Local–Linear Two-Stage Estimation of Local Autoregressive Geographically and Temporally Weighted Regression Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. GTWRLAR Model
2.2. Local–Constant 2SLS Estimation of the GTWRLAR Model
2.3. Local–Linear 2SLS Estimation of the GTWRLAR Model
2.4. Generating the Calibration Weights Matrix and Selecting Optimal Spatial and Temporal Bandwidths
3. Simulation Experiment
3.1. Data Generation
- (i)
- (ii)
- (iii)
- (iv)
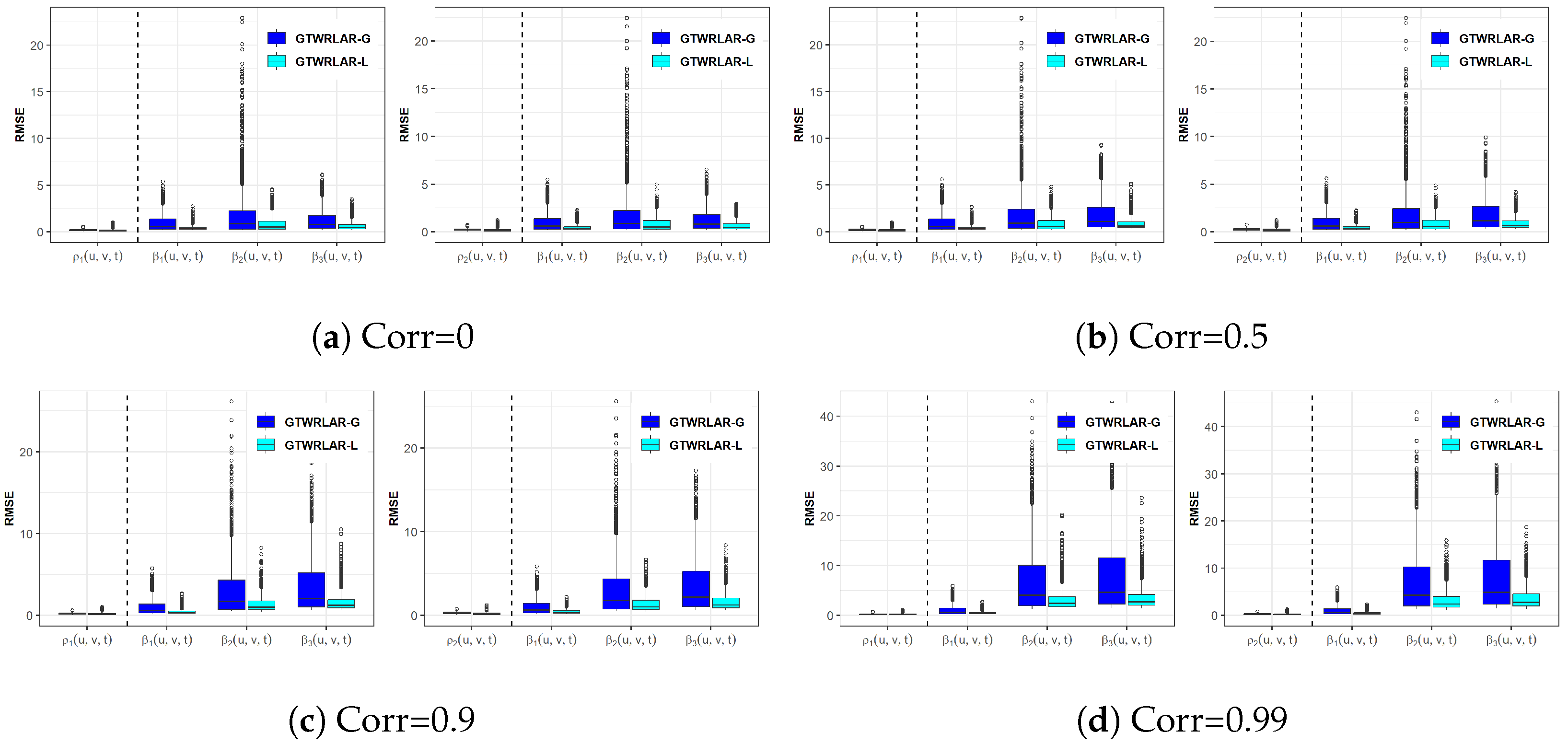
3.2. Accuracy Indicators of Simulation Effect
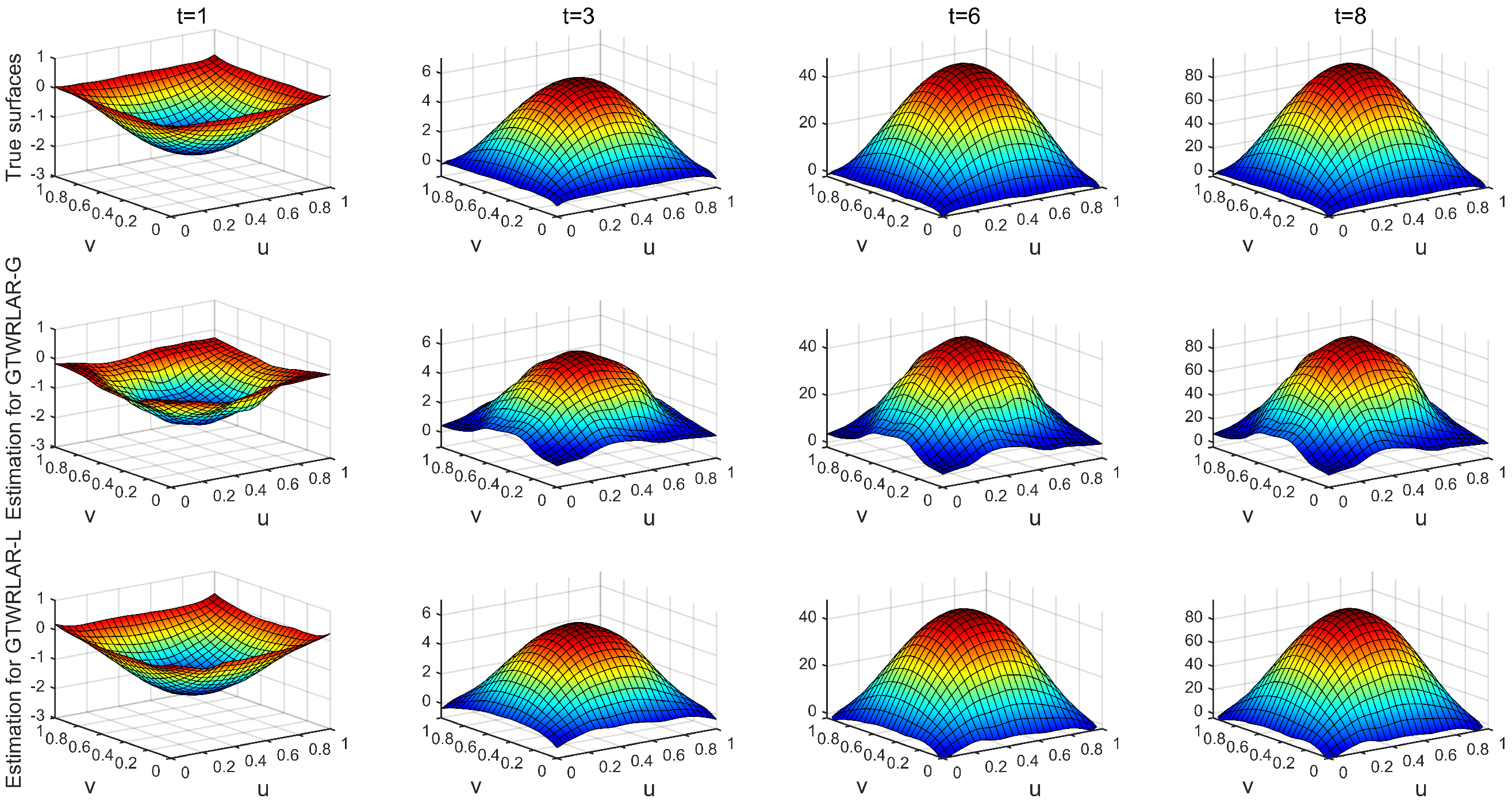
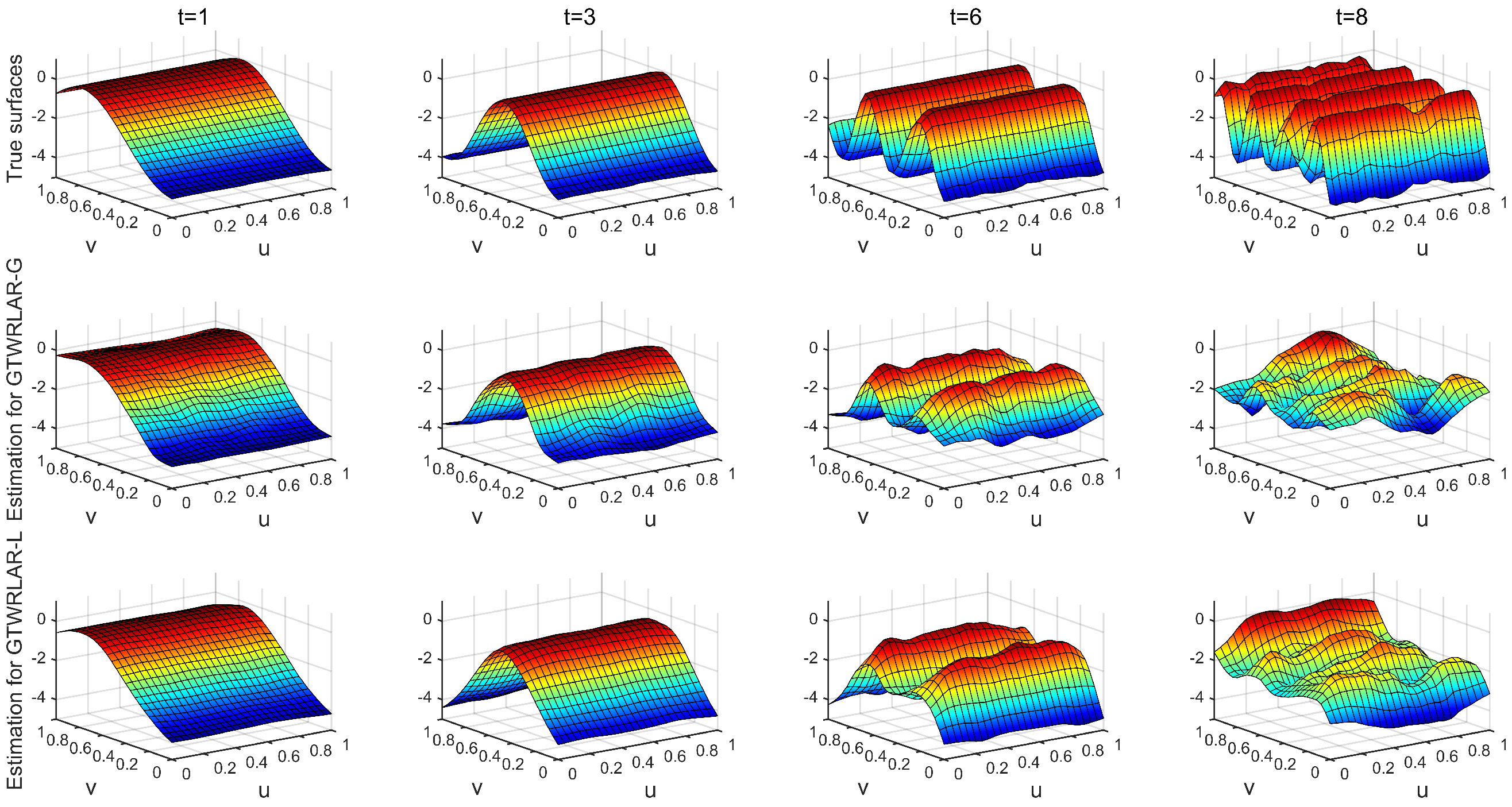
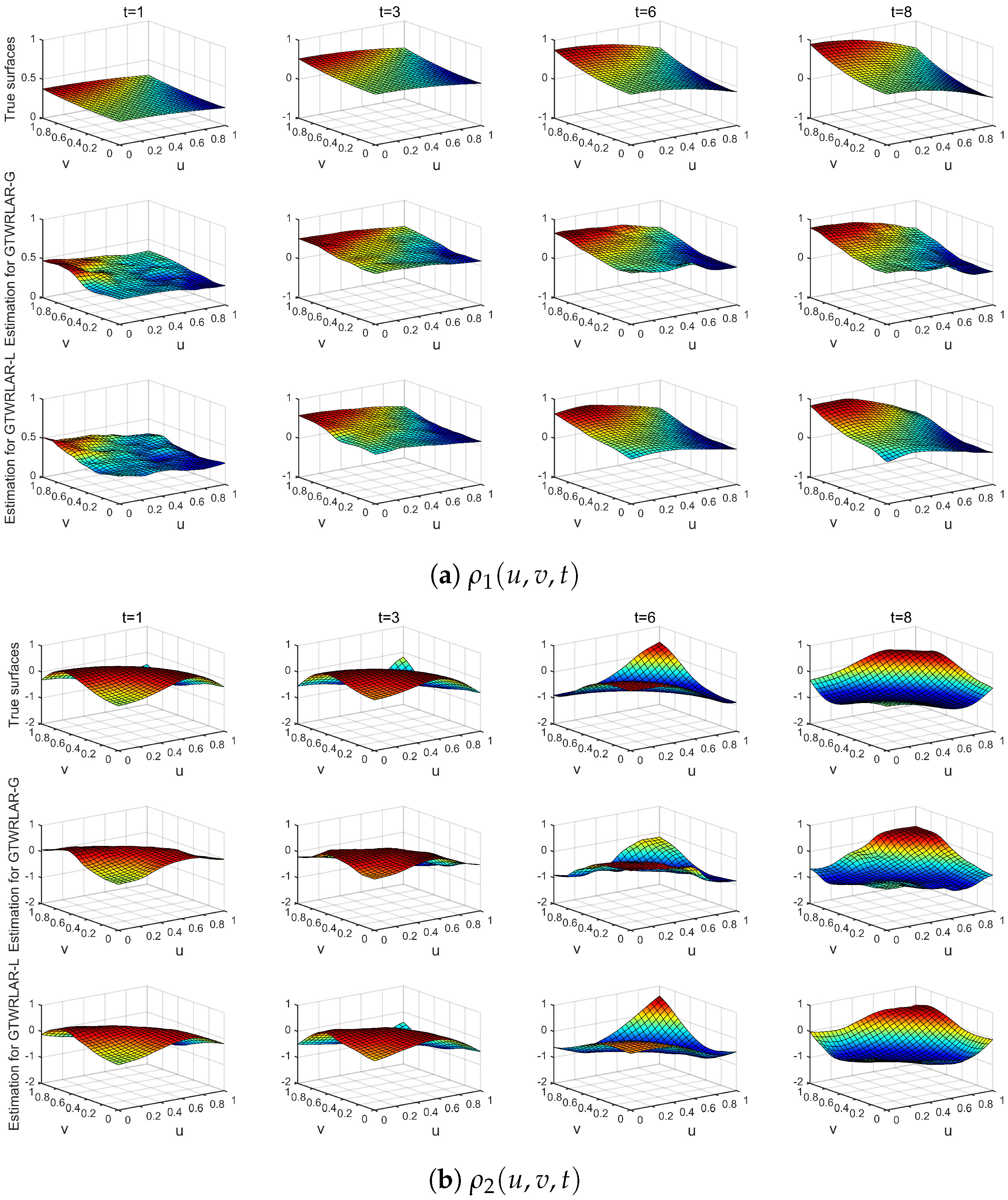
3.3. Simulation Results
4. A Real-Life Application
4.1. Data Introduction
- GDP (CNY): Per capita regional GDP;
- IIR (%): Proportion of secondary-industry added value in GDP;
- PP: Permanent population in ten thousand;
- UR (%): Proportion of urban population;
- SDE (tons): Industrial sulfur dioxide emissions;
- DPE (tons): Industrial soot and dust emissions;
- SWDR (%): Harmless treatment rate of domestic waste.
4.2. Model Construction
4.3. Result Analysis
5. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
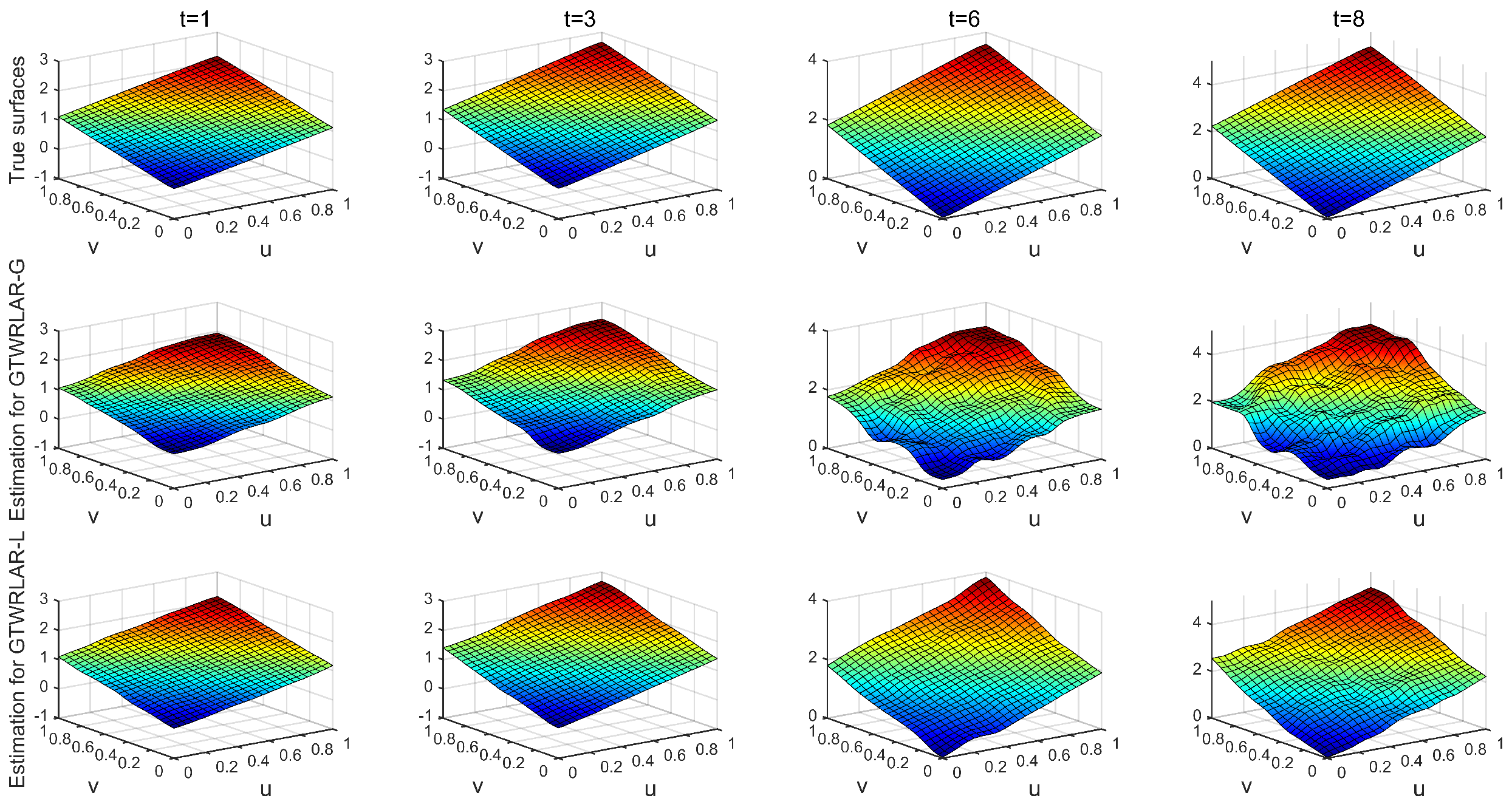
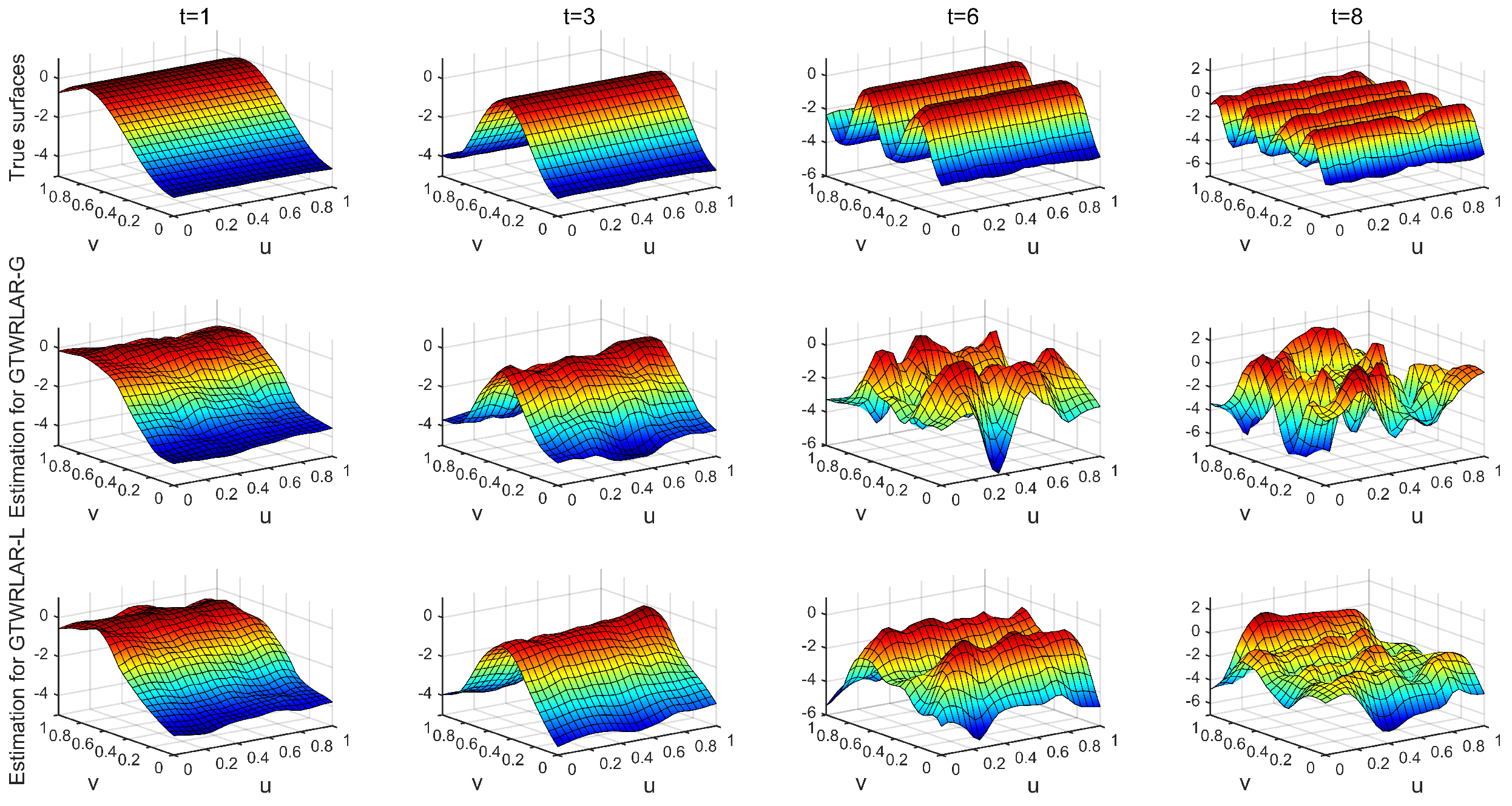
Appendix A.1. The True Surfaces and Estimated Surfaces of the Regression and Autoregressive Coefficients with the Correlation Coefficient Corr = 0.5
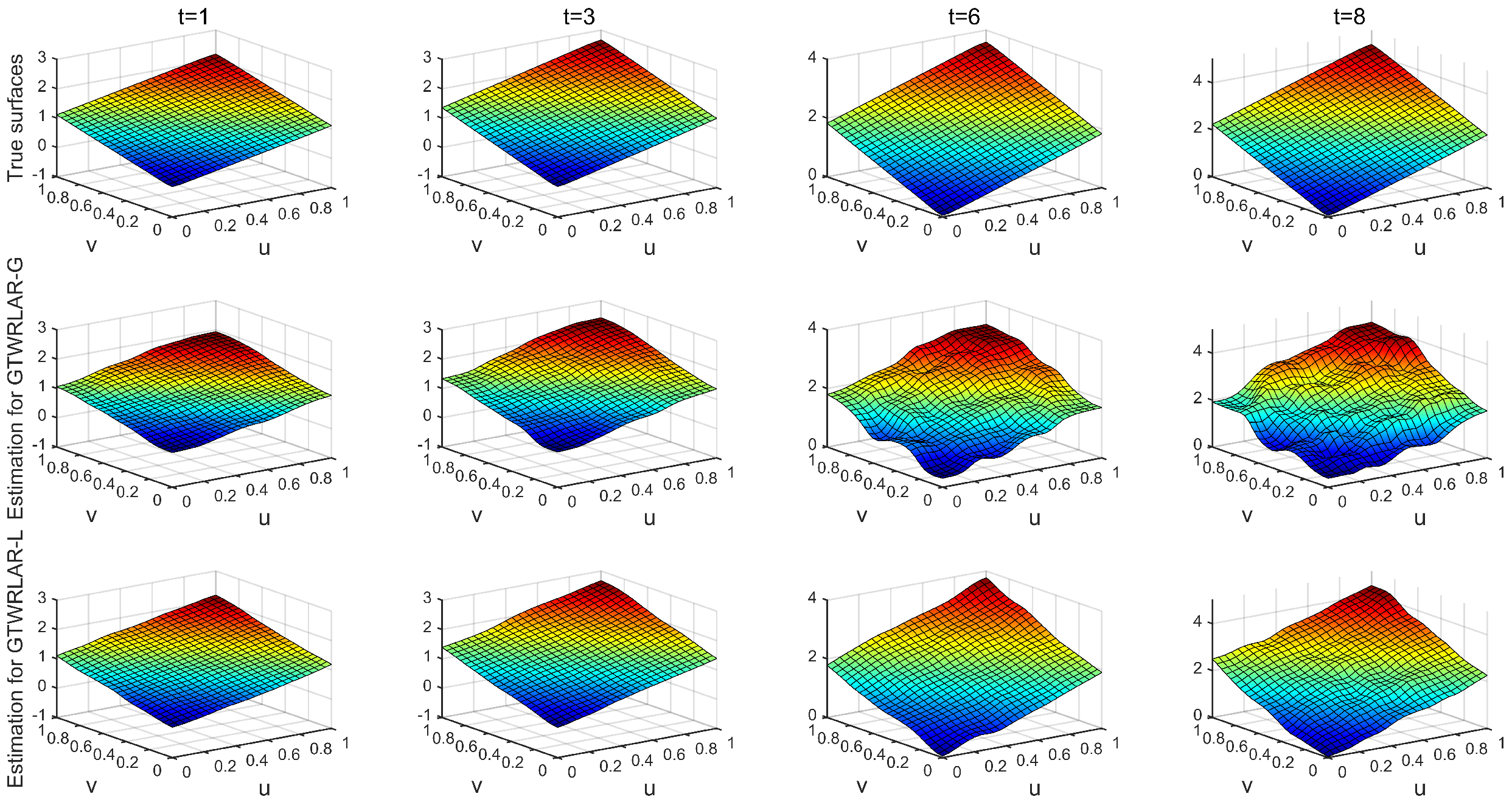


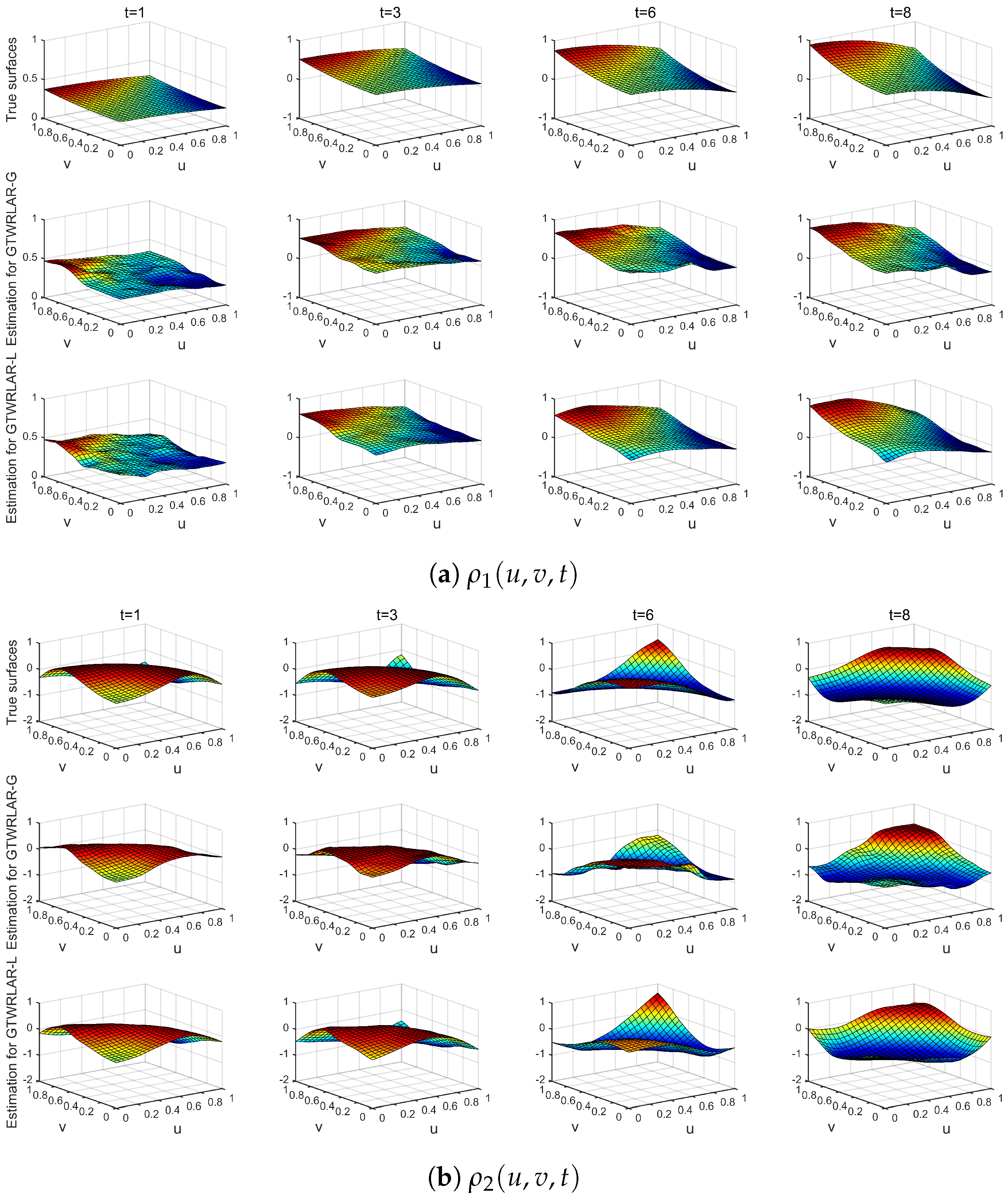
Appendix A.2. The True Surfaces and Estimated Surfaces of the Regression and Autoregressive Coefficients with the Correlation Coefficient Corr = 0.9
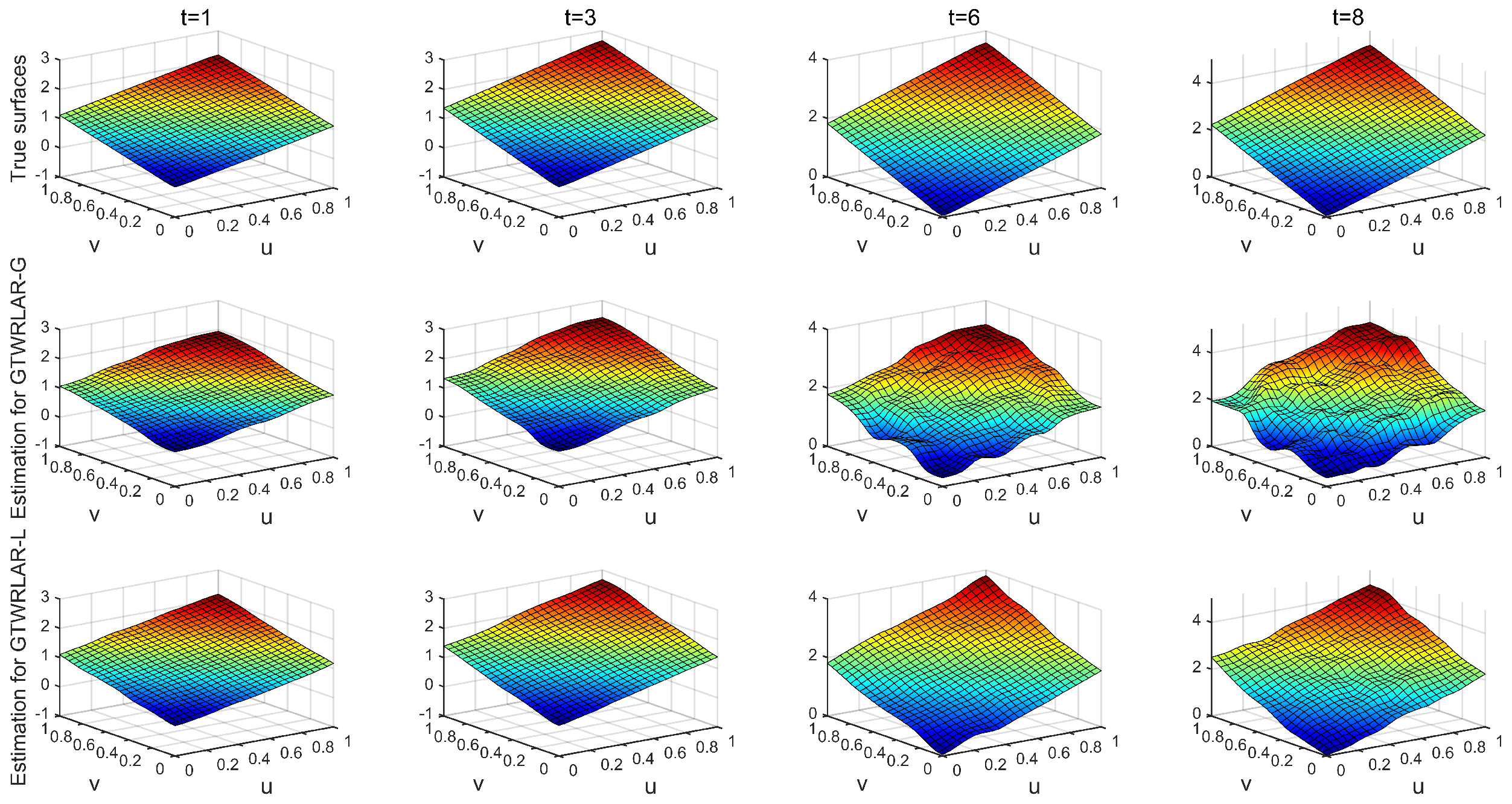

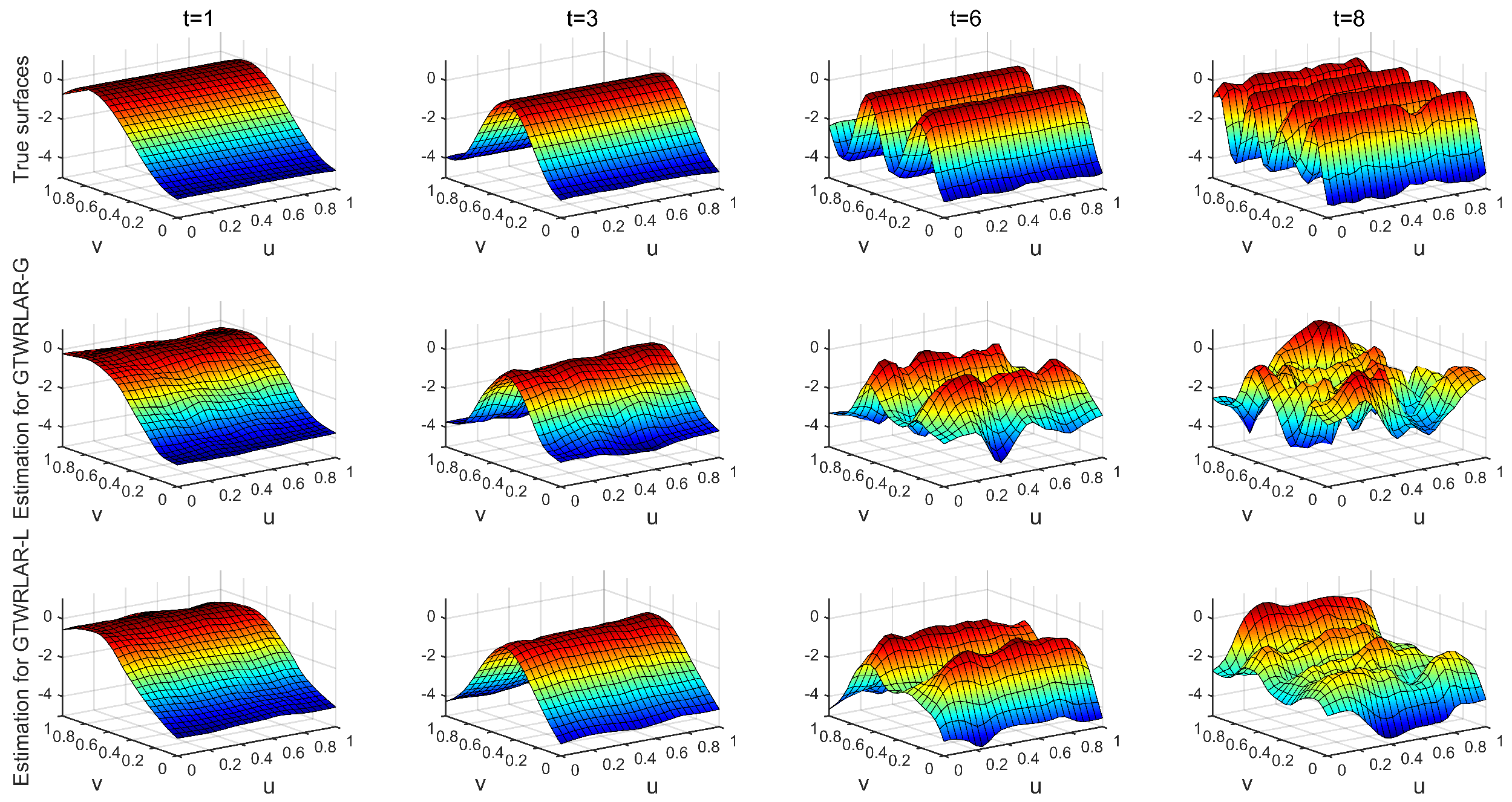
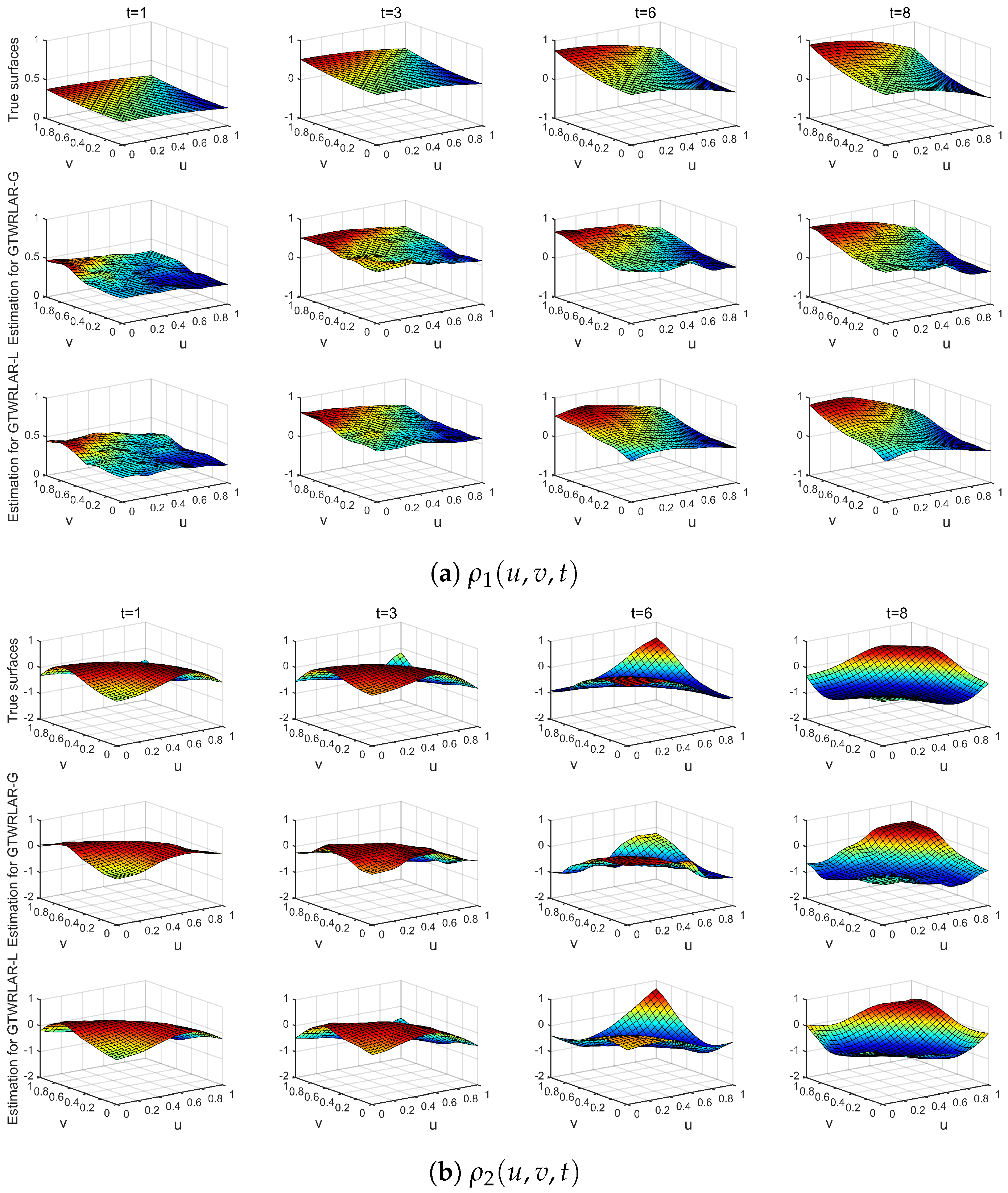
Appendix A.3. The True Surfaces and Estimated Surfaces of the Regression and Autoregressive Coefficients with the Correlation Coefficient Corr = 0.99



References
- Mcerlean, S.; Patton, M. Spatial Effects within the Agricultural Land Market in Northern Ireland. J. Agric. Econ. 2003, 54, 35–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, D. District House Price Movements in England and Wales 1997–2007:An Exploratory Spatial Data Analysis Approach. Urban Stud. 2012, 49, 1411–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunsdon, C.; Fotheringham, A.S.; Charlton, M.E. Geographically Weighted Regression: A Method for Exploring Spatial Nonstationarity. Geogr. Anal. 1996, 28, 281–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Wu, B.; Barry, M. Geographically and temporally weighted regression for modeling spatio-temporal variation in house prices. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2010, 24, 383–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotheringham, A.S.; Crespo, R.; Yao, J. Geographical and Temporal Weighted Regression (GTWR). Geogr. Anal. 2015, 47, 431–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Tang, Q.; Gong, D.Y.; Zhang, Z. Estimating ground-level PM 2.5 concentrations in Beijing using a satellite-based geographically and temporally weighted regression model. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 198, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Ma, L.; Ju, T. Independent and compound characteristics of PM2.5, ozone, and extreme heat pollution events in Korea. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2025, 197, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Z.; Wu, S.; Zhang, F.; Liu, R.; Zhou, Y. Extending geographically and temporally weighted regression to account for both spatiotemporal heterogeneity and seasonal variations in coastal seas. Ecol. Inform. 2018, 43, 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacheheb, M.; Noy, I.; Kahui, V. Marine heatwaves and commercial fishing in New Zealand. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 954, 176558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Zhang, J.; Ding, C.; Wang, Y. A geographically and temporally weighted regression model to explore the spatiotemporal influence of built environment on transit ridership. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2018, 70, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, J.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Z.; Shan, X. Exploring spatiotemporal patterns and influencing factors of ridesourcing and traditional taxi usage using geographically and temporally weighted regression method. Transp. Plan. Technol. 2023, 46, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, L.; Zhang, W.; Bao, J. Influencing factors for right turn lane crash frequency based on geographically and temporally weighted regression models. J. Saf. Res. 2023, 86, 191–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Z.M.; Mei, C.L.; Wang, H.H.; Du, W.L. Spatiotemporal effects of climate factors on childhood hand, foot, and mouth disease: A case study using mixed geographically and temporally weighted regression models. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2021, 35, 1611–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.; Chen, J.; Wu, W.; Ding, J.; Wang, L.; Zhu, Z.; Chen, D. Spatiotemporal association of urban park characteristics and physical activity levels based on GTWR: A serial cross-sectional observational study. J. Urban Manag. 2024, 13, 398–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pace, R.K.; LeSage, J. Spatial Autoregressive Local Estimation. In Recent Advances in Spatial Econometrics; Palgrave Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2004; pp. 31–51. [Google Scholar]
- Geniaux, G.; Martinetti, D. A new method for dealing simultaneously with spatial autocorrelation and spatial heterogeneity in regression models. Reg. Sci. Urban Econ. 2018, 72, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunsdon, C.; Fotheringham, A.S.; Charlton, M. Spatial nonstationarity and autoregressive models. Environ. Plan. A 1998, 30, 957–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Yan, H.; Zhang, W.; Lu, Z. A semiparametric spatial dynamic model. Ann. Stat. 2014, 42, 700–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.J.; Mei, C.L.; Xu, Q.X.; Zhang, Z. Non-Iterative Multiscale Estimation for Spatial Autoregressive Geographically Weighted Regression Models. Entropy 2023, 25, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, C.L.; Chen, F. Detection of spatial heterogeneity based on spatial autoregressive varying coefficient models. Spat. Stat. 2022, 51, 100666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Li, R.; Huang, B. A geographically and temporally weighted autoregressive model with application to housing prices. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2014, 28, 1186–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wand, M.; Jones, M. Kernel Smoothing; Taylor & Francis: Abingdon, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Mei, C.L.; Yan, X.D. Local Linear Estimation of Spatially Varying Coefficient Models: An Improvement on the Geographically Weighted Regression Technique. Environ. Plan. A 2008, 40, 986–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Yan, J.; Lin, H. A cost-effective algorithm for calibrating multiscale geographically weighted regression models. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2022, 36, 898–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotheringham, A.S.; Brunsdon, C.; Charlton, M. Geographically Weighted Regression: The Analysis of Spatially Varying Relationships; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Boots, B.; Tiefelsdorf, M. Global and Local Spatial Autocorrelation in Bounded Regular Tesselations. J. Geogr. Syst. 2000, 2, 319–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Qin, S.; Wang, Y.; Miao, C. Spatio-temporal patterns and influencing factors of the coupling between new urbanization and ecological environment in the Yellow River Basin. Resour. Sci. 2020, 166, 112300. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, M.; Wang, C.; Zhao, J.; Li, M. Spatial and temporal differentiation patterns and influencing factors of tourism economy in the Yellow River Basin. Econ. Geogr. 2020, 40, 21–29. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Ren, L.; Ma, R.; Liu, Y.; Yao, D. Analysis of spatiotemporal pattern and driving factors of carbon emissions in Zhejiang Province based on spatiotemporal geographically weighted regression model. J. Ningbo Univ. Nat. Sci. Eng. Ed. 2021, 80, 414–428. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, J.; Tian, S.; Jiang, E.; Liang, S.; Zhao, Q.; Zou, Q.; Chen, R.; Zhang, Y. Research on carbon emission status in the Yellow River Basin and the path to achieve the “dual carbon” goal. People’s Yellow River 2023, 45, 8–13. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.; Han, X. Research on spatial differentiation and influencing factors of carbon emissions in the Yellow River Basin. Econ. Surv. 2022, 39, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.R. Spatiotemporal evolution, spatial spillover effect and influencing factors of carbon emissions: An empirical study based on 79 cities in central China. China Collect. Econ. 2023, 36, 104–107. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, F. Research on the impact of urbanization on carbon emissions and spatial spillover effect in China. Technol. Innov. Manag. 2023, 44, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Cui, L.; Yan, H. Spatial heterogeneity of influencing factors of regional economic differences in the Yellow River Basin: An empirical study based on the MGWR model. Areal Res. Dev. 2023, 42, 7–13. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.; Leung, Y.; Mei, C.L.; Fung, T. Backfitting Estimation for Geographically Weighted Regression Models with Spatial Autocorrelation in the Response. Geogr. Anal. 2021, 54, 357–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.H.; Wang, S.J.; Su, Y.N. Local GMM estimation of geographically weighted autoregressive models with spatially varying coefficients. Stat. Inf. Forum 2022, 37, 3–13. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.K.; Mei, C.L.; Wang, N. Tests for spatial dependence and heterogeneity in spatially autoregressive varying coefficient models with application to Boston house price analysis. Reg. Sci. Urban Econ. 2019, 79, 103470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Coefficients | Corr | Method | Bandwidths/Ind. | Min | Q1 | Median | Q3 | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | GTWRLAR - G | |||||||
| RSS | 20,543 | 24,835 | 25,994 | 28,020 | 33,078 | |||
| AICc | 3.968 | 4.087 | 4.121 | 4.155 | 4.262 | |||
| GTWRLAR - L | ||||||||
| RSS | 3717 | 4805 | 5052 | 5349 | 6322 | |||
| AICc | 2.538 | 2.630 | 2.669 | 2.708 | 2.902 | |||
| 0.5 | GTWRLAR - G | |||||||
| RSS | 20,749 | 24,964 | 26,135 | 27,554 | 33,457 | |||
| AICc | 3.975 | 4.093 | 4.127 | 4.163 | 4.267 | |||
| GTWRLAR - L | ||||||||
| RSS | 3607 | 4687 | 4977 | 5258 | 6003 | |||
| AICc | 2.517 | 2.603 | 2.642 | 2.684 | 2.893 | |||
| 0.9 | GTWRLAR - G | |||||||
| RSS | 21,164 | 25,135 | 26,572 | 27,931 | 34,144 | |||
| AICc | 3.993 | 4.108 | 4.141 | 4.178 | 4.281 | |||
| GTWRLAR - L | ||||||||
| RSS | 3613 | 4768 | 5022 | 5290 | 6104 | |||
| AICc | 2.545 | 2.617 | 2.656 | 2.695 | 2.917 | |||
| 0.99 | GTWRLAR - G | |||||||
| RSS | 21,480 | 25,383 | 26,790 | 28,253 | 34,669 | |||
| AICc | 4.006 | 4.121 | 4.153 | 4.192 | 4.292 | |||
| GTWRLAR - L | ||||||||
| RSS | 3685 | 4834 | 5113 | 5417 | 6424 | |||
| AICc | 2.561 | 2.638 | 2.678 | 2.717 | 2.943 | |||
| 0.0 | GTWRLAR - G | |||||||
| RSS | 20,263 | 28,267 | 29,430 | 31,022 | 38,692 | |||
| AICc | 4.113 | 4.234 | 4.267 | 4.304 | 4.393 | |||
| GTWRLAR - L | ||||||||
| RSS | 5655 | 7011 | 7461 | 7964 | 9167 | |||
| AICc | 2.809 | 2.925 | 2.959 | 2.991 | 3.108 | |||
| 0.5 | GTWRLAR - G | |||||||
| RSS | 20,366 | 28,228 | 29,431 | 30,939 | 36,818 | |||
| AICc | 4.117 | 4.241 | 4.271 | 4.309 | 4.397 | |||
| GTWRLAR - L | ||||||||
| RSS | 5175 | 6836 | 7345 | 7829 | 9016 | |||
| AICc | 2.793 | 2.908 | 2.939 | 2.970 | 3.080 | |||
| 0.9 | GTWRLAR - G | |||||||
| RSS | 20,650 | 28,609 | 29,851 | 31,245 | 38,654 | |||
| AICc | 4.133 | 4.256 | 4.284 | 4.323 | 4.423 | |||
| GTWRLAR - L | ||||||||
| RSS | 5190 | 6887 | 7463 | 7874 | 9976 | |||
| AICc | 2.811 | 2.918 | 2.952 | 2.984 | 3.094 | |||
| 0.99 | GTWRLAR - G | |||||||
| RSS | 20,893 | 28,796 | 30,128 | 31,604 | 39,222 | |||
| AICc | 4.145 | 4.267 | 4.295 | 4.334 | 4.440 | |||
| GTWRLAR - L | ||||||||
| RSS | 5273 | 6925 | 7451 | 7991 | 9169 | |||
| AICc | 2.830 | 2.937 | 2.972 | 3.003 | 3.113 |
| Year | Moran’s I | Z-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | 0.719 | 9.651 | 0.000 |
| 2018 | 0.636 | 8.566 | 0.000 |
| 2019 | 0.681 | 9.152 | 0.000 |
| 2020 | 0.738 | 9.909 | 0.000 |
| 2021 | 0.680 | 9.162 | 0.000 |
| RSS | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GTWR | 82 | 5 | 0.871 | 50.342 | 0.143 |
| GTWRLAR-G | 124 | 5 | 0.888 | 43.411 | −0.363 |
| GTWRLAR-L | 299 | 5 | 0.893 | 41.495 | −0.101 |
| Min | Q1 | Median | Q3 | Max | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CE (10,000 tons): | 0.456 | 0.952 | 1.059 | 1.284 | 2.284 |
| GDP (yuan): | −2.473 | −1.039 | −0.446 | −0.261 | 0.133 |
| IIR (%): | −0.330 | 0.051 | 0.178 | 0.388 | 1.084 |
| PP: | −0.545 | −0.017 | 0.044 | 0.184 | 1.043 |
| UR (%): | −0.259 | 0.178 | 0.368 | 0.699 | 1.522 |
| SDE (tons): | −1.369 | −0.139 | −0.024 | 0.040 | 0.531 |
| DPE (tons): | −0.570 | −0.104 | −0.011 | 0.123 | 1.070 |
| SWDR (%): | −0.034 | 0.099 | 0.292 | 0.634 | 2.656 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the International Society for Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiang, D.; Hong, Z. Local–Linear Two-Stage Estimation of Local Autoregressive Geographically and Temporally Weighted Regression Model. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2025, 14, 276. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi14070276
Xiang D, Hong Z. Local–Linear Two-Stage Estimation of Local Autoregressive Geographically and Temporally Weighted Regression Model. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information. 2025; 14(7):276. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi14070276
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiang, Dan, and Zhimin Hong. 2025. "Local–Linear Two-Stage Estimation of Local Autoregressive Geographically and Temporally Weighted Regression Model" ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information 14, no. 7: 276. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi14070276
APA StyleXiang, D., & Hong, Z. (2025). Local–Linear Two-Stage Estimation of Local Autoregressive Geographically and Temporally Weighted Regression Model. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 14(7), 276. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi14070276





