Numerical Study on Detonation Initiation Process in Channels Equipped with Typical Ramjet Flameholders
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Physical Models and Calculation Methods
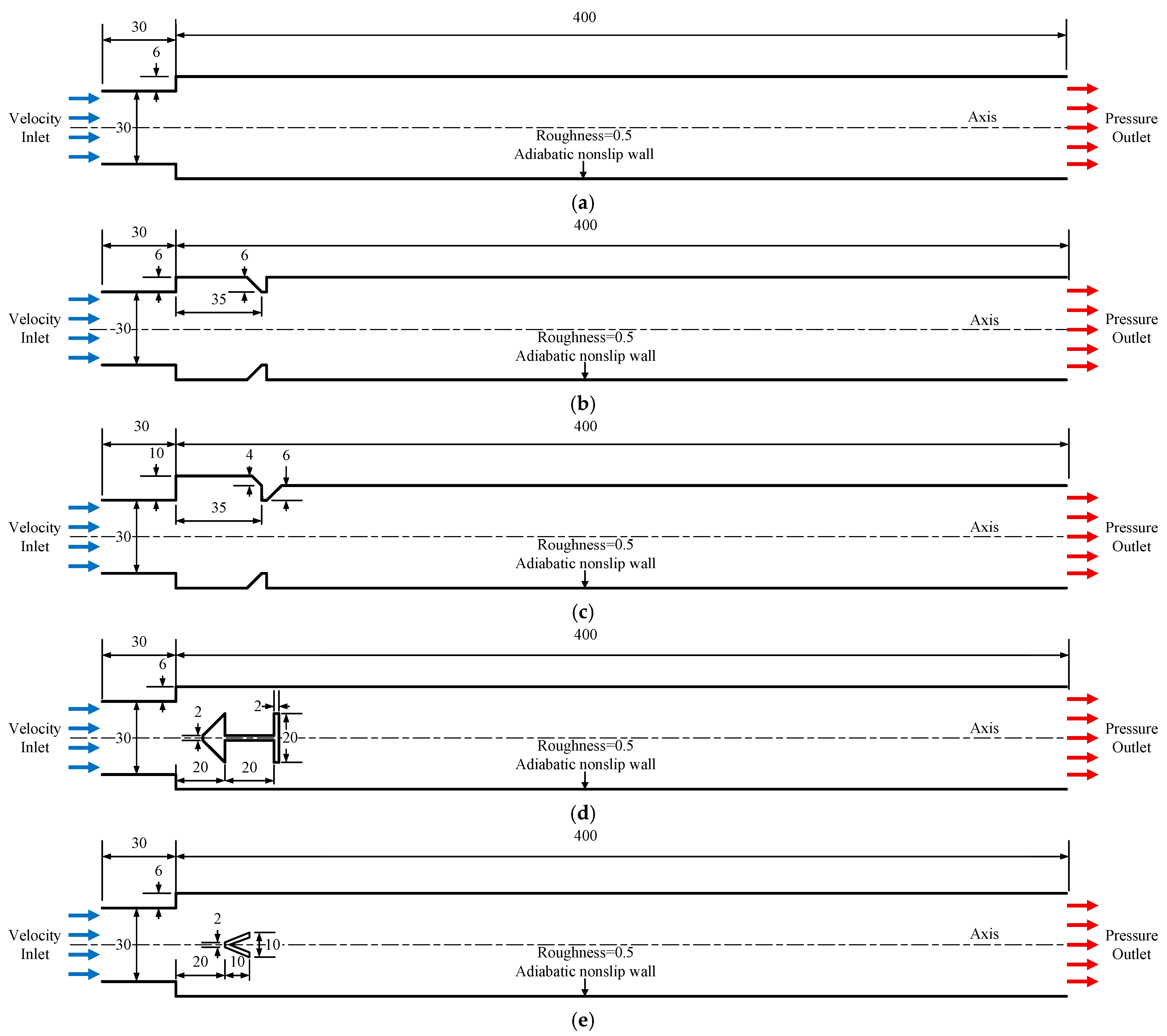
2.1. Physical Models
2.2. Calculation Methods and Validation
2.2.1. Calculation Methods
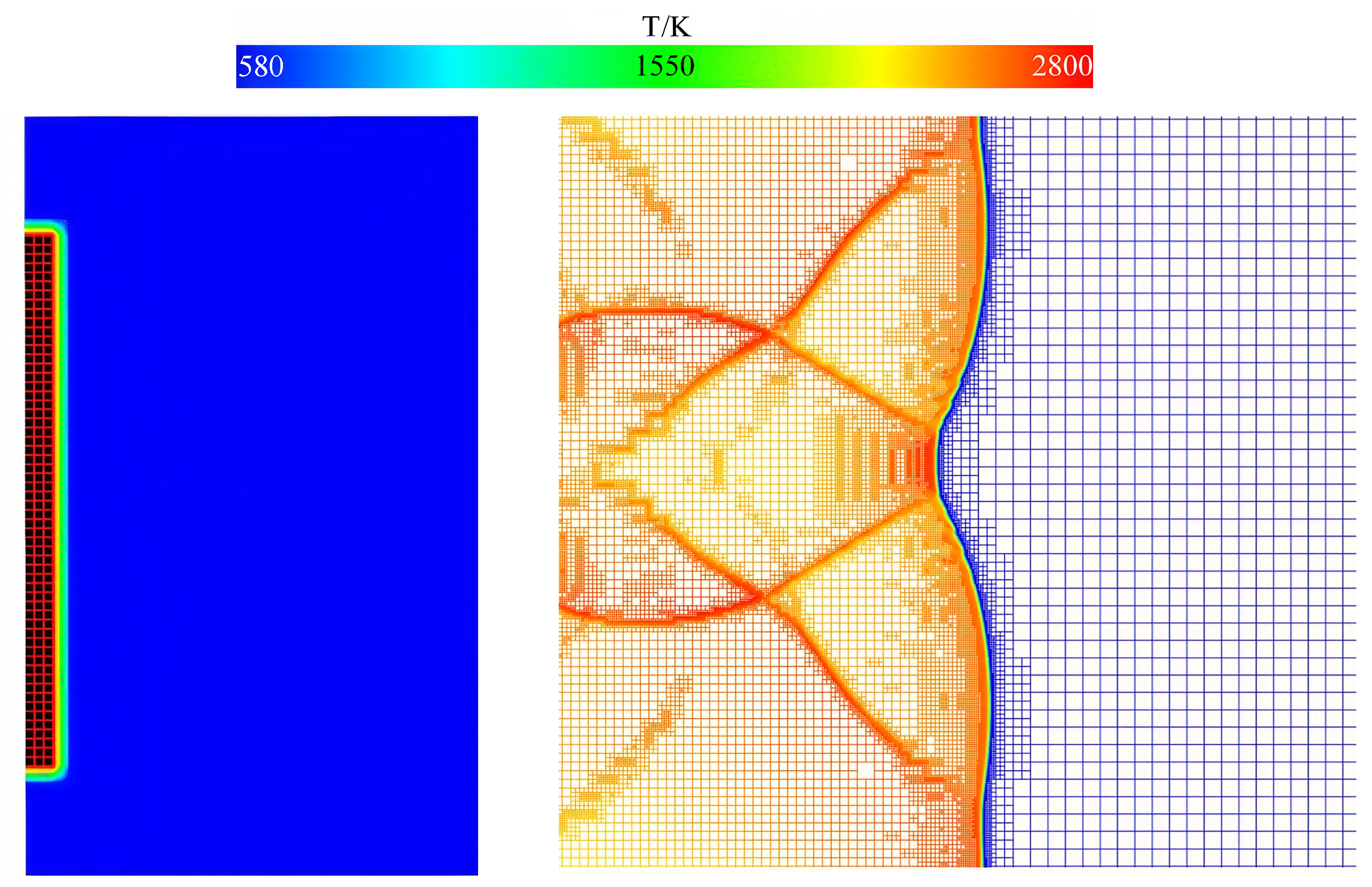
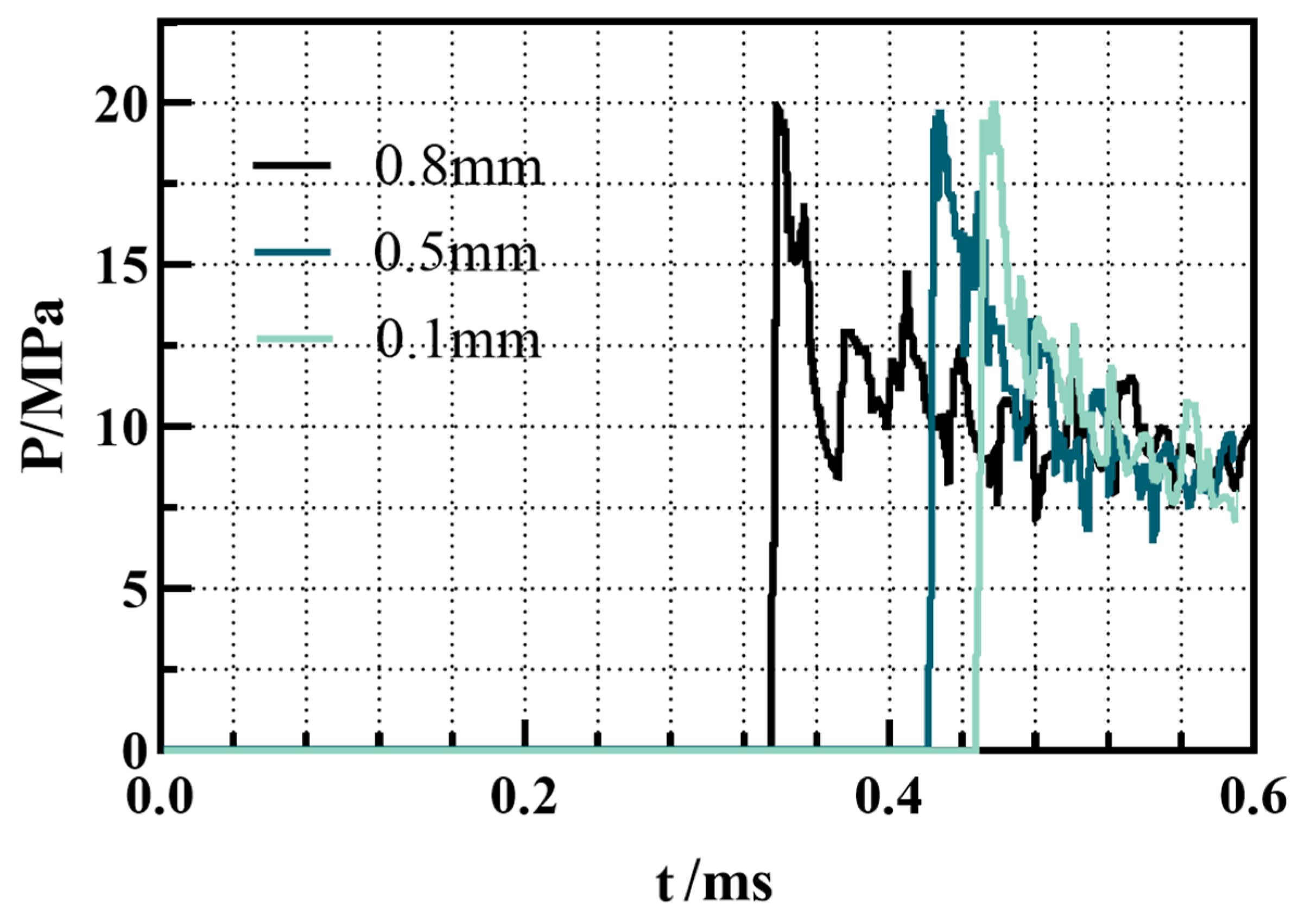
2.2.2. Validation
3. Results and Analysis
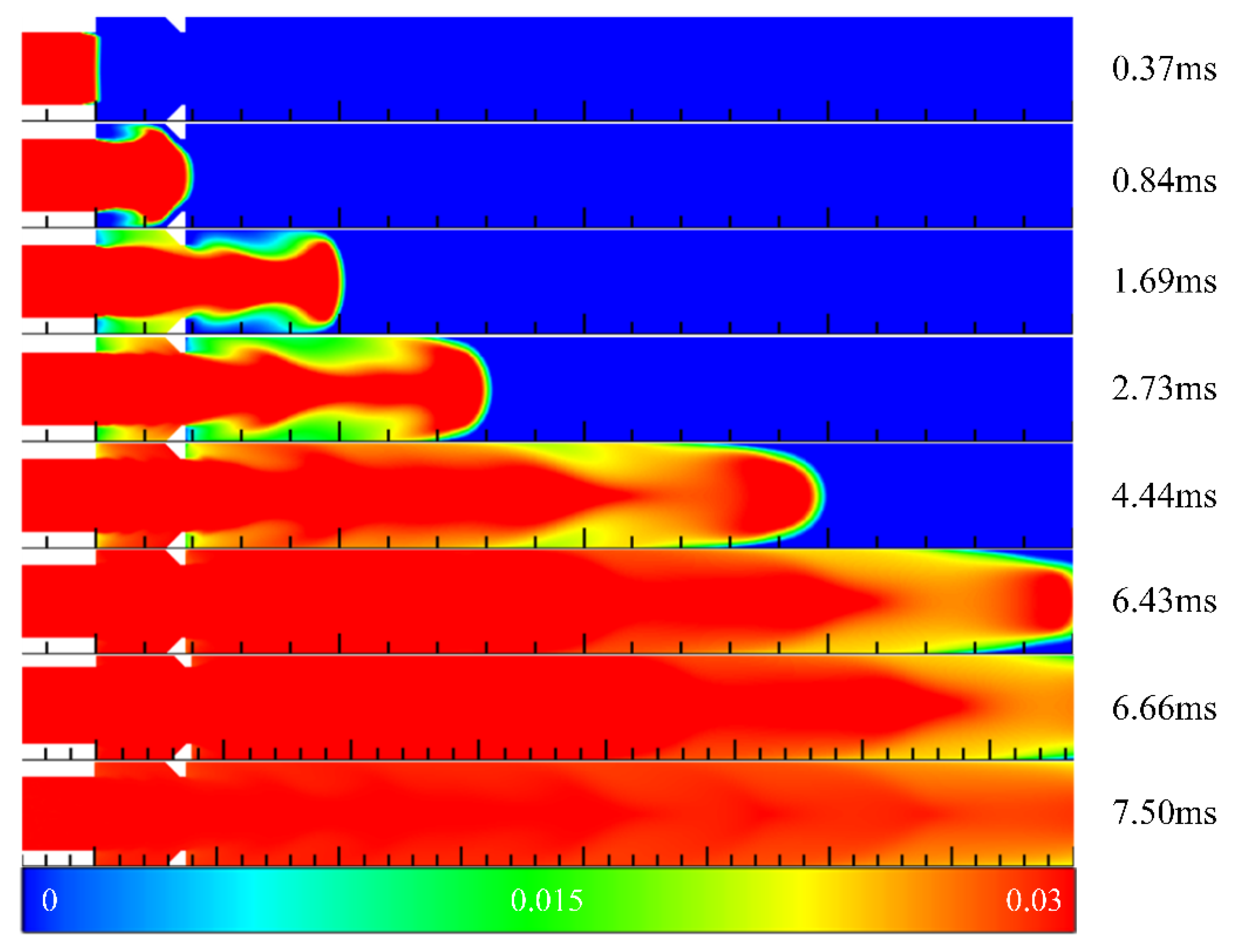
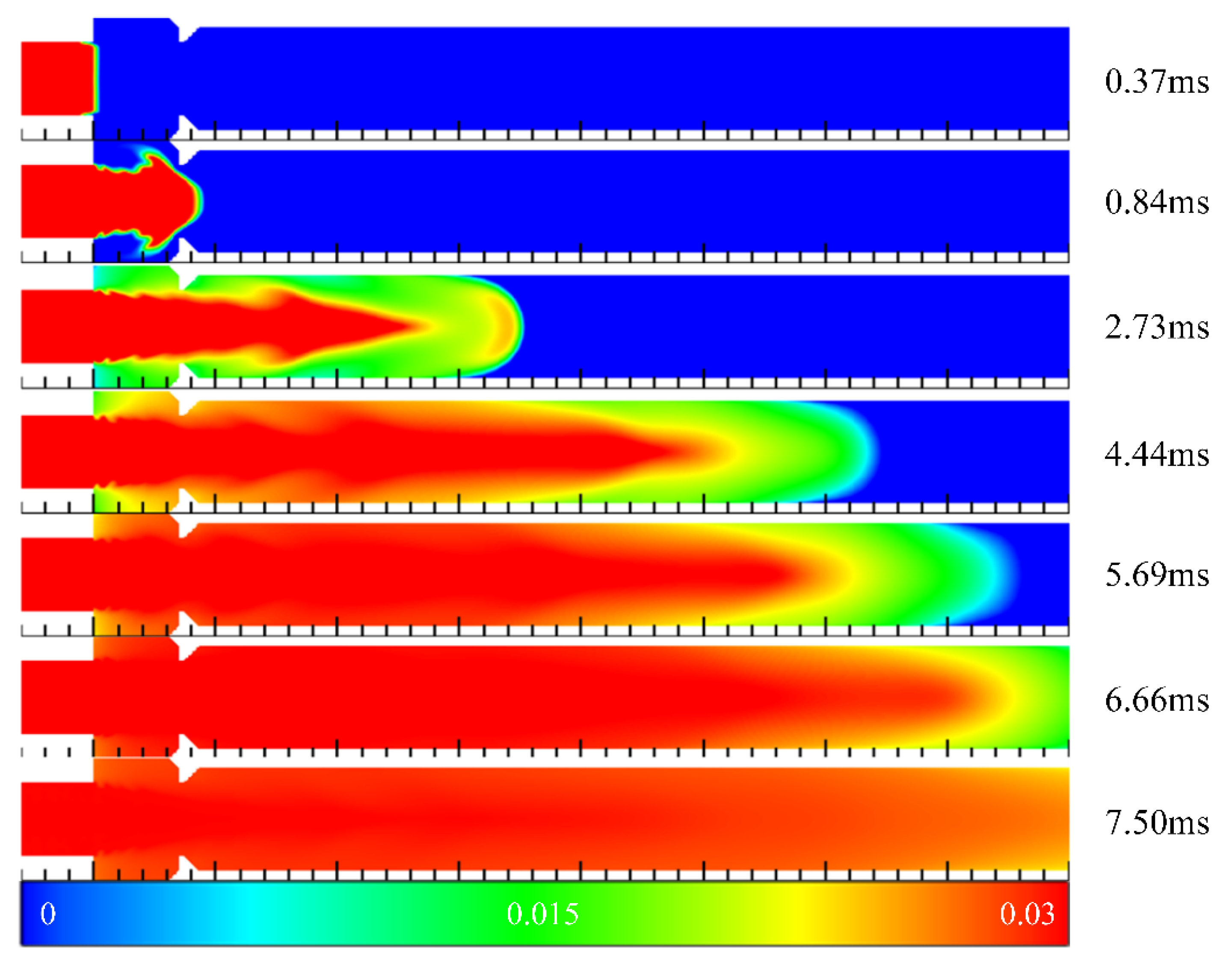
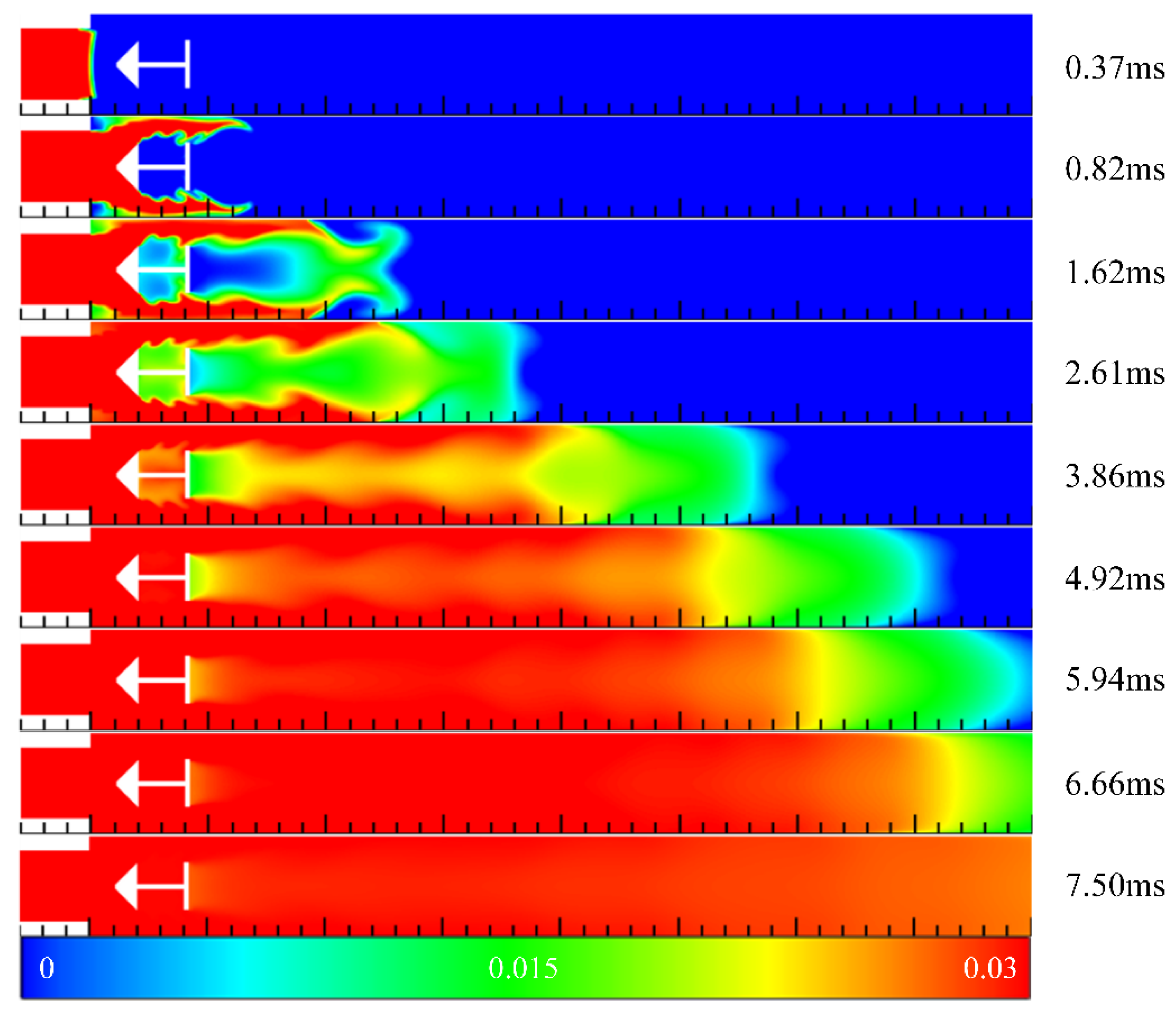
3.1. Filling Process in Channels with Typical Ramjet Flameholders
3.2. Summary of Filling Process in Channels with Typical Ramjet Flameholders
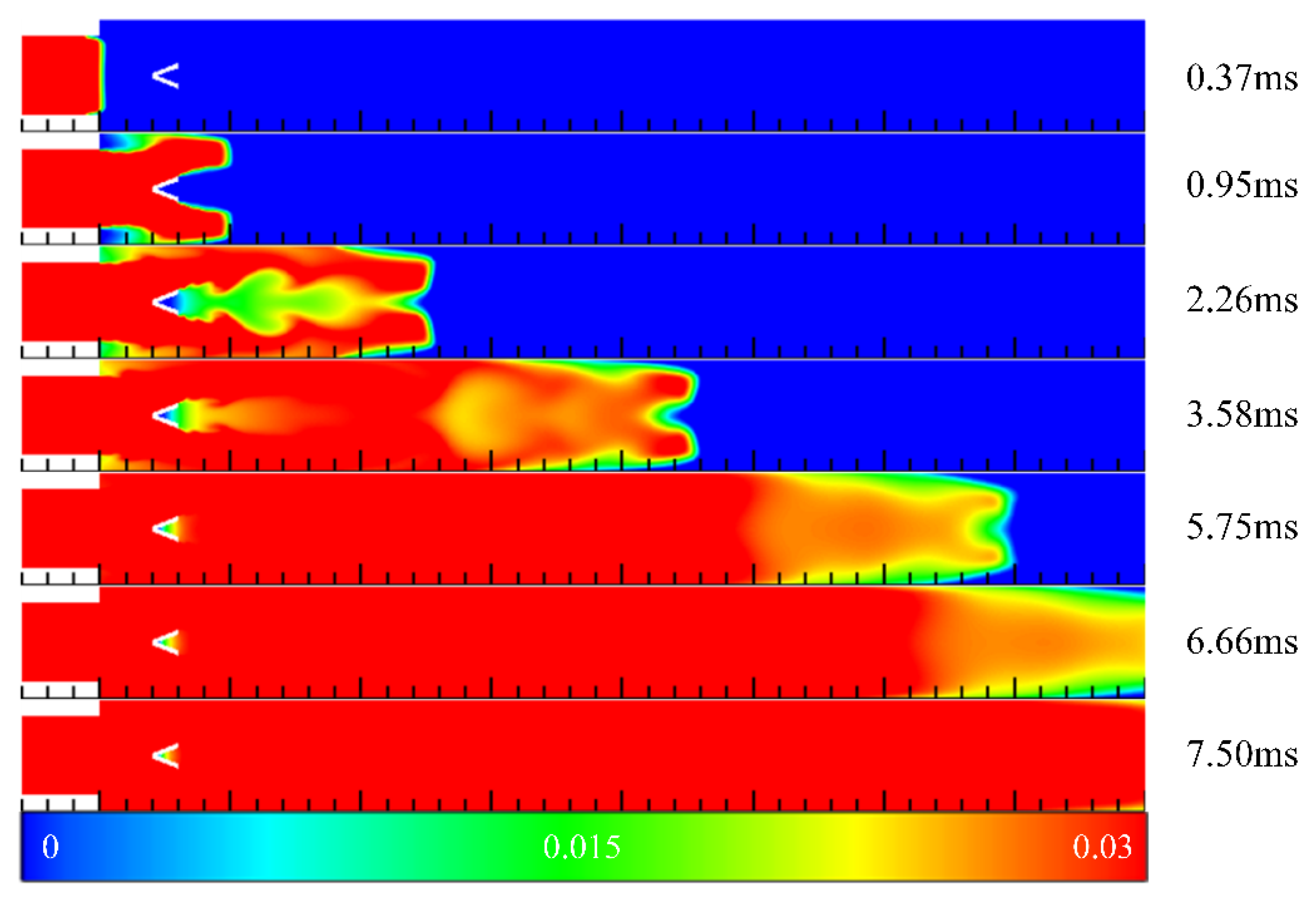
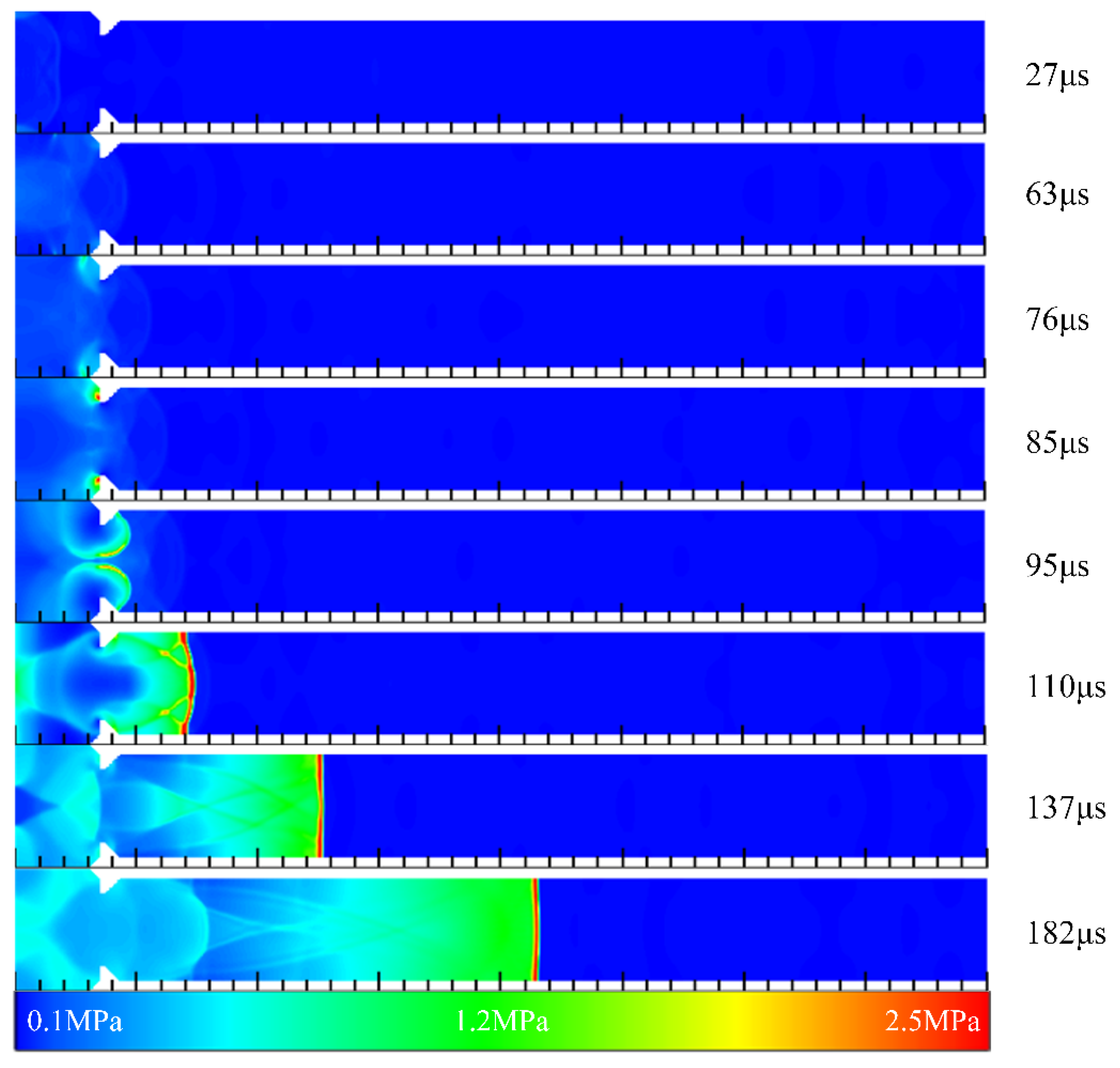
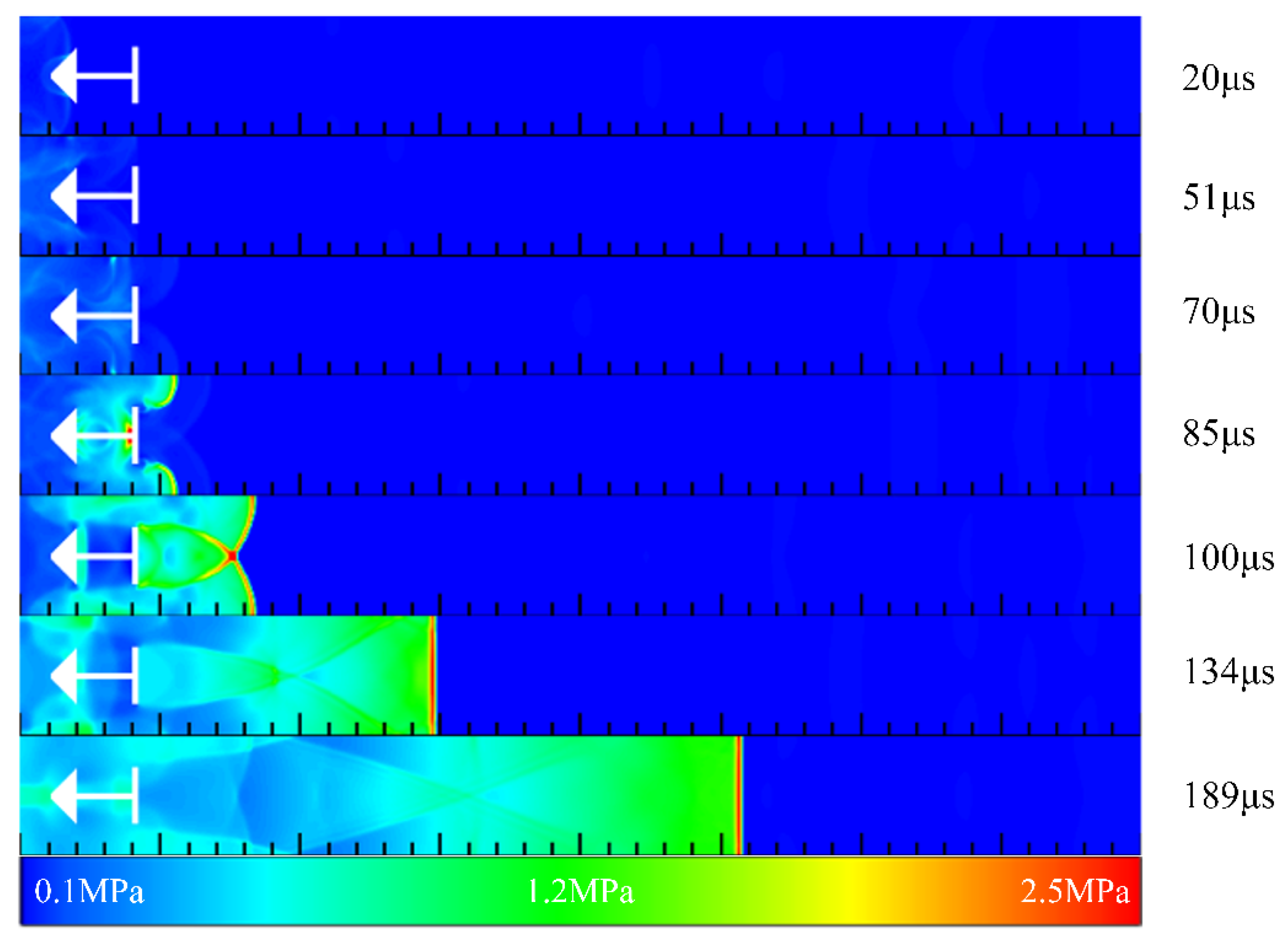
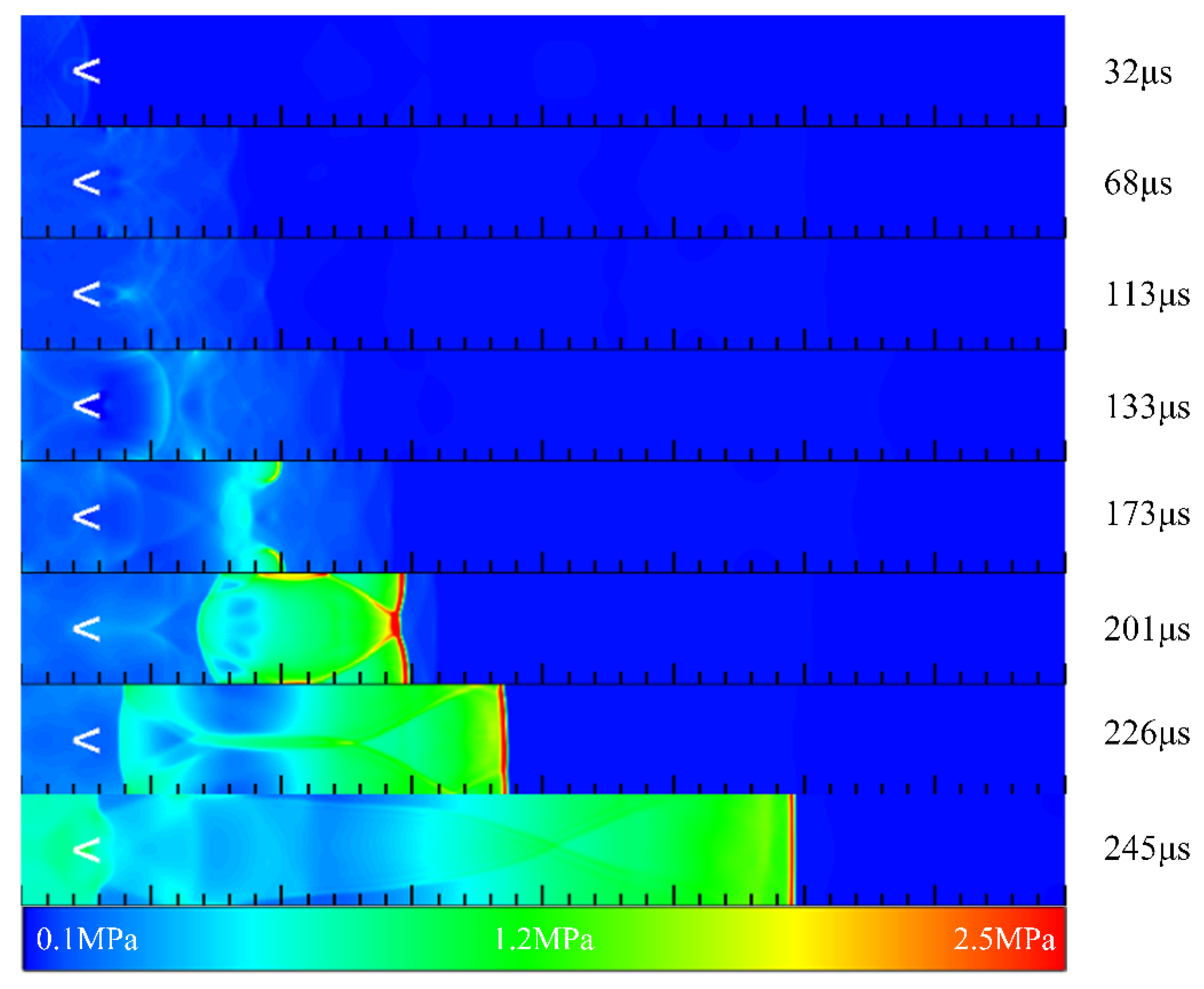
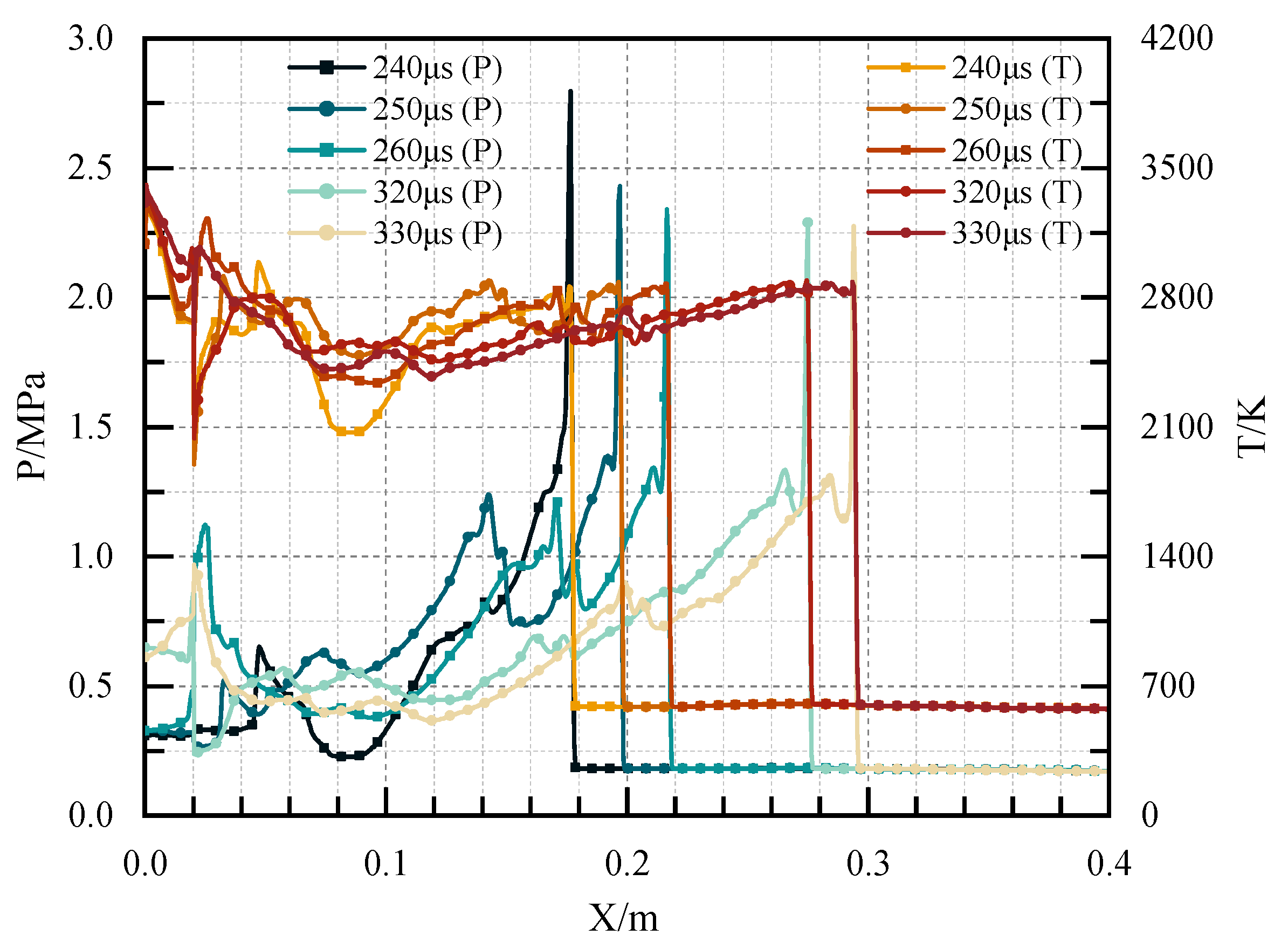
3.3. Detonation Initiation Process in Channels with Typical Ramjet Flameholders
3.4. Summary of Detonation Initiation Process in Channels with Typical Ramjet Flameholders
4. Conclusions
- (1)
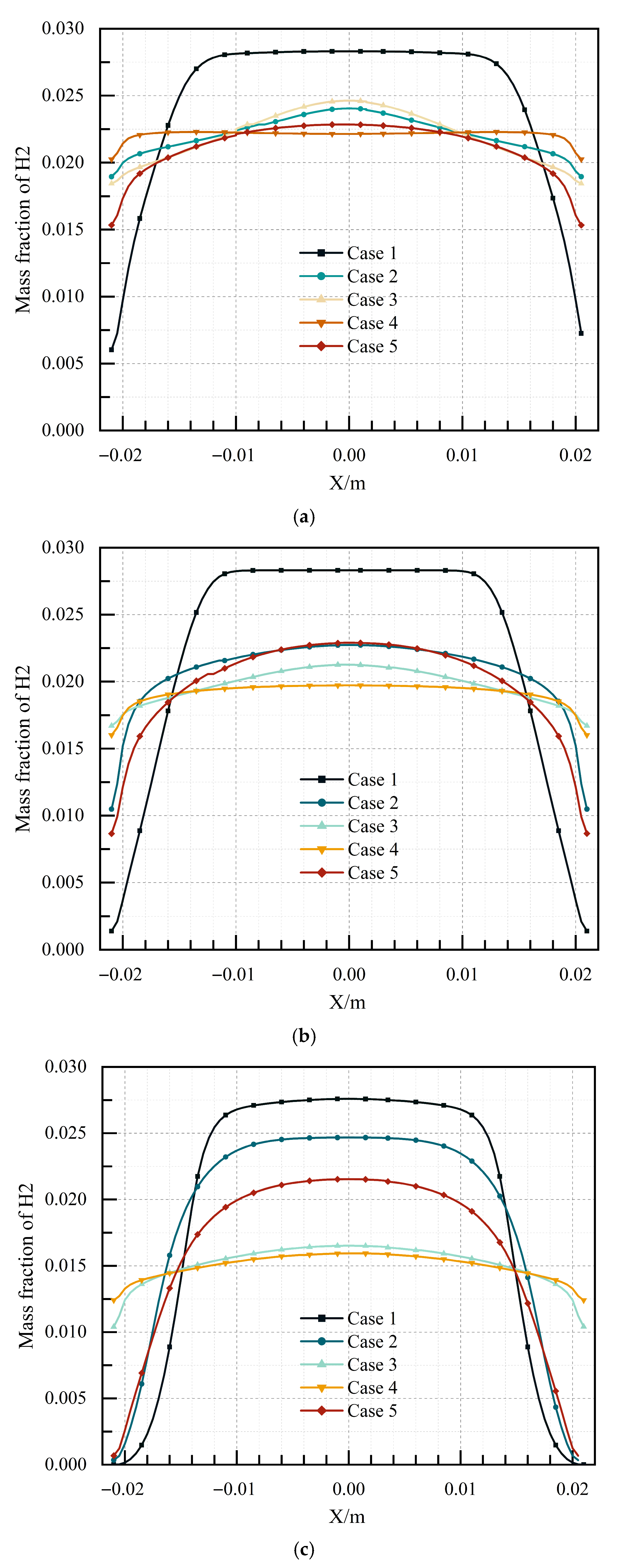
- The flameholders would affect the filling effect greatly. The blocking ratio had a great influence on the filling process, and the blocking ratio should be minimized in the design for a better filling effect. The hydrogen volume discharged from the outlet of the channel and the time for hydrogen to reach the outlet of the channel were related to the blocking ratio and the cavity aft wall inclination angle during the filling process.
- (2)
- The initiation process showed that the flameholders promoted the generation of a detonation wave. In contrast, the detonation wave could not be initiated in the channel without the flameholders despite the better filling effect. Moreover, different flameholders would change the time and position of high-pressure point formation, and the position of the high-pressure point formed by the sudden expansion cavity was the earliest. The detonation wave pressure in the case with the central cavity was the largest, and the time for generating the stable detonation wave was the shortest, followed by the sudden expansion cavity, and the V-shaped groove was the longest.
- (3)
- On the whole, the blockage ratio of the central cavity was very large, which was not conducive to the filling process and practical application. Not only that, but it also wasted fuel. In contrast, the blockage ratio of the sudden expansion cavity was smaller than that of the central cavity, the hydrogen concentration at the outlet was relatively even, and the detonation initiation characteristics were good, which made it the most suitable flameholder structure for PD-Ramjet in this study.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PDE | Pulse Detonation Engine |
| PD-Ramjet | Pulse Detonation-based Ramjet |
| DDT | Deflagration to detonation transition |
| C-J | Chapman–Jouguet |
| EDC | Eddy dissipation concept |
| PISO | Pressure implicit with splitting of operators |
| CEA | Chemical equilibrium and applications |
References
- Roy, G.D.; Frolov, S.M.; Borisov, A.A.; Netzer, D.W. Pulse Detonation Propulsion: Challenges, Current Status, and Future Perspective. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2004, 30, 545–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wei, L.; Qin, W.; Zhao, X.; Xiao, J. Effects of Mixture Initial Conditions on Deflagration to Detonation Transition Enhanced by Transverse Jets. Energy 2024, 304, 132225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Qin, W.; Huang, J. Reheat Effect on the Improvement in Efficiency of the Turbine Driven by Pulse Detonation. Def. Technol. 2024, 31, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Liu, J.; Qin, W.; Wei, L.; Yang, Y. Numerical Study on the Deflagration to Detonation Transition Promoted by Transverse Jet. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2023, 136, 108206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Qin, W.; Li, J.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, J. Effects of Detonation Initial Conditions on Performance of Pulse Detonation Chamber-Axial Turbine Combined System. Energy 2023, 278, 127765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Huang, J.; Wang, Y.; Wei, L.; Qin, W. Numerical Study of Back-Propagation Suppression and Intake Loss in an Air-Breathing Pulse Detonation Engine. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2022, 126, 107566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wei, L.; Qin, W.; Liang, Z.; Zhang, K. Oxygen Concentration Distribution in a Pulse Detonation Engine with Nozzle–Ejector Combinational Structures. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part G J. Aerosp. Eng. 2021, 235, 2059–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Fan, W. Principle and Key Technology of Pulse Detonation Engine; Northwestern Polytechnical University Press: Xi’an, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Frolov, S.M. Liquid-Fueled, Air-Breathing Pulse Detonation Engine Demonstrator: Operation Principles and Performance. J. Propuls. Power 2006, 22, 1162–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wei, L.; Li, H.; Pan, Z.; Huang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z. Ignition Energy Effect on Detonation Initiation by Single and Two Successive Ignitions. Therm. Sci. 2020, 24, 4209–4220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brophy, C.M.; Netzer, D.; Forster, L.T.D. Detonation Studies of JP-10 with Oxygen and Air for Pulse Detonation Engine Development. In Proceedings of the 34th AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference and Exhibit, Cleveland, OH, USA, 13–15 July 1998; American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics Inc., AIAA: Cleveland, OH, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Qin, W.; Huang, J.; Wei, L.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Numerical Investigation of the Effect of Jet Intensity from Internal Jet Tube on Detonation Initiation Characteristics. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 13732–13745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Hui, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, J.; Qin, W.; Yang, Y. Numerical Study of Hydrogen Ratio Effect on Detonation Initiation Characteristics of Aviation Kerosene with Hydrogen Addition. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2024, 152, 109353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Tang, T.; Zhang, J.; Xiong, D.; Wang, H.; Sun, M. Analysis of influencing factors on numerical simulation of transverse jet in supersonic flow. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2023, 15, 16878132231214949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, S.; Jeung, I.; Parent, B.; Choi, J. Numerical investigation of transverse hydrogen jet into supersonic crossflow using detached-eddy simulation. AIAA J. 2010, 48, 1047–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, D.; Candler, G. Hybrid Reynolds-averaged and large-eddy simulation of normal injection into a supersonic crossflow. J. Propul. Power 2010, 26, 533–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, T.R.; Hoke, J.L.; Brown, M.S.; Gord, J.R.; Schauer, F.R. Experimental Study of Deflagration-to-Detonation Enhancement Techniques in a H2/Air Pulsed-Detonation Engine. In Proceedings of the 38th AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference and Exhibit, Indianapolis, IN, USA, 7–10 July 2002; AIAA International: Indianapolis, IN, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, L.; Wang, Z.; Qin, W.; Zhang, L. Numerical Study on Detonation Initiation Process in the Chamber with Characteristic Structures of the Dual-Mode Scramjet Combustor. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part G J. Aerosp. Eng. 2023, 237, 701–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xiao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Long, H.; Zhang, Z.; Li, M.; Zhan, Y. Numerical Study on Detonation Initiation Process in a Reverse Ignition Boosted Detonation Chamber. Phys. Fluids 2024, 36, 105118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Rong, K.; Zeng, H.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, P. Advances in Shock Wave Focusing and Induced. J. Propuls. Technol. 2015, 36, 1441–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosikov, V.A.; Torunov, S.I.; Dudin, S.V. Smoothing the Front of the Detonation Wave in Experiments with Multipoint Initiation. In Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Equations of State for Matter, Elbrus, Kabardino-Balkaria, Russia, 1–6 March 2018; IOP Publishing Ltd.: Bristol, UK, 2019; Volume 1147, p. 012027. [Google Scholar]
- Ishii, K.; Akiyoshi, T.; Gonda, M.; Murayama, M. Effects of Flame Jet Configurations on Detonation Initiation. In Shock Waves, Proceedings of the 26th International Symposium on Shock Waves, Göttingen, Germany, 15–20 July 2009; Hannemann, K., Seiler, F., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 239–244. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, X.; Chen, W.; Jin, K.; Deiterding, R.; Liang, J. An Experimental Study of Detonation Initiation in Supersonic Flow Using a Hot Jet. Combust. Flame 2023, 249, 112613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Z.; Yang, G.; Gao, W.; Li, S.; Shen, Q.; Sun, H. Modeling of Non-Homogeneous Premixed Hydrogen-Air Flame Acceleration and Deflagration to Detonation Transition in an Obstructed Channel. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 50, 1209–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.; Pan, J.; Quaye, E.K.; Jiang, C. Numerical Simulation of Hydrogen-Air Flame Acceleration and Detonation Initiation in Tubes Equipped with Arc Obstacles of Different Chord Lengths. Acta Astronaut. 2020, 177, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunoro Ahumada, C.; Mannan, M.S.; Wang, Q.; Petersen, E.L. Hydrogen Detonation Onset behind Two Obstructions with Unequal Blockage Ratio and Opening Geometry. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 31468–31480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habicht, F.E.; Yücel, F.C.; Gray, J.A.; Paschereit, C.O. Detonation Initiation by Shock Focusing at Elevated Pressure Conditions in a Pulse Detonation Combustor. Int. J. Spray Combust. Dyn. 2020, 12, 175682772092171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, B.; Ng, H.D. Detonation Onset Due to the Energy Accumulation Effect of Shock Wave Focusing. Acta Astronaut. 2024, 215, 264–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikitin, V.F.; Mikhalchenko, E.V.; Stamov, L.I.; Tyurenkova, V.V.; Smirnov, N.N. Evolution of the Cellular Structure of Detonation Waves under the Condition of Non-Uniform Initiation. Acta Astronaut. 2023, 213, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Huang, J.; Lei, G.; Wang, T.; Chen, J.; Han, W. Effects of Confinement on Detonation in H2–O2 Mixture with Transverse Concentration Gradient. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 18486–18497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Peng, L. Numerical Investigation on Detonation Initiation and Propagation with a Symmetric-Jet in Supersonic Combustible Gas. Aerospace 2022, 9, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarkov, A.; Kiverin, A.; Yakovenko, I. Effect of Channel Geometry on the Flame Acceleration and Transition to Detonation in Acetylene-Oxygen-Nitrogen Mixtures. Acta Astronaut. 2024, 217, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Pan, J.; Jiang, C.; Zhu, Y.; Li, J.; Quaye, E.K. Detonation Propagation Characteristics of H2/O2/AR in Multi-Angle Bifurcation Tubes. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 13248–13263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Liu, D.; Li, M.; Xiao, H. Effect of Wall Roughness on Flame Acceleration and Deflagration-to-Detonation Transition in a Narrow Channel. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 51, 880–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Pan, J.; Li, J.; Shi, X.; Quaye, E.K. Numerical Simulation of Detonation Re-Initiation in a 90° Bifurcated Channel Filled with n-Heptane/Air Mixture. Acta Astronaut. 2023, 202, 497–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Koo, I.; Lee, K.; Lee, E.; Han, H.; Jeong, S.; Kim, H.; Choi, J. Experimental Study on the Ignition Characteristics of Scramjet Combustor with Tandem Cavities Using Micro-Pulse Detonation Engine. Aerospace 2023, 10, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunik, Y.V.; Mayorov, V.O. Energy Efficiency of Detonation Combustion in Supersonic Ramjet Engines. Acta Astronaut. 2022, 194, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Liang, J.; Deiterding, R.; Che, Y.; Lin, Z. Adaptive mesh refinement based simulations of three-dimensional detonation combustion in supersonic combustible mixtures with a detailed reaction model. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy. 2016, 41, 3222–3239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jackson, C.; Jonathan, T.; Xian, S.; Irenaeus, W.; Andreas, M.; Wang, H. Three-dimensional detonation structure and its response to confinement. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2023, 39, 2915–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellenberger, M.; Ciccarelli, G. Three-dimensional behaviour of quasi-detonations. Combust. Flame 2020, 215, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordin, K.; Fureby, C.; Karl, S.; Hannemann, K. Understanding scramjet combustion using LES of the HyShot II combustor. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2017, 36, 2893–2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saghafian, A.; Terrapon, V.; Pitsch, H. An efficient flamelet-based combustion model for compressible flows. Combust. Flame 2015, 162, 652–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fureby, C.; Nilsson, T. Large Eddy Simulation of Cavity Stabilized Ramjet Combustion. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2023, 141, 108503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, A.J.; Smerina, D.M.; Thornton, M.R.; Rising, C.J.; Sosa, J.; Johnson, R.F.; Kessler, D.A.; Goodwin, G.; Ahmed, K.A. Mean Pressure Gradient Effects on the Performance of Ramjet Cavity Stabilized Flames. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2023, 141, 108533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesallam, I.M.; Attia, A.A.A.; El-Nagar, K.H.; Elsemary, I.M.M. Experimental Investigation on a Diffusion Jet Flame Performance Using a Developed Flame Holder Supplied with Air from a Concentric Pipe. Alex. Eng. J. 2023, 69, 561–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; He, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, F.; Kang, Y. Ignition, Lean Blowout, and Flame Propagation in a Combustor Using Flameholder with a Trapped Vortex Cavity. Fuel 2022, 324, 124656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westbrook, C.K.; Dryer, F.L. Simplified Reaction Mechanisms for the Oxidation of Hydrocarbon Fuels in Flames. Combust. Sci. Technol. 1981, 27, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Pan, Z.; Huang, J.; Wei, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y. Effects of Double-Jet Positions on Detonation Initiation Characteristics. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2020, 97, 105609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardeo, C.; Jessica, C.; Alexei, P.; Vadim, N.G.; Kareem, A.A. Chapman–Jouguet deflagration criteria and compressibility dynamics of turbulent fast flames for turbulence-induced deflagration-to-detonation transition. Phys. Fluids 2023, 35, 066122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciccarelli, G.; Johansen, C.; Parravani, M. The role of shock–flame interactions on flame acceleration in an obstacle laden channel. Combust. Flame 2010, 157, 2125–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


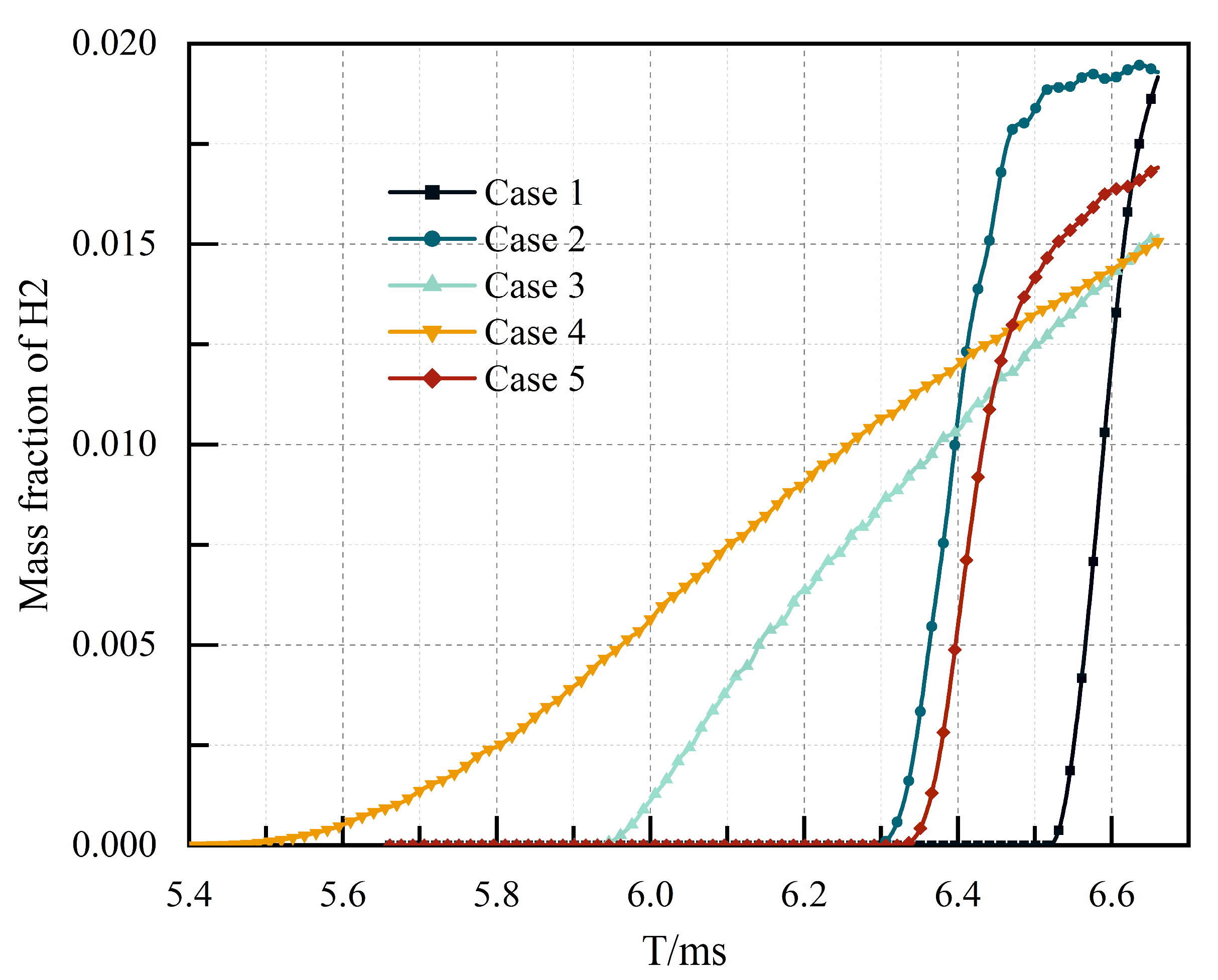
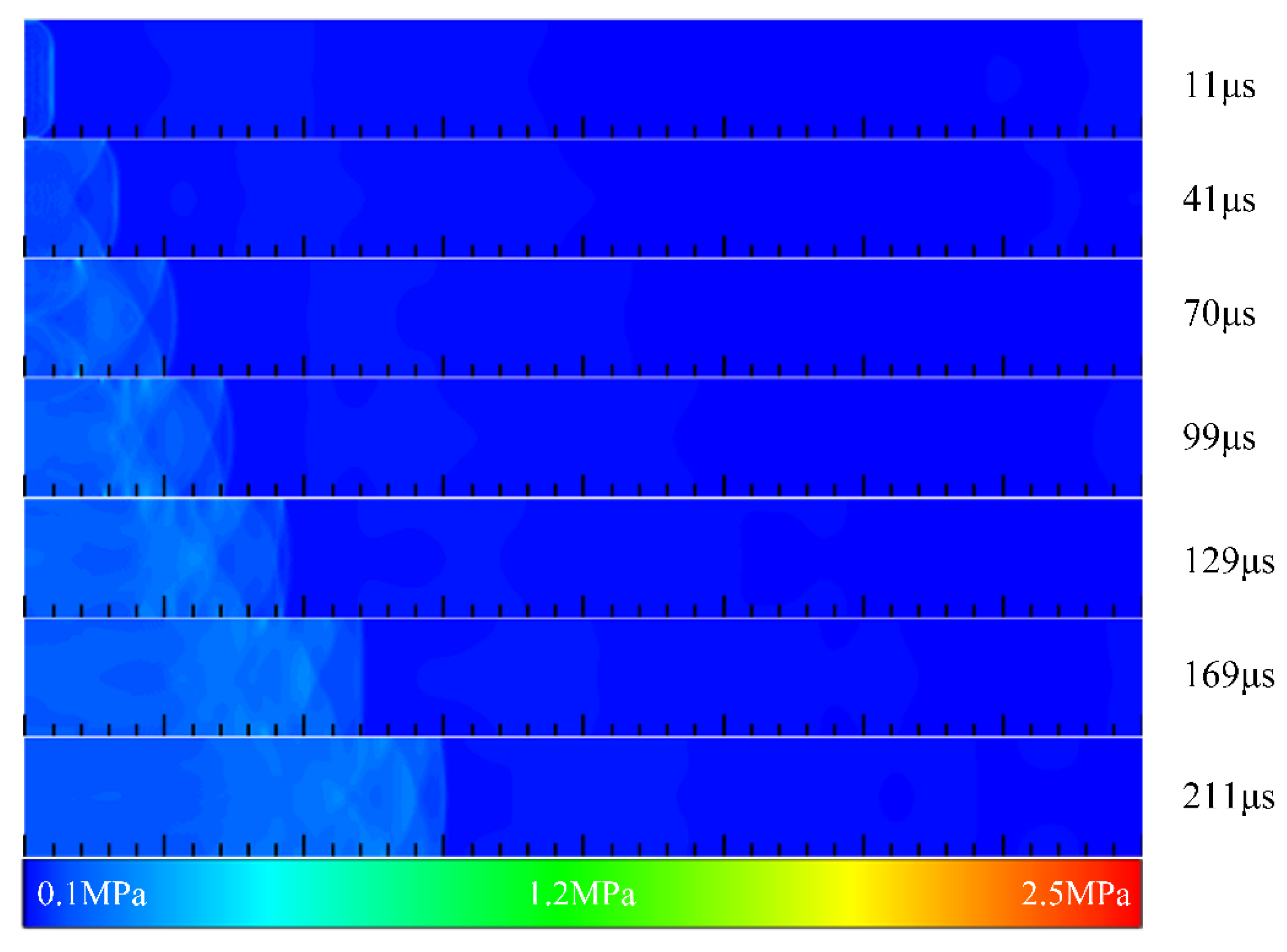

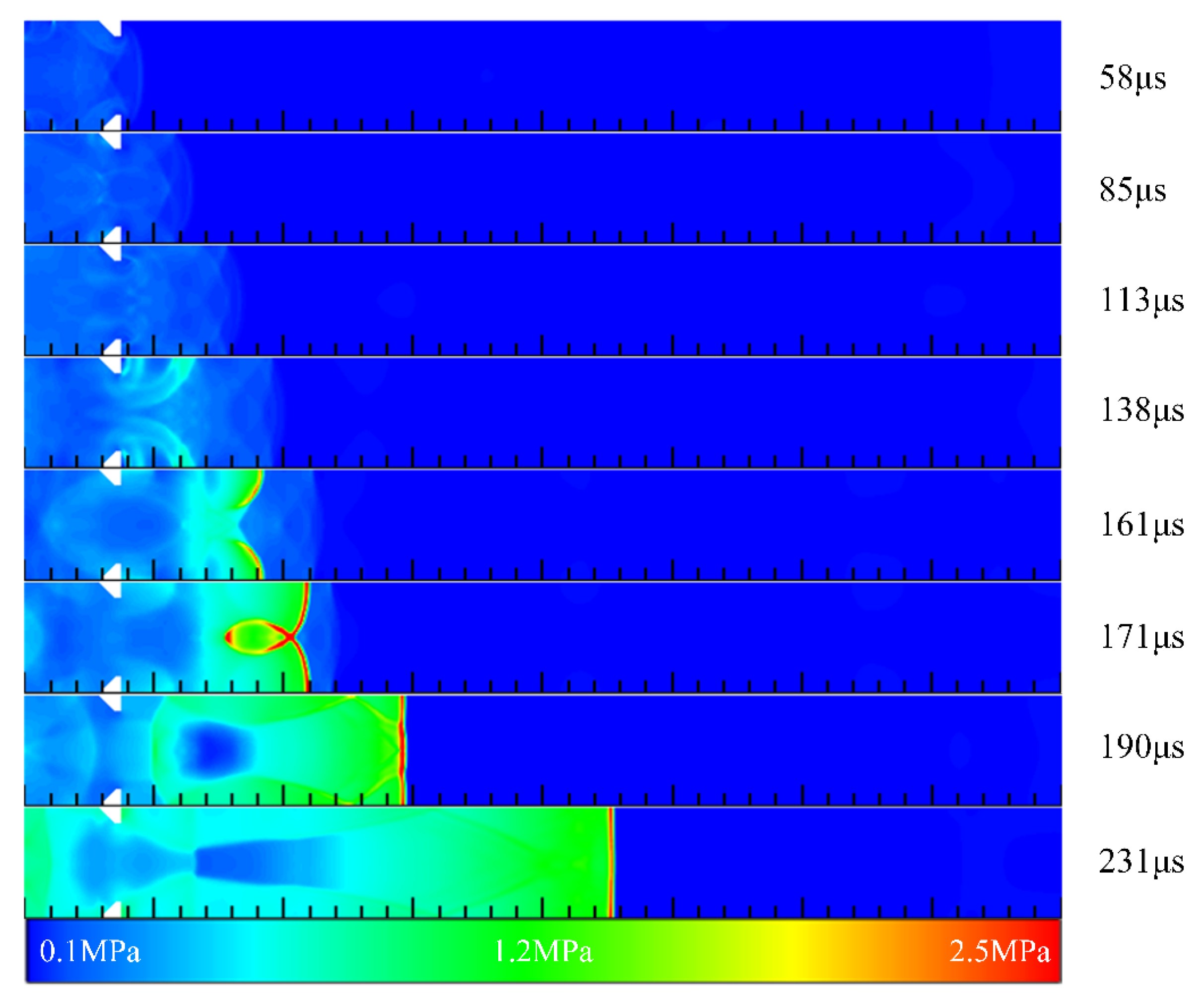
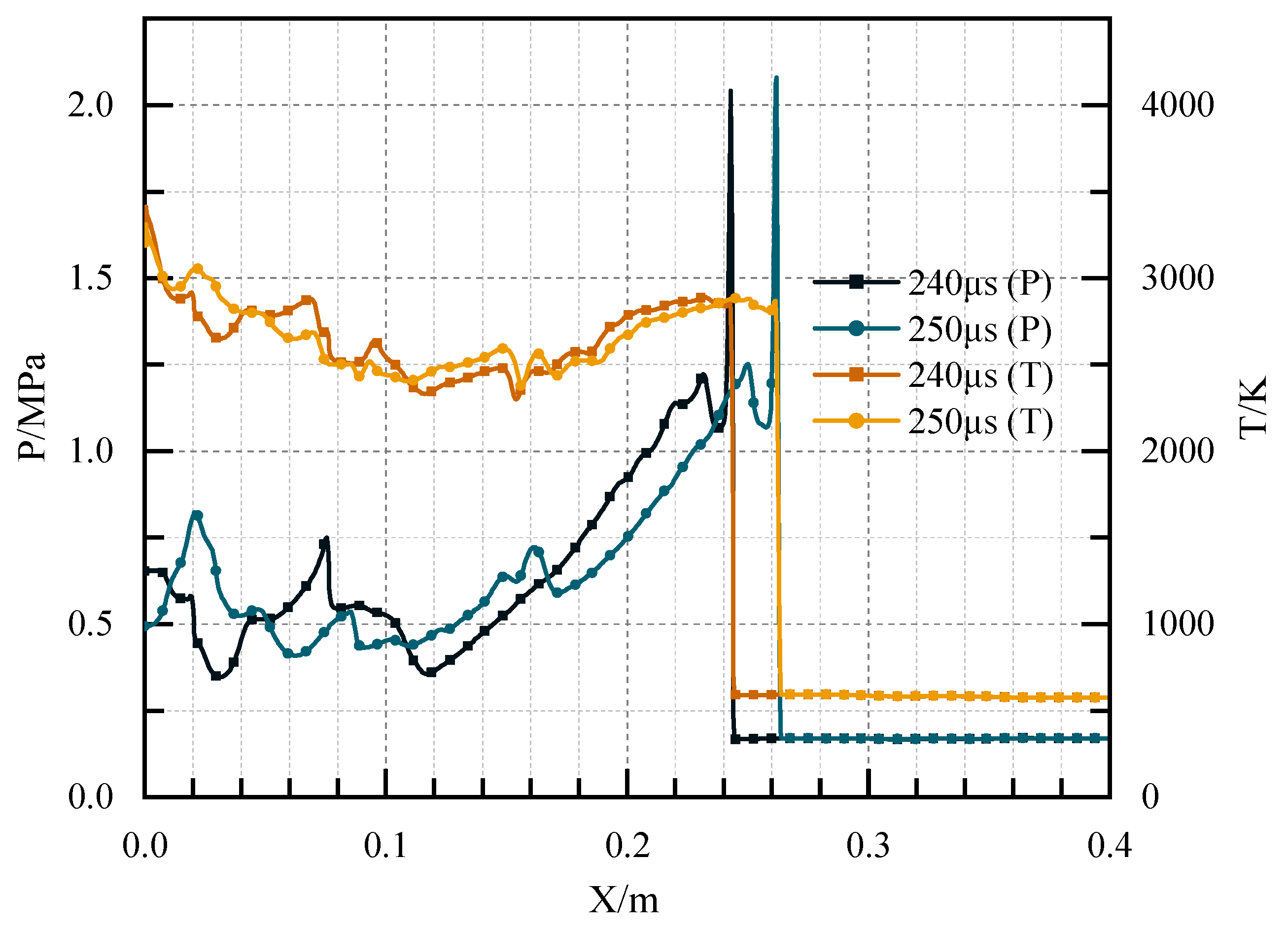


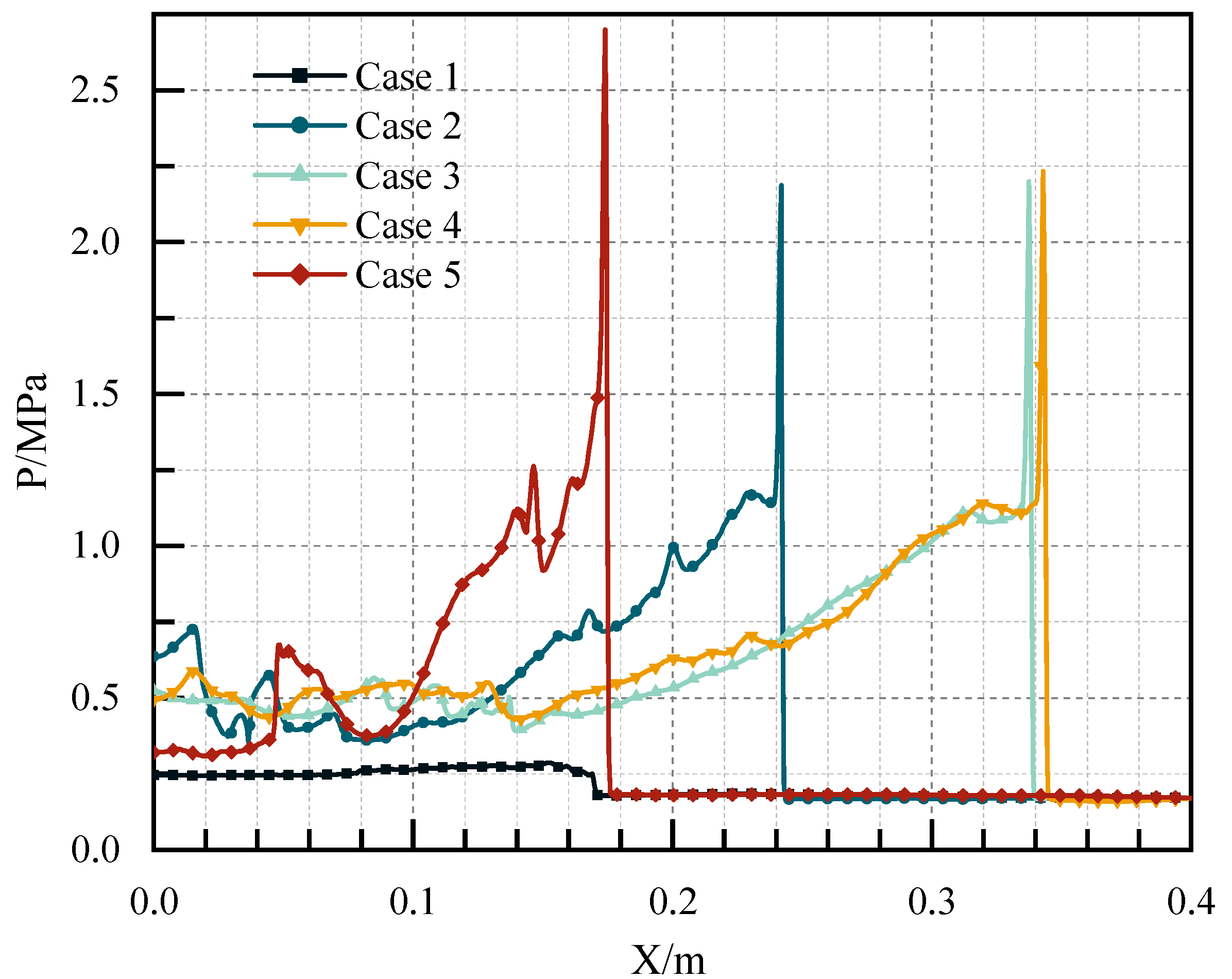
| Detonation Parameters | V/m.·s−1 | T/K | P/MPa |
|---|---|---|---|
| C-J | 1944 | 3029.1 | 1.8 |
| Case 1 | —— | —— | —— |
| Case 2 | 1921 | 2835.2 | 2.1 |
| Case 3 | 1976 | 2845.4 | 2.2 |
| Case 4 | 1980 | 2851.3 | 2.2 |
| Case 5 | 1927 | 2831.1 | 2.2 |
| Cases | Blocking Ratio | Time for Mixed Gas to Reach the Outlet/ms | Hydrogen Volume Discharged from the Outlet/g |
|---|---|---|---|
| Case 1 | 0 | 6.53 | 1.36 |
| Case 2 | 0.28 | 6.30 | 5.02 |
| Case 3 | 0.28 | 5.94 | 5.84 |
| Case 4 | 0.47 | 5.46 | 8.23 |
| Case 5 | 0.14 | 6.34 | 3.75 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, L.; Wang, Z.; Qin, W.; Zhang, Z. Numerical Study on Detonation Initiation Process in Channels Equipped with Typical Ramjet Flameholders. Aerospace 2025, 12, 972. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace12110972
Wei L, Wang Z, Qin W, Zhang Z. Numerical Study on Detonation Initiation Process in Channels Equipped with Typical Ramjet Flameholders. Aerospace. 2025; 12(11):972. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace12110972
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Lisi, Zhiwu Wang, Weifeng Qin, and Zixu Zhang. 2025. "Numerical Study on Detonation Initiation Process in Channels Equipped with Typical Ramjet Flameholders" Aerospace 12, no. 11: 972. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace12110972
APA StyleWei, L., Wang, Z., Qin, W., & Zhang, Z. (2025). Numerical Study on Detonation Initiation Process in Channels Equipped with Typical Ramjet Flameholders. Aerospace, 12(11), 972. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace12110972






