The Alkaloid Gelsemine Reduces Aβ Peptide Toxicity by Targeting Transglutaminase Type 2 Enzyme
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. In Silico Binding of Gelsemium Alkaloids to TG2
2.2. In Vitro Gelsemine Inhibition of Recombinant TG2 Activity
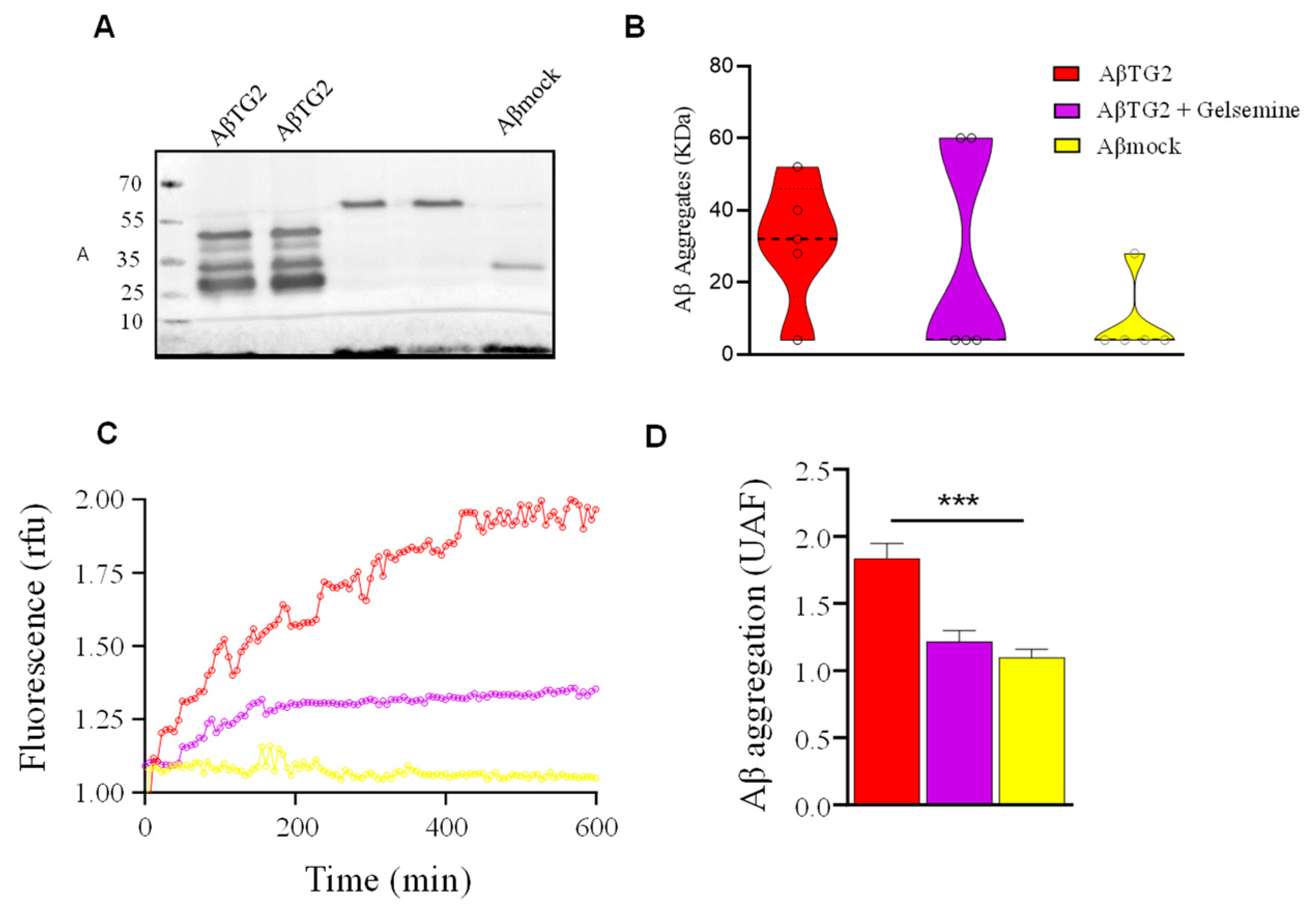
2.3. Altered β-Amyloid Aggregation by Gelsemine in the Presence of TG2
2.4. Functional Validation of Gelsemine Neuroprotective Actions in a Neuronal Model of AD
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Aβ | β-amyloid peptide |
| AD | Alzheimer’s disease |
| TG2 | Transglutaminase type 2 |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor-alpha |
| EGFR | Epidermal growth factor recepto |
| CDK2 | Cyclin-dependent kinase 2 |
| MAPK3 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 3 |
| MMGBSA | Molecular Mechanics/Generalized Born Surface Area |
| ΔG | Gibbs free energy change |
| Z-DON | 6-diazo-5-oxo-norleucine tetrapeptide, TG2 Inhibitor |
References
- Jin, G.L.; Su, Y.P.; Liu, M.; Xu, Y.; Yang, J.; Liao, K.J.; Yu, C.X. Medicinal plants of the genus Gelsemium (Gelsemiaceae, Gentianales)—A review of their phytochemistry, pharmacology, toxicology and traditional use. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 152, 33–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutt, V.; Thakur, S.; Dhar, V.J.; Sharma, A. The genus Gelsemium: An update. Pharmacogn. Rev. 2010, 4, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.Y.; Wang, Y.X. Gelsemium analgesia and the spinal glycine receptor/allopregnanolone pathway. Fitoterapia 2015, 100, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Y.; Gong, N.; Huang, J.L.; Guo, L.C.; Wang, Y.X. Gelsemine, a principal alkaloid from Gelsemium sempervirens Ait., exhibits potent and specific antinociception in chronic pain by acting at spinal alpha3 glycine receptors. Pain 2013, 154, 2452–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.E.; Li, Y.D.; Luo, Y.J.; Wang, T.X.; Wang, H.J.; Chen, S.N.; Qu, W.M.; Huang, Z.L. Gelsemine alleviates both neuropathic pain and sleep disturbance in partial sciatic nerve ligation mice. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2015, 36, 1308–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoaib, R.M.; Zhang, J.Y.; Mao, X.F.; Wang, Y.X. Gelsemine and koumine, principal active ingredients of Gelsemium, exhibit mechanical antiallodynia via spinal glycine receptor activation-induced allopregnanolone biosynthesis. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2019, 161, 136–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Huang, H.H.; Yang, J.; Su, Y.P.; Lin, H.W.; Lin, L.Q.; Liao, W.J.; Yu, C.X. The active alkaloids of Gelsemium elegans Benth. are potent anxiolytics. Psychopharmacology 2013, 225, 839–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, L.; Boujedaini, N.; Patte-Mensah, C.; Mensah-Nyagan, A.G. Pharmacological effect of gelsemine on anxiety-like behavior in rat. Behav. Brain Res. 2013, 253, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Tang, M.H.; Zeng, Z.Y.; Huang, S.J.; Zheng, X.F.; Liu, Z.Y. Suppressive Effects of Gelsemine on Anxiety-like Behaviors Induced by Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress in Mice. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Chen, C.; Wang, L. Gelsemine Exerts Neuroprotective Effects on Neonatal Mice with Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Injury by Suppressing Inflammation and Oxidative Stress via Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway. Neurochem. Res. 2023, 48, 1305–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Pan, H.; Bai, Y.; Li, H.; Yang, W.; Lin, Z.X.; Cui, W.; Xian, Y.F. Gelsemine, a natural alkaloid extracted from Gelsemium elegans Benth. alleviates neuroinflammation and cognitive impairments in Aβ oligomer-treated mice. Psychopharmacology 2020, 237, 2111–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, M.Y.; Shen, W.Z.; Wu, Y.H.; Cao, C.S.; Zhang, D.M.; Gao, J.H. Study on anti-proliferation activity and the mechanisms of alkaloid monomers from Gelsemium elegans on HepG2 cell in vitro. Zhong Yao Cai 2012, 35, 438–442. [Google Scholar]
- Venard, C.; Boujedaini, N.; Belon, P.; Mensah-Nyagan, A.; Patte-Mensah, C. Regulation of neurosteroid allopregnanolone biosynthesis in the rat spinal cord by glycine and the alkaloidal analogs strychnine and gelsemine. Neuroscience 2008, 153, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venard, C.; Boujedaini, N.; Mensah-Nyagan, A.G.; Patte-Mensah, C. Comparative Analysis of Gelsemine and Gelsemium sempervirens Activity on Neurosteroid Allopregnanolone Formation in the Spinal Cord and Limbic System. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2011, 2011, 407617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lara, C.O.; Murath, P.; Munoz, B.; Marileo, A.M.; Martin, L.S.; San Martin, V.P.; Burgos, C.F.; Mariqueo, T.A.; Aguayo, L.G.; Fuentealba, J.; et al. Functional modulation of glycine receptors by the alkaloid gelsemine. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 173, 2263–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marileo, A.M.; Gavilán, J.; San Martín, V.P.; Lara, C.O.; Sazo, A.; Muñoz-Montesino, C.; Castro, P.A.; Burgos, C.F.; Leiva-Salcedo, E.; Aguayo, L.G.; et al. Modulation of GABA(A) receptors and of GABAergic synapses by the natural alkaloid gelsemine. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 1083189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Que, W.; Wu, Z.; Chen, M.; Zhang, B.; You, C.; Lin, H.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, M.; Qiu, H.; Cheng, Y. Molecular Mechanism of Gelsemium elegans (Gardner and Champ.) Benth. Against Neuropathic Pain Based on Network Pharmacology and Experimental Evidence. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 792932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.H.; Chen, Y.X.; Fang, J.Y. Comprehensive review of targeted therapy for colorectal cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marileo, A.M.; Lara, C.O.; Sazo, A.; Contreras, O.V.; González, G.; Castro, P.A.; Aguayo, L.G.; Moraga-Cid, G.; Fuentealba, J.; Burgos, C.F.; et al. Molecular Pharmacology of Gelsemium Alkaloids on Inhibitory Receptors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Huang, T.; Pan, L.; Ding, J.; Liu, Z. Experimental and Computational Investigation of the Target and Mechanisms of Gelsemium Alkaloids in the Central Nervous System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Qiu, H.-Q.; Liu, H.; Liu, M.; Huang, Z.-Y.; Yang, J.; Su, Y.-P.; Yu, C.-X. Effects of koumine, an alkaloid of Gelsemium elegans Benth., on inflammatory and neuropathic pain models and possible mechanism with allopregnanolone. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2012, 101, 504–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, B.J.; Xu, Y.; Jin, G.L.; Liu, M.; Yang, J.; Yu, C.X. Analgesic effects and pharmacologic mechanisms of the Gelsemium alkaloid koumine on a rat model of postoperative pain. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rujjanawate, C.; Kanjanapothi, D.; Panthong, A. Pharmacological effect and toxicity of alkaloids from Gelsemium elegans Benth. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2003, 89, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Shen, J.; Liu, H.; Xu, Y.; Su, Y.-P.; Yang, J.; Yu, C.-X. Gelsenicine from Gelsemium elegans attenuates neuropathic and inflammatory pain in mice. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2011, 34, 1877–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Q.; Liu, M.; Wu, M.X.; Xu, Y.; Yang, J.; Huang, H.H.; Yu, C.X. Anti-allodynic and neuroprotective effects of koumine, a Benth alkaloid, in a rat model of diabetic neuropathy. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2014, 37, 858–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Zheng, J.; Zhu, W.; Jia, N. Nephroprotective effect of gelsemine against cisplatin-induced toxicity is mediated via attenuation of oxidative stress. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2015, 71, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillen, H. Editorial: Beta-Amyloid oligomer specific treatments for Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1034158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panes-Fernandez, J.; Godoy, P.A.; Gavilan, J.; Ramírez-Molina, O.; Burgos, C.F.; Marileo, A.; Flores-Núñez, O.; Castro, P.A.; Moraga-Cid, G.; Yévenes, G.E.; et al. TG2 promotes amyloid beta aggregates: Impact on ER-mitochondria crosstalk, calcium homeostasis and synaptic function in Alzheimer’s disease. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 162, 114596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, M.; Khosla, C. Transglutaminase 2 inhibitors and their therapeutic role in disease states. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 115, 232–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, B.; Chung, K.C. New insight into transglutaminase 2 and link to neurodegenerative diseases. BMB Rep. 2018, 51, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ientile, R.; Currò, M.; Caccamo, D. Transglutaminase 2 and neuroinflammation. Amino Acids 2015, 47, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilhelmus, M.M.M.; Tonoli, E.; Coveney, C.; Boocock, D.J.; Jongenelen, C.A.M.; Brevé, J.J.P.; Verderio, E.A.M.; Drukarch, B. The Transglutaminase-2 Interactome in the APP23 Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Cells 2022, 11, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Mouradian, M.M. Pathogenetic Contributions and Therapeutic Implications of Transglutaminase 2 in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilhelmus, M.M.; Grunberg, S.C.; Bol, J.G.; van Dam, A.M.; Hoozemans, J.J.; Rozemuller, A.J.; Drukarch, B. Transglutaminases and transglutaminase-catalyzed cross-links colocalize with the pathological lesions in Alzheimer’s disease brain. Brain Pathol. 2009, 19, 612–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinkas, D.M.; Strop, P.; Brunger, A.T.; Khosla, C. Transglutaminase 2 undergoes a large conformational change upon activation. PLoS Biol. 2007, 5, e327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.Y.; Hung, K.W.; Lau, S.F.; Butt, B.; Yuen, V.W.; Fu, G.; Chan, I.C.; Ip, F.C.F.; Fu, A.K.Y.; Ip, N.Y. Rhynchophylline Administration Ameliorates Amyloid-β Pathology and Inflammation in an Alzheimer’s Disease Transgenic Mouse Model. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2021, 12, 4249–4256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Q.; Ip, S.P.; Yuan, Q.J.; Zheng, G.Q.; Tsim, K.K.W.; Dong, T.T.X.; Lin, G.; Han, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xian, Y.F.; et al. Isorhynchophylline ameliorates cognitive impairment via modulating amyloid pathology, tau hyperphosphorylation and neuroinflammation: Studies in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Behav. Immun. 2019, 82, 264–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currò, M.; Ferlazzo, N.; Condello, S.; Caccamo, D.; Ientile, R. Transglutaminase 2 silencing reduced the beta-amyloid-effects on the activation of human THP-1 cells. Amino Acids 2010, 39, 1427–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staffler, R.; Pasternack, R.; Hils, M.; Kaiser, W.; Möller, F.M. Nucleotide binding kinetics and conformational change analysis of tissue transglutaminase with switchSENSE. Anal. Biochem. 2020, 605, 113719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shi, L.; Yang, K.; Liu, X.; Lv, X. Transglutaminase 2 regulates terminal erythroid differentiation via cross-linking activity. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 1183176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, B.R.; Yunes-Medina, L.; Johnson, G.V.W. Transglutaminase 2: Friend or foe? The discordant role in neurons and astrocytes. J. Neurosci. Res. 2018, 96, 1150–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panes, J.D.; Godoy, P.A.; Silva-Grecchi, T.; Celis, M.T.; Ramirez-Molina, O.; Gavilan, J.; Muñoz-Montecino, C.; Castro, P.A.; Moraga-Cid, G.; Yévenes, G.E.; et al. Changes in PGC-1α/SIRT1 Signaling Impact on Mitochondrial Homeostasis in Amyloid-Beta Peptide Toxicity Model. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Compound | Docking Score | ∆G Binding (kcal/mol) | Binding Site Residues (4Å Distance) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gelsemine (1′R,2′S,3S,5′S, 6′S,8′R,11′S) | −2.911 | −32.24 | R296, W341, Y351, E352, G353, W354, P375, V376, R377, K380, H441, T442 |
| Gelsemine (1′R,2′R,3R,5′S,6′S,8′R,11′S) | −2.650 | −33.19 | W341, E352, G353, W354, V376, R377, K380, T442 |
| Koumine | −2.511 | −31.35 | W341, G350, E352, G353, W354, V376, R377, K380, T442 |
| Gelsevirine (1R,2S,5S,6S,7S,8R, 11S) | −3.964 | −22.07 | L150, E155, Y159, R296, W341, W354, V431, E437, I439, H441, T442 |
| Gelsevirine (1R,5S,6S,7S,8S) | −3.514 | −40.72 | W341, Y351, E352, G353, W354, Q355, P375, V376, R377, K380, T442 |
| Gelsevirine (1R,2S,5S,6R,7S,8R, 11S) | −1.237 | −41.50 | R296, E339, W341, G350, Y351, E352, G353, W354, Q355, P375, V376, R377, K380, T442 |
| Gelsenicine | −2.204 | −21.77 | R296, E339, W341, G350, Y351, E352, G353, W354, Q355, K380, I439, T442 |
| Z-DON | −2.095 | −46.99 | L150, D151, S152, E153, E154, Y159, R296, E339, W341, G350, Y351, E352, G353, W354, Q355, P375, V376, R377, A378, S430, V431, R433, E437, I439, T442 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Panes-Fernández, J.; Marileo, A.M.; Espinoza-Rubilar, N.; Meza, M.E.; Salgado-Martínez, B.A.; Gaete-Riquelme, K.; Moraga-Cid, G.; Castro, P.A.; Burgos, C.F.; Fuentealba, J.; et al. The Alkaloid Gelsemine Reduces Aβ Peptide Toxicity by Targeting Transglutaminase Type 2 Enzyme. Plants 2025, 14, 1556. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14101556
Panes-Fernández J, Marileo AM, Espinoza-Rubilar N, Meza ME, Salgado-Martínez BA, Gaete-Riquelme K, Moraga-Cid G, Castro PA, Burgos CF, Fuentealba J, et al. The Alkaloid Gelsemine Reduces Aβ Peptide Toxicity by Targeting Transglutaminase Type 2 Enzyme. Plants. 2025; 14(10):1556. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14101556
Chicago/Turabian StylePanes-Fernández, Jessica, Ana M. Marileo, Nicole Espinoza-Rubilar, Macarena E. Meza, Bernardita A. Salgado-Martínez, Krishna Gaete-Riquelme, Gustavo Moraga-Cid, Patricio A. Castro, Carlos F. Burgos, Jorge Fuentealba, and et al. 2025. "The Alkaloid Gelsemine Reduces Aβ Peptide Toxicity by Targeting Transglutaminase Type 2 Enzyme" Plants 14, no. 10: 1556. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14101556
APA StylePanes-Fernández, J., Marileo, A. M., Espinoza-Rubilar, N., Meza, M. E., Salgado-Martínez, B. A., Gaete-Riquelme, K., Moraga-Cid, G., Castro, P. A., Burgos, C. F., Fuentealba, J., & Yévenes, G. E. (2025). The Alkaloid Gelsemine Reduces Aβ Peptide Toxicity by Targeting Transglutaminase Type 2 Enzyme. Plants, 14(10), 1556. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14101556







