Cluster Analysis of Monthly Precipitation over the Western Maritime Continent under Climate Change
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Datasets
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Dataset Used
2.2.1. Coupled Model Intercomparison Project Phase 5 (CMIP5) and Weather Research and Forecasting (WRF)
2.2.2. Climate Hazards Group InfraRed Precipitation with Station (CHIRPS) Dataset
3. Methodology
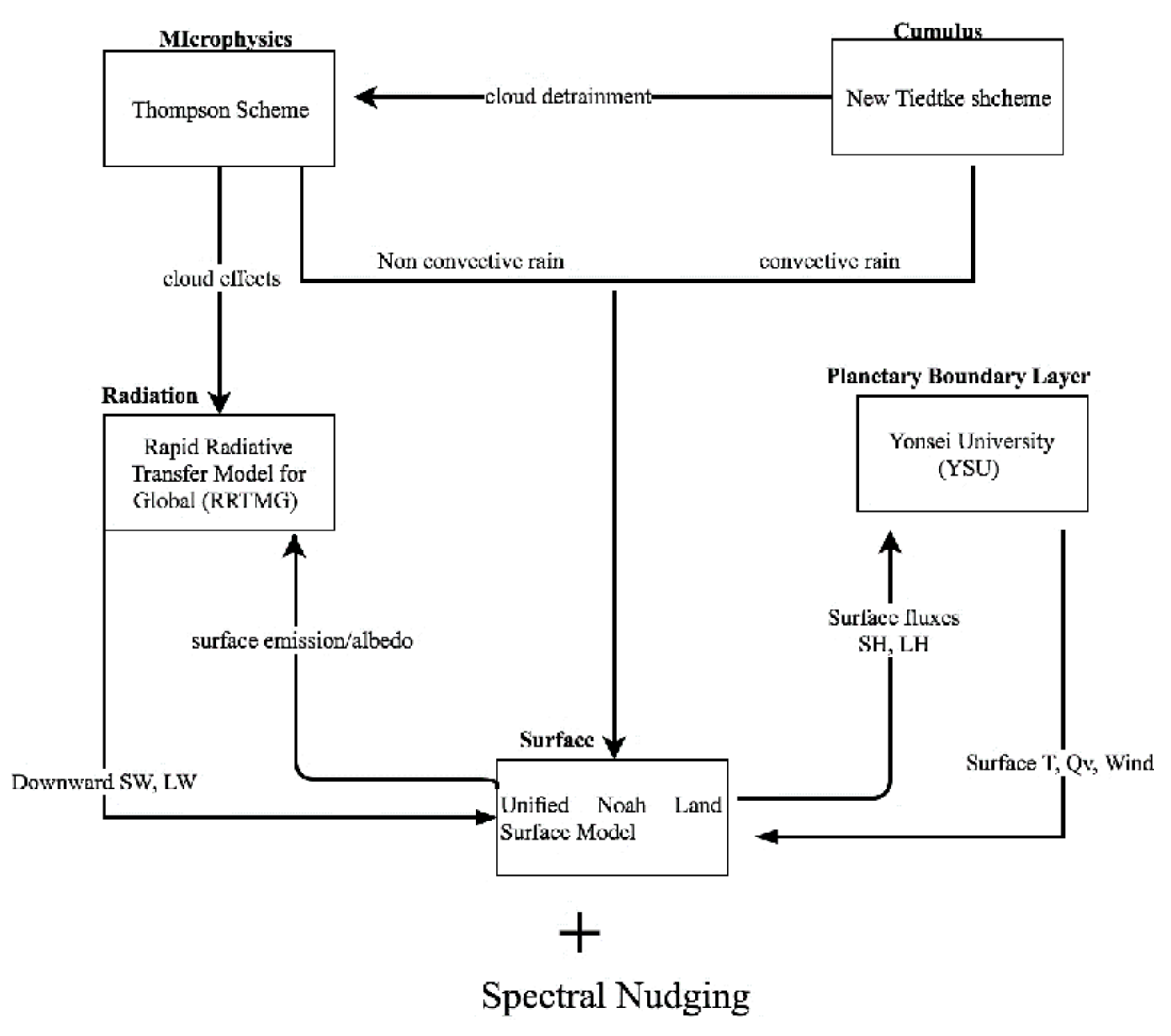
3.1. Parametrization of WRF
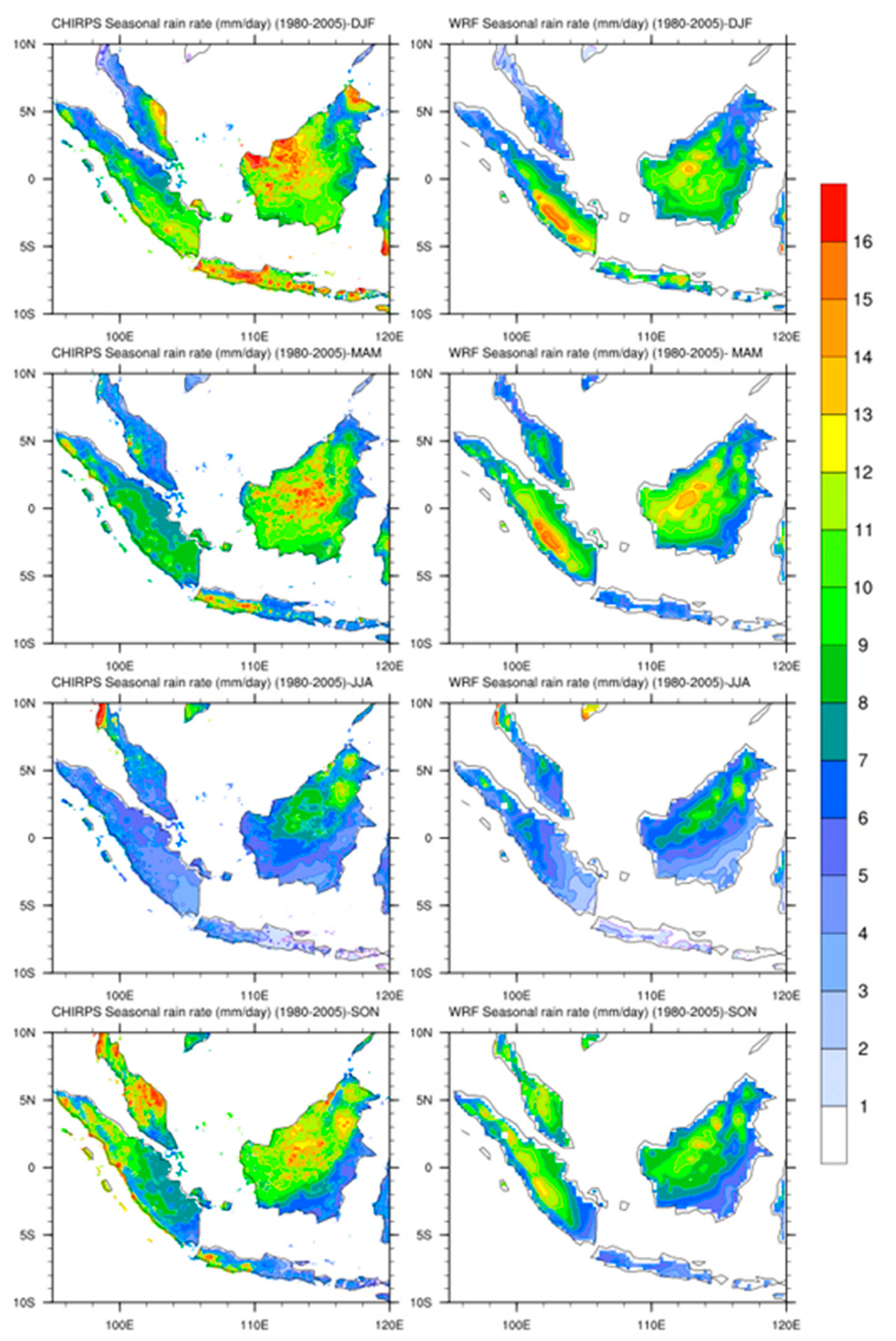
3.2. Performance of WRF in Modeling Precipitation over Study Domain
3.3. Bias Correction of the WRF Dataset
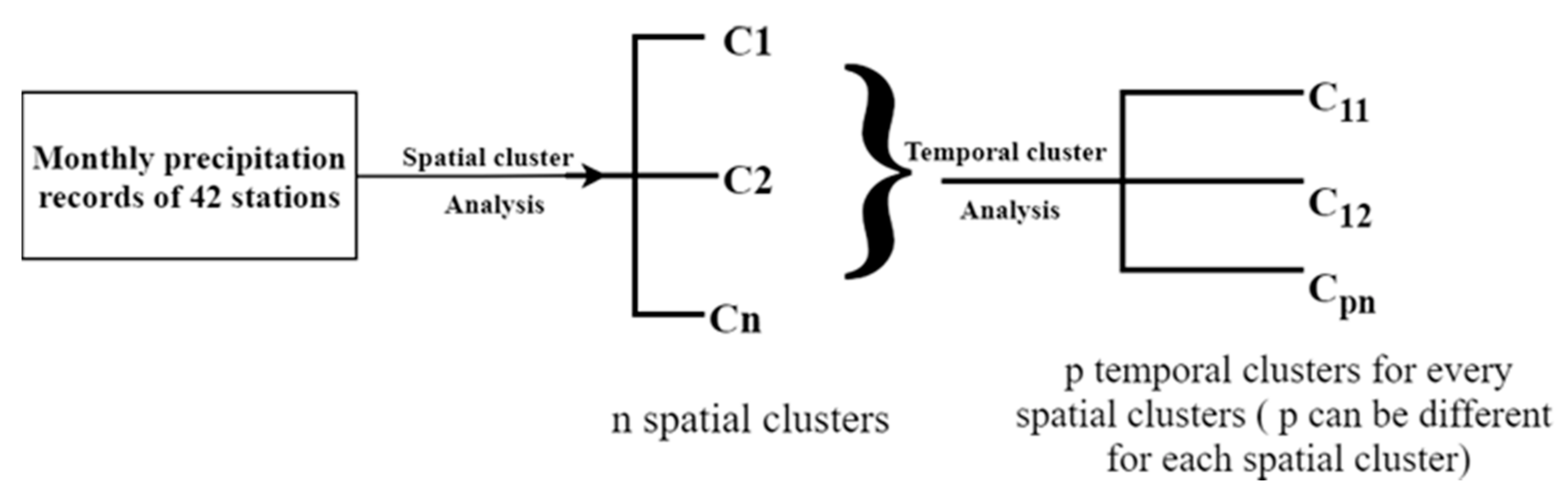
3.4. Cluster Analysis (Ward’s Method)
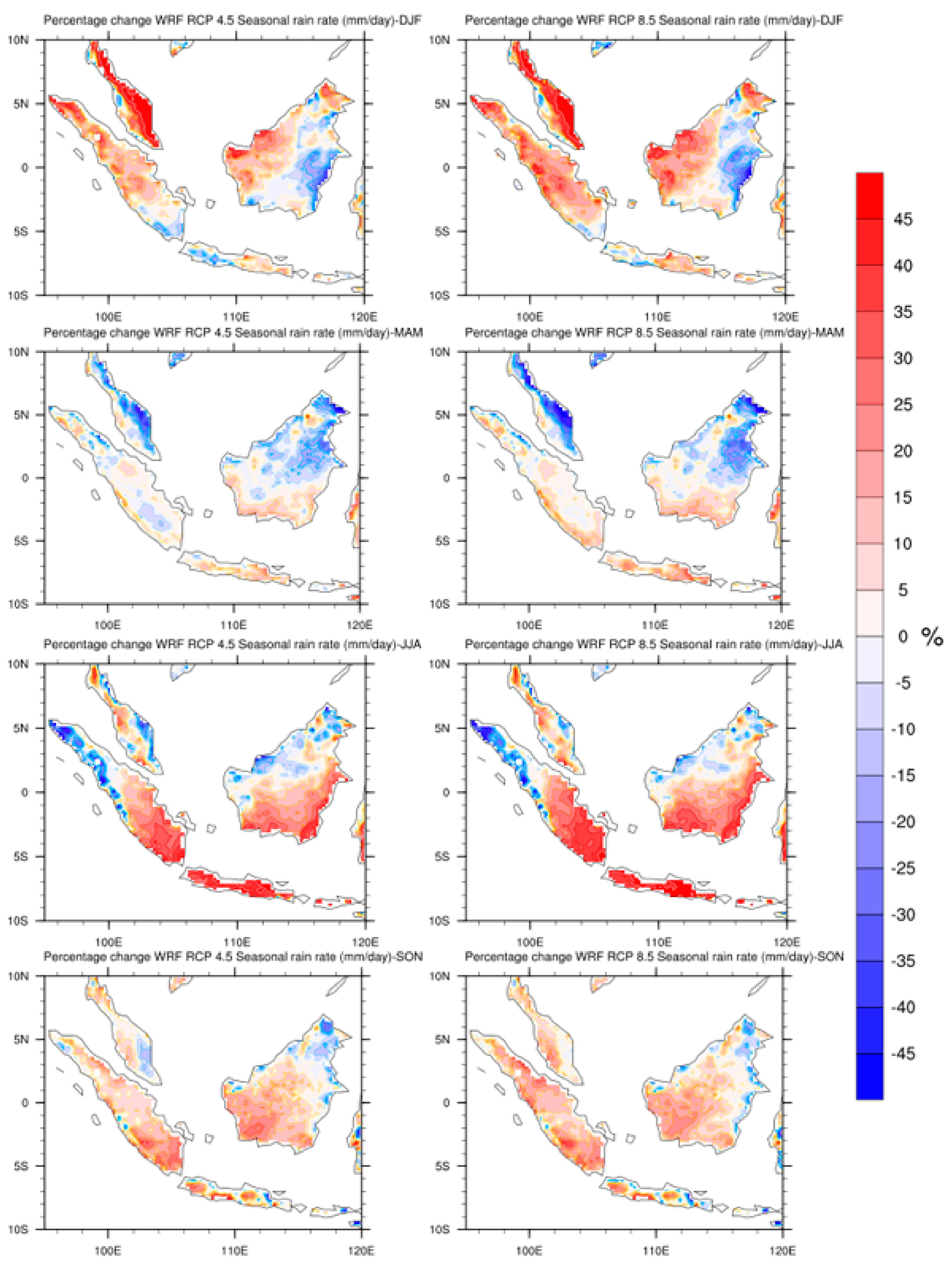
4. Results
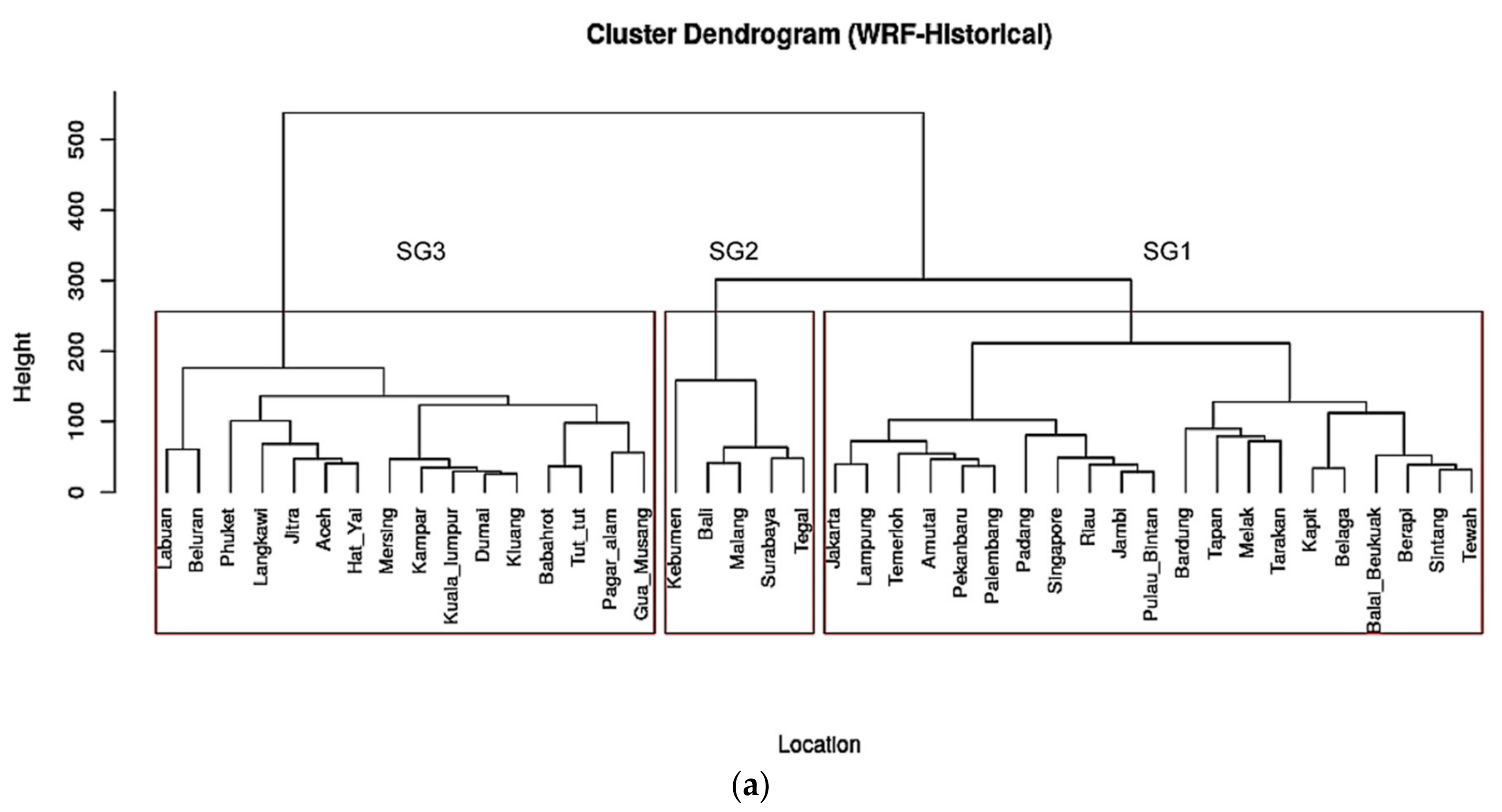
4.1. Spatial Grouping of Historical WRF Data
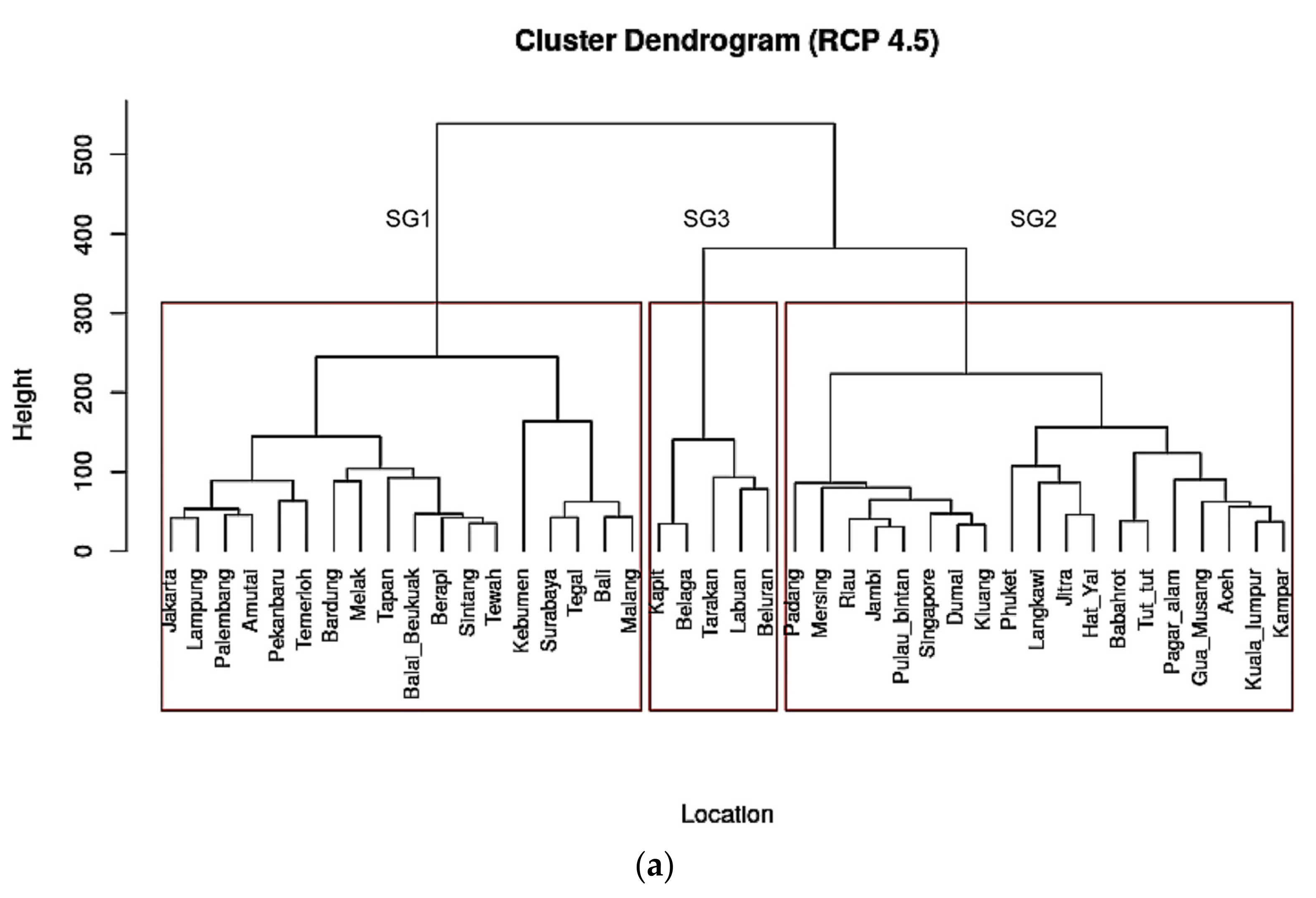
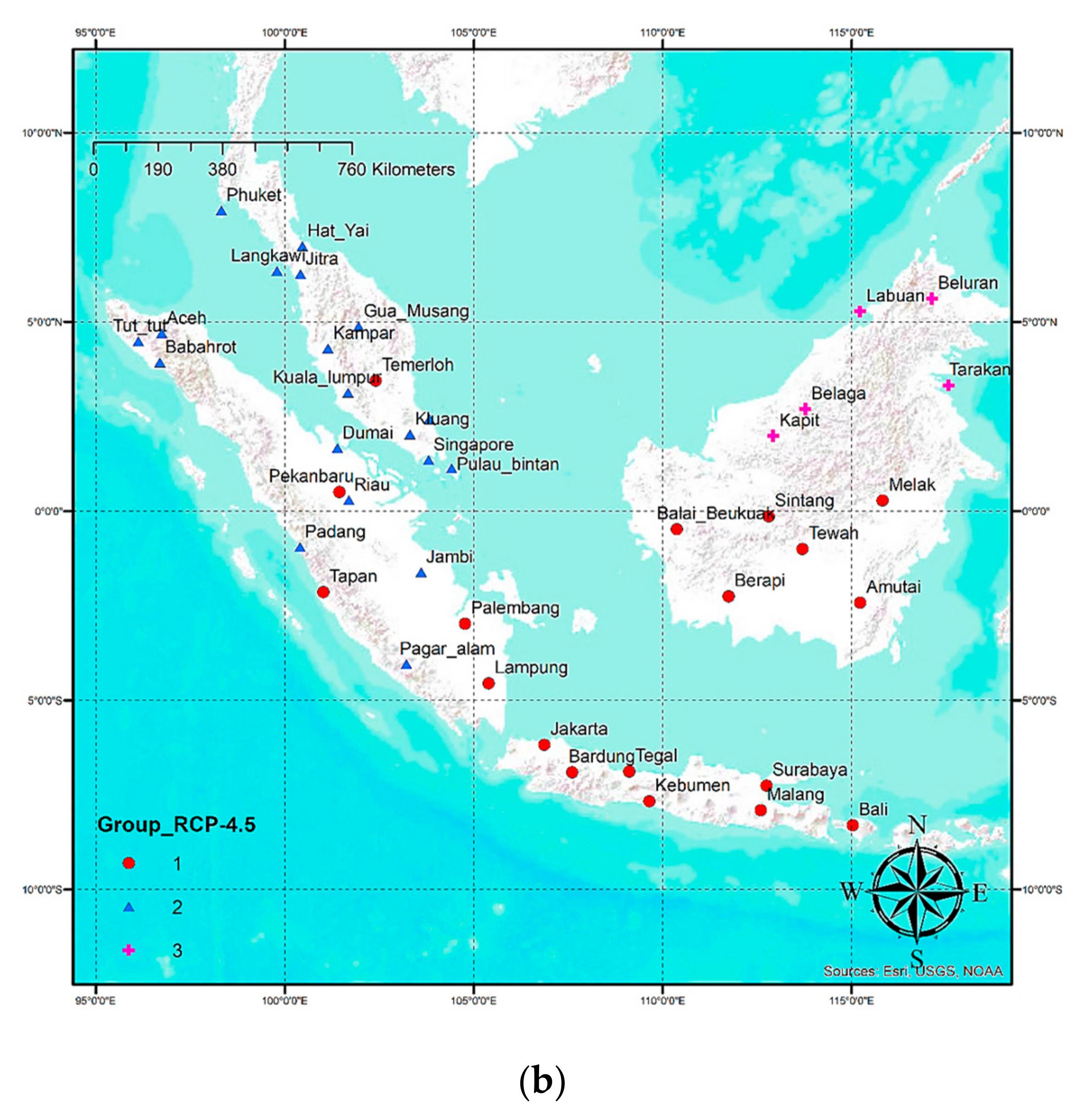
4.2. Spatial Grouping for RCP 4.5 WRF–CMIP5 Data (2030–2060)
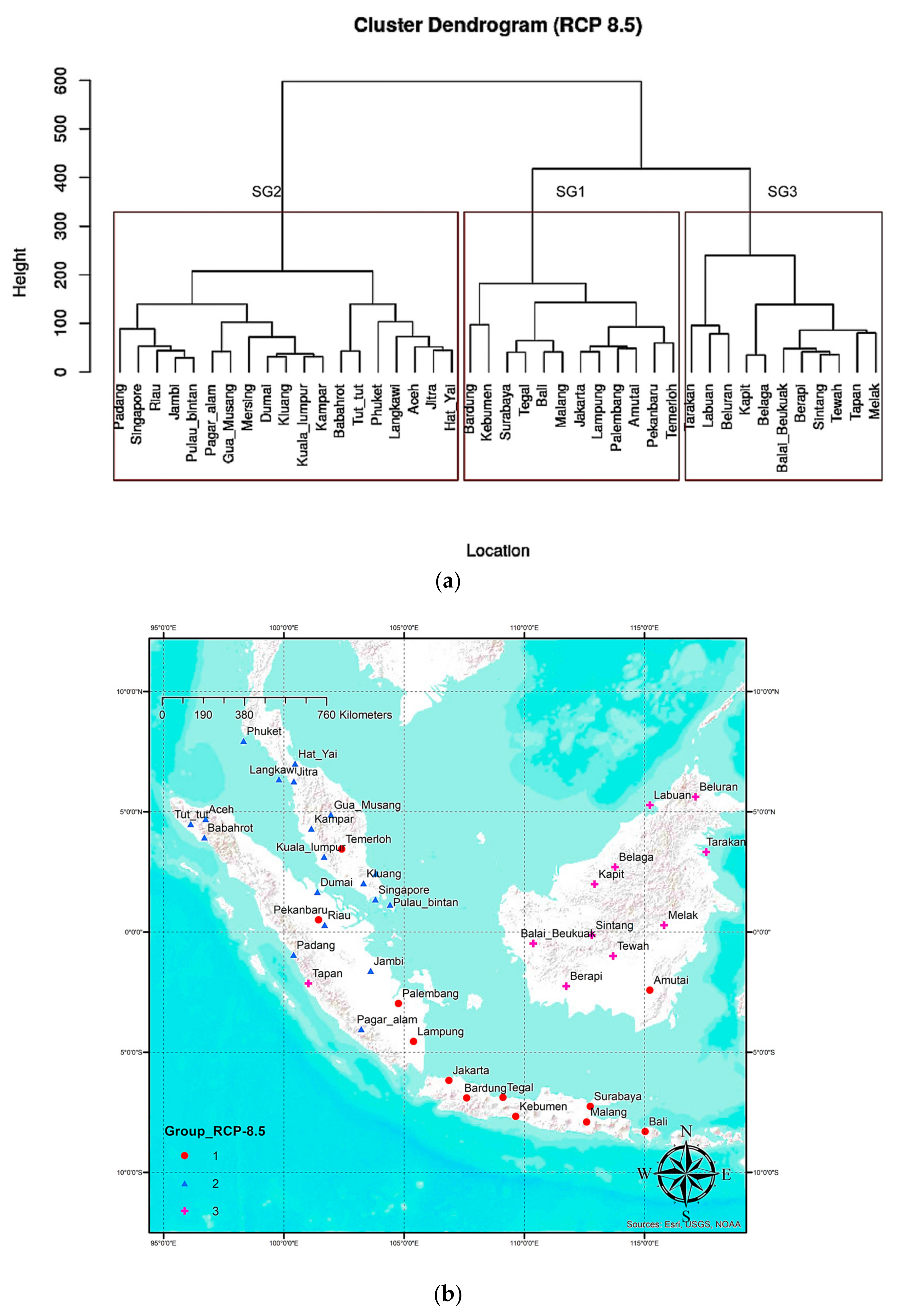
4.3. Spatial Grouping for RCP 8.5 WRF–CMIP5 Data (2030–2060)
4.4. Temporal Groupings of Historical WRF Data
4.4.1. Temporal Groups (TGs) for SG1
4.4.2. TGs for SG2
4.4.3. TGs for SG3
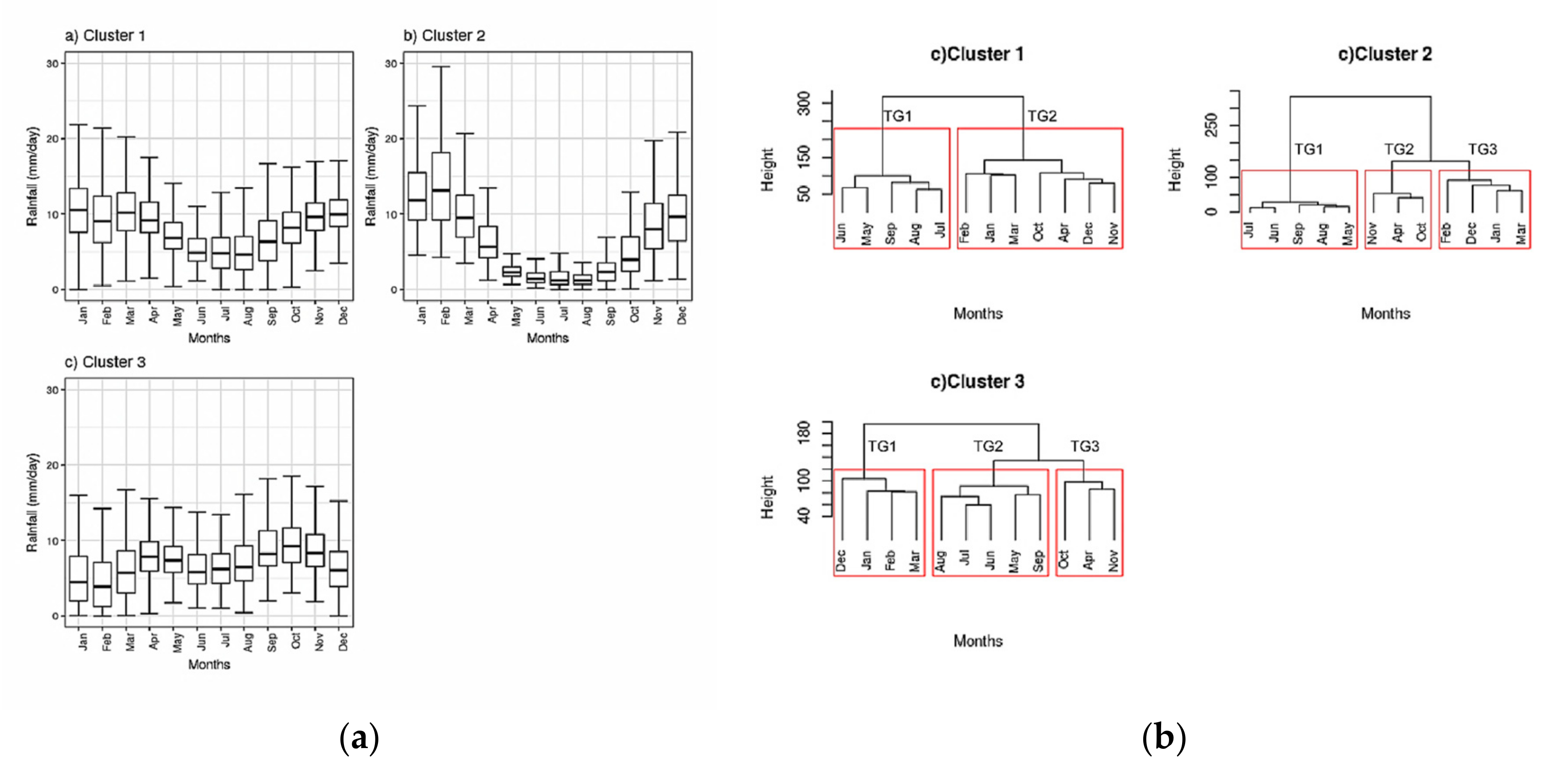
4.5. Temporal Grouping for RCP 4.5 WRF–CMIP5 Data (2030–2060)
4.5.1. TGs for SG1
4.5.2. TGs for SG2
4.5.3. TGs for SG3
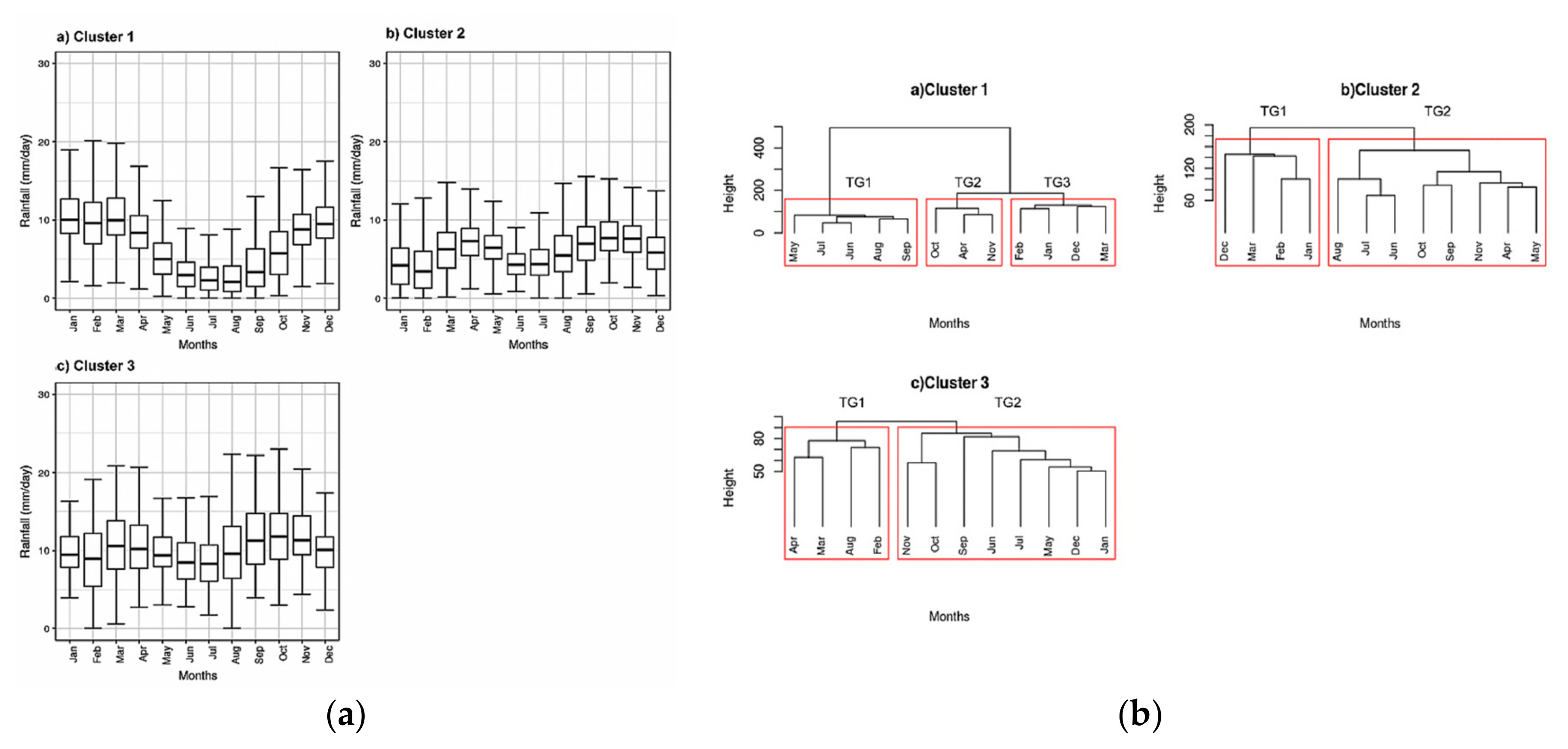
4.6. Temporal Grouping for RCP 8.5 WRF–CMIP5 Data (2030–2060)
4.6.1. TGs for SG1
4.6.2. TGs for SG2
4.6.3. TGs for SG3
5. Re-Clustering of Precipitation under Representative Concentration Pathway (RCP) Scenarios
6. Conclusions and Recommendations
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mailhot, A.; Duchesne, S.; Caya, D.; Talbot, G. Assessment of future change in intensity-duration-frequency (IDF) curves for Southern Quebec using the Canadian Regional Climate Model (CRCM). J. Hydrol. 2007, 347, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirhosseini, G.; Srivastava, P.; Stefanova, L. The impact of climate change on rainfall Intensity-Duration-Frequency (IDF) curves in Alabama. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2013, 13, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liew, S.C.; Raghavan, S.V.; Liong, S.Y. How to construct future IDF curves, under changing climate, for sites with scarce rainfall records? Hydrol. Process. 2014, 28, 3276–3287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, A.; Babel, M.S.; Weesakul, S.; Vojinovic, Z. Developing Intensity–Duration–Frequency (IDF) Curves under Climate Change Uncertainty: The Case of Bangkok, Thailand. Water 2017, 9, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olayide, O.E.; Tetteh, I.K.; Popoola, L. Differential impacts of rainfall and irrigation on agricultural production in Nigeria: Any lessons for climate-smart agriculture? Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 178, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, A.K. Climate change and challenges of water and food security. Int. J. Sustain. Built Environ. 2014, 3, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Gemmer, M.; Chen, J. Climate changes and flood/drought risk in the Yangtze Delta, China, during the past millennium. Quat. Int. 2008, 176, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhite, D.A.; Sivakumar, M.V.; Pulwarty, R. Managing drought risk in a changing climate: The role of national drought policy. Weather Clim. Extremes 2014, 3, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berga, L.; Buil, J.; Bofill, E.; De Cea, J.; Perez, J.G.; Mañueco, G.; Polimon, J.; Soriano, A.; Yagüe, J. Dams and Reservoirs, Societies and Environment in the 21st Century, Two Volume Set: Proceedings of the International Symposium on Dams in the Societies of the 21st Century, 22nd International Congress on Large Dams (ICOLD), Barcelona, Spain, 18 June 2006; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Ledec, G.; Quintero, J.D. Good Dams and Bad Dams: Environmental Criteria for Site Selection of Hydroelectric Projects; Latin America and Caribbean Region Sustainable Development Working Paper Series; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Han, B.-P.; Liu, Z. Tropical and Sub-Tropical Reservoir Limnology in China: Theory and Practice; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2011; Volume 91. [Google Scholar]
- Bates, B. Climate Change and Water: IPCC Technical Paper VI; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Donat, M.G.; Lowry, A.L.; Alexander, L.V.; O’Gorman, P.A.; Maher, N. More extreme precipitation in the world’s dry and wet regions. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2016, 6, 508–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoof, J.T.; Robeson, S.M. Projecting changes in regional temperature and precipitation extremes in the United States. Weather Clim. Extremes 2016, 11, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotstayn, L.D.; Ryan, B.F.; Penner, J.E. Precipitation changes in a GCM resulting from the indirect effects of anthropogenic aerosols. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2000, 27, 3045–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; Gupta, A.D.; Babel, M. Spatial disaggregation of bias-corrected GCM precipitation for improved hydrologic simulation: Ping River Basin, Thailand. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2007, 11, 1373–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turco, M.; Llasat, M.C.; Herrera, S.; Gutiérrez, J.M. Bias correction and downscaling of future RCM precipitation projections using a MOS-Analog technique. J. Geophys. Res.Atmos. 2017, 122, 2631–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenberth, K.E. Changes in precipitation with climate change. Clim. Res. 2011, 47, 123–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Climate Change 2014–Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability: Regional Aspects; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.-P. East Asian Monsoon; World Scientific: Singapore, 2004; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Neale, R.; Slingo, J. The maritime continent and its role in the global climate: A GCM study. J. Clim. 2003, 16, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.-H. Why precipitation is mostly concentrated over islands in the Maritime Continent. J. Atmos. Sci. 2008, 65, 1428–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murtagh, F.; Legendre, P. Ward’s hierarchical agglomerative clustering method: Which algorithms implement Ward’s criterion? J. Classif. 2014, 31, 274–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, J.H., Jr. Hierarchical grouping to optimize an objective function. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1963, 58, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, C.-K.; Koh, T.-Y.; Chun-Fung Lo, J.; Bhatt, B.C. Principal component analysis of observed and modeled diurnal rainfall in the Maritime Continent. J. Clim. 2011, 24, 4662–4675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, A.; Hsieh, C. Empirical orthogonal function analysis of rainfall and runoff series. Water Resour. Manag. 1991, 4, 235–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopalan, B.; Lall, U. A k-nearest-neighbor simulator for daily precipitation and other weather variables. Water Resour. Res. 1999, 35, 3089–3101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Hur, A.; Guyon, I. Detecting stable clusters using principal component analysis. Funct. Genom.: Methods Protoc. 2003, 159–182. [Google Scholar]
- Steinbach, M.; Karypis, G.; Kumar, V. A Comparison of Document Clustering Techniques. In Proceedings of the KDD Workshop on Text Mining, Boston, MA, USA, 20–23 August 2000; pp. 525–526. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, S.C. Hierarchical clustering schemes. Psychometrika 1967, 32, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Karypis, G. Evaluation of hierarchical clustering algorithms for document datasets. In Proceedings of the eleventh international conference on Information and knowledge management, McLean, VA, USA, 4–9 November 2002; pp. 515–524. [Google Scholar]
- Taguchi, Y.; Iwadate, M.; Umeyama, H. Principal component analysis-based unsupervised feature extraction applied to in silico drug discovery for posttraumatic stress disorder-mediated heart disease. BMC Bioinform. 2015, 16, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blashfield, R.K. Mixture model tests of cluster analysis: Accuracy of four agglomerative hierarchical methods. Psychol. Bull. 1976, 83, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varikoden, H.; Samah, A.; Babu, C. Spatial and temporal characteristics of rain intensity in the peninsular Malaysia using TRMM rain rate. J. Hydrol. 2010, 387, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhaila, J.; Jemain, A.A.; Hamdan, M.F.; Zin, W.Z. Comparing rainfall patterns between regions in Peninsular Malaysia via a functional data analysis technique. J. Hydrol. 2011, 411, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manton, M.; Della-Marta, P.; Haylock, M.; Hennessy, K.; Nicholls, N.; Chambers, L.; Collins, D.; Daw, G.; Finet, A.; Gunawan, D. Trends in extreme daily rainfall and temperature in Southeast Asia and the South Pacific: 1961–1998. Int. J. Climatol. 2001, 21, 269–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BMKG, Badan Meteorologi, Klimatologi, dan Geofisika. 2017. Available online: http://www.bmkg.go.id/ (accessed on 24 August 2017).
- Ramage, C.S. Role of a Tropical “Maritime Continent” in the Atmospheric Circulation. Mon. Weather Rev. 1968, 96, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Stocker, T.F., Qin, D., Plattner, G.-K., Tignor, M., Allen, S.K., Boschung, J., Nauels, A., Xia, Y., Bex, V., Midgley, P.M., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2013; p. 1535. [Google Scholar]
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). Summary for Policymakers. In Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Stocker, T.F., Qin, D., Plattner, G.-K., Tignor, M., Allen, S.K., Boschung, J., Nauels, A., Xia, Y., Bex, V., Midgley, P.M., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Funk, C.; Peterson, P.; Landsfeld, M.; Pedreros, D.; Verdin, J.; Shukla, S.; Husak, G.; Rowland, J.; Harrison, L.; Hoell, A. The climate hazards infrared precipitation with stations—A new environmental record for monitoring extremes. Sci. Data 2015, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, G.; Field, P.R.; Rasmussen, R.M.; Hall, W.D. Explicit forecasts of winter precipitation using an improved bulk microphysics scheme. Part II: Implementation of a new snow parameterization. Mon. Weather Rev. 2008, 136, 5095–5115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacono, M.J.; Delamere, J.S.; Mlawer, E.J.; Shephard, M.W.; Clough, S.A.; Collins, W.D. Radiative forcing by long-lived greenhouse gases: Calculations with the AER radiative transfer models. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.-Y.; Noh, Y.; Dudhia, J. A new vertical diffusion package with an explicit treatment of entrainment processes. Mont. Weather Rev. 2006, 134, 2318–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tewari, M.; Chen, F.; Wang, W.; Dudhia, J.; LeMone, M.; Mitchell, K.; Ek, M.; Gayno, G.; Wegiel, J.; Cuenca, R. Implementation and Verification of the Unified NOAH Land Surface Model in the WRF Model. In Proceedings of the 20th Conference on Weather Analysis and Forecasting/16th Conference on Numerical Weather Prediction, Seattle, WA, USA, 11 January 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.; Hamilton, K. Improved representation of boundary layer clouds over the southeast Pacific in ARW-WRF using a modified Tiedtke cumulus parameterization scheme. Mon. Weather Rev. 2011, 139, 3489–3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piani, C.; Haerter, J.; Coppola, E. Statistical bias correction for daily precipitation in regional climate models over Europe. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2010, 99, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilks, D.S. Statistical Methods in the Atmospheric Sciences; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2011; Volume 100. [Google Scholar]
- Katz, R. Extreme value theory for precipitation: Sensitivity analysis for climate change. Adv. Water Resour. 1999, 23, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husak, G.J.; Michaelsen, J.; Funk, C. Use of the gamma distribution to represent monthly rainfall in Africa for drought monitoring applications. Int. J. Climatol. 2007, 27, 935–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Suhili, R.H.; Khanbilvardi, R. Frequency analysis of the monthly rainfall data at Sulaimania Region, Iraq. Am. J. Eng. Res. 2014, 3, 212–222. [Google Scholar]
- Wilcke, R.A.I.; Mendlik, T.; Gobiet, A. Multi-variable error correction of regional climate models. Clim. Chang. 2013, 120, 871–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amengual, A.; Homa, V.; Romero, R.; Alonso, S.; Ramis, C. A statistical adjustment of regional climate model outputs to local scales: Application to Platja de Palma, Spain. J. Clim. 2012, 25, 939–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutjahr, O.; Heinemann, G. Comparing precipitation bias correction methods for high-resolution regional climate simulations using COSMO-CLM. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2013, 114, 511–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The R Stats Package. 2017. Available online: https://stat.ethz.ch/R-manual/R-devel/library/stats/html/00Index.html (accessed on 24 August 2017).
- Lehmann, J.; Coumou, D.; Frieler, K. Increased record-breaking precipitation events under global warming. Clim. Chang. 2015, 132, 501–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
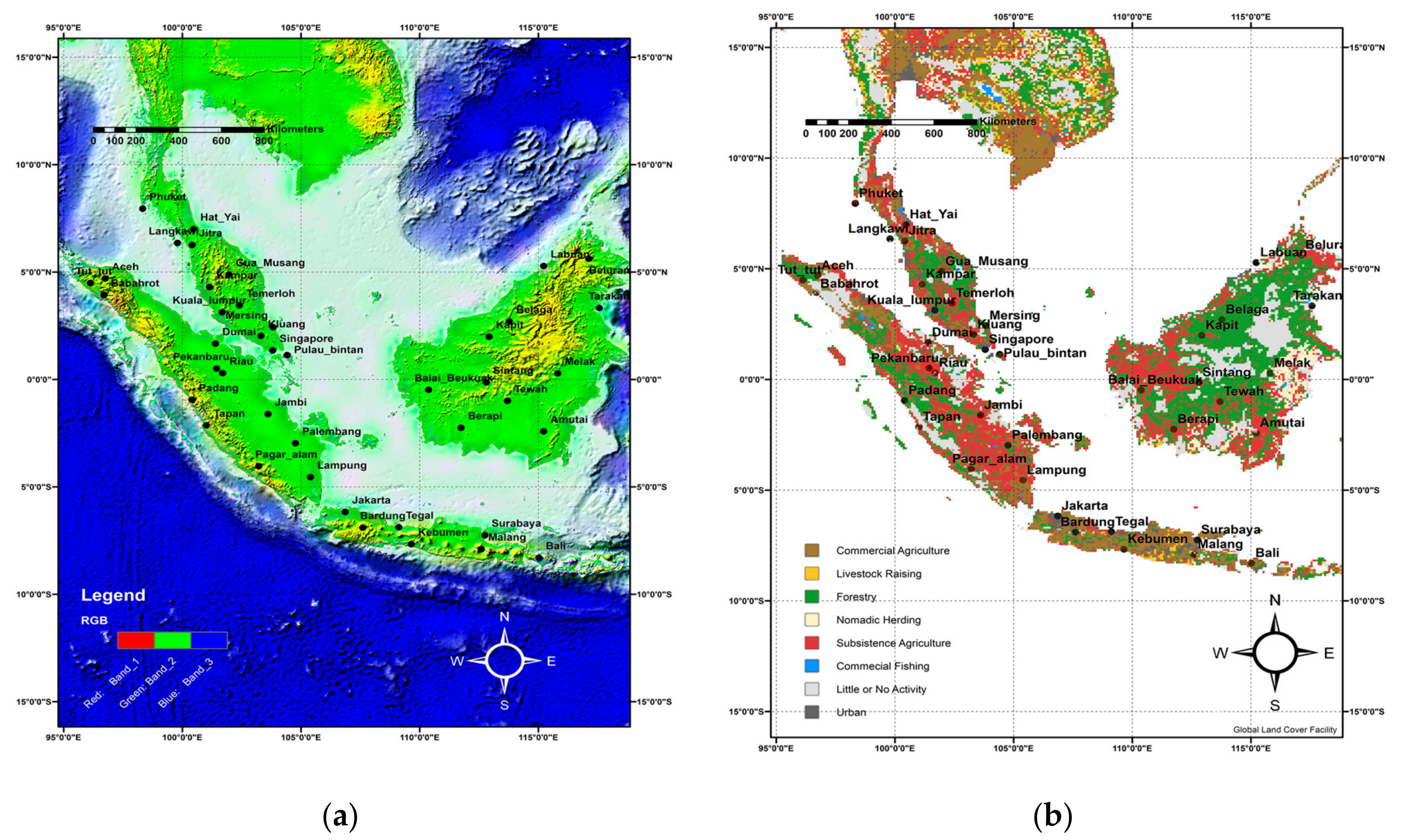

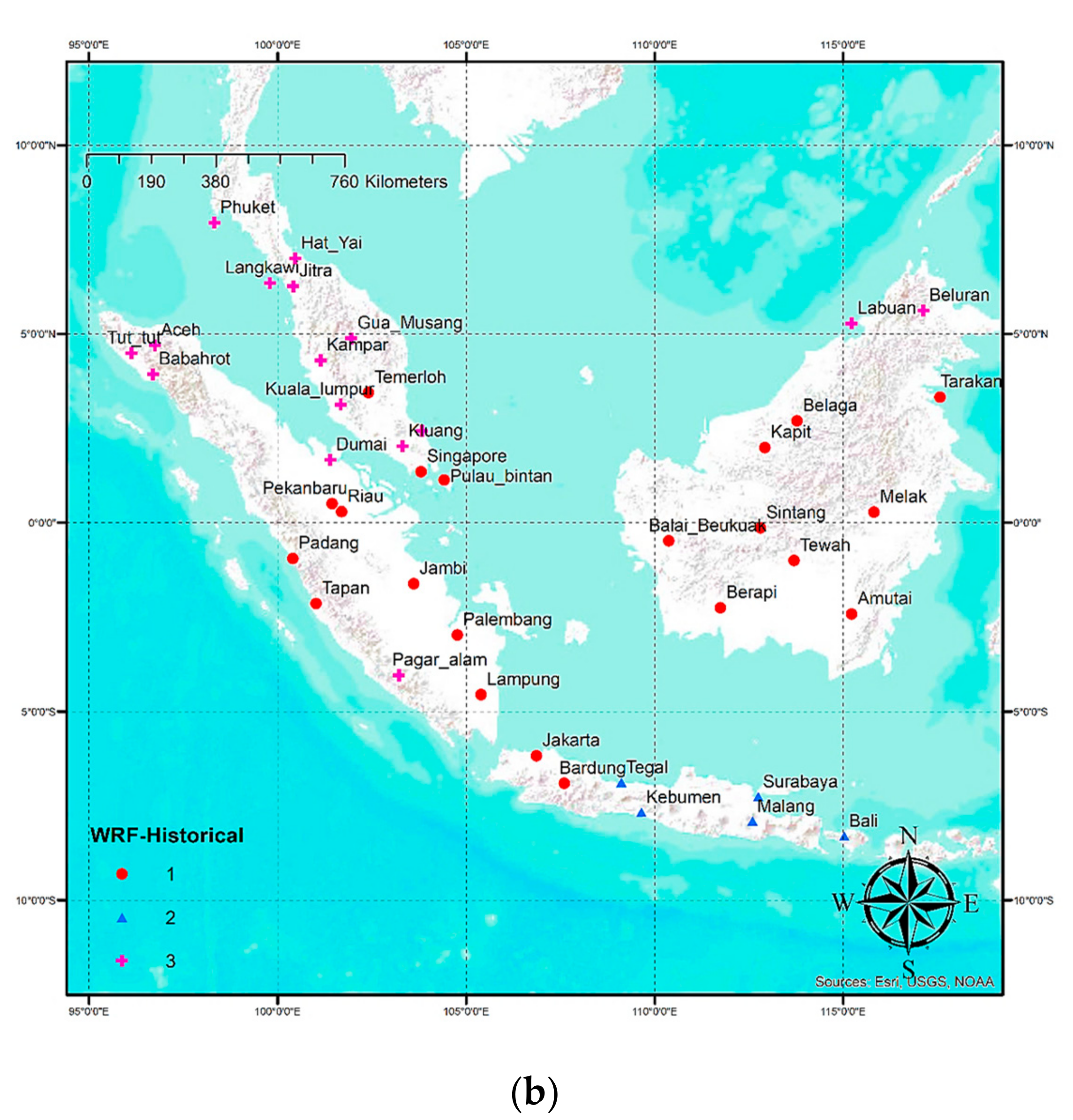

| Number | Location | Latitude (°) | Longitude (°) | Altitude (m) | Land Use | Mean Annual Precipitation (mm/day) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Java | ||||||
| 1 | Jakarta | −6.17 | 106.87 | 9 | Urban | 4.87 |
| 2 | Bardung | −6.9 | 107.61 | 704 | Urban | 5.61 |
| 3 | Surabaya | −7.25 | 112.75 | 9 | Urban | 4.66 |
| 4 | Bali | −8.3 | 115.03 | 1491 | Com Agr | 7.38 |
| 5 | Malang | −7.9 | 112.6 | 458 | Urban | 6.25 |
| 6 | Tegal | −6.879 | 109.12 | 9 | Sub Agr | 5.5 |
| 7 | Kebumen | −7.6681 | 109.65 | 57 | Com Agr | 10.13 |
| Sumatra | ||||||
| 8 | Riau | 0.2933 | 101.7 | 6 | Sub Agr | 7.71 |
| 9 | Jambi | −1.6101 | 103.613 | 45 | Sub Agr | 5.9 |
| 10 | Lampung | −4.55 | 105.4 | 32 | Com Agr | 7.45 |
| 11 | Pagar alam | −4.04 | 103.22 | 794 | Sub Agr | 7.54 |
| 12 | Padang | −0.947 | 100.41 | 59 | Forestry | 10.05 |
| 13 | Tapan | −2.14 | 101.025 | 18 | Sub Agr | 10.66 |
| 14 | Pekanbaru | 0.507 | 101.447 | 10 | Sub Agr | 7.36 |
| 15 | Aceh | 4.6951 | 96.749 | 1061 | Forest | 4.94 |
| 16 | Dumai | 1.666 | 101.4 | 14 | LA/NA | 6.63 |
| 17 | Palembang | −2.97 | 104.77 | 2 | Forest | 7.09 |
| 18 | Babahrot | 3.93 | 96.7 | 67 | Com Agr | 7.7 |
| 19 | Tut tut | 4.49 | 96.13 | 104 | Forest | 9.69 |
| Independent Islands | ||||||
| 20 | Singapore | 1.3521 | 103.81 | 58 | Urban | 6.33 |
| 21 | Pulau Bintan | 1.136 | 104.42 | 27 | Urban | 7.28 |
| Malaysia | ||||||
| 22 | Kuala lumpur | 3.13 | 101.68 | 59 | Urban | 7.26 |
| 23 | Kluang | 2.03 | 103.318 | 23 | Forest | 6.37 |
| 24 | Mersing | 2.43 | 103.83 | 9 | Forest | 6.84 |
| 25 | Temerloh | 3.448 | 102.41 | 59 | Sub Agr | 5.79 |
| 26 | Kampar | 4.3 | 101.15 | 23 | Forest | 9.41 |
| 27 | Gua Musang | 4.88 | 101.96 | 87 | Forest | 8.84 |
| 28 | Jitra | 6.264 | 100.42 | 7 | Com Agr | 6.45 |
| 29 | Langkawi | 6.35 | 99.8 | 49 | Sub Agr | 6.85 |
| 30 | Phuket | 7.95 | 98.33 | 326 | Sub Agr | 6.71 |
| 31 | Hat Yai | 7 | 100.47 | 11 | Sub Agr | 5.57 |
| Borneo | ||||||
| 32 | Labuan | 5.28 | 115.23 | 27 | Urban | 8.78 |
| 33 | Kapit | 1.99 | 112.93 | 39 | Forest | 11.05 |
| 34 | Amutai | −2.4166 | 115.23 | 16 | Sub Agr | 7.22 |
| 35 | Melak | 0.286 | 115.82 | 8 | Forest | 8.92 |
| 36 | Belaga | 2.7 | 113.78 | 48 | Forest | 10.36 |
| 37 | Beluran | 5.62 | 117.13 | 97 | LA/NA | 10.88 |
| 38 | Tarakan | 3.327 | 117.57 | 25 | LA/NA | 10.46 |
| 39 | Sintang | −0.137 | 112.81 | 579 | LA/NA | 9.87 |
| 40 | Balai Beukuak | −0.48 | 110.38 | 203 | Forest | 8.99 |
| 41 | Berapi | −2.25 | 111.75 | 70 | Sub Agr | 8.48 |
| 42 | Tewah | −1 | 113.7 | 65 | Forest | 9.56 |
| Number of SGs (with Minimum than Two Locations in a SG) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Landmass | Historical | RCP 4.5 | RCP 8.5 |
| Sumatra | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Java | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| Borneo | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| Malaysian Peninsula | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| Island Landmass | SG1 | SG2 | SG3 | Total Stations per Landmass | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HIS | RCP 4.5 | RCP 8.5 | HIS | RCP 4.5 | RCP 8.5 | HIS | RCP 4.5 | RCP 8.5 | ||
| Sumatra | 7 | 4 | 3 | 0 | 8 | 8 | 5 | 0 | 1 | 12 |
| Java | 2 | 7 | 7 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7 |
| Malaysia | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 0 | 0 | 9 |
| Borneo | 9 | 6 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 5 | 10 | 11 |
| Ind. Island | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Singh, S.K.; Lo, E.Y.-M.; Qin, X. Cluster Analysis of Monthly Precipitation over the Western Maritime Continent under Climate Change. Climate 2017, 5, 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli5040084
Singh SK, Lo EY-M, Qin X. Cluster Analysis of Monthly Precipitation over the Western Maritime Continent under Climate Change. Climate. 2017; 5(4):84. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli5040084
Chicago/Turabian StyleSingh, Saurabh K, Edmond Yat-Man Lo, and Xiaosheng Qin. 2017. "Cluster Analysis of Monthly Precipitation over the Western Maritime Continent under Climate Change" Climate 5, no. 4: 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli5040084
APA StyleSingh, S. K., Lo, E. Y.-M., & Qin, X. (2017). Cluster Analysis of Monthly Precipitation over the Western Maritime Continent under Climate Change. Climate, 5(4), 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli5040084





