Carbohydrate-Based Macromolecular Crowding-Induced Stabilization of Proteins: Towards Understanding the Significance of the Size of the Crowder
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Preparation of Proteins and Reagents
2.3. Thermal Denaturation Measurements
2.4. Circular Dichroism (CD) Measurements
2.5. Activity Measurements
3. Results
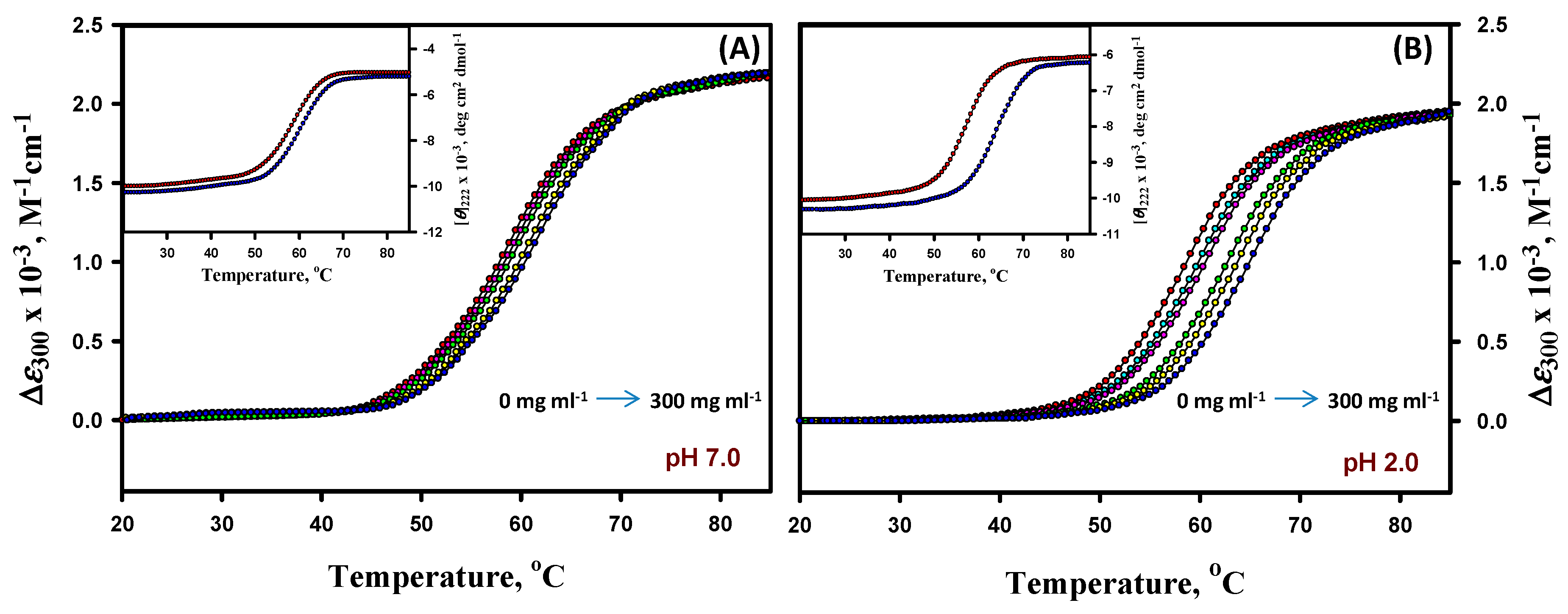
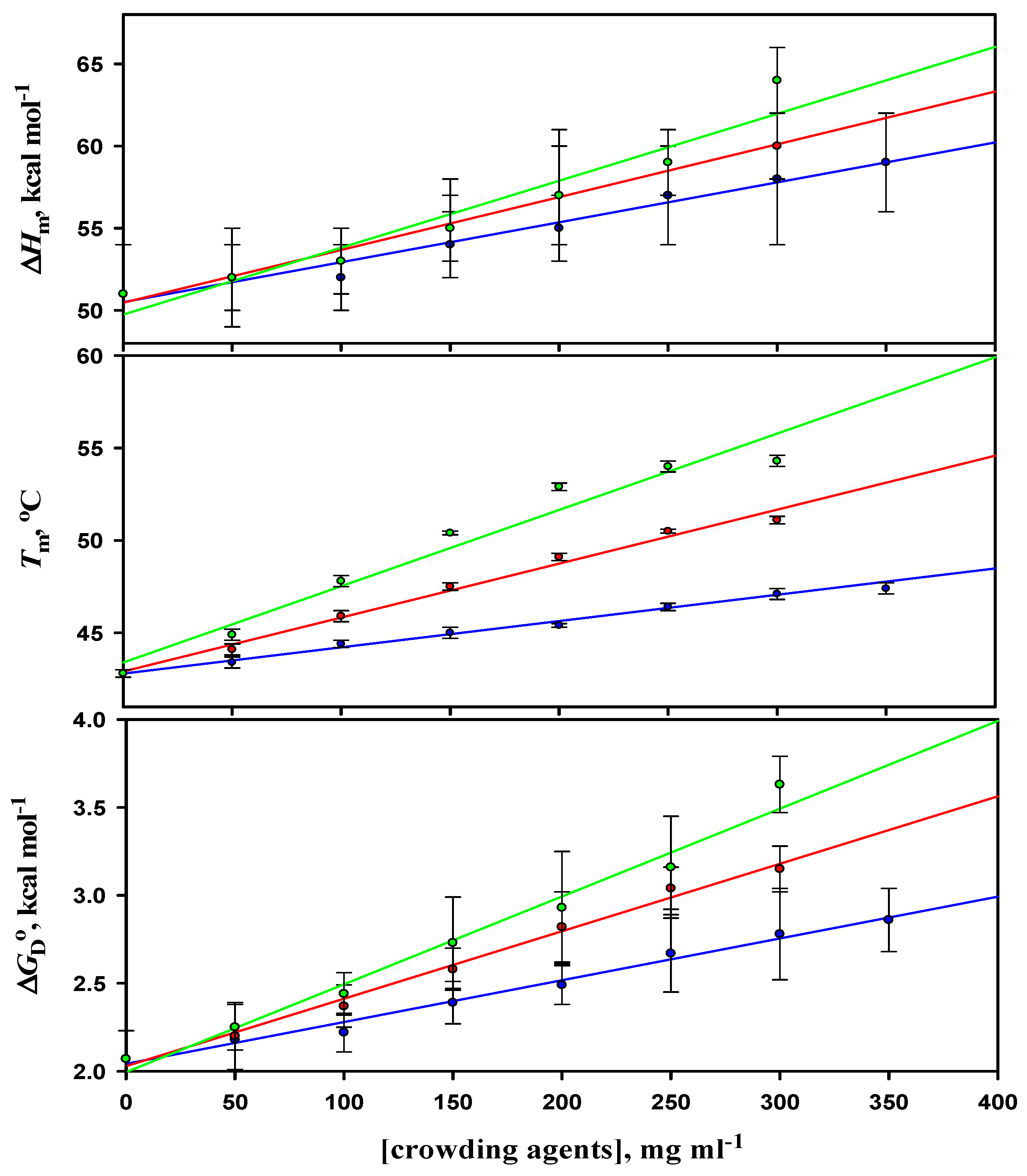
3.1. Thermal Denaturation Study of α-LA
3.2. Analysis of Denaturation Curves of α-LA
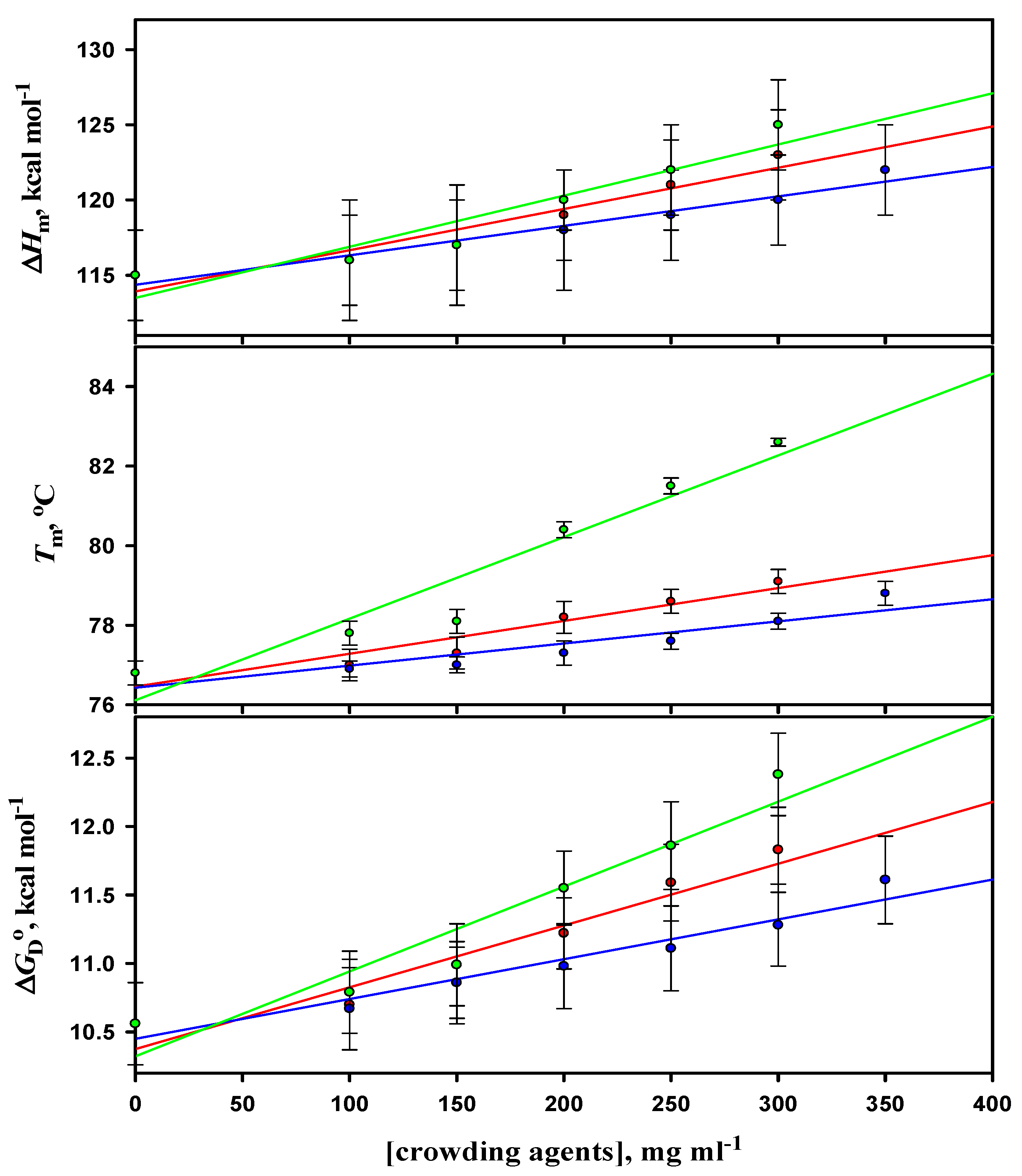
3.3. Thermal Denaturation Study of Lysozyme
3.4. Analysis of Denaturation Curves of Lysozyme
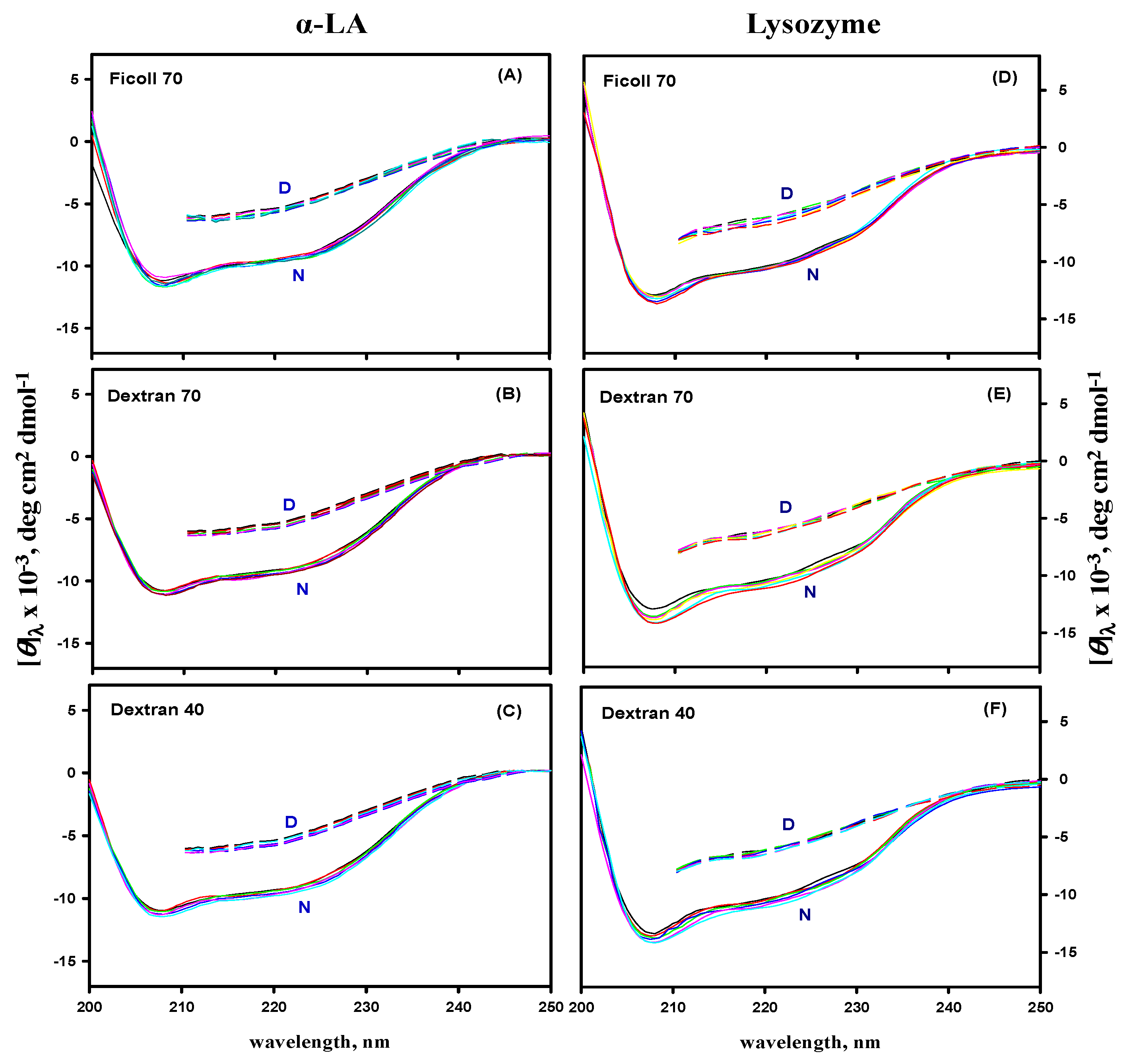
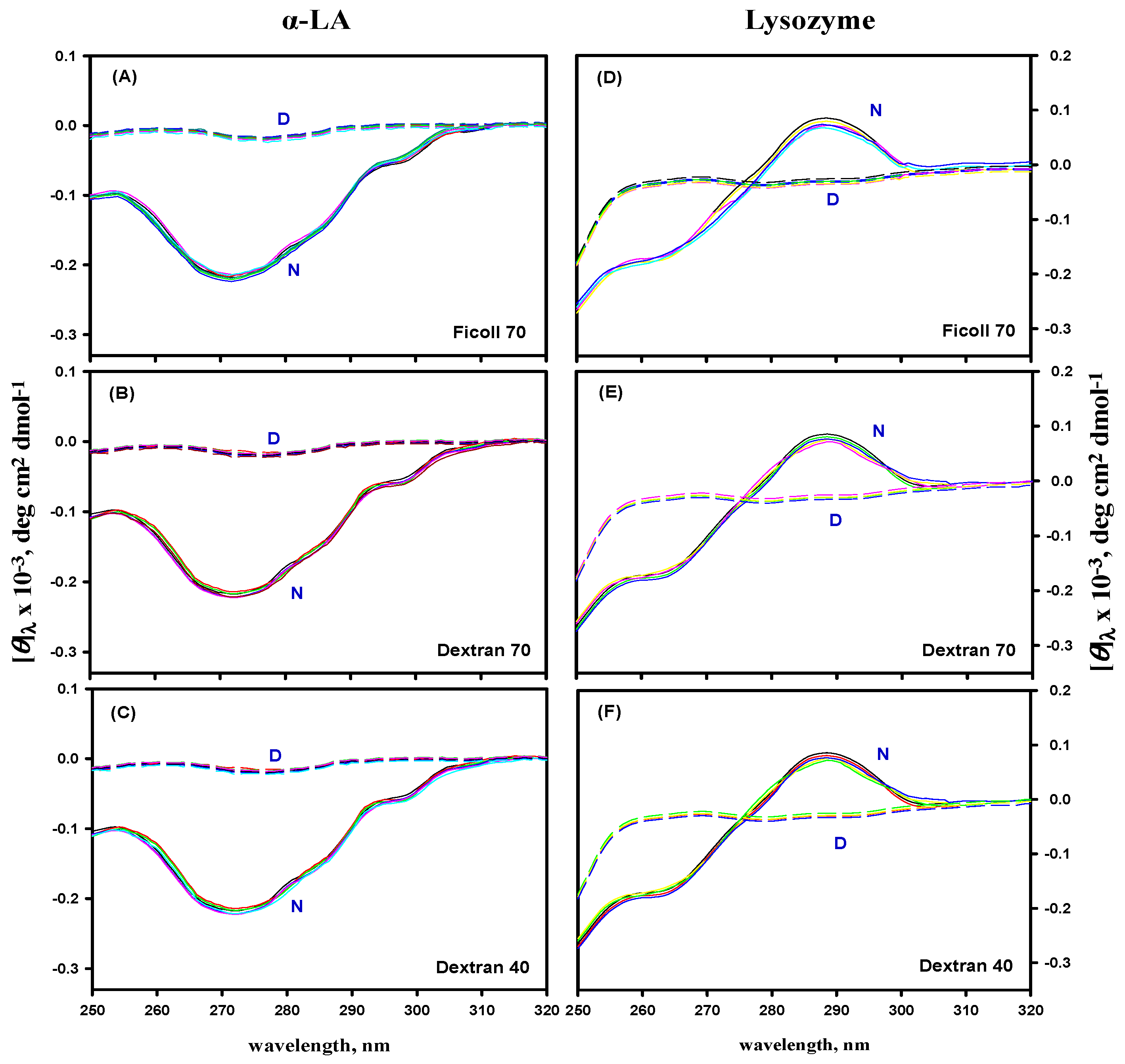
3.5. Far- and Near-UV CD Measurements
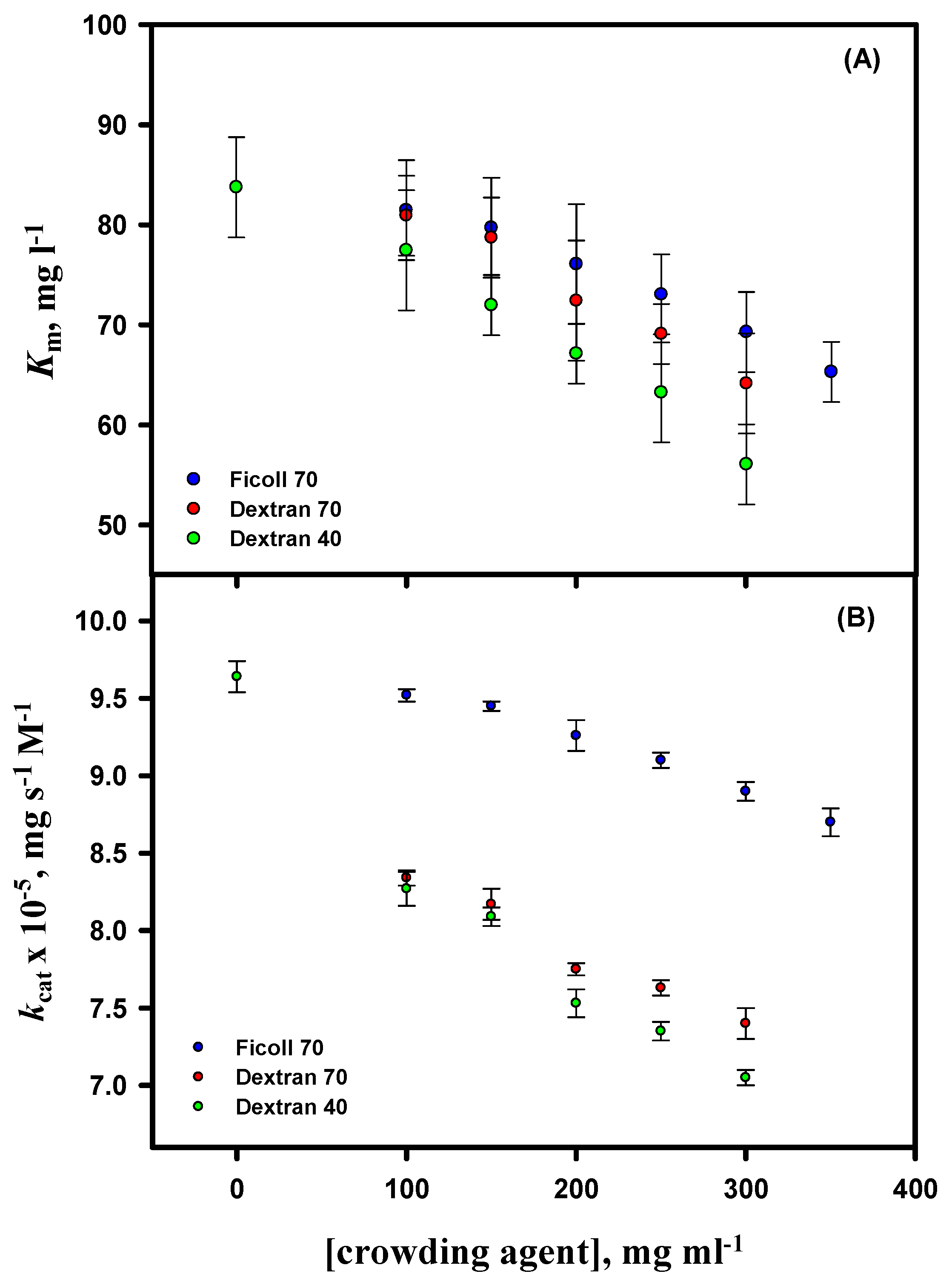
3.6. Activity Measurements
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GdmCl, | guanidinium chloride; |
| UV, | ultra-violet; |
| CD, | circular dichroism; |
| Tm, | midpoint of thermal denaturation; |
| ΔHm, | enthalpy change at Tm; |
| ΔCp, | constant-pressure heat capacity change; |
| ∆GD°, | Gibbs free energy change at 25 °C; |
| Km, | Michaelis constant; |
| kcat, | catalytic constant; |
| F70, | Ficoll 70; |
| D70, | Dextran 70; |
| D40, | Dextran 40. |
References
- Fulton, A. How crowded is the cytoplasm? Cell 1982, 30, 345–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minton, A.P. The effect of volume occupancy upon the thermodynamic activity of proteins: Some biochemical consequences. Mol. Cell Biochem. 1983, 55, 119–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmerman, S.B.; Trach, S.O. Estimation of macromolecule concentrations and excluded volume effects for the cytoplasm of Escherichia coli. J. Mol. Biol. 1991, 222, 599–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medalia, O.; Weber, I.; Frangakis, A.S.; Nicastro, D.; Gerisch, G.; Baumeister, W. Macromolecular Architecture in Eukaryotic Cells Visualized by Cryoelectron Tomography. Science 2002, 298, 1209–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, R.J.; Minton, A.P. Cell biology: Join the crowd. Nature 2003, 425, 27–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivas, G.; Ferrone, F.; Herzfeld, J. Life in a crowded world. EMBO Rep. 2004, 5, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minton, A.P. Excluded volume as a determinant of macromolecular structure and reactivity. Biopolymers 1981, 20, 2093–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, S.B.; Minton, A.P. Macromolecular crowding: Biochemical, biophysical, and physiological consequences. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 1993, 22, 27–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, R.J. Macromolecular crowding: An important but neglected aspect of the intracellular environment. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2001, 11, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, R.J. Macromolecular crowding: Obvious but underappreciated. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2001, 26, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.-X.; Rivas, G.; Minton, A.P. Macromolecular Crowding and Confinement: Biochemical, Biophysical, and Potential Physiological Consequences. Annu. Rev. Biophys. 2008, 37, 375–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, M.; Guo, Z. Effects of macromolecular crowding on the intrinsic catalytic efficiency and structure of enterobactin-specific isochorismate synthase. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 730–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodsell, D.S. Inside a living cell. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1991, 16, 203–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minton, A.P. The influence of macromolecular crowding and macromolecular confinement on biochemical reactions in physiological media. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 10577–10580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chebotareva, N.A.; Kurganov, B.I.; Livanova, N.B. Biochemical effects of molecular crowding. Biochemistry 2004, 69, 1239–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samiotakis, A.; Wittung-Stafshede, P.; Cheung, M.S. Folding, stability and shape of proteins in crowded environments: Experimental and computational approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009, 10, 572–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christiansen, A.; Wang, Q.; Cheung, M.S.; Wittung-Stafshede, P. Effects of macromolecular crowding agents on protein folding in vitro and in silico. Biophys. Rev. 2013, 5, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuznetsova, I.; Turoverov, K.; Uversky, V. What Macromolecular Crowding Can Do to a Protein. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 23090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsova, I.; Zaslavsky, B.; Breydo, L.; Turoverov, K.; Uversky, V. Beyond the Excluded Volume Effects: Mechanistic Complexity of the Crowded Milieu. Molecules 2015, 20, 1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parray, Z.A.; Shahid, S.; Ahmad, F.; Hassan, M.I.; Islam, A. Characterization of intermediate state of myoglobin in the presence of PEG 10 under physiological conditions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 99, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasreen, K.; Ahamad, S.; Ahmad, F.; Hassan, M.I.; Islam, A. Macromolecular crowding induces molten globule state in the native myoglobin at physiological pH. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 106, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beg, I.; Minton, A.P.; Hassan, M.I.; Islam, A.; Ahmad, F. Thermal Stabilization of Proteins by Mono- and Oligosaccharides: Measurement and Analysis in the Context of an Excluded Volume Model. Biochemistry 2015, 54, 3594–3603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishrat, M.; Imtaiyaz Hassan, M.; Ahmad, F.; Moosavi-Movahedi, A.A.; Islam, A. Effect of dextran on the thermodynamic stability and structure of ribonuclease A. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2016, 13, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishrat, M.; Hassan, M.I.; Ahmad, F.; Islam, A. Sugar osmolytes-induced stabilization of RNase A in macromolecular crowded cellular environment. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 115, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beg, I.; Minton, A.P.; Islam, A.; Hassan, M.I.; Ahmad, F. Comparison of the thermal stabilization of proteins by oligosaccharides and monosaccharide mixtures: Measurement and analysis in the context of excluded volume theory. Biophys. Chem. 2018, 237, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tellam, R.L.; Sculley, M.J.; Nichol, L.W.; Wills, P.R. The influence of poly(ethylene glycol) 6000 on the properties of skeletal-muscle actin. Biochem. J. 1983, 213, 651–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasahara, K.; McPhie, P.; Minton, A.P. Effect of dextran on protein stability and conformation attributed to macromolecular crowding. J. Mol. Biol. 2003, 326, 1227–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, M.S.; Klimov, D.; Thirumalai, D. Molecular crowding enhances native state stability and refolding rates of globular proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 4753–4758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stagg, L.; Zhang, S.Q.; Cheung, M.S.; Wittung-Stafshede, P. Molecular crowding enhances native structure and stability of alpha/beta protein flavodoxin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 18976–18981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perham, M.; Stagg, L.; Wittung-Stafshede, P. Macromolecular crowding increases structural content of folded proteins. FEBS Lett. 2007, 581, 5065–5069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homouz, D.; Perham, M.; Samiotakis, A.; Cheung, M.S.; Wittung-Stafshede, P. Crowded, cell-like environment induces shape changes in aspherical protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 11754–11759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homouz, D.; Stagg, L.; Wittung-Stafshede, P.; Cheung, M.S. Macromolecular crowding modulates folding mechanism of alpha/beta protein apoflavodoxin. Biophys. J. 2009, 96, 671–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, S.; Waegele, M.M.; Chowdhury, P.; Guo, L.; Gai, F. Effect of Macromolecular Crowding on Protein Folding Dynamics at the Secondary Structure Level. J. Mol. Biol. 2009, 393, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christiansen, A.; Wang, Q.; Samiotakis, A.; Cheung, M.S.; Wittung-Stafshede, P. Factors defining effects of macromolecular crowding on protein stability: An in vitro/in silico case study using cytochrome c. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 6519–6530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christiansen, A.; Wittung-Stafshede, P. Quantification of excluded volume effects on the folding landscape of Pseudomonas aeruginosa apoazurin in vitro. Biophys. J. 2013, 105, 1689–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.L.; Wu, L.J.; Chen, J.; Liang, Y. Effects of macromolecular crowding on the structural stability of human alpha-lactalbumin. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2012, 44, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, S.; Singh, L.R. Denatured state structural property determines protein stabilization by macromolecular crowding: A thermodynamic and structural approach. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aden, J.; Wittung-Stafshede, P. Folding of an unfolded protein by macromolecular crowding in vitro. Biochemistry 2014, 53, 2271–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senske, M.; Törk, L.; Born, B.; Havenith, M.; Herrmann, C.; Ebbinghaus, S. Protein Stabilization by Macromolecular Crowding through Enthalpy Rather Than Entropy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 9036–9041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.S.; Mittal, S.; Singh, L.R. Effect of Dextran 70 on the thermodynamic and structural properties of proteins. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 79, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurent, T.C. Enzyme reactions in polymer media. Eur. J. Biochem. 1971, 21, 498–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gellerich, F.N.; Laterveer, F.D.; Korzeniewski, B.; Zierz, S.; Nicolay, K. Dextran strongly increases the Michaelis constants of oxidative phosphorylation and of mitochondrial creatine kinase in heart mitochondria. Eur. J. Biochem. 1998, 254, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derham, B.K.; Harding, J.J. The effect of the presence of globular proteins and elongated polymers on enzyme activity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Proteins Proteom. 2006, 1764, 1000–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.X. Protein folding in confined and crowded environments. Arch Biochem. Biophys. 2008, 469, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homchaudhuri, L.; Sarma, N.; Swaminathan, R. Effect of crowding by dextrans and Ficolls on the rate of alkaline phosphatase-catalyzed hydrolysis: A size-dependent investigation. Biopolymers 2006, 83, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhar, A.; Samiotakis, A.; Ebbinghaus, S.; Nienhaus, L.; Homouz, D.; Gruebele, M.; Cheung, M.S. Structure, function, and folding of phosphoglycerate kinase are strongly perturbed by macromolecular crowding. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 17586–17591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pozdnyakova, I.; Wittung-Stafshede, P. Non-linear effects of macromolecular crowding on enzymatic activity of multi-copper oxidase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1804, 740–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, M.G.S.; Malys, N. What is the true enzyme kinetics in the biological system? An investigation of macromolecular crowding effect upon enzyme kinetics of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 405, 388–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vopel, T.; Makhatadze, G.I. Enzyme activity in the crowded milieu. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor, I.; Pitulice, L.; Balcells, C.; Vilaseca, E.; Madurga, S.; Isvoran, A.; Cascante, M.; Mas, F. Effect of crowding by Dextrans in enzymatic reactions. Biophys. Chem. 2014, 185, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poggi, C.G.; Slade, K.M. Macromolecular crowding and the steady-state kinetics of malate dehydrogenase. Biochemistry 2015, 54, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balcells, C.; Pastor, I.; Vilaseca, E.; Madurga, S.; Cascante, M.; Mas, F. Macromolecular Crowding Effect upon in Vitro Enzyme Kinetics: Mixed Activation–Diffusion Control of the Oxidation of NADH by Pyruvate Catalyzed by Lactate Dehydrogenase. J. Phys. Chem. B 2014, 118, 4062–4068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitulice, L.; Pastor, I.; Vilaseca, E.; Madurga, S.; Isvoran, A.; Cascante, M.; Mas, F. Influence of macromolecular crowding on the oxidation of ABTS by hydrogen peroxide catalyzed by HRP. J. Biocatal. Biotransform. 2013, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Shahid, S.; Ahmad, F.; Hassan, M.I.; Islam, A. Relationship between protein stability and functional activity in the presence of macromolecular crowding agents alone and in mixture: An insight into stability-activity trade-off. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2015, 584, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhat, M.Y.; Singh, L.R.; Dar, T.A. Trimethylamine N-oxide abolishes the chaperone activity of α-casein: An intrinsically disordered protein. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luby-Phelps, K.; Castle, P.E.; Taylor, D.L.; Lanni, F. Hindered diffusion of inert tracer particles in the cytoplasm of mouse 3T3 cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 4910–4913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venturoli, D.; Rippe, B. Ficoll and dextran vs. globular proteins as probes for testing glomerular permselectivity: Effects of molecular size, shape, charge, and deformability. Am. J. Physiol.-Ren. Physiol. 2005, 288, F605–F613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumitriu, S. Polysaccharides: Structural Diversity and Functional Versatility, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004; ISBN 9781420030822. Available online: https://books.google.co.in/books?id=kvUTPxPbkowC (accessed on 31 July 2019).
- Fodeke, A.A.; Minton, A.P. Quantitative Characterization of Polymer−Polymer, Protein−Protein, and Polymer−Protein Interaction via Tracer Sedimentation Equilibrium. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 10876–10880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohrer, M.P.; Patterson, G.D.; Carroll, P.J. Hindered diffusion of dextran and ficoll in microporous membranes. Macromolecules 1984, 17, 1170–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, M.G.; Deen, W.M. Hindered diffusion of water-soluble macromolecules in membranes. Macromolecules 1988, 21, 3474–3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granath, K.A. Solution properties of branched dextrans. J. Colloid Sci. 1958, 13, 308–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamaguchi, K.; Kurono, A. Structure of Muramidase (Lysozyme) I. The Effect of Guanidine Hydrochloride on Muramidase. J. Biochem. 1963, 54, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugai, S.; Yashiro, H.; Nitta, K. Equilibrium and kinetics of the unfolding of α-lactalbumin by guanidine hydrochloride. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Protein Struct. 1973, 328, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozaki, Y. The preparation of guanidine hydrochloride. Methods Enzym. 1972, 26, 43–50. [Google Scholar]
- Fissell, W.H.; Hofmann, C.L.; Smith, R.; Chen, M.H. Size and conformation of Ficoll as determined by size-exclusion chromatography followed by multiangle light scattering. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2010, 298, F205–F208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saunders, G. A Guide to Multi-Detector Gel Permeation Chromatography. 2012. Available online: https://www.agilent.com/cs/library/primers/Public/5990-7196EN.pdf (accessed on 31 July 2019).
- Sinha, A.; Yadav, S.; Ahmad, R.; Ahmad, F. A possible origin of differences between calorimetric and equilibrium estimates of stability parameters of proteins. Biochem. J. 2000, 345, 711–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, S.; Ahmad, F. A New Method for the Determination of Stability Parameters of Proteins from Their Heat-Induced Denaturation Curves. Anal. Biochem. 2000, 283, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becktel, W.J.; Schellman, J.A. Protein stability curves. Biopolymers 1987, 26, 1859–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurel, P.; Douzou, P. Catalytic implications of electrostatic potentials: The lytic activity of lysozymes as a model. J. Mol. Biol. 1976, 102, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cell separation, Amersham Biosciences AB 2001. Available online: https://somapps.med.upenn.edu/pbr/portal/immune/Ficcoll_info.pdf (accessed on 31 July 2019).
- Singh, R.; Haque, I.; Ahmad, F. Counteracting Osmolyte Trimethylamine N-Oxide Destabilizes Proteins at pH below Its pKa: Measurements of Thermodynamic Parameters of Proteins In The Presence And Absence Of Trimethylamine N-Oxide. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 11035–11042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Privalov, P.L. Stability of proteins: Small globular proteins. Adv. Protein Chem. 1979, 33, 167–241. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pfeil, W.; Sadowski, M.L. A scanning calorimetric study of bovine and human apo-a-lactalbumin. Stud. Biophys 1985, 109, 163–170. [Google Scholar]
- Kuhnert, D.C.; Gildenhuys, S.; Dirr, H.W. Effect of macromolecular crowding on the stability of monomeric glutaredoxin 2 and dimeric glutathione transferase A1-1. S. Afr. J. Sci. 2008, 104, 76–80. [Google Scholar]
- Beg, I.; Minton, A.P.; Islam, A.; Hassan, M.I.; Ahmad, F. The pH Dependence of Saccharides’ Influence on Thermal Denaturation of Two Model Proteins Supports an Excluded Volume Model for Stabilization Generalized to Allow for Intramolecular Electrostatic Interactions. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, G.; Timasheff, S.N. Mechanism of the stabilization of ribonuclease A by sorbitol: Preferential hydration is greater for the denatured then for the native protein. Protein Sci. A Publ. Protein Soc. 1997, 6, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cremades, N.; Sancho, J. Molten Globule and Native State Ensemble of Helicobacter pylori Flavodoxin: Can Crowding, Osmolytes or Cofactors Stabilize the Native Conformation Relative to the Molten Globule? Biophys. J. 2008, 95, 1913–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Garg, S.K.; Stivala, S.S. Assessment of branching in polymers from small angle X-ray scattering (SAXS): SAXS from model comb-branched polystyrenes. Polymer 1982, 23, 514–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smit, J.A.M.; Van Dijk, J.A.P.P.; Mennen, M.G.; Daoud, M. Polymer size exponents of branched dextrans. Macromolecules 1992, 25, 3585–3590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fissell, W.H.; Manley, S.; Dubnisheva, A.; Glass, J.; Magistrelli, J.; Eldridge, A.N.; Fleischman, A.J.; Zydney, A.L.; Roy, S. Ficoll is not a rigid sphere. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2007, 293, F1209–F1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, G.; Dubin, P.L. Adsorptive interaction of Ficoll standards with porous glass size-exclusion chromatography columns. J. Chromatogr. A 1995, 693, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Dubin, P.L. Observation of Ficoll charge using size-exclusion chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 1998, 800, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenner, J.R.; Bloomfield, V.A. Crowding effects on EcoRV kinetics and binding. Biophys. J. 1999, 77, 3234–3241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minton, A.P. Models for Excluded Volume Interaction between an Unfolded Protein and Rigid Macromolecular Cosolutes: Macromolecular Crowding and Protein Stability Revisited. Biophys. J. 2005, 88, 971–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, D.; Minton, A.P. Macromolecular crowding: Qualitative and semiquantitative successes, quantitative challenges. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Proteins Proteom. 2003, 1649, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas, G.; Minton, A.P. Toward an understanding of biochemical equilibria within living cells. Biophys. Rev. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minton, A.P. How can biochemical reactions within cells differ from those in test tubes? J. Cell Sci. 2006, 119, 2863–2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minton, A.P.; Wilf, J. Effect of macromolecular crowding upon the structure and function of an enzyme: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Biochemistry 1981, 20, 4821–4826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minton, A.P. Influence of excluded volume upon macromolecular structure and associations in ‘crowded” media. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 1997, 8, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralston, G.B. Effects of “crowding” in protein solutions. J. Chem. Educ. 1990, 67, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minton, A.P. Influence of macromolecular crowding upon the stability and state of association of proteins: Predictions and observations. J. Pharm. Sci. 2005, 94, 1668–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minton, A.P. Macromolecular crowding. Curr. Biol. 2006, 16, R269–R271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas, G.; Minton, A.P. Macromolecular Crowding In Vitro, In Vivo, and In Between. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2016, 41, 970–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minton, A.P. Effect of a Concentrated “Inert” Macromolecular Cosolute on the Stability of a Globular Protein with Respect to Denaturation by Heat and by Chaotropes: A Statistical-Thermodynamic Model. Biophys. J. 2000, 78, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benton, L.A.; Smith, A.E.; Young, G.B.; Pielak, G.J. Unexpected effects of macromolecular crowding on protein stability. Biochemistry 2012, 51, 9773–9775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikaelsson, T.; Aden, J.; Johansson, L.B.; Wittung-Stafshede, P. Direct observation of protein unfolded state compaction in the presence of macromolecular crowding. Biophys. J. 2013, 104, 694–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulothungan, S.R.; Das, M.; Johnson, M.; Ganesh, C.; Varadarajan, R. Effect of crowding agents, signal peptide, and chaperone SecB on the folding and aggregation of E. coli maltose binding protein. Langmuir 2009, 25, 6637–6648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, D.S.; Xu, K.; Logan, T.M.; Zhou, H.X. Effects of pH, salt, and macromolecular crowding on the stability of FK506-binding protein: An integrated experimental and theoretical study. J. Mol. Biol. 2005, 351, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, Y.; Miyoshi, D.; Sugimoto, N. Regulation of DNA nucleases by molecular crowding. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 4086–4093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Gierasch, L.M. Macromolecular crowding remodels the energy landscape of a protein by favoring a more compact unfolded state. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 10445–10452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, R.; Westphal, A.H.; Huberts, D.H.; Nabuurs, S.M.; Lindhoud, S.; Visser, A.J.; van Mierlo, C.P. Macromolecular crowding compacts unfolded apoflavodoxin and causes severe aggregation of the off-pathway intermediate during apoflavodoxin folding. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 27383–27394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, X.; Weise, C.F.; Sparrman, T.; Wolf-Watz, M.; Wittung-Stafshede, P. Macromolecular crowding extended to a heptameric system: The Co-chaperonin protein 10. Biochemistry 2011, 50, 3034–3044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, X.; Zhou, Z.; Bai, Y.; Choy, W.Y. 15N NMR spin relaxation dispersion study of the molecular crowding effects on protein folding under native conditions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 3916–3917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; He, H.; Li, S. Effect of Ficoll 70 on thermal stability and structure of creatine kinase. Biochemistry 2010, 75, 648–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Christiansen, A.; Samiotakis, A.; Wittung-Stafshede, P.; Cheung, M.S. Comparison of chemical and thermal protein denaturation by combination of computational and experimental approaches. II. J. Chem. Phys. 2011, 135, 175102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sarkar, M.; Smith, A.E.; Krois, A.S.; Pielak, G.J. Macromolecular crowding and protein stability. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 16614–16618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepanenko, O.V.; Povarova, O.I.; Sulatskaya, A.I.; Ferreira, L.A.; Zaslavsky, B.Y.; Kuznetsova, I.M.; Turoverov, K.K.; Uversky, V.N. Protein unfolding in crowded milieu: What crowding can do to a protein undergoing unfolding? J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2015, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.S.; Sil, P.; Chakraborty, R.; Haldar, S.; Chattopadhyay, K. Molecular Crowding Affects the Conformational Fluctuations, Peroxidase Activity, and Folding Landscape of Yeast Cytochrome c. Biochemistry 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, G.; Yuan, J.-M.; Sun, Z.; Wei, Y. Studies of effects of macromolecular crowding and confinement on protein folding and protein stability. J. Mol. Recognit. 2004, 17, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pioselli, B.; Bettati, S.; Mozzarelli, A. Confinement and crowding effects on tryptophan synthase α2β2 complex. FEBS Lett. 2005, 579, 2197–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Zhou, H.-X. Atomistic Modeling of Macromolecular Crowding Predicts Modest Increases in Protein Folding and Binding Stability. Biophys. J. 2009, 97, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.; Lin, Z.; Tsou, C.-l.; Wang, C.-c. Effects of Macromolecular Crowding on the Unfolding and the Refolding of d-Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosophospate Dehydrogenase. J. Protein Chem. 2003, 22, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanfelice, D.; Temussi, P.A. Cold denaturation as a tool to measure protein stability. Biophys. Chem. 2016, 208, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurent, T.C. The interaction between polysaccharides and other macromolecules. 5. The solubility of proteins in the presence of dextran. Biochem. J. 1963, 89, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurent, T.C.; Ogston, A.G. The interaction between polysaccharides and other macromolecules. 4. The osmotic pressure of mixtures of serum albumin and hyaluronic acid. Biochem. J. 1963, 89, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.-X. Loops, Linkages, Rings, Catenanes, Cages, and Crowders: Entropy-Based Strategies for Stabilizing Proteins. Acc. Chem. Res. 2004, 37, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, T.; Alshareedah, I.; Wang, W.; Ngo, J.; Moosa, M.M.; Banerjee, P.R. Molecular Crowding Tunes Material States of Ribonucleoprotein Condensates. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plaza del Pino, I.M.; Sanchez-Ruiz, J.M. An osmolyte effect on the heat capacity change for protein folding. Biochemistry 1995, 34, 8621–8630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.-M.; Chyan, C.-L.; Zhou, H.-X.; Chung, T.-Y.; Peng, H.; Ping, G.; Yang, G. The effects of macromolecular crowding on the mechanical stability of protein molecules. Protein Sci. A Publ. Protein Soc. 2008, 17, 2156–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokuriki, N.; Kinjo, M.; Negi, S.; Hoshino, M.; Goto, Y.; Urabe, I.; Yomo, T. Protein folding by the effects of macromolecular crowding. Protein Sci. A Publ. Protein Soc. 2004, 13, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, S.N. Applications of isothermal titration calorimetry to measure enzyme kinetics and activity in complex solutions. Thermochim. Acta 2006, 448, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, S.N.; RamLov, H.; Westh, P. Effects of osmolytes on hexokinase kinetics combined with macromolecular crowding: Test of the osmolyte compatibility hypothesis towards crowded systems. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2007, 148, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor, I.; Vilaseca, E.; Madurga, S.; Garcés, J.L.; Cascante, M.; Mas, F. Effect of Crowding by Dextrans on the Hydrolysis of N-Succinyl-l-phenyl-Ala-p-nitroanilide Catalyzed by α-Chymotrypsin. J. Phys. Chem. B 2011, 115, 1115–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morán-Zorzano, M.T.; Viale, A.M.; Muñoz, F.J.; Alonso-Casajús, N.; Eydallín, G.G.; Zugasti, B.; Baroja-Fernández, E.; Pozueta-Romero, J. Escherichia coli AspP activity is enhanced by macromolecular crowding and by both glucose-1,6-bisphosphate and nucleotide-sugars. FEBS Lett. 2007, 581, 1035–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asaad, N.; Engberts, J.B.F.N. Cytosol-Mimetic Chemistry: Kinetics of the Trypsin-Catalyzed Hydrolysis of p-Nitrophenyl Acetate upon Addition of Polyethylene Glycol and N-tert-Butyl Acetoacetamide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 6874–6875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuelli, M.A. Dextrans in Aqueous Solution. Experimental Review on Intrinsic Viscosity Measurements and Temperature Effect. J. Polym. Biopolym. Phys. Chem. 2013, 1, 13–21. [Google Scholar]
- Christiansen, A. Effects of Macromolecular Crowding on Protein Folding. In-Vitro Equilibrium and Kinetic Studies on Selected Model Systems. 2013. Available online: https://www.diva-portal.org/smash/get/diva2:665133/FULLTEXT01.pdf (accessed on 31 July 2019).
- Uversky, V.N.; E, M.C.; Bower, K.S.; Li, J.; Fink, A.L. Accelerated alpha-synuclein fibrillation in crowded milieu. Febs Lett 2002, 515, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munishkina, L.A.; Cooper, E.M.; Uversky, V.N.; Fink, A.L. The effect of macromolecular crowding on protein aggregation and amyloid fibril formation. J. Mol. Recognit. 2004, 17, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| [Crowder] (mg mL−1) | Tm (oC) | ∆Hm (kcal mol−1) | ΔCp (kcal mol−1 K−1) | ∆GDo (kcal mol−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 42.8 ± 0.2 (42.9 ± 0.2) | 51 ± 3 (51 ± 3) | 1.56 ± 0.09 | 2.07 ± 0.16 (2.08 ± 0.15) |
| Ficoll 70 | ||||
| 50 | 43.4 ± 0.3 | 52 ± 3 | 1.55 ± 0.09 | 2.18 ± 0.21 |
| 100 | 44.4 ± 0.2 | 52 ± 2 | 1.58 ± 0.06 | 2.22 ± 0.11 |
| 150 | 45.0 ± 0.3 | 54 ± 2 | 1.57 ± 0.08 | 2.39 ± 0.12 |
| 200 | 45.4 ± 0.1 | 55 ± 2 | 1.55 ± 0.07 | 2.49 ± 0.11 |
| 250 | 46.4 ± 0.2 | 57 ± 3 | 1.56 ± 0.07 | 2.67 ± 0.22 |
| 300 | 47.1 ± 0.3 | 58 ± 4 | 1.57 ± 0.06 | 2.78 ± 0.26 |
| 350 | 47.4 ± 0.3 (47.5 ± 0.2) | 59 ± 3 (59 ± 2) | 1.57 ± 0.09 | 2.86 ± 0.18 (2.87 ± 0.15) |
| Dextran 70 | ||||
| 50 | 44.1 ± 0.2 | 52 ± 3 | 1.58 ± 0.09 | 2.20 ± 0.19 |
| 100 | 45.9 ± 0.3 | 53 ± 2 | 1.57 ± 0.07 | 2.37 ± 0.12 |
| 150 | 47.5 ± 0.2 | 55 ± 2 | 1.58 ± 0.07 | 2.58 ± 0.12 |
| 200 | 49.1 ± 0.2 | 57 ± 3 | 1.56 ± 0.08 | 2.82 ± 0.20 |
| 250 | 50.5 ± 0.1 | 59 ± 2 | 1.55 ± 0.06 | 3.04 ± 0.12 |
| 300 | 51.1 ± 0.2 (51.0 ± 0.2) | 60 ± 2 (60 ± 3) | 1.55 ± 0.09 | 3.15 ± 0.41 (3.15 ± 0.16) |
| Dextran 40 | ||||
| 50 | 44.9 ± 0.3 | 52 ± 2 | 1.57 ± 0.09 | 2.25 ± 0.13 |
| 100 | 47.8 ± 0.3 | 53 ± 2 | 1.59 ± 0.07 | 2.44 ± 0.12 |
| 150 | 50.4 ± 0.1 | 55 ± 3 | 1.55 ± 0.08 | 2.73 ± 0.26 |
| 200 | 52.9 ± 0.2 | 57 ± 4 | 1.58 ± 0.08 | 2.93 ± 0.32 |
| 250 | 54.0 ± 0.3 | 59 ± 3 | 1.56 ± 0.09 | 3.16 ± 0.29 |
| 300 | 54.3 ± 0.3 (54.3 ± 0.2) | 64 ± 2 (64 ± 2) | 1.55 ± 0.09 | 3.63 ± 0.16 (3.63 ± 0.16) |
| [Dextran 40] (mg mL−1) | Tm (obs.)c (oC) | Tm (corr.)d (oC) | ∆Hm (obs.) c (kcal mol−1) | ∆Hm (corr.) d (kcal mol−1) | ΔGDº (kcal mol−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH 7.0 | |||||
| 0 | 59.9 ± 0.3 (59.8 ± 0.3) | 85.5 ± 0.3 (85.4 ± 0.3) | 93 ± 3 (93 ± 4) | 127 ± 3 (127 ± 4) | 12.80 ± 0.30 (12.75 ± 0.27) |
| 100 | 60.1 ± 0.3 | 85.7 ± 0.3 | 94 ± 3 | 128 ± 3 | 12.98 ± 0.40 |
| 150 | 60.4 ± 0.2 | 86.0 ± 0.2 | 95 ± 2 | 129 ± 2 | 13.21 ± 0.26 |
| 200 | 60.8 ± 0.2 | 86.4 ± 0.2 | 97 ± 3 | 131 ± 3 | 13.57 ± 0.24 |
| 250 | 61.7 ± 0.2 | 87.3 ± 0.2 | 99 ± 4 | 133 ± 4 | 13.88 ± 0.40 |
| 300 | 62.0 ± 0.3 (61.9 ± 0.3) | 87.6 ± 0.3 (87.5 ± 0.3) | 100 ± 2 (99 ± 2) | 134 ± 2 (133 ± 2) | 14.06 ± 0.34 (13.89 ± 0.31) |
| pH 2.0 | |||||
| 0 | 57.6 ± 0.2 (57.6 ± 0.2) | - | 84 ± 2 (84 ± 2) | - | 5.61 ± 0.13 (5.61 ± 0.13) |
| 100 | 58.8 ± 0.2 | - | 86 ± 2 | - | 5.92 ± 0.19 |
| 150 | 59.5 ± 0.3 | - | 88 ± 2 | - | 6.19 ± 0.23 |
| 200 | 61.8 ± 0.2 | - | 92 ± 3 | - | 6.78 ± 0.28 |
| 250 | 62.9 ± 0.3 | - | 94 ± 3 | - | 7.06 ± 0.29 |
| 300 | 64.1 ± 0.2 (64.0 ± 0.2) | - | 97 ± 2 (96 ± 3) | - | 7.49 ± 0.24 (7.37 ± 0.26) |
| [Dextran 40], mg mL−1 | ∆Cp, kcal mol− K−1 | ||||
| 0 | 1.60 ± 0.09 | ||||
| 100 | 1.59 ± 0.05 | ||||
| 150 | 1.58 ± 0.07 | ||||
| 200 | 1.58 ± 0.06 | ||||
| 250 300 | 1.59 ± 0.08 1.59 ± 0.07 | ||||
| pH | Dextran 40 (300 mg mL-1) | Dextran 70 (300 mg mL-1) | Ficoll 70 (300 mg mL-1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ∆Tm, °C | %∆∆GD° | ∆Tm, °C | %∆∆GD° | ∆Tm, °C | %∆∆GD° | |
| 7.0 | 11.5 | 75.36 | 8.3 | 52.17 | 4.3 | 34.29 |
| 6.5 | 9.2 | 36.64 | 7.0 | 31.25 | 3.5 | 20.17 |
| 6.0 | 6.8 | 18.67 | 5.5 | 17.53 | 2.7 | 13.89 |
| 5.5 | 4.9 | 15.23 | 4.1 | 14.62 | 2.0 | 12.22 |
| pH | Dextran 40 (300 mg mL−1) | Dextran 70 (300 mg mL−1) | Ficoll 70 (300 mg mL−1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ∆Tm, °C | %∆∆GD° | ∆Tm, °C | %∆∆GD° | ∆Tm, °C | %∆∆GD° | |
| 7.0 | 2.1 | 9.84 | 1.7 | 9.29 | 1.0 | 7.34 |
| 6.0 | 2.6 | 11.52 | 2.1 | 9.99 | 1.0 | 6.52 |
| 5.0 | 3.3 | 13.46 | 2.2 | 11.32 | 1.1 | 7.28 |
| 4.0 | 5.8 | 17.23 | 2.3 | 12.02 | 1.3 | 6.81 |
| 3.0 | 6.1 | 20.70 | 3.0 | 16.23 | - | - |
| 2.0 | 6.5 | 33.51 | 4.3 | 25.84 | - | - |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shahid, S.; Hasan, I.; Ahmad, F.; Hassan, M.I.; Islam, A. Carbohydrate-Based Macromolecular Crowding-Induced Stabilization of Proteins: Towards Understanding the Significance of the Size of the Crowder. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 477. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9090477
Shahid S, Hasan I, Ahmad F, Hassan MI, Islam A. Carbohydrate-Based Macromolecular Crowding-Induced Stabilization of Proteins: Towards Understanding the Significance of the Size of the Crowder. Biomolecules. 2019; 9(9):477. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9090477
Chicago/Turabian StyleShahid, Sumra, Ikramul Hasan, Faizan Ahmad, Md. Imtaiyaz Hassan, and Asimul Islam. 2019. "Carbohydrate-Based Macromolecular Crowding-Induced Stabilization of Proteins: Towards Understanding the Significance of the Size of the Crowder" Biomolecules 9, no. 9: 477. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9090477
APA StyleShahid, S., Hasan, I., Ahmad, F., Hassan, M. I., & Islam, A. (2019). Carbohydrate-Based Macromolecular Crowding-Induced Stabilization of Proteins: Towards Understanding the Significance of the Size of the Crowder. Biomolecules, 9(9), 477. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9090477







