Exogenous Melatonin Enhances Salt-Stress Tolerance in Festuca elata via Growth and Physiological Improvements
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effects of Exogenous MT on Leaf Area and Plant Height of Festuca elata Under Salt Stress
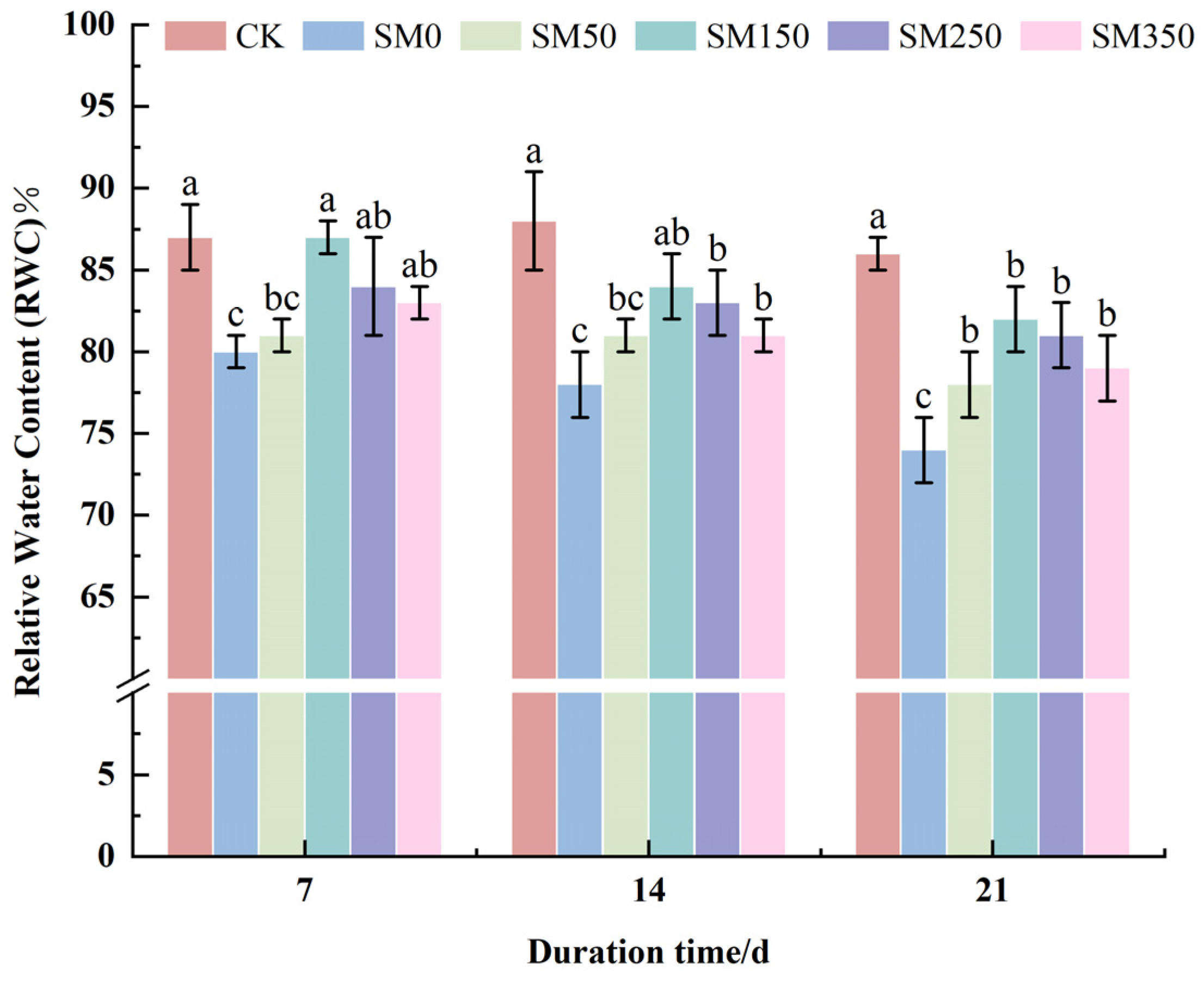
2.2. Effect of Exogenous MT on RWC of Festuca elata Under Salt Stress
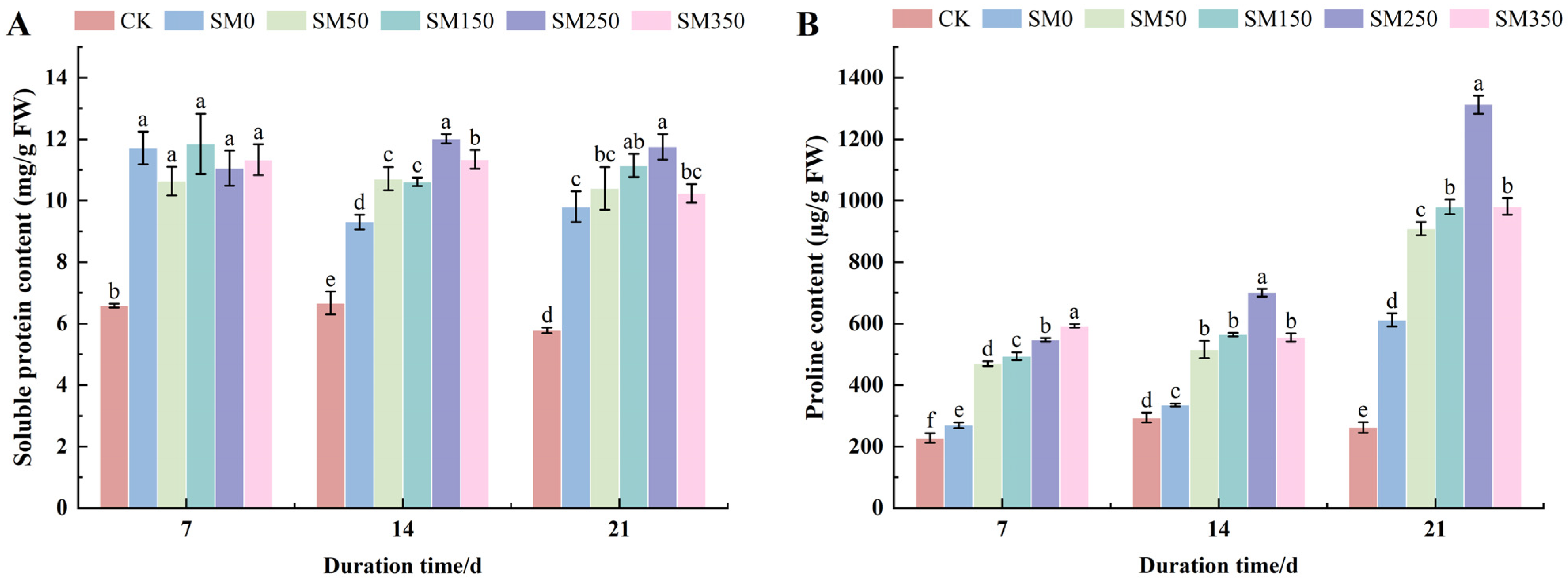
2.3. Effects of Exogenous MT on the Content of Osmoregulatory Substances in Festuca elata Under Salt Stress
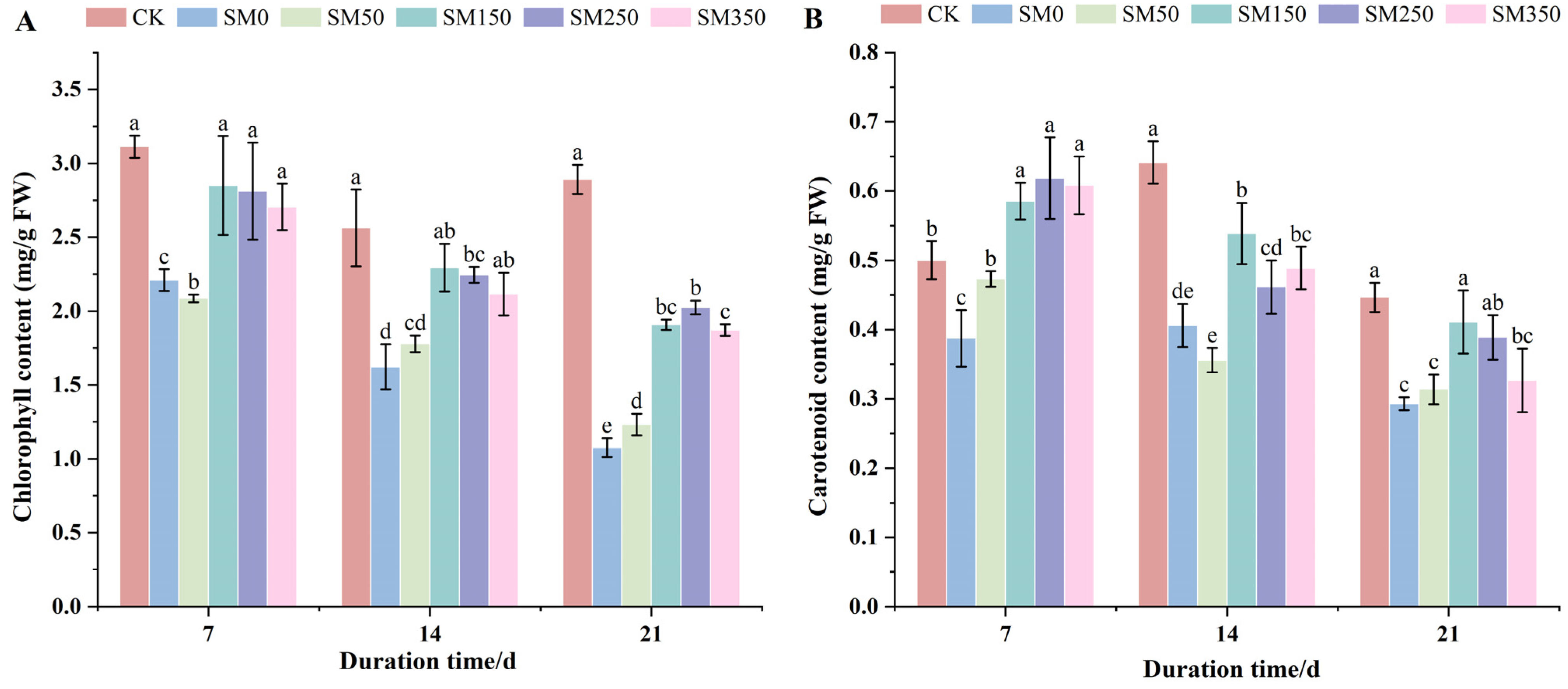
2.4. Effects of Exogenous MT on Photosynthetic Pigment Content of Festuca elata Under Salt Stress
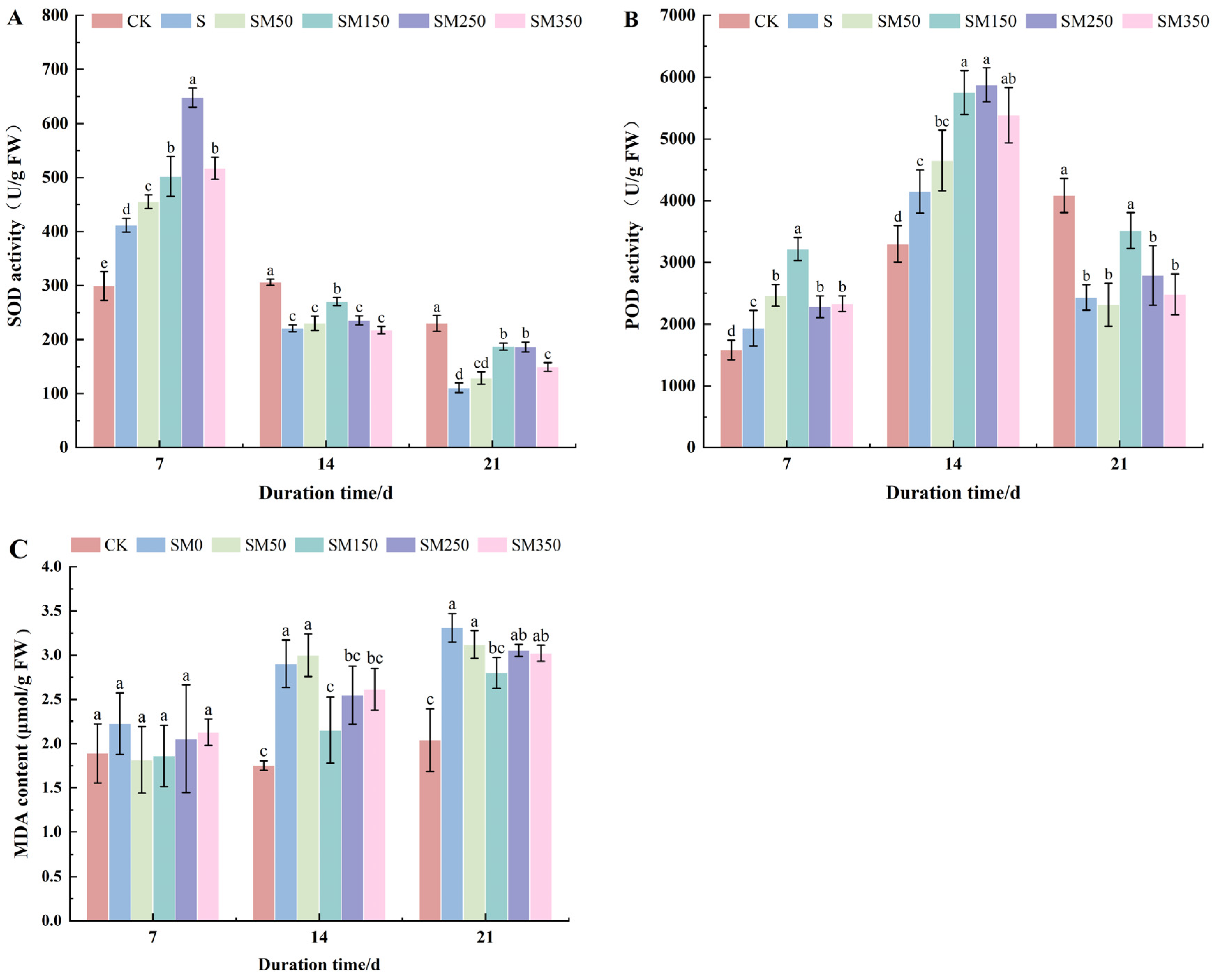
2.5. Effects of Exogenous MT on Antioxidant Enzyme Activities and MDA Content in Festuca elata Under Salt Stress
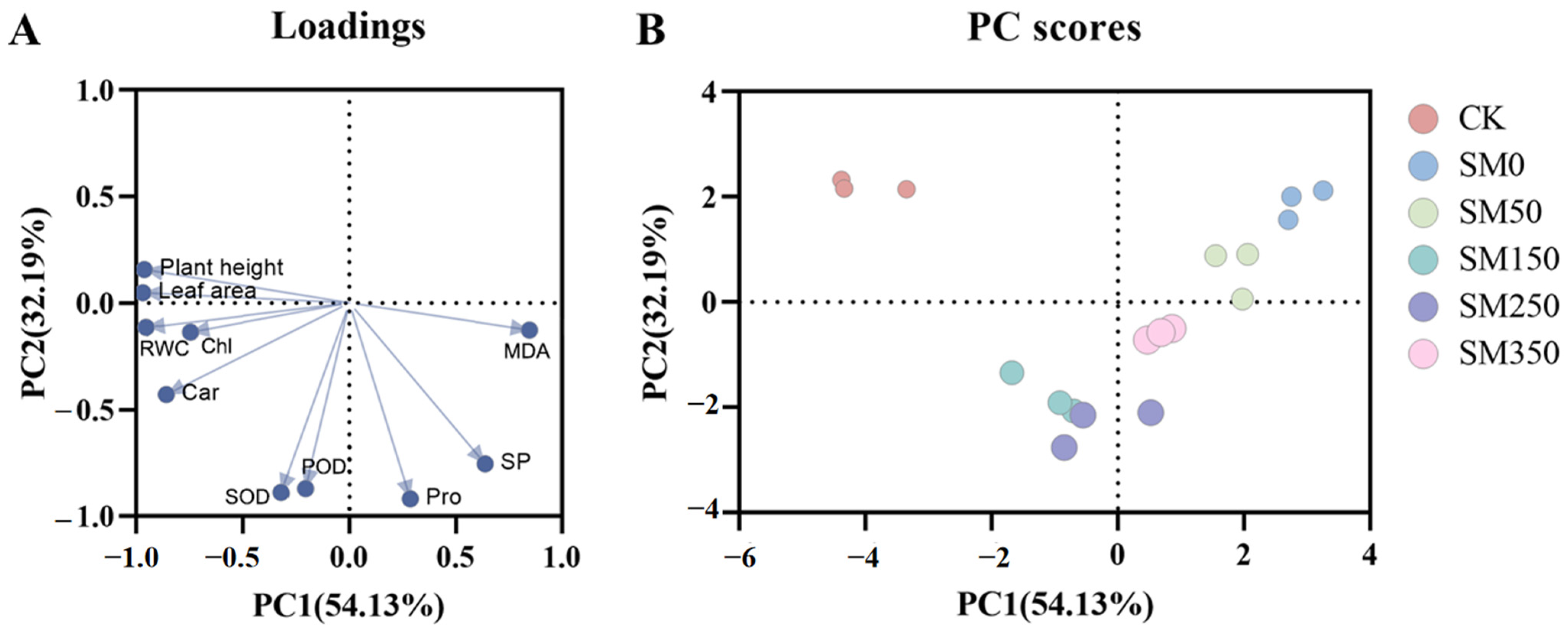
2.6. Principal Component Analysis of Exogenous MT on Festuca elata Under Salt Stress
2.7. Correlation Analysis of Exogenous MT on Festuca elata Under Salt Stress
2.8. Comprehensive Evaluation of Membership Functions of Different Concentrations of MT in Alleviating Salt Stress of Festuca elata
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Area
4.2. Plant Materials
4.3. Experimental Design
4.4. Determination Methods of Plant Growth and Physiological Indicators
4.4.1. Leaf Area and Plant Height
4.4.2. Relative Water Content
4.4.3. Photosynthetic Pigment Content
4.4.4. SP Content and Pro Content
4.4.5. Superoxide Dismutase Activity, Peroxidase Activity, and Malondialdehyde Content
4.5. Data Analysis
4.5.1. Comprehensive Evaluation by Membership Function Method
4.5.2. Data Statistics and Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, C.; Zhang, H.; Song, C.; Zhu, J.K.; Shabala, S. Mechanisms of Plant Responses and Adaptation to Soil Salinity. Innovation 2020, 1, 100017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nachshon, U. Cropland Soil Salinization and Associated Hydrology: Trends, Processes and Examples. Water 2018, 10, 1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopmans, J.; Qureshi, A.; Kisekka, I.; Munns, R.; Taleisnik, E. Critical knowledge gaps and research priorities in global soil salinity. Adv. Agron. 2021, 169, 1–191. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Jiang, P.; Ma, Y.; Geng, S.; Wang, S.; Shi, D. Physiological strategies of sunflower exposed to salt or alkali stresses: Restriction of ion transport in the cotyledon node zone and solute accumulation. Agron. J. 2015, 107, 2181–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, B.; Li, X.; VandenLangenberg, K.M.; Wen, D.; Sun, S.; Wei, M.; Li, Y.; Yang, F.; Shi, Q.; Wang, X. Overexpression of S-adenosyl-L-methionine synthetase increased tomato tolerance to alkali stress through polyamine metabolism. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2016, 12, 694–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manasa, M.; Katukuri, N.; Darveekaran Nair, S.; Haojie, Y.; Yang, Z.; Guo, R. Role of biochar and organic substrates in enhancing the functional characteristics and microbial community in a saline soil. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 269, 110737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A. Soil salinity: A global threat to sustainable development. Soil Use Manag. 2022, 38, 39–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Todd, J.L.; Luo, H. Turfgrass Salinity Stress and Tolerance-A Review. Plants 2023, 12, 925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J. Abiotic Stress Signaling and Responses in Plants. Cell 2016, 167, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelm, E.; Zhang, Y.; Testerink, C. Salt Tolerance Mechanisms of Plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2020, 71, 403–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Luo, X.; Wang, Z.; Liu, J. Mitigating Effect of Exogenous Melatonin on Salt and Drought Stress in Cyperus esculentus L. during the Tillering Stage. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Gan, L.; Wang, C.; He, T. Salt-tolerant plant growth-promoting bacteria as a versatile tool for combating salt stress in crop plants. Arch. Microbiol. 2024, 206, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, M.; Havshøi, N.; Huang, X.; Shabala, L.; Yu, M.; Fuglsang, A.; Shabala, S. Understanding the mechanistic basis of ameliorative effects of boron on salinity in barley (Hordeum vulgare). Environ. Exp. Bot. 2024, 220, 105690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Li, G.; Yang, J.; Huang, X.; Ji, Q.; Liu, Z.; Ke, W.; Hou, H. Effect of Salt Stress on Growth, Physiological Parameters, and Ionic Concentration of Water Dropwort (Oenanthe javanica) Cultivars. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 660409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tenikecier, H.; Ateş, E. Impact of Salinity on Germination and Seedling Growth of Four Cool-Season Turfgrass Species and Cultivars. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2022, 31, 1813–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jameel, J.; Anwar, T.; Siddiqi, E.H.; Alomrani, S.O. Alleviation of NaCl stress in tomato varieties by promoting morpho-physiological attributes and biochemical characters. Sci. Hortic. 2024, 323, 112496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, Q.; Gao, Y.; Liu, X. Review on the mechanisms of the response to salinity-alkalinity stress in plants. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2017, 37, 5565–5577. [Google Scholar]
- Chourasia, K.; Lal, M.; Tiwari, R.; Dev, D.; Kardile, H.; Patil, V.; Kumar, A.; Vanishree, G.; Kumar, D.; Bhardwaj, V.; et al. Salinity Stress in Potato: Understanding Physiological, Biochemical and Molecular Responses. Life 2021, 11, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, J.; Xu, H.; Zhang, D.X.; Feng, S. Chelation and nanoparticle delivery of monomeric dopamine to increase plant salt stress resistance. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 4157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinnusamy, V.; Zhu, J.; Zhu, J.K. Salt stress signaling and mechanisms of plant salt tolerance. Genet. Eng. 2006, 27, 141–177. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Shi, H.; Yang, Y.; Feng, X.; Chen, X.; Fei, X.; Lin, H.; Guo, Y. Insights into plant salt stress signaling and tolerance. J. Genet. Genom. 2023, 51, 16–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, M.; Khan, M.N.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Zhu, G. Alleviating sweetpotato salt tolerance through exogenous glutathione and melatonin: A profound mechanism for active oxygen detoxification and preservation of photosynthetic organs. Chemosphere 2024, 350, 141120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, F.; He, Q.; Chen, J.; Zhao, T. Seed priming with melatonin improves salt tolerance in cotton through regulating photosynthesis, scavenging reactive oxygen species and coordinating with phytohormone signal pathways. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 169, 113671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnao, M.B.; Hernández-Ruiz, J. Melatonin: Plant growth regulator and/or biostimulator during stress? Trends Plant Sci. 2014, 19, 789–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahedi, S.M.; Hosseini, M.S.; Fahadi Hoveizeh, N.; Gholami, R.; Abdelrahman, M.; Tran, L.P. Exogenous melatonin mitigates salinity-induced damage in olive seedlings by modulating ion homeostasis, antioxidant defense, and phytohormone balance. Physiol. Plant 2021, 173, 1682–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Wang, T.; Wang, J.; Yan, D.; Lian, Y.; Lu, Z.; Hong, Y.; Yuan, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, R. The Physiological Mechanism of Exogenous Melatonin on Improving Seed Germination and the Seedling Growth of Red Clover (Trifolium pretense L.) under Salt Stress. Plants 2024, 13, 2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yan, D.; Liu, R.; Wang, T.; Lian, Y.; Lu, Z.; Hong, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, R. The Physiological and Molecular Mechanisms of Exogenous Melatonin Promote the Seed Germination of Maize (Zea mays L.) under Salt Stress. Plants 2024, 13, 2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, F.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.; Ding, Y.; Zhong, Q.; Xu, X.; Wei, H.; Li, G. Exogenous melatonin alleviates salt stress by improving leaf photosynthesis in rice seedlings. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 163, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, D.; Lu, B.; Liu, L.; Duan, W.; Meng, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, K.; Sun, H.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, H.; et al. Exogenous melatonin improves the salt tolerance of cotton by removing active oxygen and protecting photosynthetic organs. BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acker, V.; Durand, J.L.; Perrot, C.; Roy, E.; Frak, E.; Barillot, R. Effects of atmospheric CO2 concentration on transpiration and leaf elongation responses to drought in Triticum aestivum, Lolium perenne and Festuca arundinacea. Ann. Bot. 2024, 134, 787–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, M.N.; Zhang, L.; Yang, L.; Islam, M.R.; Liu, Y.; Luo, H.; Yang, P.; Wang, Q.; Chan, Z. Transcriptomic profiling of tall fescue in response to heat stress and improved thermotolerance by melatonin and 24-epibrassinolide. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Tang, H.; Ni, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y. Impact of an arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal inoculum and exogenous methyl jasmonate on the performance of tall fescue under saline-alkali condition. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 902667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Wang, Z.; Yang, M.; Liang, H. Effects of simulated salt stress on seed germination, seedling emergence and growth of Ulmus pumila. Acta Prataculturae Sin. 2012, 21, 39–46. [Google Scholar]
- Sardar, H.; Ramzan, M.A.; Naz, S.; Ali, S.; Ejaz, S.; Ahmad, R.; Altaf, M.A. Exogenous Application of Melatonin Improves the Growth and Productivity of Two Broccoli (Brassica oleracea L.) Cultivars Under Salt Stress. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2023, 42, 5152–5166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, H.; Xie, H.; Liu, J.; Hua, J.; Xiong, M.; Song, H.; Yong, C. Effect of Exogenous Melatonin on Corn Seed Germination and Seedling Salt Damage Mitigation Under NaCl Stress. Plants 2025, 14, 1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, W.; Chen, L.; Xie, Z.M.; Peng, X. Combined transcriptome and metabolome analysis revealed pathways involved in improved salt tolerance of Gossypium hirsutum L. seedlings in response to exogenous melatonin application. BMC Plant Biol. 2022, 22, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, M.; Ning, N.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, H. Melatonin enhances salt tolerance in sorghum by modulating photosynthetic performance, osmoregulation, antioxidant defense, and ion homeostasis. Open Life Sci. 2023, 18, 20220734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, S.; Cheng, J.; Gao, Y.; Ma, N.; Wang, Y. Exogenous melatonin strengthens saline-alkali stress tolerance in apple rootstock M9-T337 seedlings by initiating a variety of physiological and biochemical pathways. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2024, 11, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziaf, K.; Amjad, M.; Pervez, M.; Iqbal, Q.; Rajwana, I.; Ayyub, M. Evaluation of different growth and physiological traits as indices of salt tolerance in hot pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). Pak. J. Bot. 2009, 41, 1797–1809. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Ning, P.; Wang, F.; Cheng, X.; Huang, X. Effects of exogenous abscisic acid (ABA) on growth and physiological characteristics of Machilus yunnanensis seedlings under drought stress. J. Appl. Ecol. 2020, 31, 1543–1550. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, X.; Mu, X.; Shao, H.; Wang, H.; Brestic, M. Global plant-responding mechanisms to salt stress: Physiological and molecular levels and implications in biotechnology. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2015, 35, 425–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Ma, X.; Wan, P.; Liu, L. Plant salt-tolerance mechanism: A review. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 495, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Lu, B.; Liu, L.; Duan, W.; Jiang, D.; Li, J.; Zhang, K.; Sun, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; et al. Melatonin promotes seed germination under salt stress by regulating ABA and GA in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 162, 506–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Yu, A.; Sun, Y.; Hu, Q.; Kang, J.; Chen, L.; Zhu, X.; Yang, Q.; Long, R. Lipid composition remodeling and storage lipid conversion play a critical role in salt tolerance in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) leaves. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2023, 205, 105144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisa, E.A.; Honfi, P.; Tilly-Mándy, A.; Mirmazloum, I. Exogenous Melatonin Application Induced Morpho-Physiological and Biochemical Regulations Conferring Salt Tolerance in Ranunculus asiaticus L. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalili, S.; Ehsanpour, A.A.; Morteza Javadirad, S. Melatonin improves salt tolerance of in vitro root culture of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). Biologia 2023, 78, 961–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardar, H.; Bashir, M.M.; Naz, S.; Nawaz, A.; Ahmad, R.; Ejaz, S.; Al-Shuraym, L.A. Melatonin mitigates adverse effects of salinity in stevia through physiological and biochemical adjustments. Sci. Hortic. 2023, 322, 112390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, C.; Wang, G.; Sui, J.; Liu, G.; Ma, F.; Bao, Z. Biostimulants alleviate temperature stress in tomato seedlings. Sci. Hortic. 2022, 293, 110712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, R.; Alsahli, A.A.; Alansi, S.; Altaf, M.A. Exogenous melatonin confers drought stress by promoting plant growth, photosynthetic efficiency and antioxidant defense system of pea (Pisum sativum L.). Sci. Hortic. 2023, 322, 112431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, J.; Wang, W.; Sun, Y. Exogenous melatonin improves growth and photosynthetic capacity of cucumber under salinity-induced stress. Photosynthetica 2016, 54, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altaf, M.A.; Shahid, R.; Ren, M.X.; Altaf, M.M.; Khan, L.U.; Shahid, S.; Jahan, M.S. Melatonin alleviates salt damage in tomato seedling: A root architecture system, photosynthetic capacity, ion homeostasis, and antioxidant enzymes analysis. Sci. Hortic. 2021, 285, 110145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Xu, T.; Wang, Z.; Fang, Y.; Xi, Z.; Zhang, Z. The ameliorative effects of exogenous melatonin on grape cuttings under water-deficient stress: Antioxidant metabolites, leaf anatomy, and chloroplast morphology. J. Pineal Res. 2014, 57, 200–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, G.; Zhao, X.; Liu, S.; Sun, F.; Zhang, C.; Xi, Y. Beneficial effects of melatonin in overcoming drought stress in wheat seedlings. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 118, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahan, M.; Guo, S.; Baloch, A.; Sun, J.; Shu, S.; Wang, Y.; Ahammed, G.; Kabir, K.; Roy, R. Melatonin alleviates nickel phytotoxicity by improving photosynthesis, secondary metabolism and oxidative stress tolerance in tomato seedlings. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 197, 110593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnao, M.; Hernández-Ruiz, J. Protective effect of melatonin against chlorophyll degradation during the senescence of barley leaves. J. Pineal Res. 2009, 46, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szafrańska, K.; Reiter, R.J.; Posmyk, M.M. Melatonin Improves the Photosynthetic Apparatus in Pea Leaves Stressed by Paraquat via Chlorophyll Breakdown Regulation and Its Accelerated de novo Synthesis. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Dang, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Zheng, H.; Li, G.; Li, J.; Zhou, F.; Khan, A.; Zhang, Z.; et al. A glutathione S-transferase regulates lignin biosynthesis and enhances salt tolerance in tomato. Plant Physiol. 2024, 196, 2989–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, S.; Tuteja, N. Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant machinery in abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2010, 48, 909–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Khan, A.; Waqas, M.; Lee, I. Silicon Regulates Antioxidant Activities of Crop Plants under Abiotic-Induced Oxidative Stress: A Review. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasanuzzaman, M.; Bhuyan, M.H.M.B.; Zulfiqar, F.; Raza, A.; Mohsin, S.M.; Mahmud, J.A.; Fujita, M.; Fotopoulos, V. Reactive Oxygen Species and Antioxidant Defense in Plants under Abiotic Stress: Revisiting the Crucial Role of a Universal Defense Regulator. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Mao, J.; Sun, Q.; Huang, B.; Ding, C.B.; Gu, Y.; Liao, J.Q.; Hu, C.; Zhang, Z.W.; Yuan, S.; et al. Exogenous melatonin enhances salt stress tolerance in maize seedlings by improving antioxidant and photosynthetic capacity. Physiol. Plant. 2018, 164, 349–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Peng, Y.; Singer, J.; Fessehaie, A.; Krebs, S.; Arora, R. Seasonal changes in photosynthesis, antioxidant systems and ELIP expression in a thermonastic and non-thermonastic Rhododendron species: A comparison of photoprotective strategies in overwintering plants. Plant Sci. 2009, 177, 607–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Ye, B. Effects of combined elevated temperature and drought stress on anti-oxidative enzyme activities and reactive oxygen species metabolism of Broussonetia papyrifera seedlings. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2016, 36, 403–410. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, W.; Li, Q.; Chu, Y.; Reiter, R.; Yu, X.; Zhu, D.; Zhang, W.; Ma, B.; Lin, Q.; Zhang, J.; et al. Melatonin enhances plant growth and abiotic stress tolerance in soybean plants. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 695–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.; Ahmed, S.; Ikram, A.U.; Hannan, F.; Yasin, M.U.; Wang, J.; Zhao, B.; Islam, F.; Chen, J. Phytomelatonin: A key regulator of redox and phytohormones signaling against biotic/abiotic stresses. Redox Biol. 2023, 64, 102805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Chen, D.; Zhang, X.; Song, L.; Dong, J.; Xu, Q.; Hu, M.; Cheng, Y.; Shen, F.; Wang, W. Mitigation of salt stress response in upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum) by exogenous melatonin. J. Plant Res. 2021, 134, 857–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dou, J.; Tang, Z.; Yu, J.; Wang, G.; An, W.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Q. Effects of exogenous melatonin on the growth and photosynthetic characteristics of tomato seedlings under saline-alkali stress. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 5172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Li, H.Y.; Wang, X.J.; Li, Q.W. Effects of exogenous melatonin on the osmotic regulation and antioxidant capacity of Ginkgo biloba seedlings under salt stress. J. Appl. Ecol. 2024, 35, 431–438. [Google Scholar]
- Hayat, S.; Ali, B.; Aiman Hasan, S.; Ahmad, A. Brassinosteroid enhanced the level of antioxidants under cadmium stress in Brassica juncea. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2007, 60, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Yue, M.; Yang, D.; Zhu, S.; Ma, N.; Meng, Q. Over-expression of SlJA2 decreased heat tolerance of transgenic tobacco plants via salicylic acid pathway. Plant Cell Rep. 2017, 36, 529–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farhangi-Abriz, S.; Torabian, S. Antioxidant enzyme and osmotic adjustment changes in bean seedlings as affected by biochar under salt stress. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 137, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bates, L.; Waldren, R.; Teare, I. Rapid determination of free proline for water-stress studies. Plant Soil 1973, 39, 205–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochba, J.; Lavee, S.; Spiegel-Roy, P. Differences in peroxidase activity and isoenzymes in embryogenic ane non-embryogenic ‘Shamouti’ orange ovular callus lines. Plant Cell Physiol. 1977, 18, 463–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Sun, Z.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Q.; Guo, X.; Li, M.; Liu, L.; Lu, J.; Guo, S.; et al. Haplotype-specific interactions of Phragmites australis with Spartina alterniflora under salt stress. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 384, 125506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodges, D.; Delong, J.; Forney, C.; Prange, R. Improving the thiobarbituric acid-reactive-substances assay for estimating lipid peroxidation in plant tissues containing anthocyanin and other interfering compounds. Planta 1999, 207, 604–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wassie, M.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Q.; Ji, K.; Chen, L. Effect of Heat Stress on Growth and Physiological Traits of Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) and a Comprehensive Evaluation for Heat Tolerance. Agronomy 2019, 9, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Plant Height | Leaf Area | RWC | Chl | Car | SP | Pro | MDA | SOD | POD | Average | Order | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.11 | 0.28 | 1.00 | 0.64 | 3 |
| SM0 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.75 | 0.24 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.10 | 6 |
| SM50 | 0.24 | 0.12 | 0.28 | 0.05 | 0.11 | 0.81 | 0.63 | 0.23 | 0.22 | 0.18 | 0.29 | 5 |
| SM150 | 0.47 | 0.55 | 0.72 | 0.59 | 0.90 | 0.92 | 0.71 | 1.00 | 0.66 | 0.59 | 0.71 | 1 |
| SM250 | 0.37 | 0.45 | 0.55 | 0.59 | 0.76 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.60 | 1.00 | 0.28 | 0.66 | 2 |
| SM350 | 0.26 | 0.23 | 0.38 | 0.49 | 0.67 | 0.88 | 0.76 | 0.42 | 0.43 | 0.24 | 0.48 | 4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, B.; Li, H.; Zhao, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y. Exogenous Melatonin Enhances Salt-Stress Tolerance in Festuca elata via Growth and Physiological Improvements. Plants 2025, 14, 2661. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14172661
Liu B, Li H, Zhao X, Wang J, Zhang Y. Exogenous Melatonin Enhances Salt-Stress Tolerance in Festuca elata via Growth and Physiological Improvements. Plants. 2025; 14(17):2661. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14172661
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Bingqi, Haimei Li, Xianhui Zhao, Junrui Wang, and Yuting Zhang. 2025. "Exogenous Melatonin Enhances Salt-Stress Tolerance in Festuca elata via Growth and Physiological Improvements" Plants 14, no. 17: 2661. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14172661
APA StyleLiu, B., Li, H., Zhao, X., Wang, J., & Zhang, Y. (2025). Exogenous Melatonin Enhances Salt-Stress Tolerance in Festuca elata via Growth and Physiological Improvements. Plants, 14(17), 2661. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14172661







