SSR-Based Analysis of Genetic Diversity and Structure of Sweet Cherry (Prunus avium L.) from 19 Countries in Europe
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
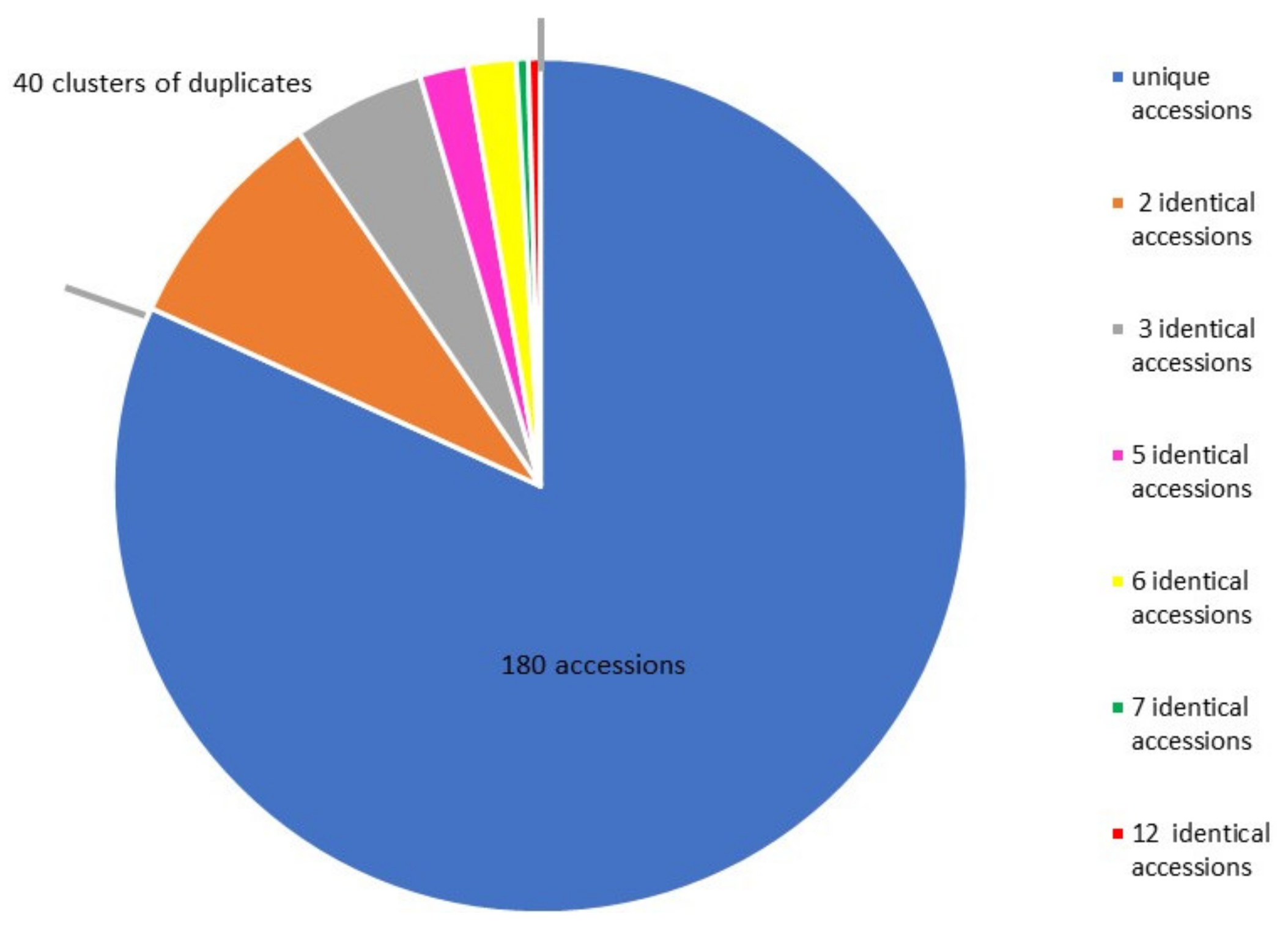
2.1. Genotype Redundancy in the European Sweet Cherry Collection
2.2. Genetic Diversity Estimation by 14 SSR Loci
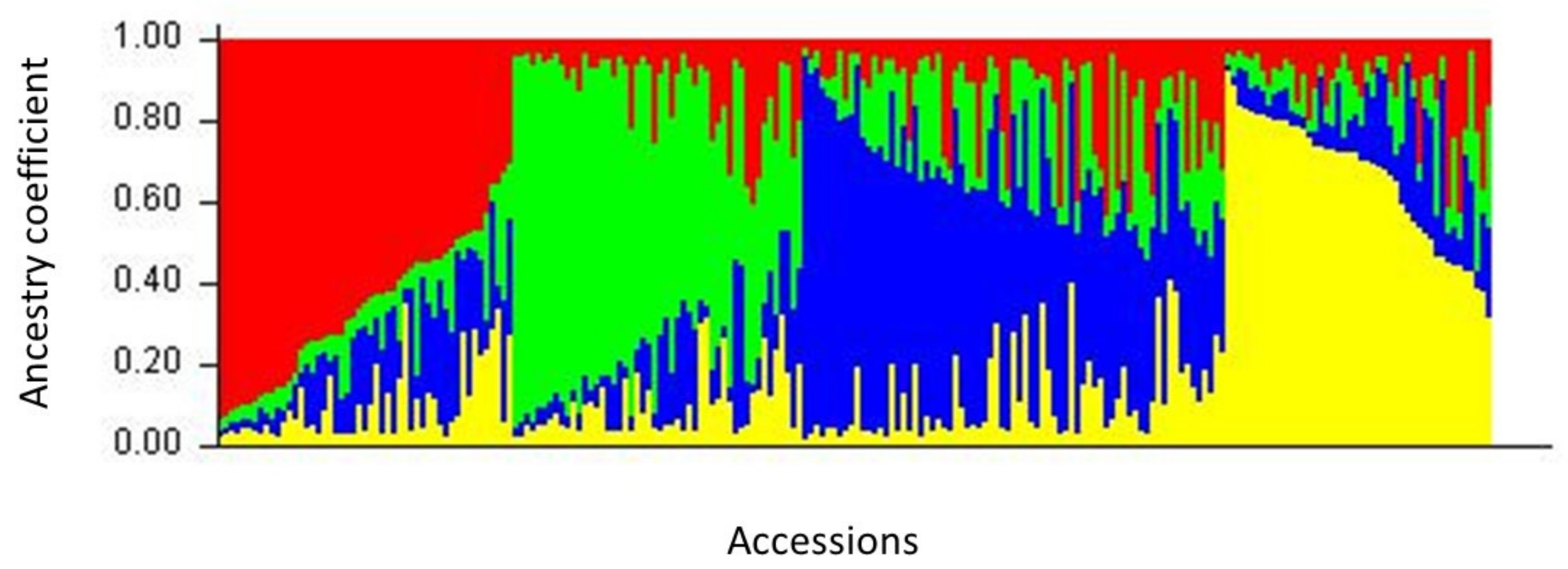
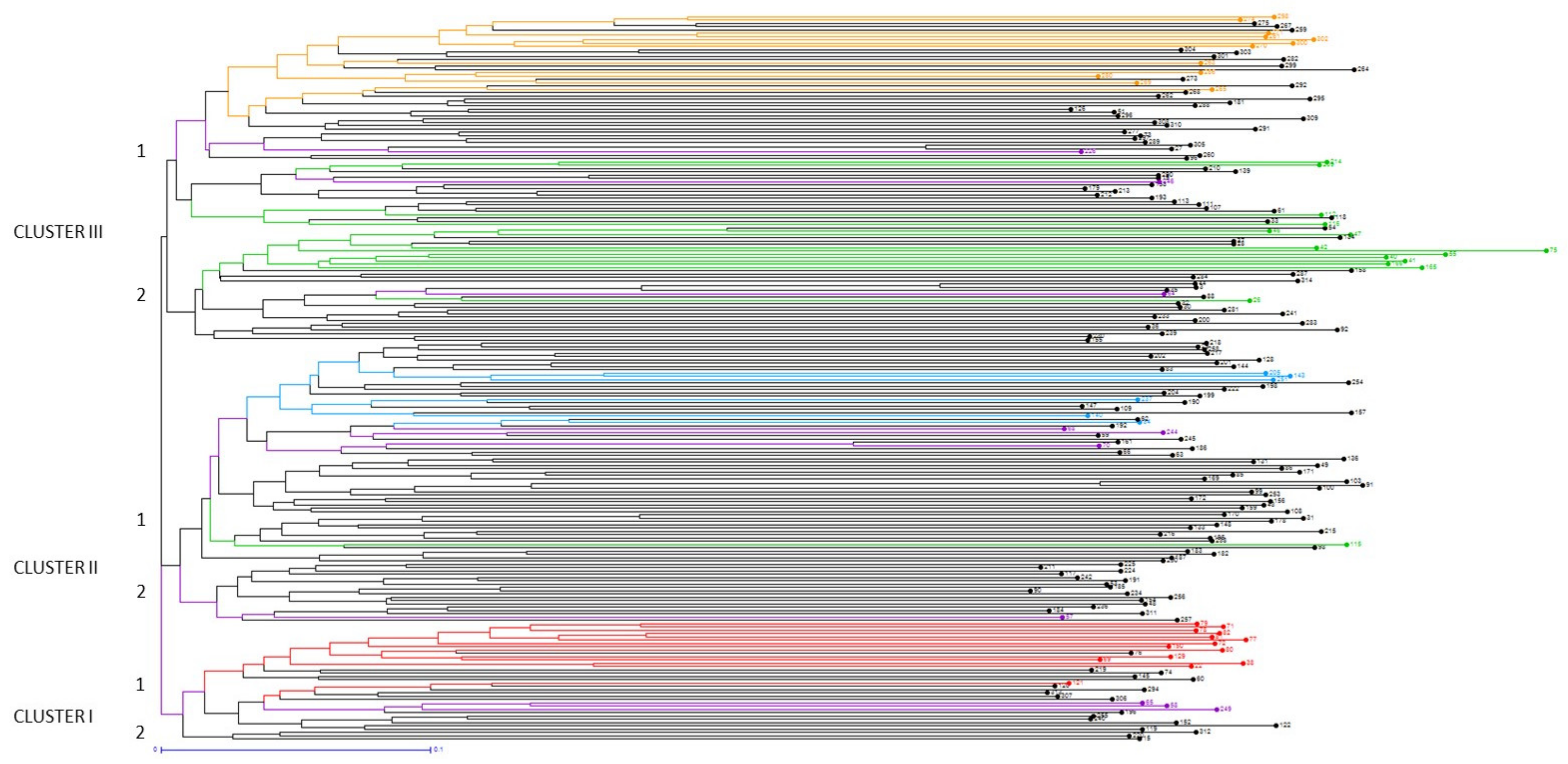
2.3. Population Structure
3. Discussion
3.1. Genotype Redundancy in the Sweet Cherry Collection
3.2. Genetic Diversity Estimation
3.3. Genetic Structure among European Accessions
3.4. Implications for Breeding Programs
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Material
4.2. DNA Extraction and SSR Genotyping
4.3. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mbow, C.; Rosenzweig, C.; Barioni, L.G.; Benton, T.G.; Herrero, M.; Krishnapillai, M.; Liwenga, E.; Pradhan, P.; Rivera-Ferre, M.G.; Sapkota, T.; et al. Food security. In Climate Change and Land: An IPCC Special Report on Climate Change, Desertification, Land Degradation, Sustainable Land Management, Food Security, and Greenhouse Gas Fluxes in Terrestrial Ecosystems; Shukla, P.R., Skea, J., Calvo Buendia, E., Masson-Delmotte, V., Pörtner, H.O., Roberts, D.C., Zhai, P., Slade, R., Connors, S., van Diemen, R., et al., Eds.; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019; in press; Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/site/assets/uploads/2019/11/08_Chapter-5.pdf (accessed on 9 September 2021).
- Gepts, P. Plant Genetic Resources Conservation and Utilization: The Accomplishments and Future of a Societal Insurance Policy. Crop Sci. 2006, 46, 2278–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weise, S.; Oppermann, M.; Maggioni, L.; van Hintum, T.; Knüpffer, H. EURISCO: The European search catalogue for plant genetic resources. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D1003–D1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Di Matteo, A.; Russo, R.; Graziani, G.; Ritieni, A.; di Vaio, C. Characterization of autochthonous sweet cherry cultivars (Prunus avium L.) of Southern Italy for fruit quality, bioactive compounds and antioxidant activity. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 2782–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serradilla, M.J.; Fotirić Akšić, M.; Manganaris, G.A.; Ercisli, S.; González-Gómez, D.; Valero, D. Fruit Chemistry, Nutritional Benefits and Social Aspects of Cherries. In Cherries: Botany, Production and Uses, 1st ed.; Quero-García, J., Iezzoni, A., Puławska, J., Lang, G., Eds.; CABI: Oxfordshire, UK; Boston, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 420–442. [Google Scholar]
- Antognoni, F.; Potente, G.; Mandrioli, R.; Angeloni, C.; Freschi, M.; Malaguti, M.; Hrelia, S.; Lugli, S.; Gennari, F.; Muzzi, E.; et al. Fruit Quality Characterization of New Sweet Cherry Cultivars as a Good Source of Bioactive Phenolic Compounds with Antioxidant and Neuroprotective Potential. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iezzoni, A.; Wünsch, A.; Höfer, M.; Giovannini, D.; Jensen, M.; Quero-García, J.; Campoy, J.A.; Vokurka, A.; Barreneche, T. Biodiversity, germplasm resources and breeding methods. In Cherries: Botany, Production and Uses, 1st ed.; Quero-García, J., Iezzoni, A., Puławska, J., Lang, G., Eds.; CABI: Oxfordshire, UK; Boston, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 36–59. [Google Scholar]
- Leterme, E. Les Fruits Retrouvés; Editions du Rouergue: Rodez, France, 1995; p. 287. [Google Scholar]
- Ordidge, M.; Litthauer, S.; Venison, E.; Blouin-Delmas, M.; Fernandez-Fernandez, F.; Höfer, M.; Kägi, C.; Kellerhals, M.; Marchese, A.; Mariette, S.; et al. Towards a Joint International Database: Alignment of SSR Marker Data for European Collections of Cherry Germplasm. Plants 2021, 10, 1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nybom, H.; Lācis, G. Recent Large-Scale Genotyping and Phenotyping of Plant Genetic Resources of Vegetatively Propagated Crops. Plants 2021, 10, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schüller, E.; Fernández, F.F.; Antanaviciute, L.; Anhalt-Brüderl, U.; Spornberger, A.; Forneck, A. Autochthonous Austrian Varieties of Prunus avium L. Represent a Regional Gene Pool, Assessed Using SSR and AFLP Markers. Genes 2021, 12, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krmpot, T.; Radoš, L.J.; Vokurka, A. Genetic Characterization of Autochthonous Sweet Cherry Genotypes (Prunus avium L.) using SSR markers. Genetika 2020, 52, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.; Xuan, H.; Sedl, P. Assessment of genetic diversity of Czech sweet cherry cultivars using microsatellite markers. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2015, 63, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariette, S.; Tavaud, M.; Arunyawat, U.; Capdeville, G.; Millan, M.; Salin, F. Population structure and genetic bottleneck in sweet cherry estimated with SSRs and the gametophytic self-incompatibility locus. BMC Genet. 2010, 11, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Campoy, J.A.; Lerigoleur-Balsemin, E.; Christmann, H.; Beauvieux, R.; Girollet, N.; Quero-García, J.; Dirlewanger, E.; Barreneche, T. Genetic diversity, linkage disequilibrium, population structure and construction of a core collection of Prunus avium L. landraces and bred cultivars. BMC Plant Biol. 2016, 16, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Höfer, M.; Braun-Lüllemann, A.; Schiffler, J.; Schuster, M.; Flachowsky, H. Pomological and molecular characterization of sweet cherry cultivars (Prunus avium L.) of the German Fruit Genebank. OpenAgrar Repos. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganopoulos, V.I.; Kazantzis, K.; Chatzicharisis, I.; Karayiannis, I.; Tsaftaris, A. Genetic diversity, structure and fruit trait associations in Greek sweet cherry cultivars using microsatellite-based (SSR/ISSR) and morpho-physiological markers. Euphytica 2011, 181, 237–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarino, C.; Santoro, S.; de Simone, L.; Cipriani, G. Prunus avium: Nuclear DNA study in wild populations and sweet cherry cultivars. Genome 2009, 52, 320–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Vaio, C.; Villano, C.; Marallo, N. Molecular analysis of native cultivars of sweet cherry in Southern Italy. Hortic. Sci. 2015, 42, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marchese, A.; Giovannini, D.; Leone, A.; Mafrica, R.; Palasciano, M.; Cantini, C.; di Viano, C.; de Salvador, F.R.; Giacalone, G.; Carusol, T.; et al. S-genotype identification, genetic diversity and structure analysis of Italian sweet cherry germplasm. Tree Genet. Genomes 2017, 13, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muccillo, L.; Colantuoni, V.; Sciarrillo, R.; Baiamonte, G.; Salerno, G.; Marziano, M.; Sabatino, L.; Guarino, C. Molecular and environmental analysis of Campania (Italy) sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.) cultivars for biocultural refugia identification and conservation. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanys, V.; Baniulis, D.; Morkunaite-Haimi, S.; Siksnianiene, J.B.; Frercks, B.; Gelvonauskiene, D.; Stepulaitiene, I.; Staniene, G.; Siksnianas, T. Characterising the genetic diversity of Lithuanian sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.) cultivars using SSR markers. Sci. Hortic. 2012, 142, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wünsch, A.; Hormaza, J.I. Molecular characterisation of sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.) genotypes using peach (Prunus persica (L.) Batsch) SSR sequences. Heredity 2002, 89, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clarke, J.B.; Tobutt, K.R. Development and characterization of polymorphic microsatellites from Prunus avium ‘Napoleon’. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2003, 3, 578–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schueler, S.; Tusch, A.; Schuster, M.; Ziegenhangen, B. Characterization of microsatellites in wild and sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.)—Markers for individual identification and reproductive processes. Genome 2003, 46, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacis, G.; Rashal, I.; Ruisa, S.; Trajkovski, V.; Iezzoni, A. Assesment of genetic diversity of Latvian and Swedish sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.) genetic resources collections by using SSR (microsatellite) markers. Sci. Hortic. 2009, 121, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan, S.P.; Russell, K. Characterization of novel microsatellites and development of multiplex PCR for large-scale population studies in wild cherry, Prunus avium. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2004, 4, 429–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patzak, J.; Henychová, A.; Paprštein, F.; Sedlák, J. Evaluation of Genetic Variability Within Sweet Cherry (Prunus avium L.) Genetic Resources by Molecular SSR Markers. Acta Sci. Pol. Hortorum Cultus 2019, 18, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinosio, S.; Marroni, F.; Zuccolo, A.; Vitulo, N.; Mariette, S.; Sonnante, G.; Aravanopoulos, F.A.; Ganopoulos, I.; Palasciano, M.; Vidotto, M.; et al. A draft genome of sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.) reveals genome-wide and local effects of domestication. Plant J. 2020, 103, 1420–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quero-García, J.; Schuster, M.; López-Ortega, G.; Charlot, G. Sweet cherry varieties and improvement. In Cherries: Botany, Production and Uses, 1st ed.; Quero-García, J., Iezzoni, A., Puławska, J., Lang, G., Eds.; CABI: Oxfordshire, UK; Boston, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 60–94. [Google Scholar]
- Urrestarazu, J.; Denancé, C.; Ravon, E.; Guyader, A.; Guisnel, R.; Feugey, L.; Poncet, C.H.; Lateur, M.; Houben, P.; Ordidge, M.; et al. Analysis of the genetic diversity and structure across a wide range of germplasm reveals prominent gene flow in apple at the European level. BMC Plant Biol. 2016, 16, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, C.; Kappel, F. Inbreeding, Coancestry, and Founding Clones of Sweet Cherries from North America. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 2004, 129, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herrero, M.; Santiago, J.; Wünch, A. Flowering, fruit set and development. In Cherries: Botany, Production and Uses, 1st ed.; Quero-García, J., Iezzoni, A., Puławska, J., Lang, G., Eds.; CABI: Oxfordshire, UK; Boston, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 14–36. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Sebolt, A.M.; Sooriyapathirana, S.S.; Wang, D.; Bink, M.C.; Olmstead, J.W.; Iezzoni, A.F. Fruit size QTL analysis of an F1 population derived from a cross between a domesticated sweet cherry cultivar and a wild forest sweet cherry. Tree Genet. Genomes 2010, 6, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edge-Garza, D.A.; Rowland, T.V.; Haendiges, S.; Peace, C. A high-throughput and cost-efficient DNA extraction protocol for the tree fruit crops of apple, sweet cherry, and peach relying on silica beads during tissue sampling. Mol. Breed. 2014, 34, 2225–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, J.B.; Tobutt, K.R. A standard set of accessions, microsatellites and genotypes for harmonising the fingerprinting of cherry collections for the ECPGR. Acta Hortic. 2009, 814, 615–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilanova, S.; Romero, C.; Abbott, A.G.; Llacer, G.; Badenes, M.L. An apricot (Prunus armeniaca L.) F2 progeny linkage map based on SSR and AFLP markers, mapping plum pox virus resistance and self-incompatibility traits. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2003, 107, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosyara, U.R.; Bink, M.C.A.M.; van de Weg, E.; Zhang, G.; Wang, D.; Sebolt, A.; Dirlewanger, E.; Quero-Garcia, J.; Schuster, M.; Iezzoni, A.F. Fruit size QTL identification and the prediction of parental QTL genotypes and breeding values in multiple pedigreed populations of sweet cherry. Mol. Breed. 2013, 32, 875–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandefur, P.; Oraguzie, N.; Peace, C. A DNA test for routine prediction in breeding of sweet cherry fruit color, Pav-Rf-SSR. Mol. Breed. 2016, 36, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirlewanger, E.; Cosson, P.; Tavaud, M.; Aranzana, M.J.; Poizat, C.; Zanetto, A.; Arus, P.; Laigret, F. Development of microsatellite markers in peach [Prunus persica (L.) Batsch] and their use in genetic diversity analysis in peach and sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2002, 105, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aranzana, M.J.; Pineda, A.; Cosson, P.; Dirlewanger, E.; Ascasibar, J.; Cipriani, G.; Dunson-Ryder, C.D.; Testolin, R.; Abbott, A.G.; King, G.J.; et al. A set of simple-sequence repeat (SSR) markers covering the Prunus genome. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2003, 106, 819–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmstead, J.W.; Sebolt, A.M.; Cabrera, A.; Sooriyapathirana, S.S.; Hammar, S.; Iriarte, G.; Wang, D.; Chen, C.Y.; van der Knaap, E.; Iezzoni, A.F. Construction of an intra-specific sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.) genetic linkage map and synteny analysis with the Prunus reference map. Tree Genet. Genomes 2008, 4, 897–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menjja, M.; Garcia-Mas, J.; Howad, W.; Badenes, M.L.; Arùs, P. Prunus microsatellite marker transferability across rosaceous crops. Tree Genet. Genomes 2004, 6, 689–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peakall, R.; Smouse, P.E. GenAlEx 6.5: Genetic analysis in Excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research—An update. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 2537–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Denancé, C.; Muranty, H.; Durel, C.-E. MUNQ—Malus UNiQue genotype code for grouping apple accessions corresponding to a unique genotypic profile. Portail Data INRAE 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muranty, H.; Denancé, C.; Feugey, L.; Crépin, J.-L.; Barbier, Y.; Tartarini, S.; Ordidge, M.; Troggio, M.; Lateur, M.; Nybom, H.; et al. Using whole-genome SNP data to reconstruct a large multi-generation pedigree in apple germplasm. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalinowski, S.T.; Taper, M.L.; Marshall, T.C. Revising how the computer program CERVUS accommodates genotyping error increases success in paternity assignment. Mol. Ecol. 2007, 16, 1099–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrier, X.; Flori, A.; Bonnot, F. Data analysis methods. In Genetic Diversity of Cultivated Tropical Plants, 1st ed.; Hamon, P., Seguin, M., Perrier, X., Glaszmann, J.C., Eds.; Enfield Science Publishers: Montpellier, France, 2003; pp. 43–76. [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard, J.K.; Stephens, M.; Donnelly, P. Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 2000, 155, 945–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evanno, G.; Regnaut, S.; Goudet, J. Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software STRUCTURE: A simulation study. Mol. Ecol. 2005, 14, 2611–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Perrier, X.; Jacquemoud-Collet, J.P. DARwin Software. 2006. Available online: http://darwin.cirad.fr/ (accessed on 9 September 2021).

| SSR Locus | Na | Allele Range | Rare Alleles | PIC | Ho | He | Fis | HW |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BPPCT034 | 15 | 214–258 | 6 # & ## | 0.786 | 0.95 | 0.81 | −0.17 | *** |
| BPPCT037 | 10 | 127–170 | 2 # | 0.799 | 0.85 | 0.82 | −0.04 | NS |
| CPPCT006 | 12 | 173–203 | 4 # | 0.750 | 0.78 | 0.78 | 0 | NS |
| CPPCT022 | 9 | 245–259 | 2 # & ## | 0.626 | 0.64 | 0.68 | 0.06 | NS |
| CPSCT038 | 6 | 184–203 | 1 # | 0.570 | 0.63 | 0.63 | 0 | NS |
| EMPa002 | 5 | 105–131 | 3 ## | 0.363 | 0.55 | 0.46 | −0.2 | NS |
| EMPa004 | 11 | 160–212 | 6 # & ## | 0.678 | 0.73 | 0.73 | 0 | NS |
| EMPa017 | 9 | 229–246 | 5 # & ## | 0.358 | 0.35 | 0.38 | 0.08 | NS |
| EMPa018 | 14 | 82–119 | 8 # & ## | 0.640 | 0.61 | 0.68 | 0.1 | NS |
| EMPaS02 | 8 | 134–152 | 1 | 0.775 | 0.77 | 0.8 | 0.04 | NS |
| EMPaS06 | 12 | 203–229 | 4 # | 0.838 | 0.85 | 0.85 | 0 | NS |
| EMPaS12 | 10 | 112–155 | 5 # & ## | 0.733 | 0.79 | 0.77 | −0.03 | NS |
| EMPaS14 | 7 | 168–213 | 3 # & ## | 0.558 | 0.65 | 0.63 | −0.03 | NS |
| PAV-Rf-SSR | 9 | 343–363 | 3 # | 0.737 | 0.78 | 0.77 | −0.01 | NS |
| Total | 137 | |||||||
| Mean | 9.8 | 0.658 | 0.71 | 0.70 | −0.01 |
| Collection | N | Na | Rare Alleles | Private Alleles | PIC | Ho | He | Fis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Landraces | 111 | 9.1 | 65 | 16 | 0.661 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.01 |
| Early Selections and Modern Breeding Cultivars | 104 | 7.3 | 29 | 8 | 0.639 | 0.72 | 0.69 | −0.02 |
| Cluster | K1 | K2 | K3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| K1 | - | - | - |
| K2 | 0.1004 | - | - |
| K3 | 0.1835 | 0.1178 | - |
| K4 | 0.1303 | 0.0996 | 0.1920 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barreneche, T.; Cárcamo de la Concepción, M.; Blouin-Delmas, M.; Ordidge, M.; Nybom, H.; Lacis, G.; Feldmane, D.; Sedlak, J.; Meland, M.; Kaldmäe, H.; et al. SSR-Based Analysis of Genetic Diversity and Structure of Sweet Cherry (Prunus avium L.) from 19 Countries in Europe. Plants 2021, 10, 1983. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10101983
Barreneche T, Cárcamo de la Concepción M, Blouin-Delmas M, Ordidge M, Nybom H, Lacis G, Feldmane D, Sedlak J, Meland M, Kaldmäe H, et al. SSR-Based Analysis of Genetic Diversity and Structure of Sweet Cherry (Prunus avium L.) from 19 Countries in Europe. Plants. 2021; 10(10):1983. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10101983
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarreneche, Teresa, María Cárcamo de la Concepción, Marine Blouin-Delmas, Matthew Ordidge, Hilde Nybom, Gunars Lacis, Daina Feldmane, Jiri Sedlak, Mekjell Meland, Hedi Kaldmäe, and et al. 2021. "SSR-Based Analysis of Genetic Diversity and Structure of Sweet Cherry (Prunus avium L.) from 19 Countries in Europe" Plants 10, no. 10: 1983. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10101983
APA StyleBarreneche, T., Cárcamo de la Concepción, M., Blouin-Delmas, M., Ordidge, M., Nybom, H., Lacis, G., Feldmane, D., Sedlak, J., Meland, M., Kaldmäe, H., Kahu, K., Békefi, Z., Stanivuković, S., Đurić, G., Höfer, M., Galik, M., Schüller, E., Spornberger, A., Sirbu, S., ... Quero-García, J. (2021). SSR-Based Analysis of Genetic Diversity and Structure of Sweet Cherry (Prunus avium L.) from 19 Countries in Europe. Plants, 10(10), 1983. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10101983







