The Soil Nutrient Digital Mapping for Precision Agriculture Cases in the Trans-Ural Steppe Zone of Russia Using Topographic Attributes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dong, W.; Wu, T.; Luo, J.; Sun, Y.; Xia, L. Land Parcel-Based Digital Soil Mapping of Soil Nutrient Properties in an Alluvial-Diluvia Plain Agricultural Area in China. Geoderma 2019, 340, 234–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Minasny, B.; Wu, C. Mapping Key Soil Properties to Support Agricultural Production in Eastern China. Geoderma Reg. 2017, 10, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savin, I.Y.; Ovechkin, S.V. On the Updating of Medium-Scale Soil Maps. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2014, 47, 987–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBratney, A.B.; Mendonça Santos, M.L.; Minasny, B. On Digital Soil Mapping. Geoderma 2003, 117, 3–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrouays, D.; Grundy, M.; Hartemink, A.E.; Hempel, J.; Heuvelink, G.B.M.; Hong, S.Y.; Lagacherie, P.; Lelyk, G.; Mcbratney, A.B.; Mckenzie, N.J.; et al. GlobalSoilMap: Toward a Fine-Resolution Global Grid of Soil Properties. Adv. Agron. 2014, 125, 93–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dokuchaev, V.V. Our Steppes—At One Time and Now; Yevdokimoff Press: St. Petersburg, Russia, 1892. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Jenny, H. Factors of Soil Formation, A System of Quantitative Pedology; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1941. [Google Scholar]
- Jenny, H. Derivation of State Factor Equations of Soils and Ecosystems. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1961, 25, 385–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehnatkesh, A.; Ayoubi, S.; Jalalian, A.; Sahrawat, K.L. Relationships between Soil Depth and Terrain Attributes in a Semi Arid Hilly Region in Western Iran. J. Mt. Sci. 2013, 10, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenzie, N.J.; Gessler, P.E.; Ryan, P.J.; O’Connell, D.A. The role of terrain analysis in soil mapping. In Terrain Analysis: Principles and Applications; Wilson, J.P., Gallant, J.C., Eds.; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 245–265. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, I.D.; Gessler, P.E.; Nielsen, G.A.; Peterson, G.A. Soil Attribute Prediction Using Terrain Analysis. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1993, 57, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odeha, I.O.A.; McBratney, A.B.; Chittleborough, D.J. Spatial Prediction of Soil Properties from Landform Attributes Derived from a Digital Elevation Model. Geoderma 1994, 63, 197–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florinsky, I.V.; Eilers, R.G.; Manning, G.R.; Fuller, L.G. Prediction of Soil Properties by Digital Terrain Modelling. Environ. Model. Softw. 2002, 17, 295–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulder, V.L.; de Bruin, S.; Schaepman, M.E.; Mayr, T.R. The Use of Remote Sensing in Soil and Terrain Mapping—A Review. Geoderma 2011, 162, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopp, N.V.; Nechaeva, T.V.; Savenkov, O.A.; Smirnova, N.V.; Smirnov, V.V. The Methods of Geomorphometry and Digital Soil Mapping for Assessing Spatial Variability in the Properties of Agrogray Soils on a Slope. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2017, 50, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takoutsing, B.; Weber, J.C.; Martín, J.A.R.; Shepherd, K.; Aynekulu, E.; Sila, A. An Assessment of the Variation of Soil Properties with Landscape Attributes in the Highlands of Cameroon. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 2496–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sena, N.C.; Veloso, G.V.; Fernandes-Filho, E.I.; Francelino, M.R.; Schaefer, C.E.G.R. Analysis of Terrain Attributes in Different Spatial Resolutions for Digital Soil Mapping Application in Southeastern Brazil. Geoderma Reg. 2020, 21, e00268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komissarov, M.; Ogura, S. Siltation and Radiocesium Pollution of Small Lakes in Different Catchment Types Far from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant Accident Site. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2020, 8, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartelletti, C.; Giannecchini, R.; Avanzi, G.D.; Galanti, Y.; Mazzali, A. The Influence of Geological–Morphological and Land Use Settings on Shallow Landslides in the Pogliaschina T. Basin (Northern Apennines, Italy). J. Maps 2017, 13, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Y.; Jiang, S.; Guo, W.; Qin, M.; Pan, J.; Bahadur, A.; Shi, G.; Luo, J.; Jin, Z.; Liu, Y.; et al. The Effect of Slope Aspect on the Phylogenetic Structure of Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungal Communities in an Alpine Ecosystem. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 126, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabbasova, I.M.; Suleymanov, R.R.; Khabirov, I.K.; Komissarov, M.A.; Garipov, T.T.; Sidorova, L.V.; Nazyrova, F.I. Multiple Assessment of the Soil Cover in the Area of Natural Monuments Tra-Tau and Yurak-Tau Monadnocks under Conditions of Technogenic Loads. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2014, 47, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suleymanov, R.; Yaparov, I.; Saifullin, I.; Vildanov, I.; Shirokikh, P.; Suleymanov, A.; Komissarov, M.; Liebelt, P.; Nigmatullin, A.; Khamidullin, R. The Current State of Abandoned Lands in the Northern Forest-Steppe Zone at the Republic of Bashkortostan (Southern Ural, Russia). Span. J. Soil Sci. 2020, 10, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suleymanov, A.R. Geomorphometric and geoinformation approach to meliorative evaluation of the territory. In Climate Change Impacts on Hydrological Processes and Sediment Dynamics: Measurement, Modelling and Management; Chalov, S., Golosov, V., Li, R., Tsyplenkov, A., Eds.; Springer Proceedings in Earth and Environmental Sciences; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 72–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forkuor, G.; Hounkpatin, O.K.L.; Welp, G.; Thiel, M. High Resolution Mapping of Soil Properties Using Remote Sensing Variables in South-Western Burkina Faso: A Comparison of Machine Learning and Multiple Linear Regression Models. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0170478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Geng, Y.; Chen, J.; Sun, C.; Haase, D.; Lausch, A. Mapping of Soil Total Nitrogen Content in the Middle Reaches of the Heihe River Basin in China Using Multi-Source Remote Sensing-Derived Variables. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingsley, J.; Lawani, S.; Esther, A.; Ndiye, K.; Sunday, O.; Penížek, V. Predictive Mapping of Soil Properties for Precision Agriculture Using Geographic Information System (GIS) Based Geostatistics Models. Mod. Appl. Sci. 2019, 13, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- John, K.; Abraham Isong, I.; Michael Kebonye, N.; Okon Ayito, E.; Chapman Agyeman, P.; Marcus Afu, S. Using Machine Learning Algorithms to Estimate Soil Organic Carbon Variability with Environmental Variables and Soil Nutrient Indicators in an Alluvial Soil. Land 2020, 9, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tranmer, M.; Murphy, J.; Elliot, M.; Pampaka, M. Multiple Linear Regression, 2nd ed.; Cathie Marsh Institute Working Paper; Cathie Marsh Institute: Manchester, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Cortes, C.; Vapnik, V. Support-Vector Networks. Mach. Learn. 1995, 20, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shmilovici, A. Support vector machines. In Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery Handbook; Maimon, O., Rokach, L., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2009; pp. 231–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witten, I.H.; Frank, E. Data Mining: Practical Machine Learning Tools and Techniques, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2005; p. 525. [Google Scholar]
- Heung, B.; Ho, H.C.; Zhang, J.; Knudby, A.; Bulmer, C.E.; Schmidt, M.G. An Overview and Comparison of Machine-Learning Techniques for Classification Purposes in Digital Soil Mapping. Geoderma 2016, 265, 62–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Wang, S.; Gao, Z.; Lv, Y. Dynamic Prediction of Soil Salinization in an Irrigation District Based on the Support Vector Machine. Math. Comput. Model. 2013, 58, 719–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parveen, N.; Zaidi, S.; Danish, M. Support Vector Regression Model for Predicting the Sorption Capacity of Lead (II). Perspect. Sci. 2016, 8, 629–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudzadeh, H.; Matinfar, H.R.; Taghizadeh-Mehrjardi, R.; Kerry, R. Spatial Prediction of Soil Organic Carbon Using Machine Learning Techniques in Western Iran. Geoderma Reg. 2020, 21, e00260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IUSS Working Group WRB. World reference base for soil resources. In International Soil Classification System for Naming Soils and Creating Legends for Soil Maps; World Soil Resources Reports No. 106; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, J.B., Jr. (Ed.) Soil Analysis Handbook of Reference Methods, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1999; p. 264. [Google Scholar]
- Pansu, M.; Gautheyrou, J. Handbook of Soil Analysis: Mineralogical, Organic and Inorganic Methods; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2006; p. 993. [Google Scholar]
- Carter, M.R.; Gregorich, E.G. (Eds.) Soil Sampling and Methods of Analysis, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008; p. 1264. [Google Scholar]
- Mallows, C.L. Some Comments on Cp. Technometrics 2000, 42, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattera, D.; Haykin, S. Support vector machines for dynamic reconstruction of a chaotic system. In Advances in Kernel Methods: Support Vector Learning; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1999; pp. 211–241. [Google Scholar]
- Cherkassky, V.; Ma, Y. Practical selection of SVM parameters and noise estimation for SVM regression. Neural Netw. 2004, 17, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hengl, T.; Heuvelink, G.B.M.; Kempen, B.; Leenaars, J.G.B.; Walsh, M.G.; Shepherd, K.D.; Sila, A.; MacMillan, R.A.; de Jesus, J.M.; Tamene, L.; et al. Mapping Soil Properties of Africa at 250 m Resolution: Random Forests Significantly Improve Current Predictions. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heuvelink, G.B.M.; Angelini, M.E.; Poggio, L.; Bai, Z.; Batjes, N.H.; van den Bosch, R.; Bossio, D.; Estella, S.; Lehmann, J.; Olmedo, G.F.; et al. Machine Learning in Space and Time for Modelling Soil Organic Carbon Change. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2020, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeraatpisheh, M.; Ayoubi, S.; Jafari, A.; Tajik, S.; Finke, P. Digital Mapping of Soil Properties Using Multiple Machine Learning in a Semi-Arid Region, Central Iran. Geoderma 2019, 338, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaber, S.M.; Lant, C.L.; Al-Qinna, M.I. Estimating Spatial Variations in Soil Organic Carbon Using Satellite Hyperspectral Data and Map Algebra. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 32, 5077–5103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaudour, E.; Gomez, C.; Fouad, Y.; Lagacherie, P. Sentinel-2 Image Capacities to Predict Common Topsoil Properties of Temperate and Mediterranean Agroecosystems. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 223, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Development Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2015; Available online: http://www.Rproject.org (accessed on 15 November 2020).
- RStudio. Integrated Development Environment for R; RStudio: Boston, MA, USA, 2015; Available online: http://www.r-studio.com (accessed on 15 November 2020).
- Gabbasova, I.M.; Garipov, T.T.; Komissarov, M.A.; Suleimanov, R.R.; Suyundukov, Y.T.; Khasanova, R.F.; Sidorova, L.V.; Komissarov, A.V.; Suleimanov, A.R.; Nazyrova, F.I. The Impact of Fires on the Properties of Steppe Soils in the Trans-Ural Region. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2019, 52, 1598–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silatsa, F.B.T.; Yemefack, M.; Tabi, F.O.; Heuvelink, G.B.M.; Leenaars, J.G.B. Assessing Countrywide Soil Organic Carbon Stock Using Hybrid Machine Learning Modelling and Legacy Soil Data in Cameroon. Geoderma 2020, 367, 114260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.-L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.-L.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Z.-L. Digital Soil Mapping Based on Empirical Mode Decomposition Components of Environmental Covariates. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2019, 70, 1109–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosleh, Z.; Salehi, M.H.; Jafari, A.; Borujeni, I.E.; Mehnatkesh, A. The Effectiveness of Digital Soil Mapping to Predict Soil Properties over Low-Relief Areas. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallant, J.C.; Dowling, T.I. A Multiresolution Index of Valley Bottom Flatness for Mapping Depositional Areas. Water Resour. Res. 2003, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahabiev, I.A.; Ryazanov, S.S.; Kolcova, T.G.; Grigoryan, B.R. Selection of a Geostatistical Method to Interpolate Soil Properties of the State Crop Testing Fields Using Attributes of a Digital Terrain Model. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2018, 51, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhuang, Q.; Wang, Q.; Jin, X.; Han, C. Mapping Stocks of Soil Organic Carbon and Soil Total Nitrogen in Liaoning Province of China. Geoderma 2017, 305, 250–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, K.; Hartemink, A.E.; Minasny, B.; Kheir, R.B.; Greve, M.B.; Greve, M.H. Digital Mapping of Soil Organic Carbon Contents and Stocks in Denmark. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assami, T.; Hamdi-Aїssa, B. Digital Mapping of Soil Classes in Algeria—A Comparison of Methods. Geoderma Reg. 2019, 16, e00215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondejar, J.P.; Tongco, A.F. Estimating Topsoil Texture Fractions by Digital Soil Mapping—A Response to the Long Outdated Soil Map in the Philippines. Sustain. Environ. Res. 2019, 29, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaziev, F.K. Soils of Bashkortostan. In Ecologic-Genetic and Agroproductive Characterization; Gilem: Ufa, Russia, 1995; Volume 1, p. 385. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Gabbasova, I.M.; Suleimanov, R.R.; Khabirov, I.K.; Komissarov, M.A.; Fruehauf, M.; Liebelt, P.; Garipov, T.T.; Sidorova, L.V.; Khaziev, F.K. Temporal changes of eroded soils depending on their agricultural use in the southern Cis-Ural region. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2016, 49, 1204–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
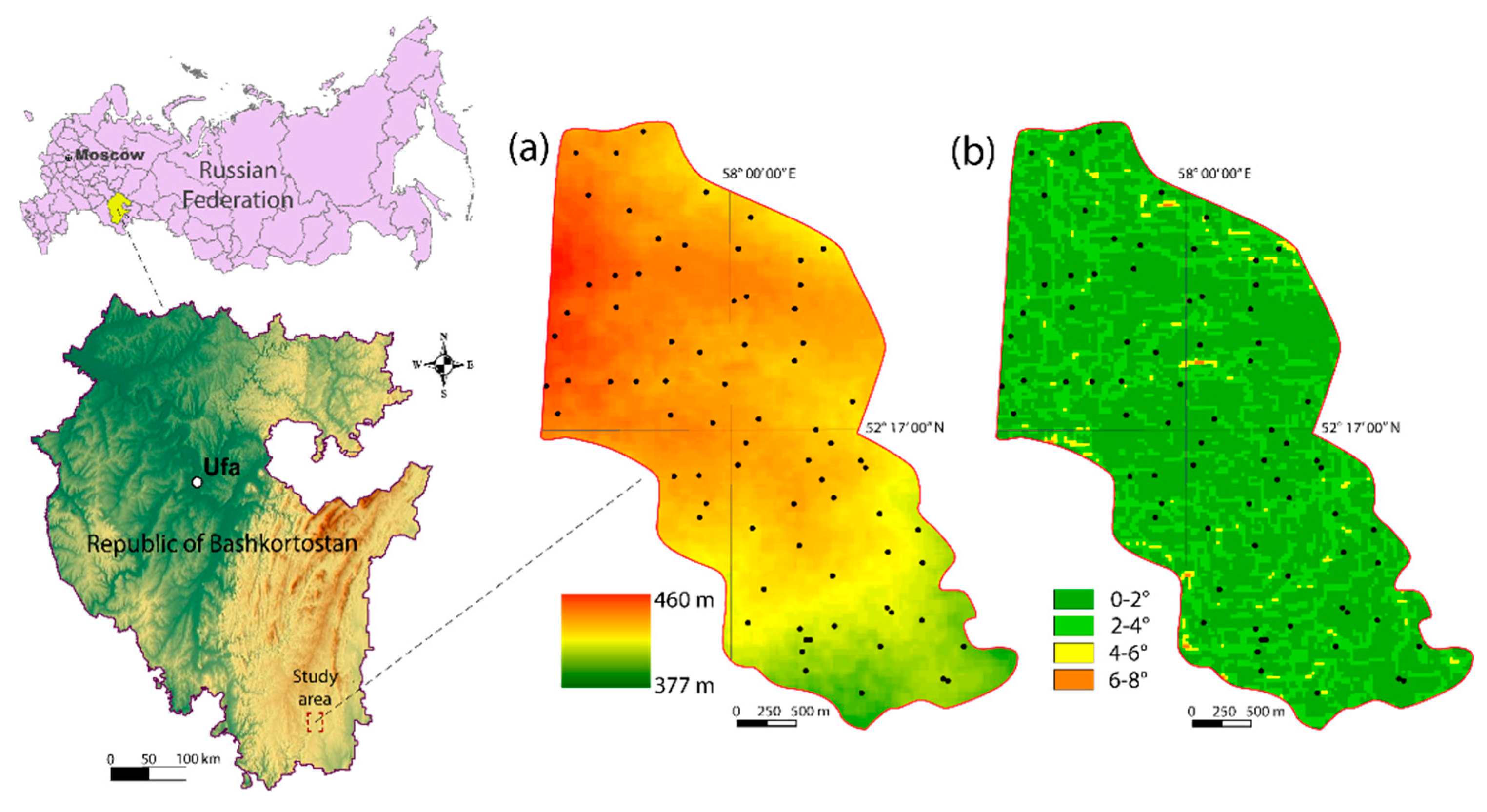
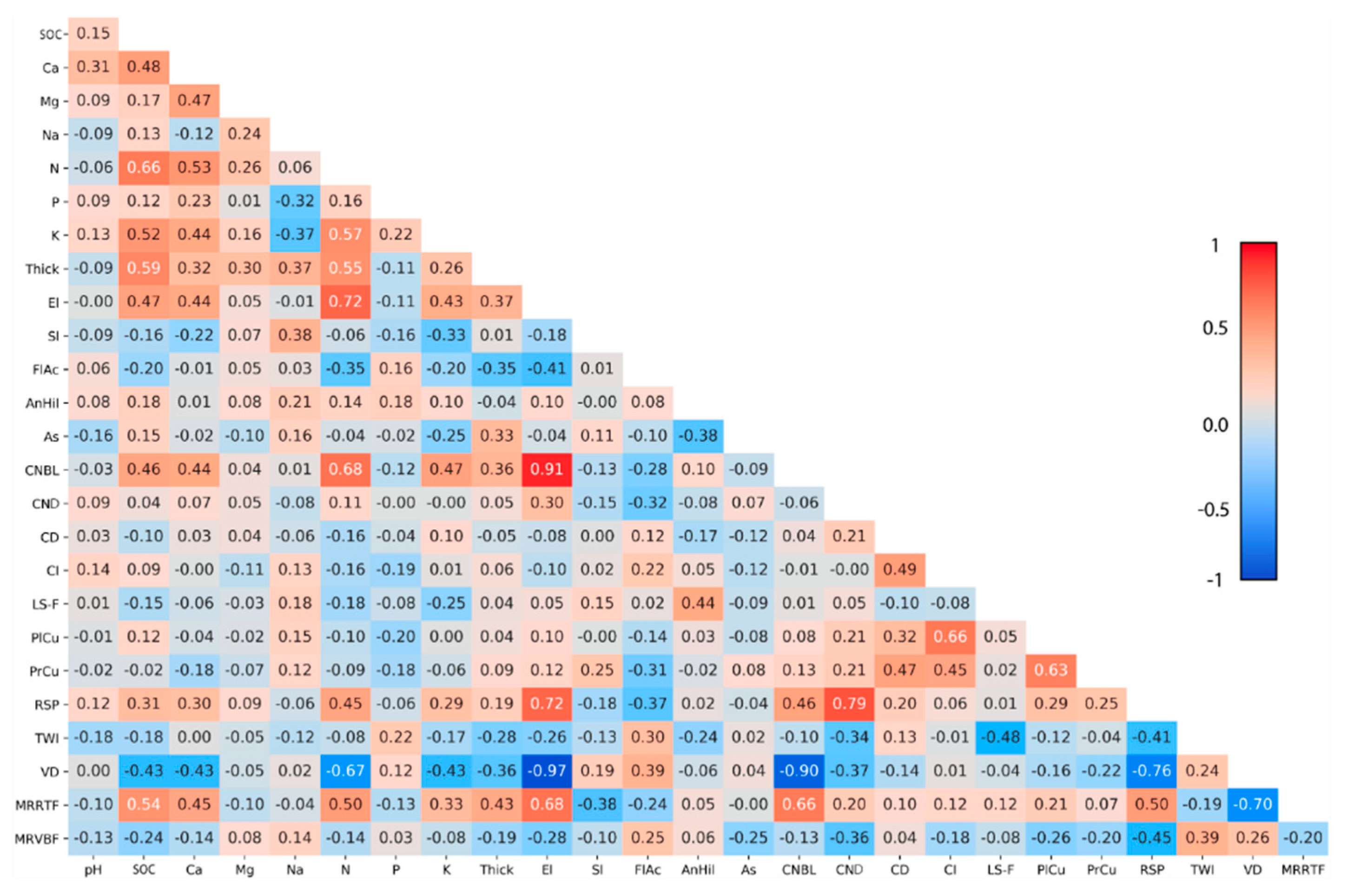

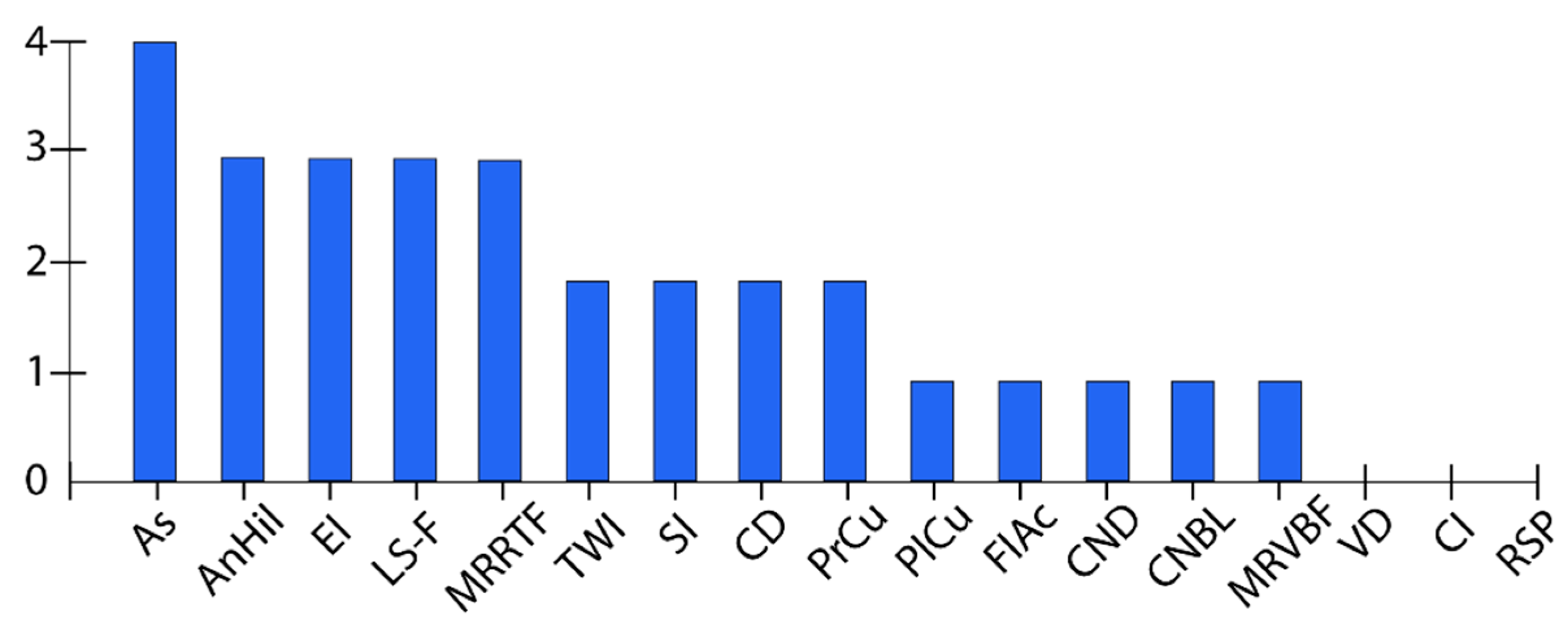


| № | Topographic Attributes | Acronym |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Elevation | El |
| 2 | Aspect | As |
| 3 | Slope | Sl |
| 4 | Profile curvature | PrCu |
| 5 | Plan curvature | PlCu |
| 6 | Flow accumulation | FlAc |
| 7 | Analytical hillshading | AnHil |
| 8 | Channel network base level | CNBL |
| 9 | Channel network distance | CND |
| 10 | Convergence index | CI |
| 11 | LS-Factor | LS-F |
| 12 | Topographic wetness index | TWI |
| 13 | Valley depth | VD |
| 14 | Closed depressions | CD |
| 15 | Relative slope position | RSP |
| 16 | Multiresolution ridge top flatness | MRRTF |
| 17 | Multiresolution valley bottom flatness | MRVBF |
| Parameter | SOC, % | The Thickness of AB Horizon, (cm) | pH (H2O) | N Alkaline Hydrolyzable, mg kg−1 | Exchangeable Cations | Available | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ca2+ | Mg2+ | Na+ | P2O5 | K2O | |||||
| cmol(+) kg−1 | mg kg−1 | ||||||||
| n = 76 | |||||||||
| Mean | 3.7 | 44.1 | 6.8 | 132.6 | 31.8 | 9.7 | 0.3 | 1.8 | 220.2 |
| Min | 1.8 | 18 | 6.4 | 65 | 15 | 5 | 0.04 | 0.4 | 123 |
| Max | 5.6 | 70 | 8.0 | 189 | 47 | 15 | 1.7 | 4.6 | 326 |
| SD | 0.9 | 9.3 | 0.3 | 26.6 | 6.2 | 2.2 | 0.3 | 0.8 | 52.7 |
| CV (%) | 24.3 | 20.9 | 4.4 | 20.1 | 19.5 | 22.7 | 113.3 | 44.4 | 23.9 |
| Soil Parametr | Number of Variables | Variables for Modeling | MLR | SVM | SVM Parameters | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | RMSE | R2 | RMSE | C | Gamma | |||
| SOC | 5 | AnHil, As, LS-F, TWI, MRRTF | 0.52 | 0.60 | 0.66 | 0.53 | 1 | 0.2 |
| Na | 5 | Sl, AnHil, As, PlCu, MRVBF | 0.35 | 0.21 | 0.49 | 0.20 | 1 | 0.2 |
| Ca | 4 | El, CD, PrCu, MRRTF | 0.31 | 5.84 | 0.43 | 5.33 | 1 | 0.2 |
| N | 5 | El, Sl, AnHil, LS-F, PrCu | 0.66 | 15.31 | 0.74 | 14.23 | 1 | 0.2 |
| P | 2 | AnHil, TWI | 0.11 | 1.64 | 0.16 | 0.73 | 0.1 | 0.2 |
| Mg | 2 | VD, MRRTF | 0.04 | 10.05 | 0.20 | 2.09 | 1 | 0.5 |
| K | 8 | El, CNBL, Sl, As, CND, CD, LS-F, TWI | 0.57 | 35.51 | 0.62 | 32.34 | 1 | 0.2 |
| pH | 1 | TWI | 0.03 | 6.61 | 0.02 | 0.30 | 0.1 | 0.2 |
| Thickness of AB | 3 | FlAc, As, MRRTF | 0.35 | 47.03 | 0.52 | 6.81 | 1 | 0.2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Suleymanov, A.; Abakumov, E.; Suleymanov, R.; Gabbasova, I.; Komissarov, M. The Soil Nutrient Digital Mapping for Precision Agriculture Cases in the Trans-Ural Steppe Zone of Russia Using Topographic Attributes. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2021, 10, 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi10040243
Suleymanov A, Abakumov E, Suleymanov R, Gabbasova I, Komissarov M. The Soil Nutrient Digital Mapping for Precision Agriculture Cases in the Trans-Ural Steppe Zone of Russia Using Topographic Attributes. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information. 2021; 10(4):243. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi10040243
Chicago/Turabian StyleSuleymanov, Azamat, Evgeny Abakumov, Ruslan Suleymanov, Ilyusya Gabbasova, and Mikhail Komissarov. 2021. "The Soil Nutrient Digital Mapping for Precision Agriculture Cases in the Trans-Ural Steppe Zone of Russia Using Topographic Attributes" ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information 10, no. 4: 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi10040243
APA StyleSuleymanov, A., Abakumov, E., Suleymanov, R., Gabbasova, I., & Komissarov, M. (2021). The Soil Nutrient Digital Mapping for Precision Agriculture Cases in the Trans-Ural Steppe Zone of Russia Using Topographic Attributes. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 10(4), 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi10040243









