Enhanced Resistance to Leaf Fall Disease Caused by Phytophthora palmivora in Rubber Tree Seedling by Sargassum polycystum Extract
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
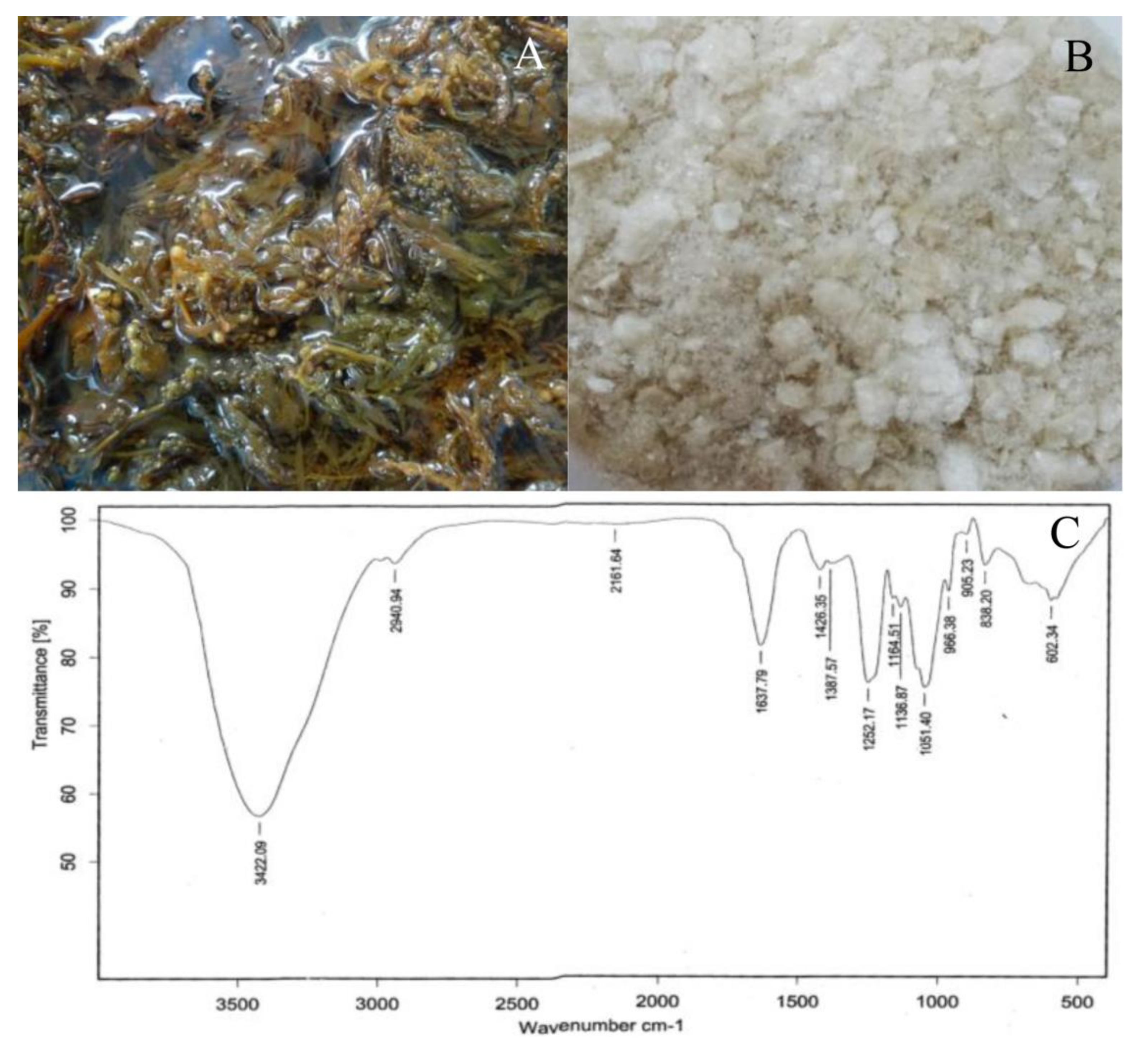
2.1. Seaweed Extract and Chemical Composition
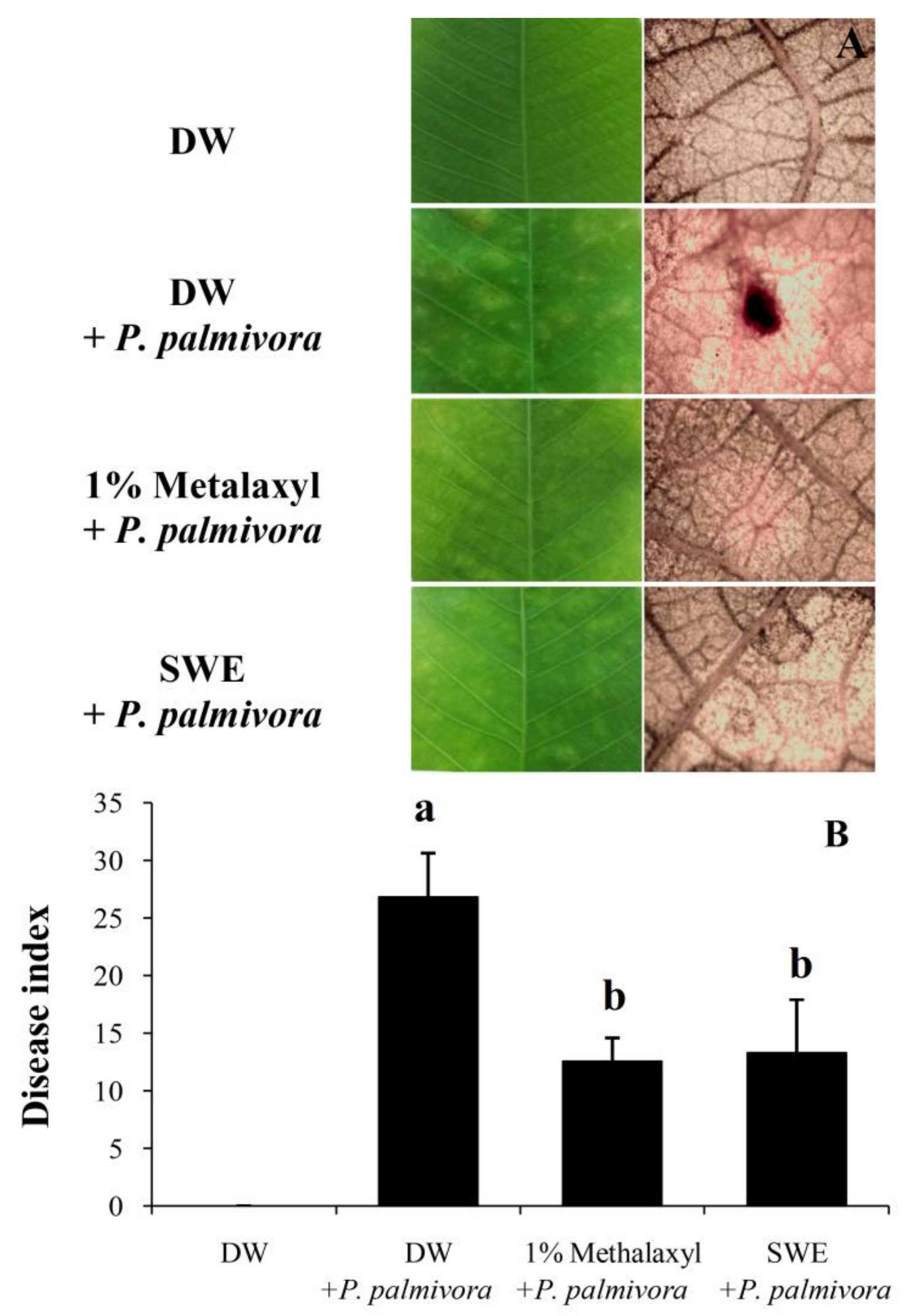
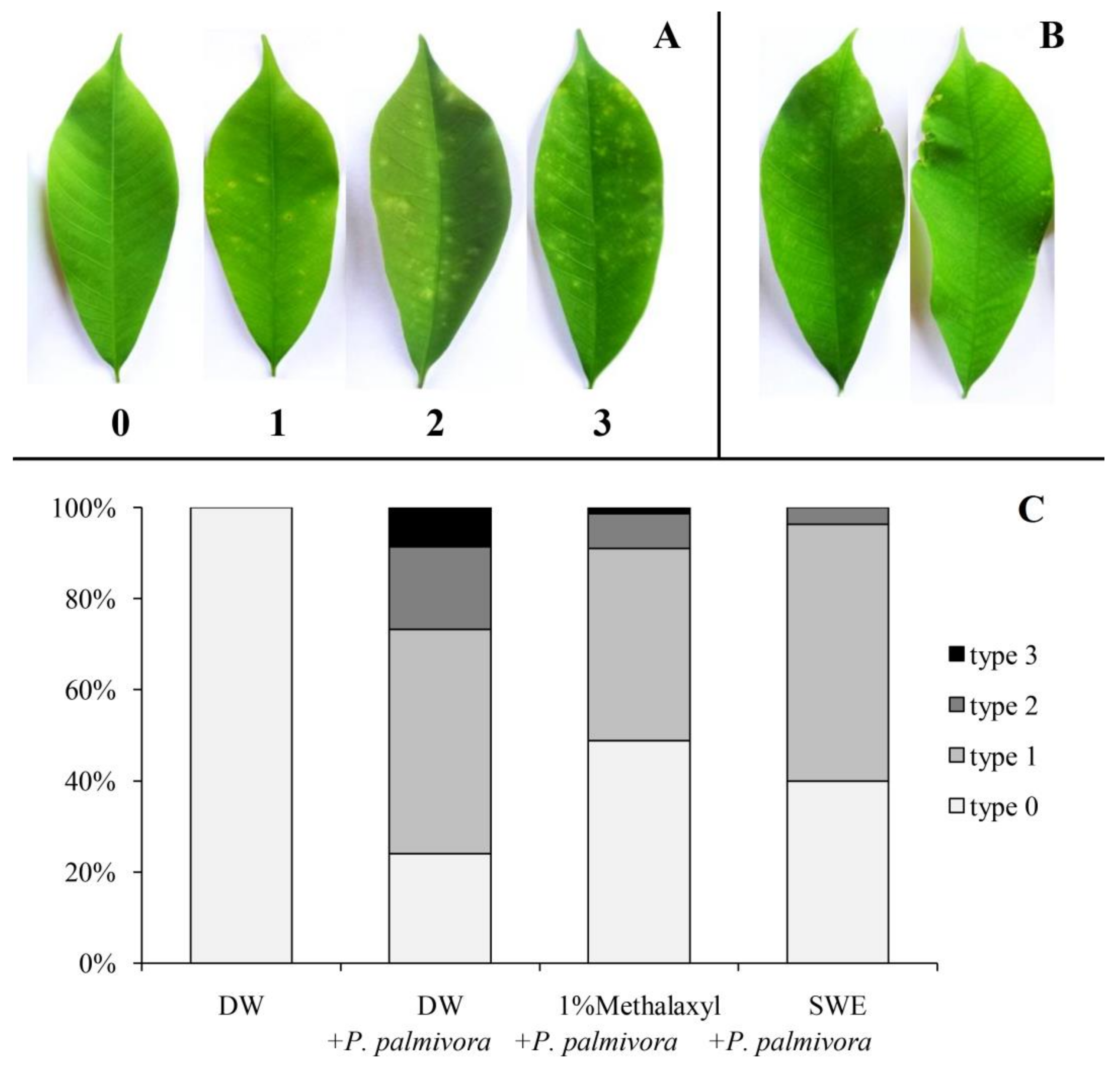
2.2. Applications of SWE against P. palmivora Infection on Rubber Tree Seedlings
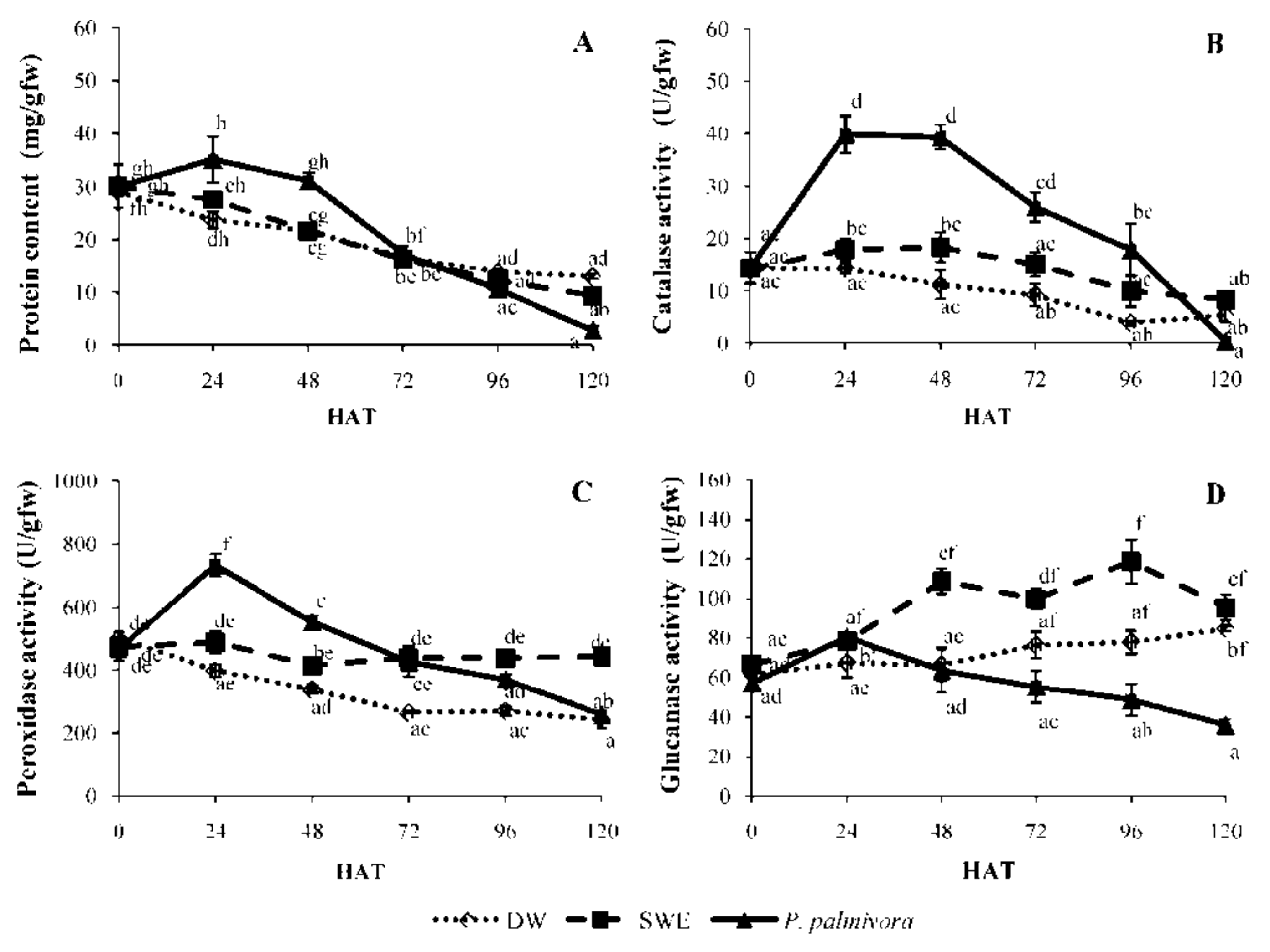
2.3. Induction of Defense-Related Enzyme Activity by SWE Comparing to P. palmivora
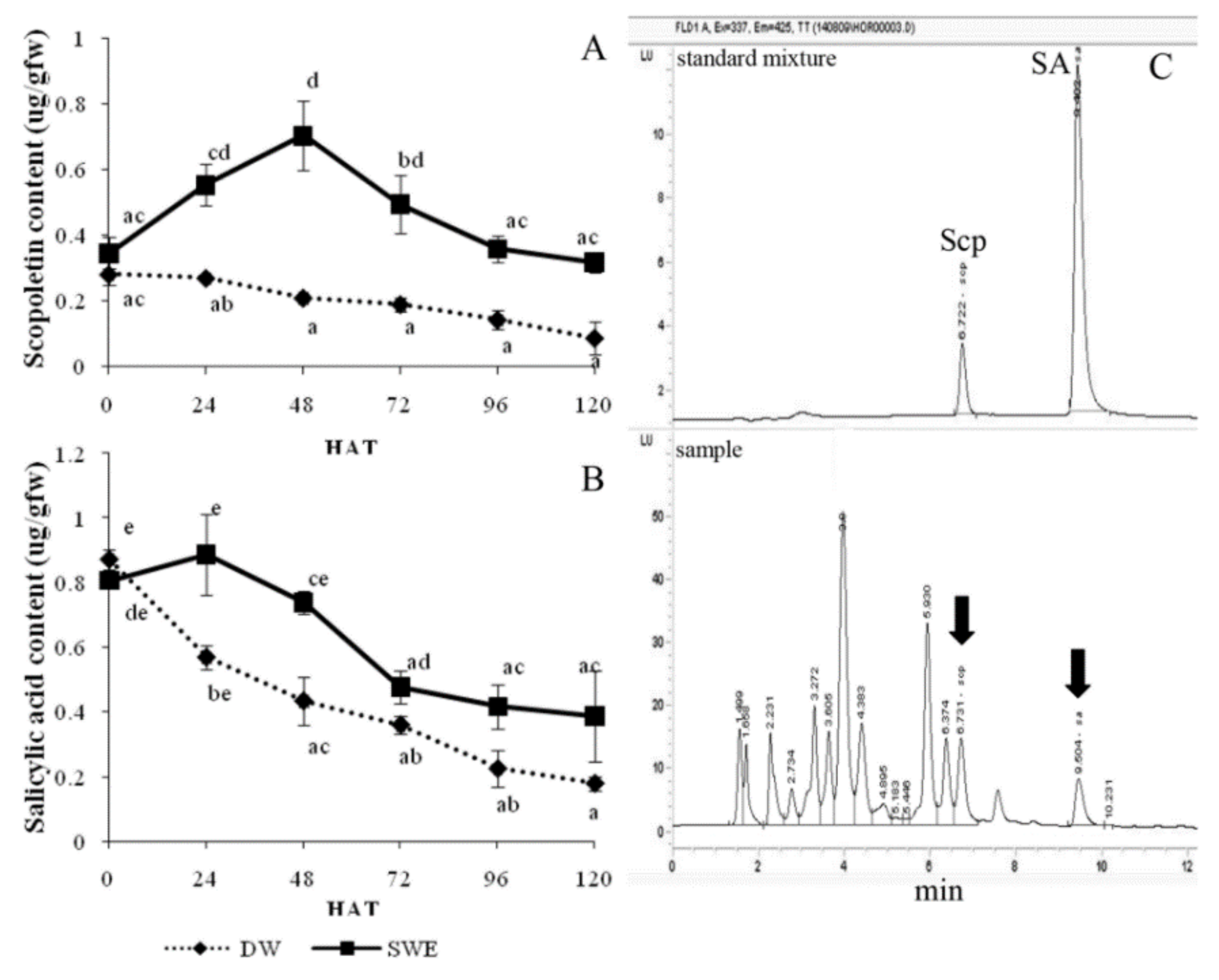
2.4. Enhancement of the Secondary Metabolite Accumulation by SWE
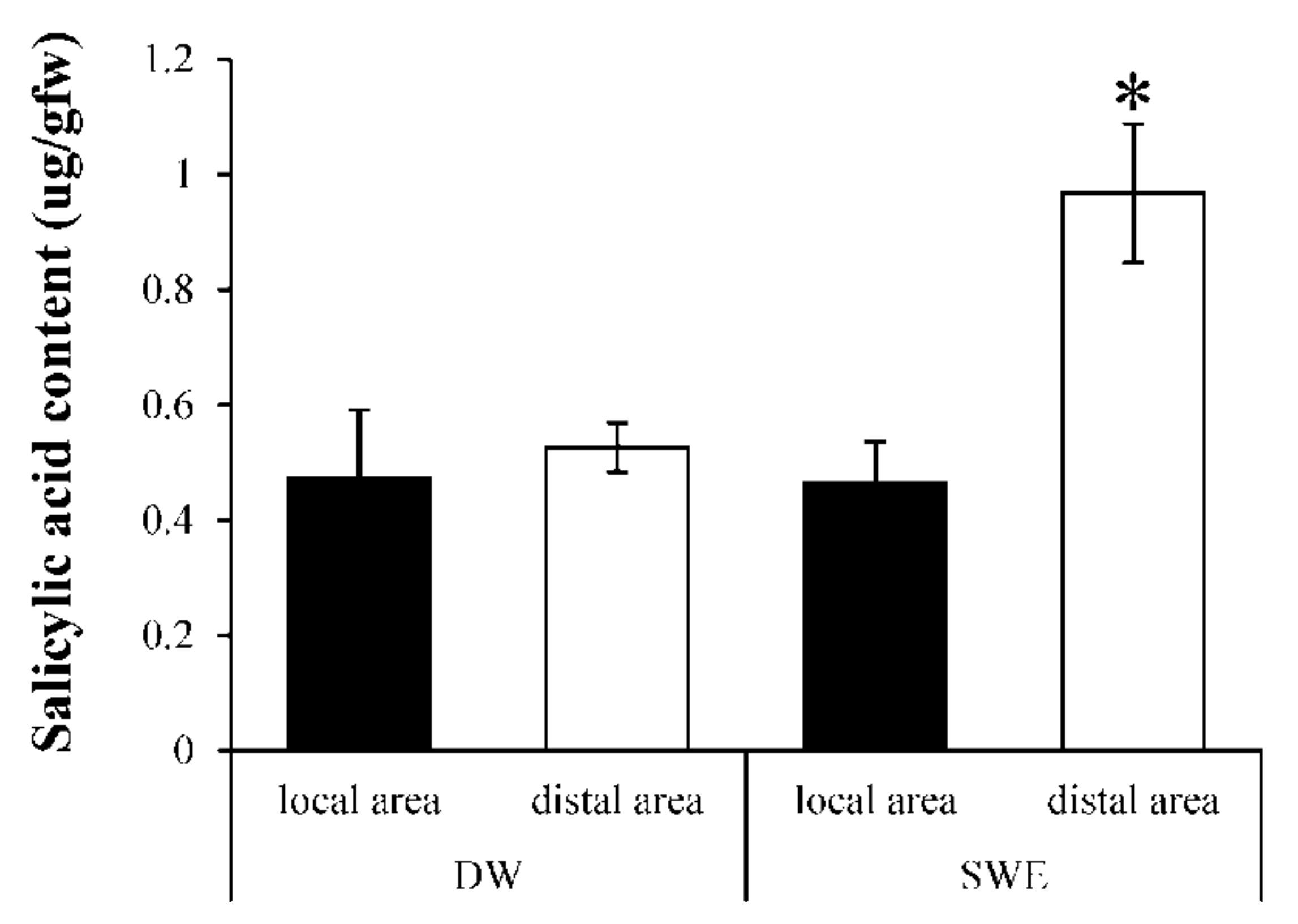
2.5. Induction of Systemic Acquired Resistant (SAR) by SWE
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Seaweed Extraction
4.2. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Analysis
4.3. Chemical Composition Determination
4.4. Biological Property Determination
4.4.1. Pathogen and Zoospore Preparation
4.4.2. Plant Treatment
4.4.3. Extraction of Defense-Related Enzyme Activity
4.4.4. Protein Content
4.4.5. Enzyme Assays
4.4.6. Scopoletin (Scp) and Salicylic Acid (SA) Contents in Leaves
4.5. Applications of SWE against P. palmivora Infection on Rubber Tree Seedlings
4.6. Lignin Staining
4.7. Statistics
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pitaloka, M.K.; Petcharat, V.; Arikit, S.; Sunpapao, A. Cephaleuros virescens, the cause of an algal leaf spot on Para rubber in Thailand. Australas. Plant Dis. Notes 2015, 10, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sdoodee, R. Phytophthora diseases of rubber. In Diversity and management of Phytophthora in Southeast Asia; Drenth, A., Guest, D.I., Eds.; ACIAR Monograph 114; ACIAR: Canberra, Australia, 2004; pp. 136–142. [Google Scholar]
- Drenth, A.; Sendal, B. Economic Impact of Phytophthora Diseases in Southeast Asia. In Diversity and Management of Phytophthora in Southeast Asia; ACIAR Monograph 114; Australian Centre for International Agricultural Research: Canberra, Australia, 2004; pp. 10–28. [Google Scholar]
- Van Loon, L.C.; Bakker, P.A.H.M.; Pieterse, C.M.J. Systemic resistance induced by rhizosphere bacteria. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 1998, 36, 453–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pieterse, C.M.J.; van Wees, S.C.M.; Hoffland, E.; van Pelt, J.A.; van Loon, L.C. Systemic Resistance in Arabidopsis Induced by Biocontrol Bacteria Is Independent of Salicylic Acid Accumulation and Pathogenesis-Related Gene Expression. Plant Cell 1996, 8, 1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pieterse, C.M.; van Wees, S.C.; van Pelt, J.A.; Knoester, M.; Laan, R.; Gerrits, H.; Weisbeek, P.J.; van Loon, L.C. A novel signaling pathway controlling induced systemic resistance in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 1998, 10, 1571–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durrant, W.E.; Dong, X. Systemic acquired resistance. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2004, 42, 185–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tucci, M.; Ruocco, M.; De Masi, L.; De Palma, M.; Lorito, M. The beneficial effect of Trichoderma spp. on tomato is modulated by the plant genotype. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2011, 12, 341–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunpapao, A.; Pornsuriya, C. Effects of chitosan treatments on para rubber leaf fall disease caused by Phytophthora palmivora Butler—A laboratory study. Songklanakarin J. Sci. Technol. 2014, 36, 507–512. [Google Scholar]
- Komárek, M.; Čadková, E.; Chrastný, V.; Bordas, F.; Bollinger, J.C. Contamination of vineyard soils with fungicides: A review of environmental and toxicological aspects. Environ. Int. 2010, 36, 138–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Davis, L.C.; Verpoorte, R. Elicitor signal transduction leading to production of plant secondary metabolites. Biotechnol. Adv. 2005, 23, 283–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derksen, H.; Rampitsch, C.; Daayf, F. Signaling cross-talk in plant disease resistance. Plant Sci. 2013, 207, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willekens, H.; Inzé, D.; Van Montagu, M.; van Camp, W. Catalases in plants. Mol. Breed. New Strateg. Plant Improv. 1995, 1, 207–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiraga, S.; Katsutomo, S.; Ito, H.; Yuko, O.; Hirokazu, M. A Large Family of Class III Plant Peroxidases. Plant Cell Physiol. 2001, 42, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vera, J.; Castro, J.; Gonzalez, A.; Moenne, A. Seaweed polysaccharides and derived oligosaccharides stimulate defense responses and protection against pathogens in plants. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 2514–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettongkhao, S.; Bilanglod, A.; Khompatara, K.; Churngchow, N. Sulphated Polysaccharide from Acanthophora spicifera Induced Hevea brasiliensis Defense Responses Against Phytophthora palmivora Infection. Plants 2019, 8, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dore, C.M.P.G.; Faustino Alves, M.G.D.C.; Pofírio Will, L.S.E.; Costa, T.G.; Sabry, D.A.; De Souza Rêgo, L.A.R.; Accardo, C.M.; Rocha, H.A.O.; Filgueira, L.G.A.; Leite, E.L. A sulfated polysaccharide, fucans, isolated from brown algae Sargassum vulgare with anticoagulant, antithrombotic, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 91, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugiono, W.S.; Adisoehono, L. Extraction optimization by response surface methodology and characterization of Fucoidan from brown seaweed Sargassum polycystum. Int. J. ChemTech Res. 2014, 6, 195–205. [Google Scholar]
- Walters, D.R.; Ratsep, J.; Havis, N.D. Controlling crop diseases using induced resistance: Challenges for the future. J. Exp. Bot. 2013, 64, 1263–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sbaihat, L.; Takeyama, K.; Koga, T.; Takemoto, D.; Kawakita, K. Induced resistance in Solanum lycopersicum by algal elicitor extracted from Sargassum fusiforme. Sci. World J. 2015, 2015, 870520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saboural, P.; Chaubet, F.; Rouzet, F.; Al-Shoukr, F.; Azzouna, R.B.; Bouchemal, N.; Picton, L.; Louedec, L.; Maire, M.; Rolland, L.; et al. Purification of a low molecular weight fucoidan for SPECT molecular imaging of myocardial infarction. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 4851–4867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ale, M.T.; Maruyama, H.; Tamauchi, H.; Mikkelsen, J.D.; Meyer, A.S. Fucose-containing sulfated polysaccharides from brown seaweeds inhibit proliferation of melanoma cells and induce apoptosis by activation of caspase-3 in vitro. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 2605–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Xie, E.; Zheng, K.; Fredimoses, M.; Yang, X.; Zhou, X.; Wang, Y.; Yang, B.; Lin, X.; Liu, J.; et al. Nutritional and chemical composition and antiviral activity of cultivated seaweed Sargassum naozhouense Tseng et Lu. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kannan, S. FTIR and EDS analysis of the seaweeds Sargassum wightii (brown algae) and Gracilaria corticata (red algae). Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2014, 3, 341–351. [Google Scholar]
- El Modafar, C.; Elgadda, M.; El Boutachfaiti, R.; Abouraicha, E.; Zehhar, N.; Petit, E.; El Alaoui-Talibi, Z.; Courtois, B.; Courtois, J. Induction of natural defence accompanied by salicylic acid-dependant systemic acquired resistance in tomato seedlings in response to bioelicitors isolated from green algae. Sci. Hortic. 2012, 138, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heil, M.; Bostock, R.M. Induced systemic resistance (ISR) against pathogens in the context of induced plant defences. Ann. Bot. 2002, 89, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minibayeva, F.; Beckett, R.P.; Kranner, I. Roles of apoplastic peroxidases in plant response to wounding. Phytochemistry 2015, 112, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almagro, L.; Gómez Ros, L.V.; Belchi-Navarro, S.; Bru, R.; Ros Barceló, A.; Pedreño, M.A. Class III peroxidases in plant defence reactions. J. Exp. Bot. 2009, 60, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Shi, X.; Li, B.; Zhang, Q.; Liang, W.; Wang, C. Salicylic acid confers enhanced resistance to Glomerella leaf spot in apple. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 106, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.; Ramkissoon, A.; Ramsubhag, A.; Jayaraj, J. Ascophyllum extract application causes reduction of disease levels in field tomatoes grown in a tropical environment. Crop Prot. 2016, 83, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanseem, I.; Joseph, A.; Thulaseedharan, A. Induction and differential expression of β-1,3-glucanase mRNAs in tolerant and susceptible Hevea clones in response to infection by Phytophthora meadii. Tree Physiol. 2005, 25, 1361–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraris, L.; Gentile, I.A.; Matta, A. Activation of Glycosidases as a Consequence of Infection Stress in Fusarium Wilt of Tomato. J. Phytopathol. 1987, 118, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeandet, P.; Hébrard, C.; Deville, M.A.; Cordelier, S.; Dorey, S.; Aziz, A.; Crouzet, J. Deciphering the role of phytoalexins in plant-microorganism interactions and human health. Molecules 2014, 19, 18033–18056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Churngchow, N.; Rattarasarn, M. Biosynthesis of scopoletin in Hevea brasiliensis leaves inoculated with Phytophthora palmivora. J. Plant Physiol. 2001, 158, 875–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutsadee, C.; Nunta, C. Induction of peroxidase, scopoletin, phenolic compounds and resistance in Hevea brasiliensis by elicitin and a novel protein elicitor purified from Phytophthora palmivora. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2008, 72, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryals, J.A.; Neuenschwander, U.H.; Willits, M.G.; Molina, A.; Steiner, H.-Y.; Hunt, M. Systemic Acquired Resistance. Plant Cell 1996, 8, 1809–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klarzynski, O.; Descamps, V.; Plesse, B.; Yvin, J.-C.; Kloareg, B.; Fritig, B. Sulfated Fucan Oligosaccharides Elicit Defense Responses in Tobacco and Local and Systemic Resistance against Tobacco Mosaic Virus. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2003, 16, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rioux, L.E.; Turgeon, S.L.; Beaulieu, M. Effect of season on the composition of bioactive polysaccharides from the brown seaweed Saccharina longicruris. Phytochemistry 2009, 70, 1069–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubois, M.; Gilles, K.A.; Hamilton, J.K.; Rebers, P.A.; Smith, F. Colorimetric Method for Determination of Sugars and Related Substances. Anal. Chem. 1956, 28, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dische, Z.; Shettles, L.B. A specific color reaction of methylpentoses and a spectrophotometric micromethod for their determination. J. Biol. Chem. 1948, 175, 595–603. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dodgson, K.; Price, R. A note on the determination of the ester sulphate content of sulphated polysaccharides. Biochem. J. 2015, 84, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bitter, T.; Muir, H.M. A modified uronic acid carbazole reaction. Anal. Biochem. 1962, 4, 330–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, A.M.; Mau-Lastovicka, T.; Rezaaiyan, R. Total Phenolics and High-Performance Liquid Chromatography of Phenolic Acids of Avocado. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1987, 35, 921–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanwun, T.; Muhamad, N.; Chirapongsatonkul, N.; Churngchow, N. Hevea brasiliensis cell suspension peroxidase: Purification, characterization and application for dye decolorization. AMB Express 2013, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, T.; Frenkel, C. Involvement of Hydrogen Peroxide in the Regulation of Senescence in Pear. Plant Physiol. 2008, 59, 411–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shannon, L.M.; Kay, E.; Lew, J.Y. Peroxidase isozymes from horseradish roots. I. Isolation and physical properties. J. Biol. Chem. 1966, 241, 2166–2172. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Santos, T.; Villanueva, J.R.; Nombela, C. Production and catabolite repression of Penicillium italicum beta-glucanases. J. Bacteriol. 1977, 129, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ederli, L.; Madeo, L.; Calderini, O.; Gehring, C.; Moretti, C.; Buonaurio, R.; Paolocci, F.; Pasqualini, S. The Arabidopsis thaliana cysteine-rich receptor-like kinase CRK20 modulates host responses to Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000 infection. J. Plant Physiol. 2011, 168, 1784–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parry, D. Plant Pathology in Agriculture; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Gurav, S.; Gurav, N. Herbal Drug Microscopy. In Indian Herbal Drug Microscopy; Springer-Verlag: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 15–196. [Google Scholar]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khompatara, K.; Pettongkhao, S.; Kuyyogsuy, A.; Deenamo, N.; Churngchow, N. Enhanced Resistance to Leaf Fall Disease Caused by Phytophthora palmivora in Rubber Tree Seedling by Sargassum polycystum Extract. Plants 2019, 8, 168. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants8060168
Khompatara K, Pettongkhao S, Kuyyogsuy A, Deenamo N, Churngchow N. Enhanced Resistance to Leaf Fall Disease Caused by Phytophthora palmivora in Rubber Tree Seedling by Sargassum polycystum Extract. Plants. 2019; 8(6):168. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants8060168
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhompatara, Khemmikar, Sittiporn Pettongkhao, Arnannit Kuyyogsuy, Nuramalee Deenamo, and Nunta Churngchow. 2019. "Enhanced Resistance to Leaf Fall Disease Caused by Phytophthora palmivora in Rubber Tree Seedling by Sargassum polycystum Extract" Plants 8, no. 6: 168. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants8060168
APA StyleKhompatara, K., Pettongkhao, S., Kuyyogsuy, A., Deenamo, N., & Churngchow, N. (2019). Enhanced Resistance to Leaf Fall Disease Caused by Phytophthora palmivora in Rubber Tree Seedling by Sargassum polycystum Extract. Plants, 8(6), 168. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants8060168



