Improved Smart Pillow for Remote Health Care System
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Evolution of Measurement of Core Body Temperature (MCBT)
1.2. Core Body Temperature Minimum (CBTM) from the Smart Pillow
2. Materials and Methods
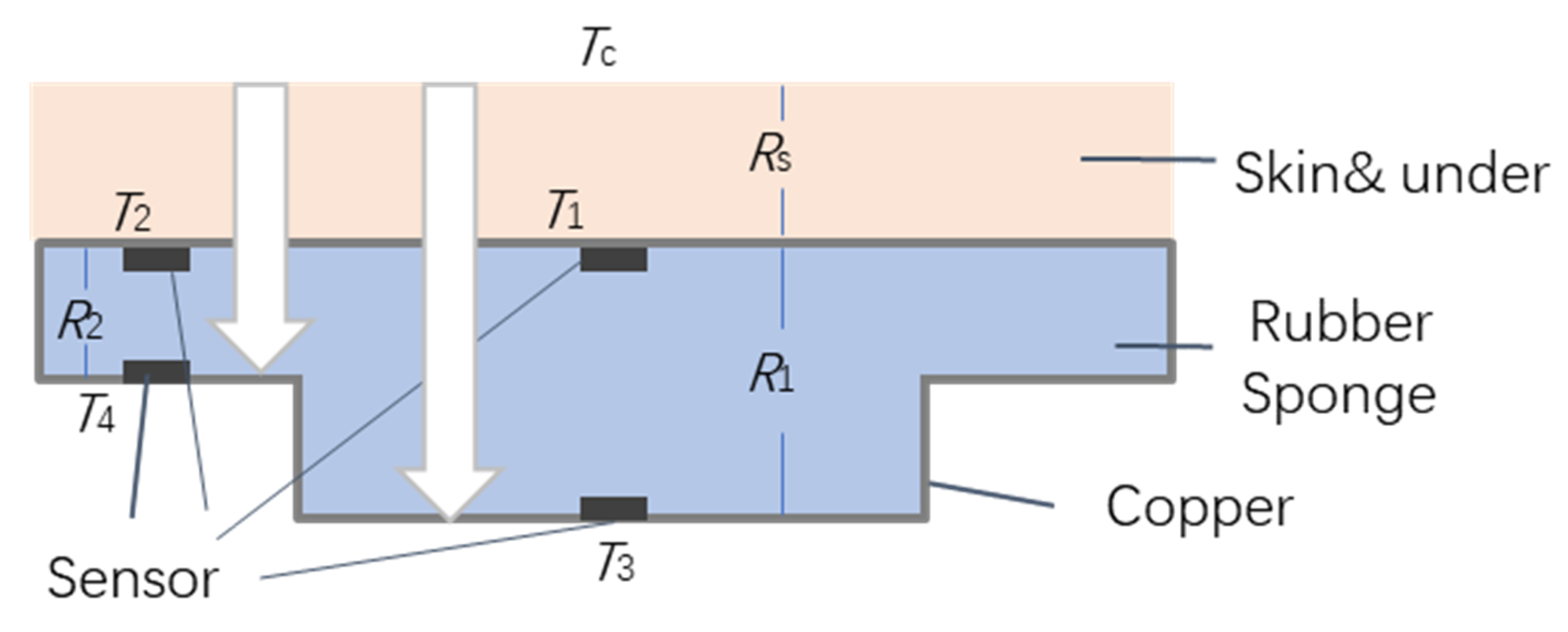
2.1. Bioheat Transfer Principles
2.2. CBT from the Smart Magic Pillow
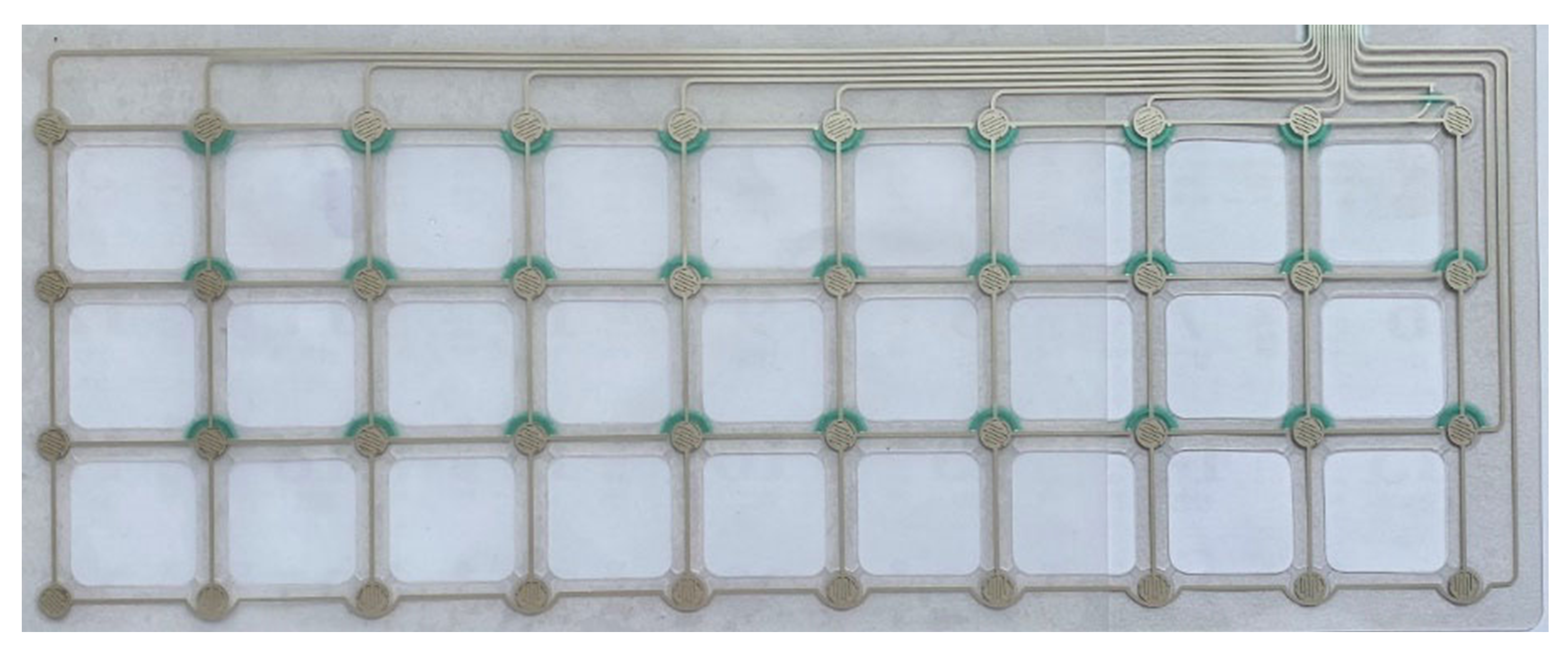
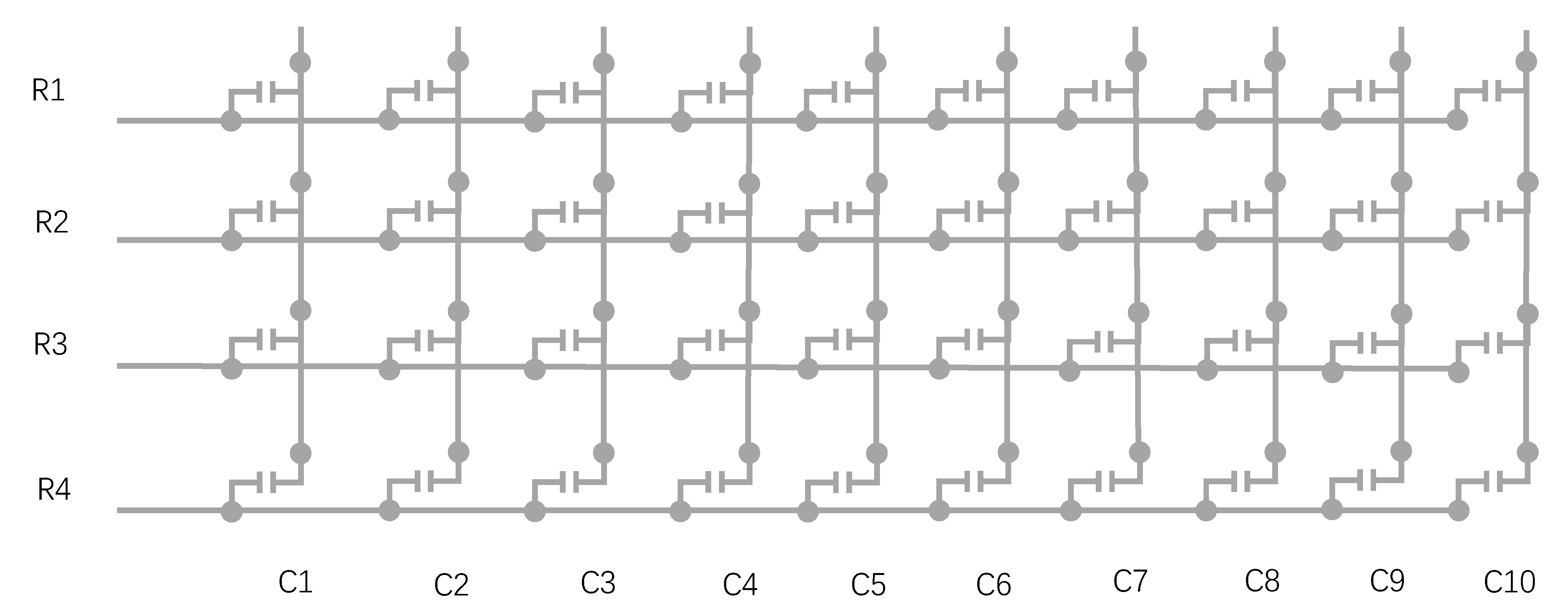
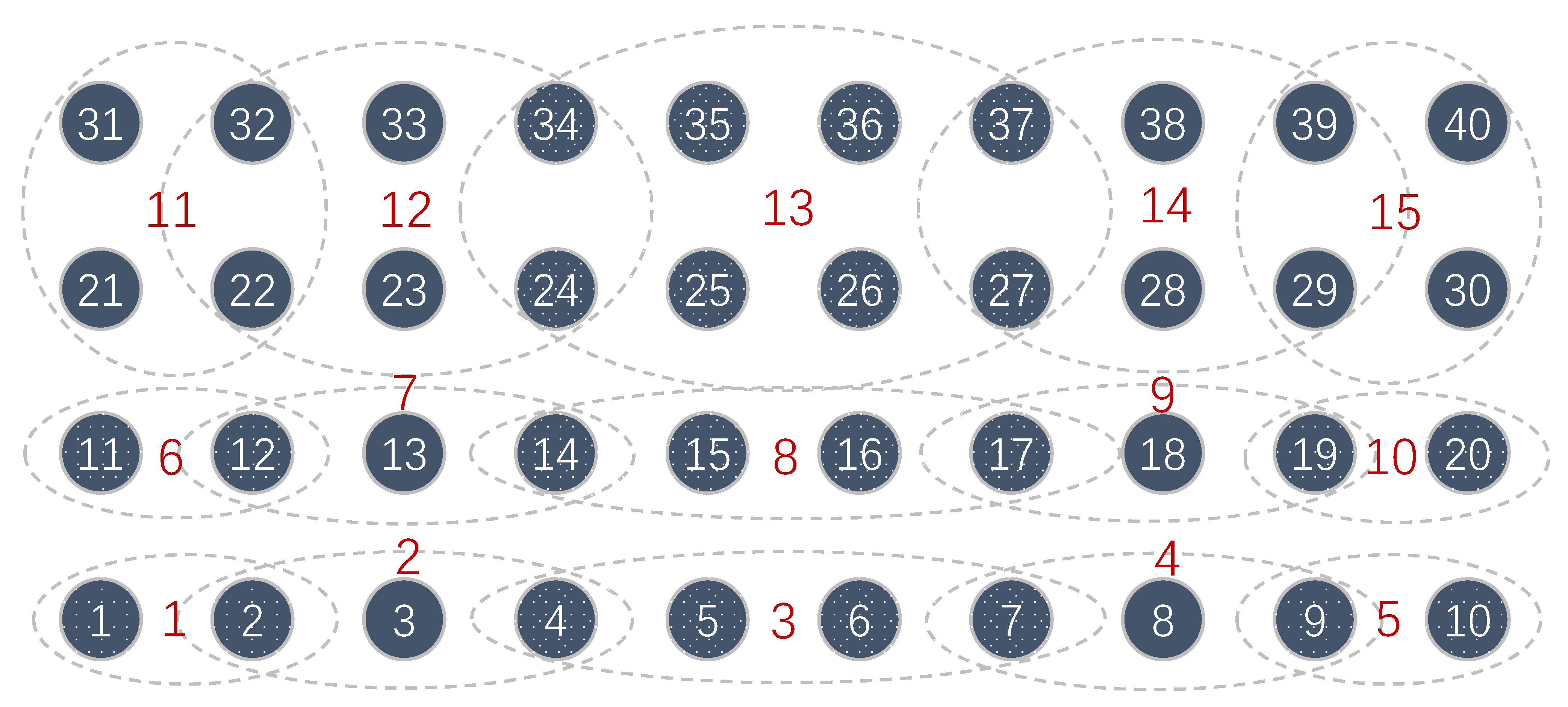
2.3. Force-Pad Element Concept
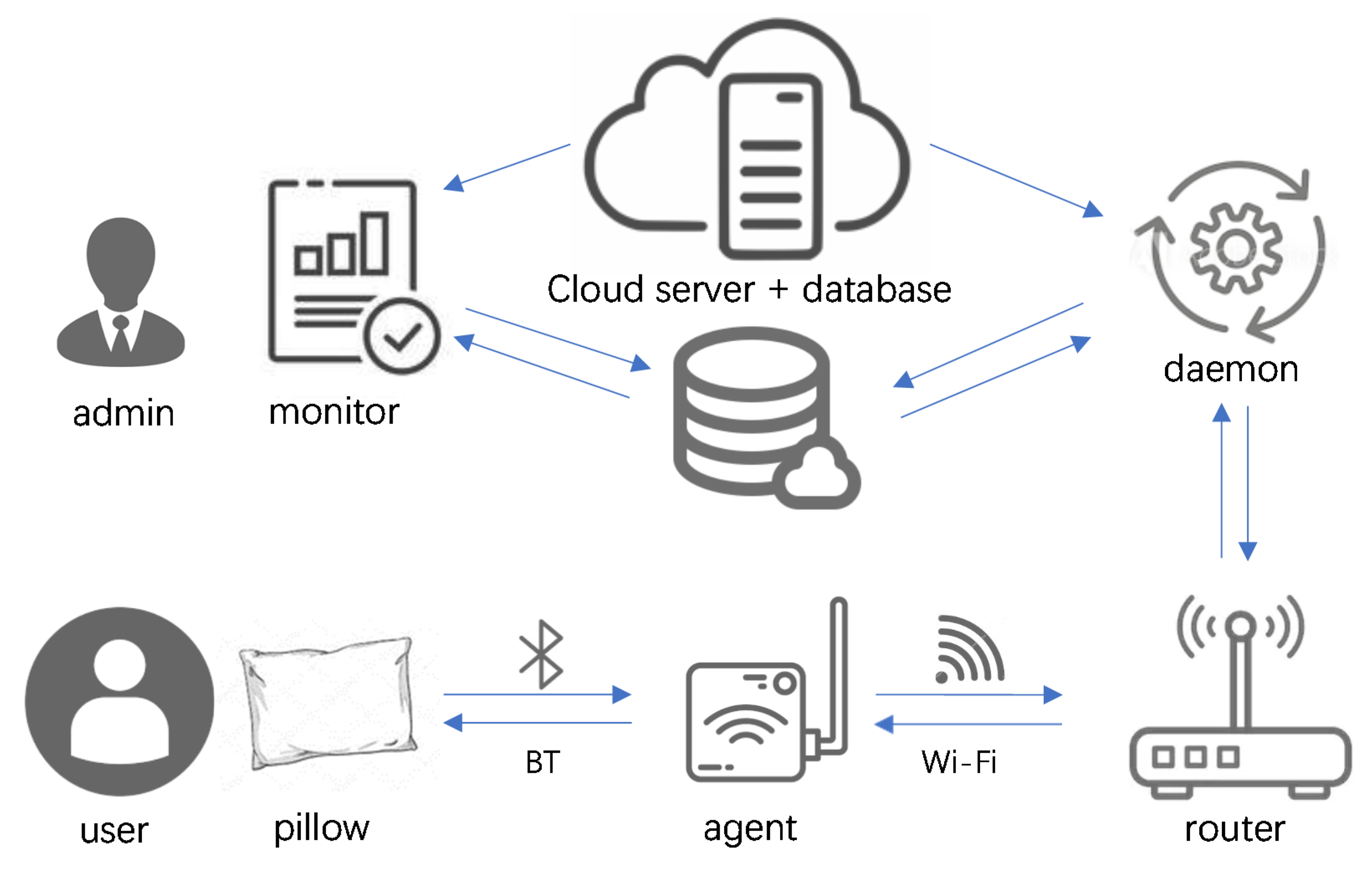
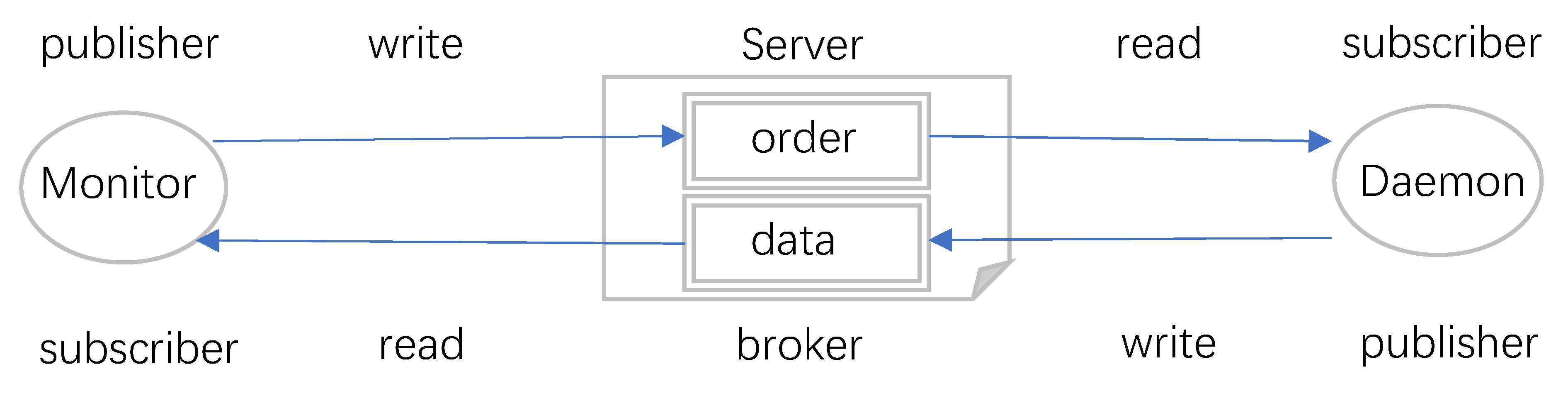
2.4. Key Roles in the System Implementation
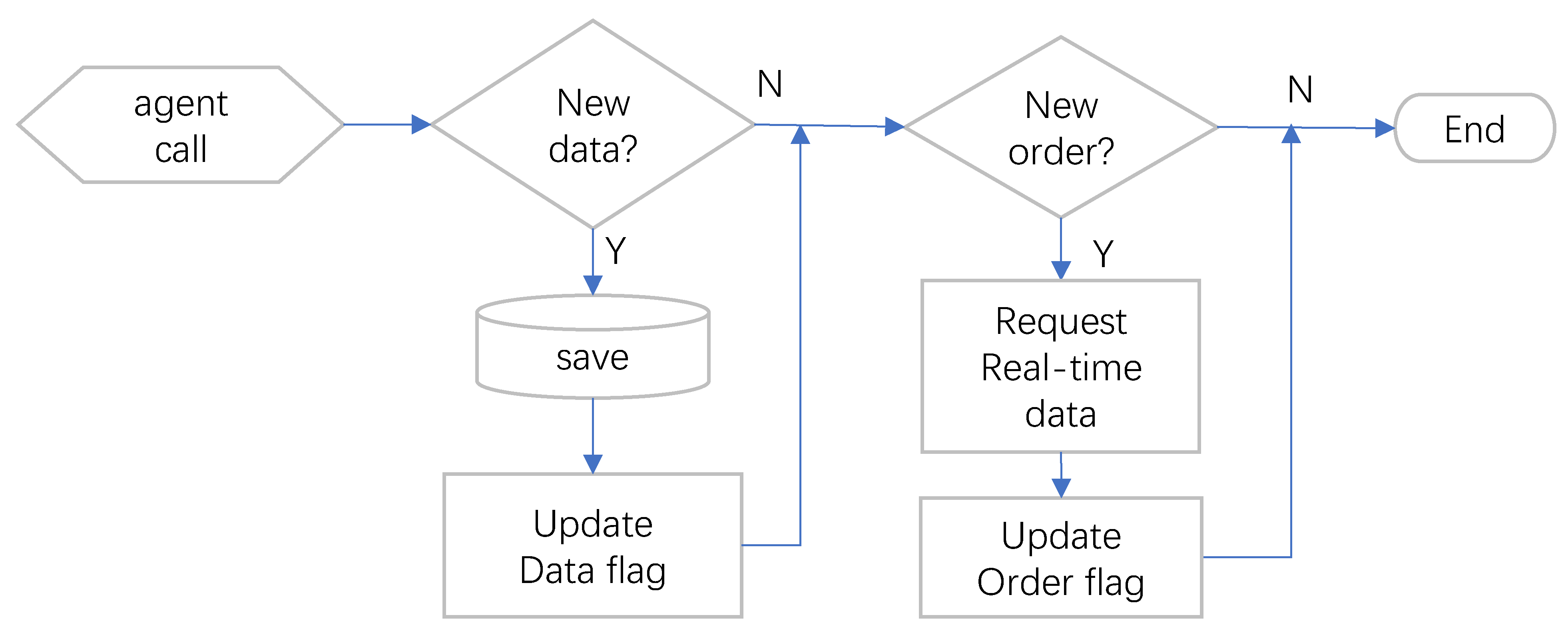
2.5. Proactive Monitoring Practice
3. Results
3.1. Thermal Simulation of the Smart Pillow
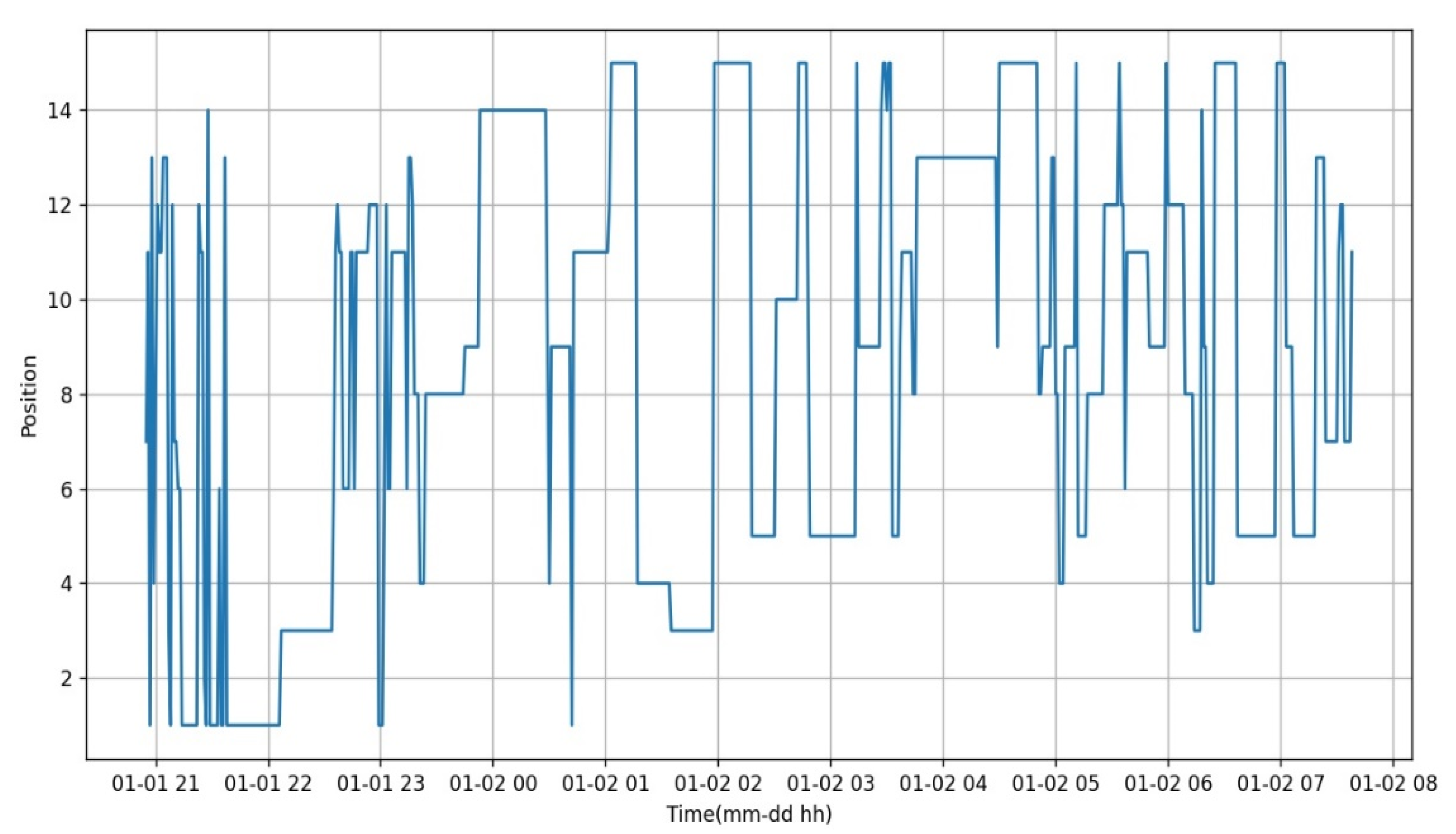
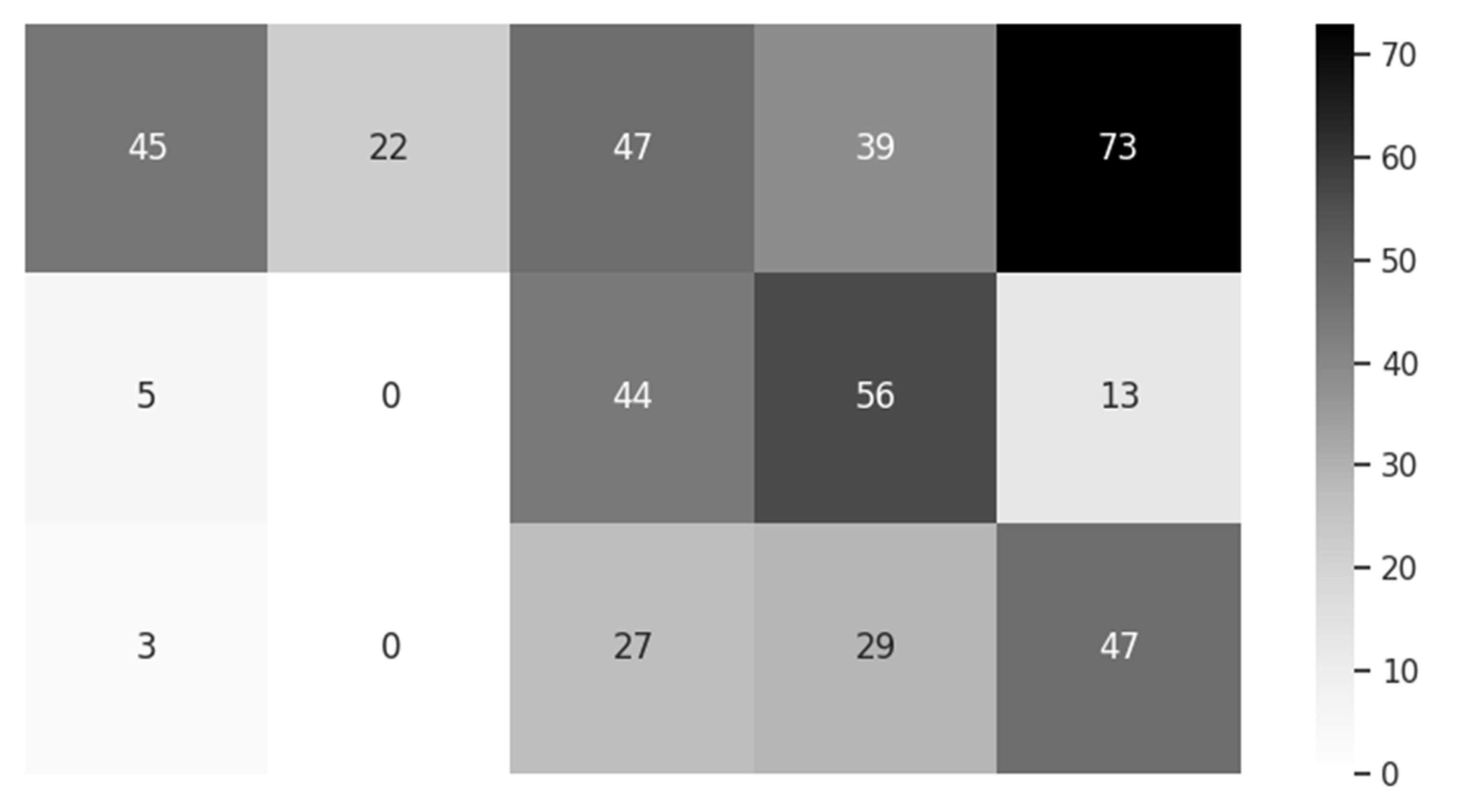
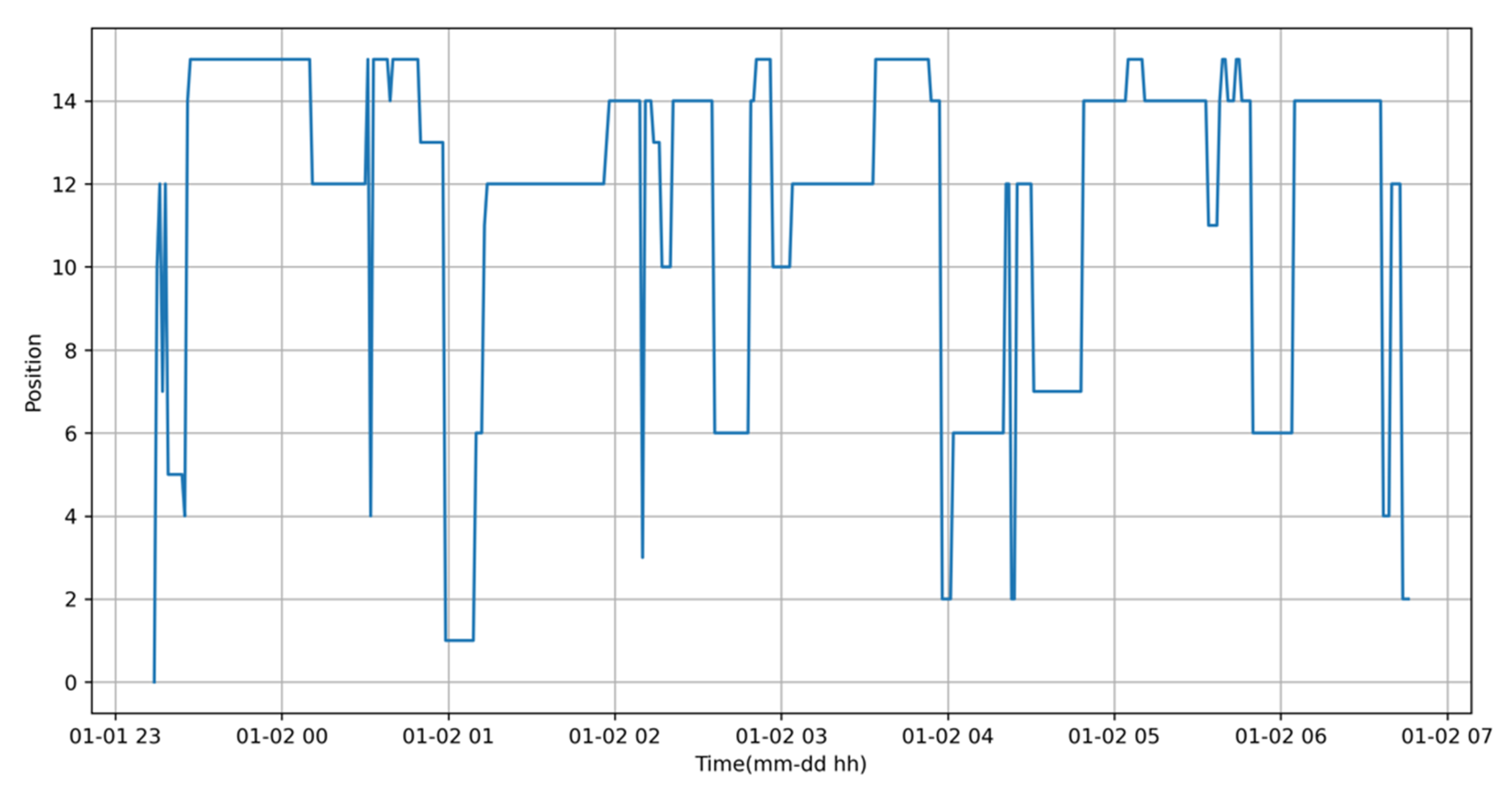
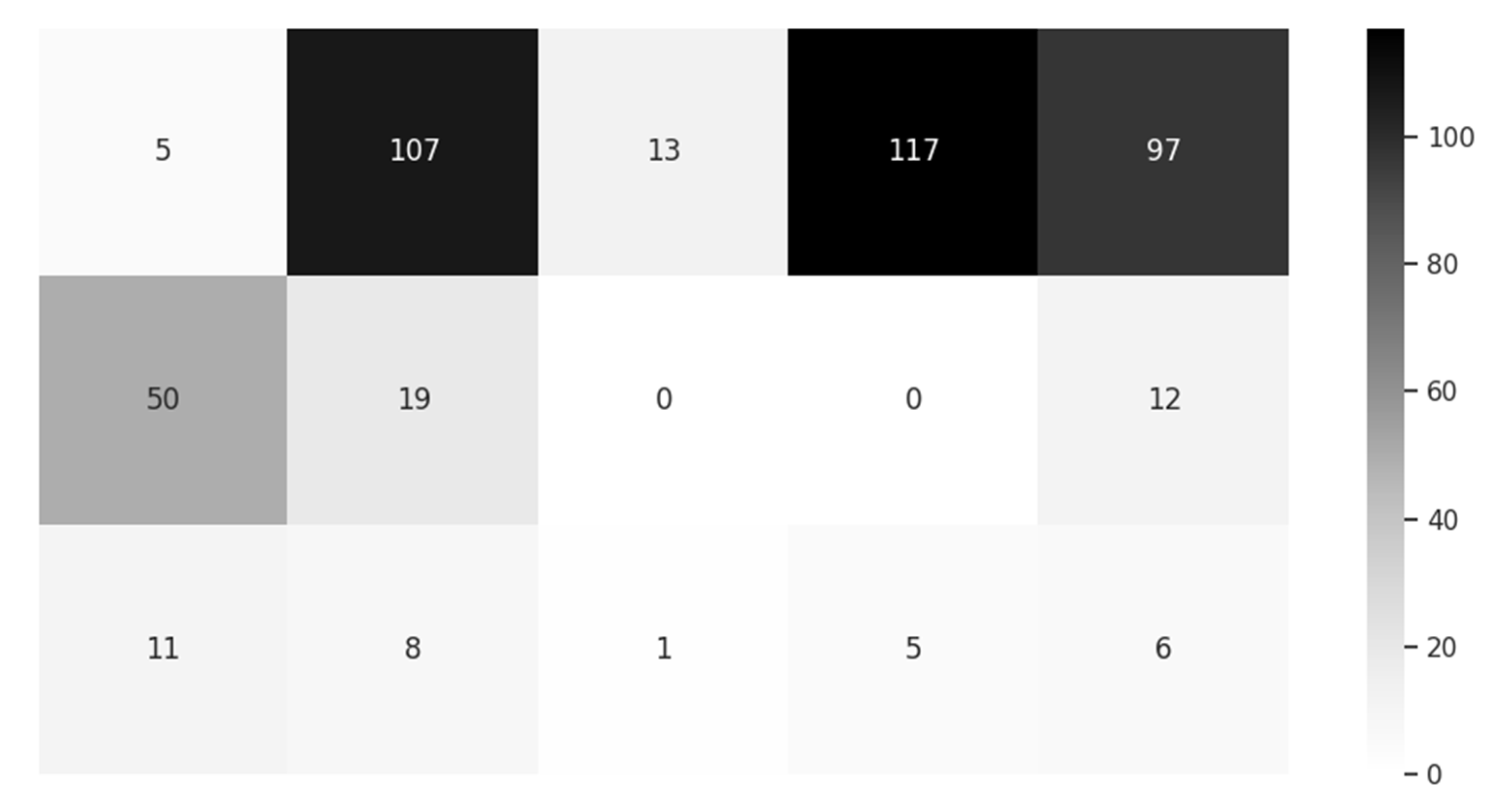
3.2. Sample Data from the Smart Pillow
3.3. Comparision with ZHF and DHF Approaches
4. Conclusions
Further Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fox, R.H.; Solman, A.J.; Isaacs, R.; Fry, A.J.; Macdonald, I.C. A New Method for Monitoring Deep Body Temperature from the Skin Surface. Clin. Sci. Mol. Med. 1973, 44, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunga, H.-C.; Sandsund, M.; Reinertsen, R.E.; Sattler, F.; Koch, J. A non-invasive device to continuously determine heat strain in humans. J. Therm. Biol. 2008, 33, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshraghi, Y.; Nasr, V.; Parra-Sanchez, I.; Van Duren, A.; Botham, M.; Santoscoy, T.; Sessler, D.I. An Evaluation of a Zero-Heat-Flux Cutaneous Thermometer in Cardiac Surgical Patients. Anesth. Analg. 2014, 119, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 3M. SpotOn Temperature Monitoring System Model 370 Operator Manual; 3M: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2020; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Yamakage, M.; Namiki, A. Deep temperature monitoring using a zero-heat-flow method. J. Anesth. 2003, 17, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazgaoker, S.; Ketko, I.; Yanovich, R.; Heled, Y.; Epstein, Y.; Savyon, M.; Itay, K.; Ran, Y.; Yuval, H.; Yoram, E. Measuring core body temperature with a non-invasive sensor. J. Therm. Biol. 2017, 66, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Draeger Temperature Monitoring System. Available online: https://www.draeger.com/de_de/Hospital/Products/Accessories-and-Consumables/Patient-Monitoring-Accessories/Tcore-Temperature-Monitoring-System (accessed on 24 November 2020).
- Kitamura, K.-I.; Zhu, X.; Chen, W.; Nemoto, T. Development of a new method for the noninvasive measurement of deep body temperature without a heater. Med. Eng. Phys. 2010, 32, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; Zhou, C.; He, C.; Li, Y.; Ye, X. Development of an improved wearable device for core body temperature monitoring based on the dual heat flux principle. Physiol. Meas. 2017, 38, 652–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.; Zeng, P.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, H.; Yu, H. Wearable Continuous Body Temperature Measurement Using Multiple Artificial Neural Networks. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2018, 14, 4395–4406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Tamura, T.; Tang, Z.; Chen, W.; Kanaya, S. Structural Optimization of a Wearable Deep Body Thermometer: From Theoretical Simulation to Experimental Verification. J. Sens. 2015, 2016, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, T.; Huang, M.; Togawa, T. Body Temperature, Heat Flow, and Evaporation. In Seamless Healthcare Monitoring; Tamura, T., Chen, W., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Khafajiy, M.; Baker, T.; Chalmers, C.; Asim, M.; Kolivand, H.; Fahim, M.; Waraich, A. Remote health monitoring of elderly through wearable sensors. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2019, 78, 24681–24706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghayvat, H.; Awais, M.; Pandya, S.; Ren, H.; Akbarzadeh, S.; Mukhopadhyay, S.C.; Chen, C.; Gope, P.; Chouhan, A.; Chen, W. Smart Aging System: Uncovering the Hidden Wellness Parameter for Well-Being Monitoring and Anomaly Detection. Sensors 2019, 19, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahbazi, Z.; Byun, Y.-C. Towards a Secure Thermal-Energy Aware Routing Protocol in Wireless Body Area Network Based on Blockchain Technology. Sensors 2020, 20, 3604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majumder, S.; Mondal, T.K.; Deen, M.J. Wearable Sensors for Remote Health Monitoring. Sensors 2017, 17, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Chiu, C. A Smart Pillow for Health Sensing System Based on Temperature and Humidity Sensors. Sensors 2018, 18, 3664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S. Prediction of body temperature from smart pillow by machine learning. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation (ICMA), Tianjin, China, 4–7 August 2019; pp. 421–426. [Google Scholar]
- Bergman, T.L.; Lavine, A.S.; Incropera, F.P. Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer, 7th ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Filipoiu, F.; Bogdan, A.; Cârstea, I. Computer-aided analysis of the heat transfer in skin tissue. In Proceedings of the 3rd WSEAS International Conference on Finite Differences—Finite Elements—Finite Volumes—Boundary Elements; World Scientific and Engineering Academy and Society (WSEAS): Stevens Point, WI, USA; pp. 53–59.
- Pompei, F. Ambient and Perfusion Normalized Temperature Detector. U.S. Patent US6056435, 2 May 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Sadun, A.S.; Jalani, J.; Sukor, J.A. Force Sensing Resistor (FSR): A Brief Overview and the Low-Cost Sensor for Active Compliance Control. Proc. SPIE 2016, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Port Forwarding Definition. PC Magazine. Available online: https://www.pcmag.com/encyclopedia_term/0,1237,t=port+forwarding&i=49509,00.asp (accessed on 25 November 2020).
- TCP Keepalive Mechanism. Available online: https://tldp.org/HOWTO/TCP-Keepalive-HOWTO/overview.html (accessed on 25 November 2020).
- ngrok Network Inspector. Available online: https://ngrok.com (accessed on 25 November 2020).
- MQTT Protocol Specifications. Available online: https://mqtt.org/ (accessed on 25 November 2020).
- Xie, C. Interactive Heat Transfer Simulations for Everyone. Phys. Teach. 2012, 50, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrovicova, E.; Kamath, Y.K. Heat transfer in human hair. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2019, 41, 387–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Incropera, F.P.; DeWitt, D.P. Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2nd ed.; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Engineering Toolbox, Thermal Conductivity of Selected Materials and Gases. Available online: https://www.engineeringtoolbox.com/thermal-conductivity-d_429.html (accessed on 24 November 2020).
- Teunissen, L.P.J.; Klewer, J.; De Haan, A.; De Koning, J.J.; Daanen, H.A.M. Non-invasive continuous core temperature measurement by zero heat flux. Physiol. Meas. 2011, 32, 559–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Name | Strength | Weakness |
|---|---|---|
| Port Forwarding | Common in routers | Security concerns, Use of public IP |
| KeepAlive | Persistent connection | Occupation of system resources |
| ngrok | Security tunnel, Inherent safer | Reliance on third party technology |
| Polling | Avoids most weaknesses | Persistent delay, Risk of potential race conditions |
| Material Name | K (W/m·°C) | ρ (kg/m3) | C (J/kg·°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hair | 0.37 | 1300 | 10,000 |
| Air | 0.026 | 1.17 | 1007 |
| Cellularized Rubber | 0.045 | 100 | - |
| Cotton Pillowcase | 0.077 | 245 | 1300 |
| Parameter | ZHF Method | DHF Method | Smart Magic Pillow |
|---|---|---|---|
| Heater | Yes | No | No |
| Initial Response | 10 min [8] | 20 min | Uncertain |
| Accuracy | 0.3–0.4 °C | 0.1–0.5 °C | 0.2 °C |
| Comfort | Low | Mild | High |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, S.; Chiu, C. Improved Smart Pillow for Remote Health Care System. J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2021, 10, 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/jsan10010009
Li S, Chiu C. Improved Smart Pillow for Remote Health Care System. Journal of Sensor and Actuator Networks. 2021; 10(1):9. https://doi.org/10.3390/jsan10010009
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Songsheng, and Christopher Chiu. 2021. "Improved Smart Pillow for Remote Health Care System" Journal of Sensor and Actuator Networks 10, no. 1: 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/jsan10010009
APA StyleLi, S., & Chiu, C. (2021). Improved Smart Pillow for Remote Health Care System. Journal of Sensor and Actuator Networks, 10(1), 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/jsan10010009





