Challenges of Managing Maritime Cultural Heritage in Asia in the Face of Climate Change
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Maritime Heritage and Climate Change
2.1. Records of Environmental and Social Change
2.2. Embodied Resilience—Heritage of Sustainability
2.3. Heritage of Connections
3. Environmental Dynamics in Coastal Areas
3.1. Ecological Changes
3.2. Storms and Storm Surges
3.3. Flooding
3.4. Coastal Erosion and Sedimentation
3.5. Sea-Level Change
4. Preserving Maritime Heritage in Asia
4.1. Baseline Heritage Inventories
4.2. Vulnerability Mapping
4.3. Digital Documentation
4.4. Secure and Accessible Archives
4.5. Physical Preservation
5. Discussion and Recommendations
5.1. Scale and Accessibility
5.2. Logistics, Budgets, and Capacity
5.3. Criteria for Prioritization
5.4. Governance and Transboundary Management
5.5. Institutional Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IPCC. Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability; IPCC: Cambridge, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Bertolin, C. Preservation of cultural heritage and resources threatened by climate change. Geosciences 2019, 9, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Casey, A.; Becker, A. Institutional and conceptual barriers to climate change adaptation for coastal cultural heritage. Coast. Manag. 2019, 47, 169–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cazenave, A. Anthropogenic global warming threatens world cultural heritage. Environ. Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 051001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dastgerdi, A.S.; Sargolini, M.; Pierantoni, I. Climate change challenges to existing heritage policy. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fatoric, S.; Seekamp, E. Are cultural heritage and resources threatened by climate change? A systematic literature review. Clim. Change 2017, 142, 227–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, B. Resilient cultural heritage for a future of climate change. J. Int. Aff. 2020, 73, 101–120. [Google Scholar]
- Hambrecht, G.; Rockman, M. International approaches to climate change and cultural heritage. Am. Antiq. 2017, 82, 627–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harkin, D.; Davies, M.; Hyslop, E.; Fluck, H.; Wiggins, M.; Merritt, O.; Barker, L.; Deery, M.; McNeary, R.; Westley, K. Impacts of climate change on cultural heritage. MCCIP Sci. Rev. 2020, 16, 616–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haugen, A.; Mattsson, J. Preparations for climate change’s influences on cultural heritage. Int. J. Clim. Change Strateg. Manag. 2011, 3, 386–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jigyasu, R. Managing cultural heritage in the face of climate change. J. Int. Aff. 2020, 73, 87–100. [Google Scholar]
- Orr, S.; Richards, J.; Fatoric, S. Climate change and cultural heritage: A systematic literature review (2016–2020). Hist. Environ. Policy Pract. 2021, 12, 434–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimann, L.; Vafeidis, A.; Brown, S.; Hinkel, J.; Tol, R. Mediterranean UNESCO World Heritage at risk from coastal flooding and erosion due to sea-level rise. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sesana, E.; Gagnon, A.; Bertolin, C.; Hughes, J. Adapting cultural heritage to climate change risks: Perspectives of cultural heritage experts in Europe. Geosciences 2018, 8, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sesana, E.; Gagnon, A.; Bonazza, A.; Hughes, J. An integrated approach for assessing the vulnerability of World Heritage Sites to climate change impacts. J. Cult. Herit. 2020, 41, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, P.; Aarrevaara, E. Review of potential risk factors of cultural heritage sites and initial modelling for adaptation to climate change. Geosciences 2018, 8, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezcurra, P.; Rivera-Collazo, I. An assessment of the impacts of climate change on Puerto Rico’s cultural heritage with a case study on sea-level rise. J. Cult. Herit. 2018, 32, 198–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, M.; Baird, T.; James, M.; Ram, Y. Climate change and cultural heritage: Conservation and heritage tourism in the anthropocene. J. Herit. Tour. 2015, 11, 10–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sesana, E.; Gagnon, A.; Ciantelli, C.; Cassar, J.; Hughes, J. Climate change impacts on cultural heritage: A literature review. Clim. Chang. 2020, 12, e710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciski, M.; Rzasa, K. Threats to cultural heritage caused by the global sea level rise as a result of global warming. Water 2021, 13, 2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vousdoukas, M.; Clarke, J.; Ranasignghe, R.; Reimann, L.; Khalaf, N.; Trang, M.D.; Ouweneel, B.; Sabour, S.; Iles, C.; Trisos, C.; et al. African heritage sites threatened as sea-level rise accelerates. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2022, 12, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherry, K.; Marks, L.; Adamek, R.; Lyon, B. Younger and older coastal fishers face catastropic loss after Hurricane Katrina. In Traumatic Stress and Long-Term Recovery; Cherry, K., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 327–348. [Google Scholar]
- McKernan, J.; Mulcahy, K. Hurricane Katrina: A cultural Chernobyl. J. Arts Manag. Law Soc. 2008, 38, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICOMOS. The Future of Ourt Pasts: Engaging Cultural Heritage in Climate Action; International Council on Monuments and Sites: Paris, France, 2019; pp. 1–63. [Google Scholar]
- Seekamp, E.; Jo, E. Resilience and transformation of heritage sites to accommodate for loss and learning in a changing climate. Clim. Chang. 2020, 162, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollesen, J.; Callanan, M.; Dawson, T.; Fenger-Nielson, R.; Friesen, T.; Jensen, A.; Markham, A.; Martens, V.; Pitulko, V.; Rockman, M. Climate change and the deteriorating archaeolgical and environmental archives of the Arctic. Antiquity 2018, 92, 573–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmgaard, S.; Thuestad, A.; Myrvoll, E.; Barlinghaug, S. Monitoring and managing human stressors to coastal cultural heritage in Svalbard. Humanities 2019, 8, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nicu, I.; Stalsberg, K.; Rubensdotter, L.; Martens, V.; Flyen, A.-C. Coastal erosion afftecting cultural heritage in Svalbard. A case study in Hiorthhamn (Adventfjorden)—An abandoned mining settlement. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reeder-Myers, L. Cultural heritage at risk in the twenty-first century: A vulnerability assessment of coastal archaeolgical sites in the United States. J. Isl. Coast. Archaeol. 2015, 10, 436–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, E.; Hambly, J.; Dawson, T. Learning from loss: Eroding coastal heritage in Scotland. Humanities 2017, 6, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marzeion, B.; Levermann, A. Loss of cultural world heritage and currently inhabited places to sea-level rise. Environ. Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 034001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, P.; Edwards McKinnon, E.; Feener, R.M.; Tai, Y.S.; Ardiansyah; Parnell, A.; Nizamuddin; Sieh, K.; Majewski, J. The historic trading port of Lamri on the North Sumatran Coast. Bull. L’Ecole Fr. D’Extreme-Orient 2020, 105, 115–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, P.; Sieh, K.; Tai, Y.; McKinnon, E.E.; Parnell, A.; Ardiansyah; Feener, R.M.; Ismail, N.; Nizamuddin; Majewski, J. Archaeological evidence that a late 14th-century tsunami devastated the coast of northern Sumatra and redirected history. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 11679–11686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feener, R.M.; Daly, P.; Lum, L.; Edwards McKinnon, E.; Ardiansyah; Nizamuddin; Ismail, N.; Tai, Y.S.; Sieh, K. Islamization and the formation of vernacular burial monuments in 15th-century northern Sumatra. Indones. Malay World 2021, 49, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieh, K.; Daly, P.; Edwards McKinnon, E.; Pilarczyk, J.; Chiang, H.; Horton, B.; Rubin, C.; Shen, C.; Ismail, N.; Vane, C.; et al. Penultimate predecessors of the 2004 Indian Ocean tsunami in Aceh, Sumatra: Stratigraphic, archaeological, and historical evidence. J. Geophys. Res.-Solid Earth 2015, 120, 308–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tai, Y.S.; Daly, P.; Edwards McKinnon, E.; Parnell, A.; Feener, R.M.; Majewski, J.; Ismail, N.; Sieh, K. The impacts of Ming and Qing dynasty maritime bans on trade ceramics recovered from coastal settlements in northern Sumatra, Indonesia. Archaeol. Res. Asia 2020, 21, 100174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feener, R.M.; Daly, P.; Frachetti, M.; Mujah, I.; Irawani, M.; Taran, J.; Zaki, A.; Maasa, F.; Shamran, M.; Zahara, M.; et al. The Maldives Heritage Survey. Antiquity 2021, 95, E16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brabec, E.; Chilton, E. Toward an ecology of cultural heritage. Chang. Time 2015, 346, 266–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Daly, P.; Feener, R.M. Rebuilding Asia Following Natural Disasters: Approaches to Reconstruction in the Asia-Pacific Region; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Daly, P.; Rahamayati, Y. Cultural heritage and community recovery in post-tsunami Aceh. In From the Ground Up: Persepectives on Post-Tsunami and Post-Conflict Aceh; Daly, P., Feener, R.M., Reid, A., Eds.; ISEAS Press: Singapore, 2012; pp. 57–78. [Google Scholar]
- Daly, P.; Winter, T. The Routledge Handbook of Heritage in Asia; Routledge: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- De Jong, W.; Snelder, D.; Ishikawa, N. Transborder Governance of Forests, Rivers, and Seas; Routledge: London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Horton, B.; Khan, N.; Cahill, N.; Lee, J.; Shaw, T.; Garner, A.; Kemp, A.; Engelhart, S.; Rahmstorf, S. Estimating global mean sea-level rise and its uncertainties by 2100 and 2300 using an expert survey. npj Clim. Atmos. Sci. 2020, 3, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majewski, J.; Meltzner, A.; Switzer, A.; Shaw, T.; Li, T.; Bradley, S.; Walker, J.S.; Kopp, R.; Samanta, D.; Natawidjaja, D.H.; et al. Extending instrumental sea-level records using coral microatolls, an example from Southeast Asia. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2021GL095710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saintilan, N.; Khan, N.; Ashe, E.; Kelleway, J.; Rogers, K.; Woodroffe, C.; Horton, B. Thresholds of mangrove survival under rapid sea-level rise. Science 2020, 368, 1118–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, J.S.; Kopp, R.; Little, C.; Horton, B. Time of emergence of modern rates of sea-level rise by 1863. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, J.S.; Kopp, R.; Shaw, T.; Cahill, N.; Khan, N.; Barber, D.; Ashe, E.; Brain, M.; Clear, J.; Corbett, D.; et al. Common era sea-level budgets across the U. S. Atlantic coast. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, T. Geocultural Power: China’s Quest to Revive the Silk Roads for the Twenty-First Century; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, M. Cultural History of the Sea: Volumn 1; Bloomsbury Academic: New York, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Abu-Lughod, J. Before European Hegemony: The World System A. D. 1250–1350; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhuri, K. Trade and Civilisation in the Indian Ocean: An Economic History from the Rise of Islam to 1750; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Hamashita, T.; Selden, M.; Grove, L. China, East Asia and the Global Economy: Regional and Historical Perspectives; Routledge: London, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Miksic, J. Singapore & the Silk Road of the Sea: 1300–1800; NUS Press: Singapore, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Reid, A. Southeast Asia in the Age of Commerce, 1450–1680; Yale University Press: New Haven, CT, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Reid, A. Southeast Asia in the Early Modern Era: Trade, Power, and Belief; Cornell University Press: Ithaca, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Schottenhammer, A. The East Asian Mediterranean: Maritime Crossroads of Culture, Commerce and Human Migration; Harrassowitz Verlag: Wiesbaden, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Alexandrakis, G.; Manasakis, C.; Kampanis, N. Economic and societal impacts on cultural heritage sites, resulting from natural effects and climate change. Heritage 2019, 2, 279–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, T.; Nguyen, T.; Luong, T.; Luc, H. Tourism and beach erosion: Valuing the damage of beach erosion for tourism in the Hoi An World Heritage site, Vietnam. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2019, 21, 2113–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeder-Myers, L.; McCoy, M. Preparing for the future impacts of megastorms on archaeolgical sites: An evaluation of flooding from Hurricane Harvey, Houston, Texas. Am. Antiq. 2019, 84, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liritzis, I.; Westra, A.; Miao, C. Disaster geoarchaeology and natural cataclysms in world cultural evolution: An overview. J. Coast. Res. 2019, 35, 1307–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, C.; Horton, B.; Sieh, K.; Pilarczyk, J.; Daly, P.; Ismail, N.; Parnell, A. Highly variable recurrence of tsunamis in the 7400 years before the 2004 Indian Ocean tsunami. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 16019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boger, R.; Perdikaris, S.; Rivera-Collazo, I. Cultural heritage and local ecological knowledge under threat: Two Caribbean examples from Barbuda and Puerto Rico. J. Anthropol. Archaeol. 2019, 7, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abulafia, D. The Boundless Sea: A Human History of the Oceans; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Paine, L. The Sea and Civilization: A Maritime History of the World; Atlantic Books: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Gipouloux, F. The Asian Mediterranean: Port Cities and Trading Networks in China, Japan and Southeast Asia, 13th—21st Century; Edward Elgar: Cheltenham, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Graf, A.; Chua, B. Port Cities in Asia and Europe; Routledge: London, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Haneda, M. Asian Port Cities, 1600—1800: Local and Foreign Cultural Interactions; NUS Press: Singapore, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Feener, R.M.; Ishikawa, N.; Daly, P. Big data in the humanities: New interdisciplinary opportunities and new challenges for data management. J. Jpn. Soc. Inf. Knowl. 2021, 31, 440–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, P. Cycles of destruction and reconstruction: Responding to disasters in the Asia-Pacific region. In Rebuilding Asia: Approaches to Post-Disaster Reconstruction in the Asia-Pacific Region; Daly, P., Feener, R.M., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2016; pp. 1–56. [Google Scholar]
- Anthony, A.; Atwood, J.; August, P.; Bryron, C.; Cobb, S.; Foster, C.; Fry, C.; Gold, A.; Hagos, K.; Heffner, L.; et al. Coastal lagoons and climate change: Ecological and social ramifications in the US. Atlantic and Gulf coast ecosystems. Ecol. Soc. 2009, 14, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Silliman, B. Climate Change, human impacts, and coastal ecosystems in the Anthropocene. Curr. Biol. 2019, 29, 1021–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, T.P.; Kerry, J.T.; Simpson, T. Large-scale bleaching of corals on the Great Barrier Reef. Ecology 2018, 99, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pisapia, C.; Burn, D.; Prachett, M. Changes in the population and community structure of corals during recent disturbances (February 2016–October 2017) on Maldivian coral reefs. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuart-Smith, R.; Brown, C.; Ceccarelli, D.; Edger, G. Ecosystem restructuring along the Great Barrier Reef following mass coral bleaching. Nature 2018, 560, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaijaroen, P. Long-lasting income shocks and adaptatons: Evidence from coral bleaching in Indonesia. J. Dev. Econ. 2019, 136, 119–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoegh-Guldberg, O.; Pendleton, L.; Kaup, A. People and the changing nature of coral reefs. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2019, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ives, T.; McBridge, K.; Waller, J. Surveying coastal archaeological sites damaged by Hurricane Sandy in Rhode Island, USA. J. Isl. Coast. Archaeol. 2018, 13, 66–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Gong, P.; Hu, H.; Jia, W.; Liu, X.; Gao, W. Spatial variability of human subsistence strategies during the Longshan period and its possible physical environmental contexts in the Yellow-Huai River area, East China. Sci. Cult. 2021, 7, 105–116. [Google Scholar]
- Chapkanski, S.; Brocard, G.; Lavigne, F.; Tricot, C.; Meilianda, E.; Ismail, N.; Majewski, J.; Goiran, J.-P.; Alfian, D.; Daly, P.; et al. Fluvial and coastal landform changes in the Aceh River delta (northern Sumatra) during the century leading to the 2004 Indian Ocean tsunami. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2021, 47, 1127–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulos, S.E.; Panagopoulou, A.; Kotinas, C. An oceanographic insight in the submergence and resilence of the Pavlopetri archaeological site. Sci. Cult. 2022, 8, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevieri, G.; Galasso, C.; D’Ayala, D.; DeJesus, R.; Oreta, A.; Grio, M.; Ibabao, R. A multi-hazard risk prioritisation framework for cultural heritage assets. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 20, 1391–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, I.; Johnston, R.; Selby, K. Climate change and cultural heritage: A landscape vulnerability framework. J. Isl. Coast. Archaeol. 2021, 16, 553–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choy, S.; Crofts, N.; Fisher, R.; Choh, N.L.; Nickle, S.; Oury, C.; Slaska, K. The UNESCO/PERSIST Guidelines for the Selection of Digital Heritage for Long-Term Preservation; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald, L. Digital Heritage: Applying Digital Imaging to Cultural Heritage; Routledge: London, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- O’Neill, B.; Stapleton, L. Digital cultural heritage standards: From silo to semantic web. AI Soc. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parry, R. Recoding the Museum: Digital Heritage and the Technologies of Change; Routledge: London, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Alberts, H.; Hazen, H. Maintaining authenticity and integrity at cultural World Heritage sites. Geogr. Rev. 2010, 100, 56–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamborrino, R.; Wendrich, W. Cultural heritage in context: The temples of Nubia, digital technologies and the future of conservation. J. Inst. Conserv. 2017, 40, 168–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Galili, E.; Rosen, B. Preserving the maritime cultural heritage of the Mediterranean, a cradle of cultures, religions and civilizations—The holy land perspective. J. Coast. Conserv. 2010, 14, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L. Uses of Heritage; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Winter, T.; Daly, P. Heritage in Asia: Converging forces, conflicting values. In The Routledge Handbook of Heritage in Asia; Daly, P., Winter, T., Eds.; Routledge: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, R.; Zarandona, J. Heritage destruction in Myanmar’s Rakhine state: Legal and illegal iconoclasm. Int. J. Herit. Stud. 2019, 26, 519–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maarleveld, T. The maritime paradox: Does international heritage exist? Int. J. Herit. Stud. 2012, 18, 418–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manhart, C. The Afghan cultural heritage crisis: UNESCO’s response to the destruction of statues in Afghanistan. Am. J. Archaeol. 2001, 105, 387–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
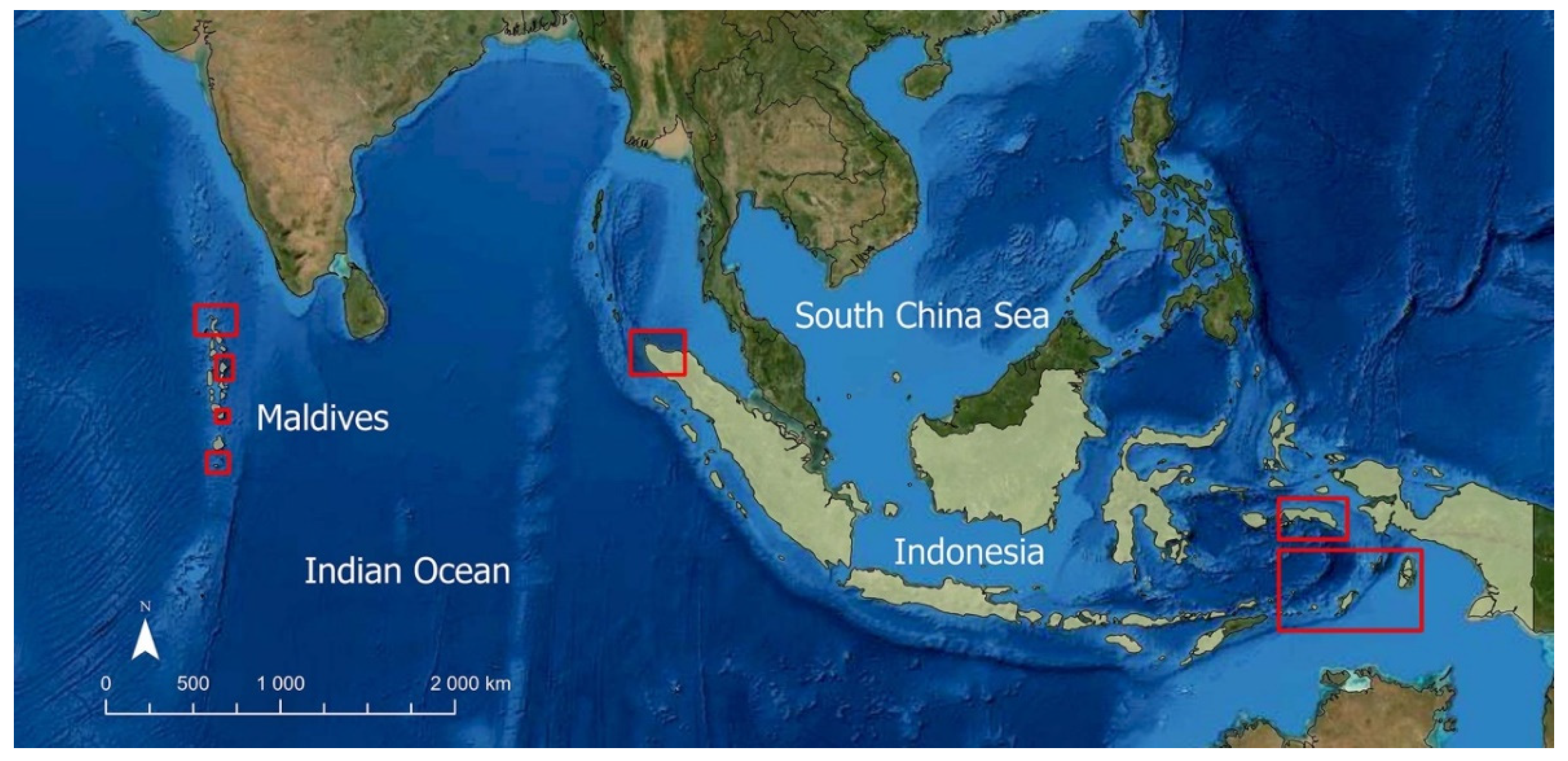
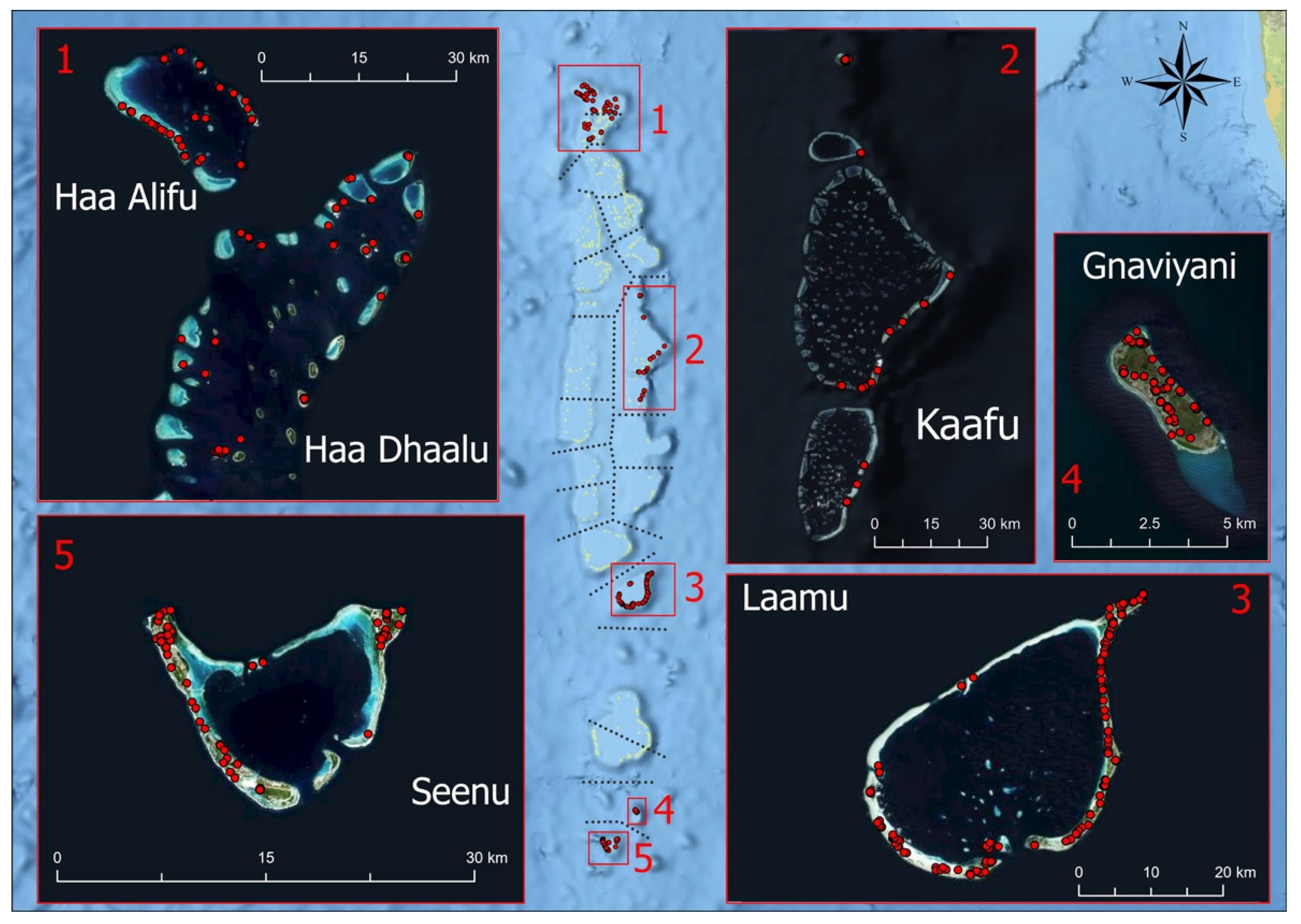




| Maldives Phase 1 | Maldives Phase 2 | Indonesia Phase 1 | Indonesia Phase 2 | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Site Records | 365 | 146 | 1028 | 81 | 1620 |
| Feature Records | 4817 | 518 | 5869 | 638 | 11,842 |
| Object Records | 1022 | 280 | 48,707 | 198 | 50,207 |
| Recorded Oral Histories | 37 | 10 | N/A | 33 | 80 |
| 3d Visualizations | N/A | 23 | N/A | 48 | 71 |
| Digitized Manuscripts | 1091 | 15 | N/A | 20 | 1126 |
| Count | Percent of Total Sites | |
|---|---|---|
| Condition of Heritage Site | ||
| Excellent | 13 | 9% |
| Partially Damaged | 101 | 71% |
| Completely destroyed | 24 | 16% |
| No Longer Extent | 1 | 0.70% |
| Submerged | 3 | 2% |
| Source of Attrition | ||
| Coastal Erosion | 54 | 38% |
| Flooding | 14 | 9% |
| Salt Intrusion | 1 | 0.7% |
| Sea-Level Change | 9 | 6% |
| Tsunami | 27 | 19% |
| Future Environmental Vulnerabilities | ||
| Coastal Erosion | 61 | 43% |
| Flooding | 17 | 12% |
| Salt Intrusion | 5 | 3% |
| Sea-Level Change | 82 | 57% |
| Tsunami | 73 | 51% |
| Preservation Status | ||
| Not Preserved | 114 | 80% |
| Preserved | 28 | 19% |
| Need for Preservation | ||
| Immediate | 2 | 1% |
| Urgent | 12 | 8% |
| Moderate | 53 | 37% |
| Low | 51 | 35% |
| N/A | 24 | 16% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Daly, P.; Feener, R.M.; Ishikawa, N.; Mujah, I.; Irawani, M.; Hegyi, A.; Baranyai, K.; Majewski, J.; Horton, B. Challenges of Managing Maritime Cultural Heritage in Asia in the Face of Climate Change. Climate 2022, 10, 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli10060079
Daly P, Feener RM, Ishikawa N, Mujah I, Irawani M, Hegyi A, Baranyai K, Majewski J, Horton B. Challenges of Managing Maritime Cultural Heritage in Asia in the Face of Climate Change. Climate. 2022; 10(6):79. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli10060079
Chicago/Turabian StyleDaly, Patrick, R. Michael Feener, Noboru Ishikawa, Ibrahim Mujah, Maida Irawani, Alexandru Hegyi, Krisztina Baranyai, Jedrzej Majewski, and Benjamin Horton. 2022. "Challenges of Managing Maritime Cultural Heritage in Asia in the Face of Climate Change" Climate 10, no. 6: 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli10060079
APA StyleDaly, P., Feener, R. M., Ishikawa, N., Mujah, I., Irawani, M., Hegyi, A., Baranyai, K., Majewski, J., & Horton, B. (2022). Challenges of Managing Maritime Cultural Heritage in Asia in the Face of Climate Change. Climate, 10(6), 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli10060079





