Estimating Daily NO2 Ground Level Concentrations Using Sentinel-5P and Ground Sensor Meteorological Measurements
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
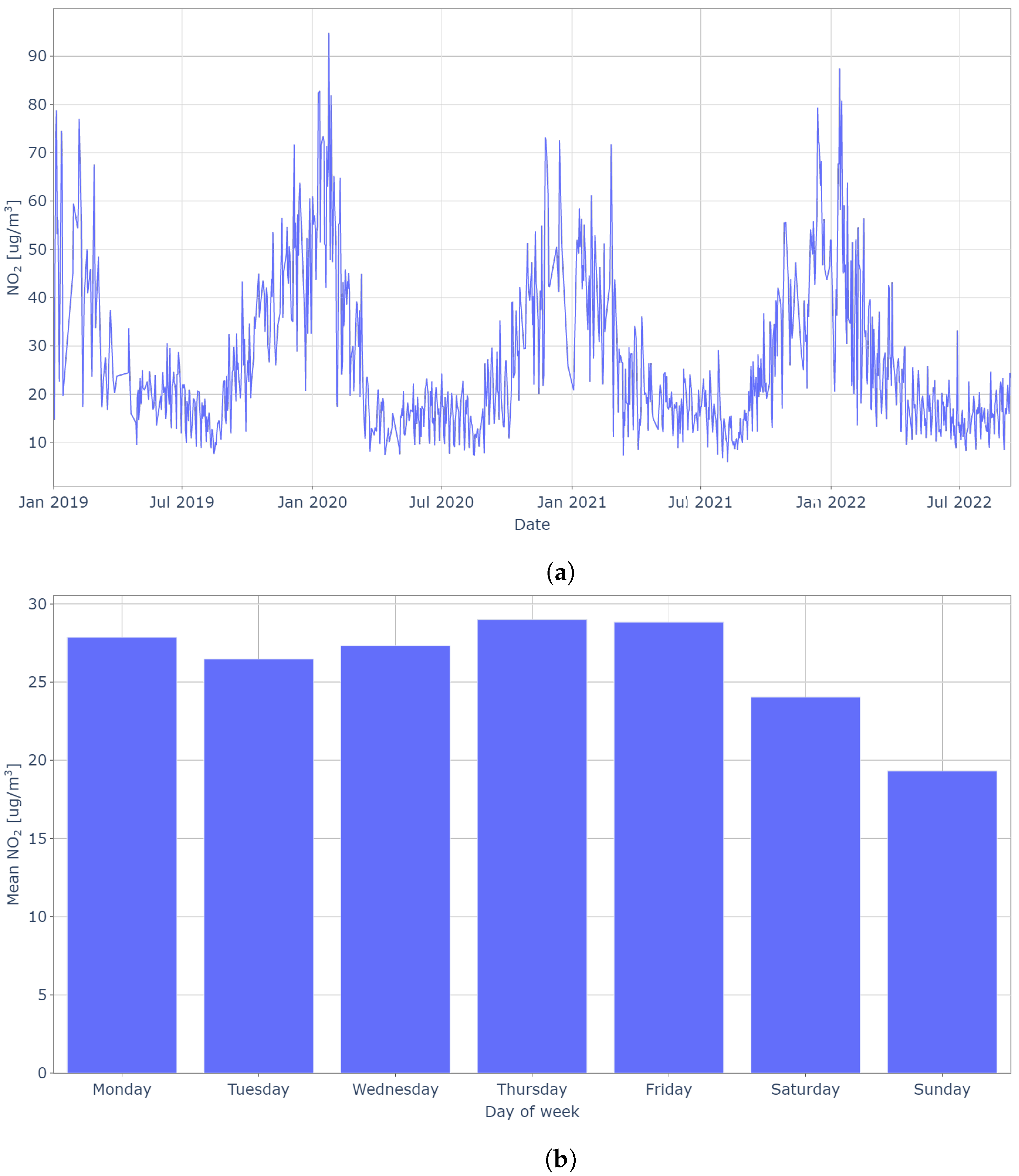
2.1. NO Ground Sensors Data
2.2. Meteorological Ground Sensors Data
2.3. Satellite Data
2.4. Data Pre-Processing
2.5. Methods
2.6. Computational Regression Models
2.6.1. Long Short-Term Memory Algorithm
2.6.2. Random Forest
2.6.3. Support Vector Regression
2.6.4. Decision Tree Regression
2.6.5. Gradient Tree Boosting
2.6.6. Multi-Layer Perceptron Regressor
2.6.7. B-Spline Regressor
2.6.8. Kriging Regressor
2.7. Training and Testing of the Models
2.7.1. Training
2.7.2. Testing
3. Results
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ANN | Artificial Neural Network |
| API | Application Programming Interface |
| ARPA | Agenzia Regionale per la Protezione Ambientale |
| CO | Carbon Monoxide |
| COPD | Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease |
| COVID | Corona Virus Disease |
| CV | Cross Validation |
| DIAS | Data and Information Access Services |
| DL | Deep Learning |
| DTM | Digital Terrain Model |
| DTR | Decision Tree Regression |
| EEA | European Environment Agency |
| ETS | Extreme Triple Smoothing |
| ESA | European Space Agency |
| EU | European Union |
| EUMETSAT | European Union Meteorological Satellites |
| GB | Gradient Boosting |
| GOES | Geostationary Operational Environment Satellite |
| GTB | Gradient Tree Boosting |
| LMICs | Low- and Middle-Income Countries |
| LR | Linear Regression |
| LSTM | Long Short-Term Memory |
| MCM | Metropolitan City of Milan |
| MDPI | Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute |
| ML | Machine Learning |
| MLPR | Multi-Layer Perceptron Regressor |
| MLR | Multiple Linear Regression |
| MODIS | Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer |
| NASA | National Aeronautics and Space Administration |
| NN | Neural Network |
| NO | Nitrogen Dioxide |
| NO | Nitrogen Monoxide |
| O | Ozone |
| ODC | Open Data Cube |
| OMI | Ozone Monitoring Instrument |
| PM | Particulate Matter |
| RF | Random Forest |
| RMSE | Root Mean Square Error |
| SARIMA | Seasonal Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average |
| SDGs | Sustainable Development Goals |
| SO | Sulphur Dioxide |
| SVM | Support Vector Machine |
| SVR | Support Vector Regression |
| TROPOMI | TROPOspheric Measurement Instrument |
| UN | United Nations |
| USA | United States of America |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| WMO | World Meteorological Organization |
| XGB | Extreme Gradient Boost |
References
- European Environment Agency. Health Impacts of Air Pollution in Europe, 2021; EEA: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations. The 17 Sustainable Development Goals. Available online: https://sdgs.un.org/goals (accessed on 25 September 2022).
- Trushna, T.; Tiwari, R.R. Establishing the National Institute for Research in Environmental Health, India. Bull. World Health Organ. 2022, 100, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Lu, W. Exposure to Nitrogen Dioxide and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 15133–15145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyagi, S.; Chaudhary, M.; Ambedkar, A.K.; Sharma, K.; Gautam, Y.K.; Singh, B.P. Metal Oxide Nanomaterials based sensors for monitoring environmental NO2 and its impact on plant ecosystem: A Review. Sens. Diagn. 2022, 1, 106–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Environment Agency. Emissions from Road Traffic and Domestic Heating behind Breaches of EU Air Quality Standards across Europe; European Environment Agency: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Pruitt, E. Review of the primary national ambient air quality standards for oxides of nitrogen. Fed. Regist 2018, 83, 17226–17278. [Google Scholar]
- Piccoli, A.; Agresti, V.; Balzarini, A.; Bedogni, M.; Bonanno, R.; Collino, E.; Colzi, F.; Lacavalla, M.; Lanzani, G.; Pirovano, G.; et al. Modeling the Effect of COVID-19 Lockdown on Mobility and NO2 Concentration in the Lombardy Region. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EEA. Air Quality Standards; European Environment Agency: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- ESA. Copernicus in Detail; European Space Agency: Paris, France, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Reimann, S.; Wegener, R.; Claude, A.; Sauvage, S. Updated Measurement Guideline for NOx and VOCs; Actris: Dübendorf, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kramer, H.J.; Copernicus: Sentinel-5P (Precursor—Atmospheric Monitoring Mission). Publication Title: Copernicus: Sentinel-5P—Satellite Missions—eoPortal Directory. European Space Agency, Paris, France. 2012. Available online: https://www.eoportal.org/satellite-missions/copernicus-sentinel-5p#ground-segment (accessed on 25 August 2022).
- Pinder, R.W.; Klopp, J.M.; Kleiman, G.; Hagler, G.S.W.; Awe, Y.; Terry, S. Opportunities and challenges for filling the air quality data gap in low- and middle-income countries. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 215, 116794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WMO Weather Stations; World Meteorological Organization (WMO): Geneva, Swizerland, 2021; Available online: http://www.wmo.int/datastat/wmodata_en.html (accessed on 7 May 2021).
- Long, S.; Wei, X.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, R.; Xu, J.; Wu, K.; Li, Q.; Li, W. Estimating daily ground-level NO2 concentrations over China based on TROPOMI observations and machine learning approach. Atmos. Environ. 2022, 289, 119310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araki, S.; Shima, M.; Yamamoto, K. Spatiotemporal land use random forest model for estimating metropolitan NO2 exposure in Japan. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 634, 1269–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Choi, H.; Im, J.; Park, S.; Shin, M.; Song, C.K.; Kim, S. Estimation of surface-level NO2 and O3 concentrations using TROPOMI data and machine learning over East Asia. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 288, 117711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Dong, H.; Zhang, Z.; Yuan, Y. An Ensemble Model-Based Estimation of Nitrogen Dioxide in a Southeastern Coastal Region of China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Christakos, G. Space-time mapping of ground-level PM2.5 and NO2 concentrations in heavily polluted northern China during winter using the Bayesian maximum entropy technique with satellite data. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2018, 11, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Sun, K.; Hu, J.; Xue, T.; Xu, H.; Wang, M. Estimating 2013–2019 NO2 exposure with high spatiotemporal resolution in China using an ensemble model. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 292, 118285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naseer, E.; Basit, A.; Bhatti, M.K.; Siddique, M.A. Machine Learning for Area-Wide Monitoring of Surface Level Concentration of NO2 Using Remote Sensing Data; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.Y.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, T.H.; Ou, C.Q.; Guo, Y. A kriging-calibrated machine learning method for estimating daily ground-level NO2 in mainland China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 690, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekiya, T.; Miyazaki, K.; Eskes, H.; Sudo, K.; Takigawa, M.; Kanaya, Y. A comparison of the impact of TROPOMI and OMI tropospheric NO2 on global chemical data assimilation. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2022, 15, 1703–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Di, B.; Luo, Y.; Grieneisen, M.L.; Zeng, W.; Zhang, S.; Deng, X.; Tang, Y.; Shi, G.; Yang, F.; et al. A robust approach to deriving long-term daily surface NO2 levels across China: Correction to substantial estimation bias in back-extrapolation. Environ. Int. 2021, 154, 106576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheibenreif, L.; Mommert, M.; Borth, D. Toward Global Estimation of Ground-Level NO2 Pollution With Deep Learning and Remote Sensing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Brunner, D.; Kuhlmann, G. Importance of satellite observations for high-resolution mapping of near-surface NO2 by machine learning. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 264, 112573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diémoz, H.; Barnaba, F.; Magri, T.; Pession, G.; Dionisi, D.; Pittavino, S.; Tombolato, I.K.; Campanelli, M.; Ceca, L.S.D.; Hervo, M.; et al. Transport of po valley aerosol pollution to the northwestern Alps–Part 1: Phenomenology. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 3065–3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cedeno Jimenez, J.R.; Oxoli, D.; Brovelli, M.A. Enabling Air Quality Monitoring with the Open Data Cube: Implementation for Sentinel-5P and Ground Sensor Observations. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sensing And Spat. Inf. Sci. 2021, XLVI-4/W2-2021, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wu, Y.; Bao, Y.; Liu, B.; Petropoulos, G.P. Near-Surface NO2 Concentration Estimation by Random Forest Modeling and Sentinel-5P and Ancillary Data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ARPA Lombardia. Dati Sensori Aria: Open Data Regione Lombardia; ARPA: Milan, Italy, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Lombardia, A. Criteri di Rilevamento—Aria/Qualità Dell’Aria: ARPA Lombardia; ARPA: Milan, Italy, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Earth Science Data Systems. Available online: https://www.earthdata.nasa.gov/sensors/omi (accessed on 15 October 2022).
- van Geffen, J.H.G.M.; Eskes, H.J.; Boersma, K.F.; Veefkind, J.P. TROPOMI ATBD of the Total and Tropospheric NO2 Data Products; Royal Netherlands Meteorological Institute, Ministry of Infrastructure and Water Management: Utrecht, The Netherlands, 2022; p. 88. [Google Scholar]
- STDelftCorp. HARP Manual; Science and Technology: Delft, The Netherlands, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Di, Q.; Amini, H.; Shi, L.; Kloog, I.; Silvern, R.; Kelly, J.; Sabath, M.B.; Choirat, C.; Koutrakis, P.; Lyapustin, A.; et al. Assessing NO2 concentration and model uncertainty with high spatiotemporal resolution across the contiguous united states using ensemble model averaging. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 1372–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gariazzo, C.; Carlino, G.; Silibello, C.; Renzi, M.; Finardi, S.; Pepe, N.; Radice, P.; Forastiere, F.; Michelozzi, P.; Viegi, G.; et al. A multi-city air pollution population exposure study: Combined use of chemical-transport and random-Forest models with dynamic population data. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 724, 138102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamińska, J.A. A random forest partition model for predicting NO2 concentrations from traffic flow and meteorological conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Li, C.; Liu, D.; Grieneisen, M.L.; Yang, F.; Chen, C.; Zhan, Y. Hybrid deep learning models for mapping surface NO2 across China: One complicated model, many simple models, or many complicated models? Atmos. Res. 2022, 278, 106339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, P.Y.; Su, H.J.; Lee, H.Y.; Chen, Y.C.; Hsiao, Y.P.; Huang, J.W.; Teo, T.A.; Wu, C.D.; Spengler, J.D. Using land-use machine learning models to estimate daily NO2 concentration variations in Taiwan. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 317, 128411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Hoogh, K.D.; Gulliver, J.; Hoffmann, B.; Hertel, O.; Ketzel, M.; Bauwelinck, M.; Donkelaar, A.V.; Hvidtfeldt, U.A.; Katsouyanni, K.; et al. A comparison of linear regression, regularization, and machine learning algorithms to develop Europe-wide spatial models of fine particles and nitrogen dioxide. Environ. Int. 2019, 130, 104934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, W.Y.; Koh, D.; Mohtar, A.A.A.; Latif, M.T. Statistical Analysis and Predictive Modelling of Air Pollutants Using Advanced Machine Learning Approaches. In 2020 IEEE Asia-Pacific Conference on Computer Science and Data Engineering, CSDE 2020; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; ISBN 9781665419741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Yuan, Q.; Gao, M.; Li, T. A new perspective to satellite-based retrieval of ground-level air pollution: Simultaneous estimation of multiple pollutants based on physics-informed multi-task learning. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 857, 159542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iskandaryan, D.; Sabatino, S.D.; Ramos, F.; Trilles, S. Exploratory Analysis and Feature Selection for the Prediction of Nitrogen Dioxide. AGILE GISci. Ser. 2022, 3, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, A. Practical Time Series Analysis: Prediction with Statistics and Machine Learning, 1st ed.; O’Reilly Media: Sebastopol, CA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Speiser, J.L.; Miller, M.E.; Tooze, J.; Ip, E. A comparison of random forest variable selection methods for classification prediction modeling. Expert Syst. Appl. 2019, 134, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parbat, D.; Chakraborty, M. A python based support vector regression model for prediction of COVID19 cases in India. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2020, 138, 109942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Watanachaturaporn, P.; Varshney, P.K.; Arora, M.K. Decision tree regression for soft classification of remote sensing data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 97, 322–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biau, G.; Cadre, B.; Rouvière, L. Accelerated gradient boosting. Mach. Learn. 2019, 108, 971–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mao, F.; Zhou, X.; Song, Y. Environmental and Human Data-Driven Model Based on Machine Learning for Prediction of Human Comfort. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 132909–132922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unser, M.; Aldroubi, A.; Eden, M. B-spline signal processing. I. Theory. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1993, 41, 821–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krivoruchko, K. Empirical Bayesian Kriging; ESRI: Redlands, CA, USA, 2012; p. 5. [Google Scholar]
- Oxoli, D.; Cedeno Jimenez, J.R.; Brovelli, M.A. Assessment of Sentinel-5P Performance for Ground-Level Air Quality Monitoring: Preparatory Experiments over the COVID-19 Lockdown Period. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2020, XLIV-3/W1-2020, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathieu, E.; Ritchie, H.; Rodés-Guirao, L.; Appel, C.; Giattino, C.; Hasell, J.; Macdonald, B.; Dattani, S.; Beltekian, D.; Ortiz-Ospina, E.; et al. Coronavirus Pandemic (COVID-19). In Our World in Data; University of Oxford: Oxford, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]











| Dataset | Spatial Resolution (km × km) | Temporal Resolution |
|---|---|---|
| ARPA NO | Non-regular gridding | 1-h |
| ARPA Meteorological | Non-regular gridding | 10-min |
| Sentinel-5P | 3.5 × 5 | 1 day |
| Used Temporal Resolution | Variable | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Daily | NO | Sentinel-5P |
| Day of the week | - | |
| Month | - | |
| Daily (average from 12:00 h to 15:00 h) | NO | ARPA atm. pollution |
| Temperature | ARPA meteo | |
| Wind speed | ARPA meteo | |
| Wind direction | ARPA meteo | |
| Precipitation | ARPA meteo | |
| Global radiation | ARPA meteo | |
| Relative humidity | ARPA meteo | |
| Daily (average from 15:00 h of previous day to 12:00 h current day) | NO | ARPA atm. pollution |
| Temperature | ARPA meteo | |
| Wind speed | ARPA meteo | |
| Wind direction | ARPA meteo | |
| Precipitation | ARPA meteo | |
| Global radiation | ARPA meteo | |
| Relative humidity | ARPA meteo |
| Periodical Sampling | Random Sampling | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Type of Model | Model | RMSE (µg/m3) | RMSE (µg/m3) |
| Machine Learning | LSTM | 3.77 | 6.82 |
| Random Forest | 3.70 | 7.13 | |
| Support Vector Reg. | 3.99 | 6.37 | |
| Decision Tree Reg. | 4.93 | 9.61 | |
| Gradient Tree Boosting | 3.53 | 6.80 | |
| MLPR | 3.23 | 6.42 | |
| Linear Models | Kriging | 3.78 | 6.11 |
| B-Spline | 4.19 | 6.63 | |
| Model Combination | Voting (MLPR + Kriging) | 3.50 | 6.06 |
| Stacking (MLPR + Kriging) | 3.55 | 5.98 | |
| Feature Selection | RF Feat. Sel. + Voting (MLPR + Kriging) | 2.89 | 6.09 |
| CV Feat. Sel. + Voting (GTB + Kriging) | 3.21 | 5.99 | |
| Correlation > 0.6 + Voting (MLPR + Kriging) | 4.15 | 6.87 |
| RF Selected Features | Features with Pearson Corr > 0.5 |
|---|---|
| Satellite NO | Satellite NO |
| Temperature at satellite passage time | Temperature at satellite passage |
| Wind speed at satellite passage time | Global radiation at satellite passage |
| Wind direction at satellite passage time | Relative humidity at satellite passage time |
| Global radiation at satellite passage time | Temperature before satellite passage |
| Temperature before satellite passage | Global radiation before satellite passage time |
| Wind speed before satellite passage | |
| Global radiation before satellite passage time | |
| Weekday/weekend classifier | |
| Day of the week | |
| The month of measurement |
| Data | Measure | Value (µg/m) |
|---|---|---|
| Ground Truth | Mean | 17.69 |
| Standard Deviation | 6.40 | |
| Minimum | 8.187 | |
| Maximum | 43.14 | |
| Model estimation | Mean | 18.18 |
| Standard Deviation | 5.97 | |
| Minimum | 7.41 | |
| Maximum | 37.493 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cedeno Jimenez, J.R.; Pugliese Viloria, A.d.J.; Brovelli, M.A. Estimating Daily NO2 Ground Level Concentrations Using Sentinel-5P and Ground Sensor Meteorological Measurements. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2023, 12, 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi12030107
Cedeno Jimenez JR, Pugliese Viloria AdJ, Brovelli MA. Estimating Daily NO2 Ground Level Concentrations Using Sentinel-5P and Ground Sensor Meteorological Measurements. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information. 2023; 12(3):107. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi12030107
Chicago/Turabian StyleCedeno Jimenez, Jesus Rodrigo, Angelly de Jesus Pugliese Viloria, and Maria Antonia Brovelli. 2023. "Estimating Daily NO2 Ground Level Concentrations Using Sentinel-5P and Ground Sensor Meteorological Measurements" ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information 12, no. 3: 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi12030107
APA StyleCedeno Jimenez, J. R., Pugliese Viloria, A. d. J., & Brovelli, M. A. (2023). Estimating Daily NO2 Ground Level Concentrations Using Sentinel-5P and Ground Sensor Meteorological Measurements. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 12(3), 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi12030107









