Belowground Interaction in Tea/Soybean Intercropping Enhances Tea Quality by Improving Soil Nutrient Dynamics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Tea/Soybean Intercropping Improves Quality of Tea Leaves
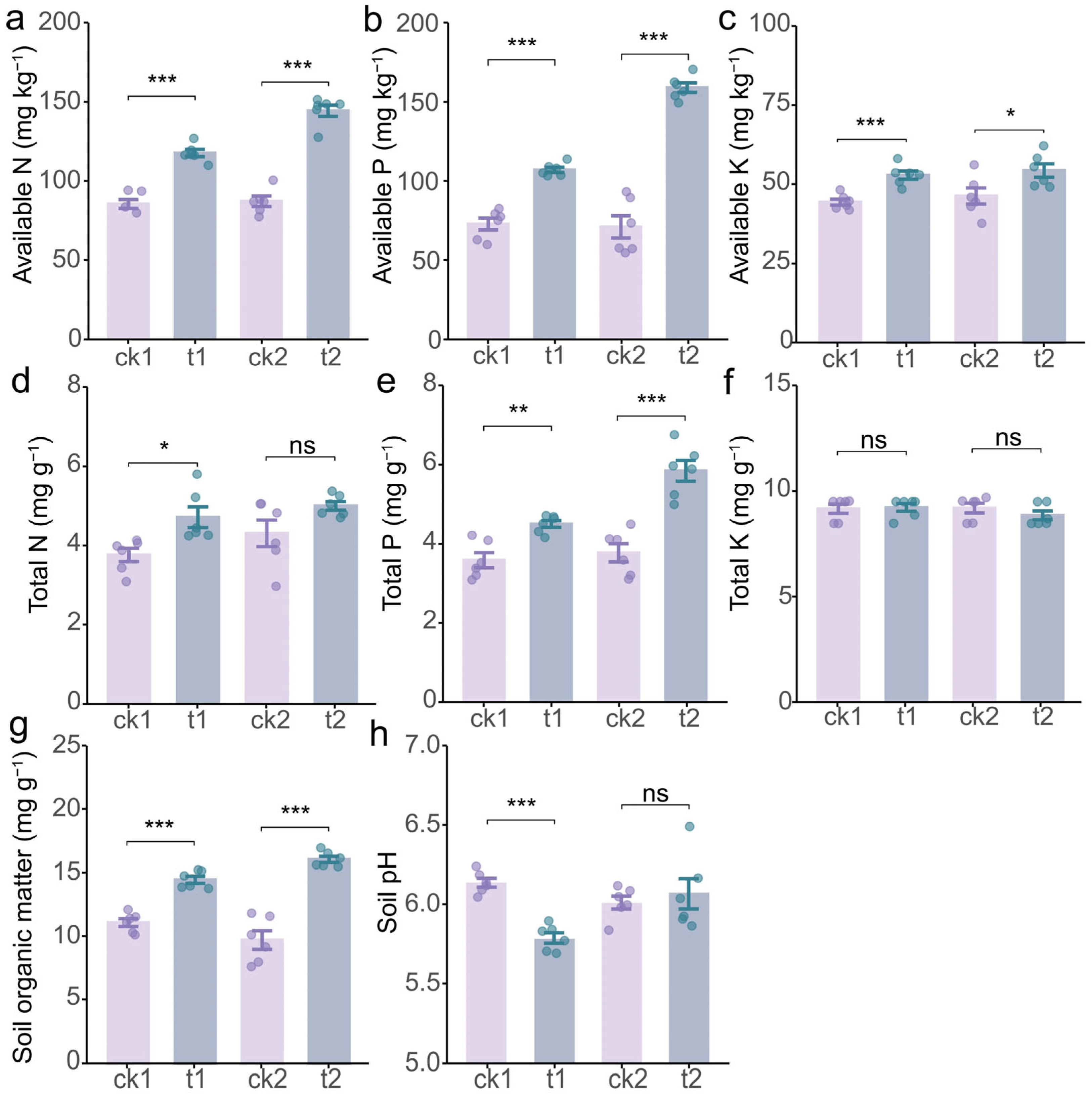
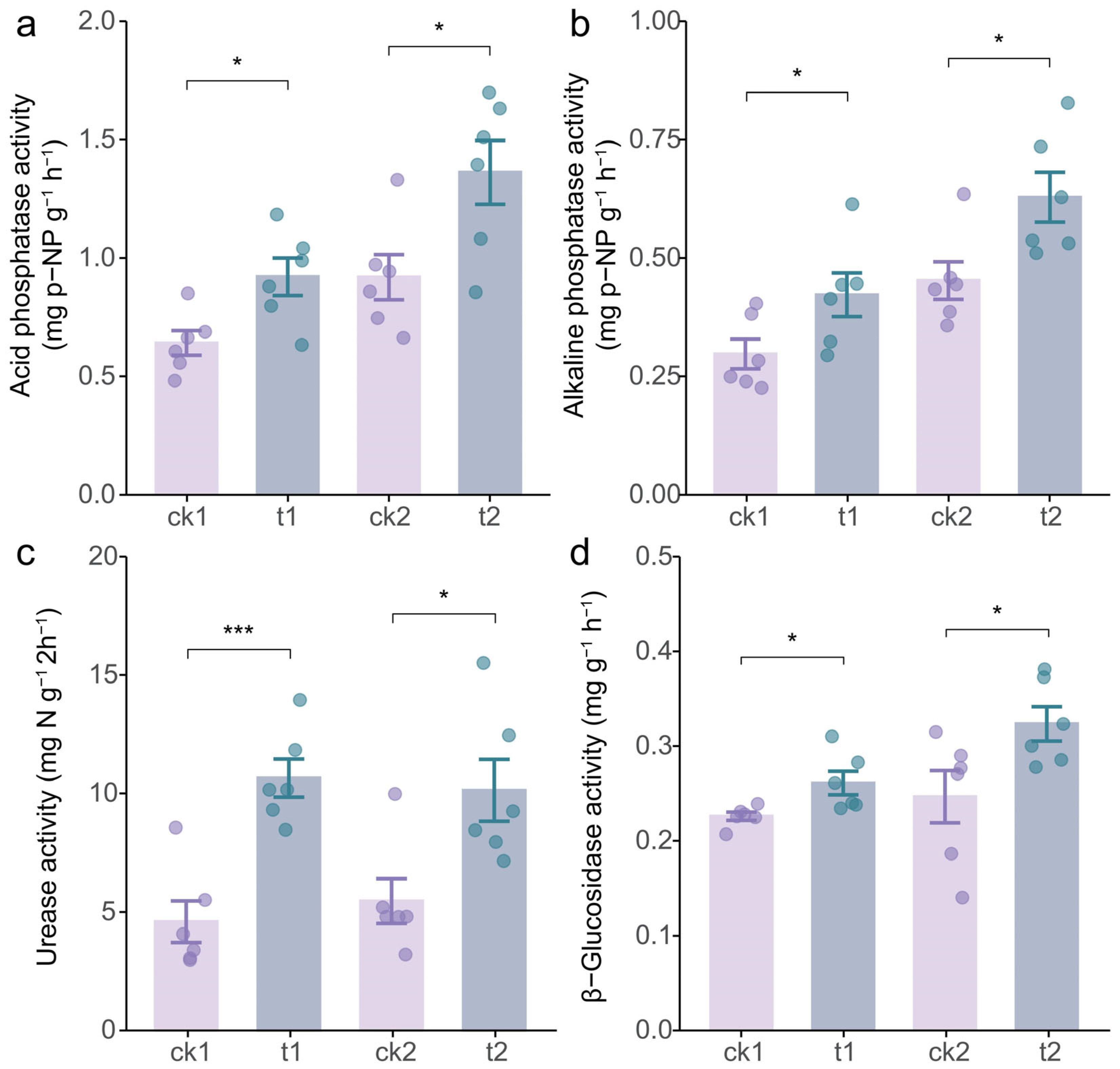
2.2. Tea/Soybean Intercropping Enhances Soil Properties of Tea Rhizosphere
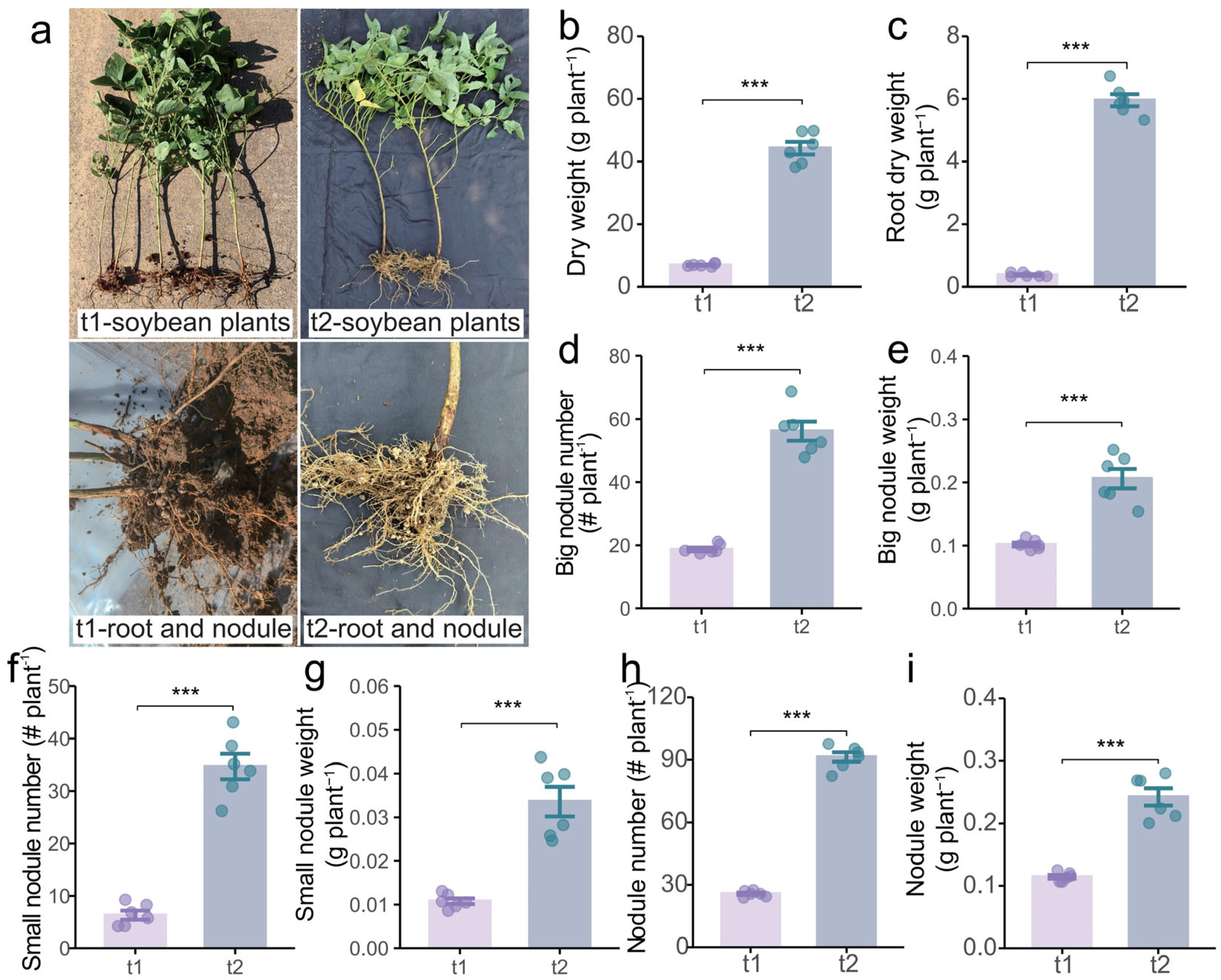
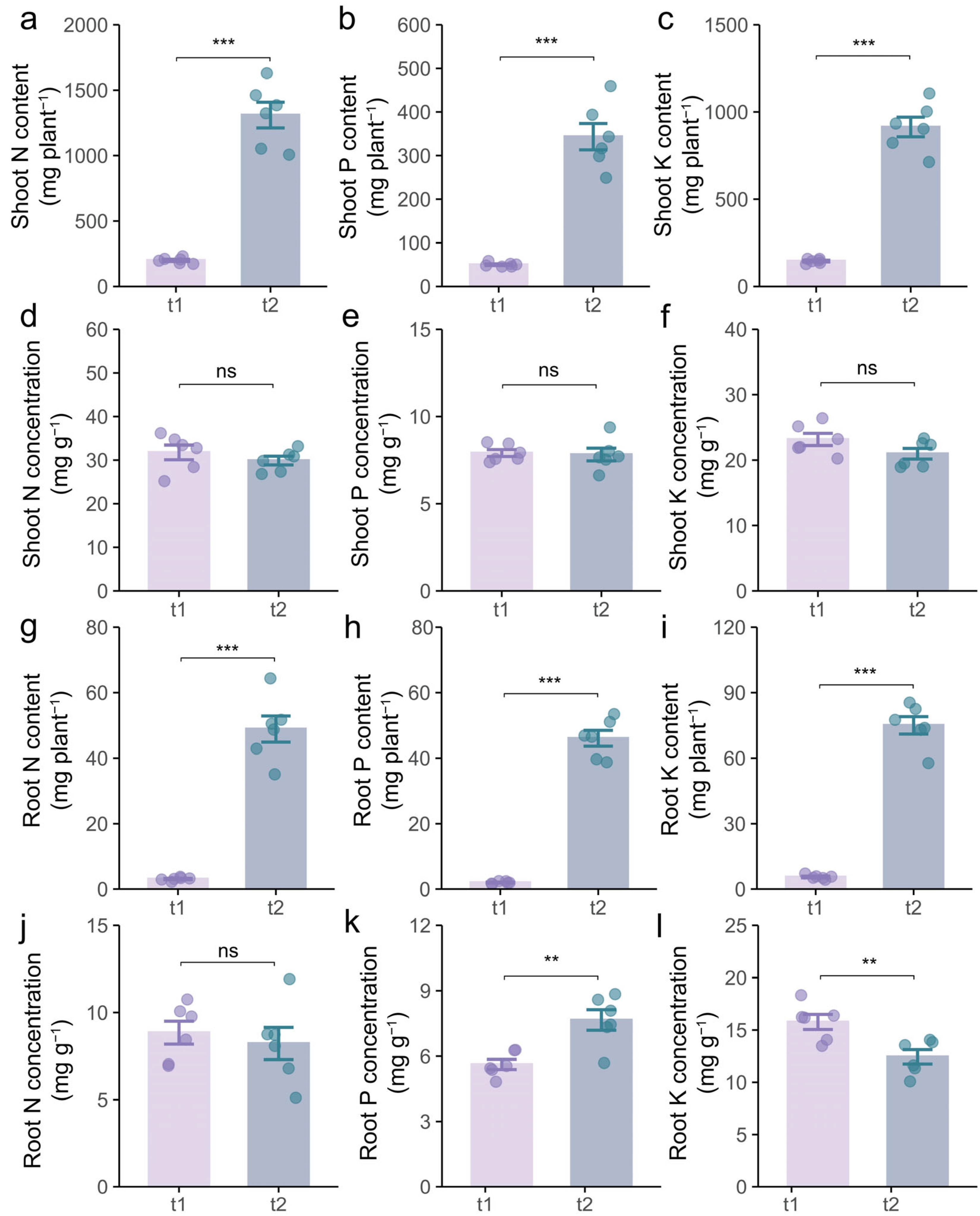
2.3. Effects of Different Stages on Growth and Nutrient Uptake of Intercropping Soybean
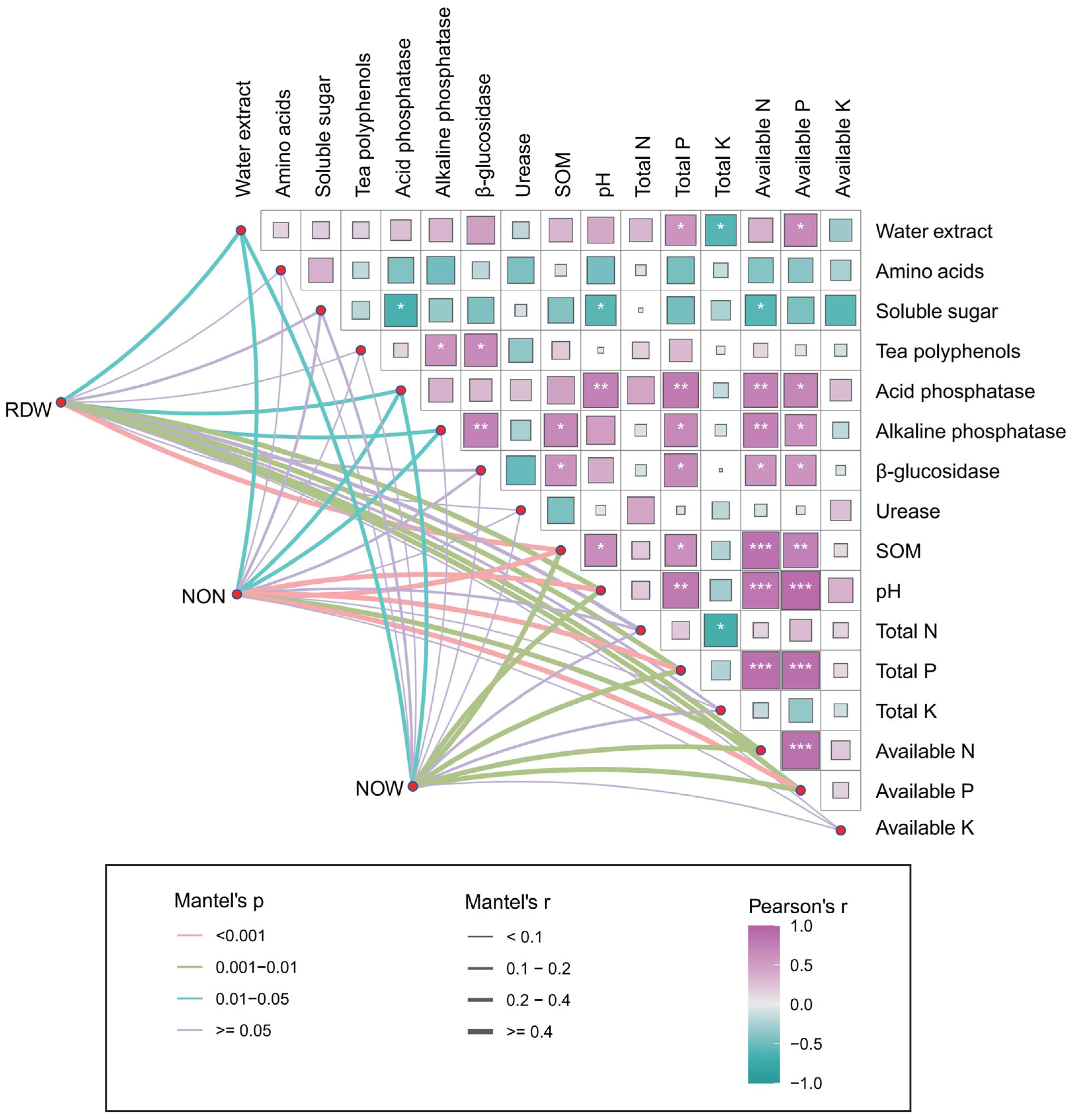
2.4. Relationship Among Soybean Growth, Soil Properties, and Tea Quality
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials and Site Description
4.2. Experimental Design and Sampling
4.3. Determination of Tea Quality
4.4. Measurement of Soil Fertility
4.5. Determination of Soil Enzyme Activities
4.6. Measurement of Nutrient Acquisition of Soybean Plants
- N content (mg plant−1) = Plant N concentration (mg g−1) × Plant dry weight (g plant−1)
- P content (mg plant−1) = Plant P concentration (mg g−1) × Plant dry weight (g plant−1)
- K content (mg plant−1) = Plant K concentration (mg g−1) × Plant dry weight (g plant−1)
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| N | Nitrogen |
| P | Phosphorus |
| K | Potassium |
| SOM | Soil organic matter |
| HS | Humic substance |
| pNPP | p-nitrophenyl phosphate |
| pNP | p-nitrophenol |
| pNPG | p-nitrophenyl-β-d-glucopyranoside |
Appendix A
| pH | Available N | Available P | Available K | Total N | Total P | Total K |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mg·kg−1 | mg·g−1 | |||||
| 5.83 | 79.1 | 59.56 | 42.32 | 4.67 | 5.92 | 9.45 |
Appendix B


References
- Guo, Y.J.; Sun, L.Q.; Yu, B.Y.; Qi, J. An integrated antioxidant activity fingerprint for commercial teas based on their capacities to scavenge reactive oxygen species. Food Chem. 2017, 237, 645–653. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Chen, Q.; Huang, X.; Fang, C.H. Qualitative identification of tea categories by near infrared spectroscopy and support vector machine. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2006, 41, 1198–1204. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kujawska, M.; Ewertowska, M.; Ignatowicz, E.; Adamska, T.; Szaefer, H.; Gramza-Michalowska, A.; Korczak, J.; Jodynis-Liebert, J. Evaluation of safety and antioxidant activity of yellow tea (Camellia sinensis) extract for application in food. J. Med. Food. 2016, 19, 330–336. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, H.P.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, J.; Lin, Z. Phytochemical profiles and antioxidant activities of Chinese dark teas obtained by different processing technologies. Food Res. Int. 2017, 100, 486–493. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sanlier, N.; Atik, I.; Atik, A. A minireview of effects of white tea consumption on diseases. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 82, 82–88. [Google Scholar]
- Cabrera, C.; Artacho, R.; Giménez, R. Beneficial effects of green tea—A review. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2006, 25, 79–99. [Google Scholar]
- Kanis, J.; Johnell, O.; Gullberg, B.; Allander, E.; Elffors, L.; Ranstam, J.; Dequeker, J.; Dilsen, G.; Gennari, C.; Vaz, A.L.; et al. Risk factors for hip fracture in men from southern Europe: The MEDOS study. Osteoporos. Int. 1999, 9, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Wei, G. Tea as a functional food for oral health. Nutrition 2002, 18, 443–444. [Google Scholar]
- Kaczyński, P.; Iwaniuk, P.; Jankowska, M.; Orywal, K.; Socha, K.; Perkowski, M.; Farhan, J.A.; Łozowicka, B. Pesticide residues in common and herbal teas combined with risk assessment and transfer to the infusion. Chemosphere 2024, 367, 143550. [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson, B.G. The imperial weight of tea: On the politics of plants, plantations and science. Geoforum 2022, 130, 105–114. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, S.; Nie, Q.; Tai, H.; Song, X.; Tong, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wu, X.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, D.; et al. Tea and tea drinking: China’s outstanding contributions to the mankind. Chin. Med. 2022, 17, 27. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, M.; Wang, C. Adapting tea production to climate change under rapid economic development in China from 1987 to 2017. Agronomy 2022, 12, 3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). FAOSTAT: Crops and Livestock Products-Tea Production. 2023. Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/ (accessed on 15 June 2024).
- Mao, L.; Ye, S.; Wang, S. Soil nutrient contents and stoichiometry within aggregate size classes varied with tea plantation age and soil depth in southern Guangxi in China. Soil 2022, 8, 487–505. [Google Scholar]
- Jibola-Shittu, M.Y.; Heng, Z.; Keyhani, N.O.; Dang, Y.; Chen, R.; Liu, S.; Lin, Y.; Lai, P.; Chen, J.; Yang, C.; et al. Understanding and exploring the diversity of soil microorganisms in tea (Camellia sinensis) gardens: Toward sustainable tea production. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1379879. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, T.; Li, H.; Tai, Y.; Dong, C.; Cheng, X.; Xia, E.; Chen, Z.; Li, F.; Wan, X.; Zhang, Z. Transcriptional regulation of amino acid metabolism in response to nitrogen deficiency and nitrogen forms in tea plant root (Camellia sinensis L.). Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6868. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Yang, X.; Shi, Y.; Yi, X.; Ji, L.; Cheng, Y.; Ni, K.; Ruan, J. Response of tea yield, quality and soil bacterial characteristics to long-term nitrogen fertilization in an eleven-year field experiment. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2021, 166, 103976. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Qiu, Q.; Fan, D.; Wang, X.; Zheng, X. Influence of different nitrogen sources on carbon and nitrogen metabolism and gene expression in tea plants (Camellia sinensis L.). Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 167, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kumari, M.; Thakur, S.; Kumar, A.; Joshi, R.; Kumar, P.; Shankar, R.; Kumar, R. Regulation of color transition in purple tea (Camellia sinensis). Planta 2019, 251, 35. [Google Scholar]
- KC, S.; Long, L.; Zhang, Q.; Ni, K.; Ma, L.; Ruan, J. Effect of interactions between phosphorus and light intensity on metabolite compositions in tea cultivar longjing43. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15194. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, Y.; Li, B.; Xu, C.; Raza, M.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Q.; Fu, Y.; Hu, J.; Imoulan, A.; Hussain, M.; et al. Intercropping walnut and tea: Effects on soil nutrients, enzyme activity, and microbial communities. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 852342. [Google Scholar]
- Agegnehu, G.; Amede, T.; Erkossa, T.; Yirga, C.; Henry, C.; Tyler, R.; Nosworthy, M.G.; Beyene, S.; Sileshi, G.W. Extent and management of acid soils for sustainable crop production system in the tropical agroecosystems: A review. Acta Agric. Scand. Sect. B—Soil Plant Sci. 2021, 71, 852–869. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, S.; Yuan, D.; Li, W.; He, W.; Raza, S.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Zamanian, K.; Zhao, X. Soil chemical properties depending on fertilization and management in China: A meta-analysis. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awadelkareem, W.; Haroun, M.; Wang, J.; Qian, X. Nitrogen interactions cause soil degradation in greenhouses: Their relationship to soil preservation in China. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barcelos, J.P.d.Q.; de Souza, M.; Nascimento, C.A.C.d.; Rosolem, C.A. Soil acidity amelioration improves N and C cycles in the short term in a system with soybean followed by maize-guinea grass intercropping. Geoderma 2022, 421, 115909. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Bao, X.; Sun, J.; Yang, S.; Wang, P.; Wang, C.; Wu, J.; Liu, X.; Tian, X.; et al. Long-term increased grain yield and soil fertility from intercropping. Nat. Sustain. 2021, 4, 943–950. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Stomph, T.J.; Makowski, D.; Li, H.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, F.; van der Werf, W. The productive performance of intercropping. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2201886120. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Hoffland, E.; Kuyper, T.W.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Li, H.; Zhang, F.; van der Werf, W. Syndromes of production in intercropping impact yield gains. Nat. Plants 2020, 6, 653–660. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Lambers, H.; Jing, J.; Zhang, C.; Bezemer, T.M.; Klironomos, J.; Cong, W.; Zhang, F. Belowground cascading biotic interactions trigger crop diversity benefits. Trends Plant Sci. 2024, 29, 1191–1202. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, X.; Zhang, C.; Yu, Y.; Shen, J.; van der Werf, W.; Zhang, F. Intercropping legumes and cereals increases phosphorus use efficiency; a meta-analysis. Plant Soil 2021, 460, 89–104. [Google Scholar]
- Raza, M.A.; Wang, Z.; Yasin, H.S.; Gul, H.; Qin, R.; Rehman, S.U.; Mahmood, A.; Iqbal, Z.; Ahmed, Z.; Luo, S.; et al. Effect of crop combination on yield performance, nutrient uptake, and land use advantage of cereal/legume intercropping systems. Field Crops Res. 2023, 304, 109144. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Cui, C.; Cao, Y.; Dai, J.; Cheng, X.; Hua, S.; Wang, W.; Duan, Y.; Petropoulos, E.; Wang, H.; et al. Tea plant–legume intercropping simultaneously improves soil fertility and tea quality by changing Bacillus species composition. Hortic. Res. 2022, 9, uhac046. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Lan, L.; Jin, Y.; Yu, N.; Wang, D.; Wang, E. Mechanisms underlying legume–rhizobium symbioses. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2022, 64, 244–267. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, B.; Zhang, X.; Chen, P.; Du, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, H.; Wang, X.; Yang, F.; Yong, T.; Yang, W. Improving maize’s N uptake and N use efficiency by strengthening roots’ absorption capacity when intercropped with legumes. PeerJ 2021, 9, e11658. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lai, H.; Gao, F.; Su, H.; Zheng, P.; Li, Y.; Yao, H. Nitrogen distribution and soil microbial community characteristics in a legume–cereal intercropping system: A review. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, D.; Zhang, C.; Lambers, H.; Zhang, F. Adding intercropped maize and faba bean root residues increases phosphorus bioavailability in a calcareous soil due to organic phosphorus mineralization. Plant Soil 2022, 476, 201–218. [Google Scholar]
- Soumare, A.; Sarr, D.; DiÉDhiou, A.G. Potassium sources, microorganisms and plant nutrition: Challenges and future research directions. Pedosphere 2023, 33, 105–115. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Lin, X.; Lin, W. Effects of intercropping with legume forage on the rhizosphere microbial community structure of tea plants. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1474941. [Google Scholar]
- Lyu, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, P.; Shang, Y.; Yang, X.; Wang, F.; Yu, A. Drive soil nitrogen transformation and improve crop nitrogen absorption and utilization—A review of green manure applications. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 14, 1305600. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, X.; Liao, Y.; Pan, C.; Li, X. Positive effects of intercropping on soil phosphatase activity depend on the application scenario: A meta-analysis. Soil Tillage Res. 2024, 235, 105914. [Google Scholar]
- Chamkhi, I.; Cheto, S.; Geistlinger, J.; Zeroual, Y.; Kouisni, L.; Bargaz, A.; Ghoulam, C. Legume-based intercropping systems promote beneficial rhizobacterial community and crop yield under stressing conditions. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 183, 114958. [Google Scholar]
- Landschoot, S.; Zustovi, R.; Dewitte, K.; Randall, N.P.; Maenhout, S.; Haesaert, G. Cereal-legume intercropping: A smart review using topic modelling. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 14, 1228850. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Z.; Chen, P.; Zhang, X.; Du, Q.; Zheng, B.; Yang, H.; Luo, K.; Lin, P.; Li, Y.; Pu, T.; et al. Maize-legume intercropping achieves yield advantages by improving leaf functions and dry matter partition. BMC Plant Biol. 2023, 23, 438. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Arafat, Y.; Letuma, P.; Ali, L.; Tayyab, M.; Waqas, M.; Li, Y.; Lin, W.; Lin, S.; Lin, W. Restoration of long-term monoculture degraded tea orchard by green and goat manures applications system. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Zhou, P.; Bao, Q.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Fu, H. Intercropping different legumes in tea plantation improves soil properties and tea quality components by regulating rhizosphere soil microorganisms. Agronomy 2025, 15, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciampitti, I.A.; de Borja Reis, A.F.; Córdova, S.C.; Castellano, M.J.; Archontoulis, S.V.; Correndo, A.A.; Antunes De Almeida, L.F.; Moro Rosso, L.H. Revisiting biological nitrogen fixation dynamics in soybeans. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 727021. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.; Carsky, R.J.; Lucas, E.O.; Dashiell, K. Soil N balance as affected by soybean maturity class in the Guinea savanna of Nigeria. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2003, 100, 231–240. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Z.; Qi, Y.; Chen, R.; Zhang, F.; Chen, L. Effects of phosphorus supply on the quality of green tea. Food Chem. 2012, 130, 908–914. [Google Scholar]
- Hawkesford, M.J.; Cakmak, I.; Coskun, D.; De Kok, L.J.; Lambers, H.; Schjoerring, J.K.; White, P.J. Chapter 6—Functions of macronutrients. In Marschner’s Mineral Nutrition of Plants, 4th ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2023; pp. 201–281. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, F.; Siddique, A.B.; Shabala, S.; Zhou, M.; Zhao, C. Phosphorus plays key roles in regulating plants’ physiological responses to abiotic stresses. Plants 2023, 12, 2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Chen, Y.; Zeng, L.; Cui, Y.; Li, J.; Tang, H.; Liu, J.; Tang, J. Soil nutrient deficiency decreases the postharvest quality-related metabolite contents of tea (Camellia sinensis (L.) kuntze) leaves. Food Chem. 2022, 377, 132003. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Z.; Jia, S.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, J.; Zhang, Y. Phosphate stresses affect ionome and metabolome in tea plants. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 120, 30–39. [Google Scholar]
- KC, S.; Liu, M.; Zhang, Q.; Fan, K.; Shi, Y.; Ruan, J. Metabolic changes of amino acids and flavonoids in tea plants in response to inorganic phosphate limitation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, K.; Liu, M.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, H.; Ruan, J.; Zhang, Q.; Cao, M. Metabolomics reveal that the high application of phosphorus and potassium in tea plantation inhibited amino-acid accumulation but promoted metabolism of flavonoid. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, D.; Li, J.; Ma, L.; Liu, Y.; Huang, J.; Jin, X. Unlocking tea’s potential: The synergistic role of selenium and phosphorus in enhancing tea quality. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2025, 221, 109670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mommer, L.; Hinsinger, P.; Prigent-Combaret, C.; Visser, E.J.W. Advances in the rhizosphere: Stretching the interface of life. Plant Soil 2016, 407, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, N.; Kong, C.; Wang, P.; Meiners, S.J. Root exudate signals in plant–plant interactions. Plant Cell Environ. 2021, 44, 1044–1058. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, R.; Dresbøll, D.B.; Finckh, M.R.; Justes, E.; van der Werf, W.; Fletcher, A.; Carlsson, G.; Li, L. Intercropping: Ecosystem functioning and sustainable agriculture. Plant Soil 2025, 506, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Sugiura, H.; Sugihara, S.; Kamiya, T.; Artigas Ramirez, M.D.; Miyatake, M.; Fujiwara, T.; Takuji, O.; Motobayashi, T.; Yokoyama, T.; Bellingrath-Kimura, S.D.; et al. Sulfur application enhances secretion of organic acids by soybean roots and solubilization of phosphorus in rhizosphere. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2021, 67, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soe Htet, M.N.; Hai, J.; Bo, P.T.; Gong, X.; Liu, C.; Dang, K.; Tian, L.; Soomro, R.N.; Aung, K.L.; Feng, B. Evaluation of nutritive values through comparison of forage yield and silage quality of mono-cropped and intercropped maize-soybean harvested at two maturity stages. Agriculture 2021, 11, 452. [Google Scholar]
- Dubey, R.K.; Tripathi, V.; Edrisi, S.A.; Bakshi, M.; Abhilash, P.C. Role of plant growth-promoting microorganisms in sustainable agriculture and environmental remediation. In Advances in PGPR Research; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2017; pp. 75–125. [Google Scholar]
- Rawat, P.; Das, S.; Shankhdhar, D.; Shankhdhar, S.C. Phosphate-solubilizing microorganisms: Mechanism and their role in phosphate solubilization and uptake. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2021, 21, 49–68. [Google Scholar]
- Amadou, I.; Houben, D.; Faucon, M.P. Unravelling the role of rhizosphere microbiome and root traits in organic phosphorus mobilization for sustainable phosphorus fertilization. A review. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siczek, A.; Lipiec, J. Impact of faba bean-seed rhizobial inoculation on microbial activity in the rhizosphere soil during growing season. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Bing, H.; Sun, H. Carbon demand drives microbial mineralization of organic phosphorus during the early stage of soil development. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2016, 52, 825–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Yuan, H.; Liu, D.; Cheng, L. Response of soybean root exudates and related metabolic pathways to low phosphorus stress. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0314256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Cao, J.; Zhang, F.; Li, L. Rhizosphere acidification of faba bean, soybean and maize. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 4356–4362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, B.; Chen, Q.; Lu, X.; Chen, K.; Yang, Y.; Tian, J.; Liang, C. Proton exudation mediated by GmVP2 has widespread effects on plant growth, remobilization of soil phosphorus, and the structure of the rhizosphere microbial community. J. Exp. Bot. 2023, 74, 1140–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butterly, C.R.; Baldock, J.A.; Tang, C. The contribution of crop residues to changes in soil pH under field conditions. Plant Soil 2013, 366, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Butterly, C.R.; Baldock, J.A.; Tang, C. Long-term stabilization of crop residues and soil organic carbon affected by residue quality and initial soil pH. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 587, 502–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Yu, Q. Impact of chemical composition of legume residues and initial soil pH on pH change of a soil after residue incorporation. Plant Soil 1999, 215, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Shen, J.; Zhang, X.; Wen, B.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Y.; Fang, W.; Zhu, X. Effects of soybean–tea intercropping on soil-available nutrients and tea quality. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2019, 41, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Wang, T.; Lei, X.; Cao, Y.; Liu, L.; Zou, Z.; Ma, Y.; Zhu, X.; Fang, W. Leguminous green manure intercropping changes the soil microbial community and increases soil nutrients and key quality components of tea leaves. Hortic. Res. 2024, 11, uhae018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Dong, X.; Wang, Y.; Maker, G.; Agarwal, M.; Ding, Z. Tea-soybean intercropping improves tea quality and nutrition uptake by inducing changes of rhizosphere bacterial communities. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; He, P.; Lin, T.; Liu, H.; Guo, B.; Lin, H.; Hu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Xiang, P.; Zou, L. Consecutive soybean (Glycine max) planting and covering improve acidified tea garden soil. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0254502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semenov, V.M.; Tulina, A.S.; Semenova, N.A.; Ivannikova, L.A. Humification and nonhumification pathways of the organic matter stabilization in soil: A review. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2013, 46, 355–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gecaite, V.; Ceseviciene, J.; Arlauskiene, A. Soil mineral nitrogen and mobile organic carbon as affected by winter wheat strip tillage and forage legume intercropping. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Jiang, H.; Tian, J.; Zhao, J.; Liao, H. Rhizobia enhance acquisition of phosphorus from different sources by soybean plants. Plant Soil 2011, 349, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; He, Y. Optimization of tea-leaf saponins water extraction and relationships between their contents and tea (Camellia sinensis) tree varieties. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 6, 1734–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hidayat, M.A.; Puspitaningtyas, N.; Gani, A.A.; Kuswandi, B. Rapid test for the determination of total phenolic content in brewed-filtered coffee using colorimetric paper. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 54, 3384–3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Xu, R.; Hu, B.; Li, W.; Sun, Y.; Tu, Y.; Zeng, X. Analysis of free amino acids in Chinese teas and flower of tea plant by high performance liquid chromatography combined with solid-phase extraction. Food Chem. 2010, 123, 1259–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, C.; Lu, X.; Cao, Z.; Hu, Z.; Ma, W. Long-term effects of lime application on soil acidity and crop yields on a red soil in central Zhejiang. Plant Soil 2004, 265, 101–109. [Google Scholar]
- Jafarian, Z.; Kavian, A. Effects of land-use change on soil organic carbon and nitrogen. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2013, 44, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Zhou, D.; Li, D.; Jiang, P. Growth, cadmium and zinc accumulation of ornamental sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) in contaminated soil with different amendments. Pedosphere 2012, 22, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Liu, Y.; Yan, J.; Hina, K.; Hussain, Q.; Qiu, T.; Zhu, J. Revitalizing coastal saline-alkali soil with biochar application for improved crop growth. Ecol. Eng. 2022, 179, 106594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Zhou, Q.; Tian, Z.; Cui, Y.; Liang, Y.; Wang, H. Apply biochar to ameliorate soda saline-alkali land, improve soil function and increase corn nutrient availability in the songnen plain. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 722, 137428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cramer, M.D.; Van Cauter, A.; Bond, W.J. Growth of N2-fixing African savanna Acacia species is constrained by below-ground competition with grass. J. Ecol. 2010, 98, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Nachimuthu, G.; Mason, S.; McLaughlin, M.J.; McNeill, A.; Bell, M.J. Comparison of soil analytical methods for estimating wheat potassium fertilizer requirements in response to contrasting plant K demand in the glasshouse. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabatabai, M.A. Soil enzymes. In Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 2 Microbiological and Biochemical Properties; Soil Science Society of America (SSSA) Book Series; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1994; pp. 775–833. [Google Scholar]
- Makoi, J.H.J.R.; Chimphango, S.B.M.; Dakora, F.D. Elevated levels of acid and alkaline phosphatase activity in roots and rhizosphere of cowpea (Vigna unguiculata L. Walp.) genotypes grown in mixed culture and at different densities with sorghum (Sorghum bicolor L.). Crop Pasture Sci. 2010, 61, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Yao, J.; Cai, M.; Qian, Y.; Guo, Y.; Richnow, H.H.; Blake, R.E.; Doni, S.; Ceccanti, B. Effects of petroleum contamination on soil microbial numbers, metabolic activity and urease activity. Chemosphere 2012, 87, 1273–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, C.V.; Souza, F.H.M.; Masui, D.C.; Leone, F.A.; Peralta, R.M.; Jorge, J.A.; Furriel, R.P.M. Purification and biochemical properties of a glucose-stimulated β-d-glucosidase produced by Humicola grisea var. thermoidea grown on sugarcane bagasse. J. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 53–62. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Chen, Q.; Liang, Q.; Zhao, Q.; Lu, X.; Tian, J.; Guan, Z.; Liu, C.; Li, J.; Zhou, M.; et al. Bacillus suppresses nitrogen efficiency of soybean–rhizobium symbiosis through regulation of nitrogen-related transcriptional and microbial patterns. Plant Cell Environ. 2024, 47, 4305–4322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saheewala, H.; Sanadhya, S.; Upadhyay, S.K.; Mohanty, S.R.; Jain, D. Polyphasic characterization of indigenous potassium-solubilizing bacteria and its efficacy studies on maize. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, T.; Mu, X.; Ni, E.; Wang, Q.; Li, S.; Mao, J.; Qing, D.; Li, B.; Chen, Y.; Chen, W.; et al. Belowground Interaction in Tea/Soybean Intercropping Enhances Tea Quality by Improving Soil Nutrient Dynamics. Plants 2025, 14, 1691. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14111691
Wang T, Mu X, Ni E, Wang Q, Li S, Mao J, Qing D, Li B, Chen Y, Chen W, et al. Belowground Interaction in Tea/Soybean Intercropping Enhances Tea Quality by Improving Soil Nutrient Dynamics. Plants. 2025; 14(11):1691. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14111691
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Tianqi, Xiaoyu Mu, Erdong Ni, Qinwen Wang, Shuyue Li, Jingying Mao, Dandan Qing, Bo Li, Yuan Chen, Wenjie Chen, and et al. 2025. "Belowground Interaction in Tea/Soybean Intercropping Enhances Tea Quality by Improving Soil Nutrient Dynamics" Plants 14, no. 11: 1691. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14111691
APA StyleWang, T., Mu, X., Ni, E., Wang, Q., Li, S., Mao, J., Qing, D., Li, B., Chen, Y., Chen, W., Liang, C., Wu, H., Lu, X., & Tian, J. (2025). Belowground Interaction in Tea/Soybean Intercropping Enhances Tea Quality by Improving Soil Nutrient Dynamics. Plants, 14(11), 1691. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14111691









