Non-Invasive Approach for Evaluation of Pulmonary Hypertension Using Extracellular Vesicle-Associated Small Non-Coding RNA
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Isolation of Extracellular Vesicles
2.3. RNA Isolation and Real-Time PCR
2.4. RNA Sequencing
2.5. PIWI-RNA Target Prediction and mRNA Functional Analysis
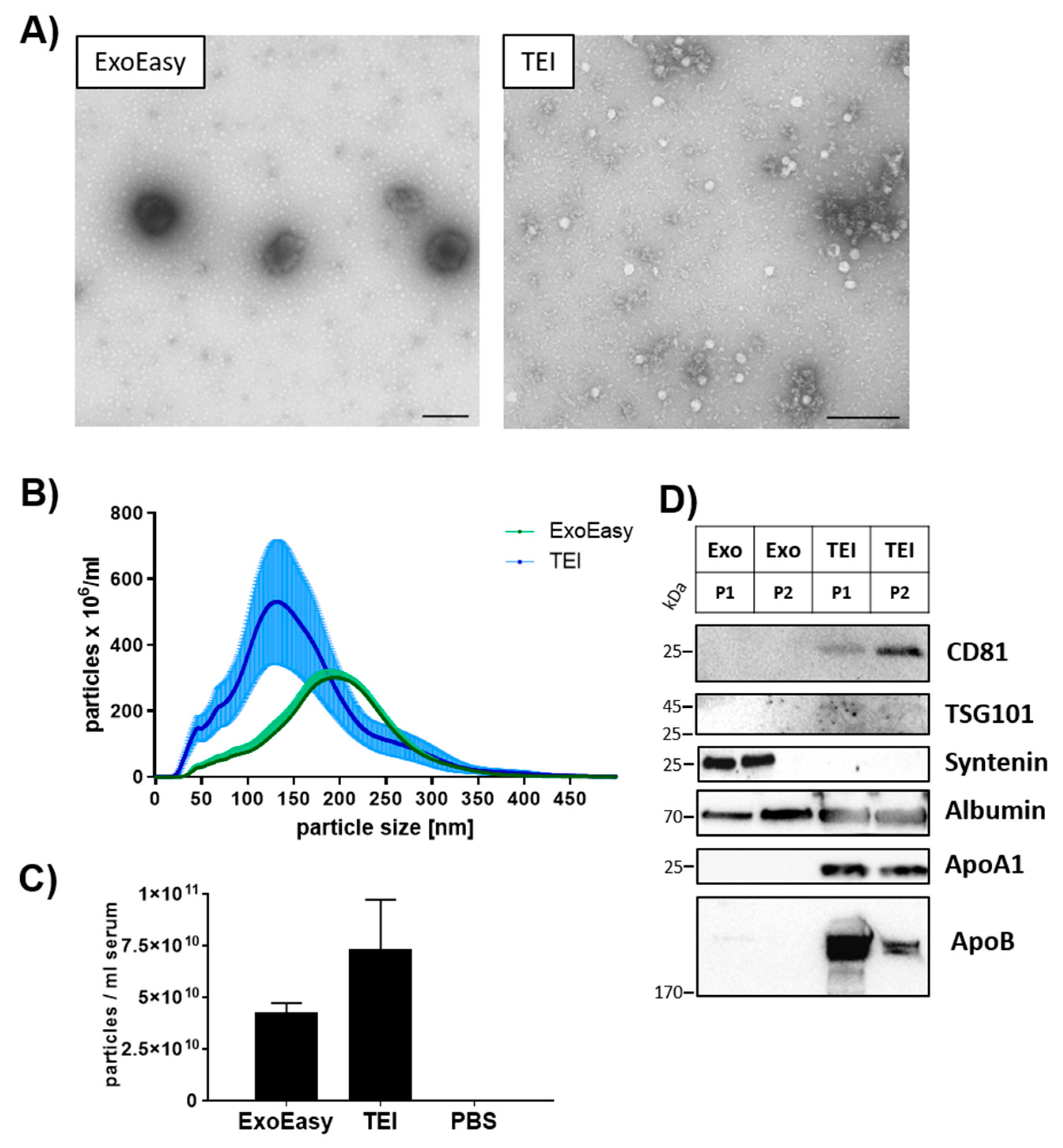
2.6. Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis
2.7. Negative Staining of Isolated EVs for Transmission Electron Microscopy
2.8. Western Blotting
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Subpopulations of Extracellular Vesicles Depend on the Isolation Method
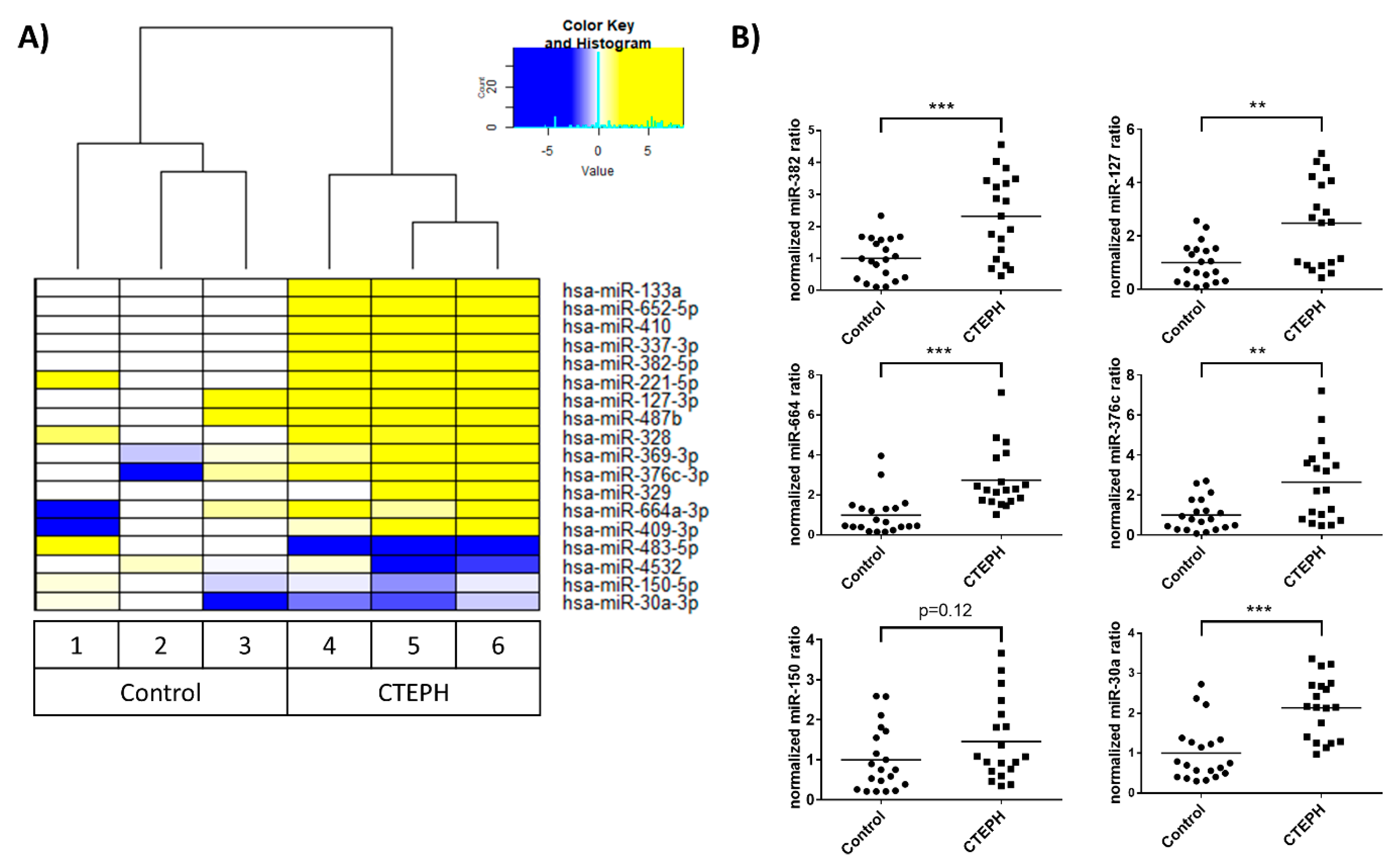
3.2. Identification of Novel miRNA-Based Biomarkers for CTEPH by RNA Sequencing
3.3. EV-Mediated miRNA Profile Depends on the EV Isolation Method
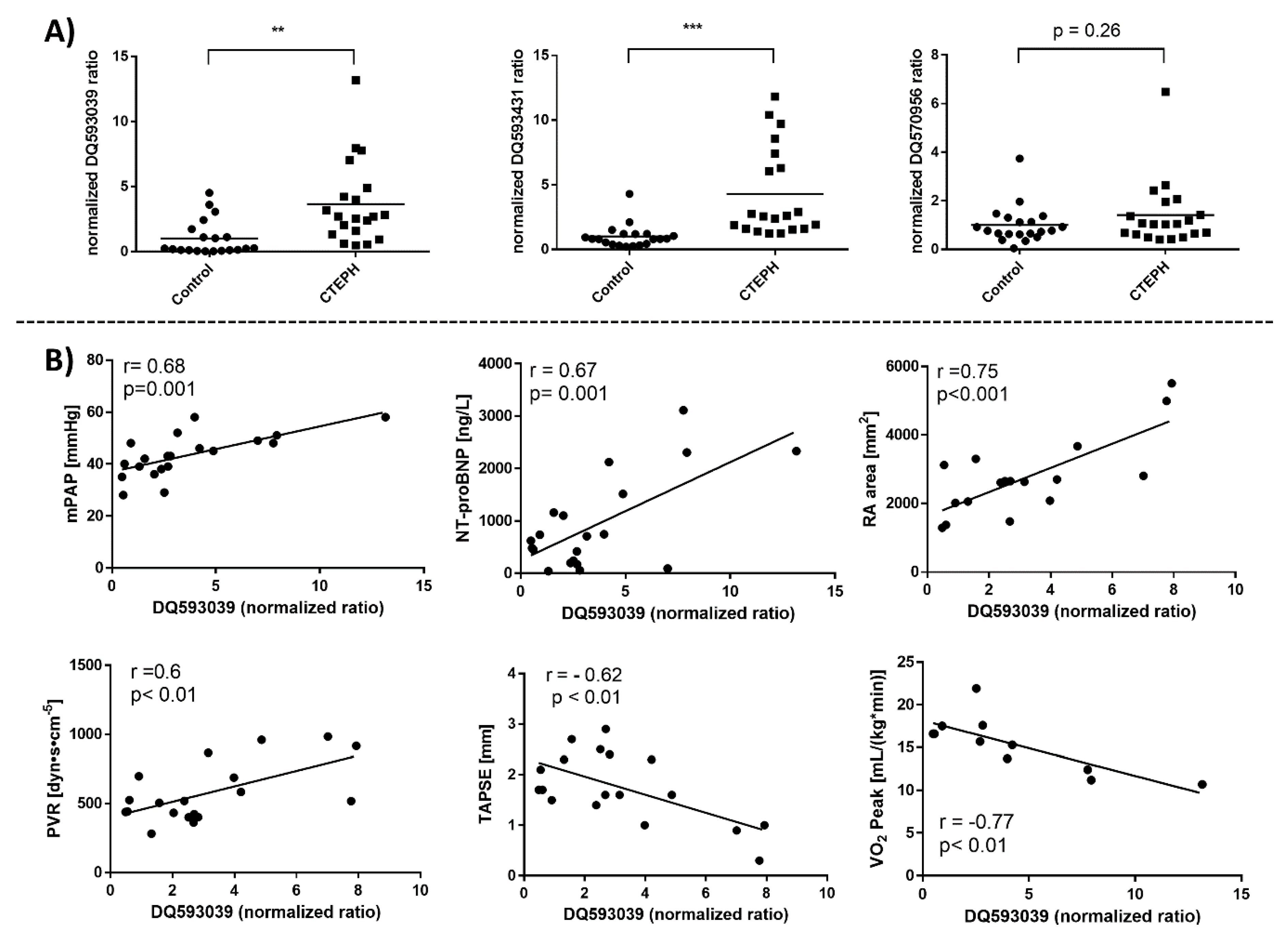
3.4. Identification of piRNAs as Novel Diagnostic Biomarkers for CTEPH
3.5. Predicted Functional Role of piRNAs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Simonneau, G.; Montani, D.; Celermajer, D.S.; Denton, C.P.; Gatzoulis, M.A.; Krowka, M.; Williams, P.G.; Souza, R. Haemodynamic definitions and updated clinical classification of pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 53, 1801913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonderman, D.; Skoro-Sajer, N.; Jakowitsch, J.; Adlbrecht, C.; Dunkler, D.; Taghavi, S.; Klepetko, W.; Kneussl, M.; Lang, I.M. Predictors of outcome in chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Circulation 2007, 115, 2153–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riedel, M.; Stanek, V.; Widimsky, J.; Prerovsky, I. Longterm follow-up of patients with pulmonary thromboembolism. Late prognosis and evolution of hemodynamic and respiratory data. Chest 1982, 81, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, R.; Wang, Y.; Wan, J.; Leng, D.; Gong, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Pang, W.; Zhai, Z.; Yang, Y. Microarray Analysis and Detection of MicroRNAs Associated with Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 8529796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viereck, J.; Thum, T. Circulating Noncoding RNAs as Biomarkers of Cardiovascular Disease and Injury. Circ. Res. 2017, 120, 381–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Henderson, H.; Spradley, C.; Li, L.; Kim, I.K.; Kumar, S.; Hong, N.; Arroliga, A.C.; Gupta, S. Circulating miRNAs as potential marker for pulmonary hypertension. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Yang, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, L.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Gu, S.; Gan, H.; Cai, J.; et al. Differentially Expressed Plasma MicroRNAs and the Potential Regulatory Function of Let-7b in Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Guo, L.J.; Liu, J.; Wang, W.; Yuan, J.X.; Zhao, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, C. MicroRNA expression profile of pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells and the effect of let-7d in chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Pulm. Circ. 2013, 3, 654–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, W.; Liu, N.; Toiyama, Y.; Kusunoki, M.; Nagasaka, T.; Fujiwara, T.; Wei, Q.; Qin, H.; Lin, H.; Ma, Y.; et al. Novel evidence for a PIWI-interacting RNA (piRNA) as an oncogenic mediator of disease progression, and a potential prognostic biomarker in colorectal cancer. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, A.; Wang, W.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Dong, Y.; Zheng, G.; Wu, Q.; Zou, M.; Du, L.; Wang, Y.; et al. A serum piRNA signature as promising non-invasive diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for colorectal cancer. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 3703–3720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weick, E.-M.; Miska, E.A. piRNAs: From biogenesis to function. Development 2014, 141, 3458–3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miglino, N.; Alexandrova, E.; Hashim, A.; Ravo, M.; Tamm, M.; Baty, F.; Brutsche, M.; Weisz, A.; Borger, P. Differential expression profile of miRNAs and piRNAs in asthmatic and non-asthmatic bronchial smooth muscle cells reveals new possible biomarkers for complex lung diseases. Eur. Respir. J. 2014, 44 (Suppl. 58), 398. [Google Scholar]
- Gatti, S.; Bruno, S.; Deregibus, M.C.; Sordi, A.; Cantaluppi, V.; Tetta, C.; Camussi, G. Microvesicles derived from human adult mesenchymal stem cells protect against ischaemia-reperfusion-induced acute and chronic kidney injury. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2011, 26, 1474–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Conde, I.; Shrimpton, C.N.; Thiagarajan, P.; Lopez, J.A. Tissue-factor-bearing microvesicles arise from lipid rafts and fuse with activated platelets to initiate coagulation. Blood 2005, 106, 1604–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellingham, S.A.; Guo, B.B.; Coleman, B.M.; Hill, A.F. Exosomes: Vehicles for the transfer of toxic proteins associated with neurodegenerative diseases? Front. Physiol. 2012, 3, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, A.; Marban, E. Exosomes: Fundamental Biology and Roles in Cardiovascular Physiology. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2016, 78, 67–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, M.; Raposo, G.; Thery, C. Biogenesis, secretion, and intercellular interactions of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 30, 255–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, F.; Yang, X.; Proebsting, S.; Hoelscher, M.; Przybilla, D.; Baumann, K.; Schmitz, T.; Dolf, A.; Endl, E.; Franklin, B.S.; et al. MicroRNA expression in circulating microvesicles predicts cardiovascular events in patients with coronary artery disease. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2014, 3, e001249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creemers, E.E.; Tijsen, A.J.; Pinto, Y.M. Circulating MicroRNAs: Novel Biomarkers and Extracellular Communicators in Cardiovascular Disease? Circ. Res. 2012, 110, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lankeit, M.; Krieg, V.; Hobohm, L.; Kolmel, S.; Liebetrau, C.; Konstantinides, S.; Hamm, C.W.; Mayer, E.; Wiedenroth, C.B.; Guth, S. Pulmonary endarterectomy in chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.; Domrachev, M.; Lash, A.E. Gene Expression Omnibus: NCBI gene expression and hybridization array data repository. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, B.; Enright, A.J.; Aravin, A.; Tuschl, T.; Sander, C.; Marks, D.S. Human MicroRNA targets. PLoS Biol. 2004, 2, e363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashim, A.; Rizzo, F.; Marchese, G.; Ravo, M.; Tarallo, R.; Nassa, G.; Giurato, G.; Santamaria, G.; Cordella, A.; Cantarella, C.; et al. RNA sequencing identifies specific PIWI-interacting small non-coding RNA expression patterns in breast cancer. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 9901–9910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.W.; Sherman, B.T.; Tan, Q.; Collins, J.R.; Alvord, W.G.; Roayaei, J.; Stephens, R.; Baseler, M.W.; Lane, H.C.; Lempicki, R.A. The DAVID Gene Functional Classification Tool: A novel biological module-centric algorithm to functionally analyze large gene lists. Genome Biol. 2007, 8, R183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentine, R.C.; Shapiro, B.M.; Stadtman, E.R. Regulation of glutamine synthetase. XII. Electron microscopy of the enzyme from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry 1968, 7, 2143–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipps, C.; Nguyen, J.H.; Pyttel, L.; Lynch, T.L.I.; Liebetrau, C.; Aleshcheva, G.; Voss, S.; Dorr, O.; Nef, H.M.; Mollmann, H.; et al. N-terminal fragment of cardiac myosin binding protein-C triggers pro-inflammatory responses in vitro. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2016, 99, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, S.; Rycak, L.; Winter, P.; Kahl, G.; Koch, I.; Rotter, B. omiRas: A Web server for differential expression analysis of miRNAs derived from small RNA-Seq data. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 2651–2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anders, S.; Huber, W. Differential expression analysis for sequence count data. Genome Biol. 2010, 11, R106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowal, J.; Arras, G.; Colombo, M.; Jouve, M.; Morath, J.P.; Primdal-Bengtson, B.; Dingli, F.; Loew, D.; Tkach, M.; Thery, C. Proteomic comparison defines novel markers to characterize heterogeneous populations of extracellular vesicle subtypes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E968–E977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonsen, J.B. What Are We Looking At? Extracellular Vesicles, Lipoproteins, or Both? Circ. Res. 2017, 121, 920–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mateescu, B.; Kowal, E.J.K.; van Balkom, B.W.M.; Bartel, S.; Bhattacharyya, S.N.; Buzás, E.I.; Buck, A.H.; de Candia, P.; Chow, F.W.N.; Das, S.; et al. Obstacles and opportunities in the functional analysis of extracellular vesicle RNA—An ISEV position paper. JEV 2017, 6, 1286095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, A.-M.; Bockstahler, M.; Hristov, G.; Weiß, C.; Fischer, A.; Korkmaz-Icöz, S.; Giannitsis, E.; Poller, W.; Schultheiss, H.-P.; Katus, H.A.; et al. Identification of novel antigens contributing to autoimmunity in cardiovascular diseases. Clin. Immunol. 2016, 173, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Hu, C.; Pan, P. Extracellular Vesicle MicroRNA Transfer in Lung Diseases. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stranska, R.; Gysbrechts, L.; Wouters, J.; Vermeersch, P.; Bloch, K.; Dierickx, D.; Andrei, G.; Snoeck, R. Comparison of membrane affinity-based method with size-exclusion chromatography for isolation of exosome-like vesicles from human plasma. J. Transl. Med. 2018, 16, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.-T.; Huang, Y.-Y.; Zheng, L.; Qin, S.-H.; Xu, X.-P.; An, T.-X.; Xu, Y.; Wu, Y.-S.; Hu, X.-M.; Ping, B.-H.; et al. Comparison of isolation methods of exosomes and exosomal RNA from cell culture medium and serum. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 40, 834–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sluijter, J.P.G.; Davidson, S.M.; Boulanger, C.M.; Iren Buzas, E.; de Kleijn, D.P.V.; Engel, F.B.; Giricz, Z.; Hausenloy, D.J.; Kishore, R.; Lecour, S.; et al. Extracellular vesicles in diagnostics and therapy of the ischaemic heart: Position Paper from the Working Group on Cellular Biology of the Heart of the European Society of Cardiology. Cardiovasc. Res. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakai, W.; Yoshida, T.; Diez, D.; Miyatake, Y.; Nishibu, T.; Imawaka, N.; Naruse, K.; Sadamura, Y.; Hanayama, R. A novel affinity-based method for the isolation of highly purified extracellular vesicles. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras-Naranjo, J.C.; Wu, H.J.; Ugaz, V.M. Microfluidics for exosome isolation and analysis: Enabling liquid biopsy for personalized medicine. Lab Chip 2017, 17, 3558–3577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buschmann, D.; Kirchner, B.; Hermann, S.; Märte, M.; Wurmser, C.; Brandes, F.; Kotschote, S.; Bonin, M.; Steinlein, O.K.; Pfaffl, M.W.; et al. Evaluation of serum extracellular vesicle isolation methods for profiling miRNAs by next-generation sequencing. JEV 2018, 7, 1481321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sódar, B.W.; Kittel, Á.; Pálóczi, K.; Vukman, K.V.; Osteikoetxea, X.; Szabó-Taylor, K.; Németh, A.; Sperlágh, B.; Baranyai, T.; Giricz, Z.; et al. Low-density lipoprotein mimics blood plasma-derived exosomes and microvesicles during isolation and detection. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vickers, K.C.; Palmisano, B.T.; Shoucri, B.M.; Shamburek, R.D.; Remaley, A.T. MicroRNAs are transported in plasma and delivered to recipient cells by high-density lipoproteins. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011, 13, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, R.M.; Zhao, S.; Ramirez Solano, M.A.; Zhu, W.; Michell, D.L.; Wang, Y.; Shyr, Y.; Sethupathy, P.; Linton, M.F.; Graf, G.A.; et al. Bioinformatic analysis of endogenous and exogenous small RNAs on lipoproteins. JEV 2018, 7, 1506198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajan, K.S.; Velmurugan, G.; Gopal, P.; Ramprasath, T.; Babu, D.D.; Krithika, S.; Jenifer, Y.C.; Freddy, A.; William, G.J.; Kalpana, K.; et al. Abundant and Altered Expression of PIWI-Interacting RNAs during Cardiac Hypertrophy. Heart Lung Circ. 2016, 25, 1013–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Li, X.; Liang, H.; Zheng, N.; Pan, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, X.; Qian, M.; Xu, B.; Zhang, Y.; et al. SNX17 produces anti-arrhythmic effects by preserving functional SERCA2a protein in myocardial infarction. Int. J. Cardiol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardziyenka, M.; Campian, M.E.; Reesink, H.J.; Surie, S.; Bouma, B.J.; Groenink, M.; Klemens, C.A.; Beekman, L.; Remme, C.A.; Bresser, P.; et al. Right ventricular failure following chronic pressure overload is associated with reduction in left ventricular mass: Evidence for atrophic remodeling. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2011, 57, 921–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delcroix, M.; Staehler, G.; Gall, H.; Grünig, E.; Held, M.; Halank, M.; Klose, H.; Vonk-Noordegraaf, A.; Rosenkranz, S.; Pepke-Zaba, J.; et al. Risk assessment in medically treated Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension patients. Eur. Respir. J. 2018, 52, 1800248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Characteristics | RNA Sequencing | qRT-PCR | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTEPH (n = 3) | Controls (n = 3) | CTEPH (n = 20) | Controls (n = 20) | |
| Sex (Male/total) | 3/3 | 3/3 | 20/20 | 20/20 |
| Age (yr) | 67 (5) | 67 (7) | 60 (11) | 56 (12) |
| PE (positive/total) | 3/3 | - | 17/17 | - |
| WHO class */NYHA * | 2 (0) | 1 (0.8) | 2.5 (0.6) | 1.2 (0.9) |
| 6-MWD (m) *‖ | 432 | - | 519 (84) | - |
| MBP (mmHg) * | 108 (20) | 104 (7) | 94 (13) | 96 (9) |
| mPAP (mmHg) * | 47 (4) | - | 43 (9) | - |
| PVR (dyn s cm−5) * | 465 (76) | - | 551 (223) | - |
| CI (L min−1 m−2) *$ | 2.7 (0.5) | - | 2.6 (0.6) | - |
| BMI | 28 (5) | 28 (3) | 27 (4) | 27 (4) |
| Arterial hypertension | 1/3 | 2/3 | 5/20 | 12/20 |
| Smoker | 0/3 | 0/3 | 2/20 (7/20 formerly) | 0/19 (4/19 formerly) |
| Coronary heart disease | 0/3 | 0/3 | 1/19 | 0/20 |
| Thrombophilia | 0/3 | - | 3/18 | - |
| Riociguat or PAH-medication | 0/3 | - | 6/20 | - |
| LVEF (%) *$‡ | 63 (9) | 64 (2) | 60 (6) | 64 (7) |
| TAPSE (cm) *$ | 1.3 (0.4) | - | 1.6 (0.7) | - |
| NT-proBNP (ng/L) *‖†∫ | 279 | - | 950 (911) | 28 (43) |
| Leucocytes * | 7.2 (1.5) | 6.4 (1) | 6.7 (2.1) | 2.8 (5.5) |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.72 m2) *§ | 85 (15) | 94 (5) | 87 (21) | 106 (19) |
| Term | Count | % Targeted Genes | p-Value | List Total | Pop Hits | Pop Total | Fold Enrichment | Bonfer-roni | Benja-mini | False Discovery Rate (FDR) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GO:0035904~aorta development | 4 | 2.857 | 0.0002 | 110 | 18 | 16,792 | 33.92 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.30 |
| GO:0060976~coronary vasculature development | 4 | 2.857 | 0.0006 | 110 | 25 | 16,792 | 24.42 | 0.31 | 0.17 | 0.82 |
| GO:0003279~cardiac septum development | 3 | 2.143 | 0.0026 | 110 | 12 | 16,792 | 38.16 | 0.83 | 0.45 | 3.89 |
| GO:0000301~retrograde transport, vesicle recycling within Golgi | 2 | 1.429 | 0.0383 | 110 | 6 | 16,792 | 50.88 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 44.33 |
| GO:0048812~neuron projection morphogenesis | 3 | 2.143 | 0.0388 | 110 | 48 | 16,792 | 9.54 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 44.75 |
| GO:1901796~regulation of signal transduction by p53 class mediator | 4 | 2.857 | 0.0469 | 110 | 124 | 16,792 | 4.92 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 51.34 |
| GO:0006355~regulation of transcription, DNA-templated | 16 | 11.429 | 0.0618 | 110 | 1504 | 16,792 | 1.62 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 61.57 |
| GO:0055085~transmembrane transport | 5 | 3.571 | 0.0746 | 110 | 244 | 16,792 | 3.13 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 68.70 |
| GO:0030154~cell differentiation | 7 | 5.000 | 0.0803 | 110 | 462 | 16,792 | 2.31 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 71.50 |
| GO:0061029~eyelid development in camera-type eye | 2 | 1.429 | 0.0812 | 110 | 13 | 16,792 | 23.49 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 71.90 |
| GO:0006888~ER to Golgi vesicle-mediated transport | 4 | 2.857 | 0.0860 | 110 | 160 | 16,792 | 3.82 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 74.04 |
| GO:0016578~histone deubiquitination | 2 | 1.429 | 0.0872 | 110 | 14 | 16,792 | 21.81 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 74.52 |
| GO:0006816~calcium ion transport | 3 | 2.143 | 0.0873 | 110 | 76 | 16,792 | 6.03 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 74.59 |
| GO:0035994~response to muscle stretch | 2 | 1.429 | 0.0990 | 110 | 16 | 16,792 | 19.08 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 79.04 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lipps, C.; Northe, P.; Figueiredo, R.; Rohde, M.; Brahmer, A.; Krämer-Albers, E.-M.; Liebetrau, C.; Wiedenroth, C.B.; Mayer, E.; Kriechbaum, S.D.; et al. Non-Invasive Approach for Evaluation of Pulmonary Hypertension Using Extracellular Vesicle-Associated Small Non-Coding RNA. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 666. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9110666
Lipps C, Northe P, Figueiredo R, Rohde M, Brahmer A, Krämer-Albers E-M, Liebetrau C, Wiedenroth CB, Mayer E, Kriechbaum SD, et al. Non-Invasive Approach for Evaluation of Pulmonary Hypertension Using Extracellular Vesicle-Associated Small Non-Coding RNA. Biomolecules. 2019; 9(11):666. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9110666
Chicago/Turabian StyleLipps, Christoph, Philipp Northe, Ricardo Figueiredo, Manfred Rohde, Alexandra Brahmer, Eva-Maria Krämer-Albers, Christoph Liebetrau, Christoph B. Wiedenroth, Eckhard Mayer, Steffen D. Kriechbaum, and et al. 2019. "Non-Invasive Approach for Evaluation of Pulmonary Hypertension Using Extracellular Vesicle-Associated Small Non-Coding RNA" Biomolecules 9, no. 11: 666. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9110666
APA StyleLipps, C., Northe, P., Figueiredo, R., Rohde, M., Brahmer, A., Krämer-Albers, E.-M., Liebetrau, C., Wiedenroth, C. B., Mayer, E., Kriechbaum, S. D., Dörr, O., Nef, H., Hamm, C. W., Keller, T., & Troidl, C. (2019). Non-Invasive Approach for Evaluation of Pulmonary Hypertension Using Extracellular Vesicle-Associated Small Non-Coding RNA. Biomolecules, 9(11), 666. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9110666





