Knockout of SlMS10 Gene (Solyc02g079810) Encoding bHLH Transcription Factor Using CRISPR/Cas9 System Confers Male Sterility Phenotype in Tomato
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
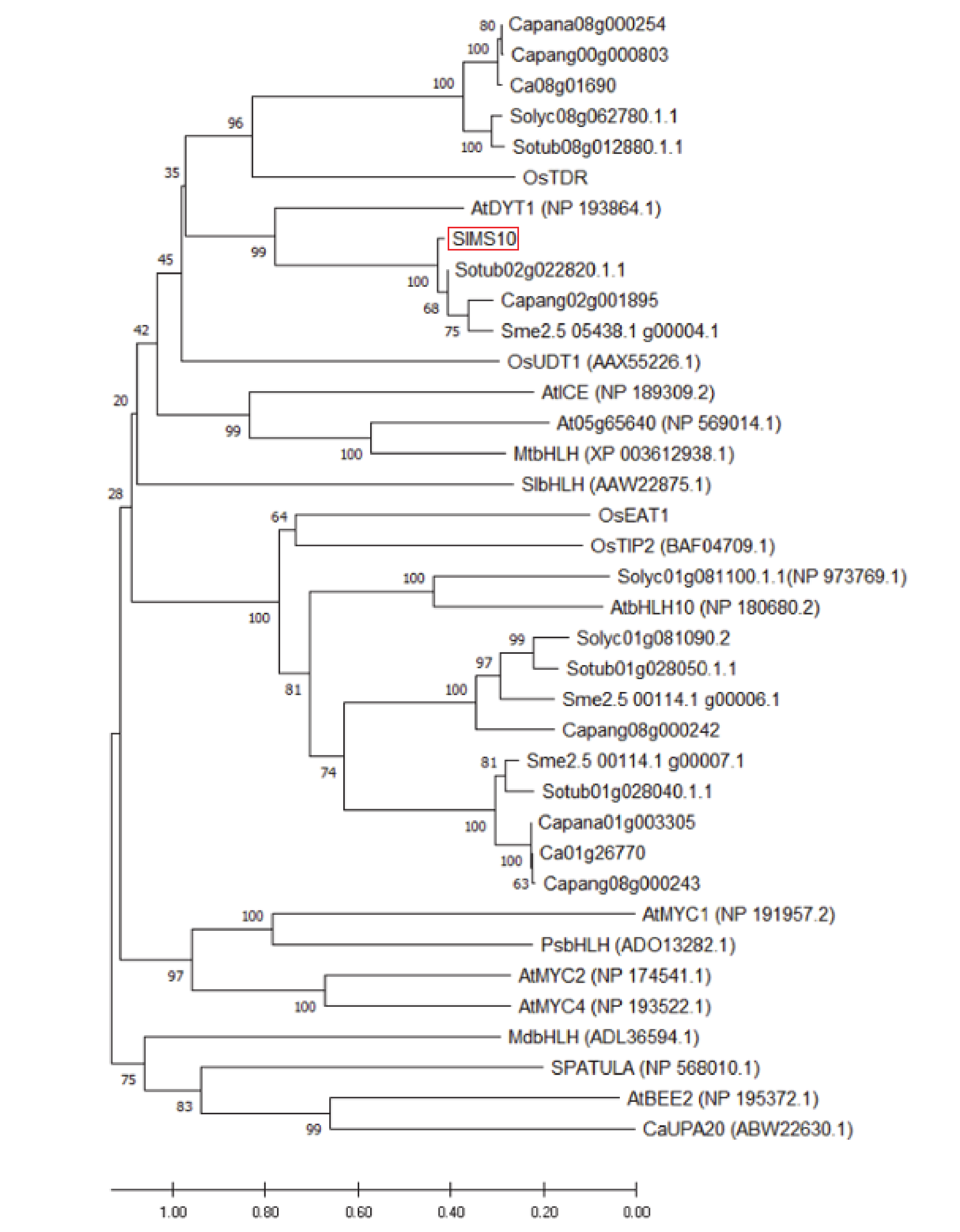
2.1. Phylogenetic Tree Analysis
2.2. sgRNA-Cas9 Vector Construction
2.3. Transformation into Tomato
2.4. Targeted Deep Sequencing and Mutation Analysis
2.5. Plant Growth and Morphological Characterization
2.6. Microscopy
2.7. RNA Isolation and RT-PCR Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Phylogenetic Analysis of SlMS10 and Other bHLH Homologues
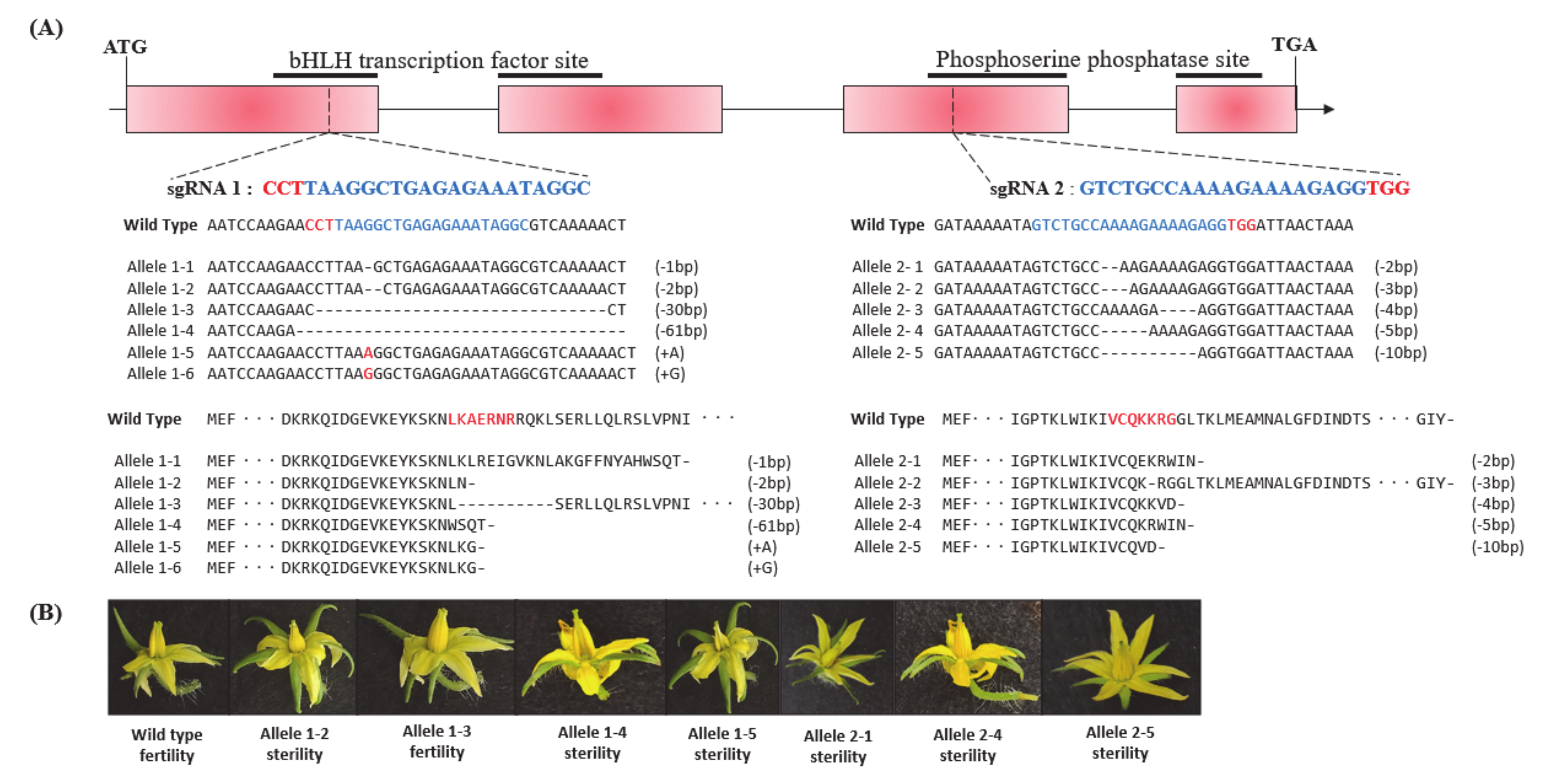
3.2. Generation of Male Sterility Lines by CRISPR/Cas9 System
3.3. Phenotypic Characterization of the cr-ms10-1-4 and cr-ms10-2-8 Mutant Lines
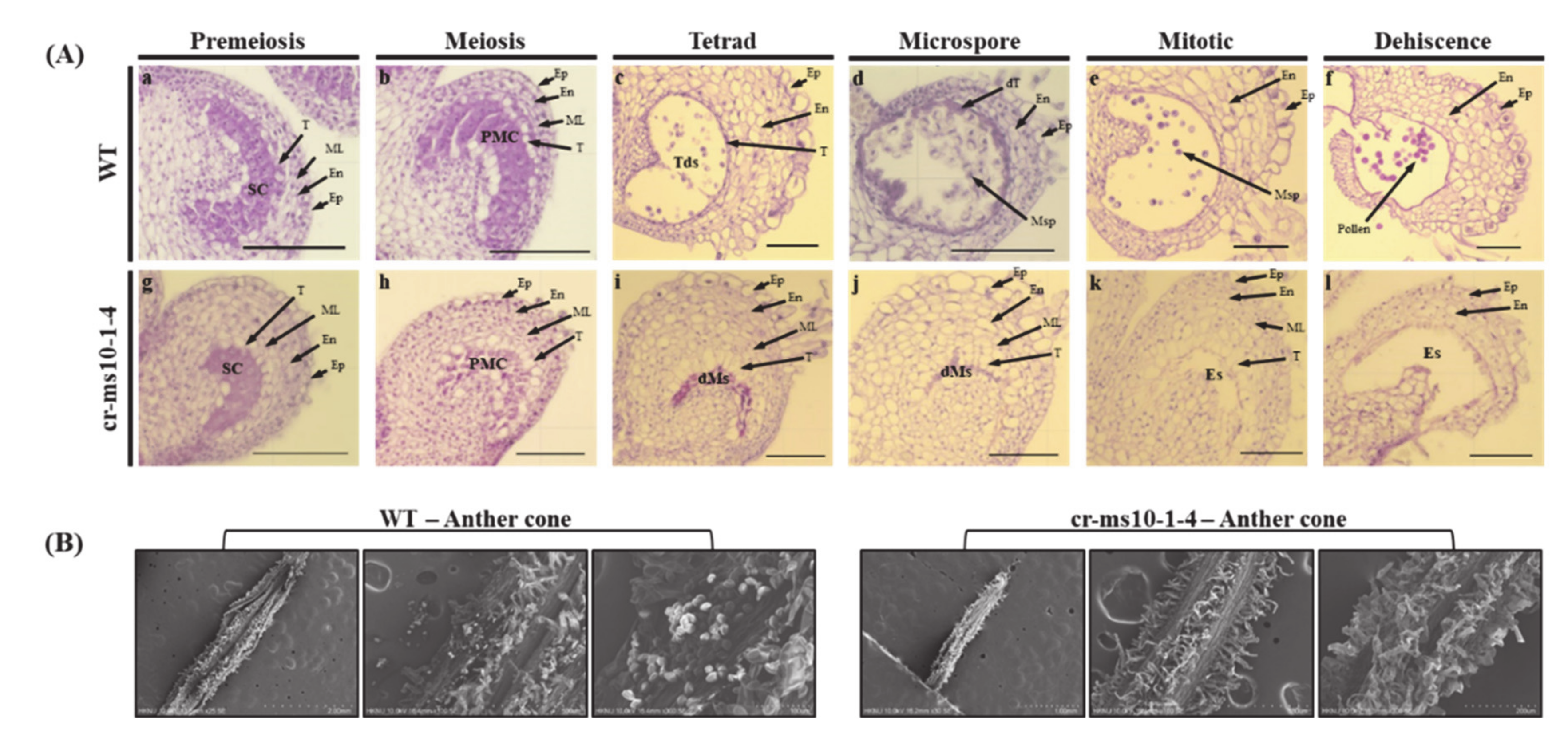
3.4. Histological Examination of Anthers to cr-ms10-1-4 Line
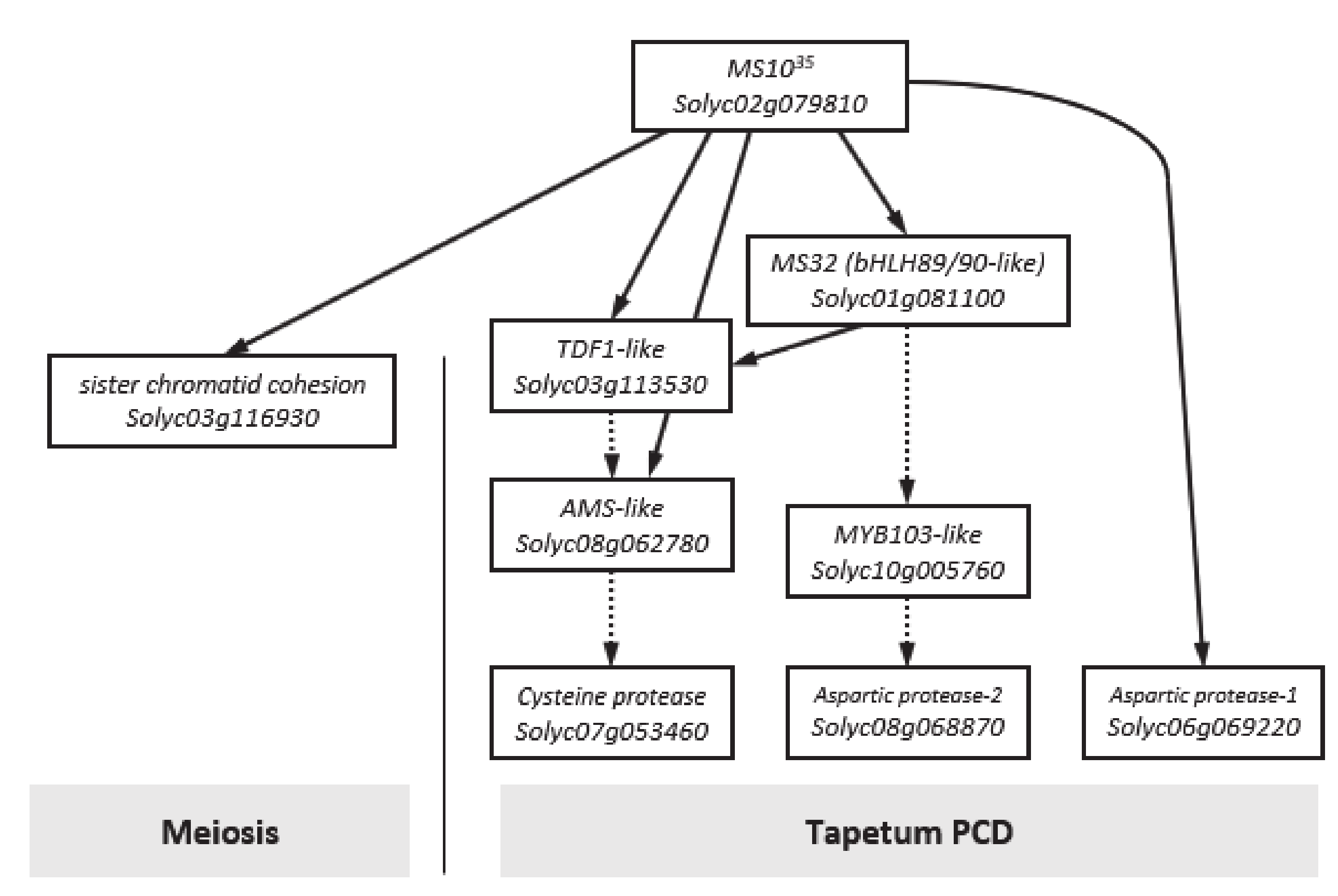
3.5. Expression Analysis of Genes Related Floral Development
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Foolad, M.R. Genome mapping and molecular breeding of tomato. Int. J. Plant Genom. 2007, 2007, 64358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.J.; Zhang, D. Molecular control of male fertility for crop hybrid breeding. Trends Plant Sci. 2018, 23, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaul, M.L.H. Male sterility in higher plants. In Male Sterility in Higher Plants; Springler: New York, NY, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Crane, M.B. Heredity of types of inflorescence and fruits in tomato. J. Genet. 1915, 5, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorman, S.W.; McCormick, S.; Rick, C. Male sterility in tomato. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 1997, 16, 31–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canales, C.; Bhatt, A.M.; Scott, R.; Dickinson, H. EXS, a putative LRR receptor kinase, regulates male germline cell number and tapetal identity and promotes seed development in Arabidopsis. Curr. Biol. 2002, 12, 1718–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.Z.; Wang, G.F.; Speal, B.; Ma, H. The EXCESS MICROSPOROCYTES1 gene encodes a putative leucine-rich repeat receptor protein kinase that controls somatic and reproductive cell fates in the Arabidopsis anther. Genes Dev. 2002, 16, 2021–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, S.L.; Xie, L.F.; Mao, H.Z.; San Puah, C.; Yang, W.C.; Jiang, L.; Ye, D. Tapetum determinant1 is required for cell specialization in the Arabidopsis anther. Plant Cell 2003, 15, 2792–2804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phan, H.A.; Iacuone, S.; Li, S.F.; Parish, R.W. The MYB80 transcription factor is required for pollen development and the regulation of tapetal programmed cell death in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 2011, 23, 2209–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sorensen, A.M.; Kröber, S.; Unte, U.S.; Huijser, P.; Dekker, K.; Saedler, H. The Arabidopsis ABORTED MICROSPORES (AMS) gene encodes a MYC class transcription factor. Plant J. 2003, 33, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Sun, Y.; Timofejeva, L.; Chen, C.; Grossniklaus, U.; Ma, H. Regulation of Arabidopsis tapetum development and function by DYSFUNCTIONAL TAPETUM1 (DYT1) encoding a putative bHLH transcription factor. Development 2006, 133, 3085–3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.B.; Zhu, J.; Gao, J.F.; Wang, C.; Li, H.; Li, H.; Huang, H. Transcription factor AtMYB103 is required for anther development by regulating tapetum development, callose dissolution and exine formation in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2007, 52, 528–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Chen, H.; Li, H.; Gao, J.F.; Jiang, H.; Wang, C.; Yang, Z.N. Defective in Tapetal development and function 1 is essential for anther development and tapetal function for microspore maturation in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2008, 55, 266–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, E.; You, C.; Wang, S.; Cui, J.; Niu, B.; Wang, Y.; Chang, F. The DYT 1-interacting proteins b HLH 010, b HLH 089 and b HLH 091 are redundantly required for A rabidopsis anther development and transcriptome. Plant J. 2015, 83, 976–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinet, M.; Bataille, G.; Dobrev, P.I.; Capel, C.; Gómez, P.; Capel, J.; Lozano, R. Transcriptional and hormonal regulation of petal and stamen development by STAMENLESS, the tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) orthologue to the B-class APETALA3 gene. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 2243–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Huang, Z.; Wang, X.; Gao, J.; Guo, Y.; Du, Y.; Hu, H. Fine mapping and molecular marker development of anthocyanin absent, a seedling morphological marker for the selection of male sterile 10 in tomato. Mol. Breed 2016, 36, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pucci, A.; Picarella, M.E.; Mazzucato, A. Phenotypic, genetic and molecular characterization of 7B-1, a conditional male-sterile mutant in tomato. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2017, 130, 2361–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Yang, M.; van Giang, T.; Wang, J.; Gao, J. B-class MADS-box TM6 is a candidate gene for tomato male sterile-1526. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2019, 132, 2125–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yang, M.; Liu, X.; Wei, K.; Cao, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, L. A putative bHLH transcription factor is a candidate gene for male sterile 32, a locus affecting pollen and tapetum development in tomato. Hort. Res. 2019, 6, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Hu, Z.; Zhao, T.; Yang, Y.; Chen, T.; Yang, M.; Zhang, B. Genome-wide analysis of bHLH transcription factor and involvement in the infection by yellow leaf curl virus in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum). BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Massari, M.E.; Murre, C. Helix-loop-helix proteins: Regulators of transcription in eucaryotic organisms. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000, 20, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, N.; Zhang, D.S.; Liu, H.S.; Yin, C.S.; Li, X.X.; Liang, W.Q.; Wen, T.Q. The rice tapetum degeneration retardation gene is required for tapetum degradation and anther development. Plant Cell 2006, 18, 2999–3014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Toledo-Ortiz, G.; Huq, E.; Quail, P.H. The Arabidopsis basic/helix-loop-helix transcription factor family. Plant Cell 2003, 15, 1749–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jeong, H.J.; Kang, J.H.; Zhao, M.; Kwon, J.K.; Choi, H.S.; Bae, J.H.; Kang, B.C. Tomato Male sterile 1035 is essential for pollen development and meiosis in anthers. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 6693–6709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Omidvar, V.; Mohorianu, I.; Dalmay, T.; Zheng, Y.; Fei, Z.; Pucci, A.; Fellner, M. Transcriptional regulation of male-sterility in 7B-1 male-sterile tomato mutant. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0170715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atanassova, B. Functional male sterility (ps-2) in tomato (Lycopesicon esculentum Mill.) and its application in breeding and hybrid seed production. Euphytica 1999, 107, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rick, C.M.; Robinson, J. Inherited defects of floral structure affecting fruitfulness in Lycopersicon esculentum. Am. J. Bot. 1951, 38, 639–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.; Zhou, K.; Liu, Y.; Deng, L.; Zhang, X.; Lin, L.; Li, C.B. A biotechnology-based male-sterility system for hybrid seed production in tomato. Plant J. 2020, 102, 1090–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, D.H.; Jung, Y.J.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, H.K.; Nam, K.H.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, M.K.; Nou, I.S.; Kang, K.K. Development of Male-Sterile Elite Lines using Marker-Assisted Backcrossing (MABC) in Tomato. Hortic. Sci. Technol. 2019, 37, 744–755. [Google Scholar]
- Hospital, F. Selection in backcross programmes. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2005, 360, 1503–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaj, T.; Gersbach, C.A.; Barbas, C.F., III. ZFN, TALEN, and CRISPR/Cas-based methods for genome engineering. Trends Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Demirci, Y.; Zhang, B.; Unver, T. CRISPR/Cas9: An RNA-guided highly precise synthetic tool for plant genome editing. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 1844–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, Y.J.; Lee, H.J.; Bae, S.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, H.K.; Kang, K.K. Acquisition of seed dormancy breaking in rice (Oryza sativa L.) via CRISPR/Cas9-targeted mutagenesis of OsVP1 gene. Plant Biotechnol. Rep. 2019, 13, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, H.J.; Abdula, S.E.; Jee, M.G.; Jang, D.W.; Cho, Y.G. High-efficiency and Rapid Agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation method using germinating rice seeds. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2011, 38, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.J.; Lee, G.J.; Bae, S.; Kang, K.K. Reduced ethylene production in tomato fruits upon CRISPR/Cas9-mediated LeMADS-RIN mutagenesis. Hortic. Sci. Technol. 2018, 36, 396–405. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.; Lim, K.; Kim, J.S.; Bae, S. Cas-analyzer: An online tool for assessing genome editing results using NGS data. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 286–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mazzucato, A.; Taddei, A.R.; Soressi, G.P. The parthenocarpic fruit (pat) mutant of tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill.) sets seedless fruits and has aberrant anther and ovule development. Development 1998, 125, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bae, S.; Park, J.; Kim, J.S. Cas-OFFinder: A fast and versatile algorithm that searches for potential off-target sites of Cas9 RNA-guided endonucleases. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1473–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, L.; Liu, Y.G. Male sterility and fertility restoration in crops. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2014, 65, 579–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atanassova, B.; Georgiev, H. Using genic male sterility in improving hybrid seed production in tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill.). Acta Horticulturae 2002, 579, 185–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawhney, V.K. Photoperiod-sensitive male-sterile mutant in tomato and its potential use in hybrid seed production. J. Hortic. Sci. Biotechnol. 2004, 79, 138–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheema, D.S.; Dhaliwal, M.S. Hybrid tomato breeding. J. New Seeds 2005, 6, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorguet, B.; Schipper, D.; van Lammeren, A.; Visser, R.G.; van Heusden, A.W. ps-2, the gene responsible for functional sterility in tomato, due to non-dehiscent anthers, is the result of a mutation in a novel polygalacturonase gene. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2009, 118, 1199–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mishra, R.; Joshi, R.K.; Zhao, K. Genome editing in rice: Recent advances, challenges, and future implications. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Yu, J.; Cheng, X.; Zong, X.; Xu, J.; Chen, M.; Liang, W. The rice basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor TDR INTERACTING PROTEIN2 is a central switch in early anther development. Plant Cell 2014, 26, 1512–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gómez, J.F.; Talle, B.; Wilson, Z.A. Anther and pollen development: A conserved developmental pathway. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2015, 57, 876–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jung, Y.J.; Kim, D.H.; Lee, H.J.; Nam, K.H.; Bae, S.; Nou, I.S.; Cho, Y.-G.; Kim, M.K.; Kang, K.K. Knockout of SlMS10 Gene (Solyc02g079810) Encoding bHLH Transcription Factor Using CRISPR/Cas9 System Confers Male Sterility Phenotype in Tomato. Plants 2020, 9, 1189. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9091189
Jung YJ, Kim DH, Lee HJ, Nam KH, Bae S, Nou IS, Cho Y-G, Kim MK, Kang KK. Knockout of SlMS10 Gene (Solyc02g079810) Encoding bHLH Transcription Factor Using CRISPR/Cas9 System Confers Male Sterility Phenotype in Tomato. Plants. 2020; 9(9):1189. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9091189
Chicago/Turabian StyleJung, Yu Jin, Dong Hyun Kim, Hyo Ju Lee, Ki Hong Nam, Sangsu Bae, Ill Sup Nou, Yong-Gu Cho, Myong Kwon Kim, and Kwon Kyoo Kang. 2020. "Knockout of SlMS10 Gene (Solyc02g079810) Encoding bHLH Transcription Factor Using CRISPR/Cas9 System Confers Male Sterility Phenotype in Tomato" Plants 9, no. 9: 1189. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9091189
APA StyleJung, Y. J., Kim, D. H., Lee, H. J., Nam, K. H., Bae, S., Nou, I. S., Cho, Y.-G., Kim, M. K., & Kang, K. K. (2020). Knockout of SlMS10 Gene (Solyc02g079810) Encoding bHLH Transcription Factor Using CRISPR/Cas9 System Confers Male Sterility Phenotype in Tomato. Plants, 9(9), 1189. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9091189







