Metabolomic Insights into the Adaptations and Biotechnological Potential of Euglena gracilis Under Different Trophic Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
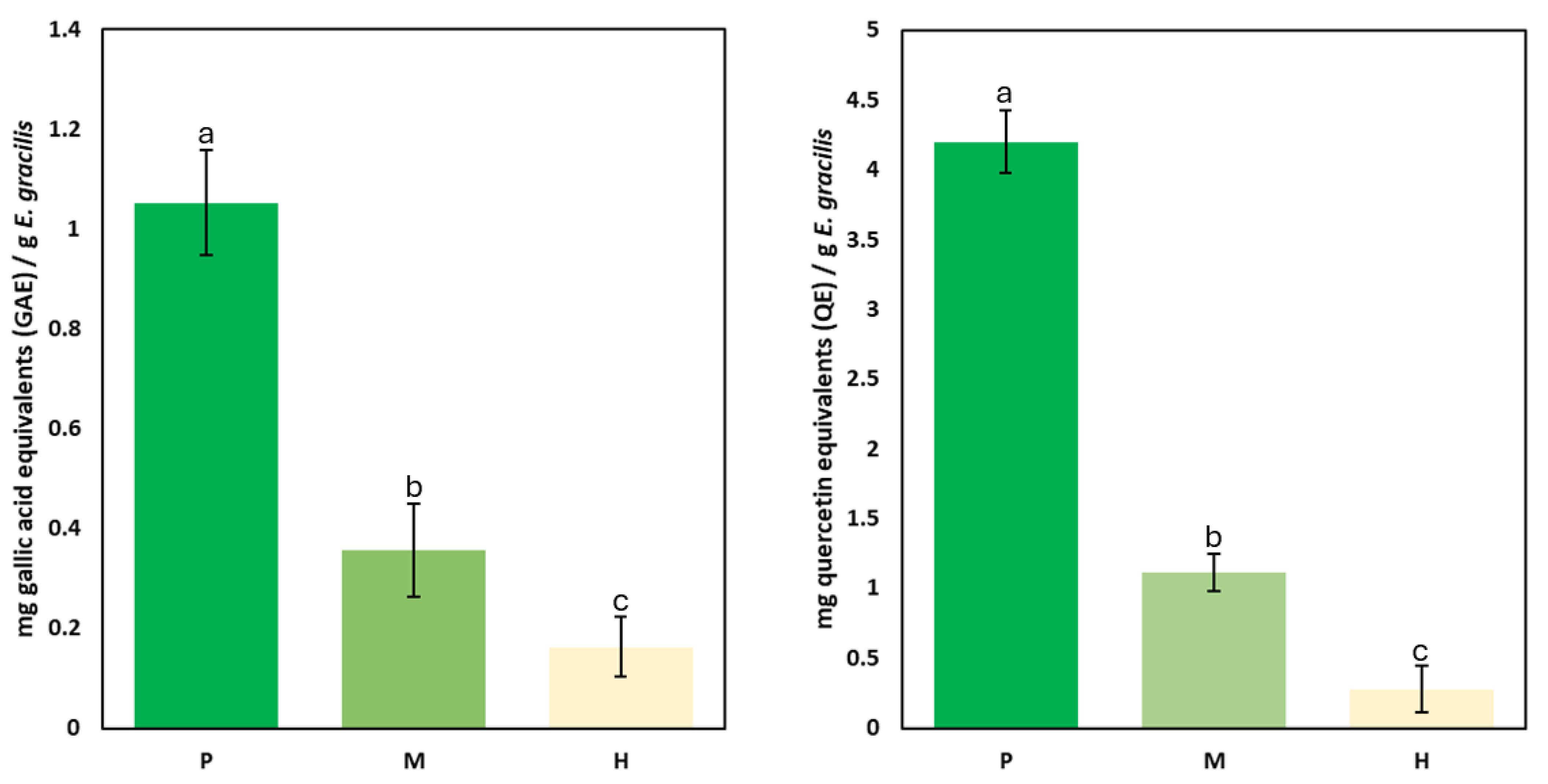
2.1. Flavonoid and Phenolic Content Across Trophic Conditions
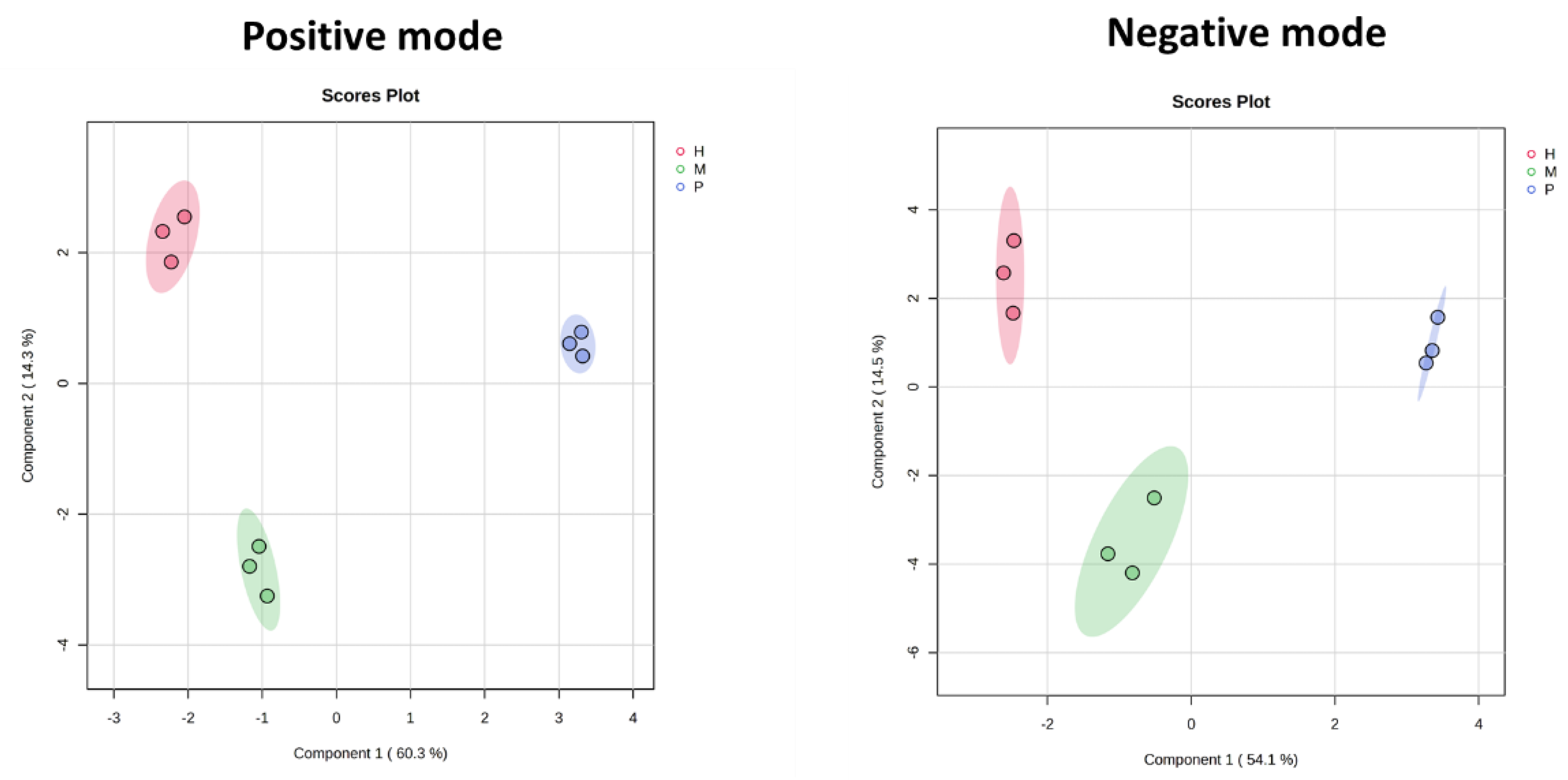
2.2. Metabolomics Overview and Global Metabolic Variability
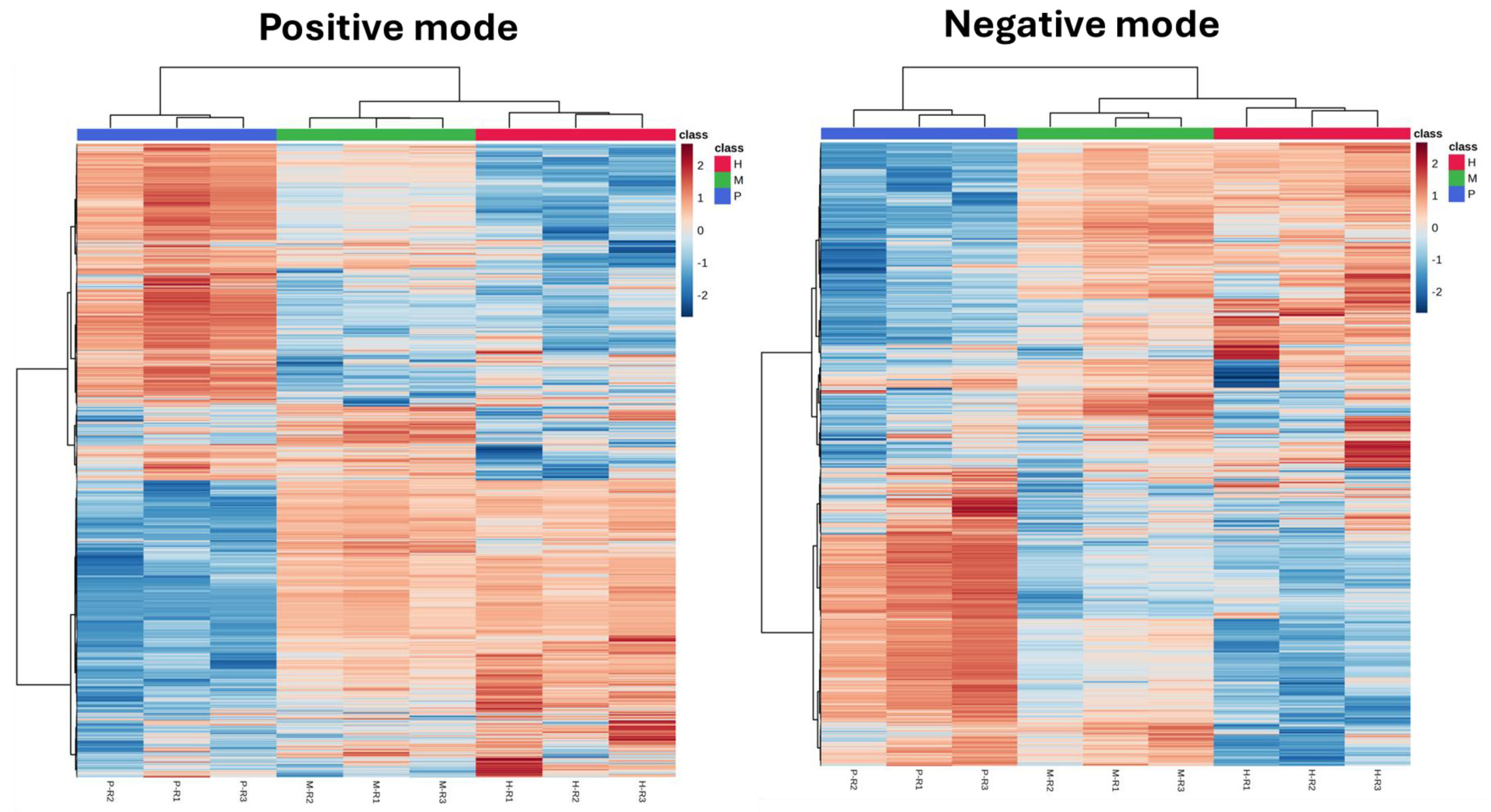
2.3. Heatmap and Clustering Analysis of Metabolic Profiles
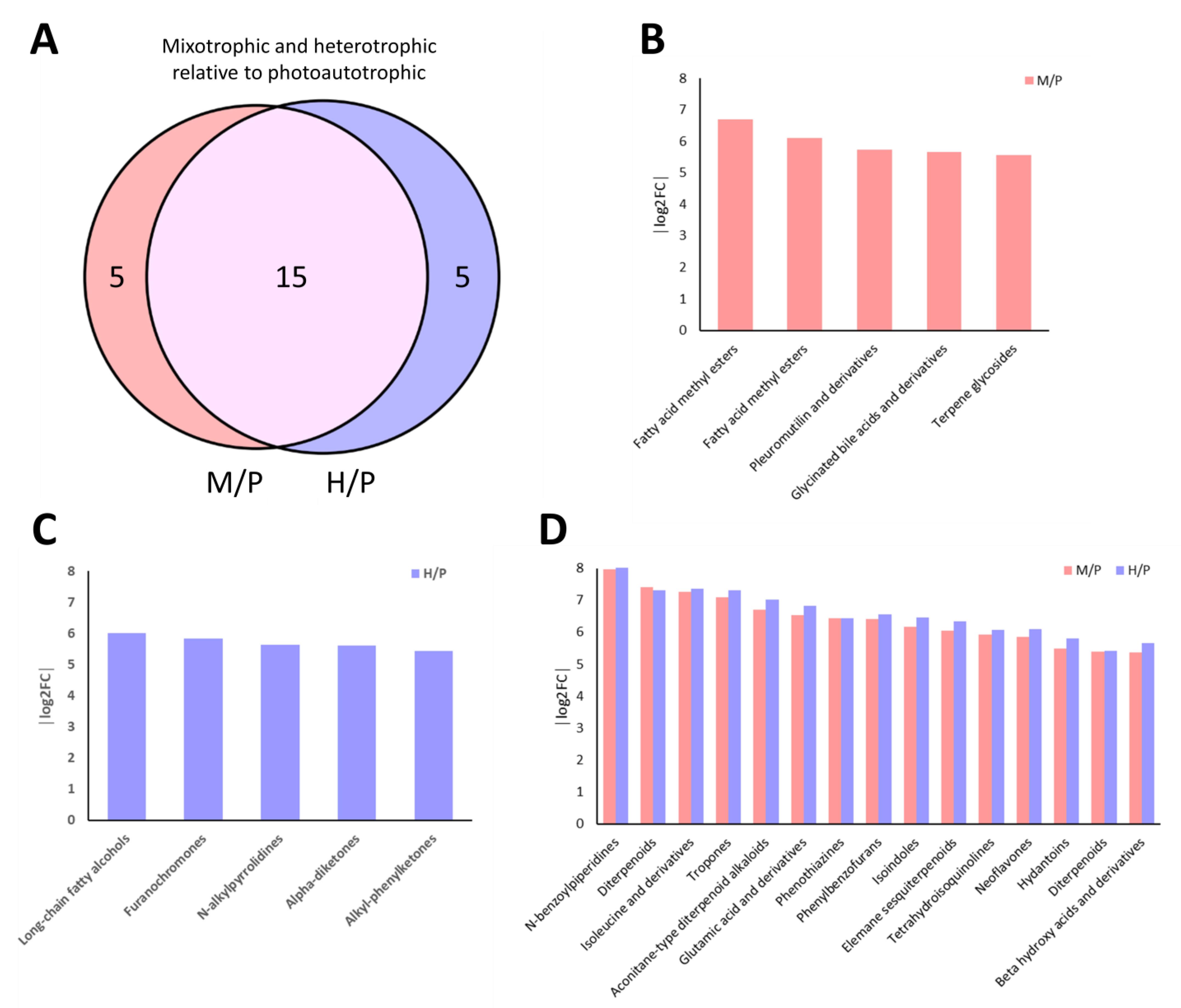
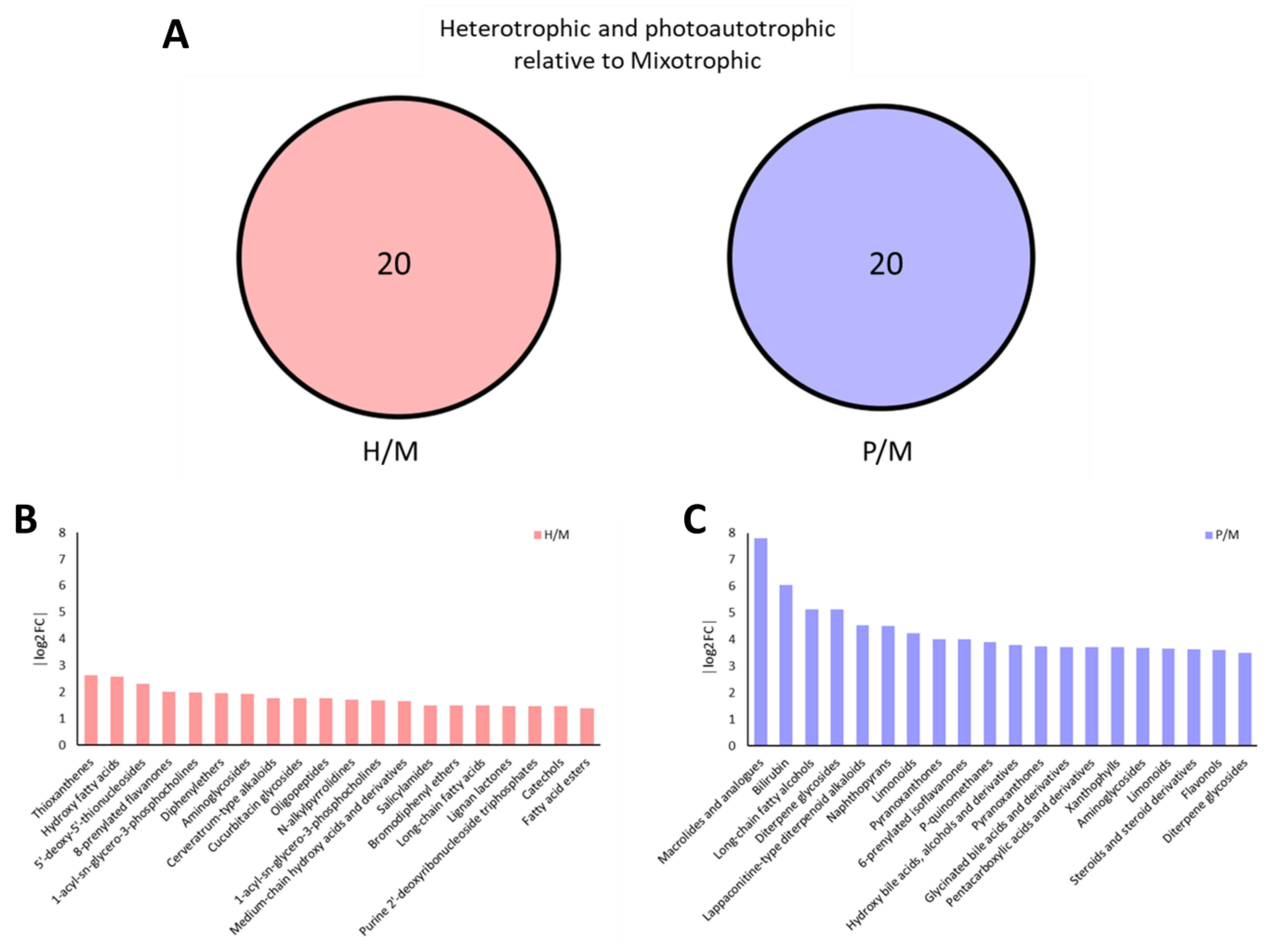
2.4. Venn Diagram Analysis Reveals Trophic-Specific Metabolites in E. gracilis
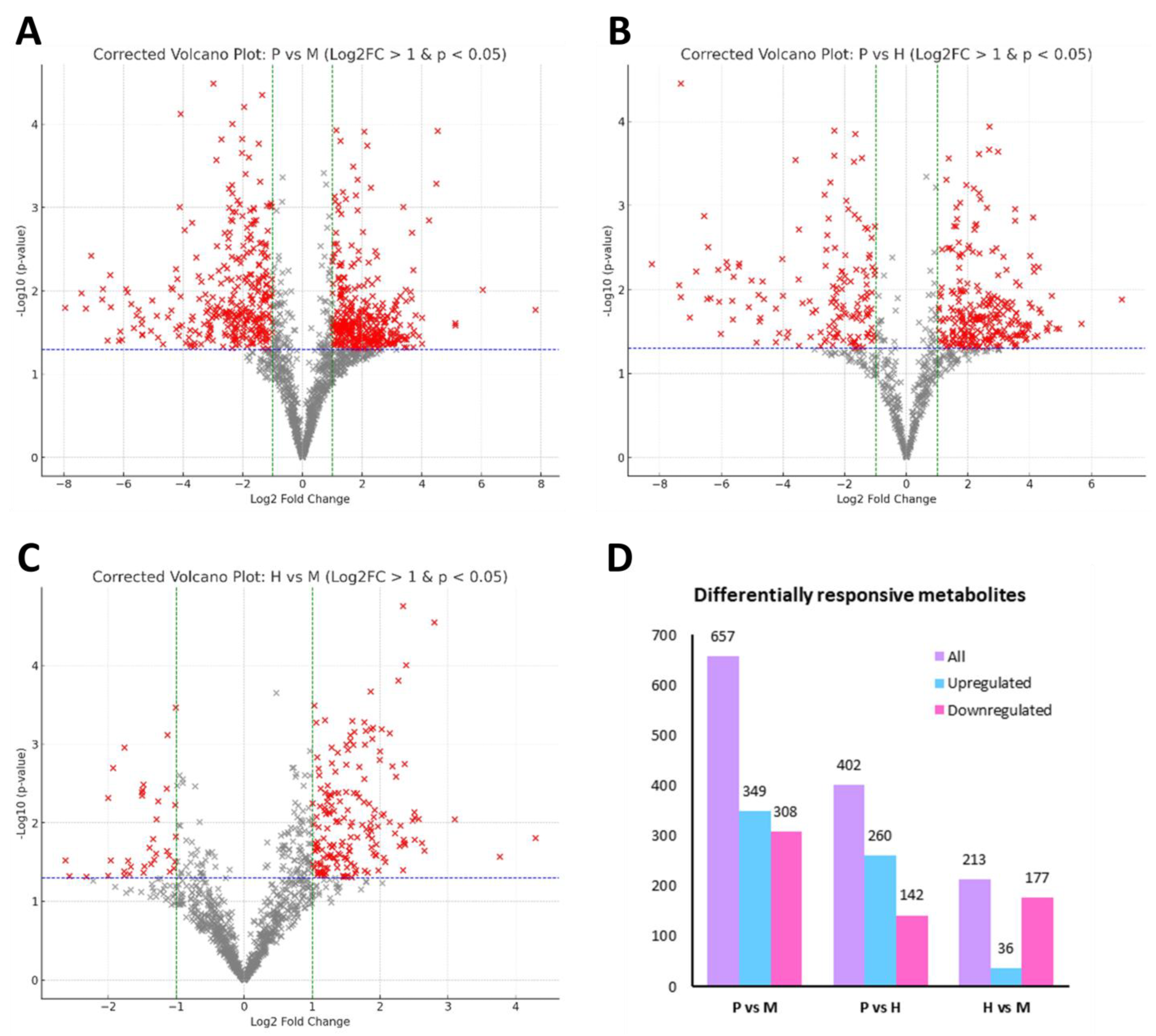
2.5. Differential Metabolite Analysis
3. Discussion
3.1. Global Metabolic Shifts Under Different Trophic Modes and Metabolic Reprogramming in Response to Ethanol and Light Availability
3.2. Metabolomic Profiling Reveals That E. gracilis Modulates Its Metabolism Drastically Across Trophic Modes, Yielding Distinct Classes of Enriched Metabolites with Potential in Biotechnological Implications
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Culture and Biomass Production
4.2. Total Phenolic and Total Flavonoids Content Analysis
4.3. Metabolomic Sample Preparation
4.4. Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS) Analysis
4.5. Data Processing and Metabolite Identification
4.6. Statistical Analysis
4.7. Comparative Metabolomics and Differential Metabolite Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Takeyama, H.; Kanamaru, A.; Yoshino, Y.; Kakuta, H.; Kawamura, Y.; Matsunaga, T. Production of antioxidant vitamins, beta-carotene, vitamin C, and vitamin E, by two-step culture of Euglena gracilis Z. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1997, 53, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamane, Y.-i.; Utsunomiya, T.; Watanabe, M.; Sasaki, K. Biomass production in mixotrophic culture of Euglena gracilis under acidic condition and its growth energetics. Biotechnol. Lett. 2001, 23, 1223–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagamine, S.; Oishi, R.; Ueda, M.; Sakamoto, T.; Nakazawa, M. Genome editing-based mutagenesis stably modifies composition of wax esters synthesized by Euglena gracilis under anaerobic conditions. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 410, 131255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buetow, D.E. The Biology of Euglena; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.; Wakisaka, M. Effect of two lignocellulose related sugar alcohols on the growth and metabolites biosynthesis of Euglena gracilis. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 303, 122950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Neill, E.C.; Trick, M.; Hill, L.; Rejzek, M.; Dusi, R.G.; Hamilton, C.J.; Zimba, P.V.; Henrissat, B.; Field, R.A. The transcriptome of Euglena gracilis reveals unexpected metabolic capabilities for carbohydrate and natural product biochemistry. Mol. Biosyst. 2015, 11, 2808–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, Y.; Tomiyama, T.; Maruta, T.; Tomita, M.; Ishikawa, T.; Arakawa, K. De novo assembly and comparative transcriptome analysis of Euglena gracilis in response to anaerobic conditions. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobáková, E.; Flegontov, P.; Skalický, T.; Lukeš, J. Unexpectedly streamlined mitochondrial genome of the euglenozoan Euglena gracilis. Genome Biol. Evol. 2015, 7, 3358–3367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inwongwan, S.; Kruger, N.J.; Ratcliffe, R.G.; O’Neill, E.C. Euglena central metabolic pathways and their subcellular locations. Metabolites 2019, 9, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novák Vanclová, A.M.G.; Zoltner, M.; Kelly, S.; Soukal, P.; Záhonová, K.; Füssy, Z.; Ebenezer, T.E.; Lacová Dobáková, E.; Eliáš, M.; Lukeš, J.; et al. Metabolic quirks and the colourful history of the Euglena gracilis secondary plastid. New Phytol. 2020, 225, 1578–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gissibl, A.; Sun, A.; Care, A.; Nevalainen, H.; Sunna, A. Bioproducts from Euglena gracilis: Synthesis and applications. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsanti, L.; Bastianini, A.; Passarelli, V.; Tredici, M.R.; Gualtieri, P. Fatty acid content in wild type and WZSL mutant of Euglena gracilis. J. Appl. Phycol. 2000, 12, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brun, P.; Piovan, A.; Caniato, R.; Dalla Costa, V.; Pauletto, A.; Filippini, R. Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Euglena gracilis Extracts. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimba, P.V.; Huang, I.S.; Gutierrez, D.; Shin, W.; Bennett, M.S.; Triemer, R.E. Euglenophycin is produced in at least six species of euglenoid algae and six of seven strains of Euglena sanguinea. Harmful Algae 2017, 63, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farjallah, A.; Roy, A.; Guéguen, C. NMR- and HRMS-based untargeted metabolomic study of metal-stressed Euglena gracilis cells. Algal Res. 2024, 78, 103383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farjallah, A.; Fillion, M.; Guéguen, C. Metabolic responses of Euglena gracilis under photoheterotrophic and heterotrophic conditions. Protist 2024, 175, 126035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, G.; Ou, D.; Chen, Z.; Gao, S.; Sun, S.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, C.; Liang, X. Metabolomics revealed the photosynthetic performance and metabolomic characteristics of Euglena gracilis under autotrophic and mixotrophic conditions. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 38, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Liu, C.; Du, M.; Zhou, X.; Hu, Z.; Lei, A.; Wang, J. Metabolic Responses of a Model Green Microalga Euglena gracilis to Different Environmental Stresses. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 662655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, K.; Nitta, T.; Atsuji, K.; Shiroyama, M.; Inoue, K.; Higuchi, C.; Nitta, N.; Oshiro, S.; Mochida, K.; Iwata, O.; et al. Characterization of sulfur-compound metabolism underlying wax-ester fermentation in Euglena gracilis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, M.; Hao, W.; Zou, Y.; Shi, M.; Jiang, Y.; Xiao, P.; Lei, A.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, L.; et al. Fatty acid and metabolomic profiling approaches differentiate heterotrophic and mixotrophic culture conditions in a microalgal food supplement ‘Euglena’. BMC Biotechnol. 2016, 16, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chisti, Y. Biodiesel from microalgae. Biotechnol. Adv. 2007, 25, 294–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Li, Y.; Wu, N.; Lan, C.Q. CO2 bio-mitigation using microalgae. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 79, 707–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, A.; Sui, F.; Li, S.; Liu, Y.; Lu, X.; Lu, Y.; Fan, Y. Transcriptome analysis of the effects of different carbon dioxide concentrations on paramylon accumulation in Euglena gracilis Z. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 393, 130114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, Q.; Li, S.; Du, X.; Fan, Y.; Wang, M.; Song, C.; Sui, F.; Liu, Y. Transcriptomic response analysis of ultraviolet mutagenesis combined with high carbon acclimation to promote photosynthetic carbon assimilation in Euglena gracilis. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1444420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakazawa, M. C2 metabolism in Euglena. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 979, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, M.J.; Zheng, B. The Role of Polyphenols in Abiotic Stress Tolerance and Their Antioxidant Properties to Scavenge Reactive Oxygen Species and Free Radicals. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Singh, S.K.; Pattanaik, S.; Wang, H.; Yuan, L. Light regulation of the biosynthesis of phenolics, terpenoids, and alkaloids in plants. Commun. Biol. 2023, 6, 1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulk, E.I.; Zamyatkina, E.B.; Birkemeyer, C.; Tarakhovskaya, E.R. Biochemical Composition of Euglena gracilis Cells during Mixotrophic Growth in the Presence of Various Organic Substrates. Russ. J. Plant Physiol. 2023, 70, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, A.; Anna, K.; Amy, G.; Donna, C.; Emery, R.J.N. Euglena gracilis (Euglenophyceae) produces abscisic acid and cytokinins and responds to their exogenous application singly and in combination with other growth regulators. Eur. J. Phycol. 2014, 49, 244–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardeland, R. Melatonin and 5-methoxytryptamine in non-metazoans. Reprod. Nutr. Dev. 1999, 39, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, J.; Miyamoto, K.; Sato, T.; Momotani, Y. Identification of Jasmonic Acid from Euglena gracilis Z as a Plant Growth Regulator. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1991, 55, 275–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inwongwan, S. Metabolic Flux Analysis in Euglena Gracilis; University of Oxford: Oxford, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, R.; Fu, W.; Du, M.; Chen, Z.-X.; Lei, A.-P.; Wang, J.-X. Carotenoids Biosynthesis, Accumulation, and Applications of a Model Microalga Euglenagracilis. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomečková, L.; Tomčala, A.; Oborník, M.; Hampl, V. The Lipid Composition of Euglena gracilis Middle Plastid Membrane Resembles That of Primary Plastid Envelopes. Plant Physiol. 2020, 184, 2052–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, U.-C.; Choi, J.K.; Kang, C.; Choi, B.-D.; Kang, S.-J. Effects of Culture Methods on the Growth Rates and Fatty Acid Profiles of Euglena gracilis. Korean J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2016, 49, 38–44. [Google Scholar]
- Yoval-Sánchez, B.; Jasso-Chávez, R.; Lira-Silva, E.; Moreno-Sánchez, R.; Rodríguez-Zavala, J.S. Novel mitochondrial alcohol metabolizing enzymes of Euglena gracilis. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 2011, 43, 519–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulut, O.; Köse, I.E.; Sönmez, Ç.; Öktem, H.A. Antioxidant activity of Micractinium sp. (Chlorophyta) extracts against H(2)O(2) induced oxidative stress in human breast adenocarcinoma cells. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 27593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedard, S.; Roxborough, E.; O’Neill, E.; Mangal, V. The biomolecules of Euglena gracilis: Harnessing biology for natural solutions to future problems. Protist 2024, 175, 126044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Q.; Hu, L.; Qin, H.; Liu, Y.; Tang, X.; Lei, A.; Wang, J. Metabolomic response of Euglena gracilis and its bleached mutant strain to light. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0224926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattahi, S.; Zabihi, E.; Abedian, Z.; Pourbagher, R.; Motevalizadeh Ardekani, A.; Mostafazadeh, A.; Akhavan-Niaki, H. Total Phenolic and Flavonoid Contents of Aqueous Extract of Stinging Nettle and In Vitro Antiproliferative Effect on Hela and BT-474 Cell Lines. Int. J. Mol. Cell Med. 2014, 3, 102–107. [Google Scholar]
- Shraim, A.M.; Ahmed, T.A.; Rahman, M.M.; Hijji, Y.M. Determination of total flavonoid content by aluminum chloride assay: A critical evaluation. LWT 2021, 150, 111932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Z.; Lu, Y.; Zhou, G.; Hui, F.; Xu, L.; Viau, C.; Spigelman, A.F.; MacDonald, P.E.; Wishart, D.S.; Li, S.; et al. MetaboAnalyst 6.0: Towards a unified platform for metabolomics data processing, analysis and interpretation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, W398–W406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Inwongwan, S.; Sriwari, S.; Pumas, C. Metabolomic Insights into the Adaptations and Biotechnological Potential of Euglena gracilis Under Different Trophic Conditions. Plants 2025, 14, 1580. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14111580
Inwongwan S, Sriwari S, Pumas C. Metabolomic Insights into the Adaptations and Biotechnological Potential of Euglena gracilis Under Different Trophic Conditions. Plants. 2025; 14(11):1580. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14111580
Chicago/Turabian StyleInwongwan, Sahutchai, Sutthiphat Sriwari, and Chayakorn Pumas. 2025. "Metabolomic Insights into the Adaptations and Biotechnological Potential of Euglena gracilis Under Different Trophic Conditions" Plants 14, no. 11: 1580. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14111580
APA StyleInwongwan, S., Sriwari, S., & Pumas, C. (2025). Metabolomic Insights into the Adaptations and Biotechnological Potential of Euglena gracilis Under Different Trophic Conditions. Plants, 14(11), 1580. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14111580





