Evolving Spatial Data Infrastructures and the Role of Adaptive Governance
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. SDIs
Governing can be considered as the totality of interactions, in which public as well as private actors participate…; attending to the institutions as contexts for these governing interactions; and establishing a normative foundation for all those activities. Governance can be seen as the totality of theoretical conceptions on governing.(p. 4)
1.2. Global Governance Trends and the Evolution of SDIs
1.3. SDI Governance Dynamics
2. Methods, Data and Cases
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. The Netherlands: Key Registry Large-Scale Topography (BGT)
3.2. Flanders: The Large-Scale Reference Map (GRB)
3.3. Comparing the Governance of the Two Cases
3.3.1. Interactions
3.3.2. Actors
4. Discussion
4.1. Self-Organisations
4.2. Mix of Governance Interactions
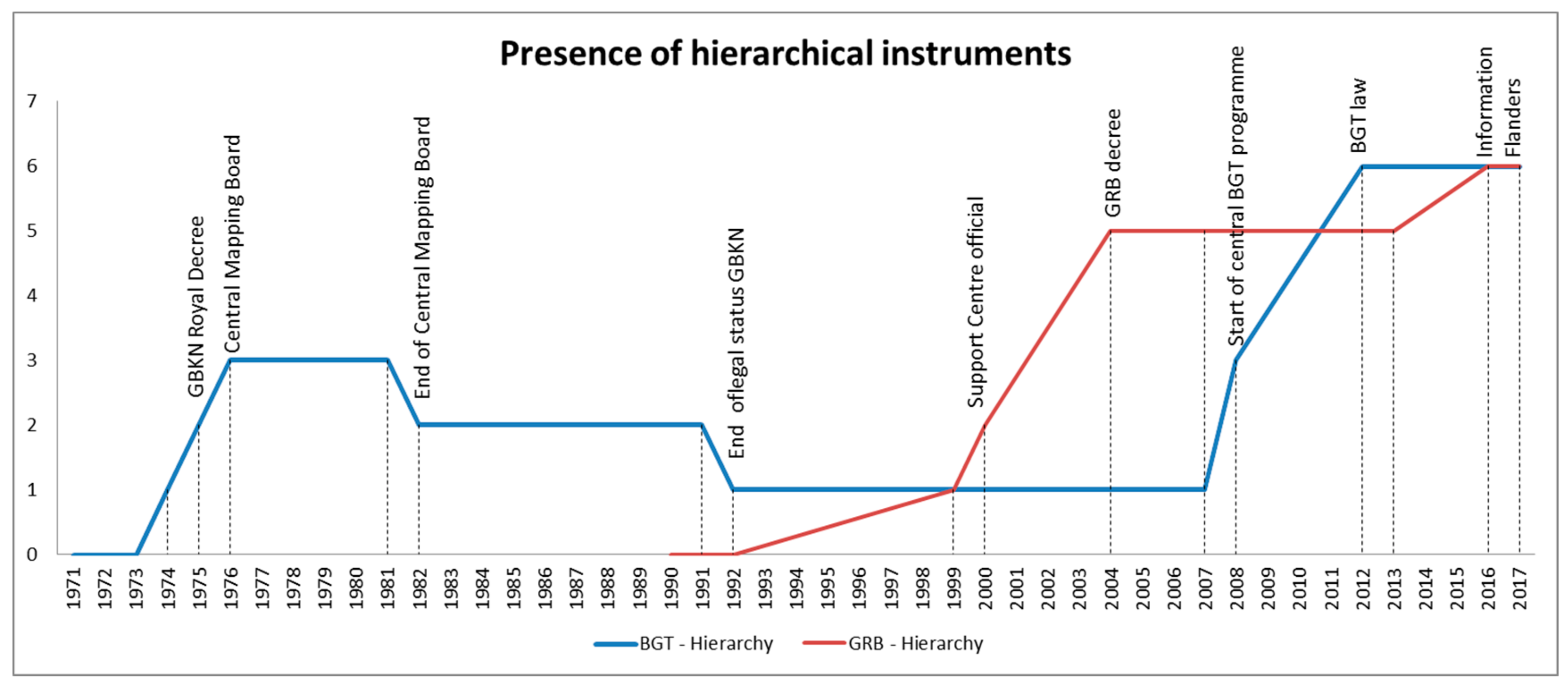
The use of hierarchical controls… runs contrary to the public management discourse on network governance, which purports that informal, horizontal networks are replacing formal, vertical/hierarchical organization. However, a shadow of hierarchy may actually facilitate the ‘joining up’ of government geospatial information systems.[33] (p. 265)
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
- 1971a, Studiecommissie Leidingenregistratie. Rapport Studiecommissie Leidingenregistratie. NGT, Vol. 1971, No. 05, pp. 91–105.
- 1971b, D.L. Rodrigues Lopes. De studiedag leidingenregistratie. NGT, Vol. 1971, No. 09, pp. 148–153.
- 1972a, G.A. van Wely. Grootschalige basiskaart van Nederland. Geodesia, Vol. 1972, No. 07, p. 200.
- 1972b, G.A. van Wely. Grootschalige basiskaart van Nederland. NGT, Vol. 1972, No. 09, pp. 144–145.
- 1973a, M.J.M. Bogaerts, G.F. de Witt, C. Koeman, G.A. van Wely, W.A. Claessen, S. Rienstra, J.A.C.E. van Roermund. Interimrapport Commissie Grootschalige basiskaart. NGT, Vol. 1973, No. 09, pp. 130–135.
- 1973b, C. Zeillemaker. Voorstellen voor de normalisatie van de bladindeling, het formaat en de nummering van grootschalige (1:2000 tot 1:500) topografische kaarten. NGT, Vol. 1973, No. 10, pp. 159–165.
- 1973c, C. Koeman. Voorstel voor bladindeling, het formaat en de nummering van de Nederlandse grootschalige kaart. NGT, Vol. 1973, No. 12, pp. 212–215.
- 1973d, J. Dubbeld. Digitaal kaarteren. NGT, Vol. 1973, No. 05, pp. 85–95.
- 1973e, Projectgroep ‘73. Digitale basiskaartering. Geodesia, Vol. 1973, No. 06, pp. 130–131.
- 1973f, Projectgroep ‘73. Het rapport ‘Digitale Basiskartering’ van de projectgroep ‘73 van de onderafdeling der Geodesie, TH-Delft. NGT, Vol. 1973, No. 09, p. 141.
- 1974a, M.J.M. Bogaerts, G.F. de Witt, C. Koeman, G.A. van Wely, P.A.M. de Vos, J.B. van Reij, W.A. Claessen, S. Rienstra, A. Waalewijn, J.A.C.E. van Roermund. Rapport van de commissie Grootschalige basiskaart. NGT, Vol. 1974, No. 11, pp. 219–237.
- 1975a, Editors. Grootschalige Basiskaart. Geodesia, Vol. 1975, No. 07, pp. 186–187.
- 1975b, Editors. Grootschalige Basiskaart. NGT, Vol. 1975, No. 09, pp. 145–146.
- 1976a, J.P. Gruijters, G.A. van Wely. Installatie centrale kaarteringsraad. Geodesia, Vol. 1976, No. 03, pp. 90–93.
- 1976b, J.P. Gruijters. Installatie centrale kaarteringsraad. NGT, Vol. 1976, No. 03, pp. 57–58.
- 1976c, W.A. Claessen. Grootschalige Basiskaart ‘het Bildt. Geodesia, Vol. 1976, No. 02, pp. 58–59.
- 1976d, W.A. Claessen. Grootschalige Basiskaart ‘het Bildt. NGT, Vol. 1976, No. 02, p. 38.
- 1977, P. Plantinga. GBKN proefproject het Bildt. NGT, Vol. 1977, No. 06, pp. 97–109.
- 1978, G.A van Wely. De vorming van Provinciale Kaarteringscommissies. Geodesia, Vol. 1978, No. 05, pp. 127–130.
- 1980, Unknown. Jaarverslag 1979 Voorlopige Centrale Kaarteringsraad. Geodesia, Vol. 1980, No. 11, p. 435.
- 1983, Unknown. Advies van de voorlopige Centrale Kaarteringsraad. Geodesia, Vol. 1983, No. 09, p. 283.
- 1984a, J. Mol. Heeft het Structuurplan Topografie en Leidingen van de BOCO zin? Geodesia, Vol. 1984, No. 01, pp. 9–11.
- 1984b, Unknown. Jaarverslag 1983 Voorlopige Centrale Kaarteringsraad. Geodesia, Vol. 1984, No. 09, pp. 311–312.
- 1984c, P. van der Molen. Privatisering van overheidstaken op het gebied van de landmeetkunde en kartografie. Geodesia, Vol. 1984, No. 07, pp. 248–254.
- 1984d, A.J.G. Zinken. Decentralisatie kadastertaken. Geodesia, Vol. 1984, No. 10, pp. 345–347.
- 1985a, J.L.G. Henssen. De ontwerp-Kadasterwet. Geodesia, Vol. 1985, No. 11, pp. 386–390.
- 1985b, C.J. Remijnse. Het Kadaster als producent en verstrekker van vastgoedinformatie. Geodesia, Vol. 1985, No. 12, pp. 440–441.
- 1986a, F.B.. Uit de Nieuwjaarstoespraken. Geodesia, Vol. 1986, No. 03, pp. 102–103.
- 1986b, Adri den Boer. GBKN-B een haalbare kaart. Geodesia, Vol. 1986, No. 06, pp. 224–225.
- 1987a, Peter Miete. Het grote geld. Geodesia, Vol. 1987, No. 12, p. 526.
- 1987b, J.B. van der Veen. De ontwikkeling van de GBKN in Overijssel. Geodesia, Vol. 1987, No. 02, pp. 47–51.
- 1988, Editors. Onderzoek naar gebruik en kosten van de grootschalige basiskaart Nederland. Geodesia, Vol. 1988, No. 07, p. 348.
- 1989a, J.W.J. Besemer, F.v.d. Gaag, W. van Pijkeren, J.H.J.M. Vos. Het Kadaster op weg naar de formatie 1990. Geodesia, Vol. 1989, No. 04, pp. 166–170.
- 1989b, L.A.H. Boeije. De toekomstige rol van de grootschalige basiskaart bij de gemeente. Geodesia, Vol. 1989, No. 02, pp. 71–76.
- 1989c, G.P.F. Pistorius. De relatie tussen de nutsbedrijven en de GBKN. Geodesia, Vol. 1989, No. 03, pp. 124–126.
- 1990a, J.G. Versteeg. Een pleidooi voor een betere bijhoudingsregeling GBKN. Geodesia, Vol. 1990, No. 03, pp. 114–118.
- 1990b, C. Zeillemaker. Gemeenten en topografie. Geodesia, Vol. 1990, No. 09, pp. 369–373.
- 1991a, Unknown. Privatisering Kadaster nu op een laag pitje. Geodesia, Vol. 1991, No. 01, p. 84.
- 1991b, J. Besemer, Wim van Pijkeren, Theo Scheele. De (onzekere) toekomst van het Kadaster. Geodesia, Vol. 1991, No. 06, pp. 258–261.
- 1991c, Editors. Kadaster. Geodesia, Vol. 1991, No. 12, p. 555.
- 1992a, Adri den Boer. Ministerraad akkoord met wetsvoorstel verzelfstandiging Kadaster. Geodesia, Vol. 1992, No. 07, pp. 310–311.
- 1992b, Berry van Osch. GBKN-overleg in impasse?. Geodesia, Vol. 1992, No. 04, pp. 160–163.
- 1992c, P. Schreuder, Z. Klaasse. Kadasterwet. Geodesia, Vol. 1992, No. 09, pp. 344–353.
- 1992d, R. Morrema. GBKN-PPP Op weg naar publiek private samenwerking. Geodesia, Vol. 1992, No. 04, pp. 142–146.
- 1992e, Unknown. Samenwerkingscontract Grootschalige Basiskaart van Nederland ondertekend. Geodesia, Vol. 1992, No. 12, p. 535.
- 1993a, Editors. De strijd om tien miljoen. Geodesia, Vol. 1993, No. 05, p. 227.
- 1993b, J. Kats. Grootschalige Basiskaart van Nederland: strijd om tien miljoen?. Geodesia, Vol. 1993, No. 09, p. 425.
- 1993c, F. Molenaars, J.A. Schaart. GBKN een zorgenkind volwassen. Geodesia, Vol. 1993, No. 04, pp. 160–164.
- 1993d, W.H. de Vos. Landelijk Samenwerkingsverband GBKN. Geodesia, Vol. 1993, No. 11, pp. 558–564.
- 1993e, J.H. van Oogen. Terreinmodel Vastgoed. Een algemene classificatie voor ruimtelijke objecten. Geodesia, Vol. 1993, No. 10, pp. 486–490.
- 1993f, Peter Mom. Over jaar of 10 is gans Vlaanderen gecardibd. Vi Matrix, Vol. 1993, No. 12, pp. 10–13.
- 1993g, Peter Mom, Vera Dua. Gewest zal nooit over eigen basisgegevens beschikken. Vi Matrix, Vol. 1993, No. 10, pp. 36–37.
- 1993h, Editors. GIS in België: verdeeldheid troef. Vi Matrix, Vol. 1993, No. 12, p. 49.
- 1993i, Peter Mom. Tien profs tekenen bestek voor een Vlaams ‘GIS-huis. Vi Matrix, Vol. 1993, No. 10, pp. 34–35.
- 1994a, Peter Mom. Belgacom talmt met participatie Cardib. Vi Matrix, Vol. 1994, No. 03, p. 42.
- 1994b, Peter Mom. Cardib valt van de ene verbazing in de andere. Vi Matrix, Vol. 1994, No. 12, pp. 38–39.
- 1994c, Peter Mom. Slechten GIS-barrière plaatst gemeenten voor nieuw obstakel. Vi Matrix, Vol. 1994, No. 03, pp. 20–23.
- 1994d, Peter Mom. Weg vrij voor GIS-Vlaanderen. Vi Matrix, Vol. 1994, No. 06, pp. 44–44.
- 1994e, Peter Mom. Vlaamse GIS-werkgroep vergadert hevig voort. Vi Matrix, Vol. 1994, No. 10, pp. 2–3.
- 1994f, Peter Mom. Optimisme over GIS Vlaanderen moet men soms van verre zoeken. Vi Matrix, Vol. 1994, No. 10, pp. 6–7.
- 1995a, J.B. van der Veen, H.T. Uitermark. Naar een objectgerichte GBKN?! Van basiskaart tot basisbestand via het objectbegrip. Geodesia, Vol. 1995, No. 02, pp. 83–88.
- 1995b, C.H.J. Lemmen. Topologie en unike objectidentificatie. Enige aspecten bij het uitwisselen van ruimtelijke gegevens. Geodesia, Vol. 1995, No. 05, pp. 231–235.
- 1995c, Peter Mom. GIS-Vlaanderen krijgt stilaan de allure van een fata morgana. Vi Matrix, Vol. 1995, No. 01, pp. 6–9.
- 1995d, Peter Mom. Regeringsbesluit GIS-Vlaanderen. Vi Matrix, Vol. 1995, No. 06, p. 47.
- 1996a, Berry van Osch. Van de redactie: De objectgerichte GBKN: wanneer komt er schot in?. Geodesia, Vol. 1996, No. 04, p. 138.
- 1996b, Theo Scheele. Themadag Objectgerichte GBKN in Zeeland. Geodesia, Vol. 1996, No. 12, pp. 553–554.
- 1997a, Ad van der Meer. Van de redactie: Objectgerichte GBKN als religieus dispuut. Geodesia, Vol. 1997, No. 04, p. 154.
- 1997b, Jaap van der Veen. Objectgerichtheid en de GBKN. Een manier om tot standaardisatie te komen. Geodesia, Vol. 1997, No. 05, pp. 227–228.
- 1997c, Berry van Osch. Zijn we wel klaar voor een Objectgerichte GBKN?. Geodesia, Vol. 1997, No. 07, p. 298.
- 1997d, René van der Schans. We zijn niet klaar voor een objectgerichte GBKN. Een reactie op Berry van Osch’ redactionele commentaar. Geodesia, Vol. 1997, No. 09, p. 397.
- 1997e, Peter Mom. Cardib onvermoeid optimistisch over Grootschalige BasisKaart Vlaanderen. Vi Matrix, Vol. 1997, No. 02, pp. 33–35.
- 1997f, Peter Mom. Interelectra gaat nu met ‘Cardib-kaart’ eigen weg. Vi Matrix, Vol. 1997, No. 09, pp. 40–42.
- 1997g, Peter Mom. Cardib en OC optimistisch over één grootschalige basiskaart. Vi Matrix, Vol. 1997, No. 12, p. 43.
- 1998, LSV-GBKN. Objectgerichte GBKN voorlopig geen haalbare kaart. Geodesia, Vol. 1998, No. 01, p. 42.
- 1999a, Landelijk Samenwerkingsverband GBKN. GBKN-vervaardiging bijna gereed. Geodesia, Vol. 1999, No. 06, p. 297.
- 1999b, J.C. Meerkerk, J.B. van der Veen. De GBKN, klaar voor de 21ste eeuw!?. Geodesia, Vol. 1999, No. 04, pp. 163–169.
- 1999c, Peter Mom. OC start scanproject. Vi Matrix, Vol. 1999, No. 02, p. 36.
- 1999d, Peter Mom. Grootschalig Referentie Bestand voor Vlaanderen haalbare kaart. Vi Matrix, Vol. 1999, No. 12, pp. 38–40.
- 1999e, Peter Gorlé. Samenwerking GIS-Vlaanderen krijgt decretale basis. Vi Matrix, Vol. 1999, No. 09, pp. 34–37.
- 2000a, J. Polman. Hink, Stap, Sprong. De geschiedenis van het ontstaan van de GBKN. Geodesia, Vol. 2000, No. 07, pp. 319–326.
- 2000b, L.M. Murre. GBKN anno 2000. De stand van zaken en het perspectief voor de toekomst. Geodesia, Vol. 2000, No. 07, pp. 327–332.
- 2000c, Editors. GIS bij wet geregeld. Vi Matrix, Vol. 2000, No. 09, p. 41.
- 2001a, L.M. Murre. Laatste GBKN in Hardinxveld/Giessendam opgeleverd. Geodesia, Vol. 2001, No. 02, p. 83.
- 2001b, J.C. Meerkerk, J.W.F.M. van Grunsven. GBKN, van aanbod naar vraaggericht. Geodesia, Vol. 2001, No. 03, pp. 117–121.
- 2001c, LSV-GBKN. Berichten uit de Stuurgroep GBKN. Geodesia, Vol. 2001, No. 12, p. 600.
- 2001d, Peter Mom. GRB Vlaanderen staat op de rails. Vi Matrix, Vol. 2001, No. 12, pp. 28–30.
- 2002a, Ad van der Meer. De GBKN een authentieke registratie? Geodesia, Vol. 2002, No. 06, p. 235.
- 2002b, Ad van der Meer. De GBKN-kip en het AR-ei. Geodesia, Vol. 2002, No. 09, p. 327.
- 2002c, N.J.M van Eekelen, E.J.M. Weesie. Instrumenten voor een uniforme GBKN. Geodesia, Vol. 2002, No. 03, pp. 108–110.
- 2002d, Adri den Boer. Geo-informatiebeleid in Tweede Kamer. Geodesia, Vol. 2002, No. 09, pp. 322–326.
- 2002e, Leen Murre. Topografie en gemeenten. Geodesia, Vol. 2002, No. 10, p. 387.
- 2002f, Peter Mom. Londerzeel prijst de dag dat GRB wordt opgeleverd. Vi Matrix, Vol. 2002, No. 06, pp. 30–31.
- 2003a, H. Schallenberg. De grootschalige basiskaart een gemeentelijke zorg. Geodesia, Vol. 2003, No. 01, pp. 4–9.
- 2003b, L.M. Murre. Nieuwe Stichting LSV GBKN van start. Geodesia, Vol. 2003, No. 09, pp. 342–345.
- 2003c, Adri den Boer. Eindrapportage Stroomlijning Basisgegevens. Geodesia, Vol. 2003, No. 05, pp. 210–212.
- 2003d, E. Scheltes, L.A. Smit, Ad van der Meer, Jan de Kruif. Gemeenten verantwoordelijk voor topografie’. Geodesia, Vol. 2003, No. 02, pp. 82–85.
- 2003e, L.M. Murre. Kunnen ‘gemeenten verantwoordelijk zijn voor topografie’?. Geodesia, Vol. 2003, No. 04, p. 179.
- 2003f, E. Dolle. RSV en TPG sluiten aan. Geodesia, Vol. 2003, No. 11, p. 457.
- 2004, Peter Mom. GRB-primeur voor Geetbets. Vi Matrix, Vol. 2004, No. 11, pp. 47–48.
- 2005, Redactie. Minister Kris Peeters volgt realisatie van geo-basisbestanden met argusogen. Vi Matrix, Vol. 2005, No. 12, pp. 44–47.
- 2006a, Adri den Boer. Themabijeenkomst basisregistraties in trek. Geo-info, Vol. 2006, No. 07, pp. 314–316.
- 2006b, L.M. Murre. Wordt de GBKN een basisregistratie?. Geo-info, Vol. 2006, No. 02, pp. 66–68.
- 2006c, Koen Vervloessem. Iedereen een gelijke manier van aanmeten en alle objecten in de juiste layer. Geoplatform, Vol. 2006, No. 09, pp. 6–9.
- 2006d, Peter van Es. GIS Vlaanderen: verleden, heden en toekomst. Geoplatform, Vol. 2006, No. 09, pp. 10–15.
- 2009a, Adri den Boer, Martin Peersmann. Martin Peersmann: 11 maanden ‘mister GBKN2BGT’. Geo-info, Vol. 2009, No. 10, pp. 4–6.
- 2009c, Nico vande Kerkhof. Vlaanderen moet leren omgaan met een gefaseerde GRB-realisatie. Geoplatform, Vol. 2009, No. 09, pp. 14–19.
- 2009b, Ronald Bokhove. Gemeenten kleuren de BGT in, maar hoe?. Geo-info, Vol. 2009, No. 11, pp. 30–32.
- 2010, Adri den Boer, Ruud van Rossem. Ruud van Rossem: nu mister BGT. Geo-info, Vol. 2010, No. 01, pp. 22–24.
- 2011, Adri den Boer. Bronhoudersoverleg BGT op naar uniformering. Geo-info, Vol. 2011, No. 07, pp. 21–22.
- 2012a, Ruud van Rossem. De BGT: van denken naar doen. Geo-info, Vol. 2012, No. 06, pp. 4–8.
- 2012b, Bart Maessen. Landelijke voorziening BGT. Geo-info, Vol. 2012, No. 06, pp. 22–24.
- 2012c, Ernst Koperdraat. Nut en noodzaak van een samenwerkingsverband van bronhouders. Geo-info, Vol. 2012, No. 06, pp. 26–29.
- 2012d, Martin Peersmann, Sieb Dijkstra. Van GBKN naar BGT in historisch perspectief. Geo-info, Vol. 2012, No. 6, pp. 38–42.
- 2013, Editors. Wet BGT door de Eerste Kamer. Geo-info, Vol. 2013, No. 08, p. 44.
- 2014, BGTweb. Valkenswaard als eerste helemaal in de BGT!. Geo-info, Vol. 2014, No. 06, p. 15.
- 2016, Roelof Keppel. Verslag FLAGIS-bijeenkomst 8 december 2015 te Lier (B). Geo-info, Vol. 2016, No. 01, p. 34.
- 2017a, Roelof Keppel; Astrid van den Hoek, Nienke Zeijlemaker. Grip op data: de puzzel van Rijkswaterstaat. Geo-info, Vol. 2017, No. 03, pp. 24–27.
- 2017b, Marcel Rietdijk; Gerlof de haan; Sandra Leijten. Met de BGT op tijdreis door de openbare ruimte. Geo-info, Vol. 2017, No. 03, pp. 30–33.
References
- Macharis, C.; Crompvoets, J. A stakeholder-based assessment framework applied to evaluate development scenarios for the spatial data infrastructure for flanders. Comput. Environ. Urban. Syst. 2014, 46, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vancauwenberghe, G. Coordination within Spatial Data Infrastructures: An Analysis of Exchange and Use of Geographical Information in Flanders; KU Leuven: Leuven, Belgium, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bregt, A.K.; Crompvoets, J.W.H.C. Geo-informatie in de netwerksamenleving, een tweeluik. Vi Matrix 2000, 55, 16–19. [Google Scholar]
- Bregt, A.K. Value added services en de nationale geo-informatie infrastructuur. In Proceedings of the Promoting value-added GI services, Den Haag, The Netherlands, 27 January 2006; pp. 77–81. [Google Scholar]
- Robichau, R.W. The mosaic of governance: Creating a picture with defintions, theories, and debates. Policy Stud. J. 2011, 39, 113–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollitt, C.; Bouckaert, G. Public Management Reform. A Comparative Analysis: New Public Management, Governance, and the Neo-Weberian State; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Vandenbroucke, D.; Crompvoets, J.; Vancauwenberghe, G.; Dessers, E.; Van Orshoven, J. A network perspective on spatial data infrastructures: Application to the sub-national sdi of flanders (Belgium). Trans. GIS 2009, 13, 105–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendriks, P.H.J.; Dessers, E.; van Hootegem, G. Reconsidering the definition of a spatial data infrastructure. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2012, 26, 1479–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mörth, U. The market turn in eu governance—The emergence of public-private collaboration. Gov. Int. J. Policy Adm. Inst. 2009, 22, 99–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rijke, J.; Brown, R.; Zevenbergen, C.; Ashley, R.; Farelly, M.; Morison, P.; van Herk, S. Fit-for-purpose governance: A framework to make adaptive governance operational. Environ. Sci. Policy 2012, 22, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuyama, F. What is governance? Governance 2013, 26, 347–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coetzee, S.; Wolff-Piggott, B. A review of sdi literature: Searching for signs of inverse infrastructures. In Cartography—Maps Connecting the World; Sluter, C.R., Cruz, C.B.M., Menezes, P.M.L., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 113–127. [Google Scholar]
- Kooiman, J. Governing as Governance; SAGE: London, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Rajabifard, A.; Feeney, M.-E.F.; Williamson, I.P. Future directions for sdi development. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2002, 4, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grus, L.; Crompvoets, J.; Bregt, A.K. Spatial data infrastructures as complex adaptive systems. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2010, 24, 439–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhoest, K.; Bouckaert, G.; Peters, B.G. Janus-faced reorganization: Specialization and coordination in four oecd countries in the period 1980–2005. Int. Rev. Adm. Sci. 2007, 73, 325–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hood, C. The “new public management” in the 1980s: Variations on a theme. Account. Organ. Soc. 1995, 20, 93–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The White House. Coordinating geographic data acquisition and access: The national spatial data infrastructure. In Executive Order 12906; Federal Register: Washington, DC, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Masser, I.A.N. All shapes and sizes: The first generation of national spatial data infrastructures. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 1999, 13, 67–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gore, A. Creating a Government that Works Better & Costs Less; Report of the National Performance Review; Status Report; US Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1994.
- Rajabifard, A.; Feeney, M.E.; Williamson, I.; Masser, I. National sdi initiatives. In Developing Spatial Data Infrastructures: From Concept to Reality; Williamson, I., Rajabifard, A., Feeney, M.-E.F., Eds.; Taylor & Francis: London, UK, 2003; pp. 99–114. [Google Scholar]
- Crompvoets, J.; Bregt, A.; Rajabifard, A.; Williamson, I. Assessing the worldwide developments of national spatial data clearinghouses. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2004, 18, 665–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborne, S.P. The New Public Governance: Emerging Perspectives on the Theory and Practice of Public Governance; Routledge: Abingdon-on-Thames, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Worthy, B. More open but not more trusted? The effect of the freedom of information act 2000 on the united kingdom central government. Governance 2010, 23, 561–582. [Google Scholar]
- European Parliament. Directive 2003/98/ec of the European Parliament and of the Council of 17 November 2003 on the Re-Use of Public Sector Information; European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Geographic Information Panel. Place Matters: The Location Strategy for Het United Kingdom; Communities and Local Government: London, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, H.S.; Hvingel, L.; Schrøder, L. Open government data—A key element in the digital society. In Proceedings of the Second Joint International Conference on Electronic Government and the Information Systems Perspective, and Electronic Democracy, Prague, Czech Republic, 26–28 August 2013; pp. 167–180. [Google Scholar]
- Bregt, A.K.; Castelein, W.T.; Grus, L.; Eertink, D. De Effecten van een Open Basisregistratie Topografie (Brt); Wageningen University: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Welle Donker, F. Public sector geo web services: Which business model will pay for a free lunch? In Sdi Convergence. Research, Emerging Trends, and Critical Assessment; Van Loenen, B., Besemer, J.W.J., Zevenbergen, J.A., Eds.; Optima Grafische Communicatie: Delft, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 35–50. [Google Scholar]
- Maguire, D.J.; Longley, P.A. The emergence of geoportals and their role in spatial data infrastructures. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2005, 29, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koerten, H. Taming Technology. The Narrative Anchor Reconciling Time, Territory and Technology in Geoinformation Infrastructures; Delft University of Technology: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Sanz, E. Open governments and their cultural transitions. In Open Government: Opportunities and Challenges for Public Governance; Gascó-Hernández, M., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Lance, K.T.; Georgiadou, Y.; Bregt, A.K. Cross-agency coordination in the shadow of hierarchy: ‘Joining up’ government geospatial information systems. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2009, 23, 249–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, G.A. Document analysis as a qualitative research method. Qual. Res. J. 2009, 9, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryman, A. Social Research Methods, 4th ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, J. A Matter of Record; Polity Press: Cambridge, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Ministerie van Infrastructuur en Milieu. Monitorrapportage Juli 2017: Bgt Voortgang Transitie; Ministerie van Infrastructuur en Milieu: Den Haag, The Netherlands, 2017.
- Vlaamse Raad. Handelingen 7-8-9-10-11, Vergaderingen van November 1992; Vlaamse Raad: Brussels, Belgium, 1992; pp. 237–254. [Google Scholar]
- Kok, B.; van Loenen, B. How to assess the success of national spatial data infrastructures? Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2005, 29, 699–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minkov, M.; Hofstede, G. Clustering of 316 european regions on measures of values. Cross-Cult. Res. 2014, 48, 144–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikonomou, I. The ‘nationalisation’ of the galileo programme. In Theorizing European Space Policy; Hoerber, T.C., Sigalas, E., Eds.; Lexington Books: Lanham, MD, USA, 2016; pp. 141–158. [Google Scholar]
- Publieke Dienstverlening op de Kaart (PDOK). Available online: www.pdok.nl (accessed on 19 July 2017).
- Jessop, B. Governance and meta-governance: On reflexivity, requisite variety and requisite irony. In Governance, as Social and Political Communication; Manchester University Press: Manchester, UK, 2003; pp. 101–116. [Google Scholar]
- Dietz, T.; Ostrom, E.; Stern, P.C. The struggle to govern the commons. Science 2003, 302, 1907–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edelenbos, J.; Bregt, A.; Broesie, R.; Dammers, E.; Meyer, H.; Neumann, D.; Warmerdam, M. An action perspective fot the delta. In New Perspectives on Urbanizing Deltas; Meyer, H., Bregt, A., Dammers, E., Edelenbos, J., Eds.; MUST Publishers: Amersfoort, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 173–187. [Google Scholar]
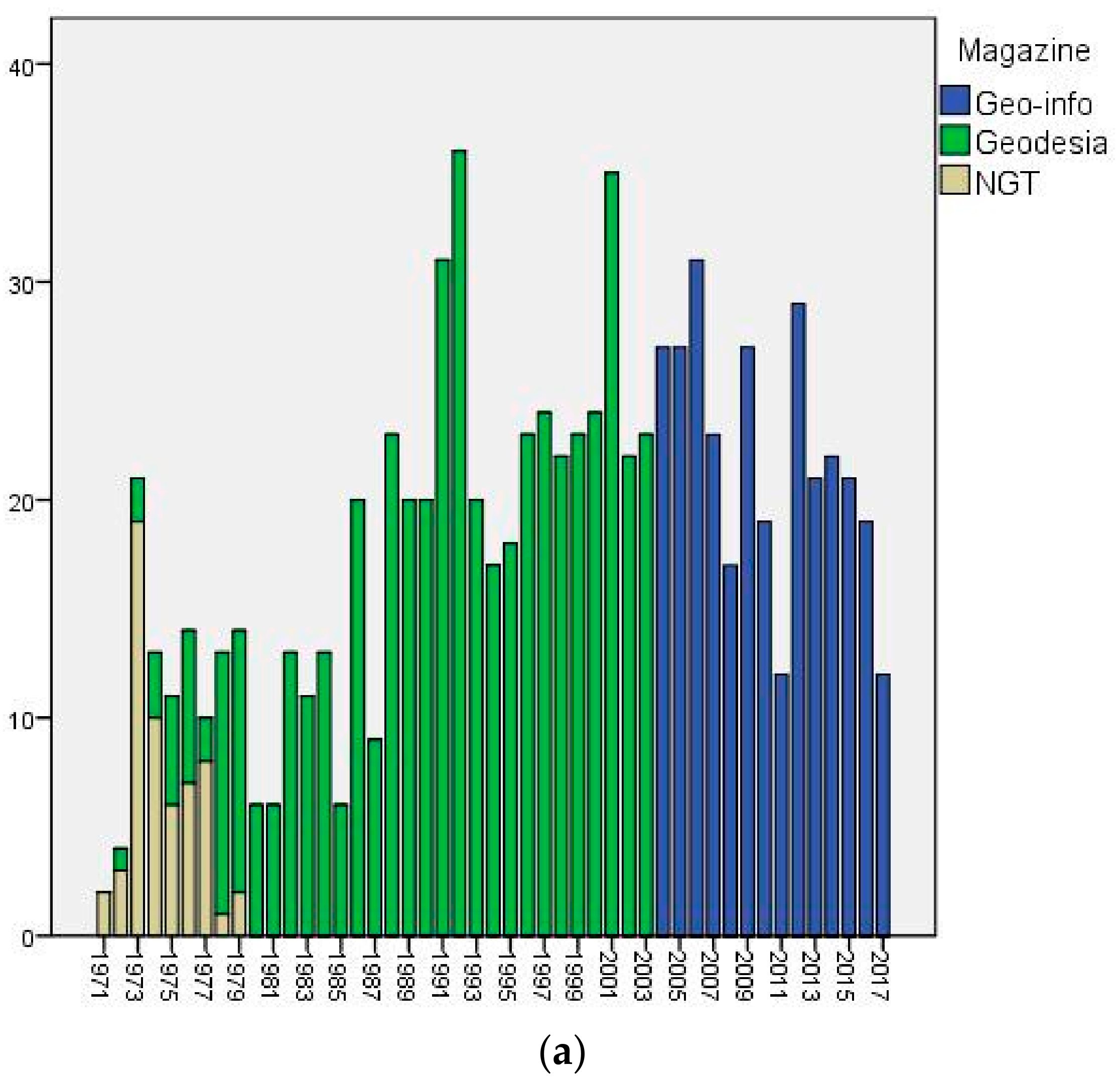
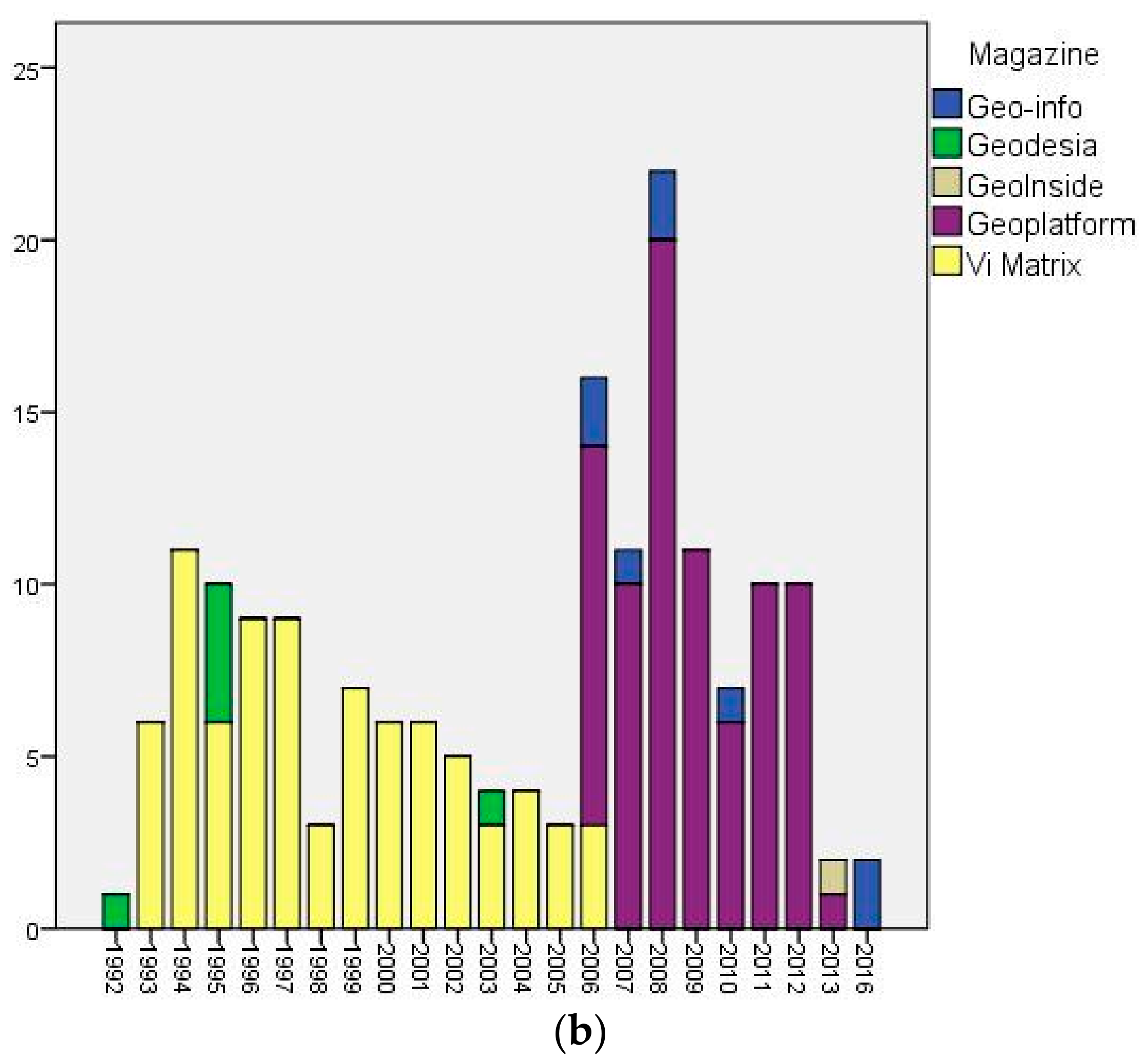

| Magazine | Active Period | Coverage |
|---|---|---|
| Nationaal Geodetisch Tijdschrift (NGT) | 1971–1979 | The Netherlands |
| Geodesia | 1959–2003 | The Netherlands |
| Geo-info | 2004–now | The Netherlands |
| Vi-Matrix | 1993–2010 | The Netherlands and Flanders 1 |
| GeoInside | 2011–2013 | The Netherlands |
| GeoPlatform Vlaanderen | 2006–2013 | Flanders |
| Year | Governance Changes BGT | Year | Governance Changes GRB |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1975 | Royal Decree GBKN | 1990 | Start of Cardib |
| 1982 | End of the Central Mapping Board | 1992 | GIS Flanders intervention by Minister |
| 1992 | Cadastre and national government pull-back, start of public-private partnerships | 1999 | End of Cardib, start of GRB |
| 2008 | Start of BGT programme | 2004 | GRB official decree |
| 2012 | New governance for transition to BGT | 2007 | Start of AGIV 1 |
| 2017 | New governance structure for greater cohesion between spatial key registries | 2015 | Integration of GRB in e-government services, establishment of Information Flanders |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sjoukema, J.-W.; Bregt, A.; Crompvoets, J. Evolving Spatial Data Infrastructures and the Role of Adaptive Governance. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2017, 6, 254. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi6080254
Sjoukema J-W, Bregt A, Crompvoets J. Evolving Spatial Data Infrastructures and the Role of Adaptive Governance. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information. 2017; 6(8):254. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi6080254
Chicago/Turabian StyleSjoukema, Jaap-Willem, Arnold Bregt, and Joep Crompvoets. 2017. "Evolving Spatial Data Infrastructures and the Role of Adaptive Governance" ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information 6, no. 8: 254. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi6080254
APA StyleSjoukema, J.-W., Bregt, A., & Crompvoets, J. (2017). Evolving Spatial Data Infrastructures and the Role of Adaptive Governance. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 6(8), 254. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi6080254





