Modeling Housing Rent in the Atlanta Metropolitan Area Using Textual Information and Deep Learning
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Method
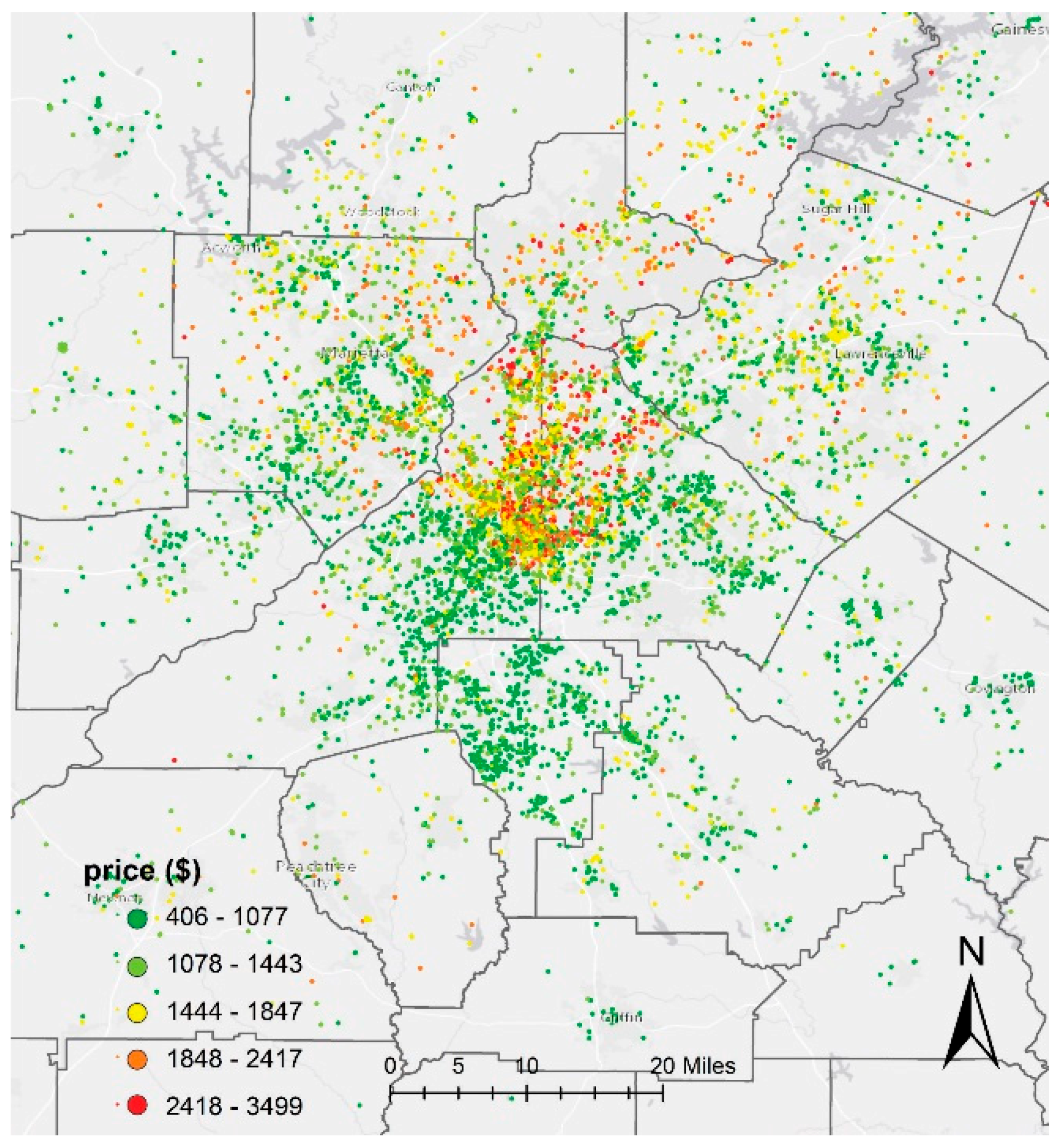
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
2.3. Data Cleaning
2.4. Experiment Design
2.4.1. Exp. I: Single Model without Textual Information
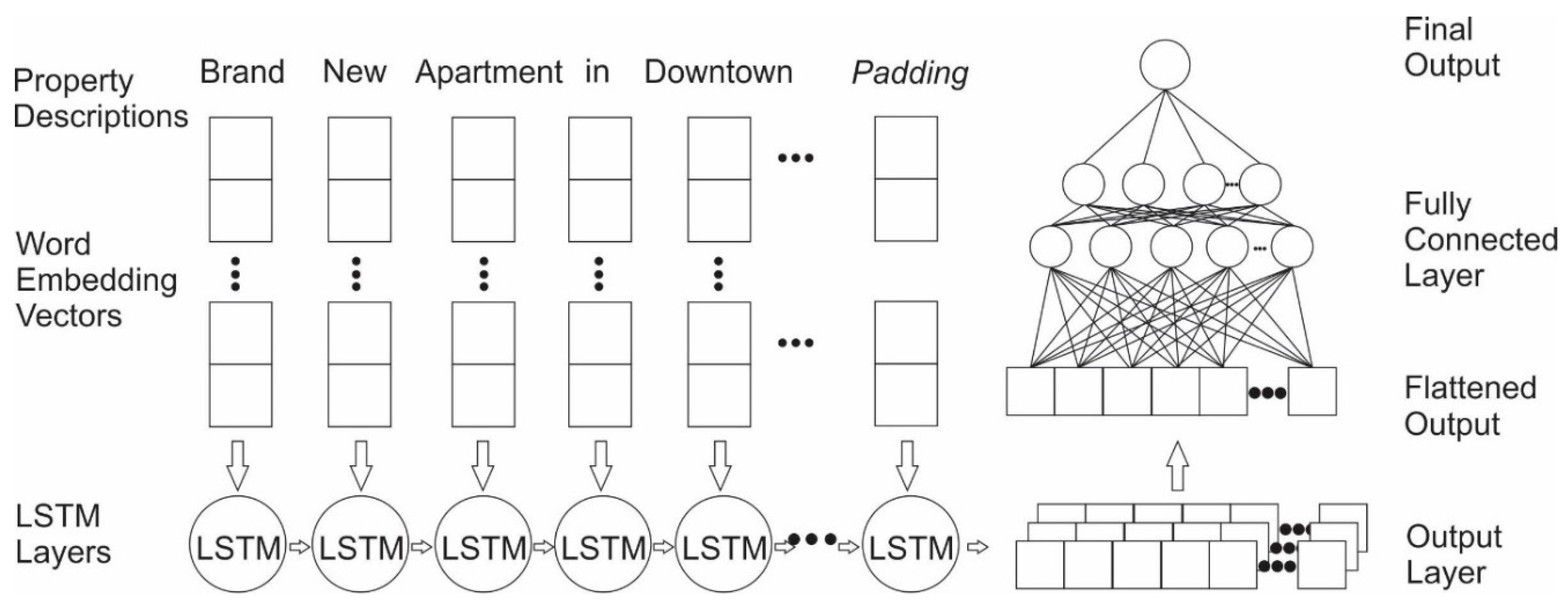
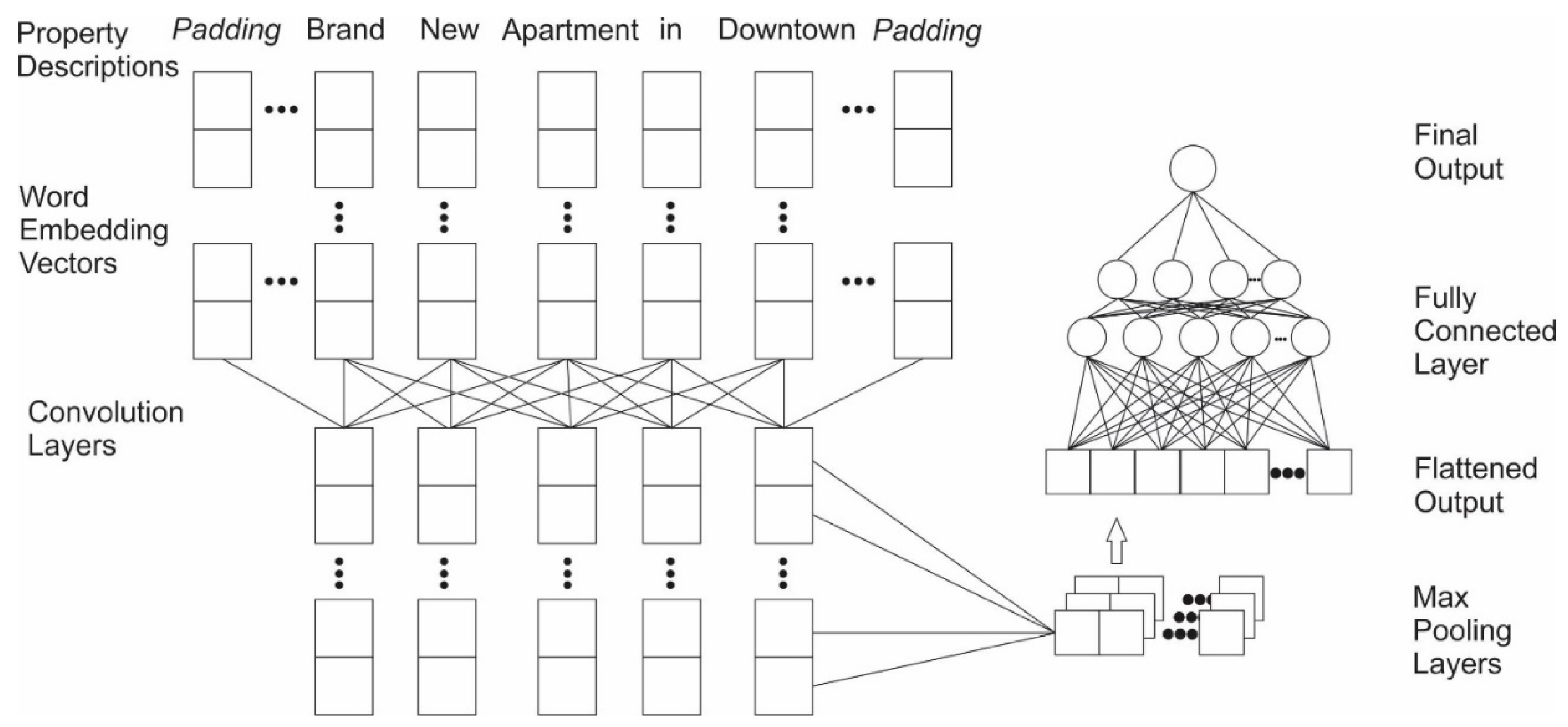
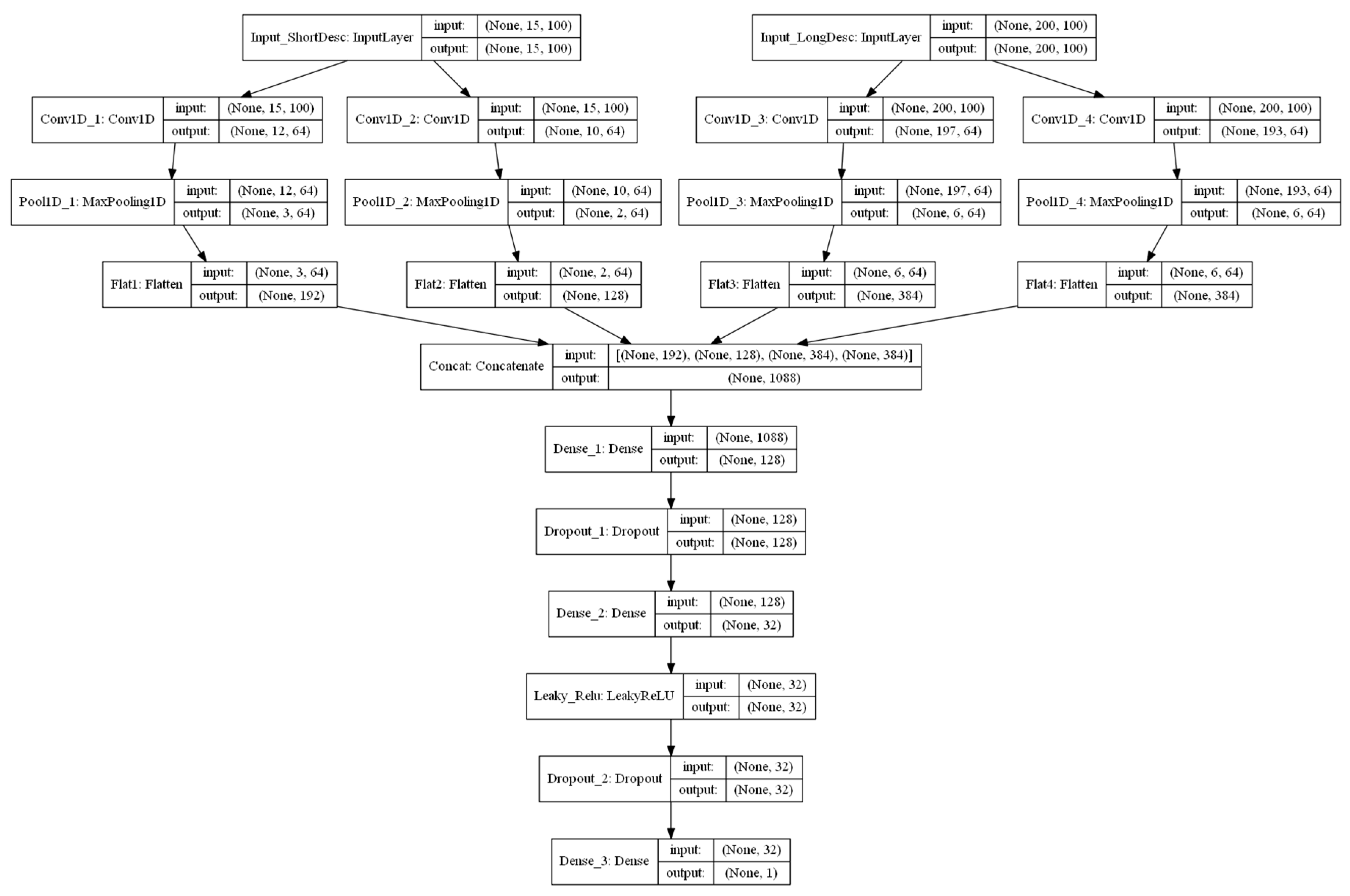
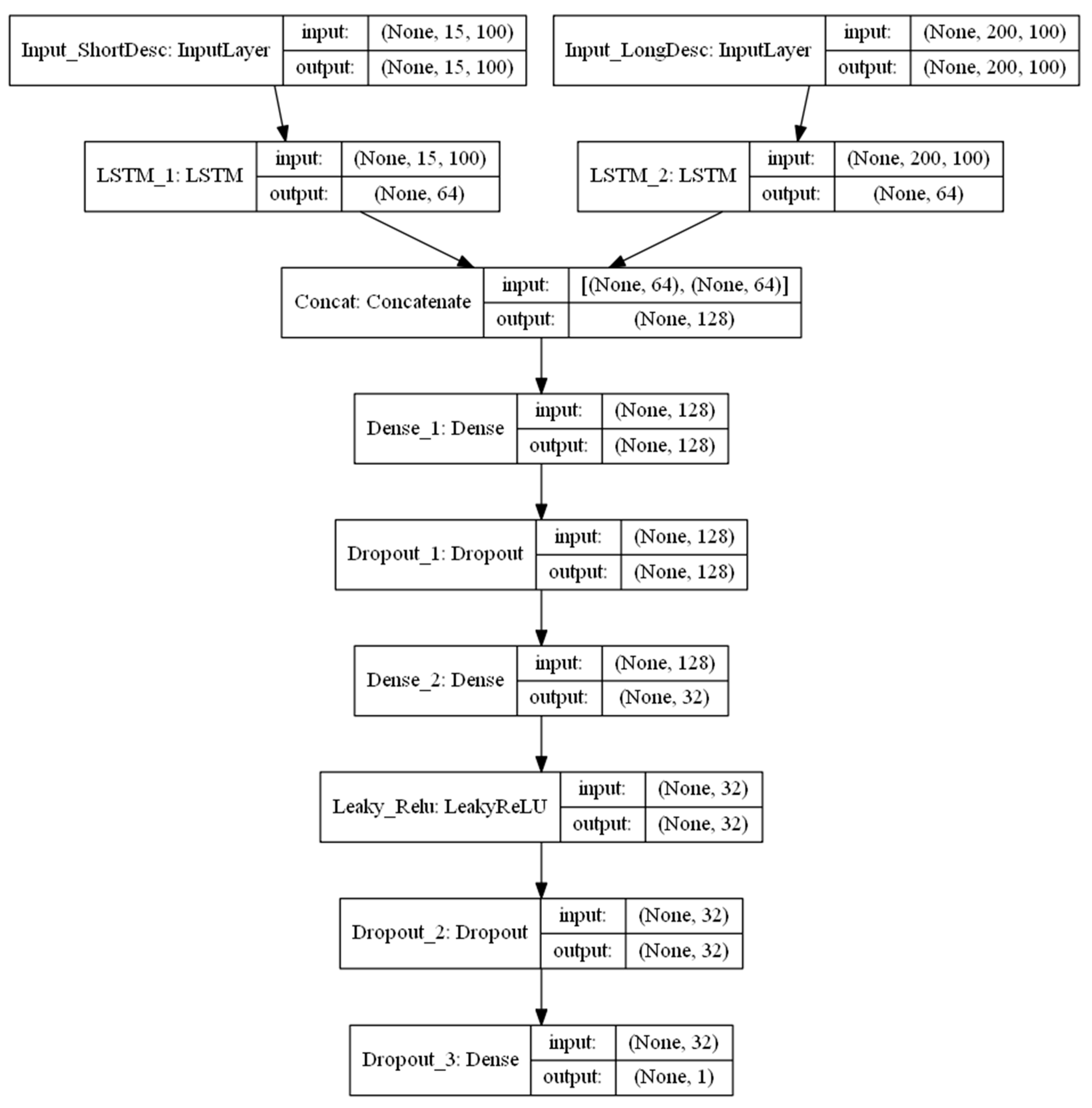
2.4.2. Exp. II: Single Model Based on Textual Information
2.4.3. Exp. III: Combined Models Using both Numeric and Textual Information
3. Results
4. Discussion and conclusion
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boeing, G.; Waddell, P. New insights into rental housing markets across the united states: Web scraping and analyzing craigslist rental listings. J. Plan. Educ. Res. 2017, 37, 457–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuegong, Z. Introduction to statistical learning theory and support vector machines. Acta Autom. Sin. 2000, 26, 32–42. [Google Scholar]
- Ramírez, K. Value of U.S. Housing Market Climbs to Record $31.8 Trillion. 2017. Available online: https://www.housingwire.com/articles/42176-value-of-us-housing-market-climbs-to-record-318-trillion (accessed on 4 May 2019).
- Alonso, W. A theory of the urban land market. Pap. Reg. Sci. 1960, 6, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clay, M.J.; Valdez, A. The Bid-rent Land Use Model of the simple, efficient, elegant, and effective model of land use and transportation. Transp. Plan. Technol. 2017, 40, 449–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Immergluck, D. Large redevelopment initiatives, housing values and gentrification: The case of the Atlanta Beltline. Urban Stud. 2009, 46, 1723–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Morales, E. Gentrification by Ground Rent Dispossession: The shadows cast by large-scale urban renewal in Santiago de Chile. Int. J. Urban Reg. Res. 2011, 35, 330–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, N. Gentrification and the Rent Gap. Ann. Assoc. Am. Geogr. 1987, 77, 462–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirmans, G.; John, B. Determinants of market rent. J. Real Estate Res. 1991, 6, 357–379. [Google Scholar]
- Kee, K.; Walt, N. Assessing the rental value of residential properties: An abductive learning networks approach. J. Real Estate Res. 1996, 12, 63–77. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, T.; Abbas, J.; Wei, Z.; Nurunnabi, M. The Effect of Sustainable Urban Planning and Slum Disamenity on The Value of Neighboring Residential Property: Application of The Hedonic Pricing Model in Rent Price Appraisal. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donovan, G.H.; Butry, D.T. The effect of urban trees on the rental price of single-family homes in Portland, Oregon. Urban For. Urban Green. 2011, 10, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranzini, A.; Schaerer, C.; Thalmann, P. Using measured instead of perceived noise in hedonic models. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2010, 15, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero, J.; Larraz, B. Interpolation methods for geographical data: Housing and commercial establishment markets. J. Real Estate Res. 2011, 33, 233–244. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, S.; Cheng, Q.; Wang, L.; Xu, D. Modeling land price distribution using multifractal IDW interpolation and fractal filtering method. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2013, 110, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselin, L.; Le Gallo, J. Interpolation of Air Quality Measures in Hedonic House Price Models: Spatial Aspects. Spat. Econ. Anal. 2006, 1, 31–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Charlton, M.; Fotheringhama, A.S. Geographically weighted regression using a non-Euclidean distance metric with a study on London house price data. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2011, 7, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Wu, B.; Barry, M. Geographically and temporally weighted regression for modeling spatio-temporal variation in house prices. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2010, 24, 383–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.Z.; Ong, S.E.; Koh, H.C. Determinants of House Price: A Decision Tree Approach. Urban Stud. 2006, 43, 2301–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Xu, X. Mapping the fine-scale spatial pattern of housing rent in the metropolitan area by using online rental listings and ensemble learning. Appl. Geogr. 2016, 75, 200–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullainathan, S.; Spiess, J. Machine Learning: An Applied Econometric Approach. J. Econ. Perspect. 2017, 31, 87–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Xie, J.; Li, G.; Mou, N.; Li, Z.; Tian, C.; Zhao, J. Social Media Big Data Mining and Spatio-Temporal Analysis on Public Emotions for Disaster Mitigation. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akita, R.; Yoshihara, A.; Matsubara, T.; Uehara, K. Deep learning for stock prediction using numerical and textual information. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE/ACIS 15th International Conference on Computer and Information Science (ICIS), Okayama-shi, Japan, 26–29 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, S.; Liu, B. Deep learning for sentiment analysis: A survey. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2018, 8, e1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Ren, F.; Wu, C.; Chen, Y.; Du, Q.; Ye, X. Using the TensorFlow Deep Neural Network to Classify Mainland China Visitor Behaviours in Hong Kong from Check-in Data. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2018, 7, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DADS. D.A.D.S. American FactFinder Results. 2018. Available online: https://factfinder.census.gov/faces/tableservices/jsf/pages/productview.xhtml?pid=PEP_2017_PEPANNRES&prodType=table (accessed on 1 May 2019).
- Kanell, M.E. Atlanta Rent Growth among Nation’s Fastest. 2018. Available online: https://www.ajc.com/business/atlanta-rent-growth-among-nation-fastest/fZ7DCMDwjEjiH004ZqzP1L/ (accessed on 1 May 2019).
- Hu, Y.; Mao, H.; McKenzie, G. A natural language processing and geospatial clustering framework for harvesting local place names from geotagged housing advertisements. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2019, 33, 714–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobler, W.R. A computer movie simulating urban growth in the Detroit region. Econ. Geogr. 1970, 46, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krige, D.G. A statistical approach to some basic mine valuation problems on the Witwatersrand. J. S. Afr. Inst. Min. Met. 1951, 52, 119–139. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Ma, Y. Ensemble Machine Learning: Methods and Applications; Springer: Manhattan, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Pennington, J.; Socher, R.; Manning, C.D. GloVe: Global Vectors for Word Representation. In Proceedings of the 2014 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), Doha, Qatar, 25–29 October 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Bengio, Y.; Simard, P.; Frasconi, P. Learning long-term dependencies with gradient descent is difficult. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 1994, 5, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeiler, M.D. ADADELTA: An Adaptive Learning Rate Method. arXiv 2012, arXiv:1212.5701. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, W.; Li, L.; Zhou, X.; Hamilton, A.; Zhang, K. Learning Air Pollution with Bidirectional LSTM RNN. In Proceedings of the 11th EAI International Conference on Mobile Multimedia Communications, Qingdao, China, 21–22 June 2018; ICST (Institute for Computer Sciences, Social-Informatics and Telecommunications Engineering): Qingdao, China, 2018; pp. 245–249. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Y.; Zhang, I.; Hong, Y.; Liang, H.; He, J. Mapping fine-scale urban housing prices by fusing remotely sensed imagery and social media data. Trans. GIS 2018, 22, 561–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appelhans, T.; Mwangomo, E.; Hardy, D.R.; Hemp, A.; Nauss, T. Evaluating machine learning approaches for the interpolation of monthly air temperature at Mt. Kilimanjaro, Tanzania. Spat. Stat. 2015, 14, 91–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
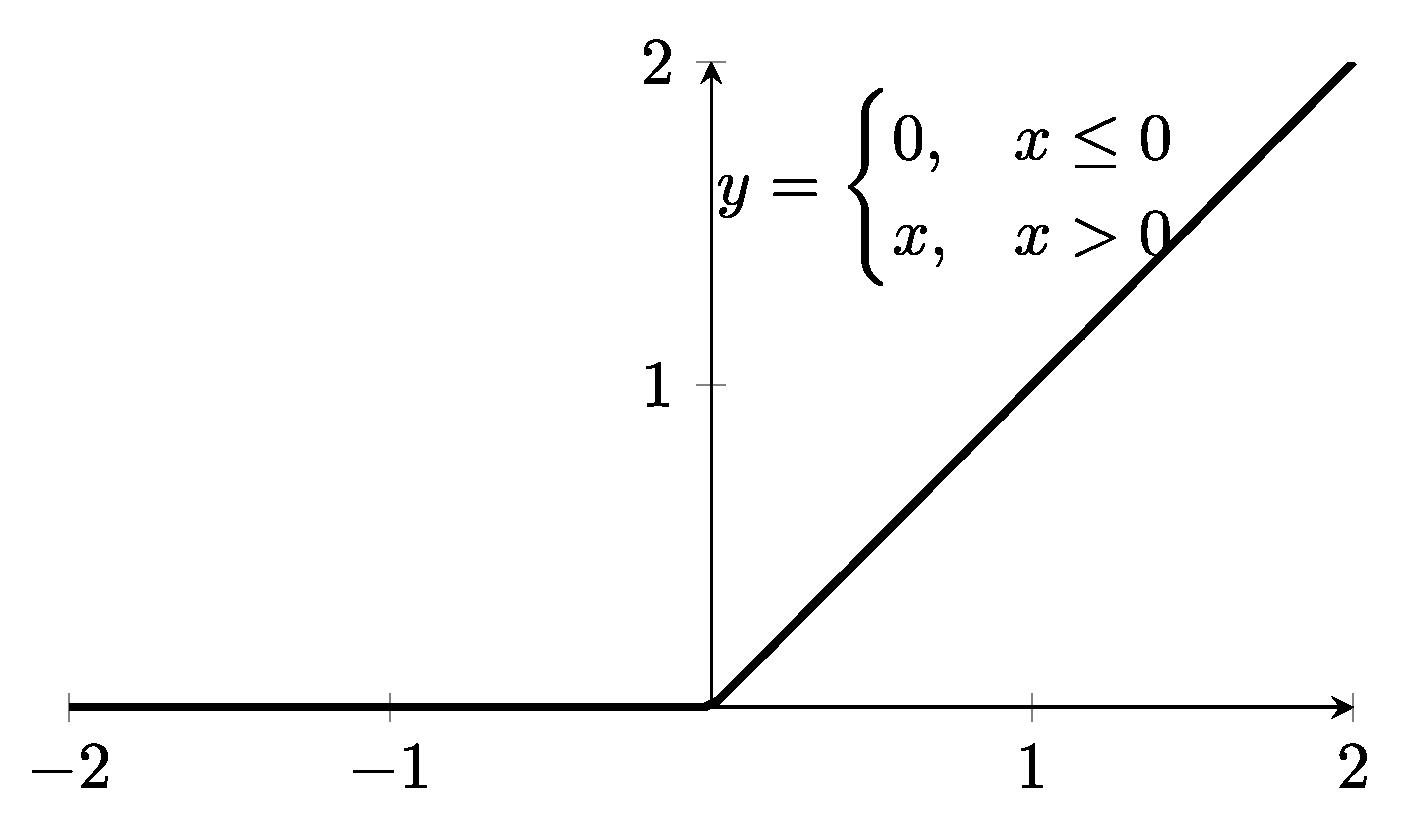
| Price ($) | Bedroom (#) | Square Footage | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| County | Mean | Std | Median | Mean | Std | Median | Mean | Std | Median | Count |
| Clayton | 975.7 | 195.5 | 953.0 | 2.1 | 0.9 | 2 | 1114.0 | 338.5 | 1059.5 | 3728 |
| Rockdale | 1043.7 | 206.7 | 1000.0 | 2.1 | 0.9 | 2 | 1170.2 | 355.1 | 1156.0 | 853 |
| Coweta | 1099.0 | 242.6 | 1050.0 | 2.1 | 0.9 | 2 | 1176.3 | 367.5 | 1154.0 | 1046 |
| Henry | 1118.9 | 240.1 | 1074.0 | 2.1 | 0.9 | 2 | 1247.6 | 386.7 | 1204.0 | 2260 |
| Paulding | 1123.5 | 221.8 | 1106.0 | 2.2 | 1.0 | 2 | 1307.9 | 461.6 | 1210.0 | 1033 |
| Cherokee | 1205.5 | 254.3 | 1189.0 | 2.1 | 0.9 | 2 | 1217.4 | 385.4 | 1160.0 | 1321 |
| Cobb | 1217.4 | 322.4 | 1182.0 | 2.0 | 0.9 | 2 | 1133.9 | 404.8 | 1100.0 | 9722 |
| Gwinnett | 1238.0 | 312.5 | 1190.0 | 2.1 | 1.0 | 2 | 1266.1 | 476.6 | 1196.0 | 8873 |
| Dekalb | 1301.8 | 420.1 | 1243.0 | 1.8 | 0.8 | 2 | 1093.7 | 372.6 | 1072.0 | 14188 |
| Fulton | 1509.1 | 495.2 | 1433.0 | 1.7 | 0.8 | 2 | 1059.6 | 348.6 | 1046.0 | 30261 |
| idw_1 | idw_2 | idw_3 | kg_Ord | kg_Univ | kg_Full_Variables | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAE | 264.702 | 284.214 | 293.514 | 256.261 | 255.491 | 219.004 |
| MAPE (%) | 20.742 | 22.072 | 22.658 | 20.172 | 20.138 | 17.749 |
| RMSE | 370.853 | 397.315 | 411.412 | 359.853 | 359.027 | 325.607 |
| Small Training | Large Training | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAE | MAPE (%) | RMSE | MAE | MAPE (%) | RMSE | |
| RF | 194.925 | 15.846 | 300.877 | 151.587 | 12.425 | 255.293 |
| BAG | 194.767 | 15.849 | 301.457 | 151.237 | 12.402 | 255.191 |
| ET | 197.246 | 15.934 | 312.839 | 153.146 | 12.531 | 263.026 |
| KNN-5 | 223.442 | 18.196 | 334.660 | 175.726 | 14.499 | 287.57 |
| KNN-10 | 226.884 | 18.575 | 334.697 | 182.711 | 15.067 | 289.153 |
| GBM | 214.492 | 17.662 | 312.705 | 205.166 | 17.025 | 300.727 |
| CART | 245.931 | 19.389 | 393.507 | 180.132 | 14.407 | 323.132 |
| EXTRA | 254.196 | 20.137 | 411.971 | 182.634 | 14.619 | 326.941 |
| ADA | 281.724 | 24.656 | 369.236 | 250.227 | 21.551 | 344.863 |
| MLP-20 | 312.400 | 25.380 | 419.337 | 278.284 | 23.023 | 381.732 |
| MAE | MAPE (%) | RMSE | |
|---|---|---|---|
| LSTM | 196.760 | 15.452 | 288.370 |
| CNN | 208.886 | 17.030 | 300.103 |
| LSA | 211.701 | 15.655 | 311.688 |
| ShortDesc | Predicted Price |
|---|---|
| 1 BEDROOM APARTMENT AVAILABLE! | 1093.51 |
| 2 BEDROOM APARTMENT AVAILABLE! | 1210.22 |
| APARTMENTS WITH GOOD CONDITION FOR RENT | 1159.77 |
| LUXURY APARTMENTS FOR RENT, DO NOT MISS | 1318.34 |
| LUXURY APARTMENTS FOR RENT, CLOSE TO BUCKHEAD | 1351.13 |
| MAE | MAPE (%) | RMSE | |
|---|---|---|---|
| bag | 145.358 | 11.703 | 227.967 |
| rf | 145.4 | 11.702 | 227.945 |
| et | 150.648 | 12.119 | 234.685 |
| gbm | 159.673 | 12.833 | 237.805 |
| knn-20 | 156.105 | 12.653 | 238.597 |
| knn-10 | 154.66 | 12.472 | 239.211 |
| mlp-20 | 172.668 | 13.859 | 254.023 |
| lr | 176.686 | 14.044 | 260.452 |
| lasso | 176.686 | 14.044 | 260.452 |
| ridge | 176.686 | 14.044 | 260.452 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, X.; Tong, W.; Li, D. Modeling Housing Rent in the Atlanta Metropolitan Area Using Textual Information and Deep Learning. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 349. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi8080349
Zhou X, Tong W, Li D. Modeling Housing Rent in the Atlanta Metropolitan Area Using Textual Information and Deep Learning. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information. 2019; 8(8):349. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi8080349
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Xiaolu, Weitian Tong, and Dongying Li. 2019. "Modeling Housing Rent in the Atlanta Metropolitan Area Using Textual Information and Deep Learning" ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information 8, no. 8: 349. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi8080349
APA StyleZhou, X., Tong, W., & Li, D. (2019). Modeling Housing Rent in the Atlanta Metropolitan Area Using Textual Information and Deep Learning. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 8(8), 349. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi8080349





