Genome-Wide Dissection of Sorghum B3 Transcription Factor Family Identifies SbLAV1 as a Critical Transcriptional Regulator of Starch Biosynthesis in Developing Sorghum Grains
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Identification of Sorghum B3 Family Members
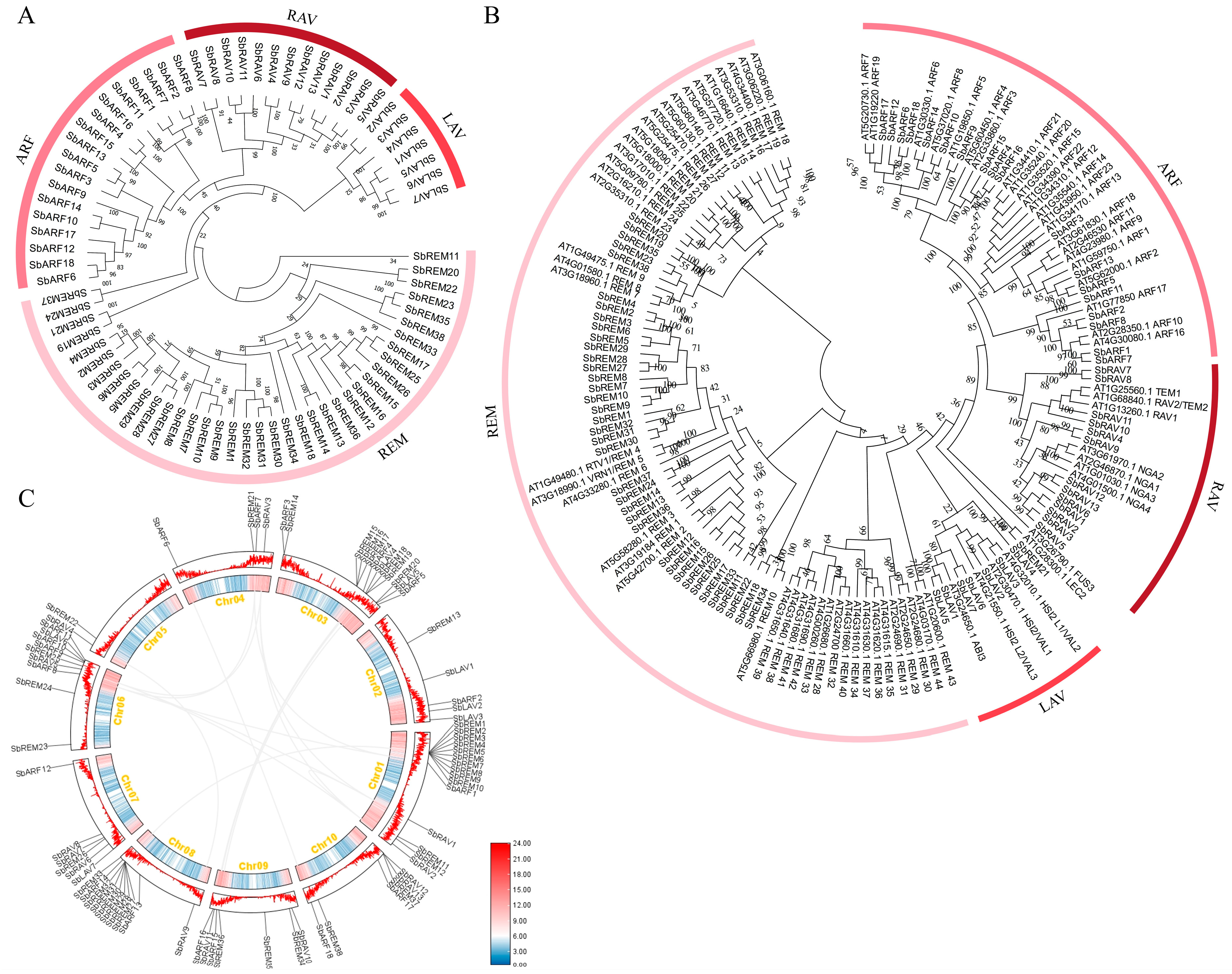
2.2. Evolution and Synteny Analysis of Sorghum B3 Family Members
2.3. Conserved Motifs, Structural Domains, and Gene Structure of Sorghum B3s
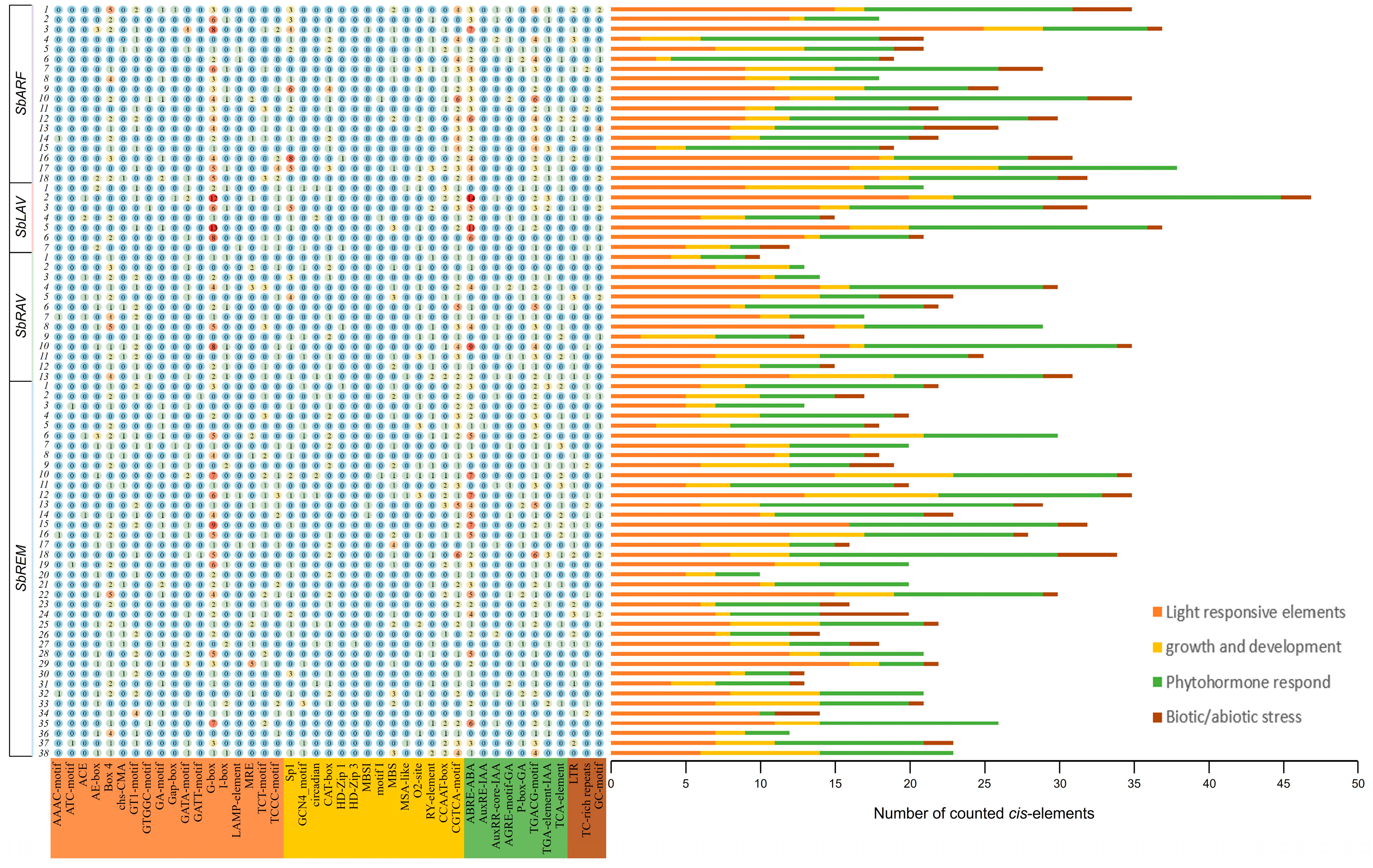
2.4. Cis-Elements Predicted within the Promoter Regions of SbB3s
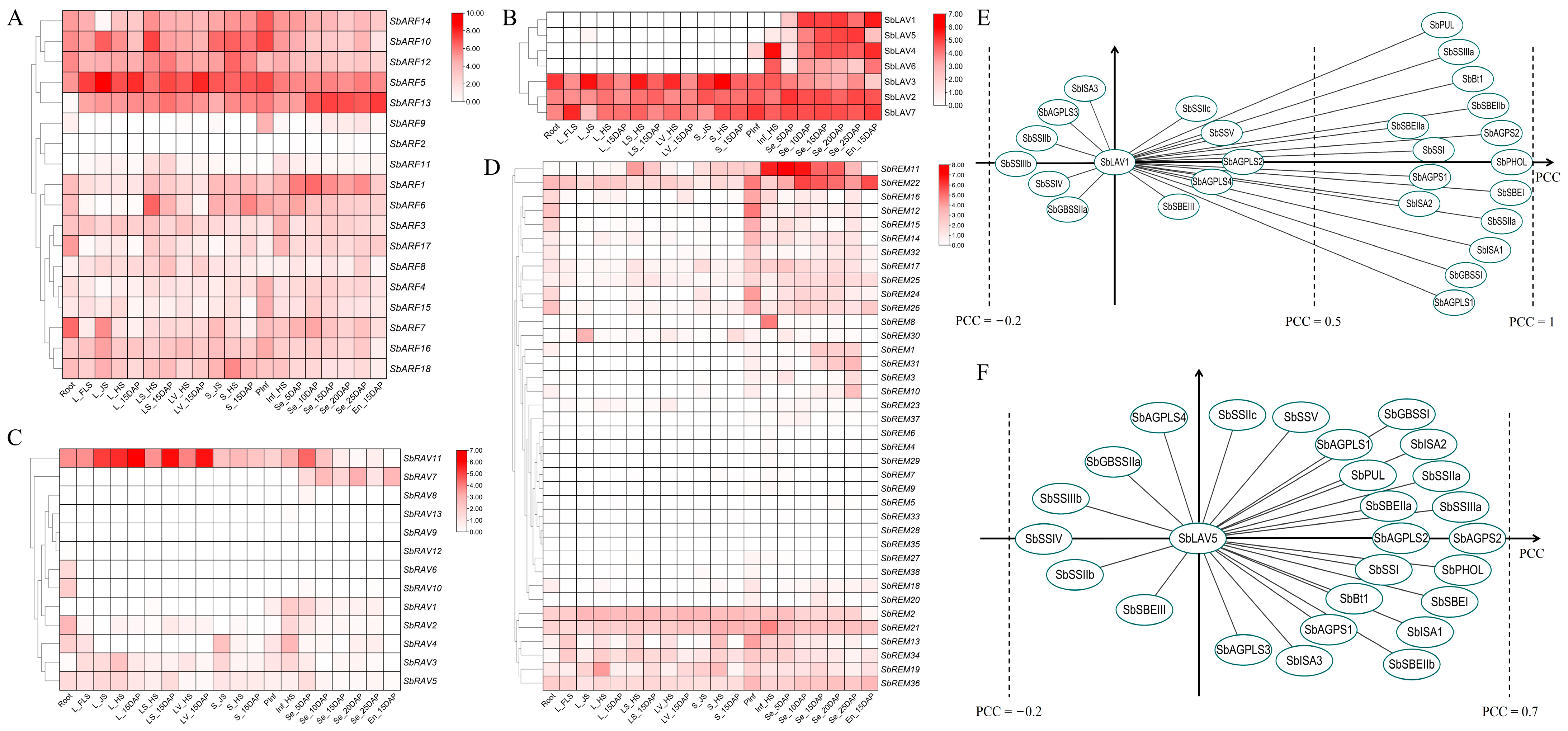
2.5. Expression Profiling of SbB3s and Co-Expression Analysis with SBRGs
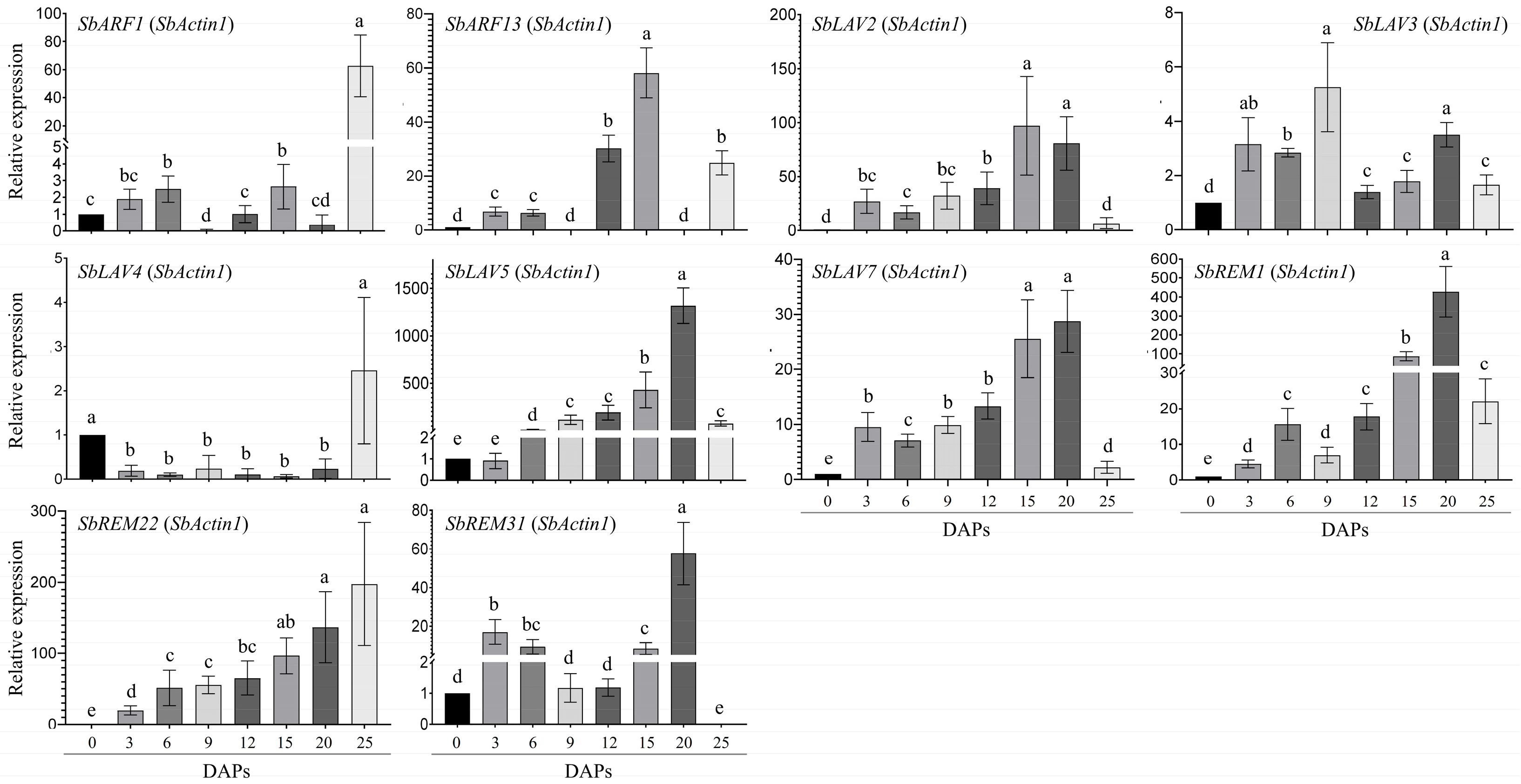
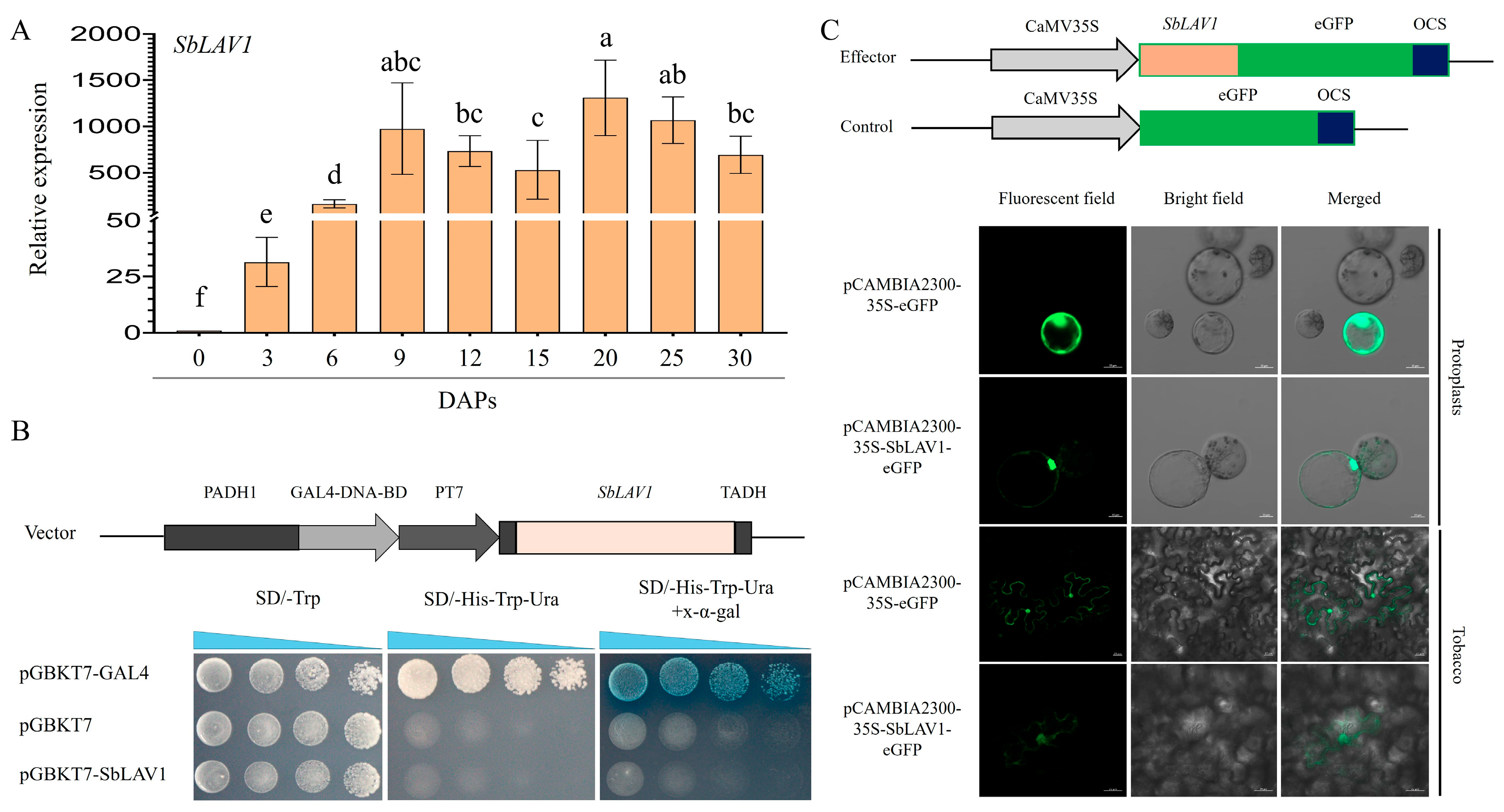
2.6. RT-qPCR Based Expression Analysis of SbB3s in Developing Sorghum Grains
2.7. Functional Properties of SbLAV1
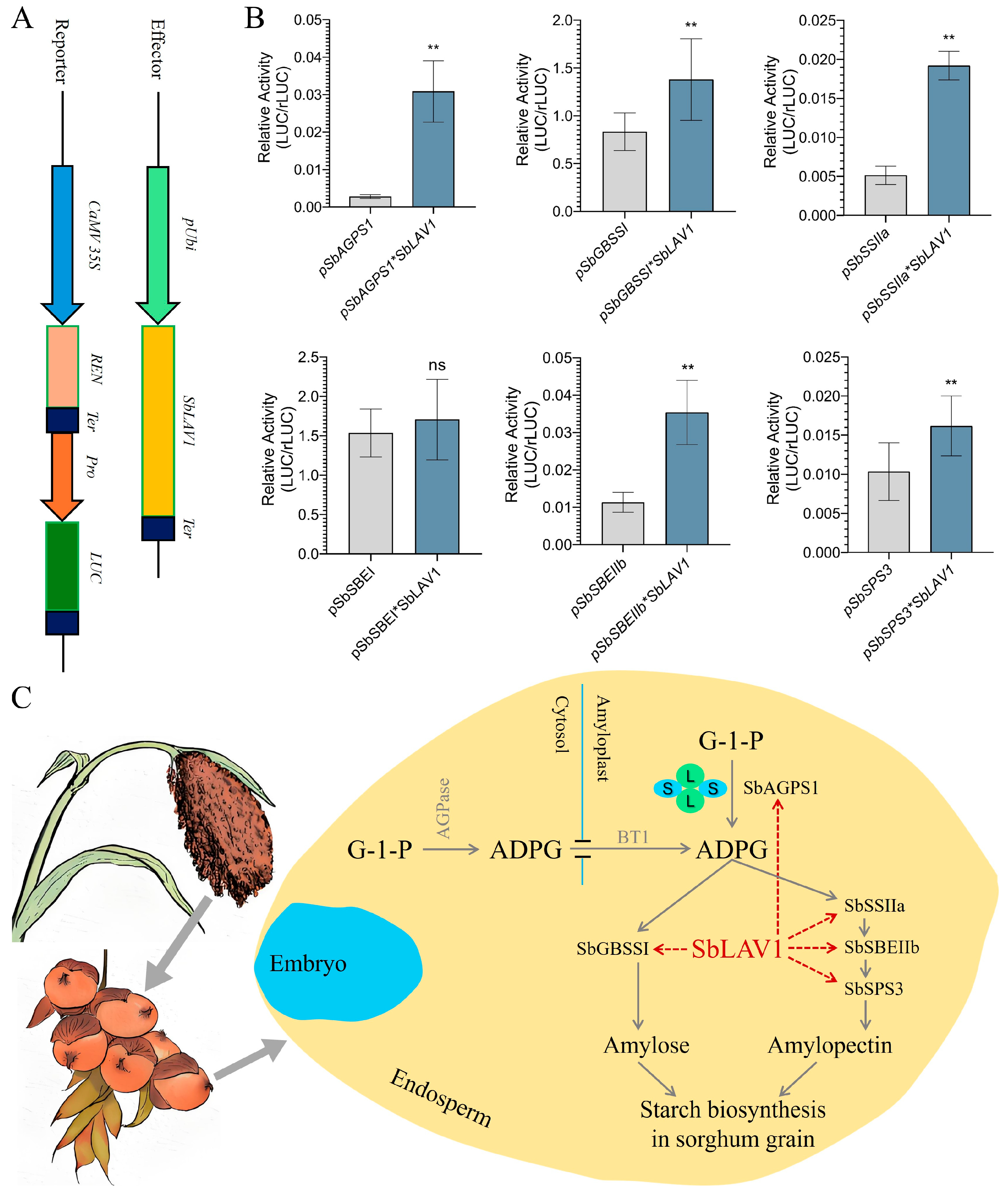
2.8. SbLAV1-Driven Transcription Activity
3. Discussion
3.1. The B3 Transcription Factor Family Is Highly Conserved in Plants
3.2. Differential Expression Patterns of Sorghum B3 Genes
3.3. SbLAV1 Protein Potentially Regulates the Starch Biosynthesis in Sorghum Grains
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials and Growth Condition
4.2. Identification of B3 TFs from the Sorghum Genome
4.3. Evolutionary and Synteny Analysis of Sorghum B3 TFs
4.4. Gene Structure Analysis, Motif and Conserved Domain Identification
4.5. Analysis of Cis-Elements
4.6. Transcriptome Data Analysis
4.7. Co-Expression Analysis with Sorghum SBRGs
4.8. Cloning and RT-qPCR Analysis
4.9. Vector Construction
4.10. Functional Property Analysis of SbLAV1
4.11. Dual-Luciferase Assay in Maize Leaf Protoplast
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AGPase | ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase |
| SS | Starch synthase |
| SBE | Starch-branching enzyme |
| DBE | Debranching enzymes |
| SP | Starch phosphorylase |
| ADPG | ADP-glucose |
| BT1 | Brittle1 |
| LAV | LEC2 [LEAFY COTYLEDON2]-ABI3 [ABSCISIC ACID INSENSITIVE3]–VAL |
| ARF | AUXIN RESPONSE FACTOR |
| RAV | RELATED TO ABI3 and VP1 |
| REM | REPRODUCTIVE MERISTEM |
| DAP | Days after pollination |
| SBRGs | Starch biosynthesis related genes |
References
- Hao, H.; Li, Z.; Leng, C.; Lu, C.; Luo, H.; Liu, Y.; Wu, X.; Liu, Z.; Shang, L.; Jing, H.C. Sorghum breeding in the genomic era: Opportunities and challenges. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2021, 134, 1899–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyles, R.E.; Brenton, Z.W.; Kresovich, S. Genetic and genomic resources of sorghum to connect genotype with phenotype in contrasting environments. Plant J. 2019, 97, 19–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, Z.; Wang, M.; Cuevas, H.E.; Chen, J.; Harrison, M.; Pugh, N.A.; Morris, G. Sorghum genetic, genomic, and breeding resources. Planta 2021, 254, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mace, E.S.; Tai, S.; Gilding, E.K.; Li, Y.; Prentis, P.J.; Bian, L.; Campbell, B.C.; Hu, W.; Innes, D.J.; Han, X.; et al. Whole-genome sequencing reveals untapped genetic potential in Africa’s indigenous cereal crop sorghum. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Luo, H.; Xu, J.; Cruickshank, A.; Zhao, X.; Teng, F.; Hathorn, A.; Wu, X.; Liu, Y.; Shatte, T.; et al. Extensive variation within the pan-genome of cultivated and wild sorghum. Nat. Plants 2021, 7, 766–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahaji, A.; Li, J.; Sánchez-López, Á.M.; Baroja-Fernández, E.; Muñoz, F.; Ovecka, M.; Almagro, G.; Montero, M.; Ezquer, I.; Etxeberria, E.; et al. Starch biosynthesis, its regulation and biotechnological approaches to improve crop yields. Biotechnol. Adv. 2014, 32, 87–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stitt, M.; Zeeman, S.C. Starch turnover: Pathways, regulation and role in growth. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2012, 15, 282–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, T.; Sun, H.; Qiao, J.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, J.; Tang, Z.; Wei, X.; Yang, J.; Yuan, Q.; et al. Cell-free chemoenzymatic starch synthesis from carbon dioxide. Science 2021, 373, 1523–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, J.S.; Ryoo, N.; Hahn, T.R.; Walia, H.; Nakamura, Y. Starch biosynthesis in cereal endosperm. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2010, 48, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, M.G.; Denyer, K.; Myers, A.M. Starch synthesis in the cereal endosperm. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2003, 6, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, J.C.; Pien, F.M.; Cao, H.; Liu, K.C. Brittle-1, an adenylate translocator, facilitates transfer of extraplastidial synthesized ADP-glucose into amyloplasts of maize endosperms. Plant Physiol. 1998, 117, 1235–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeeman, S.C.; Kossmann, J.; Smith, A.M. Starch: Its metabolism, evolution, and biotechnological modification in plants. Ann. Rev. Plant Biol. 2010, 61, 209–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, R.A.; Jenner, H.; Carrangis, L.; Fahy, B.; Fincher, G.B.; Hylton, C.; Laurie, D.A.; Parker, M.; Waite, D.; Van Wegen, S.; et al. Starch granule initiation and growth are altered in barley mutants that lack isoamylase activity. Plant J. 2002, 31, 97–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Shao, G.; Jiao, G.; Zhu, M.; Tang, S. Editing of rice endosperm plastidial phosphorylase gene OsPho1 advances its function in starch synthesis. Rice. Sci. 2021, 28, 209–211. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, Y.; Ono, M.; Utsumi, C.; Steup, M. Functional interaction between plastidial starch phosphorylase and starch branching enzymes from rice during the synthesis of branched maltodextrins. Plant Cell Physiol. 2012, 53, 869–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhmoudova, A.; Williams, D.; Brewer, D.; Massey, S.; Patterson, J.; Silva, A.; Vassall, K.A.; Liu, F.; Subedi, S.; Harauz, G.; et al. Identification of multiple phosphorylation sites on maize endosperm starch branching enzyme IIb, a key enzyme in amylopectin biosynthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 9233–9246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrero, D.M.L.; Piattoni, C.V.; Asencion Diez, M.D.; Rojas, B.E.; Hartman, M.D.; Ballicora, M.A.; Iglesias, A.A. Phosphorylation of ADP-Glucose pyrophosphorylase during wheat seeds development. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, Z.; Tetlow, I.J.; Ahmed, R.; Morell, M.K.; Emes, M.J. Protein–protein interactions among enzymes of starch biosynthesis in high-amylose barley genotypes reveal differential roles of heteromeric enzyme complexes in the synthesis of A and B granules. Plant Sci. 2015, 133, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cross, J.M.; Clancy, M.; Shaw, J.R.; Greene, T.W.; Schmidt, R.R.; Okita, T.W.; Hannah, L.C. Both subunits of ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase are regulatory. Plant Physiol. 2004, 135, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Tan, H.; Zhang, C.; Li, Q.; Liu, Q. Starch biosynthesis in cereal endosperms: An updated review over the last decade. Plant Commun. 2021, 2, 100237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, F.F.; Xue, H. Coexpression analysis identifies rice starch regulator1, a rice AP2/EREBP family transcription factor, as a novel rice starch biosynthesis regulator. Plant Physiol. 2010, 154, 927–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.C.; Xu, H.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Cai, X. OsbZIP58, a basic leucine zipper transcription factor, regulates starch biosynthesis in rice endosperm. J. Exp. Bot. 2013, 64, 3453–3466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Meng, S.; Wei, C. The NAC transcription factors OsNAC20 and OsNAC26 regulate starch and storage protein synthesis. Plant Physiol. 2020, 184, 1775–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Jiang, S.; Jiang, L.; Li, W.; Tang, Y.; He, W.; Wang, M.; Xing, J.; Cui, Y.; Lin, Q.; et al. Transcription factor OsSGL is a regulator of starch synthesis and grain quality in rice. J. Exp. Bot. 2022, 73, 3417–3430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yi, Q.; Cao, Y.; Wei, B.; Zheng, L.; Xiao, Q.; Xie, Y.; Gu, Y.; Li, Y.; Huang, H.; et al. ZmbZIP91 regulates expression of starch synthesis-related genes by binding to ACTCAT elements in their promoters. J. Exp. Bot. 2016, 67, 1327–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Xie, S.; Xiao, Q.; Wei, B.; Zheng, L.; Wang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Long, T.; Li, Y.; et al. Sucrose and ABA regulate starch biosynthesis in maize through a novel transcription factor, ZmEREB156. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Wang, Y.; Du, J.; Li, H.; Wei, B.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Yu, G.; Liu, H.; Zhang, J.; et al. ZmMYB14 is an important transcription factor involved in the regulation of the activity of the ZmBT1 promoter in starch biosynthesis in maize. FEBS J. 2017, 284, 3079–3099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Li, S.; Zhu, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Zhu, D.; Yu, J. ZmDof3, a maize endosperm-specific Dof protein gene, regulates starch accumulation and aleurone development in maize endosperm. Plant Mol. Biol. 2016, 93, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Q.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, C.; Wei, B.; Wang, Y.; Huang, H.; Li, Y.; Yu, G.; Liu, H.; et al. Transcription factor ZmNAC126 plays an important role in transcriptional regulation of maize starch synthesis-related genes. Crop. J. 2021, 9, 192–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, B.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, S. A maize NAC transcription factor, ZmNAC34, negatively regulates starch synthesis in rice. Plant Cell Rep. 2019, 38, 1473–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Dong, J.; Ji, C.; Wu, Y.; Messing, J. NAC-type transcription factors regulate accumulation of starch and protein in maize seeds. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 11223–11228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Hou, J.; Wang, X.; Li, T.; Majeed, U.; Hao, C.; Zhang, X. The NAC transcription factor NAC019-A1 is a negative regulator of starch synthesis in wheat developing endosperm. J. Exp. Bot. 2020, 71, 5794–5807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Luo, G.; Shen, L.; Yu, K.; Yang, W.; Li, X.; Sun, J.; Zhan, K.; Cui, D.; Liu, D.; et al. TubZIP28, a novel bZIP family transcription factor from Triticum urartu, and TabZIP28, its homologue from Triticum aestivum, enhance starch synthesis in wheat. New Phytol. 2020, 226, 1384–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Hao, C.; Li, T.; Majeed, U.; Liu, H.; Li, H.; Hou, J.; Zhang, X. Wheat NAC-A18 regulates grain starch and storage proteins synthesis and affects grain weight. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2023, 136, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Palmqvist, S.; Olsson, H.; Borén, M.; Ahlandsberg, S.; Jansson, C. A novel WRKY transcription factor, SUSIBA2, participates in sugar signaling in barley by binding to the sugar-responsive elements of the iso1 promoter. Plant Cell 2003, 15, 2076–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Hu, C.; Yan, X.; Jin, Y.; Chen, Z.; Guan, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhong, D.; Jansson, C.; Wang, F.; et al. Expression of barley SUSIBA2 transcription factor yields high-starch low-methane rice. Nature 2015, 523, 602–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Zheng, X.; Yang, J.; Messing, J.; Wu, Y. Maize endosperm-specific transcription factors O2 and PBF network the regulation of protein and starch synthesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 10842–10847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Q.; Huang, T.; Cao, W.; Ma, K.; Liu, T.; Xing, F.; Ma, Q.; Duan, H.; Ling, M.; Ni, X.; et al. Profiling of transcriptional regulators associated with starch biosynthesis in sorghum (Bicolor sorghum L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 999747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Liu, T.; Ling, M.; Ma, Q.; Cao, W.; Xing, F.; Huang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Duan, H.; Liu, Z. Genome-wide identification of DOF gene family and the mechanism dissection of SbDof21 regulating starch biosynthesis in sorghum. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaminathan, K.; Peterson, K.; Jack, T. The plant B3 superfamily. Trends Plant Sci. 2008, 13, 647–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Attuluri, V.P.S.; Robert, H.S. Transcriptional control of Arabidopsis seed development. Planta 2022, 255, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pekker, I.; Alvarez, J.P.; Eshed, Y. Auxin response factors mediate Arabidopsis organ asymmetry via modulation of KANADI activity. Plant Cell 2005, 17, 2899–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, J. Arabidopsis RAV1 is down-regulated by brassinosteroid and may act as a negative regulator during plant development. Cell Res. 2004, 14, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantegazza, O.; Gregis, V.; Mendes, M.A.; Morandini, P.; Alves-Ferreira, M.; Patreze, C.M.; Nardeli, S.M.; Kater, M.M.; Colombo, L. Analysis of the Arabidopsis REM gene family predicts functions during flower development. Ann. Bot. 2014, 114, 1507–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baud, S.; Kelemen, Z.; Thévenin, J.; Boulard, C.; Blanchet, S.; To, A.; Payre, M.; Berger, N.; Effroy-Cuzzi, D.; Franco-Zorrilla, J.M.; et al. Deciphering the molecular mechanisms underpinning the transcriptional control of gene expression by master transcriptional regulators in Arabidopsis seed. Plant Physiol. 2016, 171, 1099–1112. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Roscoe, T.T.; Guilleminot, J.; Bessoule, J.J.; Berger, F.; Devic, M. Complementation of seed maturation phenotypes by ectopic expression of ABSCISIC ACID INSENSITIVE3, FUSCA3 and LEAFY COTYLEDON2 in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol. 2015, 56, 1215–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, C.; Hao, G.; Wang, C.; Dirk, L.M.A.; Downie, A.B.; Zhao, T. Maize VIVIPAROUS1interacts with ABA INSENSITIVE5 to regulate GALACTINOL SYNTHASE2 expression controlling seed raffinose accumulation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 4214–4223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimault, A.; Gendrot, G.; Chaignon, S.; Gilard, F.; Tcherkez, G.; Thevenin, J.; Dubreucq, B.; Depege-Fargeix, N.; Rogowsky, P.M. Role of B3 domain transcription factors of the AFL family in maize kernel filling. Plant Sci. 2015, 236, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Guo, L.; Ji, C.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Zheng, X.; Xiao, Q.; Wu, Y. The B3 domain-containing transcription factor ZmABI19 coordinates expression of key factors required for maize seed development and grain filling. Plant Cell 2021, 33, 104–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Zhao, G.; Awais, M.; Gao, X.; Meng, W.; Lin, J.; Zhao, B.; Lai, Z.; Lin, Y.; Chen, Y. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis reveals the B3 superfamily involved in embryogenesis and hormone responses in Dimocarpus longan Lour. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 25, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Li, H.; Wang, Q.; Liu, R.; Yang, L.; Li, Q. Genome-wide identification and expression profiling of B3 transcription factor genes in Populus alba × Populus glandulosa. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1193065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, F.Y.; Weselake, R.J. Genome-wide identification and analysis of the B3 superfamily of transcription factors in Brassicaceae and major crop plants. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2013, 126, 1305–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Ma, Q.; Wei, Z.; Chen, J.; Sun, Z. Genome-wide analysis of the RAV transcription factor genes in rice reveals their response patterns to hormones and virus infection. Viruses 2021, 13, 752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, C.; Wang, H.; Zhou, Z.; Jia, J.; Zhang, Q.; Liang, C.; Li, W.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, G. Genome-wide identification of the B3 gene family in soybean and the response to melatonin under cold stress. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1091907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.B.; Ao, T.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Wu, D.; Xu, W.; Han, B.; Liu, A.Z. Genome-wide analysis of the B3 transcription factors reveals that RcABI3/VP1 subfamily plays important roles in seed development and oil storage in castor bean (Ricinus communis). Plant Divers. 2022, 44, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.K.; Xu, L.N.; Leng, Y.J.; Zhang, M.Q.; Yang, Q.Q.; Wang, S.L.; Jia, S.W.; Song, T.; Wang, R.A.; Tao, T.; et al. The OsNAC24-OsNAP protein complex activates OsGBSSI and OsSBEI expression to fine-tune starch biosynthesis in rice endosperm. Plant Biotech. J. 2023, 21, 2224–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xi, W.; Wang, X.; Li, H.; Liu, H.; Li, T.; Hou, J.; Liu, X.; Hao, C.; Zhang, X. TabHLH95-TaNF-YB1 module promotes grain starch synthesis in bread wheat. J. Genet. Genom. 2023, 50, 883–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, E.; Yu, H.; He, J.; Peng, D.; Zhu, P.; Pan, S.; Wu, X.; Wang, J.; Ji, C.; Chao, Z.; et al. The transcription factors ZmNAC128 and ZmNAC130 coordinate with Opaque2 to promote endosperm filling in maize. Plant Cell 2023, 35, 4066–4090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Chen, L.; Chen, M.; Zhou, W.; Dong, Q.; Jiang, H.; Cheng, B. The DOF-domain transcription factor ZmDOF36 positively regulates starch synthesis in transgenic maize. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, J.; Yi, Q.; Hu, Y.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y.; Huang, Y. Novel role of ZmaNAC36 in co-expression of starch synthetic genes in maize endosperm. Plant Mol. Biol. 2014, 84, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, S.; Mandal, D.; Mitra, S.; Chakraborty, S.; Nag Chaudhuri, R. ABI3 regulates ABI1 function to control cell length in primary root elongation zone. Plant J. 2024, 120, 2437–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Qiao, L.; Chen, J.; Rong, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Cui, X.; Xu, J.; Hou, X.; Dong, C.H. Arabidopsis REM16 acts as a B3 domain transcription factor to promote flowering time via directly binding to the promoters of SOC1 and FT. Plant J. 2020, 103, 1386–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Y.; Guo, Q.; Lin, R. The B3-domain transcription factor VAL1 regulates the floral transition by repressing FLOWERING LOCUS T. Plant Physiol. 2019, 181, 236–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Wang, H.; Guo, L.; Wu, X.; Xiao, Q.; Wang, J.; Wang, Q.; Ma, G.; Wang, W.; Wu, Y. ABA-induced phosphorylation of basic leucine zipper 29, ABSCISIC ACID INSENSITIVE 19, and Opaque2 by SnRK2.2 enhances gene transactivation for endosperm filling in maize. Plant Cell 2022, 34, 1933–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.H.; Zheng, R.; Tokheim, C.; Dong, X.; Fan, J.; Wan, C.; Tang, Q.; Brown, M.; Liu, J.S.; Meyer, C.A.; et al. Determinants of transcription factor regulatory range. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, R.M.; Wagler, T.N.; Quijada, P.; Doebley, J. A distant upstream enhancer at the maize domestication gene tb1 has pleiotropic effects on plant and inflorescent architecture. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, 594–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letunic, I.; Khedkar, S.; Bork, P. SMART: Recent updates, new developments and status in 2020. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D458–D460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Derbyshire, M.K.; Yamashita, R.A.; Marchler-Bauer, A. NCBI’s conserved domain database and tools for protein domain analysis. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2020, 69, e90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools: Anintegrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gong, X.; Li, J.; Yan, Z.; Sun, A.; Zheng, Y.; Yin, M.; Xiao, Q.; Liu, Z. Genome-Wide Dissection of Sorghum B3 Transcription Factor Family Identifies SbLAV1 as a Critical Transcriptional Regulator of Starch Biosynthesis in Developing Sorghum Grains. Plants 2025, 14, 1701. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14111701
Gong X, Li J, Yan Z, Sun A, Zheng Y, Yin M, Xiao Q, Liu Z. Genome-Wide Dissection of Sorghum B3 Transcription Factor Family Identifies SbLAV1 as a Critical Transcriptional Regulator of Starch Biosynthesis in Developing Sorghum Grains. Plants. 2025; 14(11):1701. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14111701
Chicago/Turabian StyleGong, Xiangling, Jing Li, Zheyu Yan, Anqi Sun, Yi Zheng, Min Yin, Qianlin Xiao, and Zhizhai Liu. 2025. "Genome-Wide Dissection of Sorghum B3 Transcription Factor Family Identifies SbLAV1 as a Critical Transcriptional Regulator of Starch Biosynthesis in Developing Sorghum Grains" Plants 14, no. 11: 1701. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14111701
APA StyleGong, X., Li, J., Yan, Z., Sun, A., Zheng, Y., Yin, M., Xiao, Q., & Liu, Z. (2025). Genome-Wide Dissection of Sorghum B3 Transcription Factor Family Identifies SbLAV1 as a Critical Transcriptional Regulator of Starch Biosynthesis in Developing Sorghum Grains. Plants, 14(11), 1701. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14111701





