Hepatic Expression of ACBP Is a Prognostic Marker for Weight Loss After Bariatric Surgery
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Quantification of Hepatic and Adipose Tissue ACBP/DBI Expression
2.3. Isolation of Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells (PBMCs)
2.4. Cell Culture and Stimulation
2.5. Histological Evaluation
2.6. Determination of Serum ACBP/DBI Levels
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
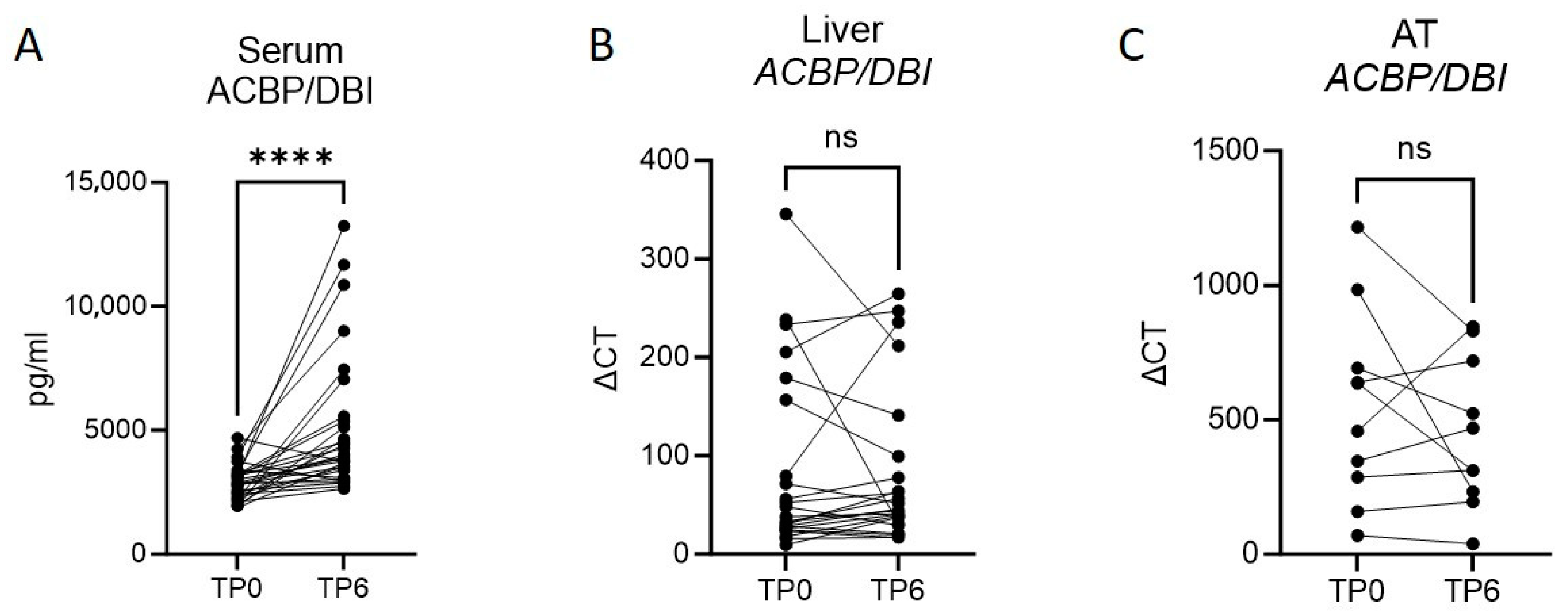
3.1. Bariatric Surgery-Induced Weight Loss Ameliorates Metabolic Function and Increases ACBP/DBI in Serum
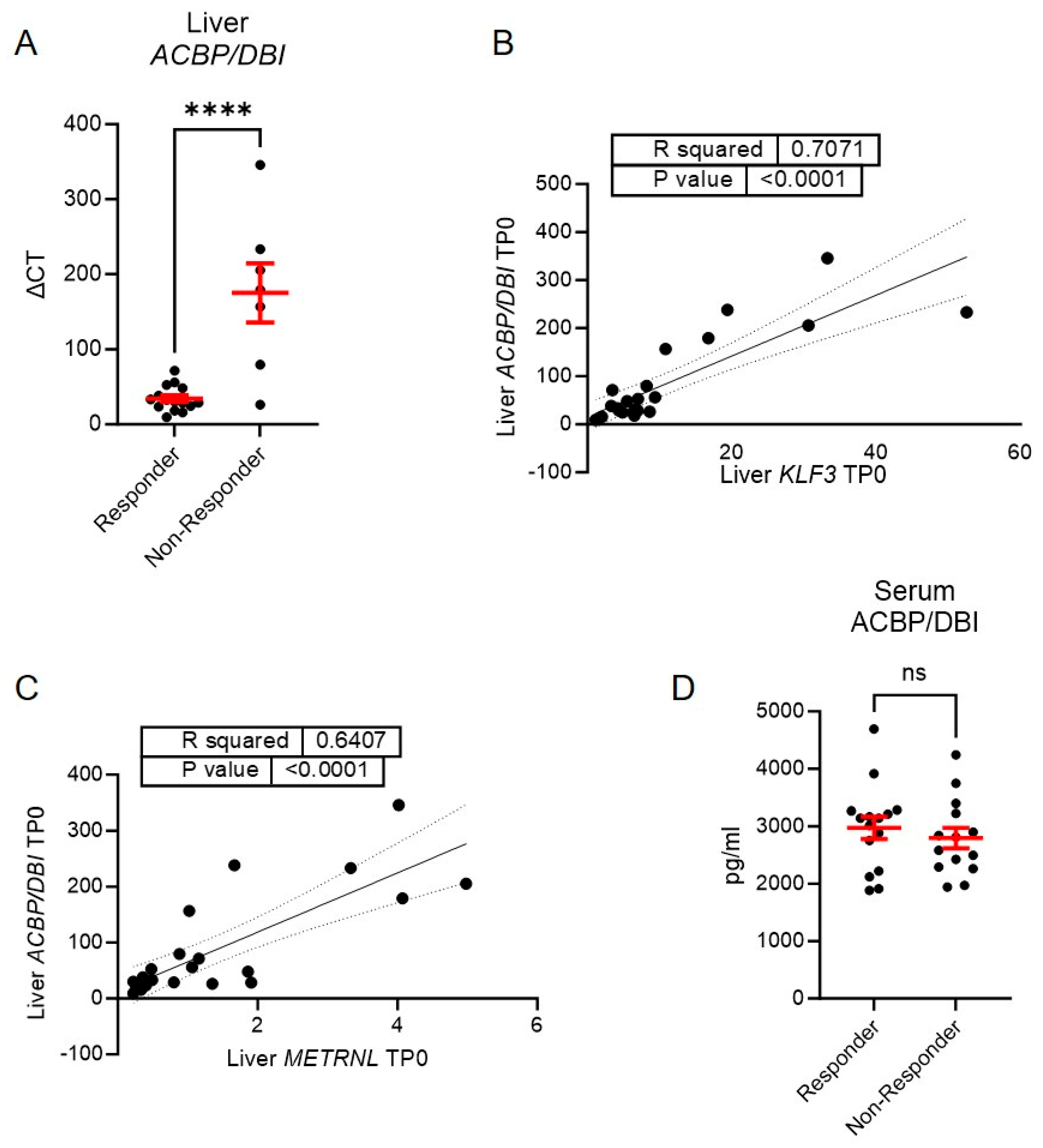
3.2. A Lower Expression of Liver ACBP/DBI Is Observed in Those with a Subsequent Augmented Weight Loss
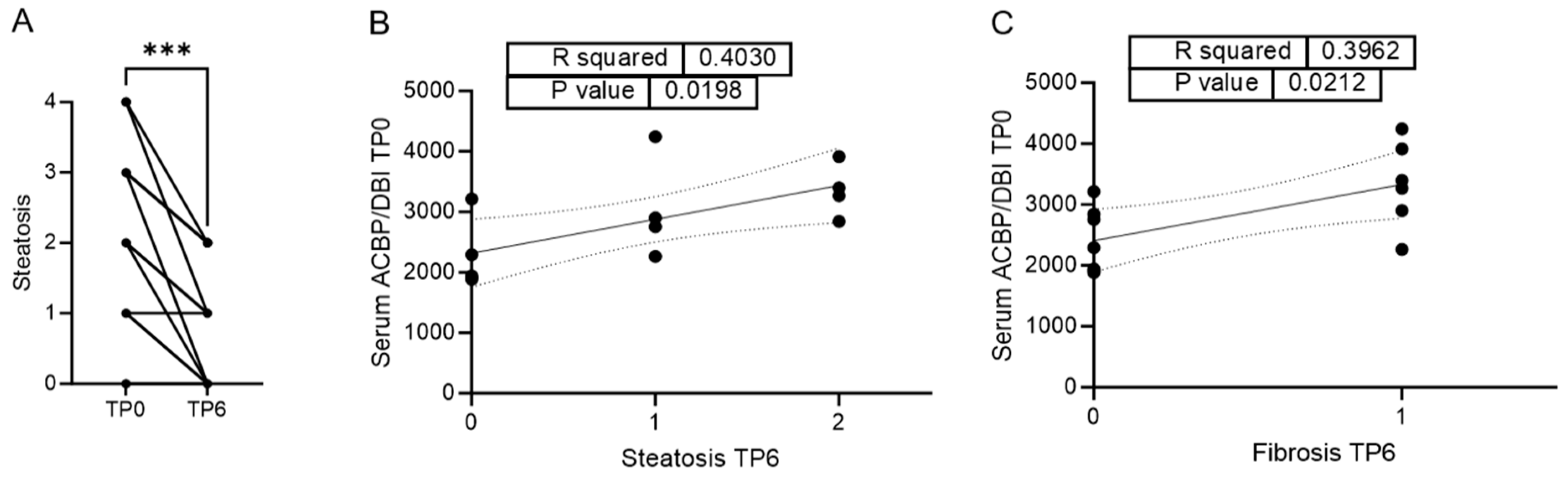
3.3. Serum ACBP/DBI Positively Correlates with Reduction of Steatosis and Fibrosis Six Months After LAGB
3.4. Serum ACBP/DBI Predicts NAS Six Months After LAGB
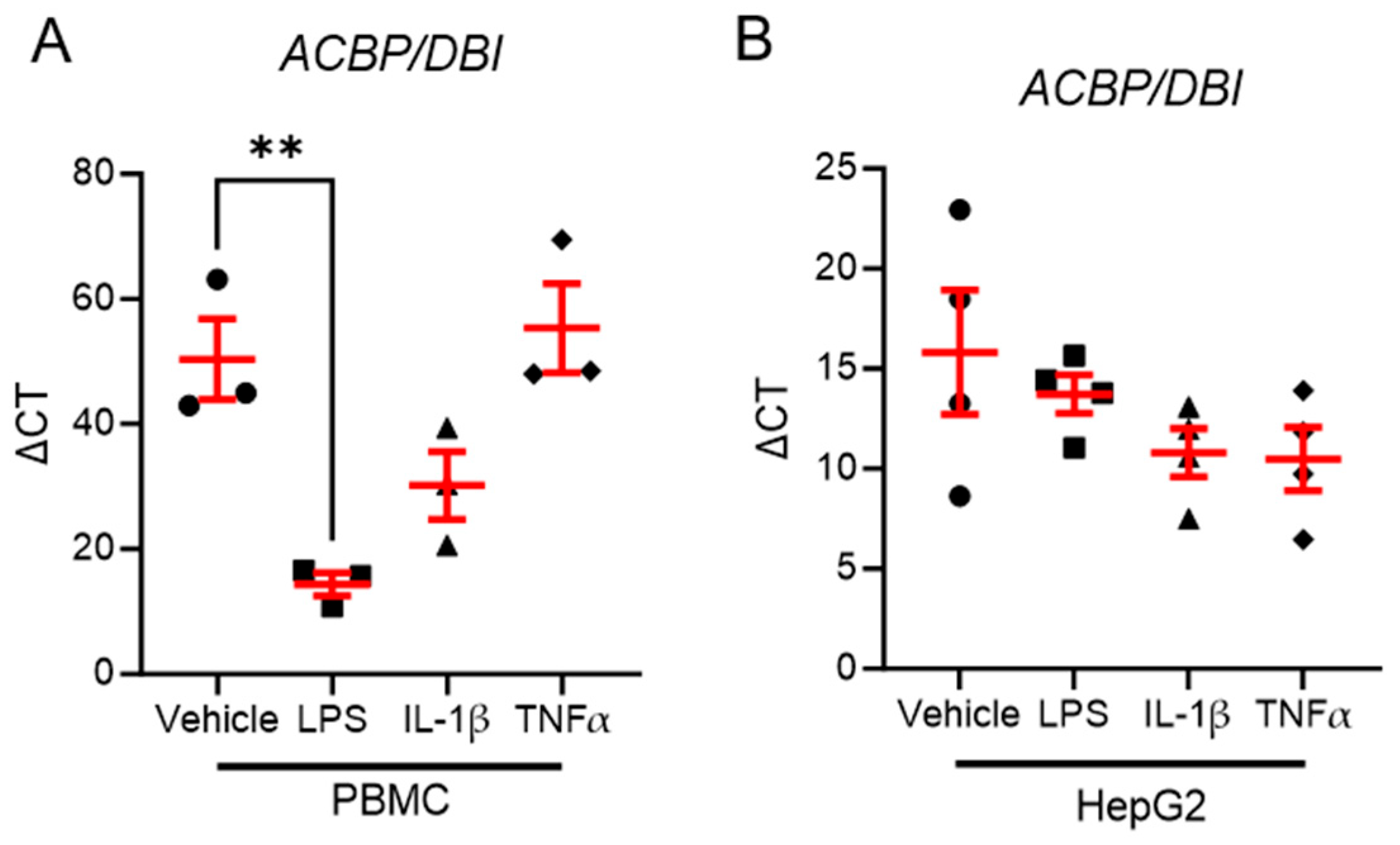
3.5. LPS Stimulation Reduces ACBP/DBI Expression in Human PBMCs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC). Worldwide trends in underweight and obesity from 1990 to 2022: A pooled analysis of 3663 population-representative studies with 222 million children, adolescents, and adults. Lancet 2024, 403, 1027–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Muniesa, P.; Mártinez-González, M.A.; Hu, F.B.; Després, J.P.; Matsuzawa, Y.; Loos, R.J.F.; Moreno, L.A.; Bray, G.A.; Martinez, J.A. Obesity. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles-Messance, H.; Mitchelson, K.A.J.; De Marco Castro, E.; Sheedy, F.J.; Roche, H.M. Regulating metabolic inflammation by nutritional modulation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 146, 706–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilg, H.; Zmora, N.; Adolph, T.E.; Elinav, E. The intestinal microbiota fuelling metabolic inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 40–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melson, E.; Ashraf, U.; Papamargaritis, D.; Davies, M.J. What is the pipeline for future medications for obesity? Int. J. Obes. 2024, 49, 433–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miras, A.D.; le Roux, C.W. Mechanisms underlying weight loss after bariatric surgery. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 10, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grander, C.; Jaschke, N.; Enrich, B.; Grabherr, F.; Mayr, L.; Schwärzler, J.; Effenberger, M.; Adolph, T.E.; Tilg, H. Gastric banding-associated weight loss diminishes hepatic Tsukushi expression. Cytokine 2020, 133, 155114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grander, C.; Grabherr, F.; Enrich, B.; Meyer, M.; Mayr, L.; Schwärzler, J.; Pedrini, A.; Effenberger, M.; Adolph, T.E.; Tilg, H. Hepatic Meteorin-like and Krüppel-like Factor 3 are Associated with Weight Loss and Liver Injury. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2021, 130, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moschen, A.R.; Molnar, C.; Wolf, A.M.; Weiss, H.; Graziadei, I.; Kaser, S.; Ebenbichler, C.F.; Stadlmann, S.; Moser, P.L.; Tilg, H. Effects of weight loss induced by bariatric surgery on hepatic adipocytokine expression. J. Hepatol. 2009, 51, 765–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adolph, T.E.; Grabherr, F.; Mayr, L.; Grander, C.; Enrich, B.; Moschen, A.R.; Tilg, H. Weight Loss Induced by Bariatric Surgery Restricts Hepatic GDF15 Expression. J. Obes. 2018, 2018, 7108075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedro, J.M.B.; Sica, V.; Madeo, F.; Kroemer, G. Acyl-CoA-binding protein (ACBP): The elusive ‘hunger factor’ linking autophagy to food intake. Cell Stress 2019, 3, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, A.; Moriceau, S.; Sica, V.; Anagnostopoulos, G.; Pol, J.; Martins, I.; Lafarge, A.; Maiuri, M.C.; Leboyer, M.; Loftus, J.; et al. Metabolic and psychiatric effects of acyl coenzyme A binding protein (ACBP)/diazepam binding inhibitor (DBI). Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christian, C.A.; Herbert, A.G.; Holt, R.L.; Peng, K.; Sherwood, K.D.; Pangratz-Fuehrer, S.; Rudolph, U.; Huguenard, J.R. Endogenous positive allosteric modulation of GABA(A) receptors by diazepam binding inhibitor. Neuron 2013, 78, 1063–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duran, J.M.; Anjard, C.; Stefan, C.; Loomis, W.F.; Malhotra, V. Unconventional secretion of Acb1 is mediated by autophagosomes. J. Cell Biol. 2010, 188, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjithaya, R.; Jain, S.; Farré, J.C.; Subramani, S. A yeast MAPK cascade regulates pexophagy but not other autophagy pathways. J. Cell Biol. 2010, 189, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bravo-San Pedro, J.M.; Sica, V.; Martins, I.; Pol, J.; Loos, F.; Maiuri, M.C.; Durand, S.; Bossut, N.; Aprahamian, F.; Anagnostopoulos, G.; et al. Acyl-CoA-Binding Protein Is a Lipogenic Factor that Triggers Food Intake and Obesity. Cell Metab. 2019, 30, 754–767.e759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, A.; Chen, H.; Anagnostopoulos, G.; Montégut, L.; Lafarge, A.; Motiño, O.; Castedo, M.; Maiuri, M.C.; Clément, K.; Terrisse, S.; et al. Effects of acyl-coenzyme A binding protein (ACBP)/diazepam-binding inhibitor (DBI) on body mass index. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motiño, O.; Lambertucci, F.; Anagnostopoulos, G.; Li, S.; Nah, J.; Castoldi, F.; Senovilla, L.; Montégut, L.; Chen, H.; Durand, S.; et al. ACBP/DBI protein neutralization confers autophagy-dependent organ protection through inhibition of cell loss, inflammation, and fibrosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2207344119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleiner, D.E.; Brunt, E.M.; Van Natta, M.; Behling, C.; Contos, M.J.; Cummings, O.W.; Ferrell, L.D.; Liu, Y.C.; Torbenson, M.S.; Unalp-Arida, A.; et al. Design and validation of a histological scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2005, 41, 1313–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunt, E.M.; Janney, C.G.; Di Bisceglie, A.M.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Bacon, B.R. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: A proposal for grading and staging the histological lesions. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1999, 94, 2467–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pucci, A.; Batterham, R.L. Mechanisms underlying the weight loss effects of RYGB and SG: Similar, yet different. J. Endocrinol. Invest. 2019, 42, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moschen, A.R.; Molnar, C.; Geiger, S.; Graziadei, I.; Ebenbichler, C.F.; Weiss, H.; Kaser, S.; Kaser, A.; Tilg, H. Anti-inflammatory effects of excessive weight loss: Potent suppression of adipose interleukin 6 and tumour necrosis factor alpha expression. Gut 2010, 59, 1259–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montégut, L.; Joseph, A.; Chen, H.; Abdellatif, M.; Ruckenstuhl, C.; Martins, I.; Madeo, F.; Kroemer, G. DBI/ACBP is a targetable autophagy checkpoint involved in aging and cardiovascular disease. Autophagy 2023, 19, 2166–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, S.; Thiemermann, C. Role of Metabolic Endotoxemia in Systemic Inflammation and Potential Interventions. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 594150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Lier, D.; Geven, C.; Leijte, G.P.; Pickkers, P. Experimental human endotoxemia as a model of systemic inflammation. Biochimie 2019, 159, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monte, S.V.; Caruana, J.A.; Ghanim, H.; Sia, C.L.; Korzeniewski, K.; Schentag, J.J.; Dandona, P. Reduction in endotoxemia, oxidative and inflammatory stress, and insulin resistance after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery in patients with morbid obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Surgery 2012, 151, 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera, L.O.; Trindade, E.N.; Leite, C.; Abegg, E.H.; Trindade, M.R.M. Preoperative Level of Leptin Can Be a Predictor of Glycemic Control for Patients with Diabetes Undergoing Bariatric Surgery. Obes. Surg. 2020, 30, 4829–4833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mechanick, J.I.; Apovian, C.; Brethauer, S.; Timothy Garvey, W.; Joffe, A.M.; Kim, J.; Kushner, R.F.; Lindquist, R.; Pessah-Pollack, R.; Seger, J.; et al. Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Perioperative Nutrition, Metabolic, and Nonsurgical Support of Patients Undergoing Bariatric Procedures—2019 Update: Cosponsored by American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists/American College of Endocrinology, The Obesity Society, American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery, Obesity Medicine Association, and American Society of Anesthesiologists. Obesity 2020, 28, O1–O58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seifert, G.; Fagnocchi, L.; Edozie, M.; Herrmann, S.; Baumann, H.; Panzeri, I.; Mewes, S.; Aicher, D.; Runkel, M.; Lässle, C.; et al. The DECON pilot project investigates predictive markers for successful bariatric surgery. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 13401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motiño, O.; Lambertucci, F.; Joseph, A.; Durand, S.; Anagnostopoulos, G.; Li, S.; Carbonnier, V.; Nogueira-Recalde, U.; Montégut, L.; Chen, H.; et al. ACBP/DBI neutralization for the experimental treatment of fatty liver disease. Cell Death Differ. 2024, 32, 434–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL); European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD); European Association for the Study of Obesity (EASO). EASL-EASD-EASO Clinical Practice Guidelines on the management of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD). J. Hepatol. 2024, 81, 492–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Parameter | TP0 | TP6 | n | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 37.23 ± 10.86 | - | 30 | - |
| Sex (F/M) | 25/5 (83%/17%) | - | 30 | - |
| Weight (kg) | 122.3 ± 18.8 | 102.3 ± 17.1 | 30 | <0.0001 |
| BMI | 42.69 ± 3.54 | 35.8 ± 4.52 | 30 | <0.0001 |
| HOMA-IR | 3.5 (2.7–6.8) | 2.4 (1.5–3.4) | 30 | <0.0001 |
| Insulin (µU/mL) | 15.30 (11.75–27.53) | 11.00 (7.08–14.68) | 30 | <0.0001 |
| Leptin (ng/mL) | 30.11 (26.37–32.31) | 17.04 (12.26–25.03) | 29 | <0.0001 |
| CRP (mg/dL) | 0.82 ± 0.46 | 0.63 ± 0.34 | 26 | 0.0081 |
| FIB-4 Score | 0.86 ± 0.48 | 0.84 ± 0.37 | 24 | 0.0248 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meyer, M.; Gruber, P.; Plattner, C.; Enrich, B.; Zollner, A.; Jukic, A.; Effenberger, M.; Grander, C.; Tilg, H.; Grabherr, F. Hepatic Expression of ACBP Is a Prognostic Marker for Weight Loss After Bariatric Surgery. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 1173. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15081173
Meyer M, Gruber P, Plattner C, Enrich B, Zollner A, Jukic A, Effenberger M, Grander C, Tilg H, Grabherr F. Hepatic Expression of ACBP Is a Prognostic Marker for Weight Loss After Bariatric Surgery. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(8):1173. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15081173
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeyer, Moritz, Paul Gruber, Christina Plattner, Barbara Enrich, Andreas Zollner, Almina Jukic, Maria Effenberger, Christoph Grander, Herbert Tilg, and Felix Grabherr. 2025. "Hepatic Expression of ACBP Is a Prognostic Marker for Weight Loss After Bariatric Surgery" Biomolecules 15, no. 8: 1173. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15081173
APA StyleMeyer, M., Gruber, P., Plattner, C., Enrich, B., Zollner, A., Jukic, A., Effenberger, M., Grander, C., Tilg, H., & Grabherr, F. (2025). Hepatic Expression of ACBP Is a Prognostic Marker for Weight Loss After Bariatric Surgery. Biomolecules, 15(8), 1173. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15081173





