Spatiotemporal Distribution and Evolution of Global World Cultural Heritage, 1972–2024
Abstract
1. Introduction
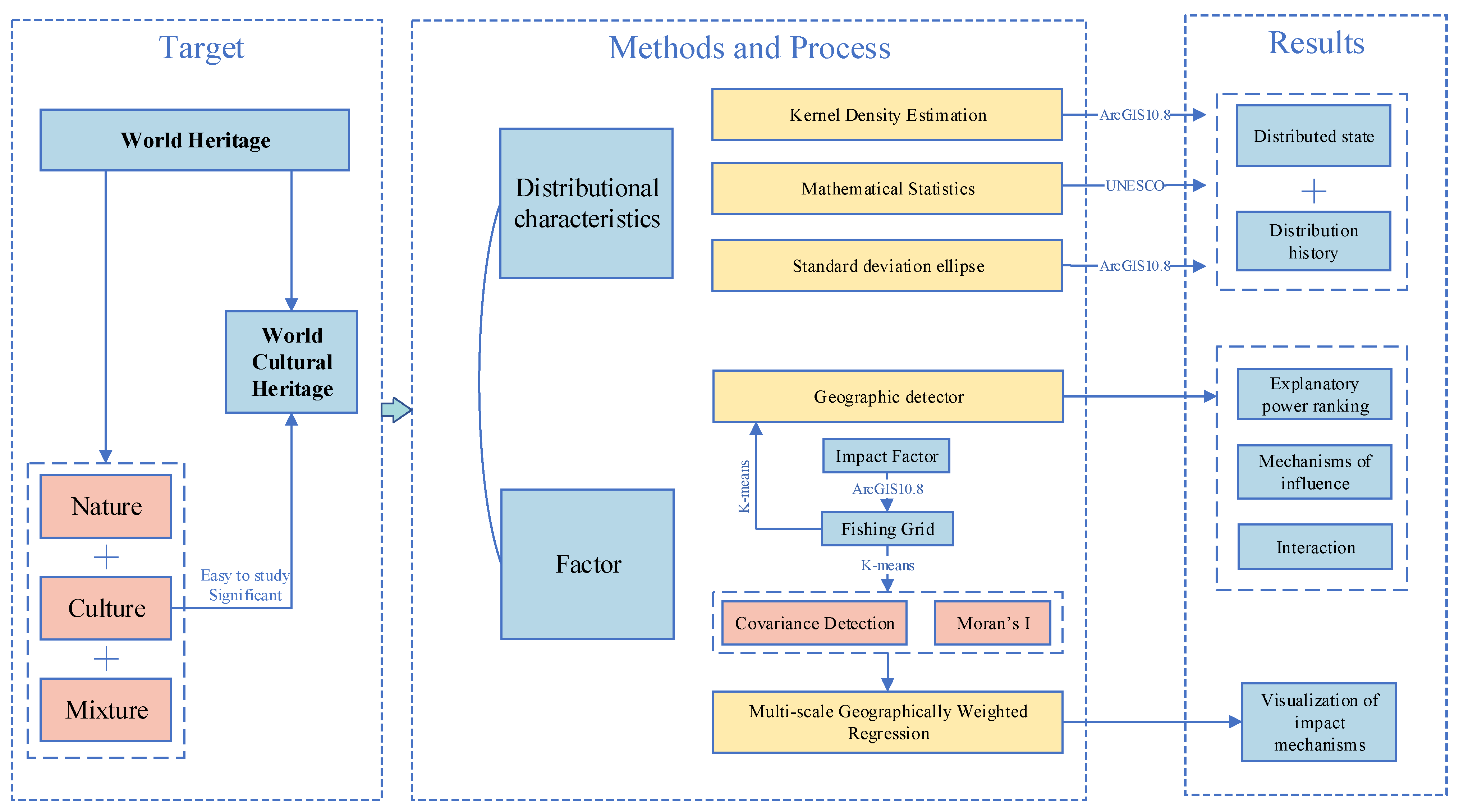
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Data Processing
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Kernel Density Estimation
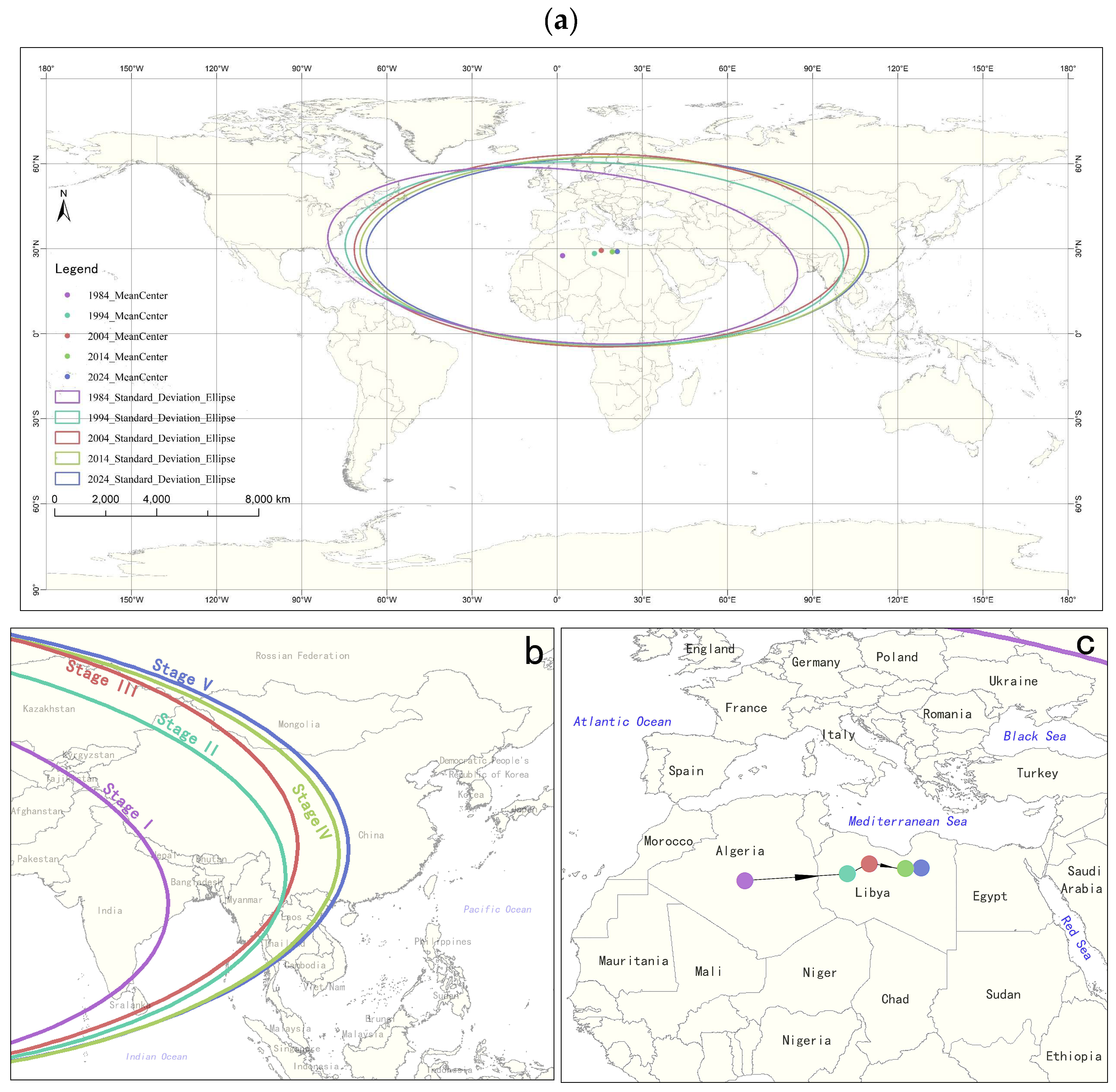
2.2.2. Standard Deviation Ellipse
2.2.3. Geographic Detector
2.2.4. Multi-Scale Geographically Weighted Regression
3. Results
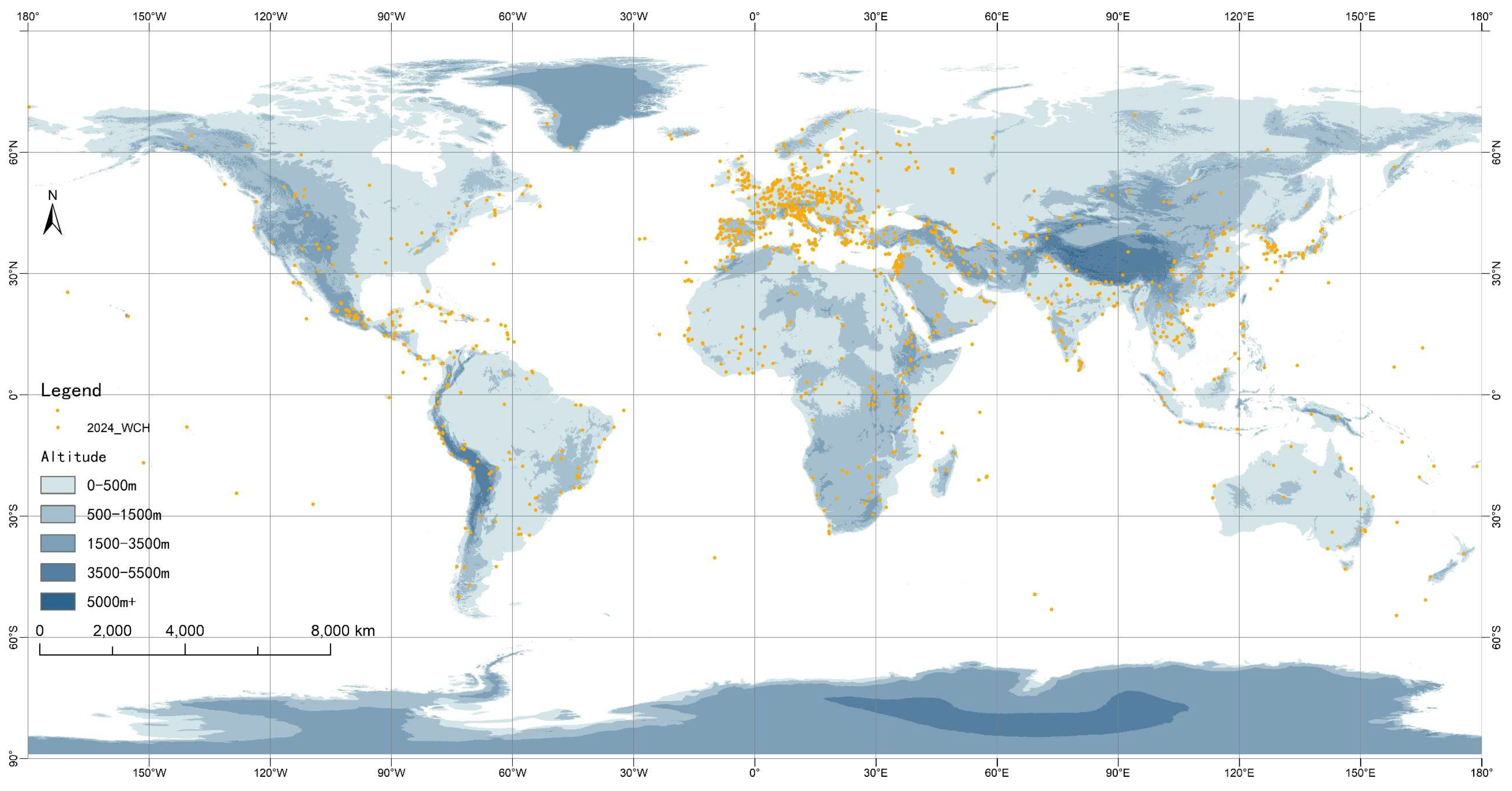
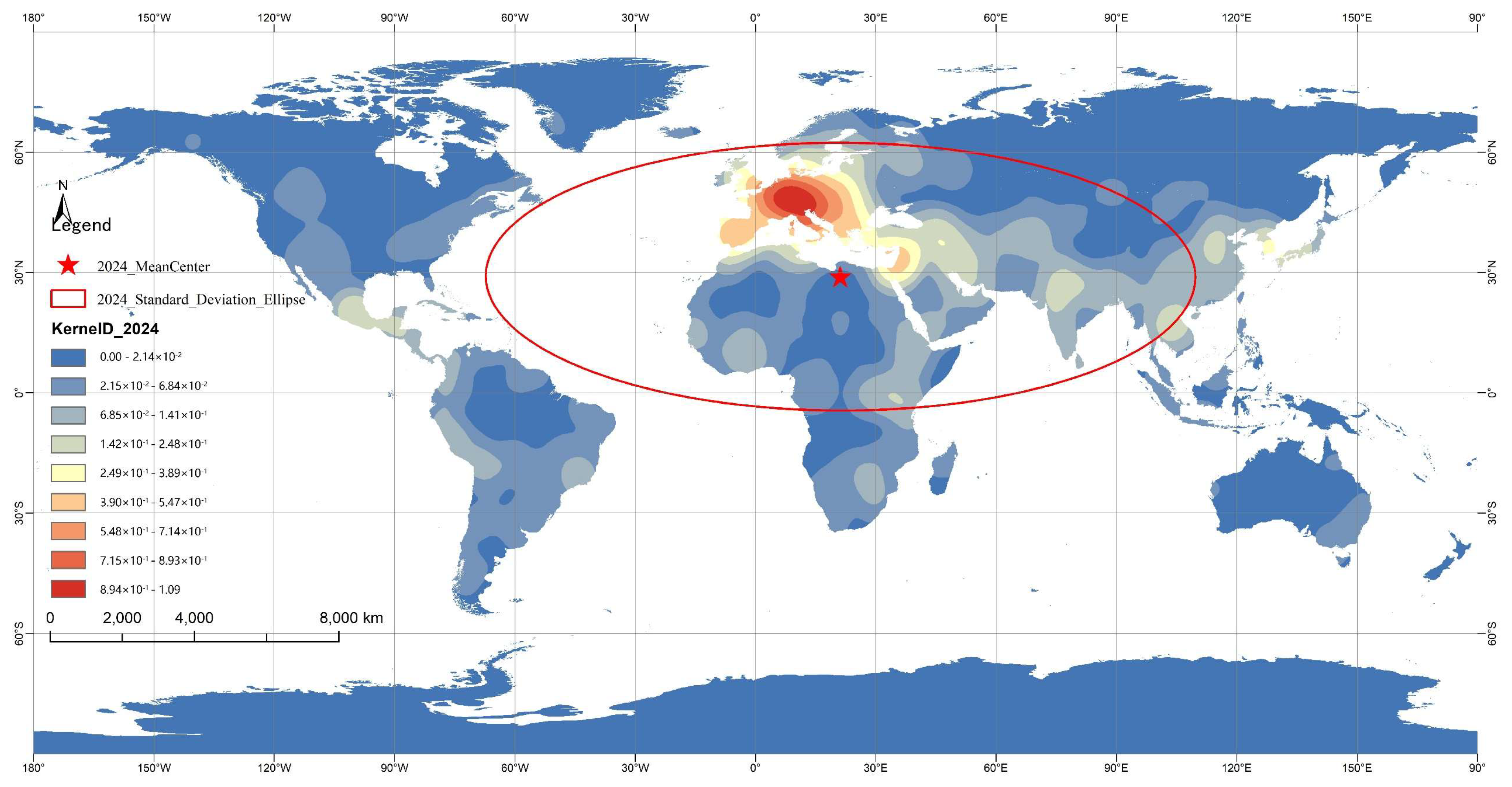
3.1. Spatial Distribution Characteristics
3.2. Spatial–Temporal Evolution Characteristics
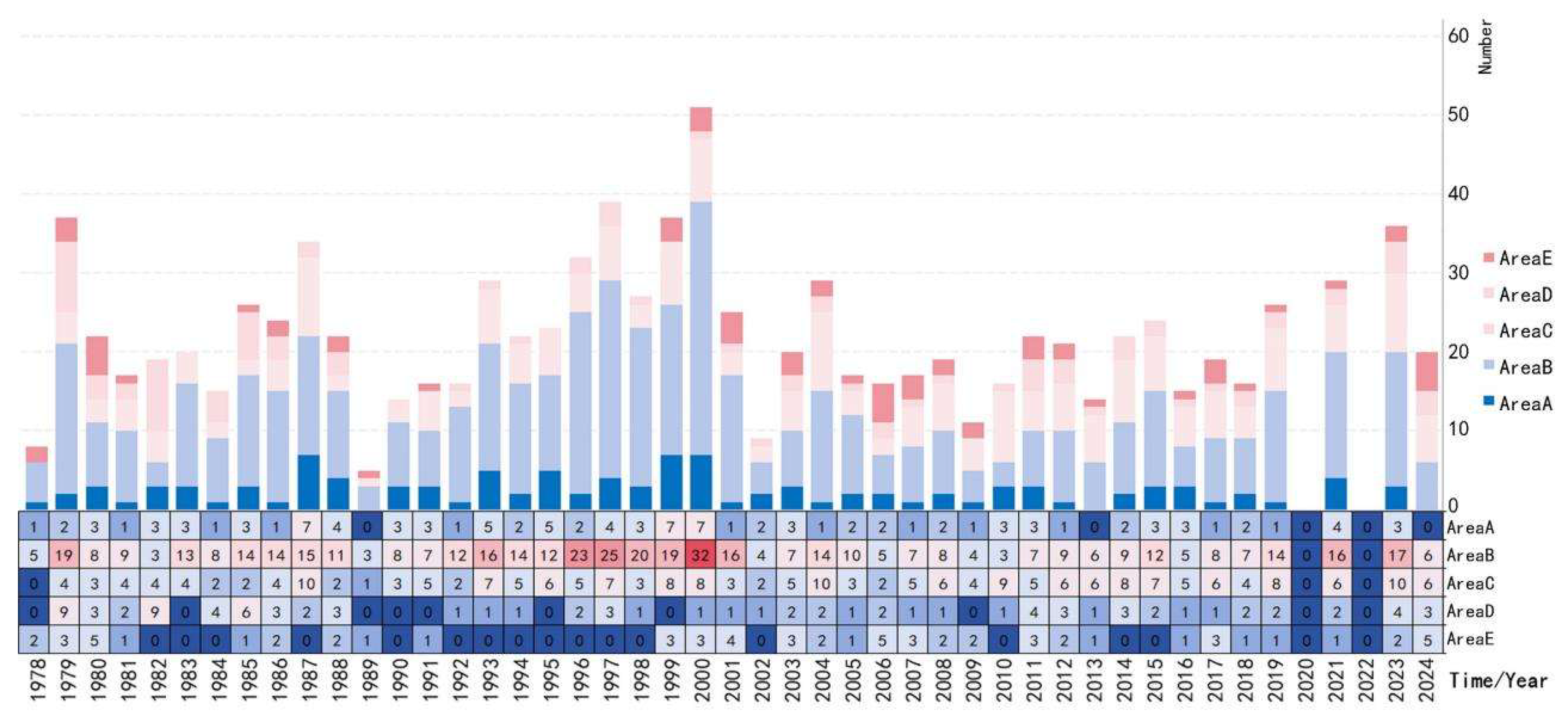
3.2.1. Evolutionary Characteristics from Regions
3.2.2. Evolutionary Characteristics from the Holistic Perspective
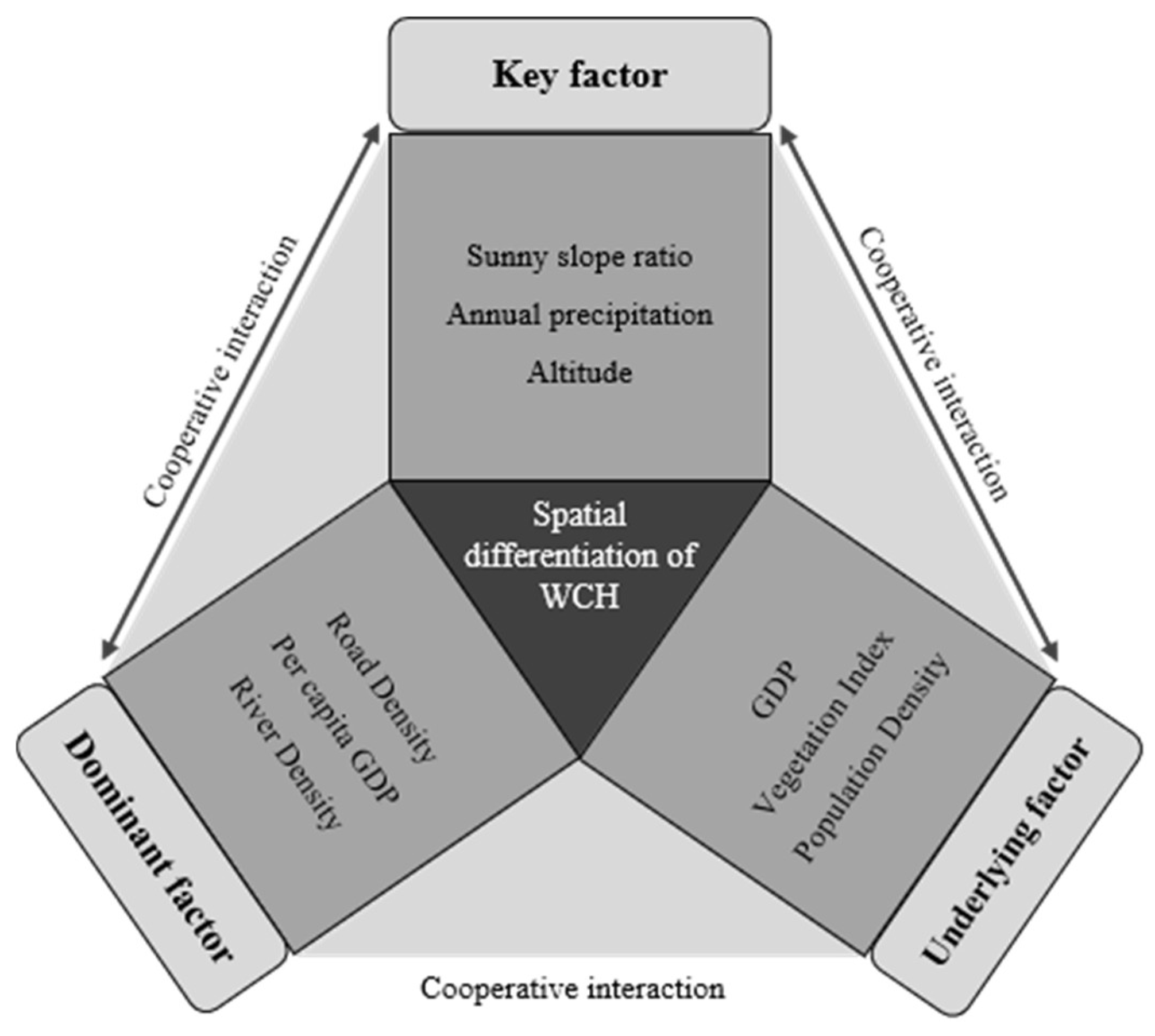
3.3. Affecting Factors of Spatial Distribution
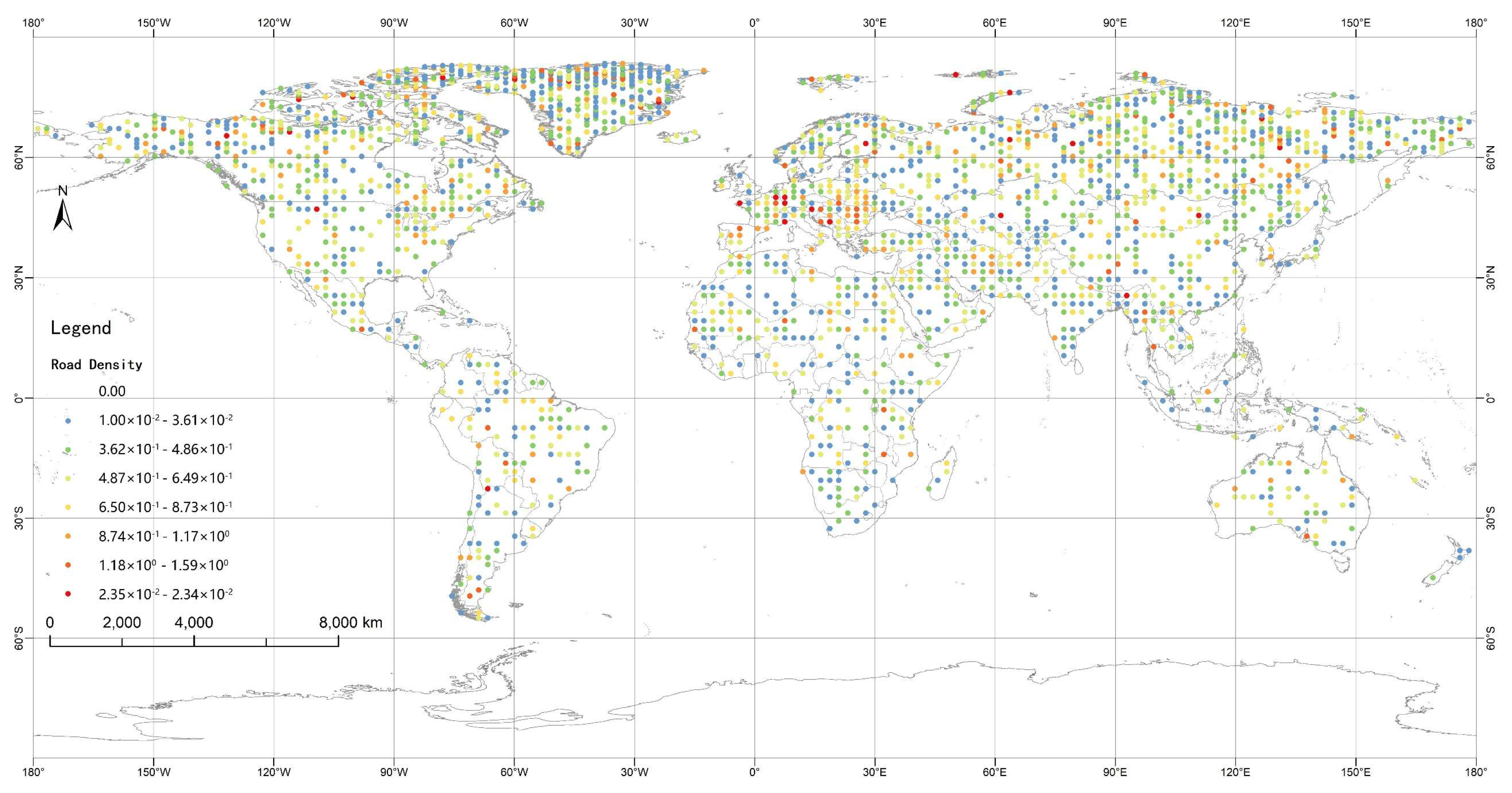
3.3.1. Affecting Factor Selection and Data Processing
3.3.2. Influencing Factor Ranking and Interaction Detection Results
3.3.3. The Spatial Mechanism of Influencing Factors
4. Discussion
4.1. Spatial Distribution and Evolution of WCH
4.2. Mechanism of Action of the Effect Factor
4.3. Suggestion and Limitations
4.3.1. Policy Recommendations
4.3.2. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hill, A. ‘The Battle for Abu Simbel’: Archaeology and Postcolonial Diplomacy in the Unesco Campaign for Nubia. J. Contemp. Hist. 2021, 56, 502–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNESCO. Convention for the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage (World Heritage Convention)(1); UNESCO: Paris, France, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Rouhi, J. Definition of Cultural Heritage Properties and Their Values By the Past. Asian J. Sci. Technol. 2017, 8, 7109–7114. [Google Scholar]
- Zwegers, B. Aachen Cathedral and the Beginnings of World Heritage; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erb-Satullo, N.L. Archaeomaterials, Innovation, and Technological Change. Adv. Archaeomater. 2020, 1, 36–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Ahmad, Y.; Mohidin, H.H.B. The Development of the Concept of Architectural Heritage Conservation and Its Inspiration. Built Herit. 2023, 7, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y. Influence of Architectural Heritage on the Identity and Present-day Value of American-designed Universities’ Campuses in Asia. Built Herit. 2020, 4, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, P.M. Cultural Landscapes: Integrating Culture and Nature to Uplift Global Sustainability Through the Lenses of the Un Sdgs 2030 Agend; Springer: Singapore, 2023; pp. 61–78. [Google Scholar]
- Zerbe, S. Traditional Cultural Landscapes—A Theoretical Framework; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgin, C.; Elveren, A.Y. Unpacking the Economic Impact of Tourism: A Multidimensional Approach to Sustainable Development. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 478, 143947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damnjanović, I. Overtourism Effects: Positive and Negative Impacts for Sustainable Development; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertacchini, E.; Liuzza, C.; Meskell, L.; Saccone, D. The Politicization of Unesco World Heritage Decision Making. Public Choice 2016, 167, 95–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keay, S.J.; Parcak, S.H.; Strutt, K.D. High Resolution Space and Ground-based Remote Sensing and Implications for Landscape Archaeology: The Case From Portus, Italy. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2014, 52, 277–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Krishnamurthy, S.; Roders, A.P.; van Wesemael, P. Community Participation in Cultural Heritage Management: A Systematic Literature Review Comparing Chinese and International Practices. Cities 2020, 96, 102476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wei, J.; Hu, C. The Spatial Distribution of World Heritages in China. Geogr. Res. 2010, 29, 2080–2088. Available online: https://www.dlyj.ac.cn/EN/10.11821/yj2010110016 (accessed on 15 July 2024).
- Ying, G.; Wang, X.; Fan, X.; Shao, Y.; Guo, H.; Wang, C.; Liu, H. Geographical Distribution Characteristics of African World Heritages. Prog. Geogr. 2013, 32, 958–966. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, G. Statistical Analysis on Geographical Distribution of World Heritage. Geogr. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2009, 25, 104–108. [Google Scholar]
- Van Westen, C.J. Remote Sensing and Gis for Natural Hazards Assessment and Disaster Risk Management; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katapidi, I. The Role of Conservation Policies in Local Understandings of Heritage in Living Heritage Places: A Greek Testimony. Int. J. Herit. Stud. 2023, 29, 275–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Dupre, K.; McIlwaine, C. The Impacts of World Cultural Heritage Site Designation and Heritage Tourism on Community Livelihoods: A Chinese Case Study. Tour. Manag. Perspect. 2022, 43, 100994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, C.; Hurka, S.; Knill, C. Four Styles of Regulation and Their Implications for Comparative Policy Analysis. J. Comp. Policy Anal. Res. Pract. 2017, 19, 327–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Teng, Y.; Fan, Y. Spatial Distribution and Influencing Factors of Traditional Villages in Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region. J. Guilin Univ. Technol. 2021, 41, 580–588. [Google Scholar]
- UNESCO. World Heritage List. 2024. Available online: https://whc.unesco.org/en/list/ (accessed on 20 January 2025).
- National Centers for Environmental Information. Geoid Height Geotiff. 2022. Available online: https://www.ncei.noaa.gov/products/etopo-global-relief-model (accessed on 15 July 2024).
- Esrimitchel, A. The Esri Guide to Gis Analysis, Volume 2: Spartial Measurements and Statistics. In Esri Guide to Gis Analysis; ESRI Press: Redlands, CA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Fisher, N.I.; Lewis, T.; Embleton, B.J.J. Statistical Analysis of Spherical Data; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y. Study on the Spatial Distribution Characteristics and Promotion Approach of Network Concern of China’s World Heritage Sites. J. Yanshan Univ. Philos. Soc. Sci. 2023, 24, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Peng, S. Study on the Spatial Distribution of Traditional Villages and Their Influencing Factors in Guizhou Province Based on Geodetectors. Agric. Technol. 2024, 44, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotheringham, A.S.; Yang, W.; Kang, W. Multiscale Geographically Weighted Regression (mgwr). Ann. Am. Assoc. Geogr. 2017, 107, 1247–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Luo, X.; Chen, Y. Spatial Pattern and Influencing Factors of Rural Multifunctionality at County Level in China. Prog. Geogr. 2019, 38, 1316–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Chen, Y.; Cao, W.; Yu, R.; Rong, P.; Cheng, J. Spatial Pattern and Its Influencing Factors of National-level Cultural Heritage in China. Herit. Sci. 2024, 12, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Congressional Research Service; Benjamin Hayes. The Antiquities Act: History, Current Litigation, and Considerations for the 116th Congress; 20. Available online: https://purl.fdlp.gov/GPO/gpo137783 (accessed on 16 April 2025).
- Ennahid, S. Africa, North: Historical Archaeology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, I. Blood Symbolism at the Root of Symbolic Culture? African Hunter-gatherer Perspectives. J. Anthropol. Archaeol. 2024, 76, 101627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varela, S.L.L. Mexico’s Heritage and Management; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeSoucey, M.; Elliott, M.A.; Schmutz, V. Rationalized Authenticity and the Transnational Spread of Intangible Cultural Heritage. Poetics 2019, 75, 101332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santa, E.D.; Tiatco, S.A. Tourism, Heritage and Cultural Performance: Developing a Modality of Heritage Tourism. Tour. Manag. Perspect. 2019, 31, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Li, S. Associative Cultural Landscape Approach to Interpreting Traditional Ecological Wisdom: A Case of Inuit Habitat. Front. Archit. Res. 2024, 13, 79–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irfan, M.; Mir, S.A.; Bali, B.S.; Afzal, A.; Bhat, N.A.; Bhat, N.; Bashir, A.; Nazir, M. Unveiling the Geoheritage, Cultural Geomorphology and Geotourism Potential of Zanskar Region, Nw Himalaya, India. Geomorphology 2024, 462, 109354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; He, Y. Human-land Relationship in the Construction of Historical Settlements Based on Complex Adaptive System (cas) Theory: Evidence From Shawan in Guangfu Region, China. Herit. Sci. 2024, 12, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
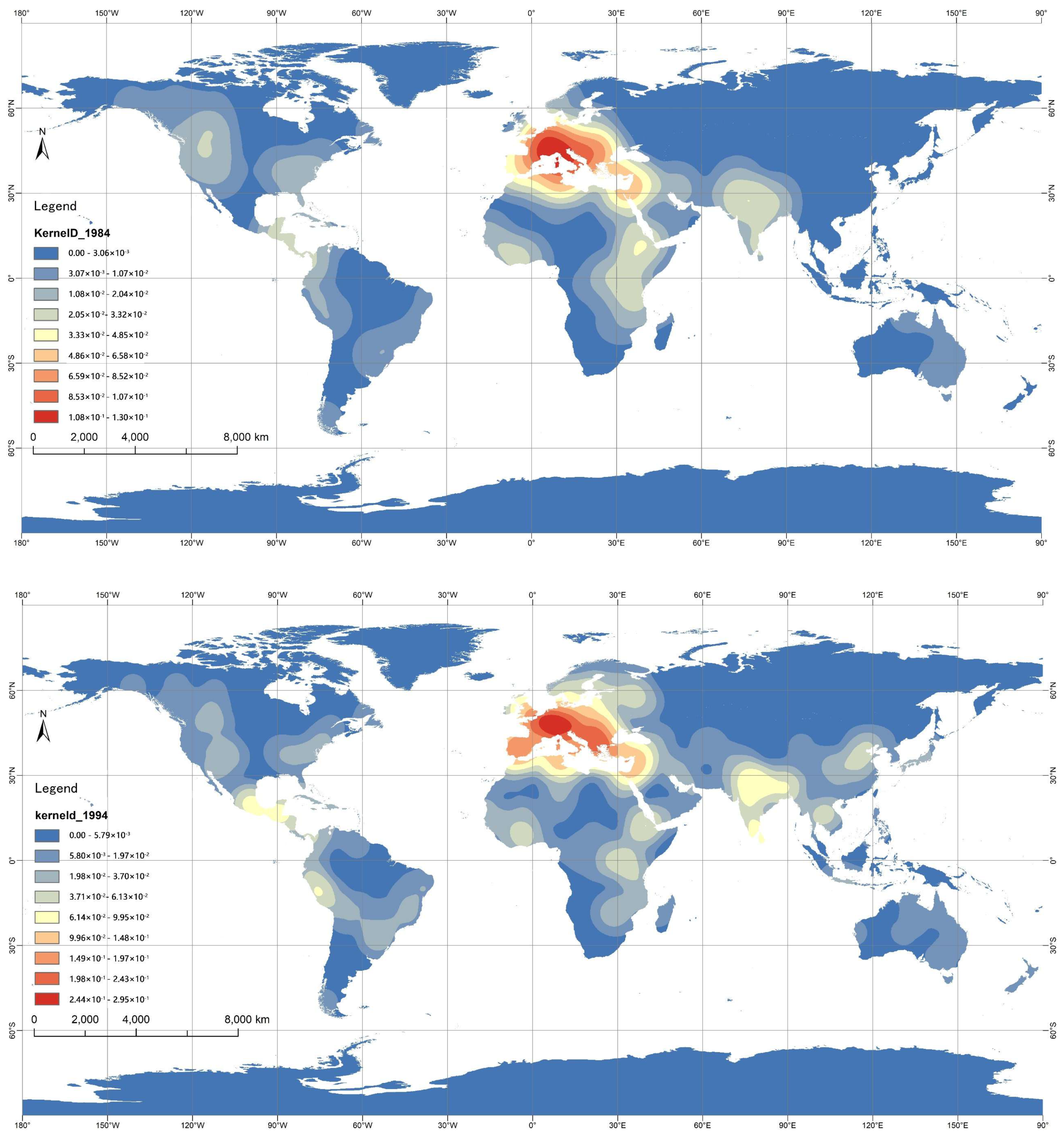
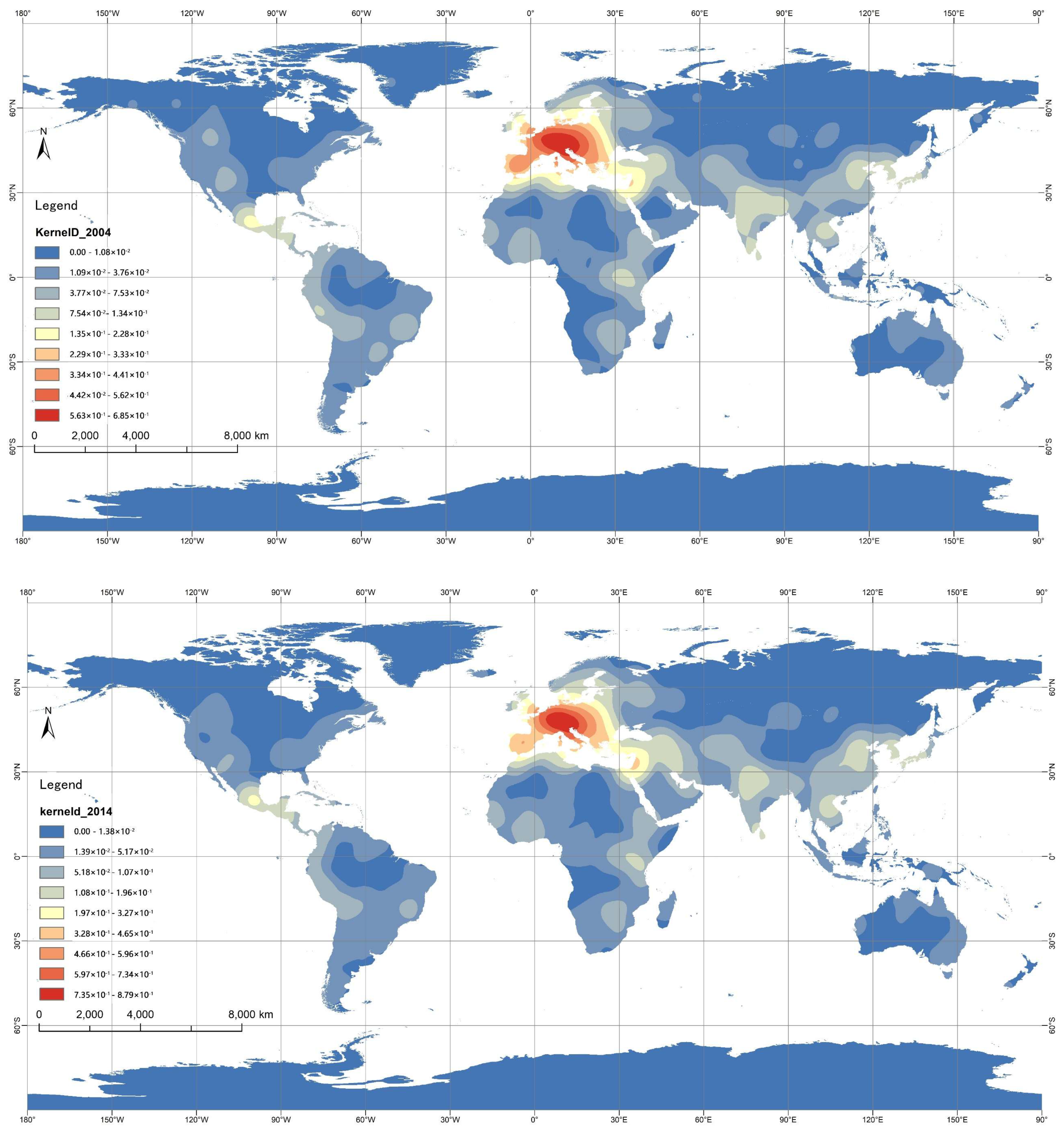

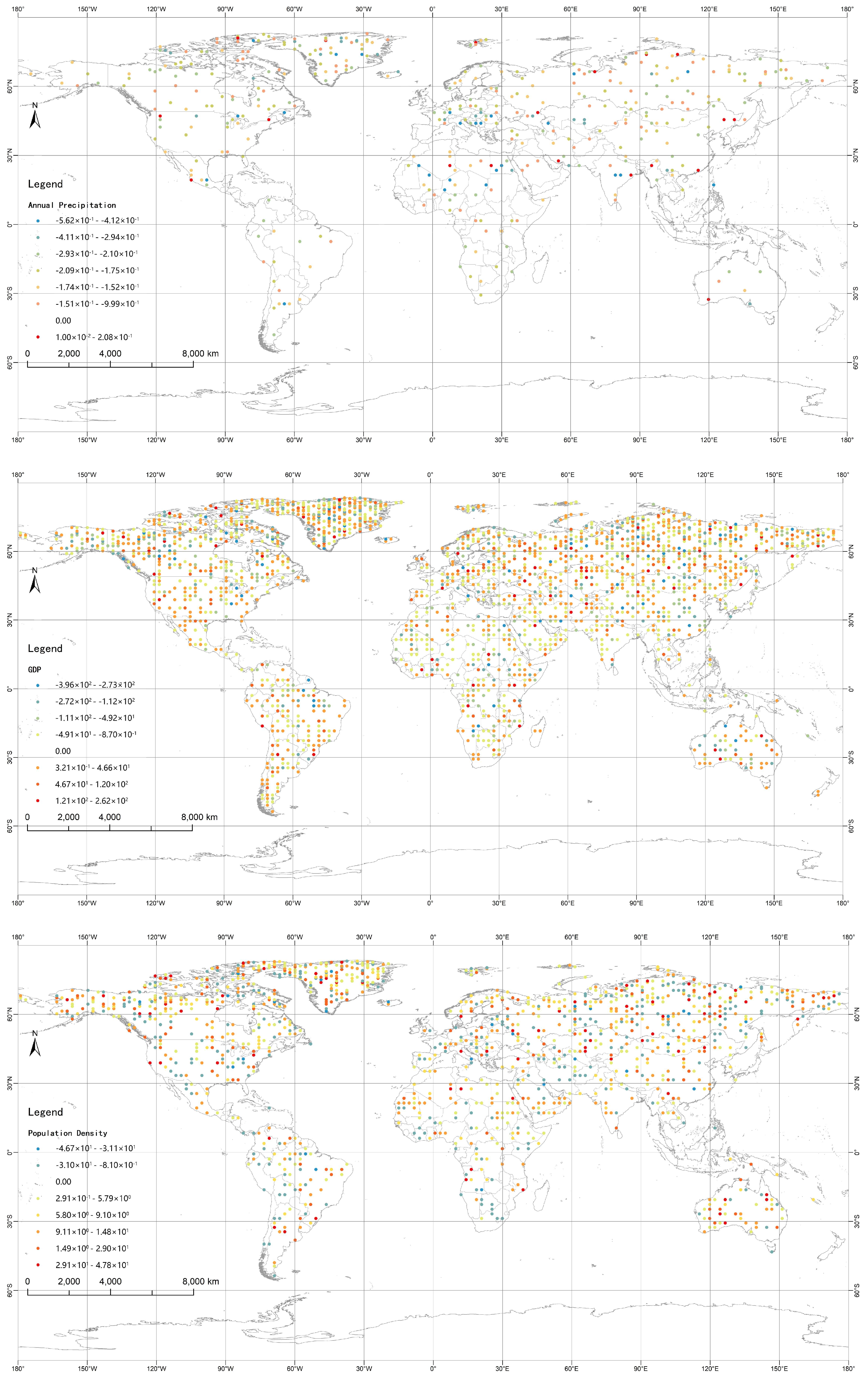
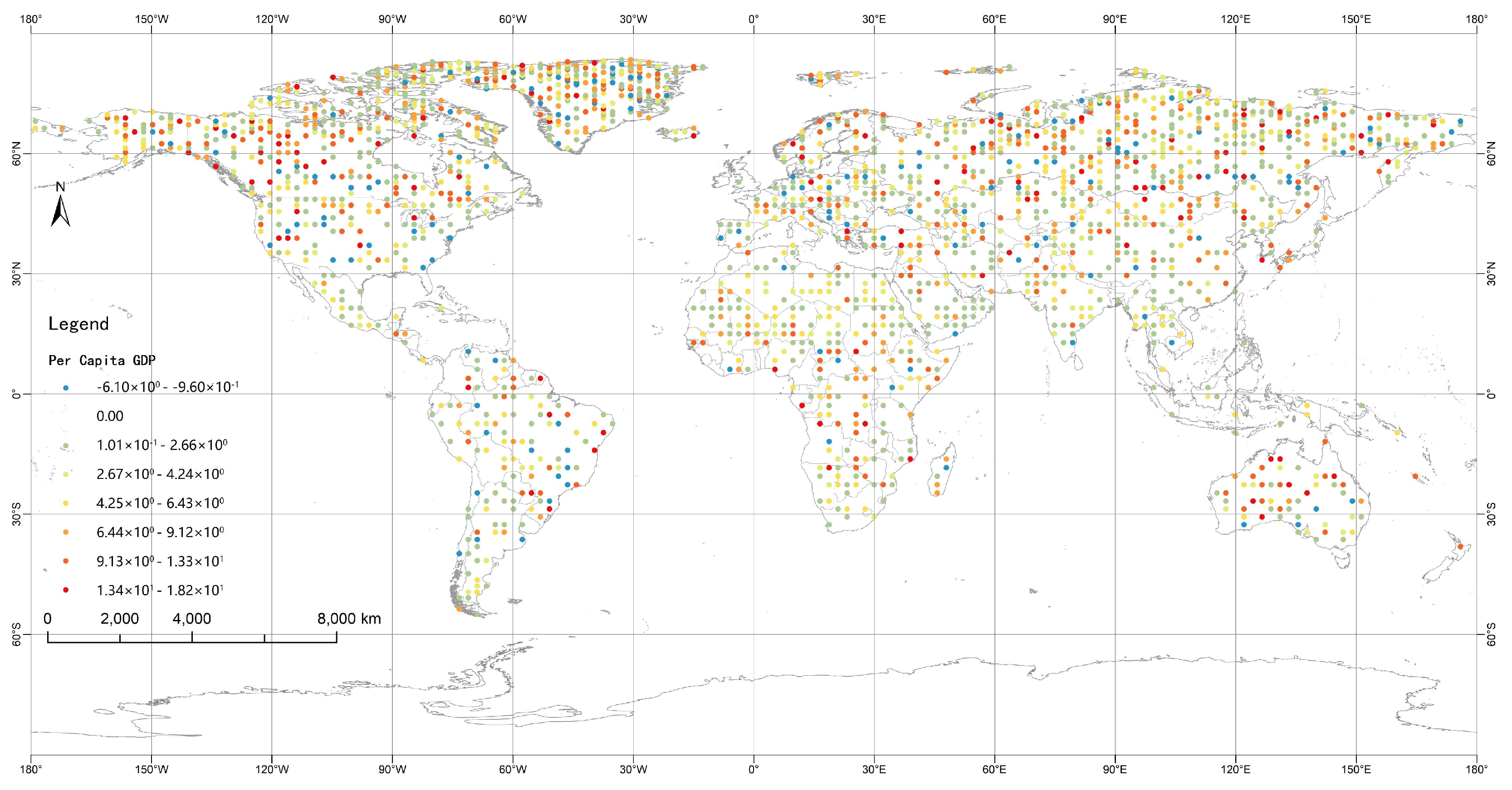
| Area | Area Type | Number of WCH | Number of WMH | Proportion (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Latin America and the Caribbean | Area-A | 103 | 8 | 12.26 |
| Europe and North America | Area-B | 490 | 12 | 46.85 |
| Asia and the Pacific | Area-C | 211 | 12 | 24.20 |
| Arab States | Area-D | 87 | 3 | 7.85 |
| Africa | Area-E | 61 | 5 | 8.83 |
| Total | 952 | 40 | 100 |
| Year | Stage | Azimuth Angle | Area (km2) | Long Axis (km) | Short Axis(km) | Oblateness | Mean Center | Change Direction and Distance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1984 | Stage I | 95.107 | 9.841 × 107 | 9242.718 | 3389.191 | 0.633 | E 1°55′13″, N 27°31′42″ | —— |
| 1994 | Stage II | 92.292 | 1.101 × 108 | 9783.174 | 3582.118 | 0.634 | E 13°6′44″, N 28°17′31″ | EN, 1249.005 km |
| 2004 | Stage III | 90.243 | 1.153 × 108 | 9692.170 | 3787.436 | 0.609 | E 15°33′5″, N 29°22′16″ | EN, 297.223 km |
| 2014 | Stage IV | 90.500 | 1.159 × 108 | 9898.134 | 3728.782 | 0.623 | E 19°26′45″, N 28°54′19″ | ES, 436.373 km |
| 2024 | Stage V | 90.128 | 1.150 × 108 | 9846.938 | 3718.663 | 0.622 | E 21°12′11″, N 28°57′42″ | EN, 195.922 km |
| Type | Factor | Number | Calculation Method | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Natural Factors | Road Density | X1 | Gridded road miles/Gridded area | km/km2 |
| River Density | X2 | Gridded water system miles/Gridded area | km/km2 | |
| Aspect Ratio | X3 | Gridded aspect area/Gridded area | % | |
| Vegetation Index | X4 | ArcGIS raster extraction | % | |
| Altitude | X5 | ArcGIS raster extraction | m | |
| Annual precipitation | X6 | ArcGIS raster extraction | mm | |
| Societal Factor | GDP | X7 | ArcGIS raster extraction | Million |
| Population Density | X8 | Gridded population/Gridded area | pcs/km2 | |
| Per capita GDP | X9 | GDP/Population | USD |
| Factor | q-Value and Ranking | p-Value and Significance Level | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Road Density (X1) | 0.280 | 1 | 0.000 | 0.01 |
| Per capita GDP (X9) | 0.183 | 2 | 0.000 | 0.01 |
| River Density (X2) | 0.162 | 3 | 0.000 | 0.01 |
| Altitude (X5) | 0.070 | 4 | 0.000 | 0.01 |
| Annual Precipitation (X6) | 0.051 | 5 | 0.000 | 0.01 |
| Aspect Ratio (X3) | 0.047 | 6 | 0.000 | 0.01 |
| Vegetation Index (X4) | 0.044 | 7 | 0.000 | 0.01 |
| GDP (X7) | 0.043 | 8 | 0.000 | 0.01 |
| Population Density (X8) | 0.034 | 9 | 0.000 | 0.01 |
| X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | X8 | X9 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | 0.280 | ||||||||
| X2 | 0.327 ↗ | 0.162 | |||||||
| X3 | 0.297 ↗ | 0.167 ↗ | 0.047 | ||||||
| X4 | 0.313 ↗ | 0.171 ↗ | 0.076 ↗ | 0.044 | |||||
| X5 | 0.295 ↗ | 0.171 ↗ | 0.094 ↗ | 0.088 ↗ | 0.070 | ||||
| X6 | 0.315 ↗ | 0.182 ↗ | 0.072 ↗ | 0.097 ↖ | 0.097 ↗ | 0.051 | |||
| X7 | 0.312 ↗ | 0.200 ↗ | 0.093 ↖ | 0.093 ↖ | 0.113 ↖ | 0.101 ↖ | 0.043 | ||
| X8 | 0.300 ↗ | 0.189 ↗ | 0.080 ↗ | 0.081 ↖ | 0.100 ↗ | 0.090 ↖ | 0.064 ↗ | 0.034 | |
| X9 | 0.400 ↗ | 0.323 ↗ | 0.241 ↖ | 0.259 ↖ | 0.247 ↗ | 0.267 ↖ | 0.203 ↗ | 0.211 ↗ | 0.183 |
| Factor | GWR Bandwidth | MGWR Analysis Parameters and Results | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bandwidth | Positive | Negative | Proportion of p ≤ 0.05 | ||
| Road Density (X1) | 81.000 | 44.000 | 98% | 2% | 43.25% |
| River Density (X2) | 5580.000 | 100% | 0% | 0.54% | |
| Aspect Ratio (X3) | 5580.000 | 0% | 100% | 42.93% | |
| Vegetation Index (X4) | 5580.000 | 0% | 100% | 100% | |
| Altitude (X5) | 3854.000 | 50% | 50% | 0% | |
| Annual Precipitation (X6) | 107.000 | 34% | 66% | 7.57% | |
| GDP(X7) | 44.000 | 48% | 52% | 38.81% | |
| Population Density (X8) | 55.000 | 64% | 36% | 23.66% | |
| Per Capita GDP (X9) | 55.000 | 73% | 27% | 39.61% | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the International Society for Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, Y.; Han, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, Z.; Dai, J. Spatiotemporal Distribution and Evolution of Global World Cultural Heritage, 1972–2024. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2025, 14, 190. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi14050190
Lu Y, Han Q, Zhang Z, Sun Z, Dai J. Spatiotemporal Distribution and Evolution of Global World Cultural Heritage, 1972–2024. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information. 2025; 14(5):190. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi14050190
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Yangyang, Qingwen Han, Zheng Zhang, Zhong Sun, and Jian Dai. 2025. "Spatiotemporal Distribution and Evolution of Global World Cultural Heritage, 1972–2024" ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information 14, no. 5: 190. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi14050190
APA StyleLu, Y., Han, Q., Zhang, Z., Sun, Z., & Dai, J. (2025). Spatiotemporal Distribution and Evolution of Global World Cultural Heritage, 1972–2024. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 14(5), 190. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi14050190






