A Spatial Case-Based Reasoning Method for Healthy City Assessment: A Case Study of Middle Layer Super Output Areas (MSOAs) in Birmingham, England
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
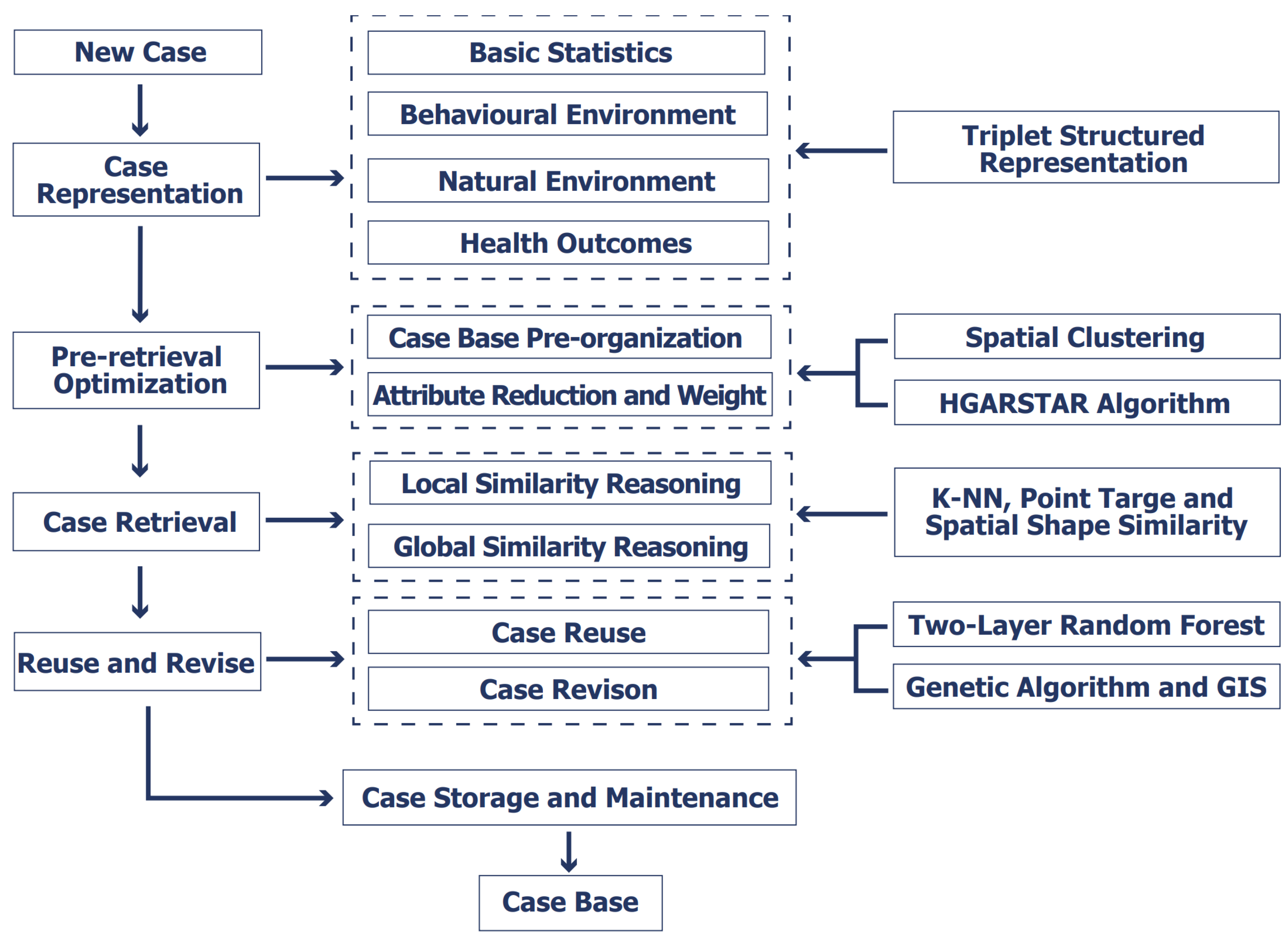
2.1. Research Framework
2.2. Establishment of a Case Database
2.2.1. Data Sources
2.2.2. Spatial Case Representation
2.3. Case Pre-Organization
2.4. Attribute Reduction and Weight Assignment
2.5. Integrated Reasoning of Attribute and Spatial Similarity
2.5.1. Calculation of Attribute Feature Similarity
2.5.2. Calculation of Spatial Feature Similarity
- Calculation of Similarity for Spatial Point Targets
- 2.
- Calculation of Spatial Relationship Morphology Similarity
- 3.
- Comprehensive Similarity
2.6. Case Reuse
2.7. Case Revision
3. Case Study and Results Analysis
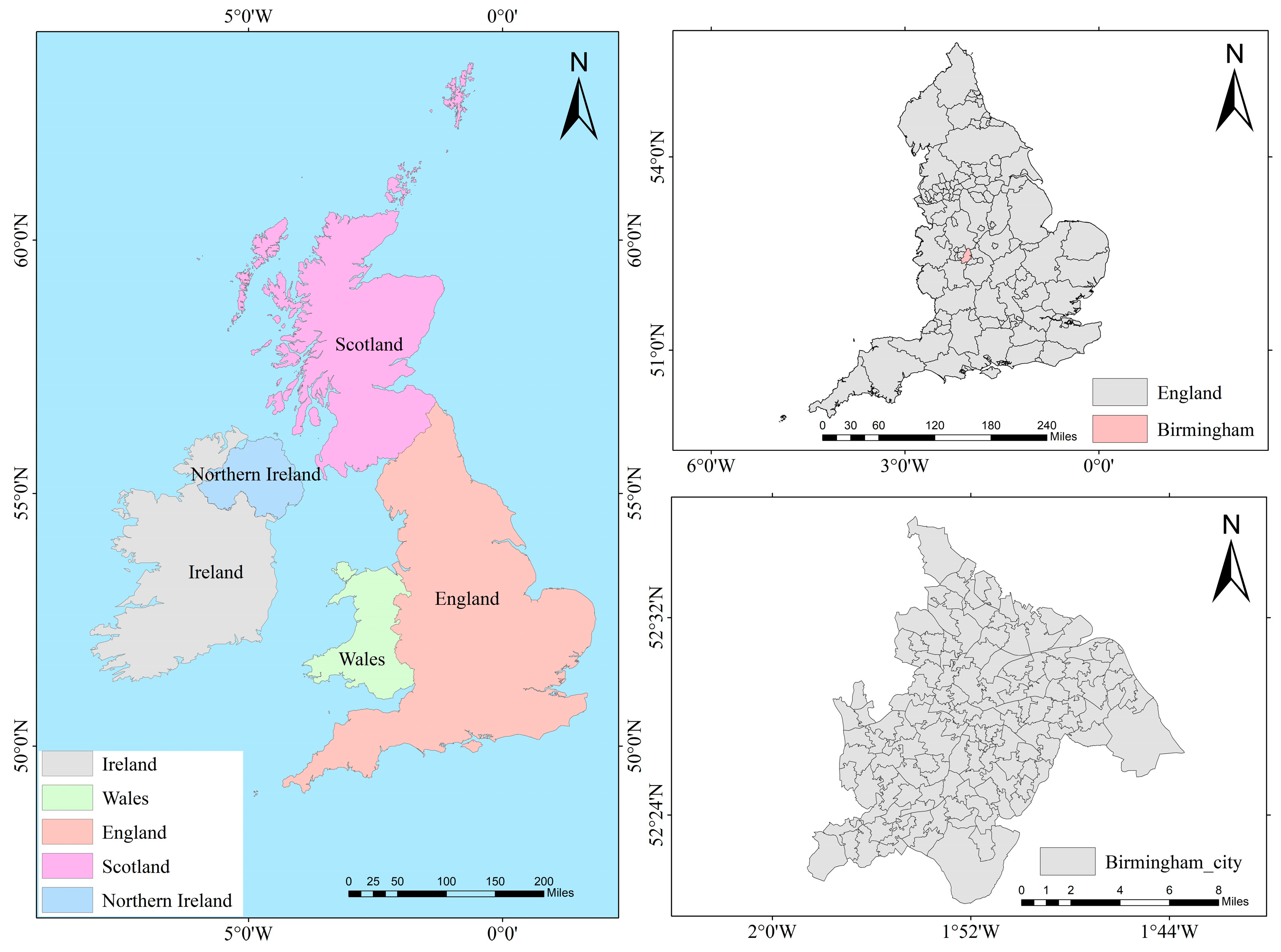
3.1. Construction of the Case Base
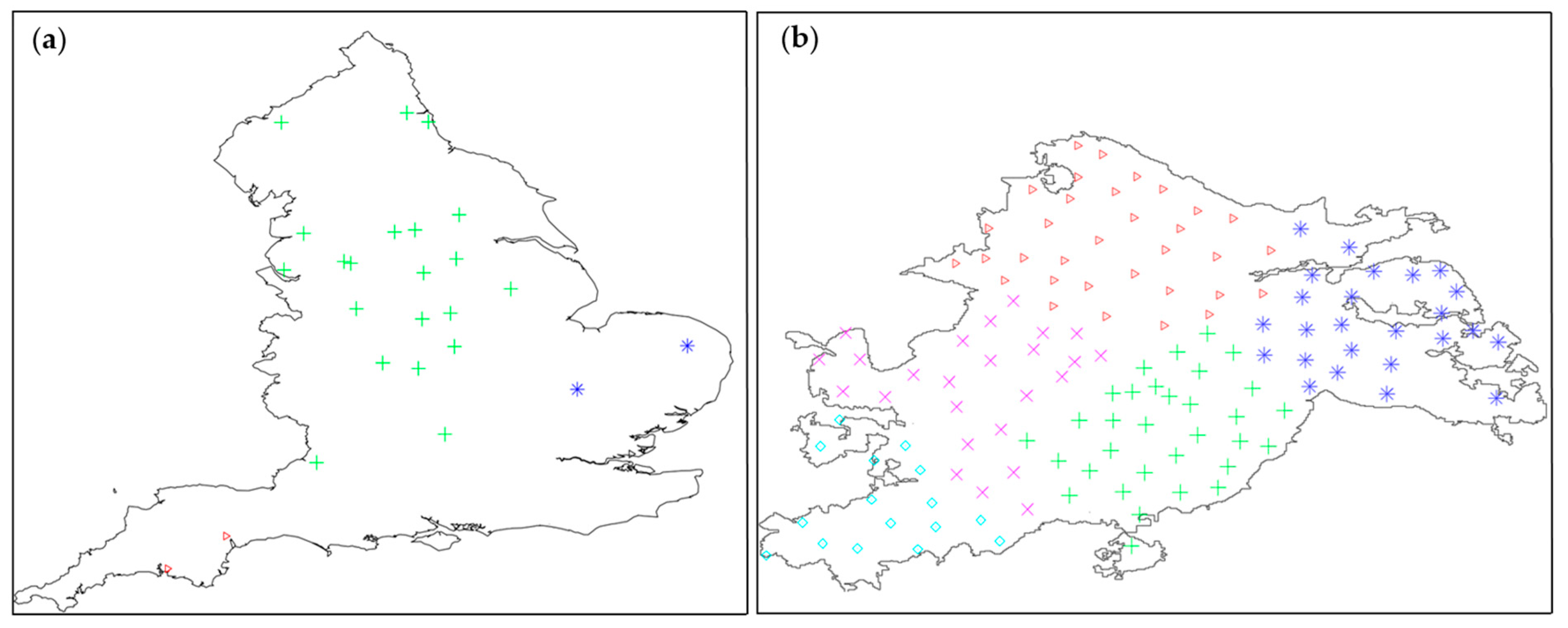
3.2. Spatial Clustering Organization of Case Library
3.3. Feature Extraction and Weight Allocation
3.4. Case Retrieval and Revision
3.5. Experiment and Result Analysis
3.5.1. Experiment One: Comparison with Traditional Evaluation Methods
3.5.2. Experiment Two: Comparison with Other Case-Based Reasoning Methods
3.5.3. Experiment Three: Real-World Application
3.6. Discussion Summary
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Simos, J.; Spanswick, L.; Palmer, N.; Christie, D. The role of health impact assessment in Phase V of the Healthy Cities European Network. Health Promot. Int. 2015, 30 (Suppl. S1), i71–i85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Tan, S.; Li, M.; Dong, M. Research on active planning intervention strategies for healthy cities. Urban Plan. 2022, 46, 61–76. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bai, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zotova, O.; Pineo, H.; Siri, J.; Liang, L.; Luo, X.; Kwan, M.-P.; Ji, J.; Jiang, X.; et al. Healthy cities initiative in China: Progress, challenges, and the way forward. Lancet Reg. Health-West. Pac. 2022, 27, 100539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Qin, W.; Zhang, S.; Qi, F.; Li, X.; Lan, X. Assessing the construction of a Healthy City in China: A conceptual framework and evaluation index system. Public Health 2023, 220, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boeing, G.; Higgs, C.; Liu, S.; Giles-Corti, B.; Sallis, J.F.; Cerin, E.; Lowe, M.; Adlakha, D.; Hinckson, E.; Moudon, A.V. Using Open Data and Open-Source Software to Develop Spatial Indicators of Urban Design and Transport Features for Achieving Healthy and Sustainable Cities. Lancet Glob. Health 2022, 10, e907–e918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowe, M.; Arundel, J.; Hooper, P.; Rozek, J.; Higgs, C.; Roberts, R.; Giles-Corti, B. Liveability aspirations and realities: Implementation of urban policies designed to create healthy cities in Australia. Soc. Sci. Med. 2020, 245, 112713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsyth, A.; Slotterback, C.S.; Krizek, K.J. Health impact assessment in planning: Development of the design for health HIA tools. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2010, 30, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Netherton, A.; McLarty, K.; Petrokofsky, C.; Chang, M. Professional workforce training needs for Health Impact Assessment in spatial planning: A cross sectional survey. Public Health Pract. 2022, 3, 100268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Chan, E.H.W.; Du, J.; Feng, L.; Jiang, P.; Xu, Y. Developing a Health-Spatial Indicator System for a Healthy City in Small and Midsized Cities. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orsetti, E.; Tollin, N.; Lehmann, M.; Valderrama, V.A.; Morató, J. Building Resilient Cities: Climate Change and Health Interlinkages in the Planning of Public Spaces. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Li, D.; Wang, X.; Li, S. Examining component-based city health by implementing a fuzzy evaluation approach. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 93, 791–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Liu, J.; Wu, L.; Bu, Z.; Zhu, Z. Development of a Healthy Assessment System for Residential Building Epidemic Prevention. Build. Environ. 2021, 202, 108038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Leeuw, E.; Green, G.; Dyakova, M.; Spanswick, L.; Palmer, N. European Healthy Cities evaluation: Conceptual framework and methodology. Health Promot. Int. 2015, 30 (Suppl. S1), i8–i17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, K.C.; Rodrigues, M.A.; Miraglia, S.G.E.K. Health impact assessment of air pollution in Lisbon, Portugal. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2022, 72, 1307–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, J.; Zhang, X.; Ren, C.; Shi, Y.; Lee, T.-C. Spatiotemporal assessment of extreme heat risk for high-density cities: A case study of Hong Kong from 2006 to 2016. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 64, 102507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, J.; Moriyama, M.; Kazawa, K. Spatially heterogeneous associations between the built environment and objective health outcomes in Japanese cities. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2022, 33, 1205–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iungman, T.; Cirach, M.; Marando, F.; Pereira Barboza, E.; Khomenko, S.; Masselot, P.; Quijal-Zamorano, M.; Mueller, N.; Gasparrini, A.; Urquiza, J.; et al. Cooling cities through urban green infrastructure: A health impact assessment of European cities. Lancet 2023, 401, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pala, D.; Caldarone, A.A.; Franzini, M.; Malovini, A.; Larizza, C.; Casella, V.; Bellazzi, R. Deep Learning to Unveil Correlations between Urban Landscape and Population Health. Sensors 2020, 20, 2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbaz, K.; Hoteit, I.; Shaban, W.M.; Shen, S.-L. Spatiotemporal air quality forecasting and health risk assessment over smart city of NEOM. Chemosphere 2023, 313, 137636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Li, W. Spatial case revision in case-based reasoning for risk assessment of geological disasters. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2020, 11, 1052–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merghadi, A.; Yunus, A.P.; Dou, J.; Whiteley, J.; Thaipham, B.; Bui, D.T.; Avtar, R.; Abderrahmane, B. Machine learning methods for landslide susceptibility studies: A comparative overview of algorithm performance. Earth Sci. Rev. 2020, 207, 103225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, L.; Tan, X.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, K.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, M.; Zhang, Y. The application of subjective and objective method in the evaluation of healthy cities: A case study in Central China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 65, 102581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.; Guo, H.; Zhang, L.; Liang, D. Comparative Study on the Evaluation of Healthy City Construction in Typical Chinese Cities Based on Statistical Data and Land Use Data. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Xia, T.; Xi, Y.; Li, Y. Healthy Cities, A comprehensive dataset for environmental determinants of health in England cities. Sci. Data 2023, 10, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Cao, H.; Tian, G. A hybrid approach of rough set and case-based reasoning to remanufacturing process planning. J. Intell. Manuf. 2019, 30, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aamodt, A.; Plaza, E. Case-Based Reasoning: Foundational Issues, Methodological Variations, and System Approaches. Ai Commun. 2001, 7, 39–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, N.; Song, K.; Ahn, Y.; Park, M.; Jang, Y. Maintenance cost prediction for aging residential buildings based on case-based reasoning and genetic algorithm. J. Build. Eng. 2020, 28, 101006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Yu, W.W.; Yu, W.H.; Lv, L.N. Simulating urban growth through case-based reasoning. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2022, 55, 277–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Yu, W.H.; Lv, L.N.; Zang, S.Y.; Ni, H.W. An Improved Case-Based Reasoning Model for Simulating Urban Growth. Sustainability 2021, 13, 6146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.H.; Fan, H.Q.; Shen, L.Y. Case-based reasoning for selection of the best practices in low-carbon city development. Front. Eng. Manag. 2019, 6, 416–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony Jnr, B. A case-based reasoning recommender system for sustainable smart city development. AI Soc. 2021, 36, 159–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, A.G.O.; Shi, X. Applying case-based reasoning to urban planning: A new planning-support system tool. Environ. Plan. B-Plan. Des. 1999, 26, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, O.; Kim, Y.S.; Lee, N.; Jung, Y. When Collective Knowledge Meets Crowd Knowledge in a Smart City: A Prediction Method Combining Open Data Keyword Analysis and Case-Based Reasoning. J. Healthc. Eng. 2018, 2018, 7391793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Li, X.Y. Improving emergency response to cascading disasters: Applying case-based reasoning towards urban critical infrastructure. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2018, 30, 244–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Li, J. Study on emergency decision-making method of urban fire based on case-based reasoning under incomplete information. J. Saf. Sci. Technol. 2018, 14, 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.N.; Liang, Y.Z.; Sun, H.; Yang, Y.F. Emergency Response for COVID-19 Prevention and Control in Urban Rail Transit Based on Case-Based Reasoning Method. Discret. Dyn. Nat. Soc. 2020, 2020, 6689089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Chen, J.; Yao, J.; Xu, K.; Liao, Y.; Xie, H.; Gan, X. An improved spatial case-based reasoning considering multiple spatial drivers of geographic events and its application in landslide susceptibility mapping. Catena 2023, 223, 106940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Liang, F.; Sun, Y. Integrating spatial relations into case-based reasoning to solve geographic problems. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2012, 33, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Cao, Z.J. An improved case-based reasoning method and its application in endpoint prediction of basic oxygen furnace. Neurocomputing 2015, 149, 1245–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.N.; Hu, J.; Qi, J.; Ma, J.; Peng, Y.H. An integrated feature selection and cluster analysis techniques for case-based reasoning. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2015, 39, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yu, J.L.; Yu, L.A.; Sun, J. The clustering-based case-based reasoning for imbalanced business failure prediction: A hybrid approach through integrating unsupervised process with supervised process. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 2014, 45, 1225–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S.; Xie, X.; Lin, L. Two-layer random forests model for case reuse in case-based reasoning. Expert Syst. Appl. 2015, 42, 9412–9425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Q.; Deng, S.; Zheng, Z. An Adaptive Sweep-Circle Spatial Clustering Algorithm Based on Gestalt. Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2017, 6, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dearman, W.R. 13—Land and water management: Environmental geology mapping. In Engineering Geological Mapping; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 1991; pp. 339–357. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, A.; Shao, H.; Guo, Z. Weight optimization for case-based reasoning using membrane computing. Inf. Sci. 2014, 287, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamo, M.; Golobardes, E. Analysing Rough Sets weighting methods for Case-Based Reasoning Systems. Intel. Artif. Rev. Iberoam. De Intel. Artif. 2002, 6, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, S.Y. A hybrid genetic algorithm for feature subset selection in rough set theory. Soft Comput. 2014, 18, 1373–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouhana, A.; Fekih, A.; Abed, M.; Chabchoub, H. An integrated case-based reasoning approach for personalized itinerary search in multimodal transportation systems. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2013, 31, 30–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cover, T.; Hart, P. Nearest neighbor pattern classification. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theor. 2006, 13, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Yan, H. Geometry Similarity Assessment Model of Spatial Polygon Groups. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2013, 15, 635–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, M.; Yuan, S.; Chu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Fang, C. Underground Pipeline Data Matching Considering Multiple Spatial Similarities. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2015, 44, 1392–1400. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, A.; Wang, D. Trustworthiness evaluation and retrieval-based revision method for case-based reasoning classifiers. Expert Syst. Appl. 2015, 42, 8006–8013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, A.; Zhang, K.; Yu, Y.; Wang, P. An attribute difference revision method in case-based reasoning and its application. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2017, 65, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, M.A.; Abd Ghani, M.K.; Arunkumar, N.; Obaid, O.I.; Mostafa, S.A.; Jaber, M.M.; Burhanuddin, M.A.; Matar, B.M.; Abdullatif, S.K.; Ibrahim, D.A. Genetic case-based reasoning for improved mobile phone faults diagnosis. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2018, 71, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, R.; Cho, K.; Hyun, C.; Son, M. MRA-based revised CBR model for cost prediction in the early stage of construction projects. Expert Syst. Appl. 2012, 39, 5214–5222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, A.; Wang, W.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, H. A fault prediction method that uses improved case-based reasoning to continuously predict the status of a shaft furnace. Inf. Sci. 2014, 259, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.H.; Chen, H.C. A novel CBR system for numeric prediction. Inf. Sci. 2012, 185, 178–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Category | Attribute Code | Feature Attributes |
|---|---|---|
| Basic Statistics | A1 | Population |
| A2 | Area | |
| A3 | Population Density | |
| S1 | Geographical Centroid | |
| S2 | Boundary | |
| Behavior Environment | A4 | Tobacco Availability |
| A5 | Alcohol Availability | |
| A6 | Health Service Availability | |
| A7 | Physical Exercise Availability | |
| A8 | Building Density | |
| A9 | Median/Mean House Price | |
| A10 | Driving/Cycling/Walking Road Density | |
| A11 | Street View Features | |
| A12 | Satellite View Features | |
| A13 | Walkability | |
| Natural Environment | A14 | NOx/PM2.5/PM10 |
| A15 | Min/Max Temperature | |
| A16 | Rainfall | |
| A17 | Relative Humidity | |
| A18 | Snow Lying Days | |
| A19 | Sunshine Hours | |
| A20 | Wind Speed | |
| Physical Health | R1 | Asthma |
| R2 | Cancer | |
| R3 | Dementia | |
| R4 | Diabetes | |
| Mental Health | R5 | Mental Health |
| Life Expectancy | R6 | Life Expectancy |
| R7 | Healthy Life Expectancy |
| Attribute Code | Feature Indicator | Weight |
|---|---|---|
| A3 | Population Density | 0.0619 |
| A4 | Tobacco Availability | 0.0370 |
| A5 | Alcohol Availability | 0.0595 |
| A6 | Health Service Availability | 0.1618 |
| A7 | Physical Exercise Availability | 0.0822 |
| A8 | Building Density | 0.0545 |
| A9 | Median/Mean House Price | 0.0676 |
| A10 | Driving/Cycling/Walking Road Density | 0.1425 |
| A11 | Street View Features | 0.0602 |
| A12 | Satellite View Features | 0.0188 |
| A13 | Walkability | 0.1009 |
| A14 | NOx/PM2.5/PM10 | 0.1457 |
| A15 | Min/Max Temperature | 0.0074 |
| Parameter | Description | Value Range |
|---|---|---|
| M | Population Size | 5 |
| Pc | Crossover Probability | 0.8 |
| Pm | Mutation Probability | 0.1 |
| T | Termination Generation | 100 |
| Experiment | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HCSCBR | 94.32 | 89.78 | 96.57 | 93.12 | 86.98 | 85.43 | 92.27 | 89.14 | 90.16 | 87.42 | 90.52 |
| SVW | 82.56 | 89.31 | 87.10 | 90.76 | 86.75 | 84.43 | 91.34 | 88.91 | 83.60 | 86.15 | 87.09 |
| KNN | 69.43 | 72.12 | 58.24 | 65.78 | 72.12 | 60.87 | 63.76 | 73.11 | 54.04 | 67.45 | 65.69 |
| BN | 81.27 | 80.49 | 77.23 | 81.45 | 82.59 | 78.37 | 75.60 | 78.12 | 70.19 | 73.67 | 77.90 |
| ANN | 72.68 | 75.57 | 70.13 | 72.60 | 75.78 | 74.29 | 70.27 | 79.15 | 73.28 | 80.17 | 74.39 |
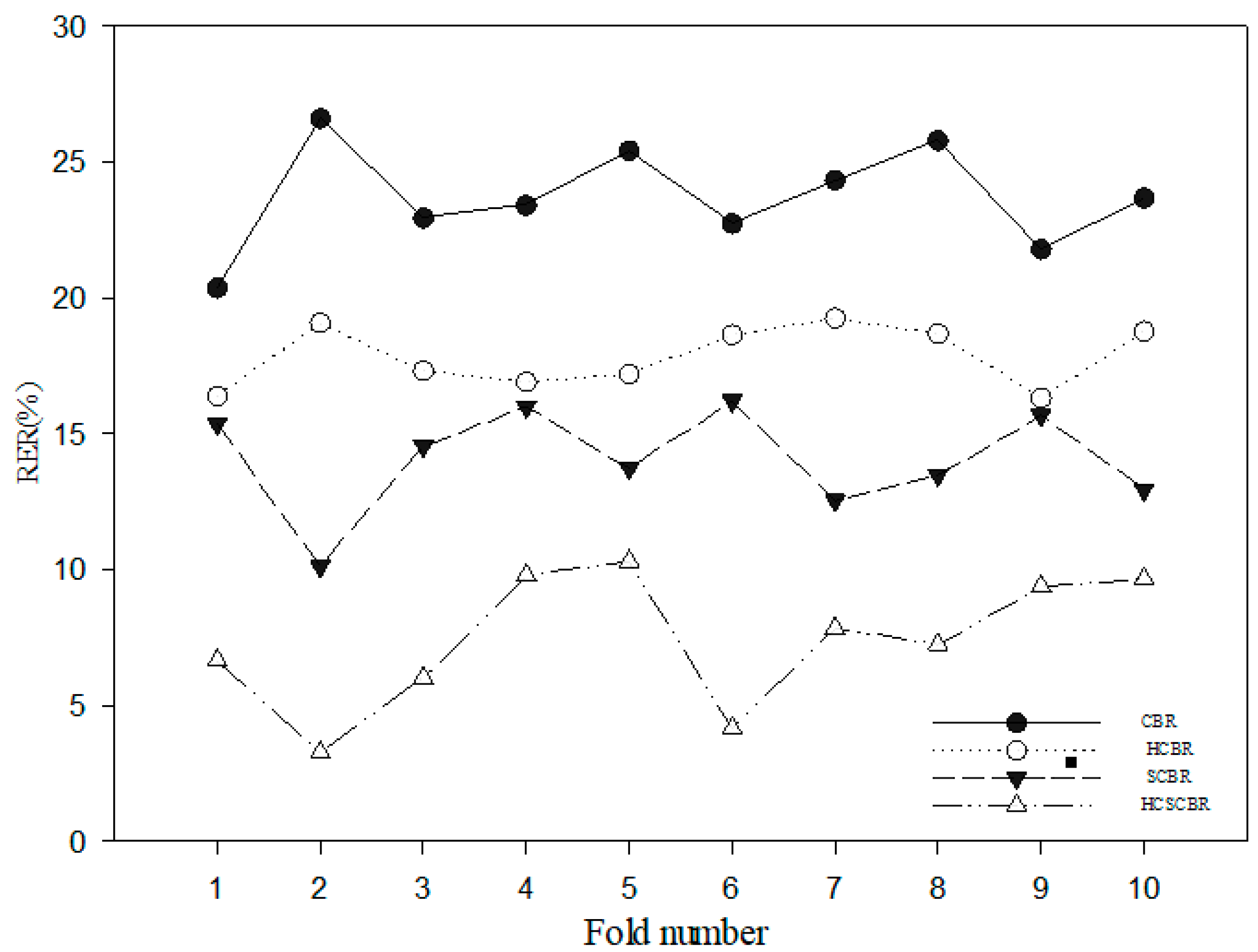
| Ten-Fold | CBR | HCBR | SCBR | HCSCBR | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RER (%) | Time (s) | RER (%) | Time (s) | RER (%) | Time (s) | RER (%) | Time (s) | |
| 1 | 20.37 | 0.2164 | 16.40 | 0.4765 | 15.36 | 0.6350 | 6.64 | 0.5560 |
| 2 | 26.60 | 0.2081 | 19.08 | 0.4870 | 10.11 | 0.6274 | 3.26 | 0.5590 |
| 3 | 22.94 | 0.2155 | 17.32 | 0.4833 | 14.56 | 0.6287 | 6.01 | 0.5574 |
| 4 | 23.41 | 0.2057 | 16.91 | 0.3965 | 15.99 | 0.7295 | 9.78 | 0.5599 |
| 5 | 25.42 | 0.3104 | 17.20 | 0.3806 | 13.74 | 0.6281 | 10.3 | 0.5599 |
| 6 | 22.74 | 0.2128 | 18.65 | 0.4757 | 16.21 | 0.6286 | 4.15 | 0.5511 |
| 7 | 24.34 | 0.2125 | 19.26 | 0.3957 | 12.54 | 0.6336 | 7.84 | 0.5602 |
| 8 | 25.79 | 0.2255 | 18.68 | 0.3918 | 13.47 | 0.7260 | 7.24 | 0.5552 |
| 9 | 21.79 | 0.3089 | 16.32 | 0.3838 | 15.69 | 0.6277 | 9.38 | 0.6513 |
| 10 | 23.68 | 0.3123 | 18.78 | 0.3915 | 12.93 | 0.7355 | 9.65 | 0.5641 |
| Average | 23.71 | 0.2428 | 17.86 | 0.4262 | 14.06 | 0.6600 | 7.43 | 0.5674 |
| Similarity Variable | Similar Cases | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 | |
| A3 | 0.8282 | 0.8311 | 0.8462 | 0.8841 | 0.8712 |
| A4 | 0.7161 | 0.9804 | 0.8316 | 0.8565 | 0.8301 |
| A5 | 0.8806 | 0.9602 | 0.9276 | 0.9293 | 0.9595 |
| A6 | 0.9028 | 0.8947 | 0.8435 | 0.9833 | 0.9319 |
| A7 | 0.7962 | 0.9393 | 0.9785 | 0.8092 | 0.9504 |
| A8 | 0.9781 | 0.9549 | 0.9317 | 0.98 | 0.9236 |
| A9 | 0.7228 | 0.8658 | 0.9671 | 0.8043 | 0.9904 |
| A10 | 0.8204 | 0.9389 | 0.9243 | 0.8173 | 0.8274 |
| A11 | 0.8756 | 0.9631 | 0.939 | 0.9877 | 0.9991 |
| A12 | 0.8577 | 0.9256 | 0.9824 | 0.9291 | 0.8108 |
| A13 | 0.9352 | 0.8588 | 0.9608 | 0.8874 | 0.9565 |
| A14 | 0.8673 | 0.941 | 0.9112 | 0.8844 | 0.8331 |
| A15 | 0.8021 | 0.8436 | 0.8554 | 0.9228 | 0.8009 |
| S1 | 0.9468 | 0.9149 | 0.8404 | 0.8894 | 0.9627 |
| S2 | 0.8154 | 0.8567 | 0.9138 | 0.959 | 0.9031 |
| R1 | 0.8132 | 0.8782 | 0.8907 | 0.801 | 0.871 |
| R2 | 0.767 | 0.882 | 0.8498 | 0.9685 | 0.9144 |
| R3 | 0.9446 | 0.9384 | 0.869 | 0.9506 | 0.8298 |
| R4 | 0.7098 | 0.8094 | 0.8524 | 0.8619 | 0.9178 |
| R5 | 0.8562 | 0.9334 | 0.9563 | 0.9627 | 0.9986 |
| R6 | 0.8816 | 0.9935 | 0.8823 | 0.8818 | 0.8912 |
| R7 | 0.8917 | 0.8004 | 0.8009 | 0.9273 | 0.9856 |
| Compatibility Calculation | Similar Cases | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 | |
| k(A3) | 0.73632 | 0.48028 | 0.68273 | 0.76047 | 0.39772 |
| k(A4) | 0.52029 | 0.22987 | 0.3179 | 0.61327 | 0.28184 |
| k(A5) | 0.56912 | 0.81926 | −0.80066 | 0.45055 | 0.10633 |
| k(A6) | 0.8992 | 0.47143 | 0.85985 | 0.3185 | −0.86412 |
| k(A7) | 0.20243 | 0.4194 | 0.38574 | 0.75552 | 0.68376 |
| k(A8) | −0.26346 | 0.71412 | 0.17521 | 0.77377 | 0.55243 |
| k(A9) | 0.40125 | 0.20773 | 0.53943 | 0.36065 | 0.43011 |
| k(A10) | 0.35066 | 0.28443 | 0.69777 | 0.77603 | 0.74197 |
| k(A11) | 0.20136 | 0.13543 | 0.83635 | 0.65208 | 0.28544 |
| k(A12) | −0.50385 | 0.46818 | 0.52366 | 0.86655 | 0.12306 |
| k(A13) | 0.70714 | −0.36584 | 0.50213 | 0.27115 | 0.70551 |
| k(A14) | 0.2015 | 0.64299 | 0.7128 | 0.26767 | 0.66865 |
| k(S1) | 0.47604 | 0.78895 | 0.23606 | −0.81431 | 0.62266 |
| k(S2) | 0.35159 | 0.87258 | 0.24634 | 0.19142 | 0.36758 |
| k (P) | −0.62203 | −0.22625 | −0.70771 | −0.81116 | −0.16647 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deng, S.; Liu, W.; Peng, Y.; Liu, B. A Spatial Case-Based Reasoning Method for Healthy City Assessment: A Case Study of Middle Layer Super Output Areas (MSOAs) in Birmingham, England. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2024, 13, 271. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi13080271
Deng S, Liu W, Peng Y, Liu B. A Spatial Case-Based Reasoning Method for Healthy City Assessment: A Case Study of Middle Layer Super Output Areas (MSOAs) in Birmingham, England. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information. 2024; 13(8):271. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi13080271
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeng, Shuguang, Wei Liu, Ying Peng, and Binglin Liu. 2024. "A Spatial Case-Based Reasoning Method for Healthy City Assessment: A Case Study of Middle Layer Super Output Areas (MSOAs) in Birmingham, England" ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information 13, no. 8: 271. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi13080271
APA StyleDeng, S., Liu, W., Peng, Y., & Liu, B. (2024). A Spatial Case-Based Reasoning Method for Healthy City Assessment: A Case Study of Middle Layer Super Output Areas (MSOAs) in Birmingham, England. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 13(8), 271. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi13080271







