning System (GPS), Galileo, and GLONASS and synthesize a picture of the planet’s surface after comparing them with the direct ones. One of the most common applications of the GNSS-R technique is altimetry, where satellites are used to measure terrain altitude, ocean levels, and sea state [45]. The passive nature of GNSS-R technology makes it suitable for utilization by CubeSat platforms, with a notable example of a GNSS-R CubeSat mission being 3Cat-2, a 6U CubeSat with the mission of demonstrating GNSS-R technologies for ice altimetry, ocean sea state monitoring, soil moisture monitoring, as well as for the observation of biomass. As its main payload, 3Cat-2 was equipped with the P(Y) & C/A ReflectOmeter (PYCARO), an instrument specifically designed to receive and compare direct and reflected GNSS signals [79]. Another similar mission was the Passive REflecTomeTrY (PRETTY), a 3U CubeSat developed by ESA for the demonstration of a GNSS-R payload capable of providing ice and sea-ice altimetry measurements with an accuracy of 0.5 m for the study of the polar regions of the Earth [80].
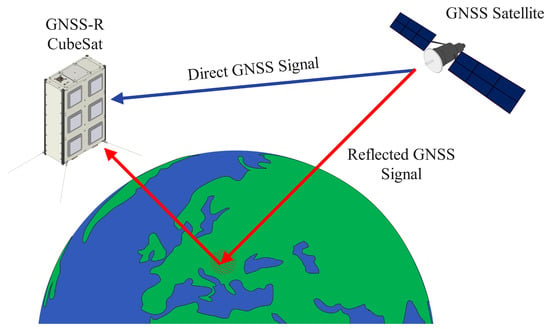
Figure 6.
A simplified illustration of the basic operating principle of Global Navigation Satellite System Reflectometry (GNSS-R) for terrain mapping and altimetry.
One of the most common Earth remote sensing application subfields for CubeSat platforms is that of atmospheric condition and weather monitoring. Satellites employed in this science field collect measurements that can help in the generation of more accurate atmospheric models and, in this way, enable more accurate and precise weather forecasting. Furthermore, apart from only being used for monitoring the conditions present at the lower levels of the atmosphere, CubeSats can also be used for the monitoring of the Earth’s ionosphere, collecting important scientific data that can be used to inform decisions and operations on space science and engineering fields such as telecommunications, the operation of satellite navigation systems, satellite functions, and efficient operation, as well as in a variety of Earth-based industrial applications such as the management and operation of electrical power networks and natural gas pipelines. Moreover, the conditions of the ionosphere can be linked, to some degree, with the conditions of the atmosphere’s lower portions. Therefore, ionospheric measurements can provide even more information on the dynamics of the Earth’s atmosphere as a whole. Therefore, over the years, a variety of CubeSat missions have been dedicated to the study of the ionosphere with some examples being the Radio Aurora Explorer (RAX) [81], the Dynamic Ionosphere CubeSat Experiment (DICE) [82], the Triplet Ionospheric Observatory-CubeSat for Ion, Neutral, Electron and MAgnetic Fields (TRIO-CINEMA) [83], and the Scintillation Observations and Response of the Ionosphere to Electrodynamics (SORTIE) [84], among a variety of others. To perform their missions, these ionospheric research CubeSats can be equipped with a multitude of different instruments such as Langmuir probes, Retarding Potential Analyzers (RPAs), Ion Drift Meters (IDMs), magnetometers, and radio occultation receivers [85].
Perhaps the most widespread method used by CubeSats in the field of atmospheric monitoring is that of Global Navigation Satellite System Radio Occultation (GNSS-RO). The basic operational principle of this technique is that as the signal emitted by the GNSS satellites travels through the Earth’s atmosphere and ionosphere, it is refracted as presented in the simplified illustration of Figure 7. The magnitude of the GNSS signal refraction depends on parameters such as the atmospheric temperature, pressure, water vapor content, and electron density. This way, a CubeSat (or any other satellite) in LEO that is equipped with specifically designed GNSS receiving elements can use the signals it is receiving from satellites belonging to GNSS constellations, such as GPS or Galileo, in order to collect data about the state of the atmosphere and ionosphere from various altitudes. This data can be subsequently used for weather-related applications, enabling near-real time weather monitoring and improving prediction capabilities, as well as for ionosphere condition monitoring [86,87].
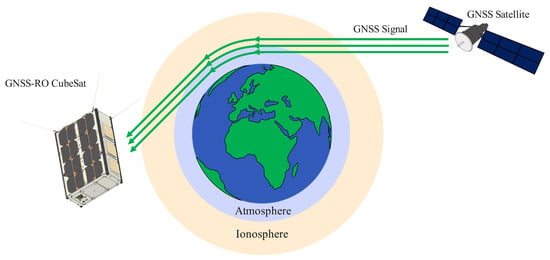
Figure 7.
A simplified illustration of the Global Navigation Satellite System Radio Occultation (GNSS-RO) concept.
The most prominent example of GNSS-RO weather monitoring CubeSats are the Low Earth Multi-Use Receiver (LEMUR) platforms, which are developed and operated by Spire Global, Inc. (Vienna, VA, USA). These satellites form the cornerstone of a LEO constellation of more than 100 CubeSats, operating in orbits with altitudes between 400 km and 650 km. The vast majority of LEMUR CubeSat platforms have a 3U form factor and their main payload comprises an in-house developed GNSS receiver which is connected to large, side mounted GNSS antennas which are used to receive the occulted GNSS signals. Furthermore, apart from monitoring atmospheric conditions via GNSS-RO, the LEMUR platforms are also equipped with AIS receivers for the monitoring of maritime traffic and Automatic Dependent Surveillance–Broadcast (ADS-B) for aircraft tracking [88,89,90]. Regarding the GNSS-RO ionosphere monitoring data provided by the LEMUR platforms, it must be noted that a comparative study [91] between the Spire constellation and ground-based ionosphere monitoring systems such as the Global Ionospheric Radio Observatory (GIRO) and Arecibo Incoherent Scatter Radar (ISR) found a good correlation in the data generated by the different systems. Furthermore, it is noted in the same study that Spire constellation’s global coverage and its direct access to the top side of the ionosphere represent significant advantages compared to ground-based systems. Another example of a GNSS-RO weather monitoring CubeSat constellation is the Community Initiative for Continuous Earth Remote Observation (CICERO), which comprises 6U CubeSats and is operated by GeoOptics, Inc. (Pasadena, CA, USA), with these satellites also being utilized in the mission of remote sensing via GNSS-R. It is important to note that the CICERO satellites were initially envisioned as microsatellites with a mass of more than 100 kg each; however, technological leaps in GNSS-RO hardware miniaturization eventually allowed the project’s satellites to acquire the more compact 6U CubeSat form [92,93,94].
Apart from the GNSS-RO technique, there are also other methods via which CubeSats are employed in the atmospheric and weather monitoring and research fields, such as radiometry. More specifically, CubeSats equipped with radiometers can be used to measure the electromagnetic radiation that is emitted, reflected, or scattered by the Earth’s surface and/or its atmosphere by operating across visible, IR, and microwave spectral bands. Most notably, microwave radiometers can be used to penetrate clouds in order to measure water vapor and precipitation (rain, snow, or hail). IR radiometers, on the other hand, provide information regarding temperature and humidity by detecting thermal radiation at varying altitudes. Finally, radiometers may also be used to monitor sea surface temperatures, soil moisture, and other variables that are known to influence weather patterns and extreme events like hurricanes and droughts. This way, satellites equipped with radiometers can provide global, real-time atmospheric and weather condition data [95,96]. In that regard, an important mission was the Temporal Experiment for Storms and Tropical Systems Technology–Demonstration (TEMPEST-D) which involved the launch of a 6U CubeSat developed by NASA’s JPL, Colorado State University, and Blue Canyon Technologies (Lafayette, CO, USA). TEMPEST-D was equipped with a millimeter-wave radiometer NASA that was capable of performing continuous measurements between 89 GHz and 165 GHz frequencies. Its mission was to demonstrate it’s payload’s capabilities in observing the time-evolution of clouds and studying the conditions that govern the transition of clouds from the non-precipitating to the precipitating state. The satellite was deployed from the ISS on 13 July 2018 and remained operational for a period of 3 years, until its eventual reentry, having successfully demonstrated the efficacy of its payload for the observation of cloud and precipitation processes [97,98].
The success of TEMPEST-D paved the way for more missions in that field of atmospheric monitoring via microwave radiometry, such as NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS). The TROPICS constellation comprises four 3U CubeSats under the mission of observing tropical systems and collecting data regarding temperature, moisture, cloud-ice, and precipitation. The data collected by the TROPICS constellation will thus help scientists to monitor, study, and better understand the dynamic phenomena and processes of tropical storms. To perform their mission, the TROPICS CubeSats, which were designed and developed through the collaborative efforts of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) Lincoln Laboratory and Blue Canyon Technologies, are equipped with a rotating, 12-channel passive microwave radiometer. This radiometer is capable of providing imagery between 90 GHz and 206 GHz, with the frequencies between 90 GHz and 118 GHz being used for temperature measurements and the frequencies between 183 GHz and 206 GHz being allocated to the performance of moisture measurements. For temperature measurements, the radiometer’s average spatial resolution is approximately 40 km and for moisture measurements, 25 km. The data collected by the TROPICS constellation is made publicly available by NASA [12,99]. Another notable NASA CubeSat mission that involved radiometry for atmospheric research was IceCube. IceCube was a 3U CubeSat equipped with a 883 GHz radiometer that was tasked with the mission of studying cloud-ice formation, a phenomenon that has great effect on the Earth’s climate. It was capable of measuring critical atmospheric cloud ice properties at altitudes between 5 km and 15 km. IceCube was deployed from the ISS on 16 May 2017 and during its operation, provided the world’s first global map regarding the distribution of atmospheric ice [100].
As of 2025, other novel atmospheric/weather monitoring technologies are also in the process of being incorporated into CubeSat platforms, with one notable upcoming atmospheric monitoring and research CubeSat mission being CloudCT. The main objective of this mission is to perform cloud tomography, revealing their external as well as internal 3D structures using equipment and techniques inspired by medical Computed Tomography (CT), and in this way, supplement existing remote sensing technologies and infrastructure used in the field of atmospheric modeling and climate prediction. More specifically, the satellites of the CloudCT constellation will be equipped with multi-spectral, polarized cameras that will be used to detect and measure the backscattered sunlight from a cloud of interest from different angles simultaneously. The data collected by the constellation will then be transmitted to Earth where they will be post-processed using computed tomography methodologies to characterize the cloud and reveal its internal structure. Initially, one precursor 3U satellite will be placed in orbit to test and demonstrate the mission concept. Should this precursor satellite successfully demonstrate its capabilities, the launch of a constellation of ten more 3U CubeSats is expected to follow. These ten CubeSats will fly in the same orbit, following each other in an Along-Track Formation (ATF) with a separation distance of 100 km between each two satellites, thus being able to simultaneously observe the target clouds from different angles. The ten CubeSats will fly in ATF using technologies that were successfully demonstrated by the NetSat mission, which was launched in 2020 [101,102].
Traditionally, Earth observation CubeSats have relied on passive sensors as their mission payloads. As mentioned before, this can mainly be attributed to the low electrical power generation capacity which stems from their small size, as there is less area available for the installation of solar cells. However, in recent years, several attempts for the incorporation of active sensors by CubeSats in the form of radars have been undertaken, with a notable example being the Radar in a CubeSat (RaInCube) mission, a 6U CubeSat developed by NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) and Tyvak Nano-Satellite Systems Inc. (Irvine, CA, USA) under the mission of demonstrating the concept of rain precipitation measurements via radar. For this reason, RaInCube was equipped with a 0.5 m deployable Ka-band parabolic antenna which is presented in Figure 8 [103]. When stowed, the antenna would be able to fit inside a 1.5U volume. Furthermore, certain attempts at the integration of SAR arrays in CubeSat platforms have also been underway in recent years. SAR arrays emit microwave energy and capture the reflected backscatter to synthesize a picture of the target. Compared to optical imaging, SAR imaging offers certain advantages. The most notable of these advantages is SAR’s ability to operate effectively regardless of light and weather conditions due to the long wavelength of microwave radiation. However, it should be noted that SAR imaging does not match the spectral and spatial information that is provided by optical imaging payloads [104,105].
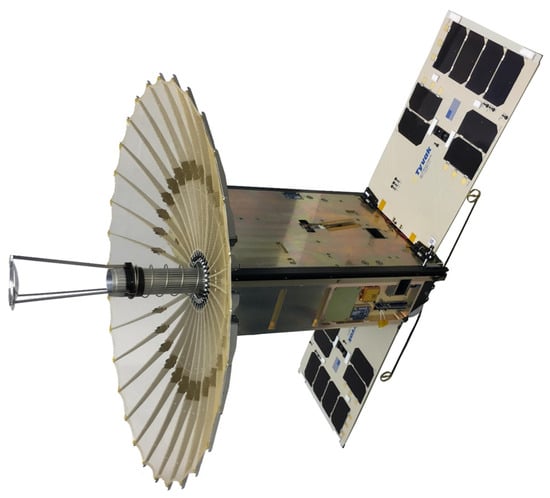
Figure 8.
An illustration of the Radar in a CubeSat (RaInCube) satellite with its parabolic radar antenna and solar panels in deployed configuration. Photo by NASA/Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL)-Caltech [106].
Regarding the efforts for the integration of SAR imaging instruments on CubeSat platforms, the Italian space agency has selected and funded the development of the SATURN program which is developed by OHB Italia S.p.A. (Milan, Italy). SATURN aims to deliver an initial demonstrative swarm of three 16U CubeSats equipped with a miniaturized SAR instrument which is developed by ARESYS S.r.l. (Vimodrone-Milan, Italy) and Airbus Italia S.p.A. (Rome, Italy). The SAR arrays of the SATURN CubeSats will operate in Multiple-Input-Multiple-Output (MIMO) mode (where all satellites will both transmit and receive signals) and are expected to deliver imagery with a 5 m resolution and a swath of 30 km. If the initial three-satellite swarm proves successful, a larger constellation comprising of 16 swarms of three satellites, distributed in four different orbits will follow. Furthermore, the SAR payloads developed for this demonstration mission may become the first commercially available SAR solutions for CubeSat applications. SATURN completed its preliminary design review in April 2024 with developmental work on the mission still continuing as of May 2025 [107,108,109]. Another relevant example can be traced on the other side of the Atlantic where SRI International, with the CubeSat Imaging Radar for Earth Science (CIRES) program, aims to deliver a 16U CubeSat equipped with a miniaturized deployable SAR payload in the form of a 5 deployable membrane. This SAR payload is also expected to provide a spatial resolution of 5 m and is designed for Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (InSAR) operations in orbits with 500 km altitude [110]. One more example is the Zhixing-3 A Spacecraft, a 6U CubeSat that was developed by Beijing Smart Satellite Space Technology Co., Ltd. (Beijing, China). It was launched on 5 September 2022 and was deployed into orbit 188 days later from the Tianzhou-4 spacecraft. Its mission was to test and validate a series of technologies vital for the company’s upcoming SAR imaging microsatellite constellation such as platform design, energy balance, operations, communication, attitude control, something that it successfully performed before eventually deorbiting [111,112].
3.2. The Role of CubeSats in Earth Science Missions
Apart from traditional Earth observation applications such as terrain imaging and atmospheric condition monitoring, CubeSats can also serve as platforms that enable researchers to conduct advanced Earth-related scientific measurements and experiments. In that regard, a standout example is the QB50 project which was coordinated by the von Karman Institute for Fluid Dynamics. QB50 culminated in the creation of an international network of fifty 2U and 3U CubeSats for the study via in situ measurements, of the, until then, least explored layer of the Earth’s atmosphere, the middle and lower thermosphere. For this mission, some of the program’s satellites utilized equipment such as Ion and Neutral Mass Spectrometers (INMS) that could read the composition of the thermosphere by detecting and measuring heavy particles such as O, O2, NO and N2. Moreover, for the study of the electron temperature in the thermosphere, multi–Needle Langmuir Probes (mNLP), which are able to probe the electron density were used in some of the CubeSats. Finally, the rest of the QB50 CubeSats measured atomic and molecular partial pressures through the use of Flux Probe EXperiment (FIPEX) which comprises separate solid electrolyte sensors [113,114,115]. Another example of an Earth science CubeSat mission is the Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-Infrared Experiment (PREFIRE), comprising two 6U CubeSats in near-polar orbits that were developed jointly by NASA and the University of Wisconsin-Madison. The two PREFIRE CubeSats are equipped with a Thermal Infrared Spectrometer (TIRS), which is used to measure the amount of energy that is emitted by the Arctic and Antarctic regions of the planet towards space in the form of FIR radiation. One of the primary goals of the PREFIRE mission is to determine the amount of thermal energy that is radiated by the snow and ice covering the Earth’s polar regions in the FIR spectrum and how this emitted energy fluctuates around the year. Furthermore, the CubeSats are also tasked with studying the polar greenhouse effect by measuring the amount of FIR thermal energy that is trapped by the cloud cover and atmospheric water vapor content of the polar regions. This data can then be used to create improved climate and ice-cover-evolution models for the two polar regions of the planet [116,117].
A notable upcoming Earth science CubeSat mission is the PREcursory electric fieLd observation CUbeSat DEmonstrator (PRELUDE), a mission involving the launch of a 6U CubeSat which is developed jointly by Nihon University, Shizuoka Prefectural University, and the University of Shizuoka under the mission of detecting local ionospheric fluctuations that indicate the upcoming occurrence of an earthquake, and in this way, aid in the prediction of upcoming earthquakes some hours in advance, offering short-term prediction and disaster mitigation capabilities. To perform its mission, the satellite will be equipped with two hybrid Very Low Frequency (VLF) sensory probes used for electric field and plasma field measurements, each in the free point of a 1.5 m extendable boom and a GNSS receiver which is going to be utilized for the monitoring of the ionosphere’s electron density [118,119]. PRELUDE is not the first CubeSat mission in this field, with past examples of CubeSat platforms which were also tasked with the mission of demonstrating the concept of earthquake prediction through the detection of disturbances in the ionosphere including QuakeSat-1 [120,121] and APSS-1 [122].
An example of a notable recently launched Earth science CubeSat mission is Electrojet Zeeman Imaging Explorer (EZIE). EZIE comprises three 6U CubeSats that were developed by the Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) of the Johns Hopkins University. The primary mission of these three satellites will be to study the formation and behavior of auroral electrojets, testing how the proposed scientific models correspond to reality and thus provide a better insight into the physics of the Earth’s magnetosphere. This way, the date collected by EZIE are expected to enable the proposition of more accurate models regarding auroras and geomagnetic storms from the scientific community. To perform their mission, the three CubeSats are equipped with the Microwave Electrojet Magnetogram (MEM) instrument. The core components of the MEM payload are four integrated 118 GHz heterodyne spectropolarimeters that will be used to detect the microwave radiation that is emitted by oxygen molecules during Zeeman splitting, which has a frequency of 118 GHz. The three EZIE CubeSats were successfully launched on 15 March 2025 onboard SpaceX’s Transporter-13 mission and are reported to operate nominally. In Figure 9, an artistic illustration of the operation of the three EZIE CubeSats is presented [123,124,125,126].
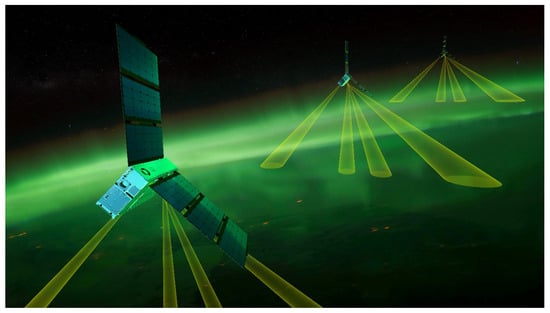
Figure 9.
An illustration of the three CubeSats of the Electrojet Zeeman Imaging Explorer (EZIE) mission during their operation. Illustration by NASA/Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory (APL)/Steve Gribben [127].
In general, it is widely accepted that Earth observation and science CubeSats, in order to perform their mission, must be orbiting the Earth and in most cases find themselves in LEO. This is reasonable, as the close proximity to the Earth correlates with greater data acquisition prospects, especially for imaging instruments, as well as with higher data transfer rates towards mission control. However, as shown by the EQUilibriUm Lunar-Earth point 6U Spacecraft (EQUULEUS), this may not always be the case, as important Earth science missions can also be performed from beyond Earth orbit. EQUULEUS was a 6U CubeSat jointly developed by the university of Tokyo and JAXA; it was launched on 16 November 2022 as a secondary payload of the Artemis I mission. The satellite demonstrated a series of trajectory control techniques, low-thrust maneuvers, orbit changes, and eventually placed itself in an orbit around the Earth–Moon L2 Lagrange point. From there, the CubeSat began the observation and mapping of the plasmasphere that surrounds the Earth by using its PHOENIX (Plasmaspheric Helium ion Observation by Enhanced New Imager in eXtreme ultraviolet) UV imager. The data collected by PHOENIX will further the scientific community’s understanding of the radiation environment around our planet and help us better prepare for future deep-space exploration missions. It should be noted that, apart from its main Earth science mission, EQUULEUS also took advantage of its position in the cislunar space to also perform lunar and asteroid exploration tasks. One of these tasks was the observation of lunar surface meteoroid impact flashes and near-Earth asteroids using the DEtection camera for Lunar impact PHenomena IN 6U Spacecraft (DELPHINUS), which was also part of its payload. Furthermore, EQUULEUS was also equipped with Cis-Lunar Object detector within THermal insulation (CLOTH), by which it would measure the size and spatial distribution of dust and solid objects such as micro-meteoroids in the cislunar space around the Earth–Moon L2 point, data that can form the basis for risk assessments for future lunar missions [128,129].
4. The Use of CubeSats as Telecommunication and Asset- Monitoring Platforms
A significant portion of the CubeSats that are currently orbiting the Earth serve the mission of enabling and facilitating communication services and applications or demonstrating state-of-the-art communication technologies. Originally, CubeSat platforms were only used for the demonstration of communication technologies and their adoption for the provision of commercial communication services was hampered by the low downlink-bandwidth that stems from the small size of antennas and electronics that can fit inside the CubeSat volume. However, the hardware developed for said technology demonstration missions and the subsequent miniaturization of telecommunications electronics and antennas that provide adequate downlink data-rates, along with the emergence and adoption of laser-optical communication technologies, have enabled CubeSats to undertake significant roles in global non-terrestrial communication. Moreover, with humanity’s increasing need for even greater data transfer capacity and with the number of proposed or under development constellations of communication CubeSats rising, the number of communications-related CubeSats in orbit is expected to increase significantly in the following years.
Communication CubeSats (and satellites in general), depending on their application and onboard equipment, may transmit in a variety of different areas of the electromagnetic spectrum which can be divided into two principal areas, the radio spectrum ranging from 3 kHz to 300 GHz and the optical spectrum which encompasses the frequencies from 300 GHz up to GHz. The examples of communication CubeSat missions discussed in the present section are primarily divided based on the region of the electromagnetic spectrum their main mission payloads are designed to operate in, namely radio telecommunication CubeSats and optical telecommunication CubeSats.
4.1. Radio Communication CubeSat Technologies
The radio spectrum is usually defined as the part of the electromagnetic spectrum that covers the frequency range between 3 Hz and 300 GHz, with the electromagnetic waves of the radio spectrum being commonly defined as radio waves. Radio waves are used extensively in all telecommunication applications and by extension, in satellite communication since the beginning of space utilization and exploration. Similarly to their larger counterparts, to perform telecommunication operations, CubeSat platforms can be equipped with a variety of telecommunication-enabling systems. In terms of hardware, the most prominent example of these telecommunication systems are antennas, with a variety of different types such as low-gain monopole, dipole, and patch antennas being designed to be compatible in terms of size with the vast majority of CubeSat platforms. Furthermore, more complex and advanced designs such as inflatable and reflectarray medium-gain or high-gain antennas may also be utilized by large and/or highly specialized CubeSat platforms, such as the ones that undertake deep-space exploration missions. These antennas are coupled with transceivers or transponders providing the CubeSats with radio communication capabilities and commonly operate in the Very High Frequency (VHF), Ultra High Frequency (UHF), S-band, or X-band spectrums [130], with Ku-, Ka-, and W-band communications also being possible. In that regard, Figure 10 presents information about the communication frequencies used by past and present CubeSat missions where it is visible that UHF, S-band, and X-band communication frequency ranges represent the most popular choices.
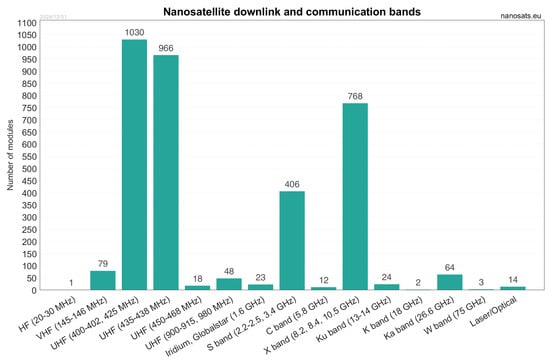
Figure 10.
An overview of the communication frequencies utilized by CubeSat and other nanosatellite platforms as of the beginning of 2025. Data and illustration by Nanosats Database/Erik Kulu [17].
Table 4 presents the designations of radio frequency bands as specified by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) [131]. These radiofrequency bands cover the spectrum that is most commonly used by satellite communication systems. In general, the different communication systems found on satellites, based on their type and application, may operate in different radio frequencies and in a considerable number of cases, a single satellite may be equipped with two or more distinct communication systems that operate in different frequencies, each intended for distinct applications. The same is true for a variety of CubeSats who, despite their small size, may be equipped with an array of different communication systems. More detailed technical information regarding the antenna designs, communication systems, and frequencies utilized by CubeSat platforms can be found in [132].

Table 4.
The radio frequency band designation according to the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) [131].
Over the last 25 years, there have been a considerable number of examples of CubeSat missions that were dedicated to the in-orbit testing and demonstration of various communication hardware such as antennas and transceivers, as well as communication related software and new telecommunication concepts. One prominent example of such a demonstration mission was GomSpace Express-4 (GomX-4) which consisted of two 6U CubeSats, GomX-4A and GomX-4B, that were developed by GomSpace, the Danish Ministry of Defense and ESA. GomX-4A and GomX-4B were tasked with the demonstration of a variety of novel technologies which included multispectral imaging for Earth observation, but most importantly, the satellites successfully demonstrated the operation of hardware and software designed telecommunication applications such as S-band Inter-Satellite Link (ISL) communications, Automatic Identification Systems (AIS), and Automatic Dependent Surveillance-Broadcast (ADS-B) application hardware [133,134]. Another prominent example of a successful telecommunication technology demonstration mission is the Integrated Solar Array and Reflectarray Antenna (ISARA) mission which was jointly developed by NASA’s JPL and the Aerospace Corporation (Chantilly, VA, USA). ISARA involved the launch of a 3U CubeSat equipped with the first ever high-gain reflectarray antenna for a CubeSat platform. This antenna operated in the Ka-band and enabled the satellite in achieving data transmission rates in the order of 100 Mbps. The successful demonstration of ISARA’s reflectarray antenna paved the way for the execution of the first ever interplanetary CubeSat mission, Mars Cube One (MarCO) [135,136]. Moreover, CubeSat platforms have also been utilized in test missions aimed at the evaluation of different radio frequencies for future applications. One such example was the W-Cube mission which utilized a 3U CubeSat that would be used to test the feasibility of using W-band frequencies for space-based telecommunications and collected data that will be used to update the existing atmospheric radio frequency channel propagation models and improve their accuracy past the 40 GHz mark [137].
The advances made through technology and concept demonstration missions such as the aforementioned ones have facilitated the development of miniaturized communication hardware and have eventually led to a series of mature, high Technology Readiness Level (TRL) solutions and the eventual development of relevant commercial products. In the last decade, a variety of CubeSat manufacturing companies including GomSpace [138], ISISPACE [139], Space Inventor (Aalborg, Denmark) [140], NanoAvionics [141], and AAC Clyde Space [142], among multiple others, offer complete solutions with regards to radio communication by providing their customers with various types of transceivers, antennas, and amplifiers specifically designed to be accommodated by CubeSat platforms of various sizes. Furthermore, there are also multiple commercial providers that specialize in the development of space communications hardware for CubeSats and other nanosatellites such as Cubecom (Stellenbosch, South Africa) and Anywaves (Toulouse, France) [143,144]. It should be noted that these examples of radio communication enabling equipment are of course utilized not only by telecommunication CubeSats in the role of their mission-enabling payloads, but practically by all other types of CubeSat also, as a means by which to transmit their mission specific data towards their operators and for telemetry, tracking, and control purposes.
In terms of commercial applications, one of the most prominent examples of the utility of telecommunication CubeSats is for the creation of constellations that will provide global Non-Terrestrial (NT) 5G Internet of Things (IoT) connectivity coverage. Such communication networks operate based on certain mobile telecommunication standards and protocols encompassed by the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP). These types of CubeSat constellations are expected to provide global connectivity services that will complement terrestrial telecommunication networks by providing coverage even to remote areas of the planet such as oceans, deserts, large forests, polar, and near-polar regions, which would otherwise be near-impossible to cover. These connectivity services will then be able to be utilized for a variety of applications which include real-time asset tracking and monitoring for cars, trains, aircraft, ships, etc. In the energy sector, IoT services can be utilized for real-time energy generation and consumption tracking, as well as for equipment and infrastructure health and status monitoring, while also enabling the execution of smart-grid strategies that would lead to optimized electrical energy usage. Furthermore, NT IoT services can greatly improve agriculture practices by enabling the use of distributed sensors that monitor environmental conditions such as temperature, moisture, and soil chemical composition and allow for the maximization of crop output, while at the same time enabling reduced water and other resource usage. Civil protection services can also utilize 5G IoT connectivity for the real-time monitoring of natural disasters and the efficient employment of response measures. Finally, space based IoT services can contribute to the improvement of healthcare services by enabling the continuous operation of a variety of real-time health monitoring sensors such as wearable medical devices and fitness trackers, as well as by enabling the operation of efficient autonomous systems such as Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAV) tasked with the transportation of medical supplies to areas with otherwise limited access [145,146,147,148].
One of the most prominent examples of a commercial 5G IoT CubeSat constellation is the one owned and operated by the Luxembourg based OQ Technology (Leudelange, Luxembourg), which is the first company to ever operate a Narrowband (NB) 5G IoT CubeSat constellation. Initially, OQ Technology utilized the two 6U CubeSats, GOMX-4A and GOMX-4B, which were developed by GomSpace and were already in orbit since 3 February 2018, in order to test and demonstrate data uplink and downlink experiments through their in-space-programmable Software Defined Radio (SDR) in what came to be known as the Tiger-1 mission, which concluded successfully in April 2020 [149]. Following this success, OQ Technology partnered with NanoAvionics and Space Inventor and proceeded with the buildup of its initial fleet of CubeSats through the launch of the Tiger-2, Tiger-4, Tiger-5, Tiger-6, Tiger-7, Tiger-8, and MACSAT 6U CubeSats, as well as the Tiger-3 non-CubeSat nanosatellite. Furthermore, the company also collaborated with the Mohammend Bin Rashid Space Centre (MBRSC) on the development and launch of the PHI-Demo 12U CubeSat [150]. The company’s goal is to develop a worldwide hybrid system which combines both terrestrial and space-based wireless communication systems in order to provide seamless 5G IoT coverage that can be used for a variety of applications. When complete, the constellation is expected to encompass approximately 60 satellites. The satellite platforms utilized by OQ Technology to this day are equipped with both COTS as well as in-house developed communication-enabling hardware and software. These satellites are placed in high-inclination, Sun-synchronous orbits, helping them achieve global coverage [151,152]. In the immediate future, OQ Technology is set to further expand its space-based infrastructure through its involvement in the ERMIS—Hellenic CubeSat Demonstration Mission and the launch of ERMIS-1 and ERMIS-2 6U CubeSats which were developed in collaboration with the National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, the University of Patras, the University of the Aegean, and the National Observatory of Athens [153].
Another prominent example of an IoT CubeSat constellation is that of SpaceBEE CubeSats, which are operated by Swarm Technologies (Mountain View, CA, USA). The SpaceBee platform is a 0.25U CubeSat, making it the smallest two-way IoT communications satellite in the world as of 2025. The main purpose of this constellation is to provide cost effective, low-data-rate IoT connectivity services to mobile sensors even in remote areas of the Earth. The extremely small size of SpaceBEE allows the launch of these satellites en masse for a very low cost, and with the launch of the final swarm of satellites on 12 June 2023, the constellation reached its peak with 150 satellites in orbit. Swarm technologies was acquired by SpaceX in July 2021 and the constellation continued providing commercial services until March 2025 as its role was eventually replaced by SpaceX’s own Starlink Direct-to-Cell constellation [154,155]. One notable example of an upcoming NB 5G IoT CubeSat constellation is the Sateliot_X (Sateliot, Barcelona, Spain) constellation which is planned to encompass at least 108 satellites within the next four years, eventually reaching a total of at least 250 individual satellites and in doing so, provide global 5G IoT service coverage that will complement the existing terrestrial networks. The 5G IoT service offered by the Sateliot_X constellation is expected to be utilized for asset monitoring and data analysis applications in a variety of fields such as railway, aircraft, and maritime transportation, precision agriculture, as well as the oil and energy industries [156,157].
CubeSat platforms may also utilize communications-related equipment to enable asset surveillance applications, with notable examples being marine and air traffic monitoring. The principal advantage of space-based surveillance systems compared to ground-based ones is the ability of the former to provide coverage over remote areas of the planet such as its oceans, deserts, mountains, as well as its polar regions. Marine-traffic monitoring takes place using Automatic Identification System (AIS) receivers and antennas designed to operate in the VHF frequency band (namely at the 156.775 MHz, 156.825 MHz, 161.975 MHz, and 162.025 MHz frequencies) which are used to broadcast information such as a ship’s identity, position, speed, and course to other ships as well as to coastal stations. Air-traffic monitoring, on the other hand, is performed using Automatic Dependent Surveillance-Broadcast (ADS-B) systems which operate at UHF frequencies, namely 978 MHz or 1090 MHz, and are used periodically to transmit data about an aircraft’s identity, intent, position, velocity, and flight altitude towards Air-Traffic-Control and other ADS-B equipped platforms [158,159,160]. As of 2025, a variety of commercial solutions regarding space-based AIS and ADS-B applications are available. Some examples of COTS AIS solutions for CubeSat applications include Alén Space’s AIS receiver payload [161], as well as the Polaris and QubeAIS receivers which are developed by Satlab A/S (Aalborg, Denmark) [162,163]. On the other hand, for ADS-B applications, there are COTS solutions like GomSpace’s NanoCom ANT1090-P compact ADS-B patch antenna [164], Alén Space’s (Vigo, Spain) ADS-B receiver payload [165], and the Satlab A/S Polaris ADS-B receiver [166]. Custom-made and in-house developed solutions have also been utilized historically.
To this day, a variety of completed and ongoing CubeSat missions have been dedicated to AIS and ADS-B applications. An example among the first CubeSat missions dedicated to AIS applications is the Canadian Advanced Nanosatellite eXperiment-6 (CanX-6), a non-standardized 6.5 kg, 200 mm × 200 mm × 200 mm CubeSat developed by the Space Flight Laboratory of the University of Toronto under the mission of demonstrating space-based AIS hardware [167,168,169]. The same non-standard CubeSat architecture was also used in the case of the AISSAT-1 and -2 missions which were managed by the Norwegian Space Centre [170,171]. Other examples of AIS CubeSat missions include AAUSat-3, AAUSat-4, and AAUSat-5 which were developed by Aalborg University [172,173,174,175]. On the other hand, the first CubeSat mission to revolve around ADS-B technologies was the GomSpace Express-1 (GomX-1), a 2U CubeSat jointly developed by GomSpace, DSE Airport Solutions, and Aalborg University which aimed to demonstrate and evaluate Software Defined Radio (SDR) operations aimed at receiving ADS-B signals from commercial aircraft over the oceans [176]. Another example of an ADS-B CubeSat mission is the GomSpace Express-3 (GomX-3), a 3U CubeSat which was developed and operated by GomSpace with the aim of demonstrating precise 3-axis attitude control, high-speed downlink SDR, and improved ADS-B technologies [177]. Examples of CubeSat missions combining both AIS and ADS-B technologies are the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) M2-A and M2-B CubeSats that were jointly developed by the University of New South Wales and the Australian Defense Force (ADF). The two M2 CubeSats were initially launched as a single 12U CubeSat and would later separate into two 2U × 2U × 1.5U individual spacecraft. Their main mission is to demonstrate in-house developed technologies that would eventually offer the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) global AIS and ADS-B tracking capabilities [178,179,180].
Due to their characteristics, CubeSat platforms represent excellent choices for the creation of large-number, cost-effective constellations providing global AIS and ADS-B coverage, with perhaps the most notable example in that field being Spire’s existing constellation of Lemur CubeSat platforms, which in addition to their GNSS-RO mission payloads are also equipped with AIS and ADS-B payloads. The CubeSats of this constellation are placed in a variety of different orbits in order for the constellation to be capable of covering areas such as oceans, polar regions, and other remote areas that would otherwise be near-impossible to cover with ground based systems [181,182]. However, it should be noted that even though CubeSats dedicated to AIS and ADS-B missions are most definitely expected to rise over the following years, performing a variety of important roles in the space segment of such tracking networks, Air-Traffic services require a hardware performance by ADS-B systems that is considerably greater than what CubeSat sized hardware is currently capable of providing, especially in terms of RF signal power, something that poses a significant hurdle in their prospects of taking over the provision of such services from larger satellite platforms [183].
4.2. Optical Communication CubeSat Missions and Applications
Apart from the traditional radio communication technologies, CubeSats in recent years have also begun incorporating laser-optical communication technologies. Optical communication utilizes light as the means of transmitting information over long distances using lasers. Compared to traditional radio communication technologies, laser-optical communications feature several advantages which include the following. First and foremost, due to the higher frequencies of the optical spectrum compared to the radio spectrum, laser-optical communication systems offer the potential for much higher data rates and a better signal/noise ratio in good atmospheric conditions. Thus, for the same data rate, laser-optical communication systems exhibit a considerably smaller size and lower overall power requirements, as well as a greater efficiency compared to radiofrequency-based communication systems. Moreover, since optical communications so far are not subject to international telecommunication regulations, no long-lead licensing authorization activities are needed for signal transmission. Finally, when compared to radiofrequency communication links, laser-optical communication links are considered safer as the narrow laser beam utilized by such systems is much more difficultly detected, intercepted, and exploited by third parties. However, it should be noted that despite their significant array of advantages, laser-optical communications also exhibit certain disadvantages when compared to radio communication technologies. For example, a much higher pointing accuracy is required of the space-platform for the execution of a laser-optical link, which in turn adds cost and complexity to the design and manufacturing of the satellite platform. Furthermore, laser-optical communications are considerably vulnerable to weather-based disruptions such as beam attenuation due to atmospheric absorption and the presence of cloud cover, fog, or rain [184,185].
The first CubeSat mission ever to attempt the realization of an optical communication link was FITSAT-1, a 1U CubeSat developed by the Fukuoka Institute of Technology for JAXA, which was deployed from the ISS on 5 October 2012. Its main mission involved the high-speed transmission of pictures via a 5.8 GHz microwave and the execution of an experimental low-light-level optical communication link with its ground station by using 50 green and 32 red 3 W LEDs by which it transmitted a 1 kHz Morse code signal. During the mission, the team of the Fukuoka Institute of Technology was successful in detecting the light signal transmitted by FITSAT-1 using a telescope equipped with a photo-multiplier. FITSAT-1 remained operational until its atmospheric reentry on 4 July 2013 [186]. Other examples of past laser-optical communication CubeSats include AeroCube-11A and AeroCube-11B, two 3U spacecrafts which were developed by the Aerospace Corporation under the mission of acquiring multispectral image data of the Earth’s surface. The second leg of their mission involved the downlink of the captured images with data-rates reaching 100 Mbps, using an on-board compact laser-optical communication system. The AeroCube-11 CubeSats successfully demonstrated the capability of combining the task of Earth observation with the very-high data transfer rates offered by laser-optical communications technologies inside the limited volume available to a 3U satellite platform [187,188].
Perhaps the most prominent example of a laser-optical communications CubeSat mission that has been completed up until this point is NASA’s Pathfinder Technology Demonstrator 3 (PTD-3) mission, which was launched on 25 May 2022. PTD-3 was a 6U LEO CubeSat developed by Terran Orbital and was equipped with the TeraByte Infrared Delivery (TBIRD) laser-optical communications payload, developed by the MIT Lincoln Laboratory under the mission of demonstrating laser-optical space-to-ground data transfer ratios that would be significantly higher than all other previously demonstrated technologies. During its mission, PTD-3 managed to perform multiple passes where it transmitted more than 1 TB of data in each, and even achieved the transmission of more than 4.8 TB of error-free, space-to-ground data during a pass that lasted approximately 5 min. Moreover, at downlink speeds of about 200 Gbps, PTD-3 also set the record for the fastest ever space-to-to-ground data transfer rate that had been achieved by satellite-based laser-optical communications equipment up to that point. A simplified concept of the laser-optical downlink operations of the PTD-3 mission is presented in Figure 11 [189,190,191]. Some CubeSat platforms have also been used in order to demonstrate inter-satellite laser-optical communications, with a notable example in that regard being FSSCat-A and FSSCat-B, two 6U CubeSats developed by the Polytechnic University of Catalonia and Tyvak International S.r.l. (Turin, Italy) which were equipped with HyperScout-2, an instrument combining a hyperspectral VNIR and a multispectral TIR imager under the mission of collecting Earth observation data that would supplement the ones collected by the Sentinel satellites of Copernicus, while also being equipped with a GNSS-Reflectometer and an L-band Radiometer which were utilized for sea-ice detection and thickness monitoring, as well as for soil moisture measurements. Apart from their Earth observation duties, the two CubeSats also featured UHF and laser-optical communication equipment for the in-orbit demonstration of inter-satellite radio and laser-optical communications [192,193].
Figure 11.
A simplified illustration of the operations concept of the Pathfinder Technology Demonstrator 3 (PTD-3) mission. Illustration by NASA/Dave Ryan [194].
Several upcoming CubeSat missions are going to involve laser-optical communication tasks, with an example being the CubeSat Laser Infrared CrosslinK (CLICK), which is going to consist of two 3U CubeSats, CLICK-B and CLICK-C. After their launch, these two CubeSats, each equipped with a full-duplex 1.5U Infrared laser-optical communications terminal, will focus on demonstrating inter-satellite laser-optical crosslink communications capable of reaching data rates of up to 20 Mbps at separation distances ranging from 25 km up to 580 km [195,196]. Another prominent example of an upcoming laser-optical communications CubeSat mission is Nice3, an educational 1U CubeSat developed by Université Côte d’Azur with the mission of establishing a space-to-ground laser optical link achieving a transmission data-rate of more than 1 Kbps [197]. Moreover, Laser-optical communication is also one of the core themes of the Greek CubeSat In-Orbit Validation (IOV) program, with four of the seven missions of the program focusing in the demonstration of space-to-ground and/or ground-to-space laser-optical communication technologies. These missions are PeakSat, Hellenic Space Dawn, OpiSat, and the ERMIS-Hellenic CubeSat Demonstration Mission [198]. One notable proposed (and potentially upcoming) CubeSat laser-optical communications mission concept is Q4. The Q4 mission concept is being jointly developed by NASA’s JPL and the Arizona State University and it would involve the launch of a mini-constellation of four 6U CubeSats that would demonstrate omnidirectional inter-satellite optical communication. For this mission, these CubeSats are proposed to be equipped with JPL’s Inter-Satellite Optical Communicator (ISOC) payload. The ISOC has the shape of an icosahedron and is equipped with multiple laser telescopes operating at 850 nm wavelengths, 1 W laser diodes, micro-electromechanical mirrors, and collimators. Due to its icosahedron shape, it would provide near-full coverage around each satellite. If successful, the ISOC is expected to provide inter-satellite data transfer rates reaching 1 Gbps up to distances of 200 km while maintaining multiple different laser-optical connections simultaneously [199].
This rising interest in laser-optical communication technologies for CubeSat applications has facilitated the development of various COTS laser-optical communication products that are now available for integration on CubeSat missions. Examples include Astrolight’s (Vilnius, Lithuania) Atlas-1 Free-Space Optics assembly and its accompanying fiber amplifier which take up a volume of 1.2U and 0.6U, respectively. According to its manufacturer, Atlas-1 can be utilized for space-to-Earth laser communication and it is capable of achieving a transmit data rate of up to 1.25 Gbps using a 1550 nm wavelength laser beam [200]. Another example of a commercially available laser-optical communication system is the SCOT20 terminal which has been developed by Tesat-Spacecom GmbH & Co. (Backnang, Germany). SCOT20 fits in a 1U volume, has a mass of approximately 1.6 kg, and is able of supporting 100 Mbps DirectTo-Earth (DTE) or bidirectional Inter-Satellite datalinks. Furthermore, SCOT20 is capable of transmitting data reliably over distances of up to 2000 km while its power consumption is just 8 W [201]. One more COTS laser-optical communications terminal available for use by CubeSat platforms is the AAC Clyde Space’s (Uppsala, Sweden) CubeCAT terminal which is designed to fit in a 1U volume. It can support bidirectional space-to-Earth optical communication operations with downlink data rates reaching 1 Gbps and an uplink data rate of up to 200 Kbps [202]. Finally, there is also the choice of Stellar Project’s (Padova, Italy) LaserCube, a two-way laser-optical communications terminal which is designed to fit inside a 2U volume and is intended to be integrated into CubeSats with a size larger than 3U [203]. All available commercial laser-optical communication solutions such as the aforementioned ones, coupled with new developments and experimental hardware are expected to enable a multitude of future CubeSat missions and applications involving data transfer via laser-optical link.
5. CubeSats as Astronomical Exploration and Research Enabling Platforms
In recent years, CubeSats have emerged as useful platforms for astronomical observation. Their low cost, modularity, and scalability potential provide a suitable candidate for replacing larger and more expensive platforms. They have been used in multiple missions, to investigate various cosmic phenomena, to study exoplanets, interstellar matter, etc. [204]. The main instruments that are utilized for these missions are UV/VIS/IR telescopes, X-ray spectrometers, solar X-ray spectrometers, gamma ray burst detectors, particle detectors, and radio interferometers. The working principles of these instruments and some notable missions will be presented hereafter.
5.1. UV/VIS/IR Telescopes
First, telescopes have been used in CubeSats for astronomical observation. They are essentially miniaturized optical telescopes that can capture light across all the spectra. Ultraviolet (UV) telescopes focus on short-wavelength radiation. This allows the study of hot and young stars and planetary atmospheres, as well as interstellar matter. For the study of planetary transits, stellar activity, and other optical phenomena, visible (VIS) telescopes are used to observe objects in the same spectrum as the human eye. Finally, IR telescopes that detect longer wavelengths are crucial for observing cooler objects like brown dwarfs and exoplanets. The Arcsecond Space Telescope Enabling Research in Astrophysics (ASTERIA) Satellite was a 6U space telescope developed by NASA’s JPL in collaboration with the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) [205]. Launched in 2017 and equipped with an optical telescope (visible and near infrared wavelengths), its main mission was demonstrating two key technologies for reducing systematic noise in photometric observations: high-precision pointing control and high-stability thermal control [206]. However, it conducted several other opportunistic observations, one of which was a marginal detection of the known transiting exoplanet 55 Cancri e. Measuring a transit depth of 374 ± 170 ppm, it was the first CubeSat to detect an exoplanet transit. The CubeSat ASTERIA is presented in Figure 12 along with its primary payload. Another CubeSat mission that utilizes a telescope for astronomical observation is SPARCS (STAR-PLANET ACTIVITY RESEARCH CUBESAT) [207]. Developed by Arizona State University and its partners, SPARCS is a 6U space observatory, capable of both near UV and far UV observations, that is scheduled to be launched in 2024–2025. It will be the first mission dedicated to monitoring the high-energy radiation environments of exoplanets throughout their lifetimes by continuously and simultaneously measuring the Far-ultraviolet (FUV) and Near-ultraviolet (NUV) emission of low-mass stars from young to old. One notable mission is also PicSat, a 3U CubeSat from Paris Observatory, developed to monitor the Beta Pictoris system [208]. It was equipped with a small off-axis optical telescope (35 mm effective diameter, F/D = 4) and its main mission was to detect a possible transit of the exoplanet Beta Pictoris b. PicSat was launched in 2018 and deployed on a 505 km Sun-synchronous orbit. However, due to malfunction of the Attitude Determination and Control System (ADCS), the satellite never actually pointed toward its target star. Its mission came to an early end after only 10 weeks of operations, when PicSat fell silent. This mission serves as a reminder of the difficulties presented in astronomical observations with CubeSats. Beyond the previously discussed missions, there are more missions that utilize CubeSat for astronomical observations, some of them already launched and some of them upcoming. CUTE (Colorado Ultraviolet Transit Experiment) is a 6U CubeSat developed by the University of Colorado Boulder designed to characterize the composition and mass loss rates of exoplanets using NUV transmission spectroscopy [209]. TOLIMAN is a 16U CubeSat that aims to perform astrometric measurements to detect exoplanets around Alpha Centauri using a high precision diffractive pupil telescope [210]. LUMIO, a 12U CubeSat from the SysNova initiative, which is designed to observe meteoroid impacts one the far side of the moon, uses a high sensitivity wide field camera capable of capturing transient luminous events [211].
Figure 12.
(a) A picture of the Arcsecond Space Telescope Enabling Research in Astrophysics (ASTERIA) 6U CubeSat during testing [212]. Cropped version of the original image [213]. Image credit: NASA/JPL. (b) ASTERIA CubeSat lens alignment. Image credit: NASA/JPL [214].
One more notable mission is Norbi-2. This 6U CubeSat was developed by Novosibirsk State University (NSU) in collaboration with OKB Fifth Generation Ltd. (Novosibirsk, Russia) and it was launched on June 27, 2023 aboard a Soyuz-2.1b rocket from the Vostochny Cosmodrome [215]. Its main objective is to conduct high-resolution solar observations using a vacuum ultraviolet (VUV) telescope called SOL, which captures images in the 17.1 nm (Fe IX/X) and 30.4 nm (He II) wavelengths [216]. These spectral lines are critical for studying solar flares, coronal mass ejections, and coronal heating, offering data important for space weather monitoring.The VUV telescope occupies 2U of the CubeSat and uses multilayer-coated optics and aluminum filters for narrowband imaging, with special attention to thermal control, contamination resistance, and optical alignment. Successfully deployed into a Sun-synchronous orbit, Norbi-2 has returned operational data and confirmed downlink performance via networks like TinyGS [217].
5.2. X-Ray Spectrometers
Moving on to the X-ray spectrometers, they are instruments capable of qualitative measurements regarding the composition of the specimen. They are used in astronomy for studying stars and galaxies, as well as supernova events and other high-energy phenomena. One notable mission that utilized this technology is the MinXSS Satellite [46]. Developed by the University of Colorado, Southwest Research Institute, NASA GSFC, and NCAR, MinXSS was a 3U CubeSat that launched in 2016 and operated for one year. Its mission was to study the X-ray emissions of the Sun, as well as their interaction with Earth’s atmosphere. The primary instrument used was Amptek X123-SDD (Amptek, Bedford, MA, USA). Weighing less than 350 g, it was capable of measuring solar spectra within the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) standard SXR range of 0.1–10 nm [218]. Another mission is HaloSat Satellite [219]. Developed by University of Iowa, HaloSat was a 6U CubeSat with the mission to constrain the mass and spatial distribution of hot gas associated with the Milky Way by mapping soft X-ray line emission from highly ionized oxygen. It utilized three identical detector units, each of them containing an X-ray detector and signal processing electronics. From the initial results, it is evident that HaloSat can advance the understanding of the hot halo of the Milky Way, and that the construction and deployment of CubeSats for astrophysics should be encouraged. In Figure 13a, HaloSat’s deployment from ISS can be seen. Beyond the previously discussed missions, there are more missions that utilize X-ray spectrometers in CubeSat, such as SpIRIT, a 6U CubeSat technology demonstrator developed by University of Melbourne [220] and CubIXSS, a 6U CubeSat funded under NASA’s Heliophysics Flight Opportunities for Research and Technology (H-FORT) program, which aims to study the creation of hot plasma in solar flares using soft X-ray spectroscopy [221].
5.3. Gamma-Ray Burst Detectors
Another application of CubeSats for astronomical observations is for gamma-ray burst detection, with one notable mission being BurstCube [222]. The BurstCube CubeSat expedition to a 6U CubeSat was developed by NASA and launched in March 2024, in order to detect and study gamma-ray bursts (GRBs), one of the most intense events in the universe and often associated with supernovae or the formation of black holes. BurstCube’s cadmium zinc telluride (CZT) detectors (see Figure 13b), which are sensitive to high-energy gamma rays, enable it to swiftly detect and pinpoint GRBs despite its compact size (6U) and low cost. It mainly acts as a supplement to larger observatories, such the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope, by providing early detection and alerts for GRBs, especially those that occur outside the coverage regions of larger spacecraft. BurstCube’s architecture enables the rapid transmission of gamma-ray data, which enables Earth-based astronomers to schedule follow-up studies at other wavelengths. A previous mission relative to this subject was GRBAlpha CubeSat. GRBAlpha is a 1U Cubesat project developed by the Technical University of Košice that was launched in March 2021, dedicated to detecting gamma-ray bursts (GRBs) from deep space to demonstrate that gamma-ray detection on a nanosatellite platform is possible [223]. GRBAlpha’s CsI(Tl) scintillation detector, developed via international collaboration, may record high-energy events associated with the death of massive stars and the formation of black holes since it can detect gamma rays with energies between 50 keV and 300 keV. Since its successful launch in March 2021, GRBAlpha has advanced the objective of employing several nanosatellites to expand global GRB monitoring by proving that small-scale, affordable GRB detection is feasible. GRBAlpha demonstrates how CubeSats might complement traditional observatories in the study of powerful cosmic occurrences in addition to assisting GRB research by transmitting real-time data on transient gamma-ray bursts.
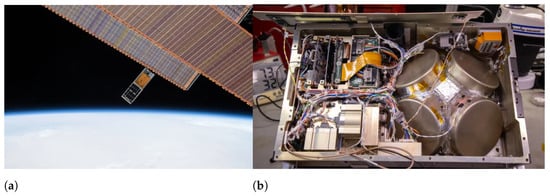
Figure 13.
(a) This photo, taken from the International Space Station, shows HaloSat’s deployment. Image credit: NASA [224]. (b) BurstCube Interior. Image credit: NASA/Jeanette Kazmierczak [225].
5.4. Particle Detectors
Particle detectors aboard CubeSats are small instruments designed to measure energetic particles in space, such as protons, electrons, and cosmic rays. These detectors are crucial for the research of space weather, radiation environments, and cosmic occurrences. By integrating particle detectors inside CubeSats, scientists may study particles from the Sun or deep space, keep an eye on space weather for potential disruptions to Earth-based systems, and offer crucial information on how radiation impacts satellite electronics. These detectors, which are often smaller versions of larger apparatuses, identify particles based on their charge and energy using solid-state detectors, scintillators, or Cherenkov detectors. CubeSats with particle detectors are inexpensive and may be set up in constellations to gradually gather larger amounts of spatial data. One notable mission is NASA’s CubeSat for Solar Particles (CuSP) mission [226]. The goal of this mission was to better understand how solar activities affect the near-Earth environment by studying solar energetic particles (SEPs) and their impact on space weather. NASA deployed the 6U CuSP CubeSat, a “space weather station,” on the Artemis I mission in 2022 to detect and analyze high-energy particles released by the Sun during solar flares and coronal mass ejections. CuSP has a magnetometer and a solar energetic particle spectrometer to monitor the magnetic fields and particle movement around it. Since SEPs may impact GPS signals, communication systems, and the condition of satellites in orbit, space weather forecasting relies on this information. Once again, CuSP shows how small, affordable CubeSats can be used to collect important scientific data on solar activity. This helps build a network of space weather monitors that may eventually give scientists and satellite operators real-time alerts and forecasts. Another mission that used particle detectors is ESRA [227]. The ESRA (Energetic particle Stream and Radiation Analyzer) CubeSat project was developed by Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL) and its launch is expected to take place in 2025. The main goal of this mission is to track and evaluate radiation and high-energy particles in Earth’s near-space environment to improve our understanding of space weather and how it affects satellite operations. An essential feature of this mission is the particle detector, which is designed specifically to study energetic particles like protons and electrons that are prevalent in the Earth’s magnetosphere and radiation belts. The detectors are designed to collect real-time data on particle movement and energy levels, as well as on how radiation levels change with solar activity and how these particles interact with and affect the magnetosphere. This information is crucial for assessing potential dangers to satellites, since high-energy particles can gradually damage spacecraft materials and interfere with electronic systems.
5.5. Radio Interferometers
CubeSats have also been used in missions incorporating radio interferometers. In these configurations, several CubeSats, each with an antenna that gathers radio waves, circle each other. By doing this synchronized movement, a “virtual telescope” is created, which is more portable, modular, and adaptable than a much bigger, ground-based radio observatory. This method works well for monitoring the Earth’s ionosphere, tracking solar radio bursts, and identifying cosmic radio sources. By adding more satellites, researchers can expand the system using CubeSat interferometers, increasing the sensitivity and resolution of their studies. This method offers a cost-effective means of obtaining precise, high-quality data, opening up fascinating prospects for space radio astronomy. One upcoming mission that incorporates radio interferometers is the Sun Radio Interferometer Space Experiment (SunRISE) [228]. Developed by NASA and its partner institutions, the SunRISE project will deploy a constellation of six 6U CubeSats, as can be seen in Figure 14, to study the origins and propagation of solar radio waves associated with solar storms. Currently expected to be launched before the end of 2025 onboard ULA’s Vulcan Centaur launch vehicle, the SunRISE CubeSats will capture radio waves from solar energetic particles (SEPs), which are produced during solar eruptions, using a coordinated arrangement of the six CubeSats. The CubeSats will employ radio interferometry to create a virtual radio telescope that can take high-resolution images of solar radio bursts to assist scientists in monitoring their velocity and positions. By providing insight into how SEPs travel through the heliosphere, the data collected will aid us to understand space weather and its potential impacts on satellites, communication systems, and humans in orbit. SunRISE’s successful demonstration will present a major advancement in solar research, demonstrating how small, coordinated satellites can achieve complex scientific goals typically reserved for larger, more expensive missions.
Figure 14.
Sun Radio Interferometer Space Experiment (SunRISE) mission—Six 6U Cubesat constellation. Image credit by Space Dynamics Laboratory/Allison Bills [229].
6. CubeSats as Platforms for Chemical and Biological Experimentation in Space
To better understand the fundamental processes of life, CubeSats have served as platforms for conducting space-borne biological and chemical experiments. The harsh environmental conditions of these experiments play a significant role in giving more in-depth details of these processes as well as for addressing the challenges of long-term human space exploration. The microgravity, the vacuum of space, the intense radiation; all these unique conditions synthesize a “laboratory” like no one else on Earth. The risks of space travel on human health should be meticulously examined, risks such as bone density loss, muscle atrophy, and also DNA damage and immune system suppression. These insights will serve as a backbone for the countermeasures to protect humans on long-term missions, to the Moon, Mars, and beyond. Furthermore, other experiments studying animals, plants, and microorganisms play a vital role in future life support systems, especially if we consider the in-space life of astronauts an even potential human settlements apart from Earth. It is worth mentioning that the ISS has been utilized as a platform for conducting biological and pharmaceutical studies by various companies, such as the German company Yuri (Meckenbeuren, Germany) [230], but in this section we are going to focus only on dedicated CubeSat platforms. Beyond biology, studies involving chemical processes and reactions in space can further deepen our understanding of these phenomena, providing essential knowledge for applications in space and on Earth.
A significant milestone in space exploration was the pioneering mission GeneSat-1 (see Figure 15a), a collaboration between NASA Ames Research Center, Stanford University, and Santa Clara University [231]. Launched in December 2006 aboard a Minotaur launch vehicle, this 3U CubeSat was the first free-flying CubeSat in LEO, with a dedicated biological mission. The payload module of this CubeSat contained an integrated fluidics system and high-precision optical sensors, capable of detecting and measuring a protein expression in Escherichia coli bacteria, namely the green fluorescent protein (GFP). This investigation on how metabolic processes and gene expression are affected by microgravity was the primary objective of this mission and it was achieved during the first week of operation. After the successful automated initiation of the experiment, the bacterial specimens were sustained by nutrient-rich growth medium in a temperature-controlled environment. In a span of only 96 h, the bacterial growth was tracked through optical density measurements and monitor the expression of the protein, using fluorescence detection. The GeneSat-1 mission not only demonstrated the feasibility of biological experiments in CubeSat missions but also paved the way for future missions to explore the biological effects of spaceflights.
Following the successful GeneSat-1 mission, NASA Ames Research Center in collaboration with Santa Clara University and the University of Texas Medical Branch continued with the development of the PharmaSat mission [232]. Based on the same CubeSat design, this mission aimed to investigate the in-space resistance of yeast to antifungal agents, providing insight about the drug efficacy in microgravity. PharmaSat was launched in May 2009 and its payload included a self-contained miniature lab with 48 fluidic microwells, microfluidics systems, and optical sensors. For the yeast samples, they were prepared six weeks before launch using Saccharomyces cerevisiae, and they were reactivated in orbit three days after launch. Alongside the growth medium, four concentration levels of the antifungal agent voriconazole were provided to the samples in order to track the yeast population growth and its viability. The produced data for the yeast growth and antifungal response were telemetered to Earth, providing key insights about the drug resistance mechanisms and the behavior of biological systems in space.
In November 2010, the Organism/Organic Exposure to Orbital Stresses (O/OREOS) mission was launched and set in an orbit of 650 km [233]. The O/OREOS CubeSat can be seen in Figure 15b and it was developed under NASA’s Astrobiology Program by NASA Ames Research Center with contributions from Santa Clara University, the University of Florida, and other institutions. This mission incorporated two main payloads, namely the Space Environment Survivability of Living Organisms (SESLO) experiment and the Space Environment Viability of Organics (SEVO) experiment. The SESLO experiment focused on studying the survival, growth, and metabolic activity of Bacillus subtilis spores and Halorubrum chaoviatoris cells. Utilizing microfluidics systems and colorimetric analysis, it measured the microbial activity three times over a six-month period. On the other hand, SEVO utilized UV-VIS spectroscopy to investigate the photostability and degradation of amino acids and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, providing real-time data regarding the behavior of these compounds through the interaction with solar radiation and cosmic rays. Both experiments met their expectations, with SESLO demonstrating the resilience of these microorganisms in space and SEVO providing unique data regarding degradation patterns of these organic compounds.
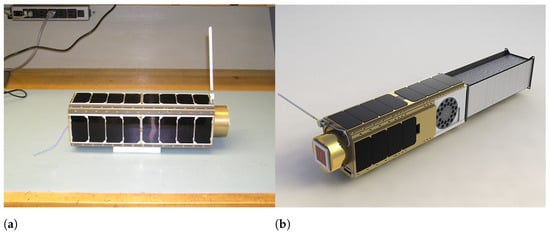
Figure 15.
(a) The CubeSat GeneSat-1. Image credit: NASA [234]. (b) The Organism/Organic Exposure to Orbital Stresses (O/OREOS) CubeSat. Illustration by NASA/Chris Beasley [235].
Built upon the concepts and hardware of the previous PharmaSat mission, the E. coli Anti-Microbial Satellite (EcAMSat) was an effort by NASA Ames research Center and Stanford University [236]. This autonomous 6U CubeSat (see Figure 16a), dedicated to biological research, was launched in November 2017, with the primary objective of studying the impact of space conditions, such as microgravity, on antibiotic resistance. Escherichia coli cells were loaded into micro-wells and stayed dormant until the initiation of the experiment, where they were re-hydrated with a nutrient rich solution, enabling their growth. After a 48 h period, E. coli cells were exposed to a commonly used antibiotic, namely the gentamicin, at various concentrations. The growth and metabolic activity of the bacteria were monitored using Alamar Blue, an indicator which changes color in response to cellular respiration. After transmitting the results back to Earth and post analysis, an exhibition of higher resistance with comparison to the control results on Earth was found. These findings not only helped understand the antibiotic resistance of E. coli but also highlighted the need for further research about microbial adaptation in space, a phenomenon that could potentially pose risks in prolonged space missions.
One significant step towards applying technologies such as the lab-on-chip (LOC) technology in space was the LabSat mission [237]. Launched in 2022, this 2U CubeSat was a collaboration between researchers from SatRevolution (Wrocław, Poland), the Wroclaw University of Science, and several other European academic institutions. The payload consisted of a controlled-environment laboratory and optical detection systems, including CCD cameras. The temperature, humidity, and light exposure were precisely maintained to allow optical conditions for biological cultivation and the use of LOC enabled the automation of important processes, such as nutrient delivery. The first objective was to assess the behavior of Fusarium culmorum, a model fungus of its resilience. The second objective was to explore the feasibility of plant cultivation in space, using Lepidium sativum seeds. Unfortunately, due to communication and power supply issues, LabSat was unable to demonstrate and investigate its objectives. However, the lessons learnt from this mission highlight the need for meticulous design methods for missions including biological experiments.
Another mission that utilized lab-on-chip technology was the AstroBio CubeSat [238], which can be seen in Figure 16b. Developed as a collaboration between the University of Bologna, Sapienza University of Rome, and the Italian Space Agency, AstroBio was launched in July 2022 aboard the maiden flight of Vega-C rocket, deployed in a circular orbit at about 5850 km of altitude. The main objective of this mission was to investigate the effects of space radiation on bio-molecules and enzymes, while aiming to validate the use of LOC for chemiluminescence-based bioassays. The payload incorporated a photosensor array to measure the CL emissions, a paper-based microfluidic analytical device (µPad), miniature peristaltic pumps for the buffer delivery and a wetness sensor to confirm the fluid delivery to the µPad. The payload box was sealed with aluminum for radiation protection and thermally regulated. In order to evaluate the enzymes and bio-molecules’ stability, a ground-based control experiment was performed to highlight the effects of radiation. In order to prevent enzyme degradation, pullulan was used, a natural polysaccharide acting as a protecting agent. Through post analysis of the results, it was observed that pullulan significantly helped the stability of the enzymes over a prolonged radiation exposure period. AstroBio successfully demonstrated how compact and automated systems such as LOC can be utilized in CubeSats, making them an excellent platform for scientific research.
Figure 16.
(a) A picture of the E. coli Anti-Microbial Satellite (EcAMSat) CubeSat. Image credit: NASA [239]. (b) An illustration of the AstroBio CubeSat. “Reproduced from Meneghin et al., Europlanet Science Congress 2020, EPSC2020-943, 2020, licensed under CC BY 4.0 license” [240].
One of the most recent missions and perhaps one of the greatest milestones in biological experimentation on CubeSats is the BioSentinel mission [241,242]. It was developed by NASA Ames Research Center, in collaboration with NASA Johnson Space Center and Jet Propulsion Laboratory and it was launched in November 2022, as part of the Artemis I mission. The aim of the 6U BioSentinel CubeSat (see Figure 17a) was to investigate the effects of deep-space radiation on organisms, namely in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, also known as budding yeast. It consisted of two primary instruments, the BioSensor payload, which is a 4U microfluidic system to cultivate and monitor the metabolic responses of the selected yeast cells, and also a Linear Energy Transfer (LET) Spectrometer, which is a radiation sensor that measures the radiation environment in terms of particle energy and dosage. An example of the utilized microfluidics cards can be seen in Figure 17b. Equipped with these instruments and using a well-established organism with genetic similarities to human cells, the evaluation of DNA damage from radiation and the repair mechanisms could be compared to the results from LEO (controlled experiment in ISS) and on Earth experiments. As already known, operations beyond LEO pose significant challenges, both engineering and scientific. Galactic cosmic rays and solar particle events introduce unpredictability and risks to living organisms and since BioSentinel lacks Earth’s protective magnetic field, it is an ideal platform for studying chronic radiation exposure. Its findings will contribute to developing and establishing protective strategies for prolonged human travel in deep space, aiding in the creation of sustainable habitats on Moon and Mars.
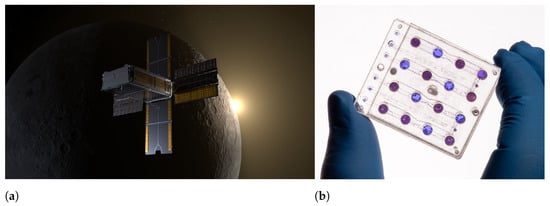
Figure 17.
(a) An illustration of the CubeSat BioSentinel. Illustration by NASA/Daniel Rutter [243]. (b) An exmple of the microfluidics cards carried by BioSentinel which contained the yeast sample to be studied. Photo by NASA/Dominic Hart [243].
Another notable mission is RVSAT-1, India’s first microbiological nanosatellite [244], which was developed by undergraduate students from RV College of Engineering under Team Antariksh [245]. Launched on 30 December 2024, aboard ISRO’s PSLV-C60 mission, RVSAT-1 is a 2U CubeSat (1.88 kg) designed to study the growth of the gut bacterium Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron in microgravity. The mission aimed to analyze bacterial behavior and the effects of prebiotics in space, with implications for astronaut health, space medicine, and microbial ecosystem management. The satellite integrated a microfluidic and optical monitoring system and successfully miniaturized lab equipment into its small form factor. It completed a two-day mission in low Earth orbit, demonstrating successful student-led space research and bio-experimentation.
7. CubeSats as Deep-Space Exploration Platforms
CubeSats have also obtained a notable and increasing role in the exploration of deep-space celestial bodies such as planets, planet-satellites, and asteroids, with a significant number of successful missions and an increasing number of planned, upcoming missions. What such CubeSat missions have in common, which is different than the vast majority of all other missions undertaken by CubeSats, is that the platforms undertaking deep-space exploration missions have to leave the Earth’s orbit. This unique mission requirement means that deep-space exploration CubeSats differ in many aspects from traditional Earth-orbiting CubeSats, with the most significant differences being found on aspects such as radiation tolerance, telecommunications equipment, propulsion, and thermal design.
More specifically, in terms of radiation tolerance, to get to their destinations, deep-space exploration CubeSats are most likely expected to travel through the Van Allen radiation belts, thus exposing their electronic equipment to the charged particles that are present in the belts. Furthermore, these CubeSats are expected to survive and operate outside the protection of the Earth’s magnetosphere, where they are constantly exposed to cosmic rays and solar energetic particle events. For these reasons, extensive radiation protection measures must be implemented for the success of these missions and the electronic components utilized have to be specifically designed and fabricated to mitigate the risks that stem from prolonged radiation exposure. When it comes to communications, telemetry, and tracking, deep-space exploration CubeSats have to overcome the extreme distance that separates them from the Earth, it is thus common for these satellites to be equipped with specifically designed, powerful communication systems and large antennas. Regarding propulsion systems, it must be noted that they can also be found on a considerable number of Earth-orbiting CubeSats, serving as a means to counter orbital decay and to perform orbital maneuvers. However, for interplanetary CubeSat missions, the existence of a propulsion system represents a necessity as it is required to generate the considerable amount of v that is required for interplanetary transfer maneuvers and/or orbital insertion in their destination celestial body. Finally, regarding thermal control systems, the high power of the subsystems commonly found on deep-space exploration CubeSats, as well as the extreme thermal environments these spacecrafts are expected to operate in, lead to the requirement for the design and implementation of robust thermal control measures [246].
For this review, deep-space exploration CubeSats will be divided into three major categories based on the celestial body they are intended to explore, namely, lunar exploration CubeSats, planetary exploration CubeSats, and asteroid exploration CubeSats. Notable past, present, and upcoming CubeSat missions that fall within these categories are analyzed in more detail in the subsections that follow.
7.1. The Role of CubeSats in Lunar Exploration Missions
Due to its close proximity to the Earth when compared to other interplanetary destinations and the renewed scientific interest in the exploration of the Earth’s natural satellite, the Moon has attracted the interest of a multitude of CubeSat missions over the last few years, with a significant number of new missions under development as of 2025.
The first CubeSat mission that visited the Moon was the Cislunar Autonomous Positioning System Technology Operations and Navigation Experiment (CAPSTONE) which is presented in Figure 18. CAPSTONE is a 12U CubeSat developed by Advanced Space, LLC. (Westminster, CO, USA), Tyvak Nano-Satellite Systems Inc., and NASA.It was launched on 28 June 2022 in a ballistic lunar trajectory and following a three-month journey, it was inserted into a near-rectilinear halo orbit (NRHO) that brought it 1,600 km off the lunar north pole surface at its closest approach and 70,000 km off the lunar south pole at its furthest point. Once there, CAPSTONE’s primary mission objective was to test and verify the calculated orbital stability of the NRHO, as well as demonstrate and validate navigation and orbital maintenance capabilities and strategies. Regarding navigation capabilities, CAPSTONE was also equipped with the Cislunar Autonomous Positioning System (CAPS) software (Advanced Space, LLC., Westminster, CO, USA) [247]. CAPS is an advanced space navigation system under development which, when fully operational, would enable spacecraft that are in orbit around the moon to determine their location in the cislunar space through peer-to-peer communication, reducing the reliance on Earth-based navigation infrastructure. If successfully deployed, CAPS will serve as a robust solution for the tracking of the ever-rising number of objects in lunar orbit, a number that is expected to rise exponentially over the next decades. In that regard, CAPSTONE was tasked with demonstrating core technical components of the CAPS by performing inter-spacecraft raging measurements with the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) robotic spacecraft which is also operating in orbit around the moon and thus help in accelerating its development. Finally, CAPSTONE was also equipped with commercial imager that would be utilized for capturing images of the Moon and the Earth. Since the beginning of its mission, CAPSTONE has operated successfully in NRHO for more than 267 days and has successfully executed all the planned orbital maintenance maneuvers. Thus, although not a lunar exploration CubeSat with the strict sense of the term, CAPSTONE has served as a precursor for both the launch of the upcoming Lunar Gateway space station which will be orbiting the moon in the same type of NRHO and will play an important role in the Artemis program and human lunar exploration, as well as paving the way for the success of a variety of other lunar exploration missions that will follow [248,249,250,251].

Figure 18.
An illustration of the Cislunar Autonomous Positioning System Technology Operations and Navigation Experiment (CAPSTONE) CubeSat in its deployed configuration. Illustration by NASA/Daniel Rutter [252].
During the launch of the Artemis I mission on 16 November 2022, a total of ten 6U CubeSats were launched as secondary payload inside the unused volume of the Orion stage adapter that connects the Orion spacecraft with the Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage (ICPS) of NASA’s Block 1A Space Launch System (SLS). These CubeSats were deployed after the separation of the Orion spacecraft from the ICPS and were sent on a Moon fly-by trajectory. Some of the CubeSats would continue on this fly-by trajectory, while others would utilize their integrated propulsion systems to insert themselves into orbits around the Moon. Of these ten CubeSats present onboard Artemis I, four were intended for the performance of lunar exploration missions and one for the demonstration of technologies relevant to future lunar exploration missions [253]. These ten CubeSats can be seen in their deployment pods on the inside of the Orion stage adapter ring of SLS’s ICPS in Figure 19.

Figure 19.
The ten CubeSats carried as secondary payloads of the Artemis I mission inside the Orion stage adapter of the Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage (ICPS). Photo by NASA/Cory Huston [254].
One of the CubeSats launched on Artemis I was the Lunar Infrared (LunIR) imaging CubeSat which was developed by Lockheed Martin Space Systems (Littleton, CO, USA) and Tyvak Nano-Satellite Systems Inc. Its payload included a low-cost, MWIR sensory instrument, developed by Lockheed Martin Space Systems which is capable of operating in both night and day, it is intended for missions that involve the mapping the surface of celestial bodies and the detection of the presence of materials on them, as well as for the identification of potential landing sites. LunIR was sent on a lunar fly-by trajectory and was tasked with the mission of acquiring spectroscopy and thermography data from the lunar surface that would demonstrate the effectiveness of its MWIR payload and its potential to be used for future missions of surface characterization and remote sensing in both the Moon and Mars. However, the occurrence of an unexpected communications issue during the lunar fly-by prohibited the satellite from acquiring the intended data from the lunar surface. Despite the inability of capturing image data of the Moon’s surface, Lockheed Martin still considered the mission successful as it demonstrated the successful integration of the MWIR payload on a CubeSat platform [255,256,257]. Another lunar exploration CubeSat present onboard Artemis I was the Lunar IceCube. This 6U CubeSat, which was jointly developed by Morehead State University, NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC), and JPL, was equipped with the 1.5U-sized Broadband Infrared Compact High Resolution Exploration Spectrometer (BIRCHES), under the mission of investigating the distribution of water, ice, and other volatile compounds such as NH3, H2S, CO2, and CH4 on the lunar regolith through spectral determination. Furthermore, the Lunar IceCube would use its scientific payload to map the distribution of said volatiles as a function latitude, local time, as well as regolith age. After its deployment, Morehead State University managed to establish a brief contact with the satellite for a period of about an hour, but a large offset from the predicted frequency was observed followed by loss of signal. Since that point, the status of the Lunar IceCube remains unknown [258,259].
One more lunar exploration CubeSat hosted as a secondary Artemis I payload was the Outstanding MOon exploration TEchnologies demonstrated by NAno Semi-Hard Impactor (OMOTENASHI). This CubeSat was part of a technology demonstration mission developed by JAXA and the University of Tokyo. The OMOTENASHI CubeSat was made up of three distinct modules. The main one was the 6U bus which featured a cold gas thruster that would be used to place the OMOTENASHI in a lunar-impact orbit. After orbital insertion, the other two modules, namely the landing probe and a solid rocket motor, would detach from the 6U bus and the motor would decelerate the landing probe even further. Eventually, the landing probe would eventually detach from the motor and perform a semi-hard landing on the lunar surface with an expected velocity between 20 m/s and 30 m/s. Before the final impact on the Moon’s surface, the landing probe would deploy an airbag that would mitigate its effects on the instruments. During the entire landing sequence, the OMOTENASHI’s landing probe would utilize its instruments to perform measurements of the radiation environment, with radiation measurements also performed on the lunar surface after the landing. However, due to loss of attitude control, no stable communication between OMOTENASHI and mission control could be established, leading to the abandonment of landing plans and the eventual loss of the mission [260,261,262]. Another lunar exploration CubeSat carried onboard Artemis I was the Lunar Polar Hydrogen Mapper (LunaH-Map) which was manufactured and operated by Arizona State University. This CubeSat would monitor and map ice deposits in the surface of the Moon’s south pole using its primary scientific payload which was the Miniature Neutron Spectrometer (Mini-NS). However, problems encountered in its propulsion system prevented LunaH-Map from entering the planned lunar orbit and performing its main mission. Nevertheless, the CubeSat managed to collect nearly three hours of data from the Moon’s surface from a distance of about 1300 km during its flyby, thus successfully demonstrating the operation of its neutron spectrometer, which managed to identify the possible existence of ice below the lunar soil, in depths reaching as deep as 1 m by detecting neutrons that indicate the presence of hydrogen. For this reason, the LunaH-Map mission is considered a partial success [263,264].
Also present onboard Artemis I was the CubeSat ArgoMoon which was developed by Argotec (San Mauro Torinese, Turin, Italy) for the Italian Space Agency. ArgoMoon was equipped with two optical cameras (a narrow-angle one with a FOV of 2.05° and a wide-angle one with a FOV of 32.5°), as well as a laser rangefinder. The satellite was also equipped with a cold-gas reaction control system. During the first phase of the mission after its deployment, ArgoMoon would perform autonomous proximity flight operations close to the SLS’s ICPS and would also observe the deployment of the other CubeSats carried by the mission. Furthermore, during its mission, ArgoMoon would capture photographs of the ICPS, the Moon, and the Earth, while also demonstrating optical communications with the Earth. However, unexpected propulsion-related anomalies meant that the maneuvers executed did not reach their intended v and prevented the ArgoMoon from completing all of its set milestones. Despite these setbacks, the CubeSat managed to capture several photographs of the Earth and the Moon and transmit them back to the Earth during its lunar and Earth fly-bys [265,266].
The high degree of mission anomalies or even complete mission loss incidents observed among the CubeSats launched as secondary payloads of NASA’s Artemis 1 mission certainly raises some questions about the underlying reasons that have led to them [267]. A common mission failure cause observed among most of the Artemis 1 CubeSats that failed regardless of their intended mission goals was the inability to establish a stable communication link with the ground control after separation from the ICPS of NASA’s SLS rocket. Even though the exact underlying issues that caused these failures have not been officially reported for all the missions, the root cause of failure in many of these missions could be an electrical power related problem. For example, prior to the launch of Artemis 1, the SLS rocket was plagued by engine problems and hydrogen leaks which, in conjunction with hurricane Ian, forced NASA to stand down from multiple launch attempts and even roll the SLS back to the Vehicle Assembly Building before its eventual successful launch on 16 November 2022. Thus, there was a delay of approximately two and a half months from the original launch date which was set to happen on 29 August 2022 [268]. During this entire time, the CubeSats remained integrated inside the ICPS adapter of the vehicle and, therefore, prolonged storage may have led to degradation of the batteries of the satellites and by extension, a power-critical situation after deployment. Moreover, prolonged storage inside the launch vehicle could also be the culprit for propulsion related anomalies of jammed valves and propulsion leaks such as the ones encountered by the LunaH-Map and OMOTENASHI CubeSats. More specifically, in the case of the LunaH-Map, a stuck valve led to the inability to perform the intended maneuvers, while in the case of OMOTENASHI, a propellant leak due to a faulty valve led to excessive tumbling and loss of attitude control.
Furthermore, other reasons could be identified as potential culprits for some of these anomalies and failures. Firstly, up until this day, only a small number of CubeSats from a very limited number of developers have ever been launched beyond the orbit of the Earth, therefore, challenges that stem from this environment, which is considerably different from the one of Earth orbit, should not be ruled out. Such a challenge could be the ionizing radiation environment that exists beyond the protection of the Earth’s magnetic field, as well as in the Van Allen radiation belts, inside which the trajectory of Artemis 1 brought the CubeSats in question. This ionizing radiation can quickly damage electrical electronic equipment including a satellite’s telecommunication elements or ADCS system which would in turn inhibit the establishment of stable communications with the spacecraft. Furthermore, the considerably different thermal environment of the translunar and lunar spaces is substantially different than that of Earth orbit entailing dangers of overheating or extensive freezing of the CubeSats, depending on the situation. Last but not least, it should not be forgotten that most of these CubeSat missions were tasked with demonstrating and validating novel technologies and a variety of never-before-flown systems set to perform state-of-the-art mission goals. Therefore, the chances of hardware failure would inherently be high. Therefore, the high failure rate observed among the CubeSats that were launched on Artemis I for lunar exploration missions underlines in the most prominent way the difficulties and risks associated with the use of CubeSat platforms for deep-space exploration missions.
However, despite these setbacks, a considerable number of new lunar exploration CubeSat missions is under development as of 2025. One of these upcoming missions is the LUnar Meteoroid Impact Observer (LUMIO). This proposed mission will utilize a 12U CubeSat orbiting the moon in a halo orbit around the Earth-Moon system’s L2 Lagrange point that would observe the meteoroid impacts happening on the far-side of the Moon. More specifically, LUMIO will utilize its custom made, LUMIO-Cam optical imager which is developed by LEONARDO S.p.A. (Florence, Italy) and is designed to operate both in the visible and NIR spectral bands (namely between 450 nm and 950 nm), to detect, quantify, as well as characterize the meteoroid impacts that take place on the far-side of the lunar surface. It will achieve this by using its payload for the detection of the flashes caused by the impacts. The meteoroid impact data collected by LUMIO from the Moon’s far-side will then complement similar data from the near-side of the Moon’s surface which are collected by Earth-based observation platforms and in this way, it will provide the scientific community with a complete image of the meteoroid environment of the Moon [269]. Moreover, it was announced by NASA on 20 September 2024 [270] that the launch of Artemis II mission is going to feature five CubeSats as secondary payloads. It has yet to be disclosed what missions these five CubeSats will perform but it is safe to assume that like Artemis I, a considerable fraction of these five CubeSats will be intended for lunar exploration missions. Furthermore, based on [271], some of the CubeSats present on future Artemis missions (Artemis III onward) are expected to be larger (or smaller) than the 6U ones launched on Artemis I as bigger CubeSat dispensers, capable of housing spacecraft of different sizes will be integrated to the Exploration Upper Stage (EUS) of the SLS Block 1B rocket.
7.2. CubeSat Missions for Planetary Exploration
So far, in the span of more than two and a half decades since the advent of CubeSats, only a single CubeSat mission to another planet has ever been undertaken. This mission was Mars Cube One (MarCO), which was coordinated by NASA and involved the launch of two 6U CubeSats, MarCO-A and MarCO-B, (which are presented in Figure 20a) into a Mars fly-by trajectory. The two CubeSats were launched on 5 May 2018 together with NASA’s InSight Mars lander and their main mission was to serve as communications relay satellites, providing a real-time 8 kbps communication link between mission control and the InSight lander during the Mars atmospheric entry, descent, and eventual landing phases, when the InSight lander would not have a direct line of sight with the Earth. The two CubeSats were equipped with a large deployable UHF antenna via which they received signals from the InSight lander and a Xband antenna, through which they communicated with NASA’s Deep Space Network (DSN). Furthermore, a powerful transponder capable of operating in both UHF (only receiving) and Xband (receiving and transmitting) spectra was present onboard, this transponder, named Iris, had been developed by NASA’s JPL. The two spacecrafts also featured cold gas propulsion systems, used for the performance of trajectory correction maneuvers during their long journey to Mars. It must be noted that normally, only one CubeSat was required for the mission, however the existence of two instead of one offered redundancy. Both CubeSats were eventually successful in executing their mission, successfully demonstrating the viability of the carry-your-own-relay concept, which can now be utilized by a variety of future interplanetary missions, reducing or even eliminating the need for the placement of dedicated relay infrastructure before the execution of the main mission. Furthermore, the two MarCO CubeSats became the smallest spacecraft to successfully complete an interplanetary mission, to this day. Finally, the two spacecraft were also equipped with wide-angle cameras which were used to verify the successful deployment of deployable components (such as solar panels) and to capture various images. With this camera, MarCO-B managed to capture several pictures of Mars during its fly-by, one of which is presented in Figure 20b [272,273,274].
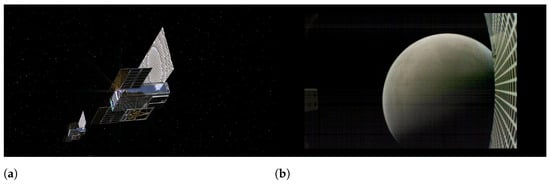
Figure 20.
(a) An artistic illustration of the Mars Cube One A (MarCO-A) and Mars Cube One B (MarCO-B) CubeSats in their deployed configuration. (b) A picture of Mars that was captured by MarCO-B on 26 November 2018. Illustration and photo by NASA/JPL-Caltech [275].
Several mission concepts which would utilize CubeSat platforms for the exploration of planets of our solar system are being studied as of 2025. One of these potential future planetary exploration missions involving CubeSats is CubeSat UV Experiment (CUVE), proposed by the University of Maryland College Park, which received funding for further development from NASA’s Planetary Science Deep Space SmallSat Studies (PSDS3) program [13]. The CUVE mission concept proposes the use of a 12U CubeSat platform for the study of the Venusian atmosphere’s dynamics by measuring its ultraviolet absorption and nightglow emissions. More specifically, it will study the so-far unknown UV “absorber” that is present in the Venusian atmosphere, which produces the characteristic UV features observed in the Venusian disc, which are used to monitor the dynamics of the Venusian atmosphere’s cloud motion. To perform this mission, the CUVE will be equipped with two scientific payloads. The first of these payloads is a low scattering Czerny–Turner image spectrometer operating in the spectrum between 190 nm and 380 nm with a spectral resolution of 0.2 nm, capable of resolving SO and SO2 concentrations in the Venusian atmosphere. The second payload will be a multispectral, Linear Variable Filter (LVF) imager operating between 320 nm and 570 nm wavelengths and featuring a 4 nm spectral resolution, this payload would provide high-resolution UV image data. Both instruments are expected to offer a spatial resolution of 3 km from an altitude of 66,000 km. The satellite is intended to be placed in an elliptical orbit around Venus and once in orbit, the expected CUVE mission duration is 6 months [276].
Two more proposed CubeSat-based planetary exploration missions are Aeolus and the Chariot to the Moons of Mars [246], with both missions having received funding through NASA’s PSDS3 program [13]. According to the mission concept, Aeolus will be a 24U CubeSat developed by NASA’s Ames Research Center that will study the vertically resolved global winds of the Martian atmosphere and its planetary-wide energy balance. The satellite’s proposed mission payload consists of three components. One of these payloads will be the Surface Radiometric Sensor Package (SuRSeP), which would monitor surface temperatures of Mars with an accuracy of 5 K, as well as the total amount of solar radiation that is reflected by the planet’s surface. Furthermore, the satellite will also be equipped with the Spatial Heterodyne Spectrometers (SHS) which, with the help of two orthogonal viewing telescopes, will be used for the measurement the atmospheric wind of the Martian atmosphere through Doppler shift in atmospheric O2 airglow emission. The SHS will be capable of measuring wind speeds between 5 m/s and 230 m/s with an accuracy of 5 m/s. Aeolus is also expected to carry the Thermal Limb Sounder (TLS), a payload that will be tasked with the measurement of the atmospheric temperature of the planet (with an accuracy of 3 K) and the detection of aerosols. If successful, Aeolus will be the first mission ever to directly measure the winds of the Martian atmosphere [277]. The Chariot to the Moons of Mars mission on the other hand is developed by Purdue University and aims to utilize a 12U CubeSat platform that would characterize and map the composition of the surfaces of the two natural satellites of Mars, Deimos and Phobos. It would achieve this by observing the surfaces of the two moons in both VNIR and TIR spectra using a multi-spectral TIR imager, a NIR point-spectrometer, and a visible spectrum optical imager. For communication with the Earth, the CubeSat is intended to be equipped with the same communication hardware suite as the CubeSats of the MarCO mission. The data collected by this mission would greatly help the scientific community in the generation of more accurate hypotheses and models about the creation of Deimos and Phobos [278].
7.3. CubeSats as Asteroid Exploration Probes
In recent years, the utilization of CubeSat platforms in asteroid exploration missions has commenced, leading to the development and execution of a variety of missions. The first and up to this day only CubeSat mission to successfully perform an asteroid fly-by was the Light Italian CubeSat for Imaging of Asteroids (LICIACube). LICIACube was a 6U CubeSat developed by the Agenzia Spaziale Italiana (ASI) as a part of NASA’s Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART) mission, which aimed to demonstrate the asteroid deflection concept by changing an asteroid’s motion in space through kinetic impact. The target of said mission was the 65803 Didymos binary system which contains the Didymos asteroid and its moon, Dimorphos. For this mission, the LICIACube was carried onboard the main DART probe (see Figure 21a) and was deployed ten days prior to DART’s impact on the Dimorphos asteroid, under the mission of acquiring images that would help the scientific community to study and better understand the effects of the DART kinetic impact vehicle on the asteroid. For this mission, LICIACube was equipped with two cameras, a narrow field of view camera and a wide field of view Gecko imager (Dragonfly Aerospace, Stellenbosch, South Africa) with an RGB Bayer pattern filter which was developed by SCS space (Stellenbosch, South Africa). The LICIACube was successful in performing its planned mission, and on 26 September 2022, flew by Dimorphos at a distance of approximately 58 km, managing to capture several images of the asteroid both before and after DART’s impact on it, with one of the images captured by the CubeSat being presented in Figure 21b [279,280,281,282]. To this day, the only other undertaken CubeSat mission which was intended for asteroid exploration was the Near-Earth Asteroid Scout (NEA Scout), a 6U CubeSat which was one of the ten CubeSats to fly on Artemis I. NEA Scout was co-developed by NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) and JPL under the mission of performing a slow fly-by of a near-Earth asteroid, during which it would utilize its payload, the NEACam optical imager, to acquire high resolution images of the asteroid. Furthermore, with a total area of 84.6 in its deployed configuration, NEA Scout’s main propulsion system was the largest solar sail until this day developed by NASA. However, contact with the satellite was never established after its deployment and the mission is considered lost [283].
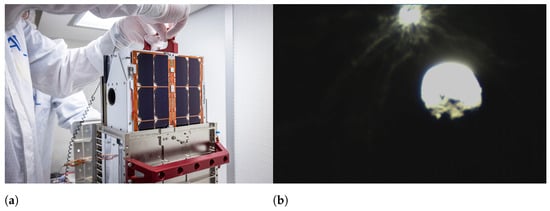
Figure 21.
(a) A stowed Light Italian CubeSat for Imaging of Asteroids (LICIACube) being integrated with the CubeSat dispenser carried by the main Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART) probe. Picture by NASA/Johns Hopkins APL/Ed Whitmanu [284]. (b) One of the pictures captured by the LICIACube on 26 September 2022, minutes after the impact of DART on the asteroid Dimorphos with the resulting dust plume being clearly visible. Picture by NASA/Agenzia Spaziale Italiana (ASI) [285].
As of the beginning of 2025, there are two more CubeSats underway to their asteroid destination. Both of these CubeSats are part of ESA’s HERA mission, which was launched on 7 October 2024. The HERA mission main probe is expected to rendezvous with the binary asteroid system 65803 Didymos on 28 December 2026 [286]. Following a successful rendezvous, HERA will begin investigating the effects DART’s kinetic impact had on the asteroid Dimorphos for a period of 6 months. Apart from its own instruments, the HERA probe also serves as a mother-ship carrying the Juventas and Milani 6U CubeSats. The two CubeSats will be deployed after the rendezvous to study the asteroid with their own instruments. The CubeSat Juventas has been developed by GomSpace and has the mission of the geophysical characterization of the Dimorphos binary system. Its main payload is the JuRa low-frequency radar which will be used to provide the first ever data of an asteroid’s subsurface and its internal structures. JuRa was developed by Institut de Planétologie et d’Astrophysique de Grenoble (IPAG) and EmTroniX (Hautcharage, Luxembourg). Juventas is also equipped with the Gravimeter for the Investigation of Small Solar System Bodies (GRASS), a collaboration of the Royal Observatory of Belgium (ROB) with EMXYS (Elche, Spain), via which it is expected to measure gravitational attraction, centrifugal forces, as well as tidal forces. Milani, on the other hand, has been developed by Tyvak International S.r.l. and its main mission involves the surface characterization and the mapping of the global composition of the Didymos asteroids. For this reason, Milani’s primary payload is the ASPECT hyperspectral imager which was developed by VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland Ltd (Espoo, Finland) and is equipped with spectral bands ranging from visible to SWIR wavelengths. The secondary scientific payload of the satellite is the Volatile In Situ Thermogravimetric Analyzer (VISTA) which will be used for the characterization of the dust clouds around the binary asteroid system. VISTA is capable of detecting dust particles smaller than 5 µm, detecting the presence of volatiles such as water while also being able to perform light organics characterization duties. Furthermore, both Juventas and Milani will be connected to the main HERA probe through ISL, and the three spacecraft together will be used for the measurement of the gravity field of the Didymos binary system through ISL Doppler. In the closing stages of the mission, the two CubeSats will also attempt to land on the Dimorphos asteroid, performing a very low speed impact. During the landing they will utilize their on-board accelerometers, gravimeters, and gyroscopes to measure the impact and bouncing properties, thus providing information about the surface response of the asteroid and by extension, its surface properties [287,288,289,290].
On 13 April 2029, the asteroid 99942 Apophis will approach the Earth at an extremely close distance, reaching a distance of about 32,000 km from the Earth’s surface during its closest approach [291]. This expected close approach of Apophis presents a window of opportunity for a variety of proposed missions targeting the asteroid. One of these proposed missions for the study of Apophis is Satis, a 12U CubeSat that would be tasked with mapping the asteroid’s inner structure, studying the properties of its regolith, as well as observing and documenting any changes that would occur to Apophis’s orbit as a result of its close approach to our planet. To achieve its mission objectives, Satis will be equipped with a hyperspectral imaging system capable of operating in both visible and NIR spectral ranges. Moreover, the satellite is expected to also be equipped with a thermal imaging system, with the inclusion of other secondary payloads such as a laser altimeter, a radar, or a gravimeter also being possible. In a manner similar to the missions of the CubeSats Juventas and Milani, the possibility of eventualy landing Satis on the asteroid is also discussed by the mission design team [292].
8. The Use of CubeSats in Novel Technology Demonstration Missions
In this final chapter, the use of CubeSat in technology missions will be explored. As already mentioned, their low-cost, rapid development, and inherent ability to reduce risks associated with the deployment of new technologies in space make CubeSats the perfect platforms for demonstrations. Given that traditional satellites have a much higher development cost and require significantly more time, it is of great challenge to use them for demonstration of emerging technologies efficiently. Before the in-space demonstration, CubeSats undergo several testing, verification, and validation procedures, to ensure the proper operation of their components under space environment conditions. One notable testing facility is the Zero-G Lab at the University of Luxembourg, which utilizes robotic manipulators to emulate zero gravity conditions [293,294]. It usually observed that after successful in space demonstrations in CubeSats, a lot of those technologies are deployed to larger satellites. Some missions mentioned in the previous sections were also demonstration missions. Missions such as ASTERIA, EQUULEUS, GomX-4, ISARA, MarCO, and Artemis I CubeSats for Lunar Demonstration are only some examples of them. However, in order to not perseverate, those missions will not be further analyzed. This section will be further subdivided into subsections for better categorization of the missions. Those categories are Propulsion and Maneuvering Demonstration, Communications, AI and Automation Technology Demonstration, Quantum Technology Demonstration, Space Environment and Radiation Testing, AI and Autonomy Demonstration, and Novel Mission Architectures and In-Orbit Demonstration.
8.1. Propulsion and Maneuvering Demonstration
The first type of demonstration missions that is going to be presented is missions involving propulsion and maneuvering in space. During space flight, it is essential to have controlled movements for maneuvering, station-keeping, docking into other satellites or space stations, re-entry into Earth’s atmosphere, and deep space exploration. One mission involving autonomous rendezvous and docking was the CubeSat Proximity Operations Demonstration (CPOD) [295]. Led by Terran Orbital and launched in May 2022, this mission aimed to demonstrate autonomous rendezvous, safe flying, and, finally, docking of two identical 3U CubeSats, using three-degree-of-freedom thrust control and a guidance, navigation, and control (GNC) framework for optimized fuel efficiency. These CubeSats were initially deployed as a single 6U configuration and then separated into two distinct 3U satellites to begin their mission. At first, they reduced their separation distance, then fine-tuned their relative positioning which established a stable formation that they maintained. Due to several hardware issues, the docking attempts were unsuccessful; however, CPOD validated critical rendezvous and proximity operations (RPO), paving the way for future missions. One other demonstration mission involving propulsion is the Vizard-ion CubeSat mission [296]. Developed by Russia’s MSU-STANDART and launched on 4 November 2024, it is a 3U nanosatellite designed to test the VERA plasma propulsion system. This system is an ablative pulsed plasma thruster, a compact and efficient propulsion technology suitable for small satellites. VERA operates by ablating a solid propellant to generate plasma pulses, providing thrust for orbital maneuvers and attitude control. The Vizard-ion mission aims to validate the performance of VERA in space, contributing to advancements in CubeSat propulsion capabilities. Additionally, the satellite carries a GNSS receiver for ionospheric studies and a 2-megapixel optical camera for Earth observation. One significant mission involving green propulsion is the AQT-D (Aqua Thruster-Demonstrator) mission [297]. Developed by the University of Tokyo, it demonstrated the use of a water-based propulsion system for CubeSats. Launched to the ISS in 2019, the 3U CubeSat carried the AQUA ResIstojet propUlsion System (AQUARIUS-1U), which utilizes less than 400 g of water to power one Delta-V Thruster (4 mN) and four Reaction Control Thrusters (1 mN each). The system heats injected water droplets in a vaporization chamber, expelling vapor through nozzles to produce thrust. This design enables precise thrust modulation, avoids nozzle icing, and uses water—a safe, storable, and abundant green propellant. On orbit, AQT-D conducted three test phases, including a 15-hour thrust operation that generated a 54 m/s delta-V, resulting in a 190 km orbital change. The propulsion system maintained three-axis control, demonstrating viability for extended CubeSat operations. With a specific impulse of ~70 s and a thrust-to-power ratio of 0.22 mN/W, AQUARIUS-1U marks a significant step in sustainable propulsion for small satellites. AQT-D’s success confirms that compact, green propulsion systems can support meaningful maneuvers and mission extensions, enabling broader applications for future space missions, including deep-space exploration.
Another mission that demonstrated re-entry capabilities was Technology Education Satellite-10 (TechEdSat-10) [298]. As part of the nanosatellite flight series TechEdSat by NASA Ames Research Center, this particular mission’s goal was to demonstrate the exo-brake technology. The exo-brake system had already been used in previous missions of this series; however, this was the largest up until then. The deployment sequence of the exo-brake can be seen in Figure 22. It was designed to deploy an umbrella-like sail to take advantage of the little atmosphere, in order to deorbit, in a controlled manner modulated from ground. This type of technology can play a significant role in the rising problem of space debris in the future.

Figure 22.
Exo-brake deployment during the Technology Education Satellite-10 (TechEdSat-10) mission, photo from ISS. Image credit: NASA [298].
Some notable missions involving novel propulsion systems are NanoSail-D2, Light-Sail 2, and Pathfinder Technology Demonstrator-1 (PTD-1). Launched in November 2010, NanoSail D-2 was a 3U CubeSat developed by NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center and Ames Research Center, with the primary mission of demonstrating the deployment of a solar sail in LEO [299,300]. Given that the sail operated without active attitude control, it provided substantial insight regarding its stability, the impact of solar radiation pressure, and aerodynamic drag. The sail also tested and validated the Triangular Rollable and Collapsible (TRAC) booms that successfully achieved passive deployment of the sail in approximately five seconds. Following this mission and LightSail 1, in June 2019, LightSail 2 was launched aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket, aiming for solar sailing demonstration [301]. Developed by The Planetary Society, this 3U CubeSat successfully deployed a 32 solar sail using TRAC booms. After the deployment and the resolving of some trivial deployment issues, LightSail 2 began its controlled sailing by orienting the sail to the Sun, effectively increasing its orbital energy, achieving measurable increase in its apogee while mitigating the orbital decay. This mission’s success proved that solar sails can effectively harness the solar photons’ pressure for sustainable propulsion. Another mission for sustainable propulsion was the Pathfinder Technology Demonstrator-1 (PTD-1) mission [302]. Launched in January 2021, this 6U CubeSat was a NASA initiative in collaboration with Tethers Unlimited, Inc. (Bothell, WA, USA) with the main objective of demonstrating, testing, and validating the HYDROS® propulsion system (Tethers Unlimited, Inc., Bothell, WA, USA) that used water electrolysis technology. After the electrolysis, hydrogen and oxygen gas were combusted in a bipropellant rocket nozzle, achieving a high specific impulse in the range of 223–241 s, close to the ground control testing. The propulsion systems occupied a volume of 2U and was subjected to multiple thrust events. Although the first event was unsuccessful, the following firings produced a substantial orbit change, validating the thruster’s ability to perform in space environment. The PTD-1’s successful demonstration set a major milestone for water propulsion systems in space, validating the feasibility of non-toxic, refuelable, and high efficiency propulsion for the next generation of space missions. Another two interesting cases are the InflateSail and DeorbitSail missions, which were pioneering European CubeSat projects developed by the Surrey Space Centre (SSC) at the University of Surrey, aiming to demonstrate innovative drag sail technologies for satellite deorbiting. InflateSail, launched in June 2017 as part of the QB50 program for the Von Karman Institute (VKI), Belgium, was a 3U CubeSat that deployed a 1-m inflatable boom and a 10 m2 drag sail, successfully re-entering the atmosphere just 72 days after launch. This marked Europe’s first successful demonstration of inflatable deorbiting technology [303]. DeorbitSail, funded by the European Commission’s FP7 program, also utilized a 3U CubeSat platform to test a larger 5 × 5 m gossamer sail supported by CFRP booms, with a complex deployment mechanism that included a translation stage and deployable solar panels which doubled as structural restraints. Both missions tackled the challenges of compact storage, precise deployment, and power management, validating the feasibility of lightweight deorbit systems to address space debris mitigation in line with international guidelines [304].
8.2. Communications, AI, and Automation Technology Demonstration
Moving on to demonstration missions involving communication technologies, one notable mission is the Pathfinder Technology Demonstrator-4 (PTD-4) [305]. Part of the PTD series, this 6U CubeSat was launched in August 2024, with the primary mission of demonstrating the Lightweight Integrated Solar Array and anTenna (LISA-T), which is essentially a deployable and high-power solar array with an X-band antenna combination. This system provides both enhanced power generation and high data rate communication, essential characteristics for extended missions. The PTD-4 CubeSat with its deployed arrays can be seen in Figure 23. Initial flight data has confirmed the proper function of on-board electronics; however, some challenges are observed in the full extension of the solar power and communication arrays [306]. This in-orbit demonstration provides useful insight regarding the performance as well as the challenges related to this type of deployable system.

Figure 23.
Pathfinder Technology Demonstrator-4 (PTD-4). Image credit: Terran Orbital Corporation [307].
One other ground-breaking mission was -Sat-1 (PhiSat-1) mission developed by ESA in collaboration with Ubotica Technologies (Dublin, Ireland) [308]. Launched in September 2020, this 6U platform was part of the Federated Satellite Systems (FSSCat) mission, with the main objective of demonstrating how Artificial Intelligence (AI) can be used on-board an Earth observation satellite. To validate the usage of AI for the detection of clouds in observation images, a feature that reduces the unnecessary data sent to ground allowing for more efficient and fast data delivery, it utilized an Intel® Movidius™ Myriad™ 2 vision processing unit (Intel, Santa Clara, CA, USA) and a deep convolutional network, known as CloudScout. It was validated that this combination of hardware and AI is feasible, since the data was processed in-orbit and then sent back to Earth, with a much-reduced data volume and high accuracy in cloud detection. -Sat-1 also demonstrated that integrating AI in on- board decision making in CubeSat operations can reduce their ground control dependence. Built upon this mission’s success, ESA developed -Sat-2 (PhiSat-2) [309]. Launched in August 2024, this 6U CubeSat’s innovation is the implementation of a convolution autoencoder image compression algorithm, tailored to the computational constraints of the CubeSat platforms, used for on-board image compression. The OBS was tested in three environments, a graphic processing unit (GPU), a vision processing unit (VPU), and a central processing unit (CPU), with the VPU-models requiring lower power but more time in comparison with the GPU-models. -Sat-2 successfully validated the AI compression algorithms, both reducing the transmission load and the computational load for in ground processing. One mission demonstrating automation technologies in CubeSats is the Starling mission, by NASA’s Ames Research Center, in collaboration with Stanford University, Blue Canyon Technologies and CesiumAstro (Austin, TX, USA) [310]. Using four 6U CubeSats, that were launched in July 2023 aboard a Lab Electron Rocket, this mission had four objectives: the Mobile Ad-Hoc Networking (MANET), the Distributed Spacecraft Autonomy (DSA), the Starling Formation-Flying Optical Experiment (StarFox), and the Reconfiguration and Orbit Maintenance Experiments Onboard (ROMEO). Each CubeSat was equipped with deployable solar panels, star trackers, reaction wheels, GPS and S-band antenna, a cold-gas propulsion system (HAMLET), a Xiphos Q75 processor, and a CesiumAstro CommPack crosslink radio. In MANET, CubeSats formed a network that could achieve >90% reliability and could support data transfers up to 50 kB. During DSA, CubeSats coordinated autonomously data collection for studying the ionospheric electron density variations and dynamically adjusted the measurement strategies. In StarFox, they could track each other’s orbits without GPS, with the orbit estimates within 1% accuracy. Finally, in ROMEO, they did not manage to autonomously plan and perform propulsive maneuvers to maintain swarm formation due to navigation filter errors. The Starling mission, despite ROMEO’s challenges, was a major step towards future deep-space swarm missions.
8.3. Space Environment and Radiation Testing
Moving on to CubeSats focused on demonstrating and testing of space environment and radiation, these satellites can test and validate the performance of radiation hardened components, error mitigation algorithms and technologies, as well as a variety of different shielding techniques. This way, radiation tolerant electronic systems can be tested in the real space environment in a cost effective and efficient manner before being incorporated into larger platforms and more complex space missions. One notable mission is Dellingr, which can be seen in Figure 24a, a 6U CubeSat launched in August 2017 aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 [311]. The primary mission focused on demonstrating and enhancing the reliability of small satellite platforms while also conducting space weather research. It was constructed containing both COTS and custom hardware with the main objective of ensuring high reliability. Dellingr contained to primary scientific instruments, the Ion-Neutral Mass Spectrometer (INMS) and a miniaturized fluxgate magnetometer system. The INMS was used to study space weather phenomena by measuring the composition in ion and neutral particles in the thermosphere and ionosphere. The fluxgate magnetometers, with two of them placed inside the CubeSat and one on a deployable boom, were designed to test the magnetic field variations; also, they tested a software-based interference compensation technique targeting of replacing the external booms in future missions. The INMS succeeded in collecting atmospheric data, the fluxgate magnetometers provided useful data and validated the uses compensation technique, and overall, Dellingr maintained higher reliability in comparison with other CubeSats. Another mission studying the radiation belt is the Compact Radiation Belt Explorer (CeREs) [312]. Launched in July 2018, this 3U CubeSat was developed by NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in collaboration with the Southwest Research Institute to study the acceleration and loss of high energy electrons in the Van Allen Belt and the transport of solar energetic particles into Earth’s magnetosphere. With the primary goal of improving our understanding of space weather phenomena impacting satellites, CeREs was equipped with the Miniaturized Electron and Proton Telescope (MERiT), a compact particle detector capable of detecting suprathermal to relativistic electrons (approximately 5 keV–8 MeV) and energetic protons (approximately 200 keV–100 MeV).This mission successfully demonstrated high-cadence electron measurements in high resolution, confirming that microbursts are a dominant mechanism for loss in radiation belt electrons, as well as provided insight on how protons with high energy penetrate Earth’s magnetosphere. Another notable mission is TRISAT-R (also denoted as TRISAT 2), a 3U CubeSat developed by the University of Maribor in collaboration with SkyLabs (Maribor, Slovenia) under the coordination of ESA and the Slovenian Ministry of Economy [313,314]. TRISAT-R can be seen in Figure 24b and it was tasked with the mission of investigating and mapping ionizing radiation in MEO by using several scientific instruments. Furthermore, the satellite was tasked with testing and demonstrating AI algorithms on high-performance COTS electronics and error mitigation techniques in the high ionizing radiation environment of MEO. TRISAT-R was launched on 13 July 2022 and remains operational as of mid-2025 with no critical radiation-based anomaly having so far been observed, its longevity serving as a testimony to the effectiveness of the radiation hardening measures applied. Another similar example is MTCube 2, a 1U CubeSat developed by the University of Montpellier under the mission of measuring the rate and mapping the distribution of errors on different types of memory storage due to radiation exposure in space over a period of two months [315].
Figure 24.
(a) Dellingr CubeSat, seen in the lab before launch. Image credit: NASA [316] (b) TRISAT-R. Image credit: Skylabs [317].
8.4. Quantum Technology Demonstration
The next demonstration mission type that is going to be presented is quantum technology demonstration without Earth’s atmosphere interference. Studying quantum effects, such as entanglement and super position, not only can deepen our knowledge regarding these fundamental physics phenomena but also provide useful solutions in quantum communication and quantum sensing. A pioneering CubeSat mission in this field is the SpooQy-1 mission, which refers to a 3U CubeSat developed by Quantum Technologies (CQT) at the National University of Singapore, in collaboration with SpeQtral (Connexis, Singapore) and other academic institutions [318]. SpooQy-1 was launched in August 2019, with the primary objective of demonstrating generation and polarization measurements of entangled photon pairs in orbit. The primary payload was the Small Photon-Entangling Quantum System-2 (SPEQS-2), which created polarization-entangled photon pairs. To test the quality of entanglement, the Bell’s inequality test was utilized. While in the best result, a Clauser–HorneShimony–Holt (CHSH) parameter value of 2.6 (plus minus 0.06) was achieved, confirming the quantum entanglement generation in space. The success of this mission paved the road for two upcoming and related demonstration missions, the SpeQtre, which will demonstrate Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) from space, using BBM92 protocol and SpeQtral-1, which aims to validate global QKD from space by testing and demonstrating QKD using both BBM92 and BB84 protocols [319]. One other upcoming mission is Responsive Operations and Key Services (ROKS) [320]. This 6U CubeSat is developed by Craft Prospect Ltd (Glasgow, UK) (CPL) in collaboration with University of Bristol and University of Strathclyde. Expected to be launched in 2025, its primary mission is to demonstrate QKD in night and cloud detection capabilities in an attempt to optimize secure quantum communication between space and Earth. Planned to operate in a Sun-synchronous 500 km orbit, it will utilize the Joint Alignment, Diode Emitter (JADE) module, necessary for the BB84 protocol, and an optical module named the GNEISS for Generating New and Extended Independent Signal States, with the goal of transmitting quantum signals through an optical beam steering system. Achieving the necessary pointing accuracy was one of the biggest challenges, however ROKS can overcome this by utilizing a mirror system to align the emitted signals to an uplink beacon from the ground station. If ROKS successfully demonstrates its objectives, it will set a milestone for CubeSat based quantum communication with enhanced cybersecurity with reduced reliance to fiber based QKD networks.
8.5. Novel Mission Architectures and In-Orbit Demonstration
In this final section, CubeSat demonstration missions with novel mission architectures will be discussed. One type of novel mission architecture is the asteroid exploration. One such mission is the NEA Scout, as previously mentioned, that intended to travel slowly past and near-Earth asteroid, utilizing a solar sail, in order to demonstrate solar sailing feasibility and gather detailed images from the asteroid. Despite its unsuccessful mission, it paved the way for the upcoming missions of HERA and Juventas, both aiming for asteroid exploration. One other notable mission is Brokkr-1, a pioneering mission from AstroForge (Huntington Beach, CA, USA) [321]. Launched in April 2023, this mission’s primary objective was to demonstrate the feasibility of asteroid mining, using in-space refinery technology. This mission was not successful since the establishment of a command uplink to activate the refinery payload was not achieved. However, building upon the lessons learned, AstroForge initiated their second mission, Odin, but this time, they did not select a CubeSat platform for this demonstration. Another novel mission architecture is that of MakerSat-0 [322]. Launched in November 2017, this 1U CubeSat was developed by Northwest Nazarene University and it was designed to study how the 3D printed polymers are degrading over time in space. Given the rise of 3D printing technology and the expansion of its potential applications in space, the commonly used materials’ degradation rate is a topic that needs to be investigated. MakerSat-0 contained two main experiments, the polymer degradation experiment, to assess mass loss and erosion on ABS, Nylon12, PEI/PC and PLA samples, and an ionizing radiation particle counter, to measure the in-orbit radiation level. From the results, it was found that PLA was the most robust polymer, with no measurable mass loss, while Nylon12 was the least robust, losing approximately 40% of its mass. The lessons learned from this mission also were utilized in the follow up mission MakerSat-1 [323]. It was launched in December 2019 and delivered to the ISS, but contrary to any other CubeSat, MakerSat-1’s structure was 3D printed in ISS using the on-board Additive Manufacturing Facility (AMF). The CubeSat was then snap-assembled and deployed in a 480 km orbit. Its scientific mission was to test the durability of PLA, PEI/PC, and ABS samples exposed in the space environment with harsh temperatures and radiation conditions. Once again, PLA was the most resilient of them with 9.9% mass loss while ABS performed the worst with 26.5% mass loss. MakerSat1’s successful demonstration set a milestone for in-space manufacturing, assembling and testing, while the results have influenced future 3D printing in the ISS.
9. Review Conclusions and Discussion
This section is dedicated to the discussion of the findings of the review of each CubeSat application field and some attempts to draw possible conclusions for the role of CubeSats in space exploration and utilization during the present as well as the immediate future. Thus, the present Section is divided into distinct subsections dedicated to each individual CubeSat application field that has been analyzed in the present work.
9.1. CubeSats in Earth Observation and Earth Science Missions
Since the advent of CubeSats, Earth observation and science has been one of the primary fields in which these platforms are employed in, with the number of satellites of this category eclipsing all the other ones. Over the years, a considerable number of missions has been undertaken with the goal of testing and demonstrating the operation of a variety of passive Earth observation instruments such as imagers, spectrometers which operate in the visual or IR bands, radiometers, as well as radar imaging instruments. Through these missions, the quality and effectiveness of such payloads have steadily improved, eventually leading to an array of mature, high-performance commercially available products such as cameras and spectrometers from a variety of different suppliers. The existence of such commercial products has contributed to the exponential rise of new Earth observation CubeSat missions, lowering the barrier of entry into the Earth observation sector and enabling institutions with otherwise limited monetary and technical resources to develop Earth observation missions of their own. Moreover, the low costs associated with the design, manufacturing, and launch of CubeSats have facilitated the creation of large constellations that are aimed at providing continuous data of the surface of the planet regarding applications such as terrain visual imaging and wildfire monitoring through the use of TIR instruments.
Apart from optical instruments, microwave sensory instruments have also been utilized by CubeSats as a means of Earth observation. More specifically, due to their low power consumption, passive microwave instruments have been heavily utilized by Earth observation and imaging CubeSat platforms, with notable examples being scatterometers which are used for missions that involve altimetry and terrain mapping through the use of the GNSS-R technique. Furthermore, despite their small size and low electrical power generation capacity, some active radar sensors have also been successfully incorporated in CubeSat missions, with a notable example being JPL’s RainCube mission which used a deployable Ka-band active mesh reflector antenna to observe precipitation processes. Moreover, as of 2025, there have been a variety of CubeSat platforms under development that aim to utilize active radar sensors in the form of SAR for Earth imaging missions from LEO altitudes. It should be noted that these SAR CubeSat concepts do not only encompass single-platforms demonstration missions but relatively large constellations as well, something that suggests a considerable degree of miniaturized SAR technology maturity.
Furthermore, in a manner similar to their large counterparts, Earth observation CubeSats have also been widely employed in the field that is dedicated to atmospheric condition and weather monitoring with Spire Global’s Lemur constellation being a well-known example, utilizing the GNSS-RO technique to access the conditions of the atmosphere and ionosphere. Another prominent example is NASA’s TROPICS constellation that utilizes radiometry to perform remote measurements on the generation and evolution of tropical storms. Furthermore, new commuted cloud tomography technologies are going to be demonstrated in the immediate future by the CloudCT mission and if they prove feasible, these new atmospheric condition monitoring technologies will help in refining the accuracy of weather monitoring and forecasting. The success of CubeSats in this specialized subfield of Earth observation is reasonable as CubeSat platforms can form the cornerstone of medium and large atmospheric monitoring constellations that provide continuous, real-time atmospheric condition data flows over large areas and therefore significantly improve weather monitoring and prediction capabilities. Therefore, the number of atmospheric research CubeSats is most certainly expected to rise significantly over the next decade.
Finally, as highlighted by the success of the QB50 mission, CubeSats can also be used as distributed cost-effective scientific measurement instruments for cutting-edge missions that may shed light to otherwise insufficiently studied regions of the Earth’s thermosphere. This success has facilitated the development of a variety of different scientific CubeSat missions which are intended for the performance of cutting-edge research tasks in a cost-effective and efficient manner, supplementing or even substituting the work of more advanced traditional satellite platforms.
9.2. The Role of CubeSats in the Telecommunication and Asset-Monitoring Fields
Despite the fact that CubeSats, due to their small size and subsequent low power generation and storage capability, are not able to directly compete with their larger counterparts for applications that require high bandwidth and data-rate capabilities, especially in the radio-spectrum telecommunication field, gradually, communication hardware miniaturization and developments made through technology demonstration missions have enabled CubeSats to find a role in certain telecommunication applications such as IoT, AIS, and ADS-B services that mainly require less bandwidth and data-rate hardware performance compared to other telecommunication applications. For such applications, CubeSats represent excellent choices as they enable the fast and affordable creation of large constellations that consist of dozens or even hundreds of CubeSats and are therefore capable of providing global connectivity coverage. With the inevitable further refinement of miniaturized communication technologies, the number of radio-based telecommunication CubeSats in orbit is most certainly expected to rise in the following years. However, the emergence of dedicated large telecommunication constellations that consist of larger and more capable satellite platforms that provide global coverage, such as SpaceX’s Starlink and Amazon’s Project Kuiper, should be expected to significantly hamper the widespread adoption of CubeSats as space-based telecommunication platforms.
On the other hand, as demonstrated by the series of successful and sometimes even record-setting laser-optical communication demonstration missions that so have so far been completed, the emergence and proliferation of miniaturized laser-optical communication technologies which are capable of enabling very-high data transmission rates with regards to hardware size and power consumption when compared to radio wave telecommunication hardware has the potential to enable CubeSats in undertaking a much more significant role in future space-based telecommunication networks as low-cost distributed instruments of large telecommunication constellations comprising solely by CubeSats or by a mixture of CubeSats and large satellite platforms. Furthermore, should proposed CubeSat technology demonstration mission concepts around omnidirectional laser-optical communication technologies such as the Q4 materialize and prove successful, new horizons in the field of laser-optical communication will be opened, enabling CubeSats to form large laser-optical communication constellations capable of simultaneously performing and maintaining inter-satellite and space-to-ground laser-optical communication links.
9.3. CubeSat Missions Dedicated to Astronomical and Heliophysics Research
Traditionally, astronomical research relied on large and complex space observatories based on the ground and large and costly space-based platforms. However, CubeSats have once again proven themselves as suitable and cost-effective platforms for in-space astrophysical studies.
By utilizing IR/VIS/UV telescopes, they have showcased their capabilities on detecting exoplanets transits and stellar radiation environments, providing valuable insight on planetes’ atmospheres and also evaluating star-planet interactions. Apart from optical telescopes, CubeSats have been using X-ray and gamma-ray detectors to study high-energy phenomena, related to solar activity and present in galactic structures. In addition, CubeSats have been utilized in radio astronomy applications and heliophysics studies. By studying and monitoring solar energetic particles, as well as monitoring the dynamics present in the radiation belts, CubeSats aid the prediction of space weather that can impact satellite operation and even astronaut safety. Finally, missions incorporating constellations have demonstrated the feasibility of a small fleet of CubeSats functioning as a unified large-scale observatory.
Despite the observed challenges in several missions, such as the high pointing accuracy need and the limited aperture size based on the platforms’ size, CubeSats are, can, and will revolutionize in-space astronomical research. By incorporating advanced optics, novel AI driven automations and distributed sensor networks in constellations, they can function as high-precision and scalable astronomical observatories.
9.4. Chemical and Biological Experimentation in Space Using CubeSat Platforms
In recent years, CubeSats have been also used as platforms for in-space chemical and biological experimentation, given their low-cost and autonomous operation. Insights provided by these studies can help the understanding of the impact of prolonged space exploration.
Several missions have conducted biological experimentation, demonstrating how microorganisms, such as E. coli and yeast respond into microgravity conditions. These pioneering missions collected useful data regarding gene expression, microbial growth, as well as drug resistance in space, with direct implications for human health during spaceflight. Other missions focused on the survivability of bacteria in long-term missions, confirming their enhanced resistance in space environment. This poses a potential challenge that needs to be investigated for future missions. Equipped with lab-on-chip technologies, other CubeSats have demonstrated their competence as compact biological research platforms. Finally, CubeSats have also been used to study how space radiation and cosmic rays impact microorganisms’ DNA as well as how they influence the degradation of organic molecules.
This type of CubeSat mission may be of the greatest importance regarding the future of space exploration. Understanding how the space environment impacts microorganisms, DNA expression, the degradation rate of molecules, and drug resistance will play a significant role in creating compensation strategies, making the overall space missions safer for humans. Any upcoming mission for prolonged time periods should incorporate all the insights from these experiments as well as strategies to mitigate the observed challenges.
9.5. The Utilization of CubeSats in Deep-Space Exploration Missions
For lunar exploration, CubeSat missions such as CAPSTONE have successfully demonstrated technologies which have paved the way for the manned exploration of the moon through the Artemis program and the upcoming assembly of the Lunar Gateway space station. Furthermore, the partial successes of certain Artemis I missions such as LunIR and LunaH-Map have demonstrated the successful integration and operation of cutting-edge scientific instruments on CubeSat platforms proving that CubeSats can be used as cost-effective lunar exploration platforms that are capable of incorporating state-of-the-art sensory instruments. Moreover, with humanity’s renewed interest in the exploration of the Moon, the continuation of the Artemis program as well as the Chinese lunar exploration program, the number of lunar exploration CubeSat missions should be expected to rise exponentially over the next decade. However, it should be noted that the considerably high number of failed and partially successful lunar exploration missions that have been undertaken to this day all but illustrates the difficulties and dangers associated with deep space exploration missions. But, even in this way, it provides the space science and engineering communities with important lessons that will undoubtedly lead to design refinement and improvements that may elevate the success prospects of future lunar and other deep space exploration missions.
For the exploration of other planets of our solar system, only a single mission has so far been undertaken, MarCO. Its noteworthy success has, however, clearly demonstrated that CubeSat platforms have the potential to perform important tasks as parts of large and complex space exploration missions as well as effectively communicate with the Earth from distances of tens of millions of kilometers despite their compact size and low power. This success will most certainly pave the way for a variety of other planetary exploration CubeSat missions over the next years as a variety of mission concepts involving the use of CubeSats for planetary exploration are, as of 2025, under design or development.
Similarly, regarding asteroid exploration missions, the inclusion of CubeSat platforms in two of the most prominent planetary defense missions that have ever been undertaken, namely NASA’s DART and ESA’s HERA, along with the results of the first, signify that CubeSats are capable of being effectively used as distributed nodes of complex, cutting-edge space exploration missions and efficiently perform crucial scientific tasks, gathering never-before acquired scientific data from objects located millions of kilometers away from the Earth. These successes, along with opportunities such as the expected close approach of the asteroid 99942 Apophis to the Earth on 13 April 2029 are expected to facilitate the development of a large number of new asteroid exploration CubeSat missions over the next decade and beyond.
9.6. CubeSats as Technology Demonstration Platforms
It is already known that CubeSat’s evolution has transformed how space missions are designed. Given their extremely low cost and development time in comparison to larger satellites, they can play a pivotal role in validating and testing novel technologies that can be scaled and transitioned to larger platforms.
Demonstrations in propulsion and maneuvering provide invaluable insight about autonomous operations, such as docking and formation maintenance which pave the way to less ground control-reliant operations, deorbiting strategies which tackle the challenges induced by space debris, and propulsion systems which can be efficient and sustainable, enabling deep-space exploration. Demonstrations in the use of AI technology in communication systems enable efficient data transmission, useful in several other missions. Furthermore, quantum technology demonstrations represent another frontier where CubeSats are making groundbreaking contributions. Studying quantum mechanics and specifically how they can be implemented to communication systems and protocols can lead to the creation of secure space networks, revolutionizing both Earth and space communication. Last but not least, CubeSats have been at the forefront of novel mission architectures, such as asteroid mining and exploration and in-space manufacturing, both leading to a new era in deep-space exploration.
It is evident that CubeSats have earned their position as indispensable tools for demonstrating, testing, and validating emerging technologies. One can say that almost every CubeSat mission is potentially a demonstration mission, since new manufacturing techniques, materials, and payloads are utilized on such cost and time efficient platforms. It is expected that as their capabilities grow, their role in supporting large-scale missions will become even more significant.
Furthermore, inter-satellite optical communication systems have progressed from theoretical concepts to flight-proven technologies, exemplified by NASA’s OCSD and MIT’s CLICK missions demonstrating data rates exceeding 200 Mbps with compact 0.5 W laser terminals weighing under 0.60 kg. These systems now leverage phase-shift keying modulation and wavelength-division multiplexing techniques previously reserved for larger platforms, enabling constellation-wide data sharing with minimal power consumption. Software-defined radio (SDR) technology has similarly matured, with platforms like the Ettus USRP B205mini and GomSpace’s SDR-100 supporting multi-band operations from VHF through Ka-band on a single hardware platform. These SDRs now commonly incorporate field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs) with radiation-aware design techniques, enabling in-orbit reconfiguration to adapt to changing mission requirements or mitigate detected anomalies.
Missions demonstrating radiation-hardened components can help in evaluating the space conditions and deepen our understanding of their impact, leading to safer operations for both systems and humans. Radiation-tolerant commercial electronics have narrowed the historical gap between commercial and space-grade components. Techniques such as triple-modular redundancy implementation at the firmware level, radiation-aware circuit layout, and selective shielding have been combined with commercial semiconductor processes like silicon-on-insulator (SOI) to create components that achieve total ionizing dose tolerance exceeding 30 krad(Si) at a fraction of traditional radiation-hardened component costs. The COTS-in-space approach has been validated by missions like ESA’s OPS-SAT and NASA’s CPOD, demonstrating commercial processors operating reliably in Low Earth Orbit for multi-year durations. Texas Instruments’ MSP430FR family of microcontrollers with ferroelectric RAM has become particularly popular for CubeSat flight computers, offering inherent radiation resistance while maintaining the low power consumption critical for CubeSat power budgets. These technological convergences have effectively raised the ceiling on CubeSat capabilities while simultaneously lowering the barrier to entry for organizations developing sophisticated space missions.
9.7. CDS Evolution and Regulatory Considerations
Currently, the CubeSat concept has gained traction beyond its original educational intent, mainly due to the enabling factors discussed in Section 2. The CDS has evolved accordingly in order to accommodate more complex and sophisticated missions, with recent major updates occurring in July 2020 (Rev. 14) and February 2022 (Rev. 14.1) [324]. Except from form factors dictation, CDS has introduced a series of testing protocols and safety measures, actively transforming it to a stabilizing force in a rapidly diversifying ecosystem. Future revisions will likely focus on enhancing interoperability standards between subsystems, accommodating the unique requirements of deep space missions, orbital debris mitigation measures, and guidelines for advanced propulsion technologies. In this sense, CDS exemplifies a rare balance between prescriptive engineering control and adaptive capacity, supporting the cohesive and safe expansion of the CubeSat market. CDS’s evolution will play a pivotal role in the upgrade of the CubeSats from standardized form to standardized function, which will ultimately lead to CubeSats serving as trusted platforms in the upcoming space economy.
Furthermore, the rapid proliferation of CubeSats has prompted significant regulatory responses worldwide, creating both challenges and opportunities for mission planners. Spectrum allocation has emerged as a critical constraint, with the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) and national regulatory bodies implementing streamlined filing procedures specifically for small satellites, though the growing congestion in popular frequency bands continues to challenge new entrants [325,326]. Orbital debris mitigation has similarly transformed from a secondary consideration to a primary design driver. For many years, a large number of space agencies and regulatory bodies required LEO CubeSats to demonstrate a 90% probability of atmospheric re-entry within 25 years of mission completion. However, with ever increasing satellite traffic in LEO, this 25-year period was not deemed adequate and on 29 September 2022, the US Federal Communications Commission (FCC) adopted a new rule for all the FCC-licensed satellites that are located in the LEO region that reduced the lifetime requirement to only 5 years after launch [327]. In a similar manner, ESA adopted the “Zero Debris approach” in 2025 in which it is stated that end-of-life time in LEO for all new ESA missions is reduced from the original 25 years to just 5 [328]. These strict regulations are driving innovations in deployable drag devices and propulsion systems for small satellites [329]. Several companies and institutions have already been implementing active and passive space debris removal systems. For instance, ClearSpace (Renens, Switzerland), a Swiss startup, is leading the ClearSpace-1 mission with the European Space Agency to actively remove space debris by capturing and deorbiting defunct satellites using a robotic arm system [330]. Another example is Astroscale (Tokyo, Japan), a Japanese company, who successfully demonstrated magnetic docking and deorbiting with its ELSA-d mission and is developing future missions like ADRAS-J2, which will use robotic arms for debris removal [331]. To further support these endeavors, passive systems for debris mitigation are developed, such as in the ESA-Dragliner project. Developed by the University of Luxembourg, in collaboration with the Finnish Meteorological Institute, it refers a passive deorbiting system employing a propellant-free plasma brake tether to safely deorbit satellites without using onboard resources [332]. Moreover, the Inter-Agency Space Debris Coordination Committee (IADC) guidelines [333] have been increasingly integrated into national licensing frameworks, while the United Nations Committee on the Peaceful Uses of Outer Space (UN COPUOS) has developed non-binding recommendations specifically addressing small satellite operations [334]. These evolving regulatory frameworks have necessitated more sophisticated mission planning tools and prompted universities and smaller organizations to form consortia to navigate compliance requirements. Despite these challenges, several jurisdictions have established regulatory sandboxes to enable innovative CubeSat missions while ensuring responsible operations, reflecting the delicate balance between fostering innovation and maintaining sustainable space activities.
9.8. CubeSat Platform Limitations and Intrinsic Challenges
The present study primarily highlighted the diverse mission and application fields CubeSat platforms can be employed in, along with some of the main reasons that have led to the widespread adoption of these spacecraft by space science and engineering entities such as commercial companies, space agencies, and educational institutions. However, during the review of all these examples of missions some cross-cutting challenges and limitations that affect the vast majority of CubeSat designs have also become apparent. Addressing these challenges through future research and subsequent technological breakthroughs would lead to even wider horizons for future CubeSat missions.
Perhaps the most significant limitation of CubeSat platforms was found to be their significantly constrained electrical power generation and storage capacity. This limitation can be attributed to the small area that is available for the installation of solar arrays on the exterior of these satellites and the limited volume available for the integration of energy storage cells. This bottleneck practically affects all CubeSat employment domains as it forces trade-offs between payload performance and mission lifetime. For example, capabilities of platforms used in the field of telecommunications are heavily impacted as transmission power is limited, while other types of CubeSats such as remote sensing and scientific ones are also affected as the mission-specific data-transmission rates they can achieve are also limited. Furthermore, remote sensing CubeSats are also affected by limited electrical power into mainly utilizing passive sensors such as imagers, spectrometers, and radiometers instead of LIDARs and active radar sensors which have, so far, not seen widespread adoption by the CubeSat industry. Such limitations could be mitigated to a degree in the following years through progressive advancements in the fields of electrical power engineering such as the introduction of higher energy density batteries and higher efficiency solar cells.
It must be noted that system miniaturization, which has enabled the accommodation of complex instruments and payloads by CubeSat platforms, also features notable drawbacks as it also encompasses certain trade-offs and cannot continue endlessly. This is mainly because the performance of certain systems is governed by physical limitations. For example, in the case of optical imaging instruments, image resolution is proportional to the optical aperture size [335]; therefore, smaller optical instruments will always yield a reduced performance compared to larger, same technology ones. Miniaturization adversely affects the performance of other remote sensing instruments such as spectrometers also [336]. In a similar manner, in the field of telecommunications, smaller antennas will feature a reduced gain and signal-to-noise ratio compared to larger ones [337]. Apart from the miniaturization of systems, the miniaturized nature of CubeSat platforms also introduces certain other physical and engineering challenges. For example, the high density of electronic components packed inside the satellite, coupled with the limited volume and area available for the implementation of thermal control measures, entails a high risk of overheating. Furthermore, from a systems engineering perspective, the small size of CubeSat platforms rarely allows for the inclusion of redundant systems, especially in the case of small and low-cost designs, something that introduces single-points-of-failure to the overall design of the satellite, jeopardizing long-term missions.
Other limitations of CubeSat platforms can also be pinpointed in the fields of attitude and orbit determination and control. Firstly, small CubeSats such as 1U and 2U ones, due to their compact size, often lack the means for precise attitude determination and control, thus limiting them to applications that do not require precise pointing capabilities of the satellite platform. Similarly, due to limited space again, a variety of CubeSats lack propulsive systems altogether or feature a very small propulsion system with limited v potential. In the case of LEO satellites this can be translated to reduced mission durations as the residual atmosphere drag effects lead to relatively quick orbital altitude degradation and eventual deorbit of the satellites. On the other hand, in the case of CubeSats used for interplanetary missions, this can be translated into a very limited v potential that is available to the satellite for the performance of trajectory correction, orbital insertion, and station keeping maneuvers.
The low cost of CubeSat development can in some cases be offset by other factors. For example, the industry-wide push for extensive use of low-cost, standardized COTS equipment can lead to high failure rates in demanding and radiation-heavy operational environments such as the Van Allen radiation belts or the interplanetary space, leading to duplicate costs because of the need for the development and launch of replacement missions, or to high initial development costs because of the need to incorporate high-cost, custom designed and built radiation tolerant components in the design of the satellite for the execution of such missions. Furthermore, to fully realize their potential, CubeSat constellations still require the design and construction of ground-based infrastructure which includes assembly, integration and testing facilities with adequate capacity, as well as a large number of dedicated ground-stations and the formation of networks. The establishment of such infrastructure is of course characterized by significant development and operation costs, something that can significantly offset the per-unit savings of the CubeSat constellations in question.
Author Contributions
Methodology, K.-P.B. and G.M.; investigation, K.-P.B. and G.M.; writing—original draft preparation, K.-P.B. and G.M.; writing—review and editing, V.K. and V.L.; supervision, V.K. and V.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
During the preparation of this manuscript/study, the authors used ChatGPT by OpenAI (version GPT-4o) and DeepSeek (version DeepSeek-V3) for supplementing the bibliographical review procedure, text refinement, and reference formatting. The authors have reviewed and edited the output and take full responsibility for the content of this publication.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Correction Statement
This article has been republished with a minor correction to the typo of Table 2. This change does not affect the scientific content of the article.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript. The list is limited only to acronyms of physical and engineering definitions, space science and engineering entities and other abbreviations commonly used in the field of astronautics. Acronyms such as mission and payload names are excluded as they may be found in the relevant sections of the main text.
| 3GPP | 3rd Generation Partnership Project |
| I2C | Inter-Integrated Circuit |
| ABS | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene |
| ADS-B | Automatic Dependent Surveillance–Broadcast |
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| AIS | Automatic Identification System |
| AOCS | Attitude and Orbit Control System |
| ASI | Agenzia Spaziale Italiana |
| ATF | Along-Track Formation |
| CAN Bus | Controller Area Network Bus |
| CDS | CubeSat Design Specification |
| CLSI | CubeSat Launch Initiative |
| CMOS | Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor |
| COMM | Communication System |
| COTS | Commercial of the Shelf |
| CPU | Central Processing Unit |
| CT | Computed Tomography |
| CZT | Cadmium Zinc Telluride |
| EPS | Electrical Power System |
| ESA | European Space Agency |
| ESPA | Evolved Expendable Launch Vehicle Secondary Payload Adapter |
| FCC | Federal Communications Commission |
| FPGA | Field-Programmable Gate Arrays |
| FUV | Far-Ultraviolet |
| GFP | Green Fluorescent Protein |
| GIRO | Global Ionospheric Radio Observatory |
| GNSS | Global Navigation Satellite System |
| GNSS-R | Global Navigation Satellite System Reflectometry |
| GNSS-RO | Global Navigation Satellite System Radio Occultation |
| GNC | Guidance, Navigation and Control |
| GPS | Global Positioning System |
| GSD | Ground Sampling Distance |
| GSFC | Goddard Space Flight Center |
| GPU | Graphic Processing Unit |
| GRBs | Gamma-Ray Bursts |
| I2C | Inter-Integrated Circuit |
| IADC | Inter-Agency Space Debris Coordination Committee |
| IDM | Ion Drift Meter |
| IEEE | Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers |
| INMS | Ion and Neutral Mass Spectrometers |
| INTA | Spanish Institute of Aerospace Technology |
| IOV | In-Orbit Validation |
| IOD | In-Orbit Demonstration |
| IR | Infrared |
| ISL | Inter-Satellite Link |
| ISR | Incoherent Scatter Radar |
| ISS | International Space Station |
| ITU | International Telecommunication Union |
| JAXA | Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency |
| JEM | Japanese Experiment Module |
| JPL | Jet Propulsion Laboratory |
| J-SSOD | JEM Small Satellite Orbital Deployer |
| LANL | Los Alamos National Laboratory |
| LEO | Low Earth Orbit |
| LET | Linear Energy Transfer |
| LIDAR | Light Detection And Ranging |
| LVF | Linear Variable Filter |
| LWIR | Long-Wave Infrared |
| MEO | Medium Earth Orbit |
| MIMO | Multiple-Input-Multiple-Output |
| MIT | Massachusetts Institute of Technology |
| MSFC | Marshall Space Flight Center |
| MWIR | Medium-Wave Infrared |
| NEA | Near-Earth Asteroid |
| NIR | Near-Infrared |
| NRCSD | Nanoracks CubeSat Deployer |
| NRHO | Near-Rectilinear Halo Orbit |
| NT | Non-Terrestrial |
| NUV | Near-Ultraviolet |
| OBDH | Onboard Data Handling |
| PEI/PC | Polyetherimide-polycarbonate |
| PLA | Polylactic acid |
| PNT | Positioning, Navigation and Timing |
| P-POD | Poly-PicoSatellite Orbital Deployer |
| PSDS3 | Planetary Science Deep Space SmallSat Studies |
| RAAF | Royal Australian Air-Force |
| RGB | Red-Green-Blue |
| RPA | Retarding Potential Analyzer |
| RPO | Rendezvous and Proximity Operations |
| SAR | Synthetic Aperture Radar |
| SDR | Software Defined Radio |
| SEPs | Solar Energetic Particles |
| SESLO | Space Environment Survivability of Living Organisms |
| SEVO | Space Environment Viability of Organics |
| SIMPLEx | Small, Innovative Missions for PLanetary Exploration |
| SHS | Spatial Heterodyne Spectrometers |
| SLS | Space Launch System |
| SPI | Serial Peripheral Interface |
| SSA | Space Situational Awareness |
| STRU | Structure |
| SWIR | Short-Wave Infrared |
| TCS | Thermal Control System |
| TIR | Thermal Infrared |
| TIRS | Thermal Infrared Spectrometer |
| TRL | Technology Readiness Level |
| TT&C | Telemetry, Tracking & Command |
| U | Unit (Basic CubeSat form factor) |
| UART | Universal Asynchronous Receiver-Transmitter |
| UHF | Ultra-High Frequency |
| ULA | United Launch Alliance |
| UN COPUOS | United Nations Committee on the Peaceful Uses of Outer Space |
| US | United States |
| UV | Ultraviolet |
| VHF | Very-High Frequency |
| VIS | Visible |
| VLF | Very-Low Frequency |
| VNIR | Visible and Near-Infrared |
| VPU | Vision Processing Unit |
| VUV | Vacuum Ultraviolet |
References
- Maini, A.K.; Agrawal, V. Introduction to Satellites and Their Applications. In Satellite Technology; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; Chapter 1; pp. 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konecny, G. Small Satellites—A Tool for Earth Observation. In Proceedings of the 20th ISPRS Congress, Commission 4, Istanbul, Turkey, 12–23 July 2004; pp. 580–582. Available online: https://www.isprs.org/proceedings/XXXV/congress/comm4/comm4.aspx (accessed on 12 January 2025).
- California Polytechnic State University. The CubeSat Program: CubeSat Design Specification, Rev. 14.1. Available online: https://www.cubesat.org/ (accessed on 5 July 2024).
- Wallops Supports Small Spacecraft Hitching Ride with Landsat 9. Available online: https://www.nasa.gov/centers-and-facilities/wallops/wallops-supports-small-spacecraft-hitching-ride-with-landsat-9/ (accessed on 12 January 2025).
- Nanoracks. CubeSat Services. Available online: https://nanoracks.com/wp-content/uploads/Cubesat-Services.pdf (accessed on 7 July 2024).
- JEM Small Satellite Orbital Deployer (J-SSOD). Available online: https://humans-in-space.jaxa.jp/en/biz-lab/experiment/facility/ef/jssod/ (accessed on 12 January 2025).
- Landsat 9 Small Satellite Deployment. Available online: https://images.nasa.gov/details/KSC-20210624-PH-JNN01_0003 (accessed on 12 January 2025).
- Libre Space Foundation. UPsat. Available online: https://libre.space/projects/upsat/ (accessed on 6 July 2024).
- Ippolito, L.J., Jr. Satellite Subsystems. In Satellite Communications Systems Engineering; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 35–48. [Google Scholar]
- Ampatzoglou, A.; Kostopoulos, V. Design, Analysis, Optimization, Manufacturing, and Testing of a 2U Cubesat. Int. J. Aerosp. Eng. 2018, 2018, 9724263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NASA. Artemis I. Available online: https://www.nasa.gov/reference/artemis-i/ (accessed on 10 July 2024).
- Blackwell, W.J.; Braun, S.; Zavodsky, B.; Velden, C.; Greenwald, T.; Herndon, D.; Bennartz, R.; DeMaria, M.; Chirokova, G.; Atlas, R.; et al. Overview of the NASA TROPICS CubeSat Constellation Mission. In Proceedings of SPIE 10769, CubeSats and NanoSats for Remote Sensing II; Pagano, T.S., Norton, C.D., Eds.; International Society for Optics and Photonics (SPIE): Bellingham, WA, USA, 2018; p. 1076908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NASA. NASA Selects CubeSat, SmallSat Mission Concept Studies. Available online: https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/news/nasa-selects-cubesat-smallsat-mission-concept-studies/ (accessed on 10 July 2024).
- Ledkov, A.; Aslanov, V. Hybrid Electrostatic Ion Beam Shepherd Schemes for Active Space Debris Removal from GEO to Disposal Orbit. Astrodynamics 2025, 9, 273–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Wang, Y.; Su, J.; Li, J.; Xu, M.; Bai, S. Relative Orbit Transfer Using Constant-Vector Thrust Acceleration. Acta Astronaut. 2025, 229, 715–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, T.K.; Akagi, J.; Droge, G. Model Predictive Control for Formation Flying Based on D’Amico Relative Orbital Elements. Astrodynamics 2025, 9, 143–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulu, E. Nanosats Database. Figures. Available online: https://www.nanosats.eu/#figures (accessed on 13 January 2025).
- Mathieu, E.; Rosado, P.; Roser, M. Space Exploration and Satellites. Our World in Data. 2022. Available online: https://ourworldindata.org/space-exploration-satellites (accessed on 13 January 2025).
- Mendoza-Hill, A. SMD Rideshare 101; NASA Science Mission Directorate: Washington, DC, USA, 2023. Available online: https://www.nasa.gov/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/rideshare-101-final.pdf (accessed on 13 January 2025).
- SpaceX. Transporter-1 Mission. 2021. Available online: https://www.spacex.com/launches/transporter-1-mission/ (accessed on 13 January 2025).
- SpaceX. SmallSat Rideshare Program. 2025. Available online: https://www.spacex.com/rideshare/ (accessed on 13 January 2025).
- Rocket Lab. In Focus Mission Overview. 2020. Available online: https://www.rocketlabusa.com/missions/missions-launched/in-focus/ (accessed on 13 January 2025).
- European Space Agency (ESA). Vega Return to Flight Proves New Rideshare Service. 2020. Available online: https://www.esa.int/Enabling_Support/Space_Transportation/Vega/Vega_return_to_flight_proves_new_rideshare_service (accessed on 13 January 2025).
- Grönland, T.-A.; Rangsten, P.; Nese, M.; Lang, M. Miniaturization of Components and Systems for Space Using MEMS-Technology. Acta Astronaut. 2007, 61, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadence PCB Solutions. Miniaturization of Satellite Technology Advancements. 2024. Available online: https://resources.pcb.cadence.com/blog/2024-miniaturization-of-satellite-technology-advancements (accessed on 13 January 2025).
- Kongsberg NanoAvionics. Mission Services. Available online: https://nanoavionics.com/mission-services/ (accessed on 13 January 2025).
- Poghosyan, A.; Golkar, A. CubeSat Evolution: Analyzing CubeSat Capabilities for Conducting Science Missions. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 2017, 88, 59–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puig-Suari, J.; Schoos, J.; Turner, C.; Wagner, T.; Connolly, R.; Block, R.P. CubeSat Developments at Cal Poly: The Standard Deployer and PolySat. In Small Payloads in Space, Proceedings of the SPIE Conference, San Diego, CA, USA, 30 July 2000; Horais, B.J., Twiggs, R.J., Eds.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2000; Volume 4136, pp. 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PC/104 Specification; Version 2.6; PC/104 Embedded Consortium: Sacramento, CA, USA, 2008; Available online: https://pc104.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/02/PC104_Spec_v2_6.pdf (accessed on 15 June 2025).
- Knap, V.; Vestergaard, L.K.; Stroe, D.-I. A Review of Battery Technology in CubeSats and Small Satellite Solutions. Energies 2020, 13, 4097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wikipedia Contributors. CSSWE CubeSat and PPOD Prior to Integration. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/CubeSat#/media/File:CSSWE_CubeSat_and_PPOD_prior_to_integration.png (accessed on 7 February 2025).
- Wikipedia Contributors. PC/104. Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/PC/104 (accessed on 13 January 2025).
- National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). CubeSat Launch Initiative Introduction. Available online: https://www.nasa.gov/cubesat-launch-initiative-introduction/ (accessed on 13 January 2025).
- European Space Agency (ESA). About Fly Your Satellite! Available online: https://www.esa.int/Education/CubeSats_-_Fly_Your_Satellite/About_Fly_Your_Satellite! (accessed on 13 January 2025).
- National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). Small Innovative Missions for Planetary Exploration (SIMPLEx). Available online: https://soma.larc.nasa.gov/simplex/ (accessed on 13 January 2025).
- ESA. Get Your Satellite Flight Ticket. Available online: https://www.esa.int/Enabling_Support/Space_Transportation/Boost/Get_your_satellite_flight_ticket (accessed on 6 May 2025).
- European Commission: Defence Industry and Space. (IOD / IOV) In-Orbit Demonstration/In-Orbit Validation. Available online: https://defence-industry-space.ec.europa.eu/eu-space/research-development-and-innovation/orbit-demonstration-and-validation-iodiov_en (accessed on 6 May 2025).
- JAXA. Innovative Satellite Technology Demonstration Program. Available online: https://www.kenkai.jaxa.jp/eng/research/innovative/innovative.html (accessed on 10 July 2024).
- Space-π. Research and Educational Project Space-π. Available online: https://en.spacepi.space/about/ (accessed on 2 June 2025).
- Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO). Official Website. Available online: https://www.isro.gov.in (accessed on 2 June 2025).
- China National Space Administration (CNSA). Official Website. Available online: https://www.cnsa.gov.cn/english/index.html (accessed on 2 June 2025).
- Golkar, A.; Salado, A. Definition of New Space—Expert Survey Results and Key Technology Trends. IEEE J. Miniaturization Air Space Syst. 2021, 2, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Union Agency for the Space Programme (EUSPA). What Is Earth Observation? Available online: https://www.euspa.europa.eu/eu-space-programme/copernicus/what-Earth-observation (accessed on 15 October 2024).
- Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA). Earth Observation Satellites. Available online: https://earth.jaxa.jp/en/eo-knowledge/eosatellite-type/index.html (accessed on 15 October 2024).
- CAST Navigation. GNSS in Earth Science Research: GNSS-RO, GNSS-R, and GNSS-GR. Available online: https://castnav.com/gnss-in-earth-science-research-gnss-ro-gnss-r-and-gnss-gr/ (accessed on 14 October 2024).
- Freeman, A.; Malphrus, B.K.; Staehle, R. CubeSat Science Instruments. In Cubesat Handbook; Cappelletti, C., Battistini, S., Malphrus, B.K., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 67–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulu, E. Nanosats Database. CubeSat Instruments List. Available online: https://www.nanosats.eu/tables#instruments (accessed on 15 October 2024).
- Simera Sense. Camera Products. Available online: https://simera-sense.com/cameras/ (accessed on 15 April 2025).
- Dragonfly Aerospace. Cubesat Cameras Product Information. Available online: https://dragonflyaerospace.com/products/ (accessed on 15 October 2024).
- Dragonfly Aerospace. Chameleon SWIR Product Information. Available online: https://dragonflyaerospace.com/products/chameleon-swir/ (accessed on 15 October 2024).
- Satlantis. Space Cameras Product Information. Available online: https://www.satlantis.com/space-cameras/ (accessed on 15 October 2024).
- ThothX (ARG2). Argus IR Spectrometers. Available online: https://www.thothx.com/technology/argus (accessed on 15 October 2024).
- Rincón-Urbina, S.R.; Cárdenas-García, J.M.; Pirazán-Villanueva, K.N.; Acero-Niño, I.F.; Hurtado-Velasco, R.H.; Cortés-García, E.D. Critical Design of the FACSAT-2 Mission CubeSat for the Observation and Analysis of the Colombian Territory. Revista UIS Ingenierías 2023, 22, 69–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO). SATHYABAMASAT. Available online: https://www.isro.gov.in/SATHYABAMASAT.html (accessed on 2 June 2025).
- Krebs, G.D. SathyabamaSat (SB Sat). Gunter’s Space Page. Available online: https://space.skyrocket.de/doc_sdat/sathyabamasat.htm (accessed on 2 June 2025).
- Sputnix. Satellites|Launched Missions|OrbiCraft-Zorkiy. Available online: https://sputnix.ru/en/satellites-sputnix/in-orbit/cubesat-6u (accessed on 2 June 2025).
- Kulu, E. Nanosats Database. OrbiCraft-Zorkiy Spacecraft. Available online: https://www.nanosats.eu/sat/orbicraft-zorkiy (accessed on 2 June 2025).
- Sputnix. Satellites|Launched Missions|Zorkiy-2M. Available online: https://sputnix.ru/en/satellites-sputnix/in-orbit/zorkij-2m (accessed on 2 June 2025).
- Kulu, E. Nanosats Database. Zorkiy-2M Spacecraft. Available online: https://www.nanosats.eu/sat/zorkiy-2m (accessed on 2 June 2025).
- Satlantis. HORACIO Successfully Launched. Available online: https://www.satlantis.com/horacio-successfully-launched/ (accessed on 9 October 2024).
- eoPortal. ANSER (Advanced Nanosatellite Systems for Earth-Observation Research) Satellite Mission. Available online: https://www.eoportal.org/satellite-missions/anser (accessed on 9 October 2024).
- European Space Agency (ESA). Vega’s Fuel-Free CubeSats to Keep Formation with Wings. Available online: https://www.esa.int/Enabling_Support/Space_Engineering_Technology/Vega_s_fuel-free_CubeSats_to_keep_formation_with_wings (accessed on 9 October 2024).
- Sánchez-Sevilleja, S.; Poyatos, D.; Masa-Campos, J.L.; Aragón, V.M.; Rodríguez, J.A.; Santiago, A. Design, Development, and Qualification of a Broadband Compact S-Band Antenna for a CubeSat Constellation. Sensors 2025, 25, 1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Oghim, S.; Mun, M.; Bang, H. A Scheduling Optimization Using Greedy Knapsack Algorithm for RANDEV CubeSat Communication and Observation Missions Analyzed with MBSE Activity Diagram. In Proceedings of the Accelerating Space Commerce, Exploration, and New Discovery Conference (ASCEND 2020), Virtual Event, 16–19 November 2020; American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics: Reston, VA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OroraTech. Forest-1 Mission Success: A Giant Leap for OroraTech. Available online: https://ororatech.com/forest-1-mission-success-a-giant-leap-for-ororatech/ (accessed on 13 October 2024).
- Fernandes, D.R.; Seifert, M. Towards a Constellation of TIR Sensors for Wildfire Detection: First Results of FOREST-1. In Proceedings of the VH-RODA 2022 Workshop, Frascati (Rome), Italy, 7–10 November 2022; Available online: https://earth.esa.int/eogateway/documents/20142/4139742/2.07_VH-RODA%202022%20-%20Thermal-IR%20Wildfire%20detection%20-%20DRFernandes.pdf (accessed on 13 October 2024).
- Spire Global. Leading Wildfire Monitoring Provider OroraTech Partners with Spire to Launch First Satellite in 2021. Press Release. Available online: https://spire.com/press-release/leading-wildfire-monitoring-provider-ororatech-partners-with-spire-to-launch-first-satellite-in-2021/ (accessed on 13 October 2024).
- OroraTech. Countdown to Liftoff: Retracing the FOREST-2 Thermal Sensor Launch into Orbit. Available online: https://ororatech.com/resources/news-blog/countdown-to-liftoff-retracing-the-forest-2-thermal-sensor-launch-into-orbit (accessed on 15 October 2024).
- Miles, A.; Maranto, D.; Xu, S.; Liang, R.; Li, Y.D.; Rock, J.; Imrit, A.A.; Kou, M.; Fatima, A.; Kasum, A.; et al. FINCH: A Blueprint for Accessible and Scientifically Valuable Remote Sensing Missions. In Proceedings of the 36th Annual Small Satellite Conference, Logan, UT, USA, 6–11 August 2022; Utah State University: Logan, UT, USA, 2022. Paper ID: SSC22-WKVII-04. Available online: https://digitalcommons.usu.edu/smallsat/2022/all2022/88/ (accessed on 15 October 2024).
- European Space Agency (ESA). Technology CubeSats | VULCAIN. Available online: https://www.esa.int/Enabling_Support/Space_Engineering_Technology/Technology_CubeSats/VULCAIN (accessed on 15 October 2024).
- Buongiorno, M.F.; Lavagna, M.R.; Labate, D.; Tudor, S.V.; Masini, A.; De Carlo, P.; Romaniello, V.; Silvestri, M.; Pirat, C. VULCAIN: A CubeSat Mission for Monitoring Volcanoes and Active Thermal Areas. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2023—IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Pasadena, CA, USA, 16–21 July 2023; pp. 265–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planet Labs PBC. Planet to Launch 36 SuperDove Satellites with SpaceX. Available online: https://www.planet.com/pulse/planet-to-launch-36-superdove-satellites-with-spacex/ (accessed on 9 October 2024).
- Gutierrez Ahumada, J.A.; Doerksen, K.; Zeller, S. Automated Fleet Commissioning Workflows at Planet. In Proceedings of the 35th Annual Small Satellite Conference, Logan, UT, USA, 7–12 August 2021; Paper ID: SSC1-XII-04. Available online: https://digitalcommons.usu.edu/smallsat/2021/all2021/214/ (accessed on 9 October 2024).
- Kulu, E. Nanosats Database. Dove Flock Satellite Constellation. Available online: https://www.nanosats.eu/sat/dove-flock (accessed on 9 October 2024).
- OroraTech. OroraTech Launches FOREST-3 with SpaceX: Their Latest Pioneering Thermal Satellite for Wildfire Detection. Available online: https://ororatech.com/resources/news-blog/ororatech-launches-forest-3-with-spacex-their-latest-pioneering-thermal-satellite-for-wildfire-detection (accessed on 14 April 2025).
- OroraTech. OroraTech Receives inCubed Co-Funding for Wildfire Monitoring Constellation. Available online: https://ororatech.com/ororatech-receives-incubed-co-funding/ (accessed on 14 April 2025).
- SpaceWatch Global. OroraTech Accelerates Deployment of Its Thermal Satellite Constellation. Available online: https://spacewatch.global/2022/10/ororatech-accelerates-deployment-of-its-thermal-satellite-constellation/ (accessed on 14 April 2025).
- OroraTech. OroraTech Launches World’s First Satellite Constellation for Wildfire Detection and Data Accumulation. Available online: https://ororatech.com/resources/news-blog/ororatech-launches-world-s-first-satellite-constellation-for-wildfire-detection-and-data-accumulation (accessed on 14 April 2025).
- Carreno-Luengo, H.; Camps, A.; Via, P.; Munoz, J.F.; Cortiella, A.; Vidal, D.; Jané, J.; Catarino, N.; Hagenfeldt, M.; Palomo, P.; et al. 3Cat-2—An Experimental Nanosatellite for GNSS-R Earth Observation: Mission Concept and Analysis. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 4540–4551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirat, C.; Hömer, A.; Dielacher, A.; Wenger, M.; Moser-Moritsch, M.; Tscherne, C.; Walker, R. Preliminary In-Orbit Results of the PRETTY ESA Technology CubeSat. In Proceedings of the Small Satellites Systems and Services Symposium (4S 2024), Palma de Mallorca, Spain, 26–30 May 2024; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2025; Volume 13546, p. 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutler, J.W.; Bahcivan, H. Radio Aurora Explorer: A Mission Overview. J. Spacecr. Rockets 2014, 51, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fish, C.S.; Swenson, C.M.; Crowley, G.; Barjatya, A.; Neilsen, T.; Gunther, J.; Azeem, I.; Pilinski, M.; Wilder, R.; Allen, D.; et al. Design, Development, Implementation, and On-orbit Performance of the Dynamic Ionosphere CubeSat Experiment Mission. Space Sci. Rev. 2014, 181, 61–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imperial College London. Space and Atmospheric Physics Research Group. Space Missions: TRIO-CINEMA. Available online: https://www.imperial.ac.uk/space-and-atmospheric-physics/research/missions-and-projects/space-missions/trio-cinema/ (accessed on 2 June 2025).
- Stromberg, E.; Crowley, G.; Azeem, I.; Fish, C.; Frazier, C.; Reynolds, A.; Swenson, A.; Tash, T.; Gleason, R.; Blay, R.; et al. Scintillation Observations and Response of The Ionosphere to Electrodynamics (SORTIE) Mission First Light. In Proceedings of the 34th Annual Small Satellite Conference, Logan, UT, USA, 1–6 August 2020. Paper ID: SSC20-WKVII-09. [Google Scholar]
- Francisco, C.; Henriques, R.; Barbosa, S. A Review on CubeSat Missions for Ionospheric Science. Aerospace 2023, 10, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Fu, E.; Wu, F.; Xu, X.; Rea, A.; Kuleshov, Y.; Biadeglgne, B. GNSS Radio Occultation for Weather and Climate Research: A Case Study in Australia. In Proceedings of the International Global Navigation Satellite Systems (IGNSS) Symposium 2007, Sydney, Australia, 4–6 December 2007; University of New South Wales: Sydney, Australia, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Zhran, M. An Evaluation of GNSS Radio Occultation Atmospheric Profiles from Sentinel-6. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2023, 26, 654–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spire Global. LEMUR Space Platform: GNSS Radio Occultation and ADS-B Data Collection. Available online: https://spire.com/space-services/lemur-space-platform/ (accessed on 18 October 2024).
- SpaceNews. SmallSat Developer Spire Entering Commercial Weather Business. Available online: https://spacenews.com/smallsat-developer-spire-entering-commercial-weather-biz/ (accessed on 18 October 2024).
- Arnold, D.; Peter, H.; Mao, X.; Miller, A.; Jäggi, A. Precise Orbit Determination of Spire Nano Satellites. Adv. Space Res. 2023, 72, 5030–5046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsythe, V.V.; Duly, T.; Hampton, D.; Nguyen, V. Validation of Ionospheric Electron Density Measurements Derived from Spire CubeSat Constellation. Radio Sci. 2020, 55, e2019RS006953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.; Lee, J.; Wang, Y.; Breitsch, B.; Morton, Y.J. Preliminary Assessment of CICERO Radio Occultation Performance by Comparing with COSMIC-1 Data. In Proceedings of the 33rd International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS+ 2020), Virtual Event, 21–25 September 2020; Institute of Navigation: Manassas, VA, USA, 2020; pp. 3888–3900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krebs, G.D. CICERO 1, …, 12 / OSM 1 CICERO. Gunter’s Space Page. Available online: https://space.skyrocket.de/doc_sdat/cicero.htm (accessed on 14 October 2024).
- GeoOptics Inc. GeoOptics Orbiting Observatory to Monitor the Changing Earth. Available online: https://geooptics.com/geooptics-orbitiing-observatory-to-monitor-the-changing-earth/ (accessed on 14 October 2024).
- EO Handbook. CEOS EO Handbook—Earth Observation Satellite Capabilities and Plans | Imaging Multi—Spectral Radiometers (VIS/IR). Available online: https://eohandbook.com/eohb2011/earth_radiometers.html (accessed on 28 January 2025).
- DA-Group. Radiometers for Satellites. Available online: https://www.da-group.com/solutions/space/radiometers-for-satellites/ (accessed on 28 January 2025).
- Padmanabhan, S.; Gaier, T.C.; Tanner, A.B.; Brown, S.T.; Lim, B.H.; Reising, S.C.; Stachnik, R.; Bendig, R.; Cofield, R. TEMPEST-D Radiometer: Instrument Description and Prelaunch Calibration. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 59, 10213–10226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NASA Earth Science Technology Office (ESTO). TEMPEST-D Deorbits After Successfully Validating Advanced Remote Sensing Instruments. Available online: https://esto.nasa.gov/tempest-d-deorbits-after-successfully-validating-advanced-remote-sensing-instruments/ (accessed on 28 January 2025).
- NASA TROPICS Mission Team. Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation Structure and Storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS). Available online: https://weather.ndc.nasa.gov/tropics/ (accessed on 15 October 2024).
- National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). NASA’s Small Spacecraft Produces First 883-Gigahertz Global Ice Cloud Map. Available online: https://www.nasa.gov/technology/nasas-small-spacecraft-produces-first-883-gigahertz-global-ice-cloud-map/ (accessed on 28 January 2025).
- von Arnim, M.; Mammadov, I.; Draschka, L.; Scharnagl, J.; Schilling, K. The CloudCT Formation of 10 Nano-Satellites for Computed Tomography to Improve Climate Predictions. In Proceedings of the 73rd International Astronautical Congress (IAC 2022), Paris, France, 18–22 September 2022; International Astronautical Federation: Paris, France, 2022. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/363891743_The_CloudCT_Formation_of_10_Nano-satellites_for_Computed_Tomography_to_Improve_Climate_Predictions (accessed on 18 October 2024).
- Scharnagl, J.; Schilling, K. The CloudCT Nano-Satellite Formation to Characterize the Interior of Clouds for Improved Climate Prediction. In Proceedings of the 11th International Workshop on Satellite and Constellations Formation Flying, Milano, Italy, 7–10 June 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Peral, E.; Statham, S.; Im, E.; Tanelli, S.; Imken, T.; Price, D.; Sauder, J.; Chahat, N.; Williams, A. The Radar-in-a-Cubesat (RAINCUBE) and Measurement Results. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2018—IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Valencia, Spain, 22–27 July 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 6297–6300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahyoub, S.; Fadil, A.; Mansour, E.M.; Rhinane, H.; Al-Nahmi, F. Fusing of Optical and Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) Remote Sensing Data: A Systematic Literature Review (SLR). Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spatial Inf. Sci. 2019, XLII-4/W12, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommervold, O.; Gazzea, M.; Arghandeh, R. A Survey on SAR and Optical Satellite Image Registration. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL). RAINCUBE 6U CubeSat [Image]. Available online: https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/images/pia22457-raincube-6u-cubesat/ (accessed on 18 October 2024).
- OHB Italia. The SATURN Mission. Available online: https://www.ohb-italia.it/the-saturn-mission/ (accessed on 11 October 2024).
- Battilana, M.; Capuani, G.; Lamarca, V.; Maioli, L.; Mancini, M.L.; Tampellini, M.; Geraec, F.; Giudici, D.; Gascione, P.; Marini, J.; et al. SATURN: A Technological Demonstration Mission for Distributed SAR Imaging. In Proceedings of the 37th Annual Small Satellite Conference, Logan, UT, USA, 5–10 August 2023; Paper ID: SSC23-WII-02. Available online: https://digitalcommons.usu.edu/smallsat/2023/all2023/15/ (accessed on 18 October 2024).
- Petrushevsky, N.; Monti Guarnieri, A.; Manzoni, M.; Prati, C.; Tebaldini, S. An Operational Processing Framework for Spaceborne SAR Formations. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rennich, P.; Wye, L.; Lee, S. SRI CubeSat Imaging Radar for Earth Science, (SRI-CIRES): Initial Flight Demonstrations. In Proceedings of the CubeSat Developers Workshop, Cal Poly State University, San Luis Obispo, CA, USA, 23–25 April 2019; Available online: http://mstl.atl.calpoly.edu/~workshop/archive/2019/Spring/Day%202/Session%201/PatrickRennich.pdf (accessed on 18 October 2024).
- Kulu, E. Nanosats Database. Zhixing-3 A Spacecraft. Available online: https://www.nanosats.eu/sat/zhixing-3a (accessed on 2 June 2025).
- Jones, A. China’s Tianzhou-4 Cargo Spacecraft Deployed a Small Satellite Before Deorbiting. SpaceNews. Available online: https://spacenews.com/chinas-tianzhou-4-cargo-spacecraft-deployed-a-small-satellite-before-deorbiting/ (accessed on 2 June 2025).
- European Commission CORDIS—EU research results. Final Report Summary—QB50 (An International Network of 50 CubeSats for Multi-Point, In-Situ Measurements in the lOwer Thermosphere and Re-Entry Research). Available online: https://cordis.europa.eu/project/id/284427/reporting (accessed on 12 October 2024).
- eoPortal. ISS: NanoRacks-QB50. Available online: https://www.eoportal.org/satellite-missions/iss-nanoracks-qb50#sensor-complement (accessed on 12 October 2024).
- Gill, E.; Sundaramoorthy, P.; Bouwmeester, J.; Zandbergen, B.; Reinhard, R. Formation Flying Within a Constellation of Nano-Satellites: The QB50 Mission. Acta Astronaut. 2013, 82, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL). Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment (PREFIRE). Available online: https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/missions/prefire/ (accessed on 12 October 2024).
- Vos, N.; L’Ecuyer, T.S.; Michaels, T. Enabling Process Science with CubeSat Intersections: An Orbit Resampling Study Inspired by PREFIRE. EGUsphere 2024, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iida, T.; Futamata, R.; Yamazaki, M.; Kamogawa, M. Design and Development of Prelude, Satellite for Seismic Precedence Detection and Verification Using VLF Radio Waves for Navigation Obtained in Orbit. In Proceedings of the 35th Annual Small Satellite Conference, Logan, UT, USA, 7–12 August 2021; Paper ID: SSSC21-WKV-08. Available online: https://digitalcommons.usu.edu/smallsat/2021/all2021/262/ (accessed on 16 October 2024).
- Iida, T.; Yamazaki, M.; Kamogawa, M. Development of a Prelude Satellite Equipped with Electric Field and Plasma Measurement Sensors Based on Statistical Evaluation of Seismic Precursors Using Artificial VLF Radio Waves Obtained from In-Orbit Observations. In Proceedings of the 36th Annual Small Satellite Conference, Logan, UT, USA, 6–11 August 2022; Paper ID: SSC22-WKP1-14. Available online: https://digitalcommons.usu.edu/smallsat/2022/all2022/203/ (accessed on 16 October 2024).
- Klofas, B.; Anderson, J.; Leveque, K. A Survey of CubeSat Communication Systems. Available online: https://www.klofas.com/papers/CommSurvey-Bryan_Klofas.pdf (accessed on 16 October 2024).
- Long, M.; Lorenz, A.; Rodgers, G.; Tapio, E.; Tran, G.; Jackson, K.; Twiggs, R.; Bleier, T.E.; Solutions, S. SSC02-IX-6 A CubeSat-Derived Design for a Unique Academic Research Mission in Earthquake Signature Detection. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/266493859_SSC02-IX-6_A_CUBESAT_DERIVED_DESIGN_FOR_A_UNIQUE_ACADEMIC_RESEARCH_MISSION_IN_EARTHQUAKE_SIGNATURE_DETECTION (accessed on 16 October 2024).
- Krebs, G.D. APSS 1 (QuakeTEC, Te Waka Āmiorangi o Aotearoa). Gunter’s Space Page. Available online: https://space.skyrocket.de/doc_sdat/quaketec.htm (accessed on 16 October 2024).
- Yee, J.-H.; Gjerloev, J.; Perez, R.; Swartz, W.H.; Misra, S.; Chidambaram, O.; Ruf, C. The EZIE Way to Measure the Ionospheric Electrojets with a Three-CubeSat Constellation. In Proceedings of the 35th Annual Small Satellite Conference, Logan, UT, USA, 7–12 August 2021; Paper ID: SSC21-VI-07. Available online: https://digitalcommons.usu.edu/smallsat/2021/all2021/177/ (accessed on 16 October 2024).
- Misra, S.; Padmanabhan, S.; Kangaslahti, P.; Montes, O.; Bosch-Lluis, J.; Cofield, R.; Ramos, I.; Yee, J.-H. The Electrojet Zeeman Imaging Explorer (EZIE) Mission and the Microwave Electrojet Magnetogram (MEM) Radiometer Instrument. In Proceedings of the 36th Annual Small Satellite Conference, Logan, UT, USA, 6–11 August 2022; Paper ID: SSC22-III-05. Available online: https://digitalcommons.usu.edu/smallsat/2022/all2022/154/ (accessed on 16 October 2024).
- Johns Hopkins APL. Electrojet Zeeman Imaging Explorer (EZIE) Spacecraft. Available online: https://ezie.jhuapl.edu/mission/ezie-spacecraft/ (accessed on 12 October 2024).
- NASA Blogs Home. EZIE Mission Blog. Available online: https://blogs.nasa.gov/ezie/ (accessed on 16 April 2024).
- NASA Scientific Visualization Studio: Electrojet Zeeman Imaging Explorer (EZIE) Mission. Available online: https://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/14542 (accessed on 15 January 2025).
- Funase, R.; Ikari, S.; Miyoshi, K.; Kawabata, Y.; Nakajima, S.; Nomura, S.; Funabiki, N.; Ishikawa, A.; Kakihara, K.; Matsushita, S.; et al. Mission to Earth–Moon Lagrange Point by a 6U CubeSat: EQUULEUS. IEEE Aerosp. Electron. Syst. Mag. 2020, 35, 30–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funase, R.; Kawabata, Y.; Nakajima, S.; Fuse, R.; Sekine, H.; Koizumi, H. EQUULEUS: Artemis-1 CubeSat to Successfully Demonstrate Trajectory Control Techniques Within the Sun–Earth–Moon Region to Enable Future Deep Space Missions by Small Satellites. In Small Satellites Systems and Services Symposium (4S 2024); SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2025; p. 135460I. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babuscia, A.; Angkasa, K. Telemetry, Tracking, and Command (TT&C). In Cubesat Handbook; Cappelletti, C., Battistini, S., Malphrus, B.K., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 221–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEEE Std 521-2019 (Revision of IEEE Std 521-2002); IEEE Standard Letter Designations for Radar-Frequency Bands. IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 1–15. [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Theoharis, P.I.; Raad, R.; Tubbal, F.; Theoharis, A.; Iranmanesh, S.; Abulgasem, S.; Khan, M.U.A.; Matekovits, L. A Survey on CubeSat Missions and Their Antenna Designs. Electronics 2022, 11, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- eoPortal. GomX-4 (GomSpace Express-4). Available online: https://directory.eoportal.org/satellite-missions/gomx-4#summary (accessed on 27 November 2024).
- León Pérez, L.; Koch, P.; Walker, R. GOMX-4—The Twin European Mission for IOD Purposes. In Proceedings of the 32nd Annual AIAA/USU Conference on Small Satellites, Logan, UT, USA, 4–9 August 2018; Paper ID: SSC18-VII-07. Available online: https://digitalcommons.usu.edu/smallsat/2018/all2018/296/ (accessed on 27 November 2024).
- NASA. Integrated Solar Array and Reflectarray Antenna (ISARA). Available online: https://www.nasa.gov/smallspacecraft/isara/ (accessed on 30 November 2024).
- Hodges, R.E.; Lewis, D.K.; Radway, M.J.; Toorian, A.S.; Aguirre, F.H.; Hoppe, D.J.; Shah, B.; Gray, A. The ISARA Mission—Flight Demonstration of a High Gain Ka-Band Antenna for 100 Mbps Telecom. In Proceedings of the 32nd Annual AIAA/USU Conference on Small Satellites, Logan, UT, USA, 4–9 August 2018; Paper ID: SSC18-VI-03. Available online: https://digitalcommons.usu.edu/smallsat/2018/all2018/292/ (accessed on 27 November 2024).
- ESA CSC: Connectivity & Secure Communications. W-Cube: CubeSat-Based W-Band Channel Measurements. Available online: https://connectivity.esa.int/projects/wcube (accessed on 27 November 2024).
- GomSpace. Communication Systems. Available online: https://gomspace.com/shop/subsystems/communication-systems/default.aspx (accessed on 21 November 2024).
- ISISPACE. Communication Systems. Available online: https://www.isispace.nl/product-category/communication-systems/ (accessed on 21 November 2024).
- Space Inventor. Equipment Catalogue. Available online: https://space-inventor.com/modules (accessed on 21 November 2024).
- NanoAvionics. CubeSat & SmallSat Components—Subsystems. Available online: https://nanoavionics.com/cubesat-components/ (accessed on 21 November 2024).
- AAC Clyde Space. Space Products & Components | Communications. Available online: https://www.aac-clyde.space/what-we-do/space-products-components/communications (accessed on 21 November 2024).
- CubeCom. Communication Systems for Satellites. Available online: https://cubecom.space/ (accessed on 27 November 2024).
- Anywaves. Space Antenna Makers. Available online: https://anywaves.com/ (accessed on 27 November 2024).
- Arifin, J. Study of CUBESAT Systems for IoT. In Proceedings of the 12th International Renewable Engineering Conference (IREC), Amman, Jordan, 14–15 April 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laursen, L. CubeSat Operators Launch an IoT Space Race: New Tech and Lower Costs Make It Possible to Monitor Devices Straight from Orbit. IEEE Spectrum, 27 March 2023. Available online: https://spectrum.ieee.org/cubesat (accessed on 21 November 2024).
- Lepcha, P.; Malmadayalage, T.D.; Örger, N.C.; Purio, M.A.; Duran, F.; Kishimoto, M.; El-Megharbel, H.A.; Cho, M. Assessing the Capacity and Coverage of Satellite IoT for Developing Countries Using a CubeSat. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ground Control. Satellite IoT Use Cases for Real-World Applications. Available online: https://www.groundcontrol.com/blog/satellite-iot-use-cases-for-real-world-applications/ (accessed on 21 November 2024).
- Luxembourg Space Agency: OQ TECHNOLOGY Concludes Its TIGER-1 Mission Successfully and Embarks on Global 5G Satellite Alliance. Available online: https://space-agency.public.lu/en/news-media/news/2020/OQTECHNOLOGY.html (accessed on 24 November 2024).
- OQ Technology Company Timeline. Available online: https://www.oqtec.space/company/timeline (accessed on 24 November 2024).
- OQ Technology. OQ Technology to Become World’s Largest 5G NB-IoT LEO Satellite Operator. Available online: https://www.oqtec.space/news/oq-technology-to-become-worlds-largest-5g-nb-iot-leo-satellite-operator (accessed on 24 November 2024).
- NewSpace Index. OQ Technology Satellite Constellation. Available online: https://www.newspace.im/constellations/oq-technology (accessed on 24 November 2024).
- OQ Technology. OQ Technology hAs Been Successfully Awarded a EUR 1.1 Million Contract to Design, Build, and Demonstrate Nanosatellites for 5G IoT and Hyperspectral Earth Observation. Available online: https://www.oqtec.com/news/oq-technology-has-been-successfully-awarded-a-eur-1-1-million-contract-to (accessed on 24 November 2024).
- Krebs, G.D. “SpaceBEE 10, …, 180”. Gunter’s Space Page. Available online: https://space.skyrocket.de/doc_sdat/spacebee-10.htm (accessed on 21 November 2024).
- Kulu, E. NewSpace Index. Swarm Technologies Satellite Constellation. Available online: https://www.newspace.im/constellations/swarm-technologies (accessed on 2 June 2025).
- eoPortal. Sateliot_X Constellation. Available online: https://www.eoportal.org/satellite-missions/sateliot-iot#eop-quick-facts-section (accessed on 21 November 2024).
- Alén Space. Alén Space Designs and Manufactures Four Satellites for SatelIoT’s 5G Constellation. Available online: https://alen.space/alen-space-designs-and-manufactures-four-satellites-for-sateliots-5g-constellation/ (accessed on 21 November 2024).
- Wu, S.; Chen, W.; Cao, C.; Zhang, C.; Mu, Z. A Multiple-CubeSat Constellation for Integrated Earth Observation and Marine/Air Traffic Monitoring. Adv. Space Res. 2021, 67, 3712–3724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornell Law School. 47 CFR §80.393—Frequencies for AIS Stations. Available online: https://www.law.cornell.edu/cfr/text/47/80.393 (accessed on 17 November 2024).
- Textron Aviation Inc. ADS-B Out Explained. Available online: https://txtav.com/en/journey/articles/articles/adsb-out-explained (accessed on 17 November 2024).
- Alén Space. AIS PAYLOAD. Available online: https://alen.space/products/ais-payload/ (accessed on 17 November 2024).
- SatLab. Polaris 4-Channel AIS Receiver. Available online: https://www.satlab.com/products/polaris-ais/ (accessed on 17 November 2024).
- Satlab. QubeAIS Receiver. Available online: https://www.satlab.com/products/qubeais/ (accessed on 17 November 2024).
- GomSpace. Compact ADS-B Patch Antenna for Aircraft Tracking. Available online: https://gomspace.com/shop/subsystems/payloads/nanocom-ads-b-patch-antenna.aspx (accessed on 17 November 2024).
- Alén Space. ADS-B Payload. Available online: https://alen.space/products/adsb-payload/ (accessed on 17 November 2024).
- SatLab. Polaris-ADSB Receiver. Available online: https://www.satlab.com/products/polaris-adsb/ (accessed on 17 November 2024).
- Coleshill, E.; Cain, J.; Newland, F.; D’Souza, I. NTS—A Nanosatellite Space Trial. Acta Astronaut. 2010, 66, 1475–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UTIAS Space Flight Laboratory. Can-X 6/NTS Automatic Identification System Receiver for Ship Tracking. Available online: https://www.utias-sfl.net/can-x-6-nts/ (accessed on 17 November 2024).
- eoPortal. CanX-6 (Canadian Advanced Nanosatellite eXperiment-6)/Nanostellite Tracking Ships (NTS). Available online: https://www.eoportal.org/satellite-missions/canx-6#canx-6-canadian-advanced-nanosatellite-experiment-6–nts (accessed on 17 November 2024).
- Skauen, A.N. Quantifying the Tracking Capability of Space-Based AIS Systems. Adv. Space Res. 2016, 57, 527–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UTIAS Space Flight Laboratory. AISSat-1, -2, and -3. Available online: https://www.utias-sfl.net/aissat-1-2-and-3/ (accessed on 17 November 2024).
- Larsen, J.A.; Mortensen, H.P. In Orbit Validation of the AAUSAT3 SDR-Based AIS Receiver. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Recent Advances in Space Technologies (RAST 2013), Istanbul, Turkey, 12–14 June 2013; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 487–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Space Agency (ESA). University Teams Selected for Phase 2 of Fly Your Satellite! Available online: https://www.esa.int/Education/CubeSats_-_Fly_Your_Satellite/University_teams_selected_for_phase_2_of_Fly_Your_Satellite%21 (accessed on 17 November 2024).
- Nielsen, J.D.; Larsen, J.A. A Decentralized Design Philosophy for Satellites. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Recent Advances in Space Technologies (RAST 2011), Istanbul, Turkey, 9–11 June 2011; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 543–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AMSAT-UK Radio Amateur Satellites. AAUSAT5 Communicates with Students on Earth. Available online: https://amsat-uk.org/2015/11/04/aausat5-communicates-with-students-on-earth/ (accessed on 17 November 2024).
- Alminde, L.K.; Christiansen, J.; Laursen, K.K.; Midtgaard, A.; Bisgaard, M.; Jensen, M.; Gosvig, B.; Birklykke, A.; Koch, P.; Le Moullec, Y. GomX-1: A Nanosatellite Mission to Demonstrate Improved Situational Awareness for Air Traffic Control. In Proceedings of the 26th Annual AIAA/USU Conference on Small Satellites, Logan, UT, USA, 13–16 August 2012; Paper ID: SSC12-I-6. Available online: https://digitalcommons.usu.edu/smallsat/2012/all2012/13/ (accessed on 17 November 2024).
- Nies, G.; Stenger, M.; Krčál, J.; Hermanns, H.; Bisgaard, M.; Gerhardt, D.; Haverkort, B.; Jongerden, M.; Larsen, K.G.; Wognsen, E.R. Mastering Operational Limitations of LEO Satellites—The GomX-3 Approach. Acta Astronaut. 2018, 151, 726–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.; Smith, B.M.; Capon, C.J.; Abay, R.; Polo, M.C.; Gehly, S.; Bowden, G.; Bright, C.; Lambert, A.; Boyce, R. SSA Experiments for the Australian M2 Formation Flying CubeSat Mission. In Proceedings of the Advanced Maui Optical and Space Surveillance Technologies Conference (AMOS), Maui, HI, USA, 15–18 September 2020; Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/345698529_SSA_Experiments_for_the_Australian_M2_Formation_Flying_CubeSat_Mission (accessed on 17 November 2024).
- UNSW Canberra Space. M2 Mission. Available online: https://www.unsw.edu.au/canberra/our-research/research-centres-institutes/unsw-canberra-space/missions/m2 (accessed on 17 November 2024).
- Brown, M.; Boyce, R.; Lambert, A.; Peters, E.; Gehly, S.; Boland, S.; Jeffreson, R.; Kremor, A.; Bateman, T.; Capon, C.; et al. Formation Flying and Change Detection for the UNSW Canberra Space ’M2’ Low Earth Orbit Formation Flying CubeSat Mission. In Proceedings of the Advanced Maui Optical and Space Surveillance Technologies Conference (AMOS), Maui, HI, USA, 27–30 September 2022; Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/374501350_Formation_Flying_and_Change_Detection_for_the_UNSW_Canberra_Space_’M2’_Low_Earth_Orbit_Formation_Flying_CubeSat_Mission (accessed on 17 November 2024).
- CORDIS—EU Research Results. SATELLITE-BASED ADS-B FOR LOWER SEPARATION-MINIMA APPLICATION (SALSA). D3.1 Compilation of SB ADS-B Space Segment Configuration. Available online: https://cordis.europa.eu/project/id/699337/results (accessed on 17 November 2024).
- Jaffer, G.; Malik, R.A.; Aboutanios, E.; Rubab, N.; Nader, R.; Eichelberger, H.U.; Vandenbosch, G.A.E. Air traffic monitoring using optimized ADS-B CubeSat constellation. Astrodyn. 2024, 8, 189–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, K. Space-Based ADS-B: Performance, Architecture and Market. In Proceedings of the 2019 Integrated Communications, Navigation and Surveillance Conference (ICNS), Herndon, VA, USA, 9–11 April 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmytryszyn, M.; Crook, M.; Sands, T. Lasers for Satellite Uplinks and Downlinks. Sci 2021, 3, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NASA. Optical Communications Overview. Available online: https://www.nasa.gov/technology/space-comms/optical-communications-overview/ (accessed on 30 October 2024).
- Tanaka, T.; Kawamura, Y.; Tanaka, T. Development and Operations of Nanosatellite FITSAT-1 (NIWAKA). Acta Astronaut. 2015, 107, 112–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pack, D.W.; Kinum, G.; Johnson, P.D.; Wilkinson, T.S.; Coffman, C.M.; Purcell, C.R.; Mauerhan, J.C.; Hardy, B.S.; Russell, R.; Mercy, K. Landsat Imagery from a CubeSat: Results and Operational Lessons from the R3 Satellite’s First 18 Months in Space. In Proceedings of the 34th Annual AIAA/USU Conference on Small Satellites, Logan, UT, USA, 1–6 August 2020; Paper ID: SSC20-II-02. Available online: https://digitalcommons.usu.edu/smallsat/2020/all2020/112/ (accessed on 31 October 2024).
- Krebs, G.D. TOMSat EagleScout, TOMSat R3 (AeroCube 11A, 11B). Gunter’s Space Page. Available online: https://space.skyrocket.de/doc_sdat/aerocube-11-r3.htm (accessed on 31 October 2024).
- Schieler, C.M.; Riesing, K.M.; Bilyeu, B.C.; Robinson, B.S.; Wang, J.P.; Roberts, W.T.; Piazzolla, S. TBIRD 200-Gbps CubeSat Downlink: System Architecture and Mission Plan. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Space Optical Systems and Applications (ICSOS), Kyoto, Japan, 14–17 November 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, C.Q. NASA’s Laser Link Boasts Record-Breaking 200-Gb/s Speed. IEEE Spectrum, 30 November 2022. Available online: https://spectrum.ieee.org/laser-communications (accessed on 31 October 2024).
- Schieler, C.M.; Bilyeu, B.C.; Chang, J.S.; Garg, A.S.; Horvath, A.J.; Riesing, K.M.; Robinson, B.S.; Wang, J.P.; Piazzolla, S.; Keer, B. Recent On-Orbit Results and ARQ Performance Analysis for the TBIRD 200-Gbps Mission. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Space Optical Systems and Applications (ICSOS), Kyoto, Japan, 13–16 November 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Space Agency (ESA). FSSCat Mission Profile. Available online: https://earth.esa.int/eogateway/missions/fsscat (accessed on 31 October 2024).
- Camps, A.; Munoz-Martin, J.F.; Ruiz-de-Azua, J.A.; Fernandez, L.; Perez-Portero, A.; Llaveria, D.; Herbert, C.; Pablos, M.; Golkar, A.; Gutierrrez, A.; et al. FSSCat Mission Description and First Scientific Results of the FMPL-2 Onboard 3CAT-5/A. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Brussels, Belgium, 11–16 July 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 1291–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, K.; NASA. CubeSat Set to Demonstrate NASA’s Fastest Laser Link from Space. Available online: https://www.nasa.gov/directorates/somd/cubesat-set-to-demonstrate-nasas-fastest-laser-link-from-space/ (accessed on 15 January 2025).
- Yenchesky, L.; Cierny, O.; Grenfell, P.; Kammerer, W.; Periera, P.D.V.; Sevigny, T.; Cahoy, K. Optomechanical Design and Analysis for Nanosatellite Laser Communications. In Proceedings of the 33rd Annual AIAA/USU Conference on Small Satellites, Logan, UT, USA, 3–8 August 2019; Paper ID: SSC19-XII-05. Available online: https://digitalcommons.usu.edu/smallsat/2019/all2019/161/ (accessed on 15 January 2025).
- Grenfell, P.; Serra, P.; Cierny, O.; Kammerer, W.; Gunnison, G.; Kusters, J.; Payne, C.; Cahoy, K.; Clark, M.; Ritz, T.; et al. Design and Prototyping of a Nanosatellite Laser Communications Terminal for the CubeSat Laser Infrared Crosslink (CLICK) B/C Mission. In Proceedings of the 34th Annual AIAA/USU Conference on Small Satellites, Logan, UT, USA, 1–6 August 2020; Paper ID: SSC20-WKVI-02. Available online: https://digitalcommons.usu.edu/smallsat/2020/all2020/37/ (accessed on 15 January 2025).
- Millour, F.; Ottogalli, S.; Maamri, M.; Stibbe, A.; Ferrero, F.; Rolland, L.; Rebeyrolle, S.; Marcotto, A.; Agabi, K.; Beaulieu, M.; et al. The Nice Cube (Nice3) Nanosatellite Project. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1808.09848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Space Agency (ESA). European Space Agency Works with Greek Ministry of Digital Governance for Secure and Resilient Connectivity. Available online: https://connectivity.esa.int/news/european-space-agency-works-greek-ministry-digital-governance-secure-and-resilient-connectivity (accessed on 1 November 2024).
- Velazco, J.E.; de la Vega, J.S. Q4—A CubeSat Mission to Demonstrate Omnidirectional Optical Communications. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, MT, USA, 7–14 March 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AstroLight. ATLAS-1 Space-to-Earth Laser Communication Terminal. Available online: https://astrolightspace.com/atlas/ (accessed on 30 October 2024).
- Tesat-Spacecom. Products: SCOT20. Available online: https://www.tesat.de/products (accessed on 30 October 2024).
- AAC Clyde Space. CubeCat Laser Communication Module. Available online: https://www.aac-clyde.space/what-we-do/space-products-components/communications/cubecat (accessed on 30 October 2024).
- Stellar Project. LaserCube: Enabling the Optical Communication Highway for Small Satellites. Available online: https://stellarproject.space/product/lasercube/ (accessed on 30 October 2024).
- Cappelletti, C.; Robson, D. CubeSat Missions and Applications. In Cubesat Handbook; Cappelletti, C., Battistini, S., Malphrus, B.K., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.; Donner, A.; Knapp, M.; Pong, C.; Smith, C.; Luu, J.; Di Pasquale, P.; Campuzano, B. On-Orbit Results and Lessons Learned from the ASTERIA Space Telescope Mission. In Proceedings of the 32nd Annual AIAA/USU Conference on Small Satellites, Logan, UT, USA, 4–9 August 2018; Paper ID: SSC18-I-08. Available online: https://digitalcommons.usu.edu/smallsat/2018/all2018/255/ (accessed on 1 February 2025).
- Knapp, M.; Seager, S.; Demory, B.-O.; Krishnamurthy, A.; Smith, M.W.; Pong, C.M.; Bailey, V.P.; Donner, A.; Di Pasquale, P.; Campuzano, B.; et al. Demonstrating High-Precision Photometry with a CubeSat: ASTERIA Observations of 55 Cancri e. Astron. J. 2020, 160, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramiaramanantsoa, T.; Bowman, J.D.; Shkolnik, E.L.; Loyd, R.O.P.; Ardila, D.R.; Barman, T.; Basset, C.; Beasley, M.; Cheng, S.; Gamaunt, J.; et al. Onboard Dynamic Image Exposure Control for the Star—Planet Activity Research CubeSat (SPARCS). Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2021, 509, 5702–5713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, M.; Lacour, S.; Crouzier, A.; David, L.; Lapeyrère, V.; Schworer, G. Short Life and Abrupt Death of PicSat, a Small 3U CubeSat Dreaming of Exoplanet Detection. In Proceedings of the SPIE Astronomical Telescopes + Instrumentation 2018: Space Telescopes and Instrumentation 2018: Optical, Infrared, and Millimeter Wave, Austin, TX, USA, 10–15 June 2018; Volume 10698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NASA Science Editorial Team. The CUTE Mission: Innovative Design Enables Observations of Extreme Exoplanets from a Small Package. NASA Science, 27 February 2024. Available online: https://science.nasa.gov/science-research/science-enabling-technology/the-cute-mission-innovative-design-enablesobservations-of-extreme-exoplanets-from-a-smallpackage/ (accessed on 1 February 2025).
- University of Sydney. The TOLIMAN Space Telescope: Searching for Habitable Planets in Alpha Centauri. Available online: https://toliman.space/ (accessed on 1 February 2025).
- Topputo, F.; Ferrari, F.; Giordano, C.; Panicucci, P.; Buonagura, C.; Martinelli, A.; Piccolo, F.; Rizza, A.; Monferrini, D.; Provinciali, L.; et al. LUMIO CubeSat: Current Status and Lessons Learnt (So Far). In Proceedings of the Small Satellites Systems and Services Symposium (4S 2024), Palma de Mallorca, Spain, 27 May–1 June 2024; Petrozzi-Ilstad, M., Ed.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA,, 2025; Volume 13546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wikimedia Commons. File: ASTERIA CubeSat Space Telescope.jpg. Available online: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:ASTERIA_CubeSat_space_telescope.jpg (accessed on 3 June 2025).
- NASA/JPL-Caltech. ASTERIA CubeSat Before Launch. Available online: https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/images/pia23406-asteria-cubesat-before-launch/ (accessed on 7 February 2025).
- Wikipedia Contributors. ASTERIA CubeSat Lens Alignment. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ASTERIA_ (accessed on 7 February 2025).
- Novosibirsk State University. NSU Successfully Launches Second Satellite. Available online: https://english.nsu.ru/news-events/news/research/nsu-successfully-launches-second-satellite-/ (accessed on 3 June 2025).
- Kuzin, S.; Bogachev, S.; Erkhova, N.; Pertsov, A.; Loboda, I.; Reva, A.; Kholodilov, A.V.; Ulyanov, A.; Kirichenko, A.; Malyshev, I.; et al. Solar VUV Telescope for Nanosatellites. Tech. Phys. 2022, 92, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TinyGS. Norby-2. Available online: https://tinygs.com/satellite/Norby-2 (accessed on 3 June 2025).
- ISO 21348:2007; Space environment (natural and artificial) — Process for determining solar irradiances. International Organization for Standardization (ISO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2007. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/39911.html (accessed on 12 June 2025).
- Kaaret, P.; Zajczyk, A.; LaRocca, D.M.; Ringuette, R.; Bluem, J.; Fuelberth, W.; Gulick, H.; Jahoda, K.; Johnson, T.E.; Kirchner, D.L.; et al. HaloSat: A CubeSat to Study the Hot Galactic Halo. Astrophys. J. 2019, 884, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenti, M.; Ortiz del Castillo, M.; Mearns, R.; McRobbie, J.; Therakam, C.; Chapman, A.; Woods, A.; Morgan, J.; Barraclough, S.; Rodriguez Mallo, I.; et al. SpIRIT Mission: In-Orbit Results and Technology Demonstrations. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2407.14034. [Google Scholar]
- NASA. NASA Selects 4 CubeSats for Space Weather Tech Development. NASA Science, 13 December 2021. Available online: https://www.nasa.gov/science-research/heliophysics/nasa-selects-4-cubesats-for-space-weather-tech-development/ (accessed on 1 February 2025).
- Gasaway, K.F.; Tian, L.; Cox, J.; Cason, N.; Nold, B.; Rusley, D.; Azimi, B.; Racusin, J.; Perkins, J.; Moss, R.; et al. BurstCube: Behind the Scenes of a Do-No-Harm I&T Production. In Proceedings of the 38th Annual AIAA/USU Conference on Small Satellites, Logan, UT, USA, 3–8 August 2024; Paper ID: SSC24-III-04. Available online: https://digitalcommons.usu.edu/smallsat/2024/all2024/88/ (accessed on 1 February 2025).
- HUN-REN. High-Energy Astronomical Observations Made Possible by Latest Small Satellite, Built Through an International Collaboration Under the Leadership of CSFK Researchers. HUN-REN News, 8 December 2020. Available online: https://hun-ren.hu/en/news/high-energy-astronomical-observations-made-possible-by-latest-small-satellite-built-through-an-international-collaboration-under-the-leadership-of-csfk-researchers (accessed on 1 February 2025).
- NASA. HaloSat. Available online: https://science.nasa.gov/resource/halosat/ (accessed on 7 February 2025).
- NASA. BurstCube. NASA Science, 2024. Available online: https://science.nasa.gov/mission/burstcube/ (accessed on 13 January 2025).
- Desai, M.I.; Allegrini, F.; Ebert, R.W.; Ogasawara, K.; Epperly, M.E.; George, D.E.; Christian, E.R.; Kanekal, S.G.; Murphy, N.; Randol, B. The CubeSat Mission to Study Solar Particles. IEEE Aerosp. Electron. Syst. Mag. 2019, 34, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado, C.A.; Deming, J.; Mosley, B.N.; Morgan, K.S.; McGlown, J.; Nelson, A.; Fernandes, P.A.; Kroupa, M.; Katko, K.; Hehlen, M.P.; et al. The Experiment for Space Radiation Analysis: A 12U CubeSat to Explore the Earth’s Radiation Belts. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Aerospace Conference (AERO), Big Sky, MT, USA, 5–12 March 2022; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, C.; Berger, S.; Bustos, J.; Redfield, B.; Vazquez, A.; Paolicelli, J. Unique Challenges of Mission Operations on SunRISE, A Low-Cost NASA Science Constellation. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, MT, USA, 2–9 March 2024; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NASA - Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL). NASA’s 6-Pack of Mini-Satellites Ready for Their Moment in the Sun. NASA Missions, 30 November 2023. Available online: https://www.nasa.gov/missions/sunrise-mission/nasas-6-pack-of-mini-satellites-ready-for-their-moment-in-the-sun/ (accessed on 1 February 2025).
- Yuri Gravity. Available online: https://yurigravity.com (accessed on 3 June 2025).
- Kitts, C.; Ronzano, K.; Rasay, R.; Mas, I.; Williams, P.; Mahacek, P.; Minelli, G.; Hines, J.; Agasid, E.; Friedericks, C.; et al. Flight Results from the GeneSat-1 Biological Microsatellite Mission. In Proceedings of the 21st Annual AIAA/USU Conference on Small Satellites, Logan, UT, USA, 13–16 August 2007; Paper ID: SSC07-XI-1. Available online: https://digitalcommons.usu.edu/smallsat/2007/all2007/69/ (accessed on 7 February 2025).
- Kitts, C.; Ronzano, K.; Rasay, R.; Mas, I.; Acain, J.; Neumann, M.; Bica, L.; Mahacek, P.; Minelli, G.; Beck, E.; et al. Initial Flight Results from the PharmaSat Biological Microsatellite Mission. In Proceedings of the 23rd Annual AIAA/USU Conference on Small Satellites, Logan, UT, USA, 10–13 August 2009; Paper ID: SSC09-IV-10. Available online: https://digitalcommons.usu.edu/smallsat/2009/all2009/27/ (accessed on 7 February 2025).
- Ehrenfreund, P.; Ricco, A.J.; Squires, D.; Kitts, C.; Agasid, E.; Bramall, N.; Bryson, K.; Chittenden, J.; Conley, C.; Cook, A.; et al. The O/OREOS Mission—Astrobiology in Low Earth Orbit. Acta Astronaut. 2014, 93, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wikipedia Contributors. GeneSat-1. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/GeneSat-1#/media/File:Genesat-1_1.jpg (accessed on 7 February 2025).
- Wikipedia Contributors. O/OREOS. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/O/OREOS#/media/File:OOREOS_Spacecraft_(PADOM_Deployed).jpg (accessed on 7 February 2025).
- Chin, M.; Spremo, S.; Snyder, T.V.; Rogers, C.; Ricco, A.J.; Chinn, T.N.; Padgen, M.R.; Henschke, M.; Parra, M.; Taylor, L.; et al. EcAMSat—NASA’s First 6U Biological Spacecraft: System Integration and Environmental Test Technical Paper. NASA Technical Reports Server (NTRS). Available online: https://ntrs.nasa.gov/api/citations/20205007906/downloads/EcAMSat-final.docx.pdf (accessed on 31 January 2025).
- Krakos, A. Lab-on-Chip Technologies for Space Research—Current Trends and Prospects. Microchim. Acta 2023, 191, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabria, D.; Trozzi, I.; Lazzarini, E.; Pace, A.; Zangheri, M.; Iannascoli, L.; Maipan Davis, N.; Gosikere Matadha, S.S.; Baratto De Albuquerque, T.; Pirrotta, S.; et al. AstroBio-CubeSat: A Lab-in-Space for Chemiluminescence-Based Astrobiology Experiments. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2023, 226, 115110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NASA. EcAMSat—NASA’s First 6U Biological Spacecraft. NASA Factsheet FS-2017-10-01-ARC. October 2017. Available online: https://www.nasa.gov/wp-content/uploads/2016/07/ecamsat_31oct2017-508.pdf (accessed on 31 January 2025).
- Meneghin, A.; Paglialunga, D.; Poggiali, G.; Pirrotta, S.; Impresario, G.; Sabatini, A.; Pacelli, C.; Nascetti, A.; Iannascoli, L.; Carletta, S.; et al. AstroBio CubeSat: A Nanosatellite for Space Astrobiology Experiments. In Proceedings of the 14th Europlanet Science Congress (EPSC), Virtual Meeting, 21 September–9 October 2020. EPSC2020-943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricco, A.J.; Santa Maria, S.R.; Hanel, R.P.; Bhattacharya, S. BioSentinel: A 6U Nanosatellite for Deep-Space Biological Science. IEEE Aerosp. Electron. Syst. Mag. 2020, 35, 6–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massaro Tieze, S.; Liddell, L.C.; Santa Maria, S.R.; Bhattacharya, S. BioSentinel: A Biological CubeSat for Deep Space Exploration. Astrobiology 2023, 23, 631–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NASA. What is BioSentinel? 2024. Available online: https://www.nasa.gov/centers-and-facilities/ames/what-is-biosentinel/ (accessed on 31 January 2025).
- Singh, S. India’s First Microbiological Nanosat, Developed by Students, to Find Ways to Keep Astronauts Healthy. The Times of India, 19 February 2025. Available online: https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/india/indias-first-microbiological-nanosat-developed-by-students-to-find-ways-to-keep-astronauts-healthy/articleshow/118370934.cms (accessed on 3 June 2025).
- Team Antariksh. Available online: https://www.teamantariksh.in/ (accessed on 3 June 2025).
- Malphrus, B.K.; Freeman, A.; Staehle, R.; Klesh, A.T.; Walker, R. Interplanetary CubeSat Missions. In Cubesat Handbook; Cappelletti, C., Battistini, S., Malphrus, B.K., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 85–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Advanced Space. CAPS™: A Peer-to-Peer Navigation and Communication Technology. Available online: https://advancedspace.com/caps/ (accessed on 14 June 2025).
- Gardner, T.; Cheetham, B.; Parker, J.; Forsman, A.; Kayser, E.; Thompson, M.; Ott, C.; DeMoudt, L.; Caudill, M.; Bolliger, M.; et al. CAPSTONE: A Summary of a Highly Successful Mission in the Cislunar Environment. In Proceedings of the 37th Annual AIAA/USU Conference on Small Satellites, Logan, UT, USA, 5–10 August 2023; Paper ID: SSC23-I-04. Available online: https://digitalcommons.usu.edu/smallsat/2023/all2023/69/ (accessed on 14 January 2025).
- Agasid, E.; Hunter, R.; Cheetham, B. Cislunar Autonomous Positioning System Technology Operations and Navigation Experiment (CAPSTONE) Pathfinder for Artemis Gateway. In Small Satellites Systems and Services Symposium (4S 2024); Petrozzi-Ilstad, M., Ed.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2025; p. 135460F. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NASA’s Technology Portfolio Management System (TechPort). Cis Lunar Autonomous Positioning System Technology Operations and Navigation Experiment (CAPSTONE) Project Profile. Available online: https://techport.nasa.gov/projects/106820 (accessed on 2 October 2024).
- NASA. What Is CAPSTONE? Available online: https://www.nasa.gov/smallspacecraft/capstone/ (accessed on 26 February 2025).
- NASA. Media Resources for CAPSTONE. Available online: https://www.nasa.gov/centers-and-facilities/ames/media-resources-for-capstone/ (accessed on 14 January 2025).
- NASA Space Science Data Coordinated Archive. Artemis I NSSDCA/COSPAR ID: 2022-156A. Available online: https://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraft/display.action?id=2022-156A (accessed on 8 October 2024).
- NASA. Orion Stage Adapter Readied for Ride on Artemis I. Available online: https://www.nasa.gov/image-article/orion-stage-adapter-readied-ride-artemis-i/ (accessed on 8 October 2024).
- Terran Orbital. LunIR: Mapping the Lunar Surface. Available online: https://terranorbital.com/missions/lunir/ (accessed on 2 October 2024).
- NASA’s Technology Portfolio Management System (TechPort). Lunar InfraRed (imaging) (LunIR) Project Profile. Available online: https://techport.nasa.gov/view/94206 (accessed on 3 October 2024).
- Foust, J. Deep Space Smallsats Face Big Challenges. SpaceNews, 17 February 2023. Available online: https://spacenews.com/deep-space-smallsats-face-big-challenges/ (accessed on 3 October 2024).
- Malphrus, B.K.; Brown, K.Z.; Garcia, J.; Conner, C.; Kruth, J.; Combs, M.S.; Fite, N.; McNeil, S.; Wilczweski, S.; Haught, K.; et al. The Lunar IceCube EM-1 Mission: Prospecting the Moon for Water Ice. IEEE Aerosp. Electron. Syst. Mag. 2019, 34, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchett, R.E.; Folta, D.C.; Hur-Diaz, S.; Hughes, K. Trajectory Design and Early Mission Operations for the Lunar IceCube Mission. In Proceedings of the AAS/AIAA Astrodynamics Specialist Conference; Big Sky, MT, USA, 13–17 August 2023, American Astronautical Society: Springfield, VA, USA, 2023; NASA Technical Reports Server, Document ID: 20230010984. Available online: https://ntrs.nasa.gov/citations/20230010984 (accessed on 3 October 2024).
- Hernando-Ayuso, J.; Campagnola, S.; Yamaguchi, T.; Ozawa, Y.; Ikenaga, T. OMOTENASHI trajectory analysis and design: Landing phase. Acta Astronaut. 2019, 156, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JAXA. OMOTENASHI (Outstanding MOon Exploration TEchnologies Demonstrated by NAno Semi-Hard Impactor). Available online: https://www.isas.jaxa.jp/home/omotenashi/img/OMOTENASHItoutline13.pdf (accessed on 3 October 2024).
- Institute of Space and Astronautical Science: ISAS–JAXA. The World’s Smalest Moon Lander. OMOTENASHI: Outstanding MOon Exploration TEchnologies Demonstrated by NAno Semi-Hard Impactor. Available online: https://www.isas.jaxa.jp/home/omotenashi/index.html (accessed on 3 October 2024).
- Hardgrove, C.; Starr, R.; Lazbin, I.; Babuscia, A.; Roebuck, B.; DuBois, J.; Struebel, N.; Colaprete, A.; Drake, D.; Johnson, E.; et al. The Lunar Polar Hydrogen Mapper CubeSat Mission. IEEE Aerosp. Electron. Syst. Mag. 2020, 35, 54–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, E. NASA’s LunaH-Map Mission Ends, Validates Science Instrument Performance. NASA Blogs, 3 August 2023. Available online: https://blogs.nasa.gov/lunah-map/2023/08/03/nasas-lunah-map-mission-ends-validates-science-instrument-performance/ (accessed on 3 October 2024).
- Lombardo, M.; Zannoni, M.; Gai, I.; Gomez Casajus, L.; Gramigna, E.; Manghi, R.L.; Tortora, P.; Di Tana, V.; Cotugno, B.; Simonetti, S.; et al. Design and Analysis of the Cis-Lunar Navigation for the ArgoMoon CubeSat Mission. Aerospace 2022, 9, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, M.; Gomez Casajus, L.; Zannoni, M.; Gai, I.; Gramigna, E.; Tortora, P.; Dotto, E.; Amoroso, M.; Pirrotta, S.; Di Tana, V.; et al. An overview of the ArgoMoon and LICIAcube flight dynamics operations. In Proceedings of the AIDAA XXVII International Congress, Materials Research Proceedings, Padova, Italy, 4–7 September 2023; Volume 37, pp. 634–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payload Space. Artemis I CubeSats Fail to Power Up. Available online: https://payloadspace.com/artemis-i-cubesats-fail-to-power-up/ (accessed on 5 June 2025).
- Bittel, J. NASA’s Artemis I Launch Has Faced Several Delays. That’s Actually Common. The Washington Post. Available online: https://www.washingtonpost.com/kidspost/2022/11/15/nasa-launches-often-delayed/ (accessed on 5 June 2025).
- Cervone, A.; Topputo, F.; Speretta, S.; Menicucci, A.; Turan, E.; Di Lizia, P.; Massari, M.; Franzese, V.; Giordano, C.; Merisio, G.; et al. LUMIO: A CubeSat for observing and characterizing micro-meteoroid impacts on the Lunar far side. Acta Astronaut. 2022, 195, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraft, R.H. NASA to Fly International CubeSats Aboard Artemis II Test Flight. NASA Blogs, 20 September 2024. Available online: https://www.nasa.gov/blogs/artemis/2024/09/20/nasa-to-fly-international-cubesats-aboard-artemis-ii-test-flight/ (accessed on 6 October 2024).
- Lane, R.; Ryals, C.; McLemore, C.; Hitt, D. NASA Space Launch System CubeSats: First Flight and Future Opportunities. In Proceedings of the 37th Annual Small Satellite Conference, Logan, UT, USA, 5–10 August 2023; Paper No. SSC23-XIII-01. Available online: https://digitalcommons.usu.edu/smallsat/2023/all2023/130/ (accessed on 6 October 2024).
- Klesh, A.T.; Baker, J.; Krajewski, J.; MarCO Flight Operations Team. MarCO: Flight Review and Lessons Learned. In Proceedings of the 33rd Annual AIAA/USU Conference on Small Satellites, Logan, UT, USA, 3–8 August 2019; Paper ID: SSC19-III-04. Available online: https://digitalcommons.usu.edu/smallsat/2019/all2019/276/ (accessed on 6 October 2024).
- Asmar, S.W.; Matousek, S. Mars Cube One (MarCO): Shifting the Paradigm in Relay Deep Space Operations. In Proceedings of the SpaceOps 2016 Conference, Daejeon, South Korea, 16–20 May 2016. AIAA Paper 2016-2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahat, N.; Decrossas, E.; Kobayashi, M.M. Mars Cube One. In CubeSat Antenna Design; Wiley-IEEE Press: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 35–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NASA. Missions: Mars Cube One (MarCO). Available online: https://science.nasa.gov/mission/marco/ (accessed on 6 October 2024).
- Cottini, V.; Aslam, S.; Gorius, N.; Hewagama, T.; Glaze, L.; Ignatiev, N.; Piccioni, G.; D’Aversa, E. CUVE—CubeSat UV Experiment: Unveil Venus’ UV Absorber with CubeSat UV Mapping Spectrometer. In Proceedings of the European Planetary Science Congress, Riga, Latvia, 17–22 September 2017; Abstract No. EPSC2017-771. Available online: https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2017EPSC...11..771C (accessed on 6 October 2024).
- Mauro, D.; Colaprete, A.; Cook, A.; Snyder, T.; Bonner, K.; Larrabee, D.; Dono-Perez, A.; Kashani, A. The Aeolus Mission Concept: An Innovative Mission to Study the Winds and Climate of Mars. In Proceedings of the 32nd Annual AIAA/USU Conference on Small Satellites, Logan, UT, USA, 4–9 August 2018; Paper ID: SSC18-V-06. Available online: https://digitalcommons.usu.edu/smallsat/2018/all2018/285/ (accessed on 6 October 2024).
- Minton, D.; Spencer, D.; Horgan, B.; Putnam, Z.; Puig-Suari, J.; Christensen, P.; Tinker, C. CHARIOT TO THE MOONS OF MARS. In Proceedings of the 49th Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, The Woodlands, TX, USA, 19–23 March 2018; Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/379116280_CHARIOT_TO_THE_MOONS_OF_MARS (accessed on 6 October 2024).
- Kantsiper, B. The Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART) Mission Electric Propulsion Trade. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, MT, USA, 4–11 March 2017; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tortora, P.; Di Tana, V. LICIACube, the Italian Witness of DART Impact on Didymos. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 5th International Workshop on Metrology for AeroSpace (MetroAeroSpace), Turin, Italy, 19–21 June 2019; pp. 314–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dotto, E.; Della Corte, V.; Amoroso, M.; Bertini, I.; Brucato, J.R.; Capannolo, A.; Cotugno, B.; Cremonese, G.; Di Tana, V.; Gai, I.; et al. LICIACube—The Light Italian Cubesat for Imaging of Asteroids In Support of the NASA DART Mission Towards Asteroid (65803) Didymos. Planet. Space Sci. 2021, 199, 105185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarpa, E.; Battezzati, N.; Ciaglia, S.; Tricarico, P.; Cotugno, B.; Fazzoletto, E.; Impresario, G. The First-Ever Asteroid Fly-By Performed by a CubeSat: Outcomes of the LICIACube Mission. In Proceedings of the 37th Annual Small Satellite Conference, Logan, UT, USA, 5–10 August 2023; Paper ID: SSC23-I-01. Available online: https://digitalcommons.usu.edu/smallsat/2023/all2023/1/ (accessed on 7 October 2024).
- Lantoine, G.; Cox, A.; Sweetser, T.; Grebow, D.; Whiffen, G.; Garza, D.; Petropoulos, A.; Oguri, K.; Kangas, J.; Kruizinga, G.; et al. Trajectory & Maneuver Design of the NEA Scout Solar Sail Mission. Acta Astronaut. 2024, 225, 77–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talbert, T. ART Gets Its CubeSat Companion, Its Last Major Piece. NASA, 1 October 2021. Available online: https://www.nasa.gov/science-research/planetary-science/dart-gets-its-cubesat-companion-its-last-major-piece/ (accessed on 8 October 2024).
- Talbert, T. First Images from Italian Space Agency’s LICIACube Satellite. NASA, 27 September 2022. Available online: https://www.nasa.gov/solar-system/first-images-from-italian-space-agencys-liciacube-satellite/ (accessed on 7 October 2024).
- European Space Agency (ESA). Hera: Examining the First Test of Asteroid Deflection, Performing the First Survey of a Binary Asteroid System. Available online: https://www.esa.int/Space_Safety/Hera (accessed on 7 October 2024).
- Goldberg, H.R.; Karatekin, O.; Ritter, B.; Herique, A.; Tortora, P.; Prioroc, C.; Gutierrez, B.G.; Martino, P.; Carnelli, I. The Juventas CubeSat in Support of ESA’s Hera Mission to the Asteroid Didymos. In Proceedings of the 33rd Annual AIAA/USU Conference on Small Satellites, Logan, UT, USA, 3–8 August 2019; Paper ID: SSC19-WKIV-05. Available online: https://digitalcommons.usu.edu/smallsat/2019/all2019/73/ (accessed on 7 October 2024).
- Ferrari, F.; Franzese, V.; Pugliatti, M.; Giordano, C.; Topputo, F. Preliminary Mission Profile of Hera’s Milani CubeSat. Adv. Space Res. 2021, 67, 2010–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hera Mission. Milani CubeSat. Available online: https://www.heramission.space/hera-mission-milani-cubesat (accessed on 7 October 2024).
- Hera Mission. Juventas CubeSat. Available online: https://www.heramission.space/hera-mission-juventas-cubesat (accessed on 7 October 2024).
- NASA. Asteroids | Apophis. Available online: https://science.nasa.gov/solar-system/asteroids/apophis/ (accessed on 7 October 2024).
- Fogliano, V.; Walker, R.; Simonetti, S.; Cabral, F.d.S.P.; Ambrosio, G.; Karatekin, O.; Ritter, B.; Güttler, C.; Soons, K. SATIS: A Mission Study for a Deep-Space CubeSat to Observe (99942) Apophis, a Near-Earth Potential Hazardous Asteroid, Before, During, and After the Earth Fly-By. In Small Satellites Systems and Services Symposium (4S 2024); SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2025; Volume 13546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivares-Mendez, M.; Makhdoomi, M.R.; Yalçın, B.C.; Bokal, Z.; Muralidharan, V.; Ortiz Del Castillo, M.; Gaudilliere, V.; Pauly, L.; Borgue, O.; Alandihallaj, M.; et al. Zero-G Lab: A Multi-Purpose Facility for Emulating Space Operations. J. Space Saf. Eng. 2023, 10, 509–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalçın, B.C.; Martinez, C.; Coloma, S.; Skrzypczyk, E.; Olivares-Mendez, M.A. Lightweight Floating Platform for Ground-Based Emulation of On-Orbit Scenarios. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 94575–94588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiegel, I.A.; Zhou, B.; Goodloe, R.; Fox, B.; DiMatteo, J. CubeSat Proximity Operations Demonstration (CPOD) Mission Results. In Proceedings of the 37th Annual AIAA/USU Conference on Small Satellites, Logan, UT, USA, 5–10 August 2023; Paper ID: SSC23-XI-01. Available online: https://digitalcommons.usu.edu/smallsat/2023/all2023/119/ (accessed on 4 February 2025).
- Space-π. Vizard-ion. Available online: https://spacepi.space/satellites/vizard-ion/ (accessed on 3 June 2025).
- Yaginuma, K.; Asakawa, J.; Nakagawa, Y.; Tsuruda, Y.; Koizumi, H.; Kakihara, K.; Yanagida, K.; Murata, Y.; Ikura, M.; Matsushita, S.; et al. AQT-D: CubeSat Demonstration of a Water Propulsion System Deployed from ISS. Trans. Jpn. Soc. Aeronaut. Space Sci. Aerosp. Technol. Jpn. 2020, 18, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NASA. TechEdSat-10 Deploys from Space Station. 2020. Available online: https://www.nasa.gov/image-article/techedsat-10-deploys-from-space-station/ (accessed on 4 February 2025).
- Katan, C. NASA’s Next Solar Sail: Lessons Learned from NanoSail-D2. In Proceedings of the 26th Annual AIAA/USU Conference on Small Satellites: Enhancing Global Awareness through Small Satellites, Logan, UT, USA, 13–16 August 2012; Paper ID: M12-1762. Available online: https://digitalcommons.usu.edu/smallsat/2012/all2012/84/ (accessed on 4 February 2025).
- Slavinskis, A.; Janhunen, P. Special Issue: Advances in CubeSat Sails and Tethers (1st Edition). Aerospace 2024, 11, 1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, D.A.; Betts, B.; Bellardo, J.M.; Diaz, A.; Plante, B.; Mansell, J.R. The LightSail 2 Solar Sailing Technology Demonstration. Adv. Space Res. 2021, 67, 2878–2889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, A.; Freedman, M.; Grist, R.; Wesson, C.; Hanson, M. Flight Qualification of a Water Electrolysis Propulsion System. In Proceedings of the 35th Annual AIAA/USU Conference on Small Satellites, Logan, UT, USA, 7–12 August 2021; Paper ID: SSC21-XI-06. Available online: https://digitalcommons.usu.edu/smallsat/2021/all2021/209/ (accessed on 5 February 2025).
- Underwood, C.; Viquerat, A.; Taylor, B.; Massimiani, C.; Duke, R.; Fellowes, S.; Schenk, M.; Stewart, B.; Bridges, C.P.; Masutti, D.; et al. The InflateSail CubeSat Mission—The First European Demonstration of Drag-Sail De-Orbiting. In Proceedings of the 4th IAA Conference on University Satellite Missions and CubeSat Workshop, Rome, Italy, 4–7 December 2017; Volume 163. [Google Scholar]
- Stohlman, O.R.; Lappas, V. Development of the Deorbitsail Flight Model. In Proceedings of the AIAA SciTech Forum, National Harbor, MD, USA, 13–17 January 2014. AIAA Paper 2014-1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, R.C.; Agasid, E.F.; Baker, C.E.; Treptow, J.V.; Mayer, D.J.; Phan, S.; De Rosee, R.; Stupl, J.; Fishman, J.L. NASA Small Spacecraft Technology (SST) Program: Recent and Upcoming Technology Demonstrations and Development Efforts. In Proceedings of the Small Satellites Systems and Services Symposium (4S 2024), Palma de Mallorca, Spain, 27 May–1 June 2024; Petrozzi-Ilstad, M., Ed.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2025; Volume 13546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NASA. NASA Begins New Deployable Solar Array Tech Demo on Pathfinder Spacecraft. 2024. Available online: https://www.nasa.gov/general/nasa-begins-new-deployable-solar-array-tech-demo-on-pathfinder-spacecraft/ (accessed on 4 February 2025).
- NASA. Pathfinder Technology Demonstrator (PTD). 2024. Available online: https://www.nasa.gov/smallspacecraft/pathfinder-technology-demonstrator/ (accessed on 4 February 2025).
- Goodwill, J.; Wilson, C.; MacKinnon, J. Current AI Technology in Space. In Precision Medicine for Long and Safe Permanence of Humans in Space; Krittanawong, C., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2025; pp. 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrisi, G.; Del Frate, F.; Schiavon, G. Artificial Intelligence Based On-Board Image Compression for the Φ-Sat-2 Mission. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2023, 16, 8063–8075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S.; Adams, C.; Alem, N.; Cannon, H.; Grashuis, R.; Hendriks, T.; Hwang, S.; Iatauro, M.; Pires, C.; Kruger, J.; et al. Starling CubeSat Swarm Technology Demonstration Flight Results. In Proceedings of the 38th Annual Small Satellite Conference; Logan, UT, USA, 5–10 August 2024, Paper ID: SSC24-I-06. Available online: https://ntrs.nasa.gov/api/citations/20240006994/downloads/SSC24_Starling_Swarm_Flight_Results.pdf (accessed on 5 February 2025).
- Kepko, L.; Santos Soto, L.; Clagett, C.; Azimi, B.; Chai, D.; Cudmore, A.; Marshall, J.; Lucas, J. Dellingr: Reliability Lessons Learned from On-Orbit. In Proceedings of the 32nd Annual AIAA/USU Conference on Small Satellites, Logan, UT, USA, 4–9 August 2018; Paper ID: SSC18-I-01. Available online: https://digitalcommons.usu.edu/smallsat/2018/all2018/250/ (accessed on 5 February 2025).
- Kanekal, S.; Lucas, J. CeREs: The Compact Radiation Belt Explorer. In Proceedings of the 32nd Annual AIAA/USU Conference on Small Satellites, Logan, UT, USA, 4–9 August 2018; Available online: https://digitalcommons.usu.edu/smallsat/2018/all2018/259/ (accessed on 5 February 2025).
- International Amateur Radio Union (IARU). TRISAT-R Satellite Coordination Details. Available online: https://iaru.amsat-uk.org/formal_detail.php?serialnum=708 (accessed on 4 February 2025).
- University of Maribor. TRISAT-R Mission Overview. Available online: https://trisat.um.si/trisat-r.html (accessed on 4 February 2025).
- University of Montpellier. Nanosatellites Projects: Our 1U Projects. Centre Spatial Universitaire Montpellier-Nîmes (CSUM). Available online: https://csum.umontpellier.fr/en/nanosatellites-projects-our-1u-projects/ (accessed on 4 February 2025).
- Mersmann, K. Dellingr: The Little CubeSat That Could. NASA. Available online: https://www.nasa.gov/solar-system/dellingr-the-little-cubesat-that-could/ (accessed on 4 February 2025).
- European Space Agency. AI CubeSat Headed to Van Allen Belts on Vega-C. Available online: https://www.esa.int/Enabling_Support/Space_Engineering_Technology/AI_CubeSat_headed_to_Van_Allen_Belts_on_Vega-C (accessed on 7 February 2025).
- Vergoossen, T.; Villar, A.; Lohrmann, A.; Lim, H.Y.; Shankar, D.; Bedington, R.; Wildfeuer, C.F.; Griffin, D.; Oi, D.K.L.; Bai, X.; et al. SpooQy-1: The First Nano-Satellite to Demonstrate Quantum Entanglement in Space. In Proceedings of the 34th Annual AIAA/USU Conference on Small Satellites, Logan, UT, USA, 1–6 August 2020; Paper ID: SSC20-WKII-02. Available online: https://digitalcommons.usu.edu/smallsat/2020/all2020/10/ (accessed on 7 February 2025).
- SpeQtral. Satellite QKD—Harnessing the Fundamental Laws of the Universe to Protect Our Most Vital Digital Communications. Available online: https://speqtralquantum.com/technology/satellite-qkd (accessed on 7 February 2025).
- Mercury, C.; Mohapatra, S.; Colquhoun, C.; Greenland, S.; Cebecauer, M.; Karagiannakis, P.; McTaggart, A.; Lowndes, D.; Stefko, M.; Rarity, J. Payload Testing of a Weak Coherent Pulse Quantum Key Distribution Module for the Responsive Operations on Key Services (ROKS) Mission. In Proceedings of the 35th Annual AIAA/USU Conference on Small Satellites, Logan, UT, USA, 7–12 August 2021; Utah State University: Logan, UT, USA, 2021. Paper ID: SSC21-IX-04. Available online: https://digitalcommons.usu.edu/smallsat/2021/all2021/195/ (accessed on 7 February 2025).
- Snowden, C. An Update on Missions 1 and 2: Same Name, New Vehicle, New Standard for Space Exploration. AstroForge, 10 January 2025. Available online: https://www.astroforge.com/updates/an-update-on-mission-1-mission-2-same-name-new-vehicle-new-standard-for-space-exploration (accessed on 7 February 2025).
- Nogales, C.; Grim, B.; Kamstra, M.; Campbell, B.; Ewing, A.; Hance, R.; Griffin, J.; Parke, S. MakerSat-0: 3D-Printed Polymer Degradation First Data from Orbit. In Proceedings of the 32nd Annual AIAA/USU Conference on Small Satellites, Logan, UT, USA, 4–9 August 2018; Paper ID: SSC18-WKIII-01. Available online: https://digitalcommons.usu.edu/smallsat/2018/all2018/434/ (accessed on 7 February 2025).
- Campbell, B.; Nogales, C.; Grim, B.; Kamstra, M.; Griffin, J.; Parke, S. On-Orbit Polymer Degradation Results from MakerSat-1: First Satellite Designed to Be Additively Manufactured in Space. In Proceedings of the 34th Annual AIAA/USU Conference on Small Satellites, Logan, UT, USA, 1–6 August 2020; Paper ID: SSC20-WKVII-04. Available online: https://digitalcommons.usu.edu/smallsat/2020/all2020/45/ (accessed on 7 February 2025).
- The CubeSat Program. CubeSat Design Specification Rev. 14.1; California Polytechnic State University: San Luis Obispo, CA, USA, 2022; Available online: https://static1.squarespace.com/static/5418c831e4b0fa4ecac1bacd/t/62193b7fc9e72e0053f00910/1645820809779/CDS+REV14_1+2022-02-09.pdf (accessed on 10 May 2025).
- Loo, C.C.; Wang, X. Navigating the Spectrum: An Overview of ITU’s Regulatory Process for Small Satellites. In Proceedings of the 38th Annual Conference on Small Satellites, Logan, UT, USA, 3–8 August 2024; Paper ID: SSC24-XI-05. Available online: https://digitalcommons.usu.edu/smallsat/2024/all2024/134/ (accessed on 7 May 2025).
- ITU Radiocommunication Sector. ITU-R Handbook on Small Satellites. Available online: https://www.itu.int/hub/publication/r-hdb-65-2023/ (accessed on 7 May 2025).
- Federal Register the Daily Journal of the United States Government. Space Innovation; Mitigation of Orbital Debris in the New Space Age. Available online: https://www.federalregister.gov/documents/2024/08/09/2024-17093/space-innovation-mitigation-of-orbital-debris-in-the-new-space-age (accessed on 7 May 2025).
- European Space Agency (ESA). ESA’s Zero Debris Approach. Available online: https://www.esa.int/Space_Safety/Clean_Space/ESA_s_Zero_Debris_approach (accessed on 7 May 2025).
- National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). Deorbit Systems—State of the Art Report. Available online: https://www.nasa.gov/smallsat-institute/sst-soa/deorbit-systems/ (accessed on 7 May 2025).
- ClearSpace. ClearSpace—In-Orbit Servicing and Space Debris Removal. 2025. Available online: https://clearspace.today/ (accessed on 5 June 2025).
- Astroscale. Astroscale: On-Orbit Servicing and Space Debris Removal Solutions. 2025. Available online: https://astroscale.com/ (accessed on 5 June 2025).
- Yalçin, B.C.; Peitso, P.; Janhunen, P.; Genzer, M.; Yli-Opas, P.; Laurila, H.; Hieta, M.; Haukka, H.; Macieira, D.; Toivanen, P.; et al. New Challenges and Opportunities of Passive Deorbiting Systems: Emulation of Micro-Gravity for the ESA-Dragliner. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Space Robotics (iSpaRo) 2024, Luxembourg, 24–27 June 2024; Available online: https://orbilu.uni.lu/handle/10993/61747 (accessed on 5 June 2025).
- Inter-Agency Space Debris Coordination Committee (IADC). Available online: https://www.iadc-home.org/what_iadc (accessed on 7 May 2025).
- Peter, H. The Importance of the UN COPUOS in the Space Debris Mitigation: What Evolution for the UN COPUOS? In Proceedings of the 8th European Conference on Space Debris (Virtual), Darmstadt, Germany, 20–23 April 2021; Flohrer, T., Lemmens, S., Schmitz, F., Eds.; ESA Space Debris Office, May 2021. Available online: https://conference.sdo.esoc.esa.int/proceedings/sdc8/paper/194 (accessed on 7 May 2025).
- Fiete, R.; Tantalo, T.; Calus, J.; Mooney, J. Image quality assessment of sparse aperture designs. In Proceedings of the 29th Applied Imagery Pattern Recognition Workshop, Washington, DC, USA, 16–18 October 2000; pp. 269–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D. IEEE Spectrum. Chip-Scale Spectrometers Compete With Performance of Standard Versions. Available online: https://spectrum.ieee.org/chipscale-spectrometers-match-peformance-of-their-big-brothers (accessed on 4 June 2025).
- Dolph Microwave. How Big Are Satellite Antennas? Available online: https://www.dolphmicrowave.com/default/how-big-are-satellite-antennas/ (accessed on 4 June 2025).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).