Role of Different Abiotic Factors in Inducing Pre-Harvest Physiological Disorders in Radish (Raphanus sativus)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Physiological Disorders in Radish
2.1. Forking/Branching
2.2. Pithiness
2.3. Splitting/Cracking
2.4. Hollowness
2.5. Internal Browning/Brown Heart/Akashin
3. Field Observations
Strategies to Reduce Physiological Disorders
- (a)
- Forking
- (b)
- Pithiness
- (c)
- Splitting/cracking
- (d)
- Hollowing
- (e)
- Internal Browning
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kaymak, H.C.; Guvenc, I.; Gurol, A. Correlation between endogenous elements and development of hollowing in the root of radish (Raphanus sativus L.) cultivars. Zemdirbyste 2010, 97, 97–104. [Google Scholar]
- Song, D.; Song, L.; Sun, Y.; Hu, P.; Tu, K.; Pan, L.; Yang, H.; Huang, M. Black heart detection in white radish by hyperspectral transmittance imaging combined with chemometric analysis and a successive projections algorithm. Appl. Sci. 2016, 6, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Choi, S.R.; Chhapekar, S.S.; Lu, L.; Ma, Y.; Lee, J.Y.; Hong, S.; Kim, Y.Y.; Oh, S.H.; Lim, Y.P. Genetic and physiological analyses of root cracking in radish (Raphanus sativus L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2019, 132, 3425–3437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lockley, R.A.; Beacham, A.M.; Grove, I.G.; Monaghan, J.M. Postharvest temperature and water status influence postharvest splitting susceptibility in summer radish (Raphanus sativus L.). J. Sci. Food. Agric. 2021, 101, 536–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghimire, S.; Adhikari, B.; Pandey, S.; Belbase, K.; Lamichhane, S.; Pathak, R. Effect of different organic manure on growth and yield of radish in Deukhuri, Dang, Nepal. Acta Sci. Agric. 2020, 4, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel, C.G. Physiological disorders of four radish (Raphanus sativus L. var. sativus) cultivars storage roots grown in controlled cabinets under varying temperatures and irrigation levels. Int. J. Farm. Allied Sci. 2016, 5, 185–198. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, D.R.; Nguyen, V.Q.; Seberry, J.A.; Haigh, A.M.; McGlasson, W.B. Growth and postharvest performance of white radish (Raphanus sativus L.). Aust. J. Exp. Agric. 2000, 40, 879–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladaniya, M.S. Physiological Disorders and Their Management. In Citrus Fruit: Biology, Technology and Evaluation; Ladaniya, M.S., Ed.; Elsevier Publishing Services: Chennai, India, 2008; pp. 451–454. [Google Scholar]
- Masarirambi, M.T.; Nxumalo, K.A.; Musi, P.J.; Rugube, L.M. Common physiological disorders of lettuce (Lactuca sativa) found in Swaziland: A review. Am.-Eurasian J. Agric. Environ. Sci. 2018, 18, 50–56. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.; Ma, Y.Y.; Liu, W.; Qiu, F. Plant Nutrition and Physiological Disorders in Fruit Crops. In Fruit Crops: Diagnosis and Management of Nutrient Constraints; Srivastava, A.K., Hu, C., Eds.; Elsevier Publishers: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 47–50. [Google Scholar]
- Yahia, E.M.; Carrillo-Lopez, A.; Sanudo, A. Physiological Disorders and Their Control. In Postharvest Technology of Perishable Horticultural Commodities; Yahia, E.M., Ed.; Elsevier Publishers: Oxford, UK, 2019; pp. 499–500. [Google Scholar]
- Peet, M.M. Physiological disorders in tomato fruit development. Acta Hortic. 2009, 821, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neerja, S. Physiological disorders in solanaceous and bulb crops: A review. Int. J. Agric. Sci. 2016, 8, 2566–2568. [Google Scholar]
- Bhat, K.L. Physiological Disorders of Vegetable Crops; Daya Publishing House: Delhi, India, 2009; pp. 73–116. [Google Scholar]
- Kathayat, K.; Rawat, M. Physiological Disorders in Vegetable Crops. In Advances in Horticultural Crop Management and Value Addition; Singh, S.K., Kaur, S., Eds.; Laxmi Publications: New Delhi, India, 2019; pp. 313–314. [Google Scholar]
- Subedi, S.; Srivastava, A.; Sharma, M.D.; Shah, S.C. Effect of organic and inorganic nutrient sources on growth, yield and quality of radish (Raphanus sativus L.) varieties in Chitwan, Nepal. SAARC J. Agric. 2018, 16, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavanya, A.V.N.; Vani, V.S.; Reddy, P.S.S.; Shashikala, P. Root yield of radish as affected by sowing dates and spacing. Int. J. Pure Appl. Biosci. 2017, 5, 1780–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dongarwar, L.N.; Kashiwar, S.R.; Ghawade, S.M.; Dongarwar, U.R. Performance of different radish (Raphanus sativus L.) varieties in black soils of Vidharbha-Maharashtra. Int. J. Plant Soil Sci. 2017, 20, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, E.S.; Ha, S.M.; Cheong, S.R.; Seo, M.W.; Kwack, Y.B.; Choi, K.J.; Chae, W.B. Optimum double-row spacing in the autumn cultivation of radish (Raphanus sativus L.). Korean J. Environ. Agric. 2015, 34, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdel, C.G. Production of well irrigated radishes (Raphanus sativus L.): 5–The influence of gibberellic acid (GA3) on growth and yield of local black radish cultivars grown under plot and furrow cultivations methods. J. Dohuk Univ. 2007, 10, 40–49. [Google Scholar]
- Sonneveld, C.; Van den Bos, A.L. Effects of nutrient levels on growth and quality of radish (Raphanus sativus L.) grown on different substrates. J. Plant Nutr. 1995, 18, 501–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalski, A.; Kaniszewski, S. Effect of organic fertilization on the quality and yield of two radish cultivars in greenhouse organic cultivation. Acta Hortic. 2017, 1164, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockley, R.A. Minimising Post-Harvest Losses in Radishes through an Understanding of Pre and Post-Harvest Factors That Influence Root Splitting. Ph.D. Thesis, Harper Adams University, Newport, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Monaghan, J.M.; Chiramba, T.; Mogren, L.M. Effect of pre- and postharvest factors on splitting in radish (Raphanus sativus). Acta Hortic. 2012, 934, 1347–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaymak, H.C.; Guvenc, I. Evaluation of radish cultivars in terms of some physiological disorders. TUBAV J. Sci. 2010, 3, 23–29. [Google Scholar]
- Konarska, A. Changes in development and structure of Raphanus sativus L. var. radicula Pers. root under aluminum stress condition. Acta Sci. Pol. Hortorum Cultus 2005, 4, 85–97. [Google Scholar]
- Torres, J.F.; Siurana, D.; Bono, M.S.; Laza, P.; Pascual-Seva, N.; San Bautista, A.; Pascual, B.; Alagarda, J.; López-Galarza, S.; Maroto, J.V. Influence of growing media on physiological disorders incidence in oriental radishes. Acta Hortic. 2013, 1013, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kano, Y.; Fukuoka, N. Effects of soil temperature on hollowness in Japanese radish (Raphanus sativus L. cv. ‘Gensuke’). Sci. Hort. 1995, 61, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kano, Y. Roles of temperature in the occurrence of hollow root in Japanese radish cv. ‘Gensuke’. J. Jpn. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 1987, 56, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fukuoka, N.; Kudou, T.; Sajiki, T.; Masuda, D.; Kanamori, Y.; Enomoto, T. Statistical analysis of the development of internal browning in Japanese radish [Raphanus sativus] in relation to thermal condition using logit model. Hortic. Res. 2007, 6, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sotta, N.; Bian, B.; Peng, D.; Hongkham, P.; Kamiya, T.; Niikura, S.; Fujiwara, T. Local boron concentrations in tuberous roots of Japanese radish (Raphanus sativus L.) negatively correlate with distribution of brown heart. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 136, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuoka, N.; Enomoto, T. Relationship between the concentration of pectin-like substances and the severity of internal browning in radish (Raphanus sativus L.) roots induced by high soil temperature. J. Hortic. Sci. Biotechnol. 2014, 89, 625–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Roy, S.; Karmakar, P.; Chaurasia, S.N.S.; Gupta, S.; Singh, B. Improved Production Technologies in Vegetable Crops; IIVR Training Manual No. 59; ICAR-Indian Institute of Vegetable Research: Varanasi, India, 2015; pp. 268–269.
- Tyagi, S.K.; Khire, A.R. Physiological and Nutritional Disorders in Vegetable Crops. In Vegetable Crops at a Glance; Tyagi, S.K., Khire, A.R., Eds.; Scientific Publishers: Jodhpur, India, 2018; pp. 432–435. [Google Scholar]
- Nishio, T. Economic and Academic Importance of Radish. In The Radish Genome; Nishio, T., Kitashiba, H., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, P.; Kumar, P.; Singh, M.K.; Kumar, R. Treasure of Vegetable Crops, 1st ed.; Sankalp Publication: Chhattisgarh, India, 2020; pp. 181–183. [Google Scholar]
- Lavanya, A.V.N.; Vani, V.S.; Reddy, P.S.S.; Chaitanya, K. Effect of sowing dates and spacing on growth and root yield of radish cv. Pusa chetki. Plant Arch. 2014, 14, 615–618. [Google Scholar]
- Asano, J. Effect of organic manures on quality of vegetables. Jpn. Agric. Res. Q. 1984, 18, 31–36. [Google Scholar]
- Heij, G.; Kobryn, J. Influence of day temperature and salt concentration on the incidence of sponginess in radish tubers (Raphanus sativus L.). NJAS Wagen. J. Life Sci. 1988, 36, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akoumianakis, K.A.; Karapanos, I.C.; Giakoumaki, M.; Alexopoulos, A.A.; Passam, H.C. Nitrogen, season and cultivar affect radish growth, yield, sponginess and hollowness. Int. J. Plant Prod. 2011, 5, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcelis, L.F.M.; Heuvelink, E.; Van Dijk, D. Pithiness and growth of radish tubers as affected by irradiance and plant density. Ann. Bot. 1997, 79, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Magendans, J.F.C. Elongation and contraction of the plant axis and development of spongy tissues in the radish tuber (Raphanus sativus L. cv. Saxa Nova). Agric. Univ. Wagening. Pap. 1991, 91, 1–57. [Google Scholar]
- Rubatzky, V.E.; Yamaguchi, M. World Vegetables: Principles, Production, and Nutritive Values; Springer Science & Business Media: Cham, Switzerland, 2012; pp. 411–412. [Google Scholar]
- Sadana, A.; Raju, S.S.; Kumar, P.V.; Sunitha, C. Effect of spacing and seed soaking with GA3 on growth, yield and quality of radish (Raphanus sativus L.). Andhra Pradesh J. Agric. Sci. 2015, 1, 80–84. [Google Scholar]
- Bonasia, A.; Gonnella, M.; Santamaria, P.; Elia, A. Substrate re-use affects yield and quality of seven radish cultivars grown in a closed soilless system. Acta Hortic. 2001, 548, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockley, R.A.; Grove, I.G.; Monaghan, J.M. Splitting in radish–does preharvest environment influence the response to postharvest handling? Acta Hortic. 2015, 1091, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockley, R.A.; Grove, I.G.; Monaghan, J.M. Minimising losses in radish (Raphanus sativus) at harvest due to splitting by manipulation of water availability during growth. Acta Hortic. 2016, 1118, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, S.; Kang, Y. Effect of drip irrigation frequency on radish (Raphanus sativus L.) growth and water use. Irrig. Sci. 2006, 24, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maia, A.H.; de Souza, M.E.; da Silva, F.C.; Rebelatto, B.F.; Silva, T.O.; Souza, V.S.; dos Santos Ferreira, L. Productivity of radish fertilized with different doses of bovine manure. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2018, 13, 963–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cecilio Filho, A.B.; Dutra, A.F.; Silva, G.S.D. Phosphate and potassium fertilization for radish grown in a latosol with a high content of these nutrients. Rev. Caatinga 2017, 30, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Sharma, D.D.; Singh, G.; Thakur, K.K.; Kumar, S. Physiological Disorders and Their Management in Apple and Pear Fruits Production; AkiNik Publications: New Delhi, India, 2019; Volume 3, pp. 1–125. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Guo, L.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, Y.; Hao, Z.; Luo, H.; Yuan, Z. Advances in Mechanisms and Omics Pertaining to Fruit Cracking in Horticultural Plants. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kano, Y.; Fukuoka, N. Relationship between the occurrence of hollowing and lignification of parenchymatous cells in the root of Japanese radish cv. Gensuke. J. Jpn. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 1992, 61, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kano, Y.; Fukuoka, N. Suppressive effects of CPPU on lignification of xylem parenchymatous cells and on hollowing in the root of Japanese radish (Raphanus sativus L.). Sci. Hortic. 1996a, 65, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kano, Y.; Fukuoka, N. Effect of planting density on the occurrence of hollow root in Japanese radish cv. Gensuke. J. Jpn. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 1991, 60, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fukuoka, N.; Kano, Y. Relationship between the development of hollowing and the separation of vessel sectors in the central region of the root of Japanese radish (Raphanus sativus L.). Sci. Hortic. 1997, 68, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuoka, N. Effect of cytokinin and auxin application on vessel differentiation and development of hollow cavity in the roots of Japanese radish (Raphanus sativus L.). J. Jpn. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 2007, 76, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kano, Y.; Fukuoka, N. Effects of auxin application on the lignification of xylem parenchymatous cells and the development of hollowness in the root of Japanese radish (Raphanus sativus L.). J. Hortic. Sci. 1996, 71, 791–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kano, Y. Effects of time of high and low temperature treatments on the growth of Japanese radish cv. ‘Gensuke’ and on the occurrence of hollow root. J. Jpn. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 1989, 57, 626–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kano, Y.; Fukuoka, N. Role of endogenous cytokinin in the development of hollowing in the root of Japanese radish (Raphanus sativus L.). Sci. Hortic. 1996, 65, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuoka, N.; Kano, Y. The difference in the development of hollowness in roots of ‘Gensuke’ radish between the early and late sowing of seeds. J. Jpn. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 1992, 60, 881–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fukuoka, N.; Ikeshita, Y.; Enomoto, T. Relationship between the occurrence of internal browning and size of xylem parenchymatous cells in roots of Japanese radish. J. Jpn. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 2010, 79, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kawashiro, H.; Takeda, H. Studies on factors influencing the occurrence of akashin a physiological disorder in radish, 1: Influences of temperature and cultivars. Bull. Chiba-Ken Agric. Exp. Stat. 1988, 29, 63–70. [Google Scholar]
- National Institute of Industrial Research. Cultivation of Fruits, Vegetables and Floriculture; NIIR Project Consultancy Services (NPSC); Kamla Nagar: New Delhi, India, 2005; pp. 425–426. [Google Scholar]
- Barker, A.V.; Bryson, G.M. Nitrogen. In Handbook of Plant Nutrition, 2nd ed.; Barker, A.V., Pilbeam, D.J., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; pp. 37–66. [Google Scholar]
- Dhaliwal, M.S. Handbook of Vegetable Crops; Kalyani Publishers: New Delhi, India, 2007; pp. 120–199. [Google Scholar]
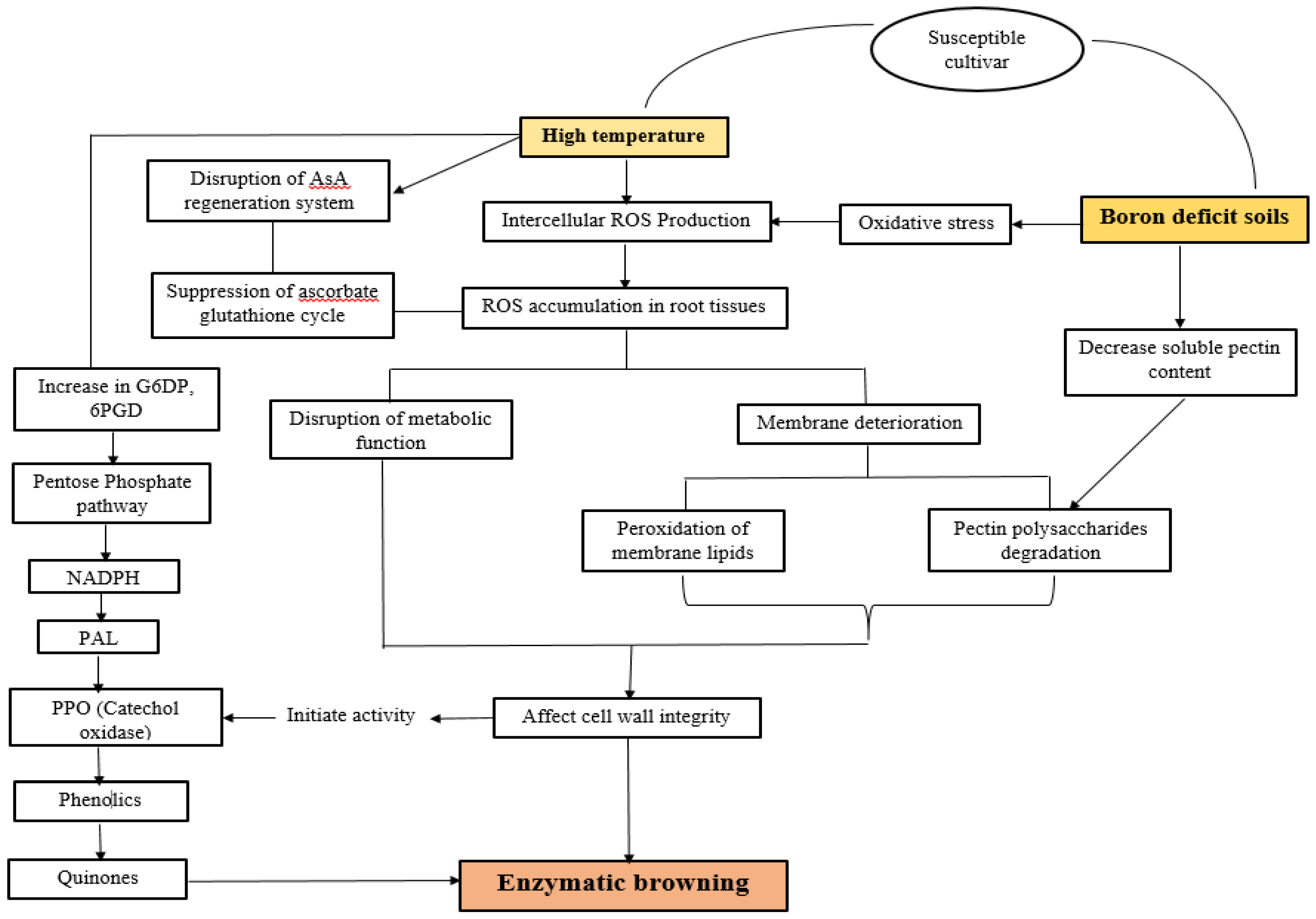
- Fukuoka, N.; Hamada, T. Effects of heat stress on the biological maillard reaction, oxidative stress, and occurrence of internal browning in Japanese radish (Raphanus sativus L.). J. Plant Physiol. 2020, 256, 153326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuoka, N.; Enomoto, T. Enzyme activity changes in relation to internal browning of Raphanus roots sown early and late. J. Hortic. Sci. Biotechnol. 2002, 77, 456–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuoka, N.; Enomoto, T. The occurrence of internal browning induced by high soil temperature treatment and its physiological function in Raphanus root. Plant Sci. 2001, 161, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuoka, N.; Miyata, M.; Hamada, T.; Takeshita, E. Occurrence of internal browning in tuberous roots of sweet potato and its related starch biosynthesis. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 135, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuoka, N.; Enomoto, T. Effects of sulfur application on enzyme activities in relation to the ascorbate-glutathione cycle and the occurrence of internal browning in Raphanus roots. J. Jpn. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 2007, 76, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, T.; Hikawa, M.; Fujisawa, T. Effect of foliar spray of gibberellin on the incidence of internal browning in roots of Japanese radish. J. Jpn. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 1997, 66, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuoka, N.; Enomoto, T. Intervarietal differences in the occurrence of internal browning and the role of ascorbic acid in Raphanus roots. J. Jpn. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 2007, 76, 144–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
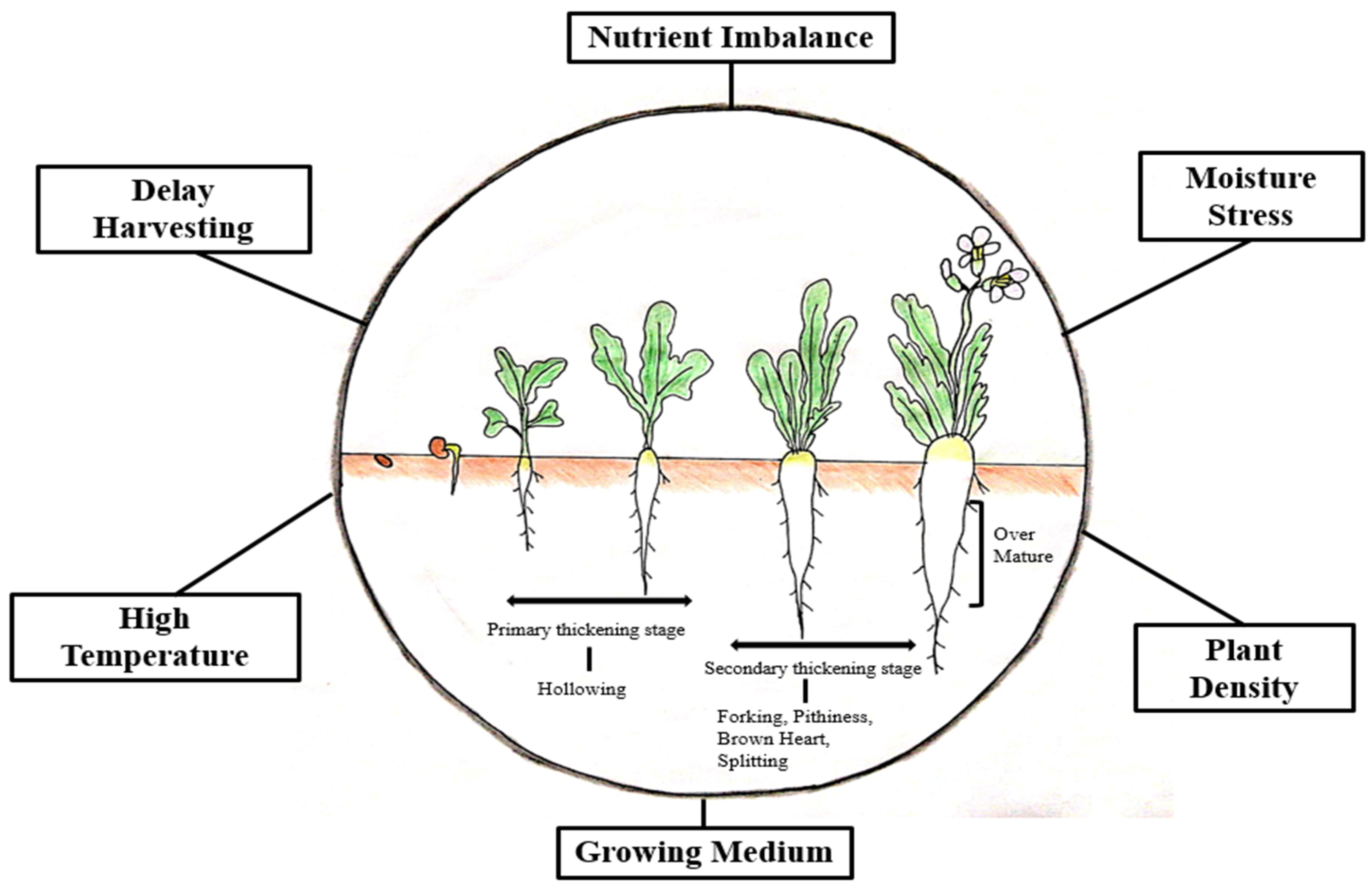




| Disorder | Abiotic Factor | Reason | Control | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Forking | Undecomposed organic matter in soil | Excessive root elongation | Use well decomposed organic matter | [16] |
| High plant density | Competition between moisture, light and nutrient increase | Maintain optimum plant density | [17] | |
| Pithiness | Delay harvesting | Development of larger cells leads to pithiness | Harvest radishes at right time | [18] |
| Plant spacing | Double row spacing (45 × 25)/wider spacing causes root enlargement | Plant radish at recommended plant and row spacing | [19] | |
| Cultivation method | Furrow cultivation leads to rapid root growth | Cultivate radish on flat beds | [20] | |
| Growing substrate | Sand increase growth rate | Use well balanced growing medium | [21] | |
| Splitting/cracking | High organic fertilization (nitrogen) | Cause parenchyma cells to expand at higher rate | Provide optimum nitrogen doses to avoid excessive cell growth | [22] |
| High water content of growing medium | Rapid cell enlargement during secondary thickening | Maintain optimum level of growing media water content | [23] | |
| Irrigation irregularity | [24,25] | |||
| Heavy metal toxicity in acidic soils | Aluminum toxicity leads to disturbance in cell anatomy | Improve soil pH | [26] | |
| Hollowness | Growing medium (coir dust)Over maturity | Increase expansion of parenchyma cells | Cultivate radish on well balanced growing mediumHarvest roots at right time | [27] |
| Varietal effect | Hollowness susceptible cultivars has rapid rate of cell enlargement | Plant cultivars tolerant to hollowness disorder | [25] | |
| Nutrient imbalance | High N causes cell expansion | Provide optimum nitrogen doses to avoid excessive cell growth | [1] | |
| High soil temperature | Increase cell lignification that promote hollowness | Plant radish during low temperature | [28,29] | |
| Internal browning | High air and soil temp | Increase enzymatic activity | Controlled temperature during later growth period | [30] |
| Nutrient imbalance | Boron deficiency affect cell wall firmness | Provide micronutrient at optimum rate | [31] | |
| Genetic effect | Resistant cultivars had high pectin content | Plant cultivars tolerant to brown heart | [32] |
| Disorder | Cause/Abiotic Factor | Cultivar | Pictorial View |
|---|---|---|---|
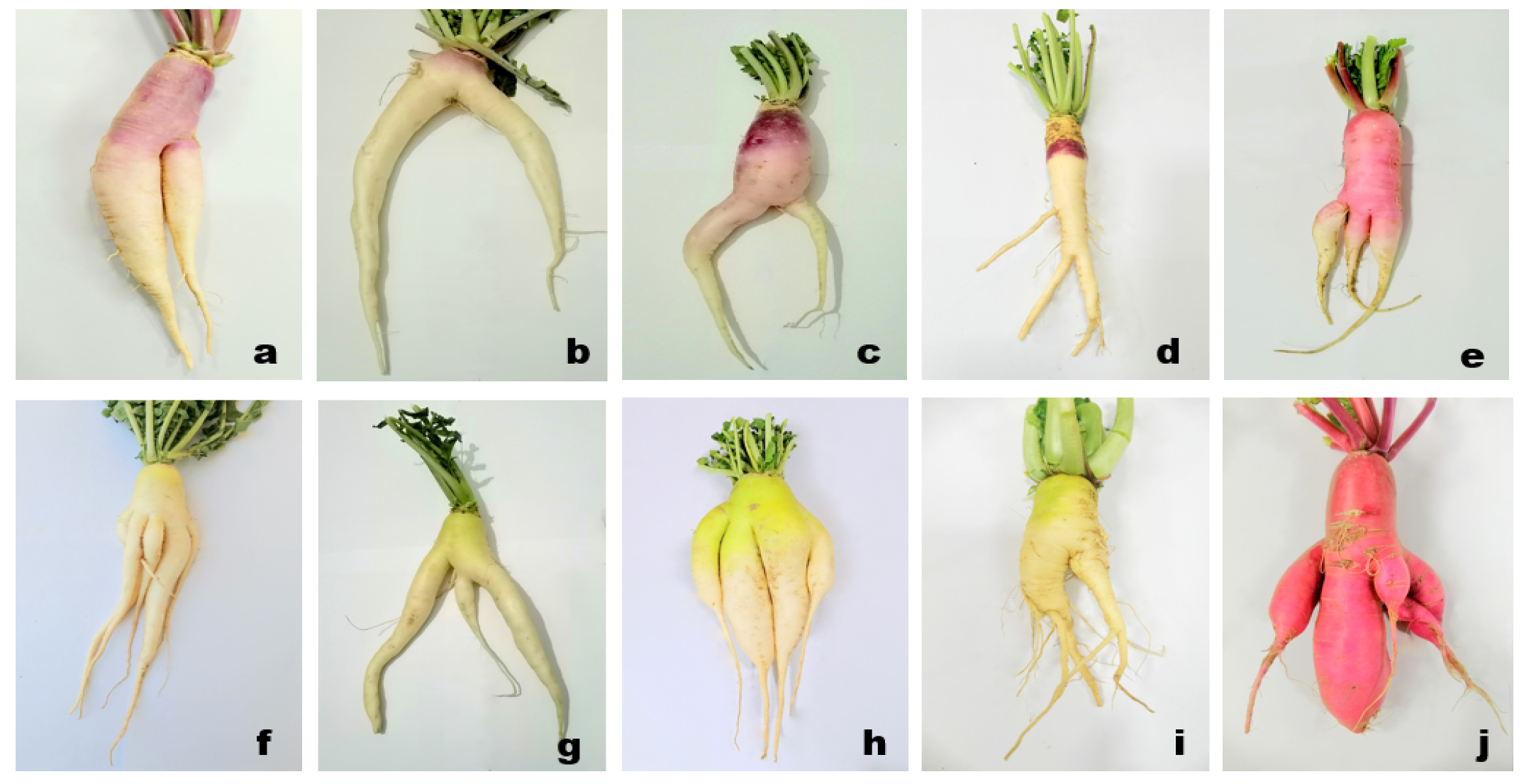
| Forking | Delay harvesting, Soil with poor physical properties (hard lumps), Close spacing (R-R = 5 cm, P-P = 75 cm) | Purple neck, Green neck, Minowase, BARI Red |  |
| Pithiness | Over maturity, early sowing (August-October), High irradiance (32.6 °C), sandy loam soil which promotes rapid growth, low soil EC (0.8 ds/m) | Lalpari, Narrow leaf, BARI Red, | 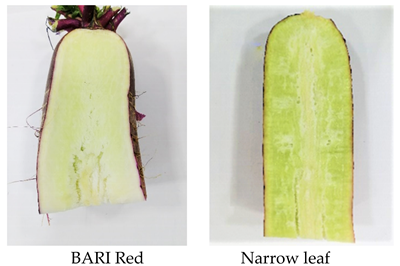 |
| Cracking/Splitting | Heavy rainfall after a long dry period (40.4 mm), high temperature during root growth (28 °C) in late sown plot, over-maturity | Belle red, Narrow leaf, Green neck, Minowase, Black ball, BARI Red |  |
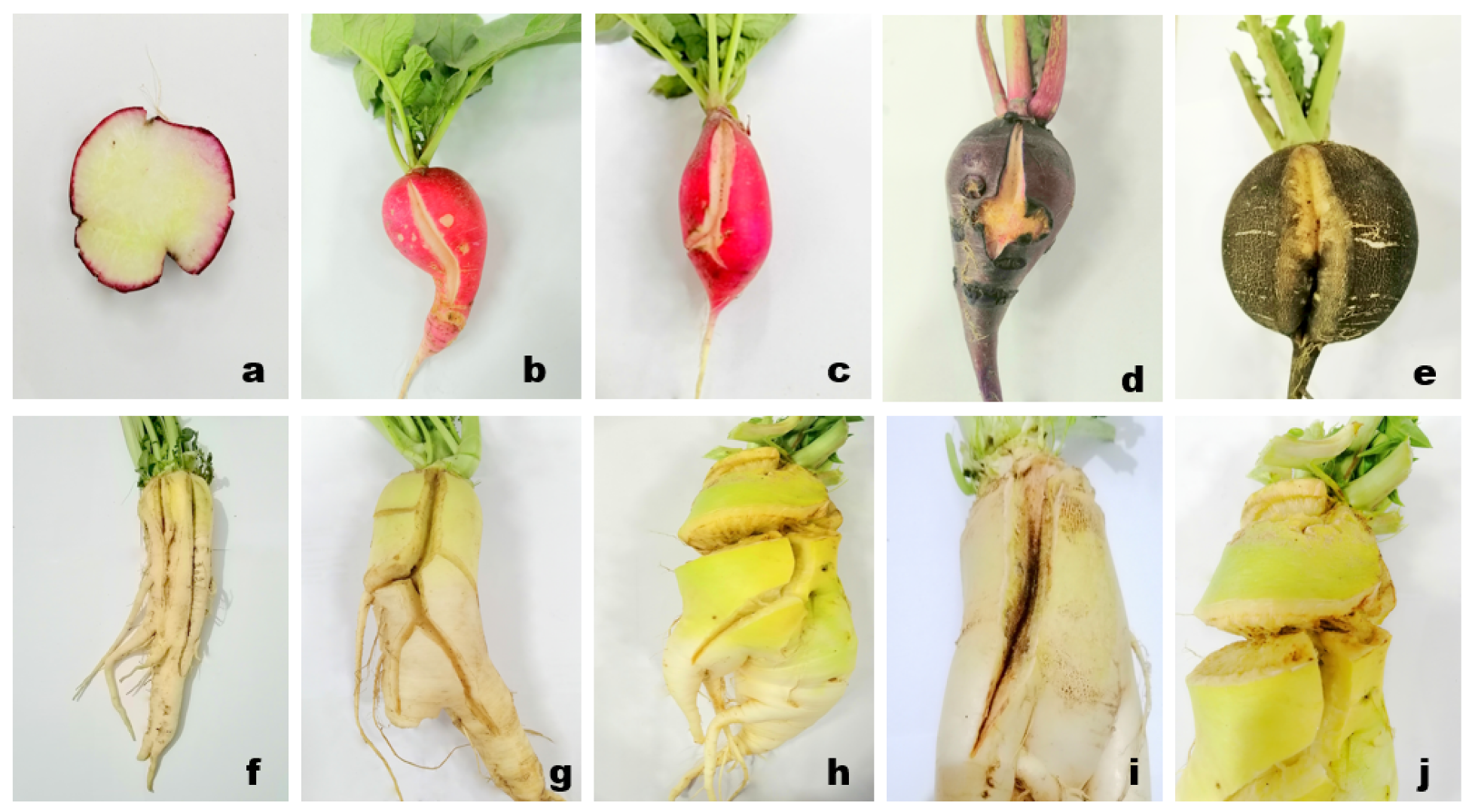
| Hollowness | High soil temperature (36.4 °C) in early sown plot, over maturity | Narrow leaf, Purple neck | 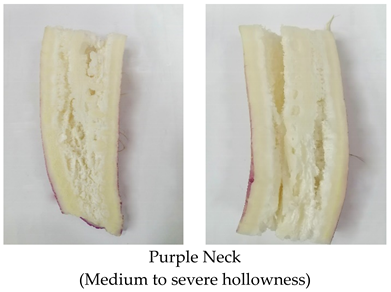 |
| Internal browning/brown heart | High soil temperature during primary thickening growth stage (30–36.4 °C), boron deficient soil (0.35 mg kg−1) | Minowase |  |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Manzoor, A.; Bashir, M.A.; Naveed, M.S.; Cheema, K.L.; Cardarelli, M. Role of Different Abiotic Factors in Inducing Pre-Harvest Physiological Disorders in Radish (Raphanus sativus). Plants 2021, 10, 2003. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10102003
Manzoor A, Bashir MA, Naveed MS, Cheema KL, Cardarelli M. Role of Different Abiotic Factors in Inducing Pre-Harvest Physiological Disorders in Radish (Raphanus sativus). Plants. 2021; 10(10):2003. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10102003
Chicago/Turabian StyleManzoor, Ayesha, Muhammad Ajmal Bashir, Muhammad Saqib Naveed, Kaiser Latif Cheema, and Mariateresa Cardarelli. 2021. "Role of Different Abiotic Factors in Inducing Pre-Harvest Physiological Disorders in Radish (Raphanus sativus)" Plants 10, no. 10: 2003. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10102003
APA StyleManzoor, A., Bashir, M. A., Naveed, M. S., Cheema, K. L., & Cardarelli, M. (2021). Role of Different Abiotic Factors in Inducing Pre-Harvest Physiological Disorders in Radish (Raphanus sativus). Plants, 10(10), 2003. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10102003








