An Efficient Plane-Segmentation Method for Indoor Point Clouds Based on Countability of Saliency Directions
Abstract
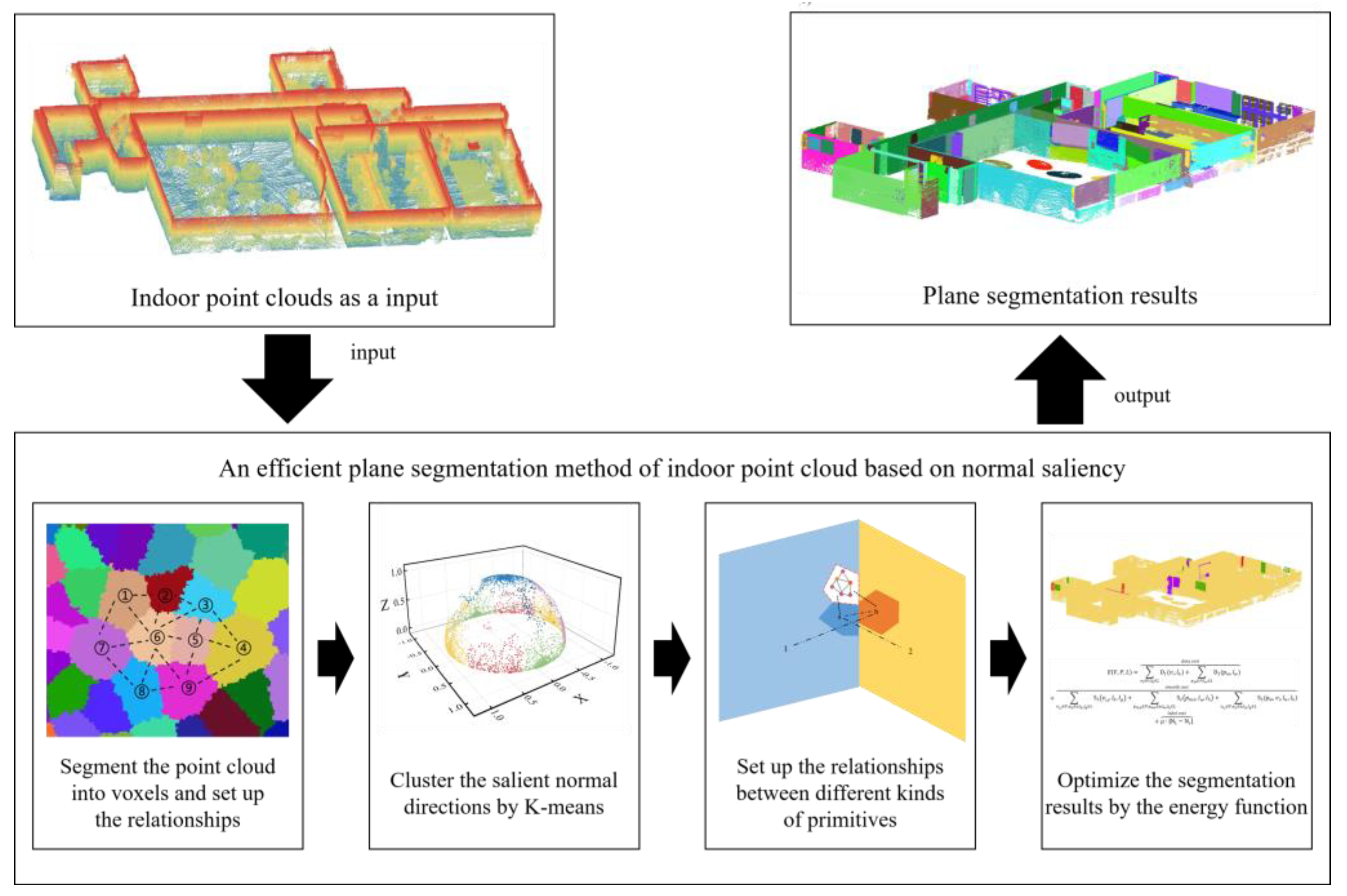
:1. Introduction
2. Related Works
3. Methodology
3.1. Motivation
3.2. Super-Voxel-Based Segmentation and Topological Relationships
3.3. Directional Saliency Analysis in Indoor Environments
3.4. Global Energy Optimization
3.4.1. Outlier Voxels
3.4.2. Relationship between Different Primitives
3.4.3. Energy Function Formulation
4. Experiments and Analysis
4.1. Dataset Description
4.2. Evaluation Metrics
4.3. Experimental Results and Qualitative Analysis
4.4. Quantitative Comparison and Evaluation
4.5. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ge, X. Automatic markerless registration of point clouds with semantic-keypoint-based 4-points congruent sets. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 130, 344–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, C.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Z.; Li, J. Fast regularity-constrained plane fitting. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 161, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tóvári, D.; Pfeifer, N. Segmentation based robust interpolation-a new approach to laser data filtering. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2005, 36, 79–84. [Google Scholar]
- Ballard, D.H. Generalizing the Hough transform to detect arbitrary shapes. Pattern Recognit. 1981, 13, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schnabel, R.; Wahl, R.; Klein, R. Efficient RANSAC for point-cloud shape detection. Comput. Graph. Forum 2007, 26, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, P.; Krainin, M.; Herbst, E.; Ren, X.; Fox, D. RGB-D mapping: Using Kinect-style depth cameras for dense 3D modeling of indoor environments. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2012, 31, 647–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, B.; Ge, X.; Xie, L.; Chen, W. Enhanced 3D mapping with an RGB-D sensor via integration of depth measurements and image sequences. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2019, 85, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vosselman, G. Point cloud segmentation for urban scene classification. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2013, 1, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, L.; Yang, F.; Zhu, H.; Li, D.; Li, Y.; Tang, L. An improved RANSAC for 3D point cloud plane segmentation based on normal distribution transformation cells. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hamid-Lakzaeian, F. Structural-based point cloud segmentation of highly ornate building façades for computational modelling. Autom. Constr. 2019, 108, 102892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Meng, Z.; Luo, H. Efficient plane extraction using normal estimation and RANSAC from 3D point cloud. Comput. Stand. Interfaces 2022, 82, 103608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, P.; Hua, X.; Yu, K.; Tao, W. Robust segmentation of building planar features from unorganized point cloud. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 30873–30884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, A.-V.; Truong-Hong, L.; Laefer, D.F.; Bertolotto, M. Octree-based region growing for point cloud segmentation. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 104, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deschaud, J.E.; Goulette, F. A Fast and Accurate plane Detection Algorithm for Large Noisy Point Clouds Using Filtered Normals and Voxel Growing. In 3DPVT; Hal Archives-Ouvertes: Paris, France, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, N.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, Q. Supervoxel-based region growing segmentation for point cloud data. Int. J. Pattern Recognit. Artif. Intell. 2021, 35, 2154007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holz, D.; Holzer, S.; Rusu, R.B.; Behnke, S. Real-Time Plane Segmentation Using RGB-D Cameras. In Robot Soccer World Cup; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 306–317. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.X.; Li, F.; Liu, F.F.; Cheng, L.N.; Guo, L.L. A global Point cloud segmentation using euclidean cluster extraction algorithm with the smoothness. Meas. Control Technol. 2016, 35, 36–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Shan, J.; Jiang, W. A global optimization approach to roof segmentation from airborne lidar point clouds. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 94, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Jung, J. Clustering-based plane segmentation neural network for urban scene modeling. Sensors 2021, 21, 8382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulikajevas, A.; Maskeliūnas, R.; Damasevicius, R.; Misra, S. Reconstruction of 3D object shape using hybrid modular neural network architecture trained on 3D models from ShapeNetCore dataset. Sensors 2019, 19, 1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kulikajevas, A.; Maskeliūnas, R.; Damaševičius, R.; Ho, E.S.L. 3D object reconstruction from imperfect depth data using extended YOLOv3 network. Sensors 2020, 20, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nozawa, N.; Shum, H.P.H.; Feng, Q.; Edmond, S.; Shigeo, M. 3D car shape reconstruction from a contour sketch using GAN and lazy learning. Vis. Comput. 2021, 38, 1317–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.T.; Eich, M.; Reid, I.; Wyeth, G. Geometrically Consistent Plane Extraction for Dense Indoor 3D Maps Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Daejeon, Korea, 9–14 October 2016; pp. 4199–4204. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Z.; Yang, B.; Hu, P.; Scherer, S. An efficient global energy optimization approach for robust 3D plane segmentation of point clouds. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 137, 112–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isack, H.; Boykov, Y. Energy-based geometric multi-model fitting. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2012, 97, 123–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monszpart, A.; Mellado, N.; Brostow, G.J.; Mitra, N.J. RAPter: Rebuilding man-made scenes with regular arrangements of planes. ACM Trans. Graph. 2015, 34, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhai, D.; Li, W.; Li, J. Toward better boundary preserved supervoxel segmentation for 3D point clouds. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 143, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sculley, D. Web-Scale K-Means Clustering. In Proceedings of the 19th International Conference, World Wide Web, 26–30 April 2010; pp. 1177–1178. [Google Scholar]
- Nurunnabi, A.; Belton, D.; West, G. Robust segmentation for large volumes of laser scanning three-dimensional point cloud data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 4790–4805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delong, A.; Osokin, A.; Isack, H.N.; Boykov, Y. Fast approximate energy minimization with label costs. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2012, 96, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Wu, B.; Li, Y.; Hu, H. A multi-primitive-based hierarchical optimal approach for semantic labeling of ALS point clouds. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, F.Y. Potts model and graph theory. J. Stat. Phys. 1988, 52, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshelham, K.; Vilariño, L.D.; Peter, M.; Kang, Z.; Acharya, D. The ISPRS benchmark on indoor modelling. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2017, 42, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lafarge, F.; Mallet, C. Creating large-scale city models from 3D-point clouds: A robust approach with hybrid representation. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2012, 99, 69–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




















| Data | Scene Range (m2) | Pts (Million) | Saliency Directions | Number of Planes | Sensor |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TUB1 | 40 × 15 | 34 | 6 | 148 | Viametris iMS3D |
| TUB2 | 30 × 20 | 14 | 3 | 145 | Zeb-Revo |
| Lab | 15 × 10 | 7 | 4 | 86 | Faro3D TLS |
| Office | 5 × 4 | 1.2 | 6 | 87 | RGB-D |
| Data | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1-Score | USR (%) | OSR (%) | Runtime (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TUB1 | 91.5 | 91.5 | 0.92 | 3.3 | 1.3 | 53 |
| TUB2 | 88.0 | 85.7 | 0.87 | 5.3 | 3.3 | 114 |
| Lab | 87.8 | 81.1 | 0.84 | 8.2 | 0.0 | 6 |
| Office | 72.7 | 73.6 | 0.73 | 6.8 | 3.5 | 14 |
| Data | Method | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1-Score | USR (%) | OSR (%) | Runtime (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TUB1 | Proposed method | 91.5 | 91.5 | 0.92 | 3.3 | 1.3 | 53 |
| RG | 63.3 | 86.93 | 0.73 | 0.0 | 11.8 | 196 | |
| RANSAC | 61.8 | 73.86 | 0.67 | 7.1 | 3.9 | 90 | |
| Global-L0 | 68.2 | 88.24 | 0.77 | 3.5 | 2.0 | 101 | |
| TUB2 | Proposed method | 88.0 | 85.7 | 0.87 | 5.3 | 3.3 | 114 |
| RG | 67.7 | 74.7 | 0.71 | 1.2 | 11.0 | 450 | |
| RANSAC | 45.2 | 46.1 | 0.46 | 17.8 | 3.9 | 214 | |
| Global-L0 | 81.4 | 68.2 | 0.74 | 10.9 | 1.3 | 550 | |
| Lab | Proposed method | 87.8 | 81.1 | 0.84 | 8.2 | 0.0 | 6 |
| RG | 72.6 | 72.6 | 0.73 | 3.8 | 7.6 | 16 | |
| RANSAC | 57.5 | 39.6 | 0.47 | 28.8 | 2.8 | 11 | |
| Global-L0 | 85.7 | 73.6 | 0.79 | 11.0 | 0.0 | 7 | |
| Office | Proposed method | 72.7 | 73.6 | 0.73 | 6.8 | 3.5 | 14 |
| RG | 24.3 | 49.4 | 0.33 | 0.6 | 37.9 | 41 | |
| RANSAC | 51.2 | 25.3 | 0.34 | 32.6 | 4.6 | 23 | |
| Global-L0 | 54.7 | 66.7 | 0.60 | 6.6 | 8.1 | 19 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ge, X.; Zhang, J.; Xu, B.; Shu, H.; Chen, M. An Efficient Plane-Segmentation Method for Indoor Point Clouds Based on Countability of Saliency Directions. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2022, 11, 247. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi11040247
Ge X, Zhang J, Xu B, Shu H, Chen M. An Efficient Plane-Segmentation Method for Indoor Point Clouds Based on Countability of Saliency Directions. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information. 2022; 11(4):247. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi11040247
Chicago/Turabian StyleGe, Xuming, Jingyuan Zhang, Bo Xu, Hao Shu, and Min Chen. 2022. "An Efficient Plane-Segmentation Method for Indoor Point Clouds Based on Countability of Saliency Directions" ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information 11, no. 4: 247. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi11040247
APA StyleGe, X., Zhang, J., Xu, B., Shu, H., & Chen, M. (2022). An Efficient Plane-Segmentation Method for Indoor Point Clouds Based on Countability of Saliency Directions. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 11(4), 247. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi11040247






