Experimental Investigation of Impulsive Coupling Characteristics of Asteroid Simulants Based on Laser Ablation Propulsion
Abstract
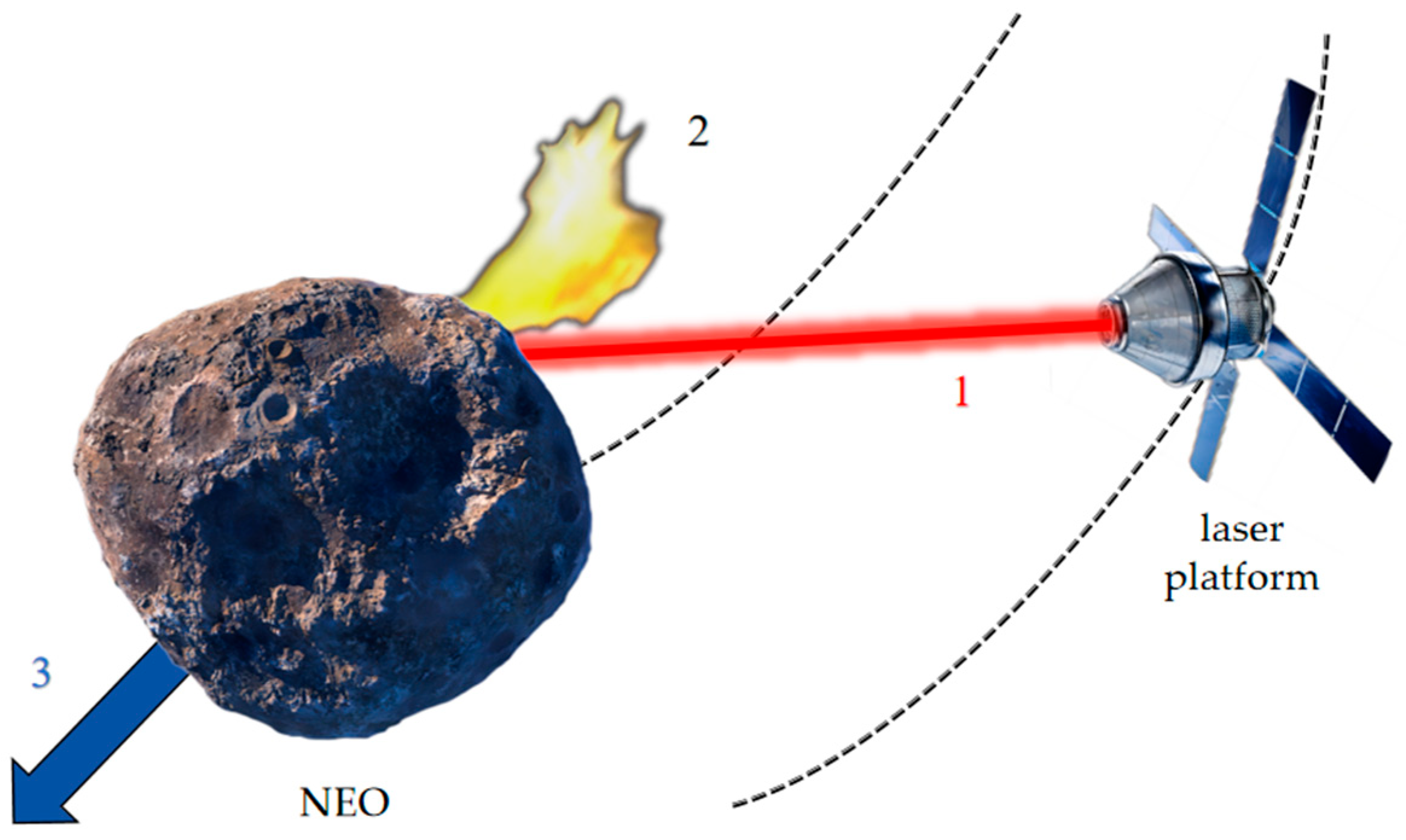
1. Introduction
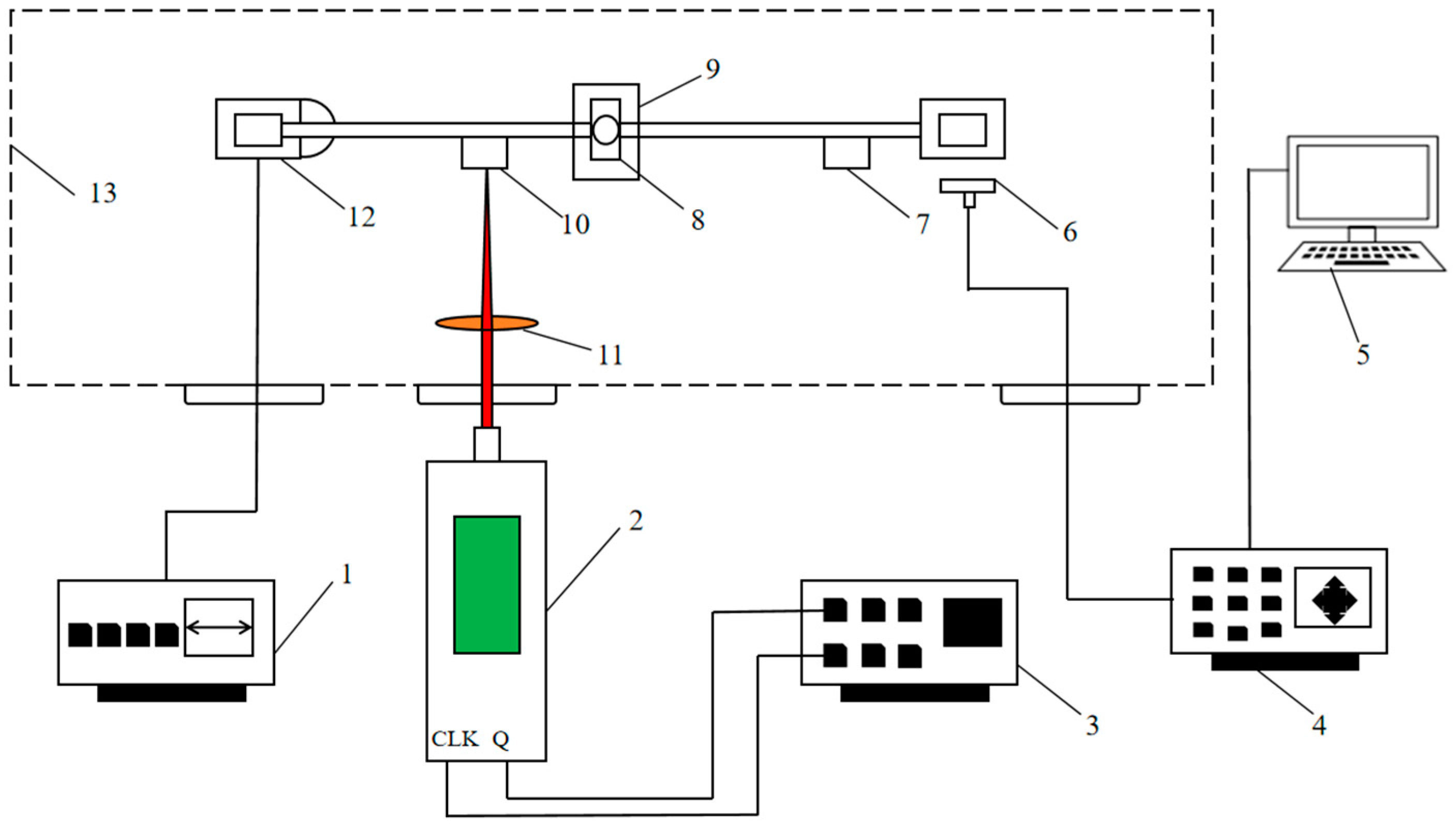
2. Experimental Set-Up
3. Method of Laser Ablation Impulse Measurement
4. Results and Discussion
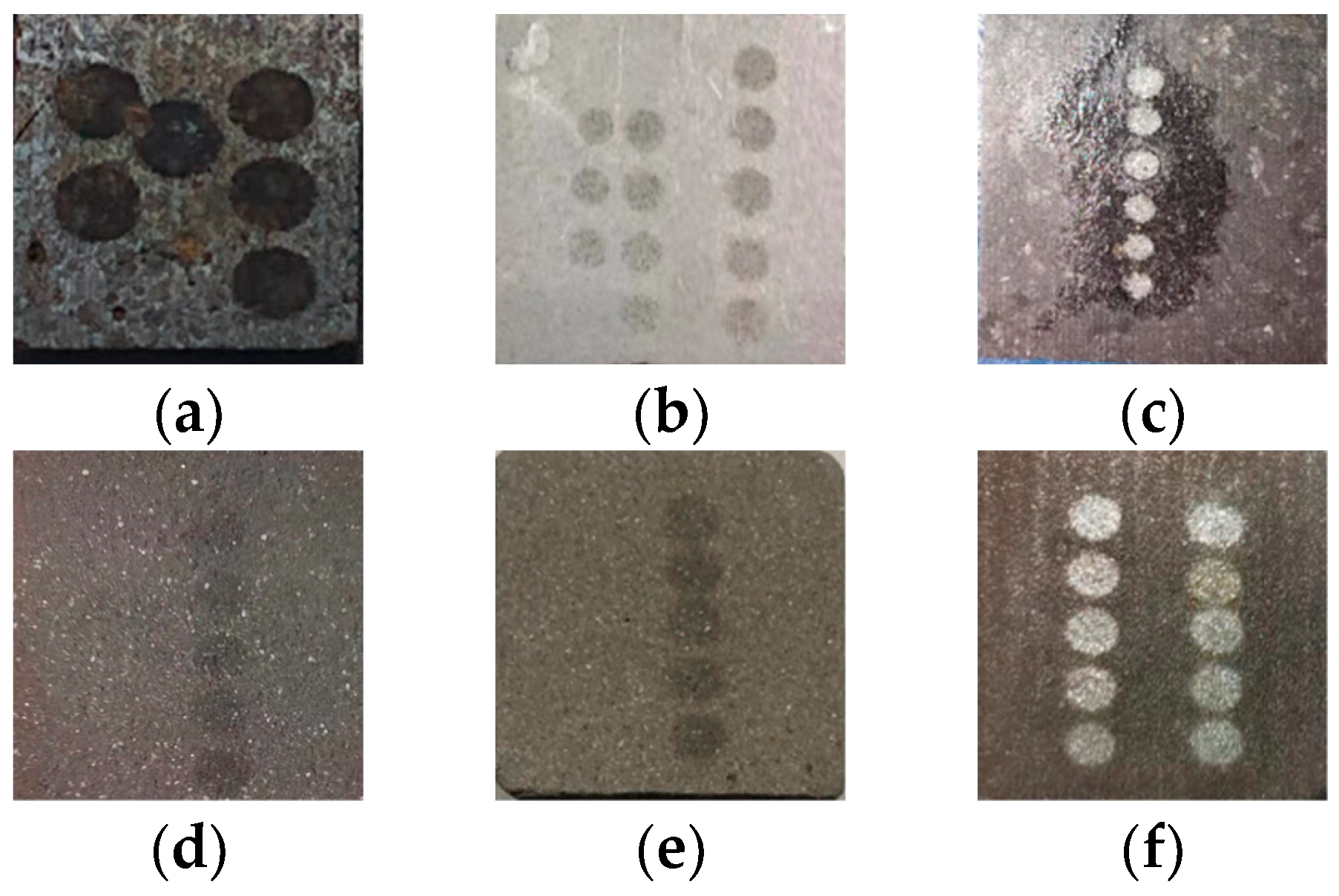
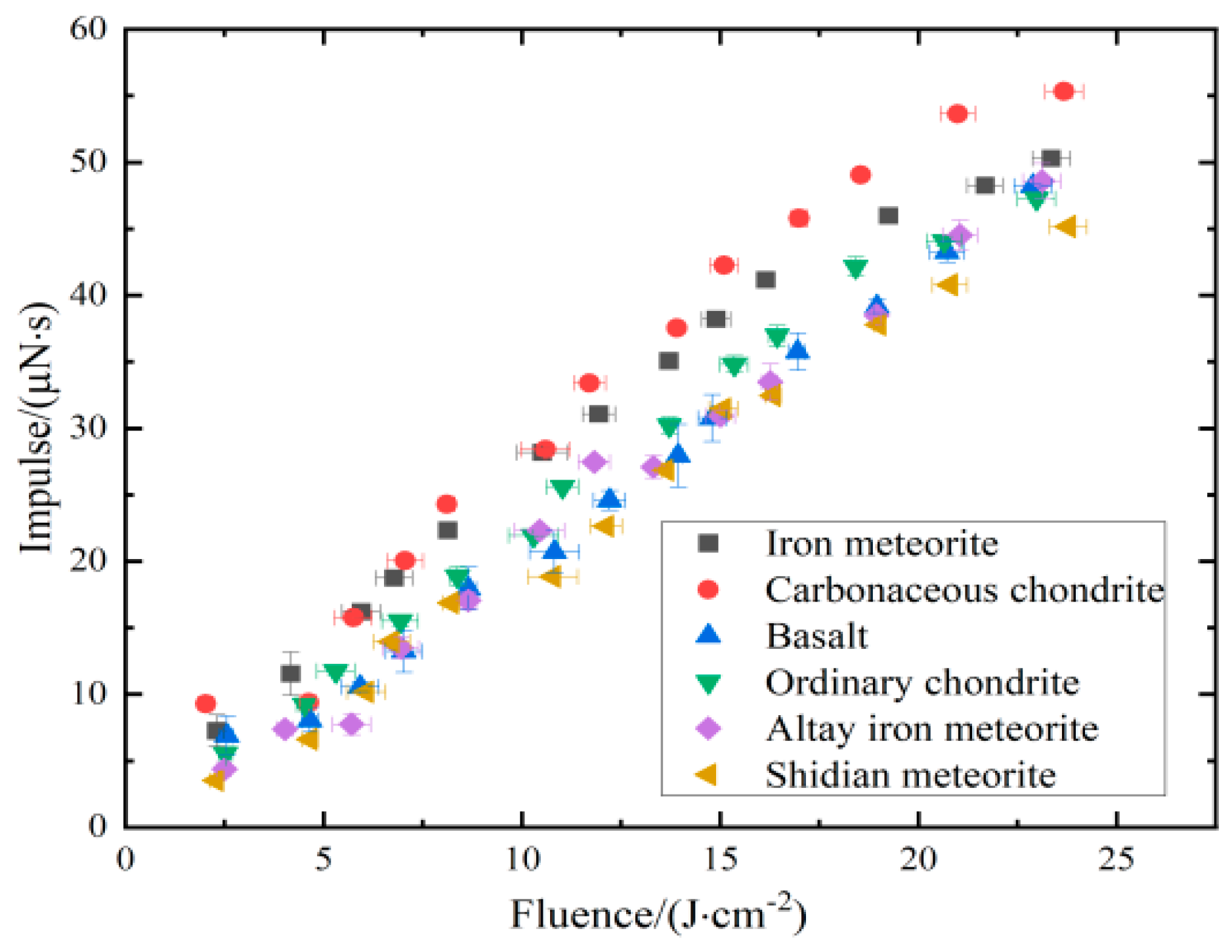
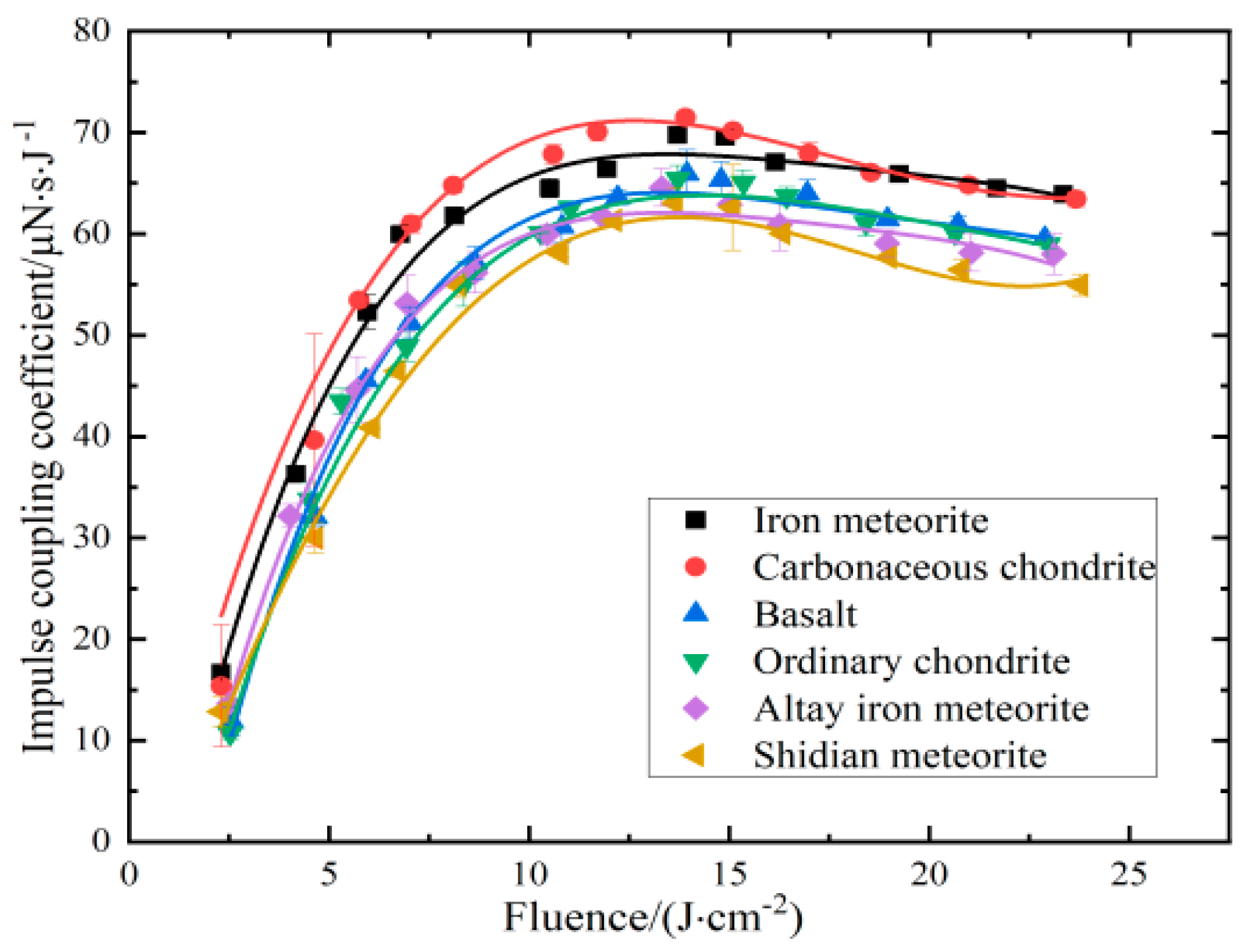
4.1. Impulse Coupling Characteristics of Asteroid Simulants
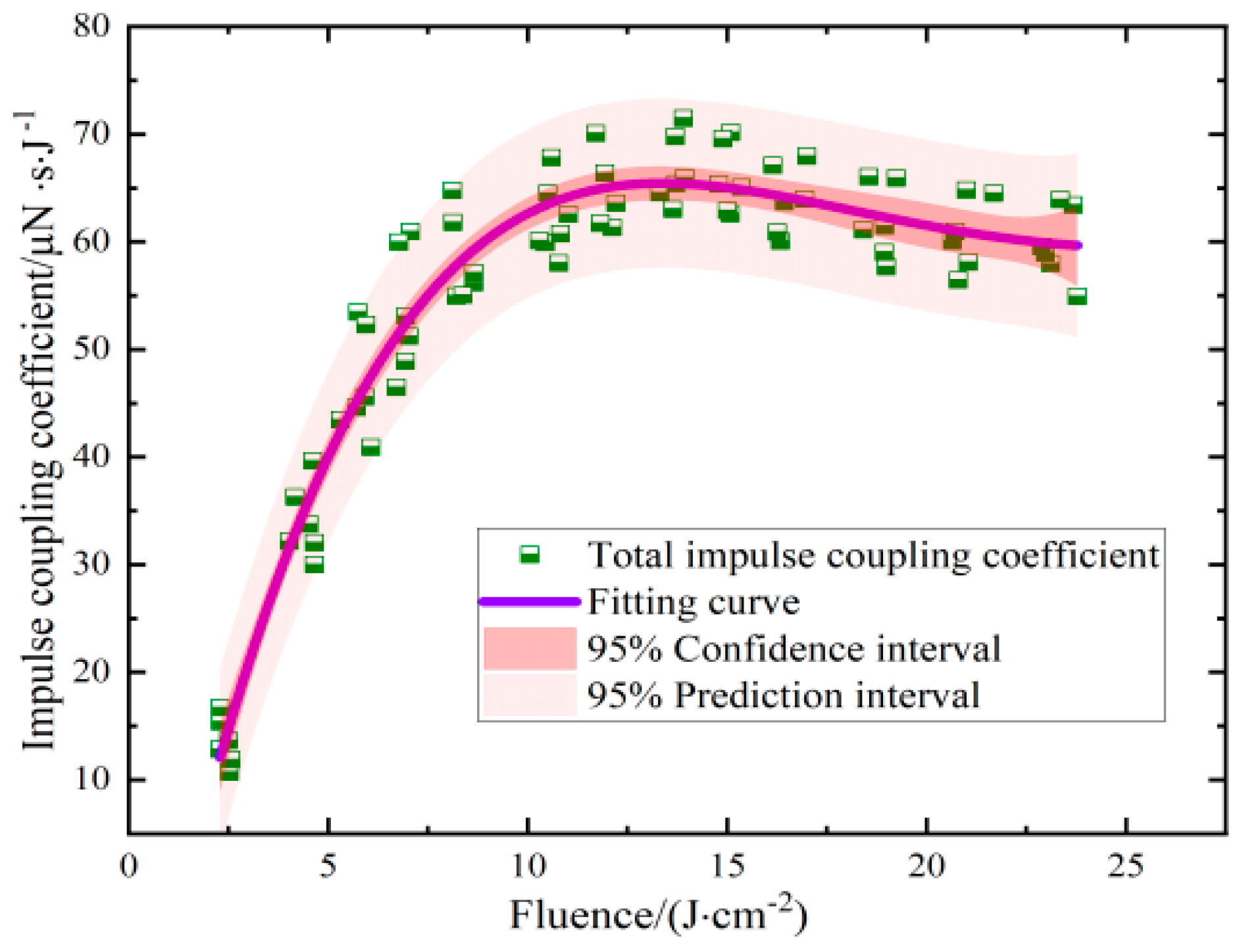
4.2. Unified Impulsive Coupling Characteristic of Multi-Materials
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| TNT | Trinitrotoluene |
| NEO | Near-Earth Objects |
| NIF | National Ignition Facility |
| LMJ | Laser Mégajoule |
| RMSE | Root Mean Square Error |
| R2 | Goodness of Fit |
| Bulk density (g/m3) | |
| Compressive strength (MPa) | |
| Porosity (%) | |
| c | Specific heat capacity (J/kg·K) |
| Thermal conductivity (W/m·K) | |
| Cm | Impulse coupling coefficient (N·s/J) |
| Torsion angle of the torsion pendulum (rad) | |
| Initial torsion angle (rad) | |
| Maximum torsion angle (rad) | |
| Time corresponding to maximum torsion angle (s) | |
| Damping ratio | |
| Natural frequency (rad/s) | |
| Rotational inertia (kg·m2) | |
| Thrust (N) | |
| Actuating arm (mm) | |
| Measure arm (mm) | |
| Arm of the impulse force (mm) | |
| Maximum displacement of the torsion pendulum (mm) | |
| Laser fluence (J/cm2) |
References
- Chapman, C.R. The hazard of near-Earth asteroid impacts on earth. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2004, 222, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.W.; Phipps, C.; Smalley, L.; Reilly, J.; Boccio, D. The Impact Imperative: Laser Ablation for Deflecting Asteroids, Meteoroids, and Comets from Impacting the Earth. AIP Conf. Proc. 2003, 664, 509–522. [Google Scholar]
- Chesley, S.R.; Ward, S.N. A Quantitative Assessment of the Human and Economic Hazard from Impact-generated Tsunami. Nat. Hazards 2006, 38, 355–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, T.; Kaiho, K.; Abe, A.; Katayama, M.; Takayama, K. Numerical simulations of hypervelocity impact of asteroid/comet on the earth. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2006, 33, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, M.; Nemati, B.; Zhai, C.; Turyshev, S.G.; Sandhu, J.; Hallinan, G.; Harding, L.K. Finding Very Small Near-Earth Asteroids using Synthetic Tracking. Astrophys. J. 2013, 782, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desmars, J.; Bancelin, D.; Hestroffer, D.; Thuillot, W. Statistical and numerical study of asteroid orbital uncertainty. Astron. Astrophys. 2013, 554, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McInnes, C.R. Deflection of near-Earth asteroids by kinetic energy impacts from retrograde orbits. Planet. Space Sci. 2004, 52, 587–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenig, J.D.; Chyba, C.F. Impact Deflection of Potentially Hazardous Asteroids Using Current Launch Vehicles. Sci. Glob. Secur. 2007, 15, 57–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasile, M.; Maddock, C.A. On the deflection of asteroids with mirrors. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astr. 2010, 107, 265–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, R.; Izzo, D.; Negueruela, C.D.; Summerer, L.; Ayre, M.; Vasile, M. Concepts for Near Earth Asteroid Deflection using Spacecraft with Advanced Nuclear and Solar Electric Propulsion Systems. J. Br. Interplanet. Soc. 2005, 59, 268–278. [Google Scholar]
- Colombo, C.; Vasile, M.; Radice, G. Semi-Analytical Solution for the Optimal Low-Thrust Deflection of Near-Earth Objects. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 2009, 32, 796–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetrisano, M.; Colombo, C.; Vasile, M. Asteroid rotation and orbit control via laser ablation. Adv. Space Res. 2016, 57, 1762–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbings, A.; Vasile, M.; Watson, I.; Hopkins, J.-M.; Burns, D. Experimental analysis of laser ablated plumes for asteroid deflection and exploitation. Acta Astronaut. 2013, 90, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Chang, H.; Ye, J.; Li, N. Impulse of planar and sphere target by nanosecond laser ablation in a large beam spot. Laser Phys. 2020, 30, 066002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilkes, A.; Brashears, T.; Lubin, P. De-Spinning Asteroids: Using Laser Ablation to Manipulate Asteroid Motion. Internal UC Santa Barbara Poster. 2015. Available online: https://www.deepspace.ucsb.edu/wp-content/uploads/2013/09/Aidan-Gilkes-RMP-Paper-Final-correct-fig-4.pdf (accessed on 5 May 2024).
- Zhang, Q.; Walsh, K.J.; Melis, C.; Hughes, G.B.; Lubin, P.M. Orbital Simulations on Deflecting Near-Earth Objects by Directed Energy. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 2016, 128, 045001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Thiry, N.; Vasile, M. Recent Advances in Laser Ablation Modelling for Asteroid Deflection Methods. In Proceedings of the SPIE Optical Engineering+ Applications, San Diego, CA, USA, 17 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Phipps, C.R.; Birkan, M.; Bohn, W.; Eckel, H.A.; Horisawa, H.; Lippert, T.; Michaelis, M.; Rezunkov, Y.; Sasoh, A.; Schall, W.; et al. Review: Laser-Ablation Propulsion. J. Propul. Power 2010, 26, 609–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergstue, G.; Fork, R.; Reardon, P. An advanced optical system for laser ablation propulsion in space. Acta Astronaut. 2014, 96, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Jin, X.; Chang, H. Cleaning space debris with a space-based laser system. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2014, 27, 805–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhargava, P.; Kumar, M.; Kumar, H.; Pandit, P.; Pandey, R.; Nath, A.K. Impulse coupling in laser-driven microtargets. Pramana 2004, 62, 923–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynam, C.; Wegner, P.; Auerbach, J.; Bowers, M.; Dixit, S.; Erbert, G.; Heestand, G.; Henesian, M.; Hermann, M.; Jancaitis, K.; et al. National Ignition Facility laser performance status. Appl. Opt. 2007, 46, 3276–3303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CEA—Direction des Applications Militaires. Laser Megajoule: Description de l’Installation LMJ. 2023. Available online: https://www-lmj.cea.fr/lmj-description.html (accessed on 6 May 2024).
- Sinko, J.E.; Phipps, C.R. Modeling CO2 laser ablation impulse of polymers in vapor and plasma regimes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 95, 131105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.; Jin, X.; Wen, M. Analytical Model for Calculating Laser Ablation Impulse Coupling Coefficient. High Power Laser Part. Beams 2013, 25, 1110–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Zhou, W.; Chang, H.; Chen, Y. Experimental Research on Impulse Coupling Characteristics and Plasma Plume Dynamics of a Nanosecond Pulsed Laser Irradiated Aluminum Target. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 205272–205281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phipps, C.R.; Harrison, R.F.; Shimada, T.; York, G.W.; Turner, T.P.; Corlis, X.F.; Steele, H.S.; Haynes, L.C. Enhanced vacuum laser-impulse coupling by volume absorption at infrared wavelengths. Laser Part. Beams 1990, 8, 281–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carslaw, H.S.; Jaeger, J.C. Conduction of heat in solids. Math. Gaz. 1959, 1, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinko, J.E.; Gregory, D.A.; Phipps, C.; Komurasaki, K.; Sinko, J. Models for laser ablation mass removal and impulse generation in vacuum. AIP Conf. Proc. 2010, 1230, 193–203. [Google Scholar]
- Phipps, C.R.; Luke, J.R. Diode Laser-Driven Microthrusters: A New Departure for Micropropulsion. AIAA J. 2002, 40, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Tu, L.; Yang, S.; Luo, J. A torsion balance for impulse and thrust measurements of micro-Newton thrusters. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2012, 83, 015105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Liu, J. Introduction to Chinese Meteorites, 1st ed.; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1993; pp. 17–61. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Hong, Y. Modeling error analysis of micro-impulse measurements. J. Propul. Technol. 2009, 30, 509–512. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, W.; Hong, Y.; Chang, H. A microNewton thrust stand for average thrust measurement of pulsed microthruster. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2013, 84, 125115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phipps, C.R.; Boustie, M.; Chevalier, J.M.; Baton, S.; Brambrink, E.; Berthe, L.; Schneider, M.; Videau, L.; Boyer, S.A.E.; Scharring, S. Laser impulse coupling measurements at 400 fs and 80 ps using the LULI facility at 1057 nm wavelength. J. Appl. Phys. 2017, 122, 193103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phipps, C.R.; Turner, T.P.; Harrison, R.F.; York, G.W.; Osborne, W.Z.; Anderson, G.K.; King, T.R. Impulse coupling to targets in vacuum by KrF, HF, and CO2 single-pulse lasers. J. Appl. Phys. 1988, 64, 1083–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burdonskii, I.N.; Leonov, A.G.; Makarov, K.N.; Yufa, V.N. Experimental investigation of laser ablation of stone polycrystalline targets. Quantum Electron. 2020, 50, 763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bindhu, C.V.; Harilal, S.S.; Tillack, M.S.; Najmabadi, F.; Gaeris, A.C. Laser propagation and energy absorption by an argon spark. J. Appl. Phys. 2003, 94, 7402–7407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sample | (g/cm3) | (MPa) | (%) | c (J/kg·K) | (W/m·K) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Basalt | 3.60 | 211.5 | 2.9 | 682 ± 35 | 3.5 ± 0.18 |
| Iron meteorite | 8.12 | 398.0 | 1.2 | 480 ± 25 | 51.0 ± 2.55 |
| Altay iron meteorite | 8.17 | 375.0 | 2.3 | 548 ± 28 | 63.0 ± 3.15 |
| Carbonaceous chondrite | 3.11 | 45.3 | 22.8 | 871 ± 44 | 1.9 ± 0.09 |
| Schieden meteorite | 2.3 | 66.1 | 20.1 | 909 ± 45 | 1.5 ± 0.08 |
| Ordinary chondrite | 3.39 | 143.3 | 1.9 | 707 ± 35 | 2.7 ± 0.14 |
| Parameter | Result | Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|
| Actuating arm (mm) | 100 | 0.52 |
| (mm) | 150 | 0.46 |
| (rad/s) | 4.83632 | 0.06004 |
| Rotational inertia (kg·m2) | 4.06753 × 10−4 | 9.0235 × 10−6 |
| Damping ratio | 9.15984 × 10−5 | 2.9854 × 10−5 |
| Fitting Curve | A0 | A1 | A2 | A3 | A4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Basalt | −4.49474 × 10−5 | 8.99946 | −0.17181 | −0.01589 | 5.11478 × 10−4 |
| Iron meteorite | 4.50431 × 10−6 | 9.91379 | −0.34793 | −0.00322 | 2.26521 × 10−4 |
| Carbonaceous chondrite | −6.17184 × 10−5 | 13.3436 | −0.89132 | 0.2634 | −3.05104 × 10−4 |
| Ordinary chondrite | 4.47812 × 10−6 | 10.43798 | −0.47363 | 0.00311 | 1.48136 × 10−4 |
| Altay iron meteorite | −4.22016 × 10−5 | 8.45032 | −0.23354 | −0.00394 | 1.61539 × 10−4 |
| Shidian meteorite | 4.54965 × 10−6 | 9.00695 | −0.26015 | −0.00777 | 3.13997 × 10−4 |
| Unified fitting curve | −23.95029 | 18.70541 | −1.38109 | 0.04228 | −4.65438 × 10−4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, Y.; Chang, H.; Zhou, W.; Jian, Z. Experimental Investigation of Impulsive Coupling Characteristics of Asteroid Simulants Based on Laser Ablation Propulsion. Aerospace 2024, 11, 388. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace11050388
Ma Y, Chang H, Zhou W, Jian Z. Experimental Investigation of Impulsive Coupling Characteristics of Asteroid Simulants Based on Laser Ablation Propulsion. Aerospace. 2024; 11(5):388. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace11050388
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Yingjie, Hao Chang, Weijing Zhou, and Zhilong Jian. 2024. "Experimental Investigation of Impulsive Coupling Characteristics of Asteroid Simulants Based on Laser Ablation Propulsion" Aerospace 11, no. 5: 388. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace11050388
APA StyleMa, Y., Chang, H., Zhou, W., & Jian, Z. (2024). Experimental Investigation of Impulsive Coupling Characteristics of Asteroid Simulants Based on Laser Ablation Propulsion. Aerospace, 11(5), 388. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace11050388






