Modeling Housing Rent in the Atlanta Metropolitan Area Using Textual Information and Deep Learning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Method
2.1. Study Area
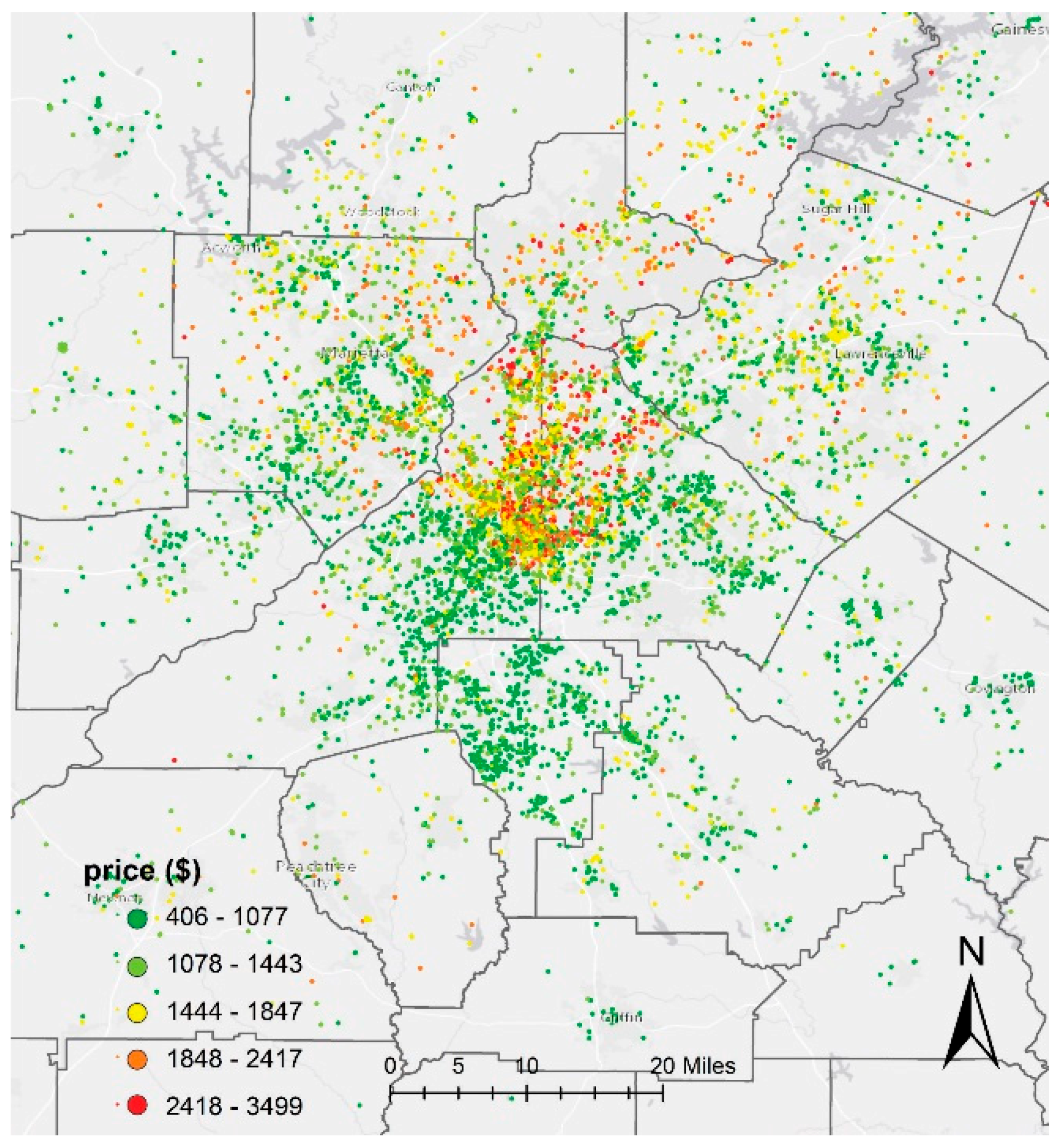
2.2. Data
2.3. Data Cleaning
2.4. Experiment Design
2.4.1. Exp. I: Single Model without Textual Information
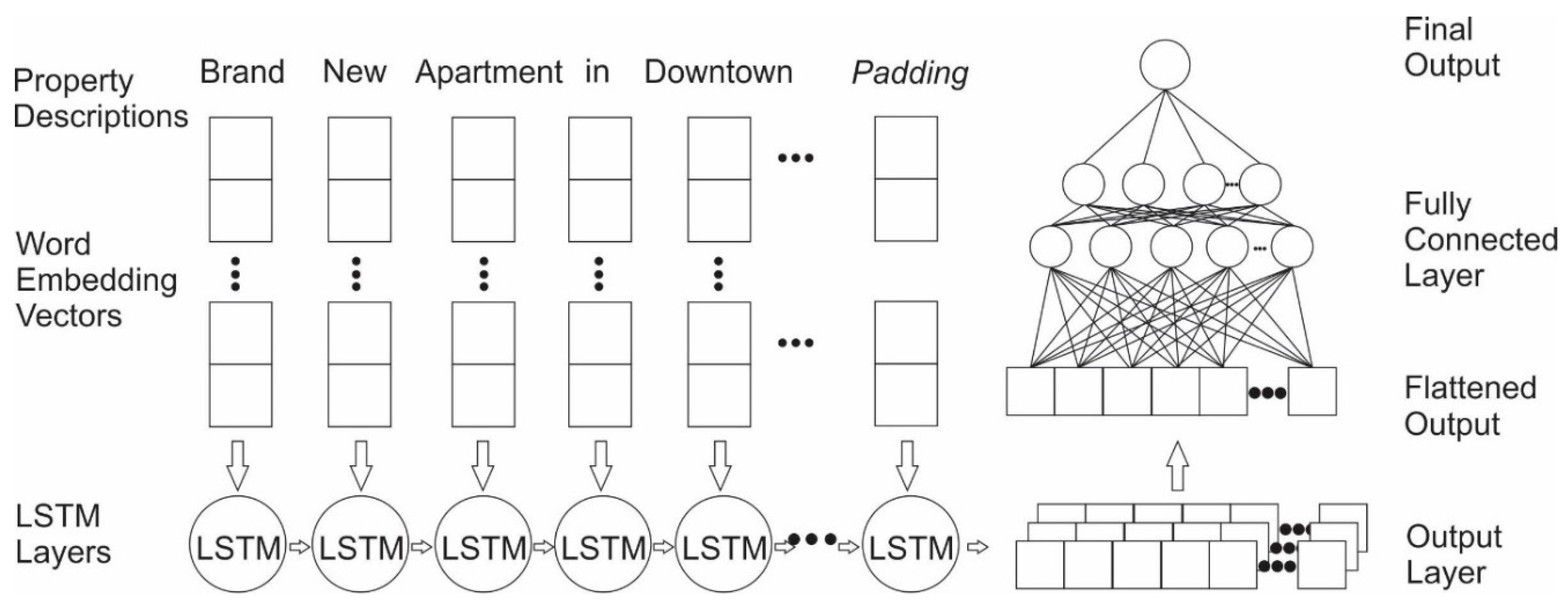
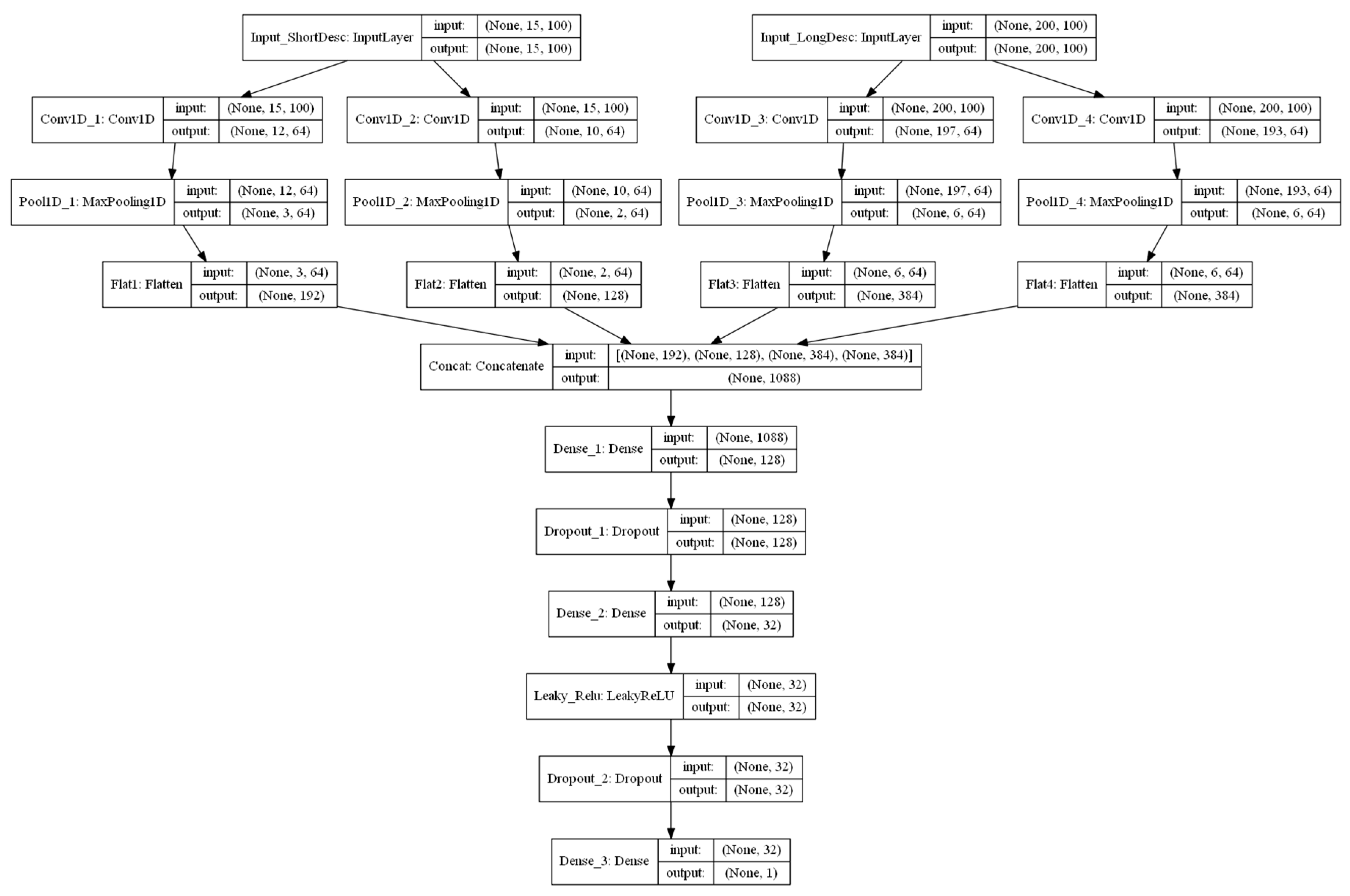
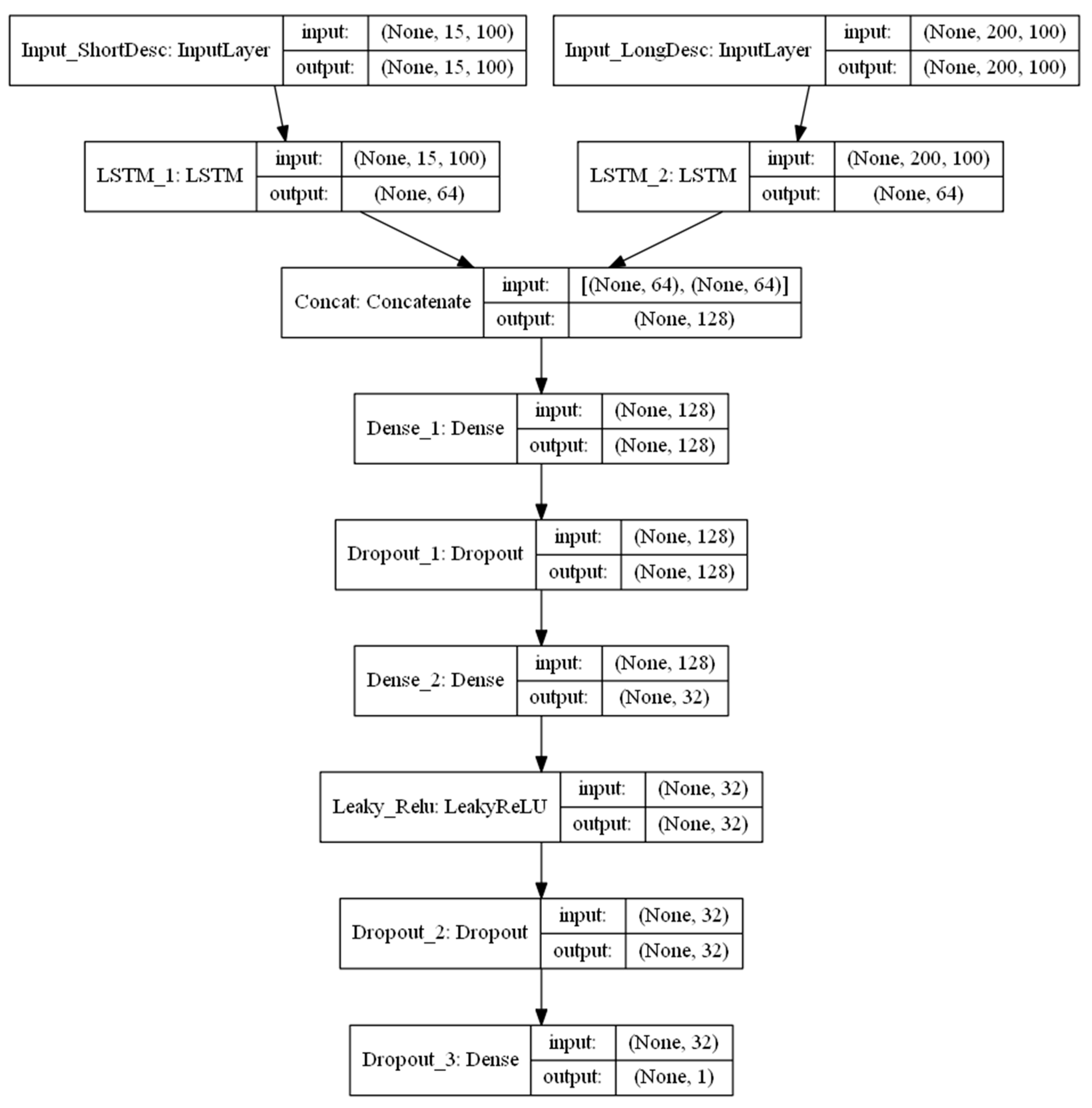
2.4.2. Exp. II: Single Model Based on Textual Information
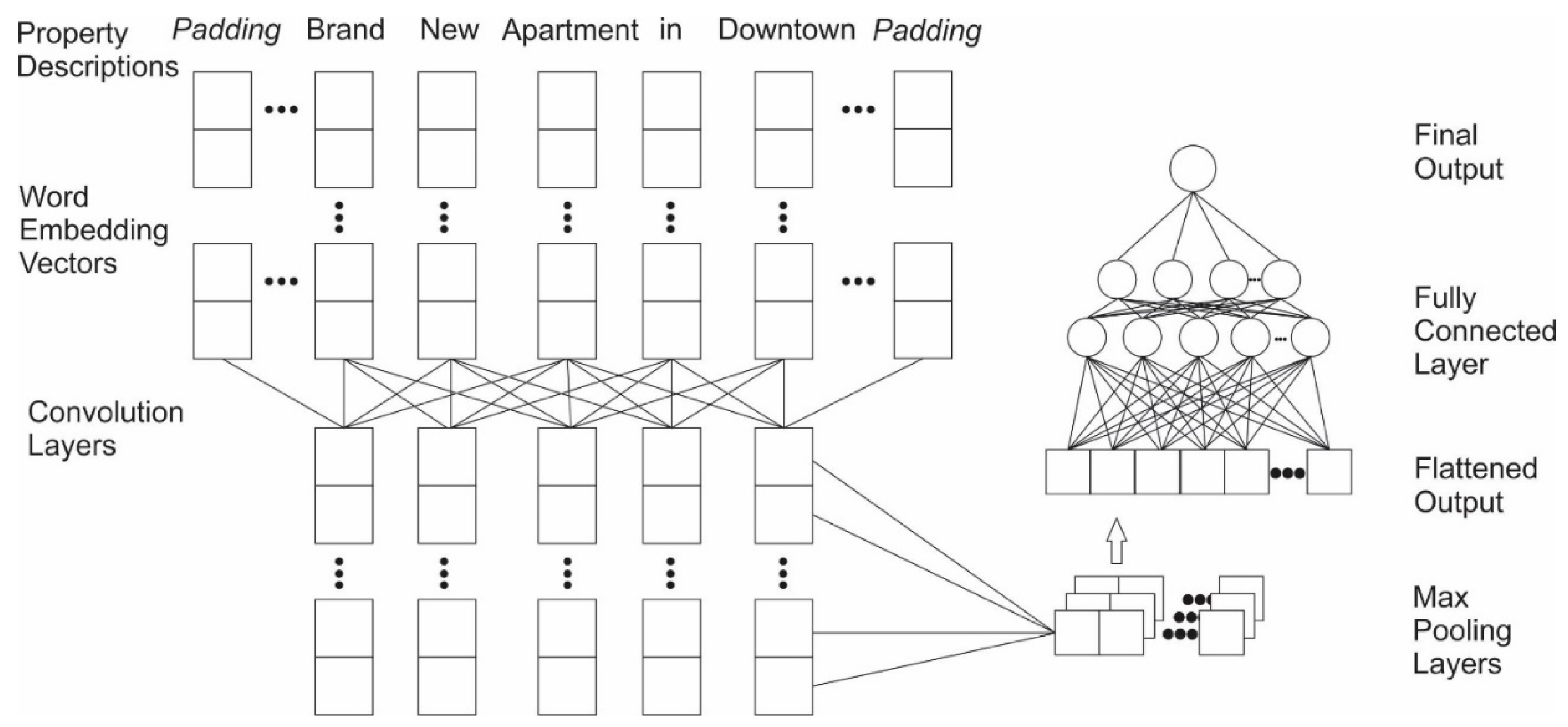
2.4.3. Exp. III: Combined Models Using both Numeric and Textual Information
3. Results
4. Discussion and conclusion
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boeing, G.; Waddell, P. New insights into rental housing markets across the united states: Web scraping and analyzing craigslist rental listings. J. Plan. Educ. Res. 2017, 37, 457–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuegong, Z. Introduction to statistical learning theory and support vector machines. Acta Autom. Sin. 2000, 26, 32–42. [Google Scholar]
- Ramírez, K. Value of U.S. Housing Market Climbs to Record $31.8 Trillion. 2017. Available online: https://www.housingwire.com/articles/42176-value-of-us-housing-market-climbs-to-record-318-trillion (accessed on 4 May 2019).
- Alonso, W. A theory of the urban land market. Pap. Reg. Sci. 1960, 6, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clay, M.J.; Valdez, A. The Bid-rent Land Use Model of the simple, efficient, elegant, and effective model of land use and transportation. Transp. Plan. Technol. 2017, 40, 449–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Immergluck, D. Large redevelopment initiatives, housing values and gentrification: The case of the Atlanta Beltline. Urban Stud. 2009, 46, 1723–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Morales, E. Gentrification by Ground Rent Dispossession: The shadows cast by large-scale urban renewal in Santiago de Chile. Int. J. Urban Reg. Res. 2011, 35, 330–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, N. Gentrification and the Rent Gap. Ann. Assoc. Am. Geogr. 1987, 77, 462–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirmans, G.; John, B. Determinants of market rent. J. Real Estate Res. 1991, 6, 357–379. [Google Scholar]
- Kee, K.; Walt, N. Assessing the rental value of residential properties: An abductive learning networks approach. J. Real Estate Res. 1996, 12, 63–77. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, T.; Abbas, J.; Wei, Z.; Nurunnabi, M. The Effect of Sustainable Urban Planning and Slum Disamenity on The Value of Neighboring Residential Property: Application of The Hedonic Pricing Model in Rent Price Appraisal. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donovan, G.H.; Butry, D.T. The effect of urban trees on the rental price of single-family homes in Portland, Oregon. Urban For. Urban Green. 2011, 10, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranzini, A.; Schaerer, C.; Thalmann, P. Using measured instead of perceived noise in hedonic models. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2010, 15, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero, J.; Larraz, B. Interpolation methods for geographical data: Housing and commercial establishment markets. J. Real Estate Res. 2011, 33, 233–244. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, S.; Cheng, Q.; Wang, L.; Xu, D. Modeling land price distribution using multifractal IDW interpolation and fractal filtering method. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2013, 110, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselin, L.; Le Gallo, J. Interpolation of Air Quality Measures in Hedonic House Price Models: Spatial Aspects. Spat. Econ. Anal. 2006, 1, 31–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Charlton, M.; Fotheringhama, A.S. Geographically weighted regression using a non-Euclidean distance metric with a study on London house price data. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2011, 7, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Wu, B.; Barry, M. Geographically and temporally weighted regression for modeling spatio-temporal variation in house prices. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2010, 24, 383–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.Z.; Ong, S.E.; Koh, H.C. Determinants of House Price: A Decision Tree Approach. Urban Stud. 2006, 43, 2301–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Xu, X. Mapping the fine-scale spatial pattern of housing rent in the metropolitan area by using online rental listings and ensemble learning. Appl. Geogr. 2016, 75, 200–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullainathan, S.; Spiess, J. Machine Learning: An Applied Econometric Approach. J. Econ. Perspect. 2017, 31, 87–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Xie, J.; Li, G.; Mou, N.; Li, Z.; Tian, C.; Zhao, J. Social Media Big Data Mining and Spatio-Temporal Analysis on Public Emotions for Disaster Mitigation. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akita, R.; Yoshihara, A.; Matsubara, T.; Uehara, K. Deep learning for stock prediction using numerical and textual information. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE/ACIS 15th International Conference on Computer and Information Science (ICIS), Okayama-shi, Japan, 26–29 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, S.; Liu, B. Deep learning for sentiment analysis: A survey. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2018, 8, e1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Ren, F.; Wu, C.; Chen, Y.; Du, Q.; Ye, X. Using the TensorFlow Deep Neural Network to Classify Mainland China Visitor Behaviours in Hong Kong from Check-in Data. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2018, 7, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DADS. D.A.D.S. American FactFinder Results. 2018. Available online: https://factfinder.census.gov/faces/tableservices/jsf/pages/productview.xhtml?pid=PEP_2017_PEPANNRES&prodType=table (accessed on 1 May 2019).
- Kanell, M.E. Atlanta Rent Growth among Nation’s Fastest. 2018. Available online: https://www.ajc.com/business/atlanta-rent-growth-among-nation-fastest/fZ7DCMDwjEjiH004ZqzP1L/ (accessed on 1 May 2019).
- Hu, Y.; Mao, H.; McKenzie, G. A natural language processing and geospatial clustering framework for harvesting local place names from geotagged housing advertisements. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2019, 33, 714–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobler, W.R. A computer movie simulating urban growth in the Detroit region. Econ. Geogr. 1970, 46, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krige, D.G. A statistical approach to some basic mine valuation problems on the Witwatersrand. J. S. Afr. Inst. Min. Met. 1951, 52, 119–139. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Ma, Y. Ensemble Machine Learning: Methods and Applications; Springer: Manhattan, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Pennington, J.; Socher, R.; Manning, C.D. GloVe: Global Vectors for Word Representation. In Proceedings of the 2014 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), Doha, Qatar, 25–29 October 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Bengio, Y.; Simard, P.; Frasconi, P. Learning long-term dependencies with gradient descent is difficult. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 1994, 5, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeiler, M.D. ADADELTA: An Adaptive Learning Rate Method. arXiv 2012, arXiv:1212.5701. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, W.; Li, L.; Zhou, X.; Hamilton, A.; Zhang, K. Learning Air Pollution with Bidirectional LSTM RNN. In Proceedings of the 11th EAI International Conference on Mobile Multimedia Communications, Qingdao, China, 21–22 June 2018; ICST (Institute for Computer Sciences, Social-Informatics and Telecommunications Engineering): Qingdao, China, 2018; pp. 245–249. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Y.; Zhang, I.; Hong, Y.; Liang, H.; He, J. Mapping fine-scale urban housing prices by fusing remotely sensed imagery and social media data. Trans. GIS 2018, 22, 561–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appelhans, T.; Mwangomo, E.; Hardy, D.R.; Hemp, A.; Nauss, T. Evaluating machine learning approaches for the interpolation of monthly air temperature at Mt. Kilimanjaro, Tanzania. Spat. Stat. 2015, 14, 91–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
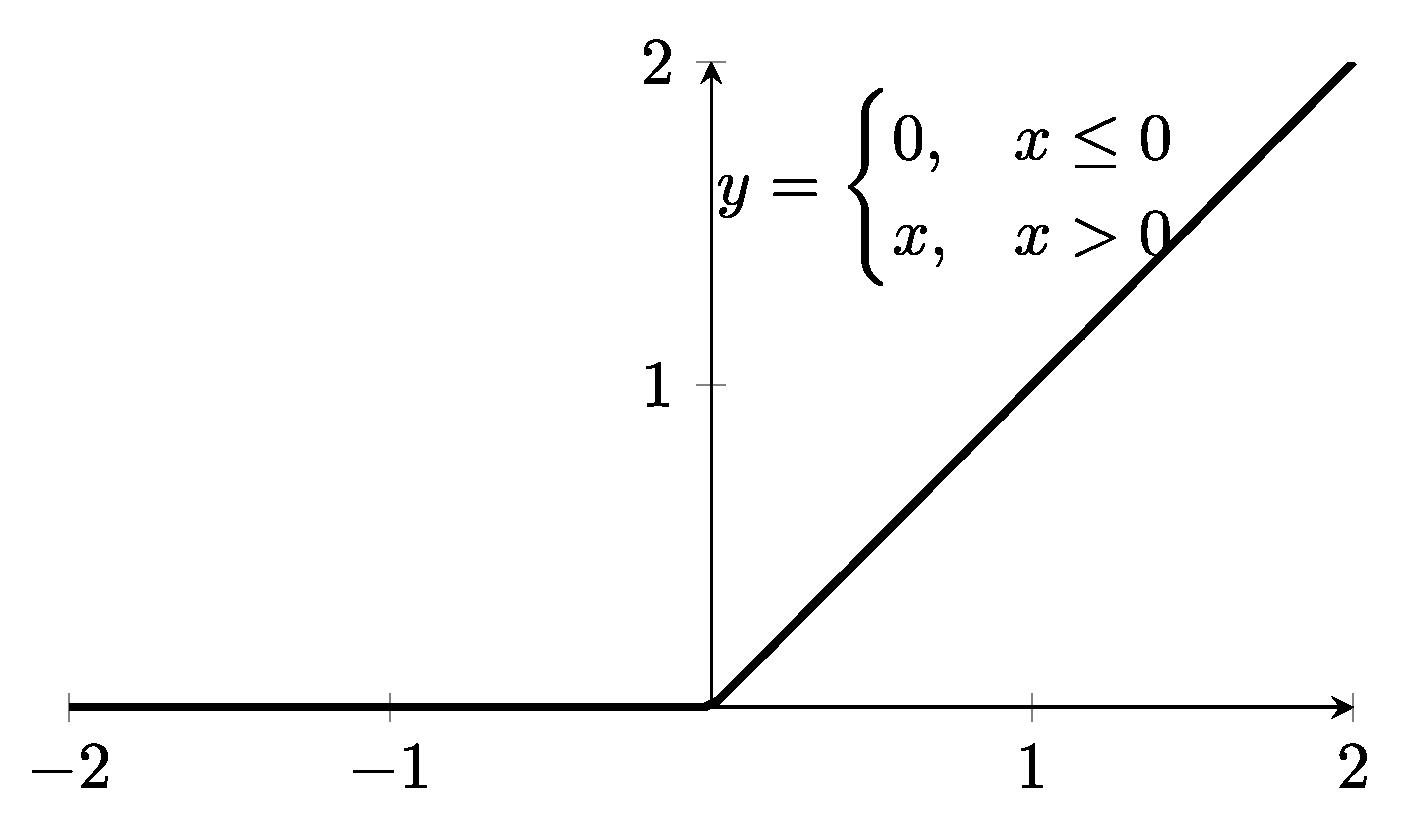
| Price ($) | Bedroom (#) | Square Footage | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| County | Mean | Std | Median | Mean | Std | Median | Mean | Std | Median | Count |
| Clayton | 975.7 | 195.5 | 953.0 | 2.1 | 0.9 | 2 | 1114.0 | 338.5 | 1059.5 | 3728 |
| Rockdale | 1043.7 | 206.7 | 1000.0 | 2.1 | 0.9 | 2 | 1170.2 | 355.1 | 1156.0 | 853 |
| Coweta | 1099.0 | 242.6 | 1050.0 | 2.1 | 0.9 | 2 | 1176.3 | 367.5 | 1154.0 | 1046 |
| Henry | 1118.9 | 240.1 | 1074.0 | 2.1 | 0.9 | 2 | 1247.6 | 386.7 | 1204.0 | 2260 |
| Paulding | 1123.5 | 221.8 | 1106.0 | 2.2 | 1.0 | 2 | 1307.9 | 461.6 | 1210.0 | 1033 |
| Cherokee | 1205.5 | 254.3 | 1189.0 | 2.1 | 0.9 | 2 | 1217.4 | 385.4 | 1160.0 | 1321 |
| Cobb | 1217.4 | 322.4 | 1182.0 | 2.0 | 0.9 | 2 | 1133.9 | 404.8 | 1100.0 | 9722 |
| Gwinnett | 1238.0 | 312.5 | 1190.0 | 2.1 | 1.0 | 2 | 1266.1 | 476.6 | 1196.0 | 8873 |
| Dekalb | 1301.8 | 420.1 | 1243.0 | 1.8 | 0.8 | 2 | 1093.7 | 372.6 | 1072.0 | 14188 |
| Fulton | 1509.1 | 495.2 | 1433.0 | 1.7 | 0.8 | 2 | 1059.6 | 348.6 | 1046.0 | 30261 |
| idw_1 | idw_2 | idw_3 | kg_Ord | kg_Univ | kg_Full_Variables | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAE | 264.702 | 284.214 | 293.514 | 256.261 | 255.491 | 219.004 |
| MAPE (%) | 20.742 | 22.072 | 22.658 | 20.172 | 20.138 | 17.749 |
| RMSE | 370.853 | 397.315 | 411.412 | 359.853 | 359.027 | 325.607 |
| Small Training | Large Training | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAE | MAPE (%) | RMSE | MAE | MAPE (%) | RMSE | |
| RF | 194.925 | 15.846 | 300.877 | 151.587 | 12.425 | 255.293 |
| BAG | 194.767 | 15.849 | 301.457 | 151.237 | 12.402 | 255.191 |
| ET | 197.246 | 15.934 | 312.839 | 153.146 | 12.531 | 263.026 |
| KNN-5 | 223.442 | 18.196 | 334.660 | 175.726 | 14.499 | 287.57 |
| KNN-10 | 226.884 | 18.575 | 334.697 | 182.711 | 15.067 | 289.153 |
| GBM | 214.492 | 17.662 | 312.705 | 205.166 | 17.025 | 300.727 |
| CART | 245.931 | 19.389 | 393.507 | 180.132 | 14.407 | 323.132 |
| EXTRA | 254.196 | 20.137 | 411.971 | 182.634 | 14.619 | 326.941 |
| ADA | 281.724 | 24.656 | 369.236 | 250.227 | 21.551 | 344.863 |
| MLP-20 | 312.400 | 25.380 | 419.337 | 278.284 | 23.023 | 381.732 |
| MAE | MAPE (%) | RMSE | |
|---|---|---|---|
| LSTM | 196.760 | 15.452 | 288.370 |
| CNN | 208.886 | 17.030 | 300.103 |
| LSA | 211.701 | 15.655 | 311.688 |
| ShortDesc | Predicted Price |
|---|---|
| 1 BEDROOM APARTMENT AVAILABLE! | 1093.51 |
| 2 BEDROOM APARTMENT AVAILABLE! | 1210.22 |
| APARTMENTS WITH GOOD CONDITION FOR RENT | 1159.77 |
| LUXURY APARTMENTS FOR RENT, DO NOT MISS | 1318.34 |
| LUXURY APARTMENTS FOR RENT, CLOSE TO BUCKHEAD | 1351.13 |
| MAE | MAPE (%) | RMSE | |
|---|---|---|---|
| bag | 145.358 | 11.703 | 227.967 |
| rf | 145.4 | 11.702 | 227.945 |
| et | 150.648 | 12.119 | 234.685 |
| gbm | 159.673 | 12.833 | 237.805 |
| knn-20 | 156.105 | 12.653 | 238.597 |
| knn-10 | 154.66 | 12.472 | 239.211 |
| mlp-20 | 172.668 | 13.859 | 254.023 |
| lr | 176.686 | 14.044 | 260.452 |
| lasso | 176.686 | 14.044 | 260.452 |
| ridge | 176.686 | 14.044 | 260.452 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, X.; Tong, W.; Li, D. Modeling Housing Rent in the Atlanta Metropolitan Area Using Textual Information and Deep Learning. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 349. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi8080349
Zhou X, Tong W, Li D. Modeling Housing Rent in the Atlanta Metropolitan Area Using Textual Information and Deep Learning. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information. 2019; 8(8):349. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi8080349
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Xiaolu, Weitian Tong, and Dongying Li. 2019. "Modeling Housing Rent in the Atlanta Metropolitan Area Using Textual Information and Deep Learning" ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information 8, no. 8: 349. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi8080349
APA StyleZhou, X., Tong, W., & Li, D. (2019). Modeling Housing Rent in the Atlanta Metropolitan Area Using Textual Information and Deep Learning. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 8(8), 349. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi8080349





