In Silico and In Vivo Pharmacological Evaluation of Iridoid Compounds: Geniposide and Asperuloside Profile Study Through Molecular Docking Assay and in the Caenorhabditis elegans Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. In Silico and Docking Studies
2.1.1. Prediction of Physicochemical and ADME Properties
2.1.2. Prediction of Ability to Cross the BBB
2.1.3. Prediction of the GP and ASP Transport Mechanism at BBB
2.1.4. Docking Studies
2.2. In Vivo Studies in Caenorhabditis elegans
2.2.1. Compounds
2.2.2. Strains and Maintenance of C. elegans
2.2.3. Antioxidant Properties
2.2.4. Body Length Assay
2.2.5. Lethality Test and LC50 Estimation
2.2.6. Anticholinesterase Activity Assay
2.2.7. Graphical Representation and Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. In Silico and Docking Studies
3.1.1. Prediction of Physicochemical and ADME Properties
3.1.2. Prediction of Ability to Cross the BBB
3.1.3. Prediction of the GP and ASP Transport Mechanism
3.1.4. Docking Studies
3.2. In Vivo Studies in C. elegans
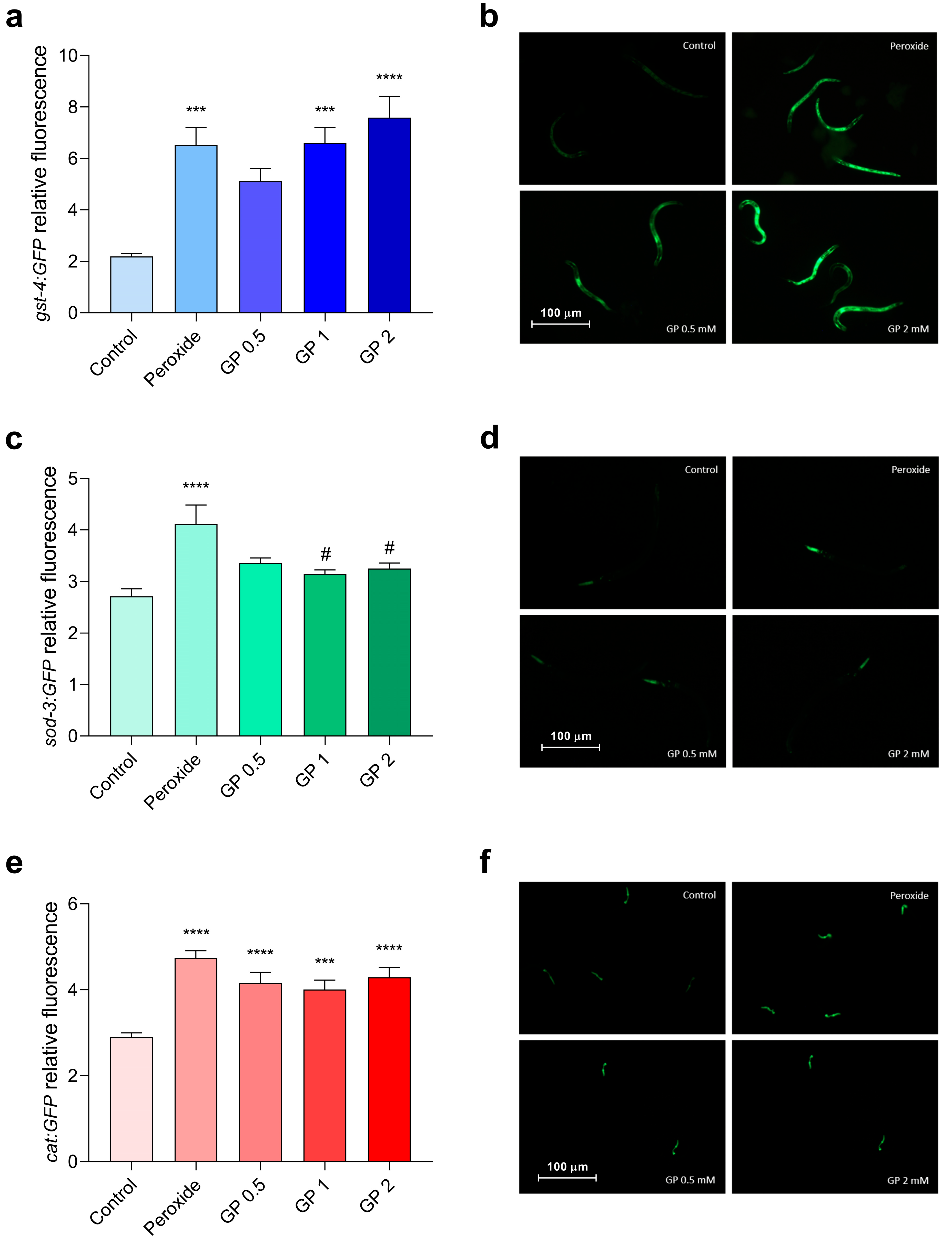
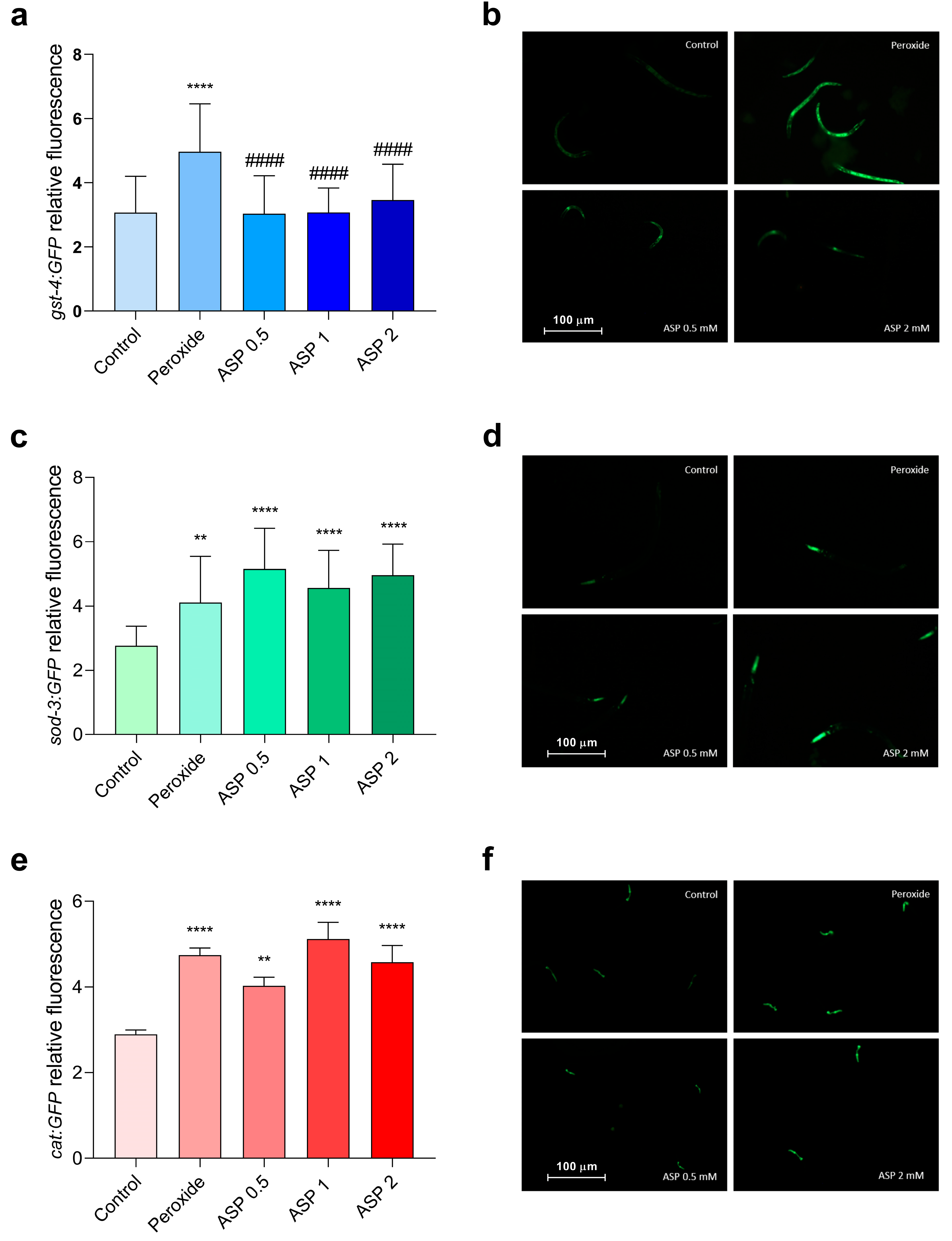
3.2.1. Antioxidant Properties of GP and ASP
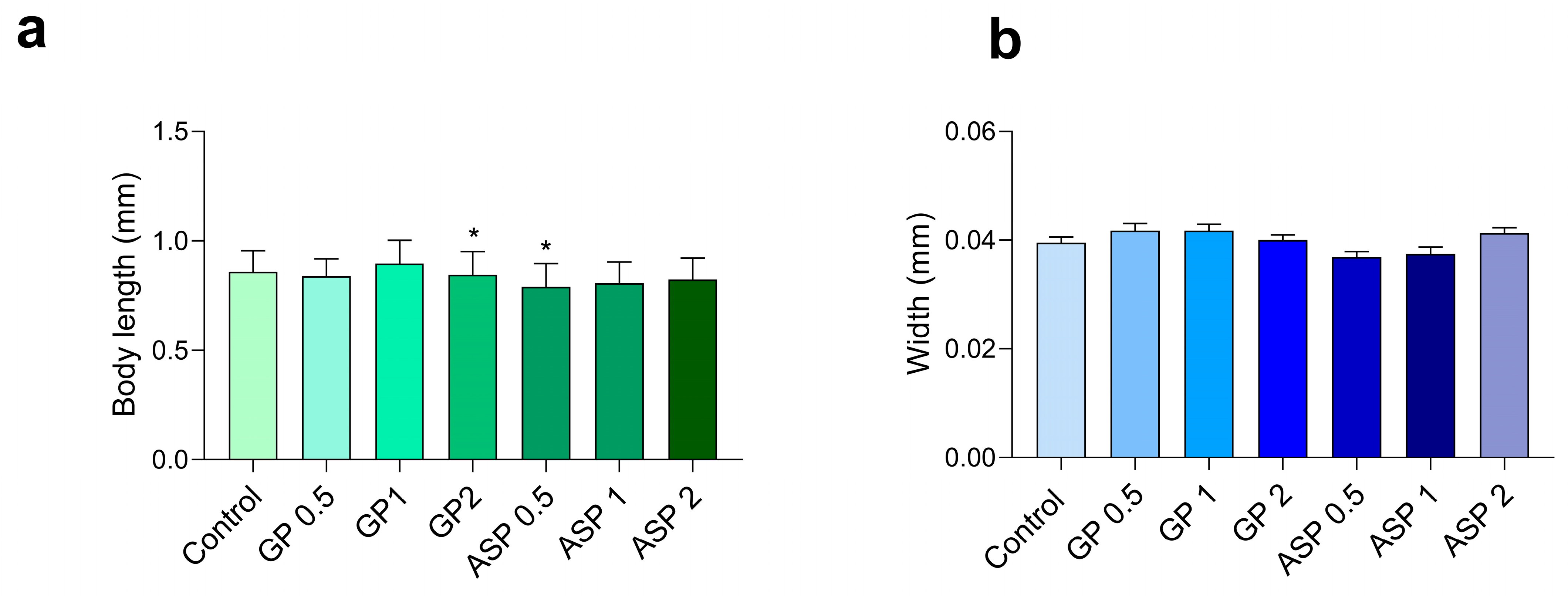
3.2.2. Body Size Assay
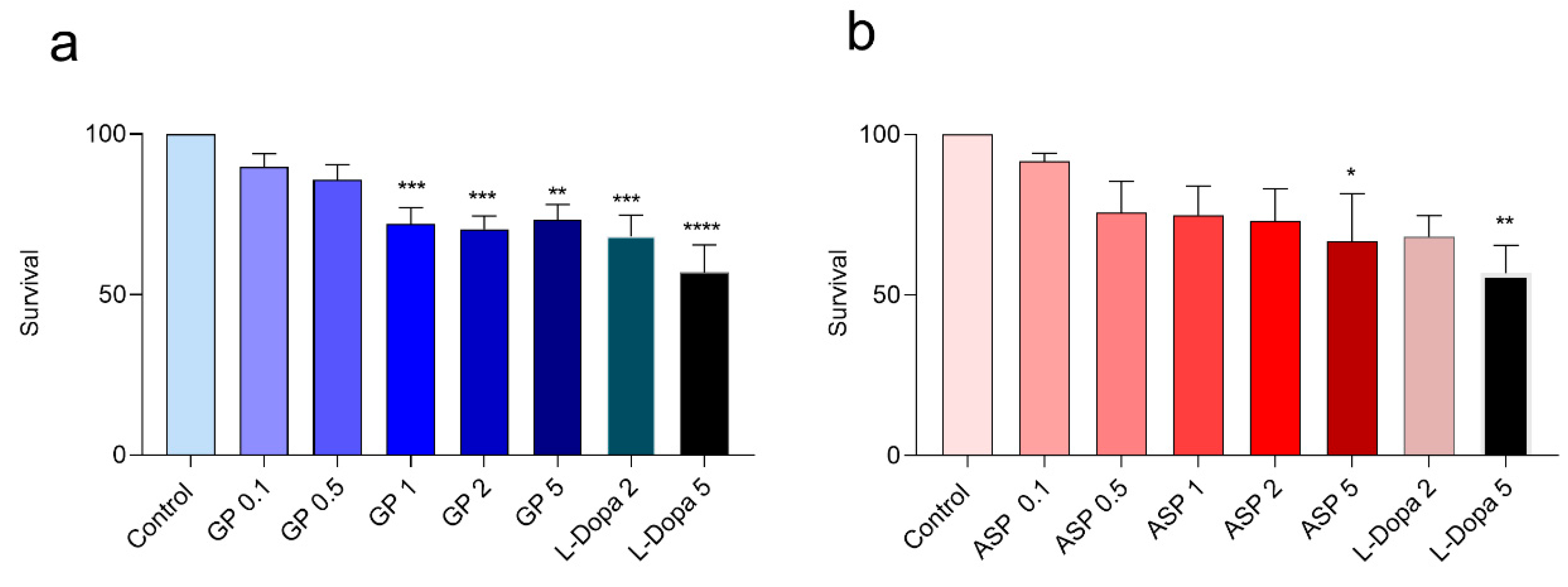
3.2.3. Survival Assay and LC50
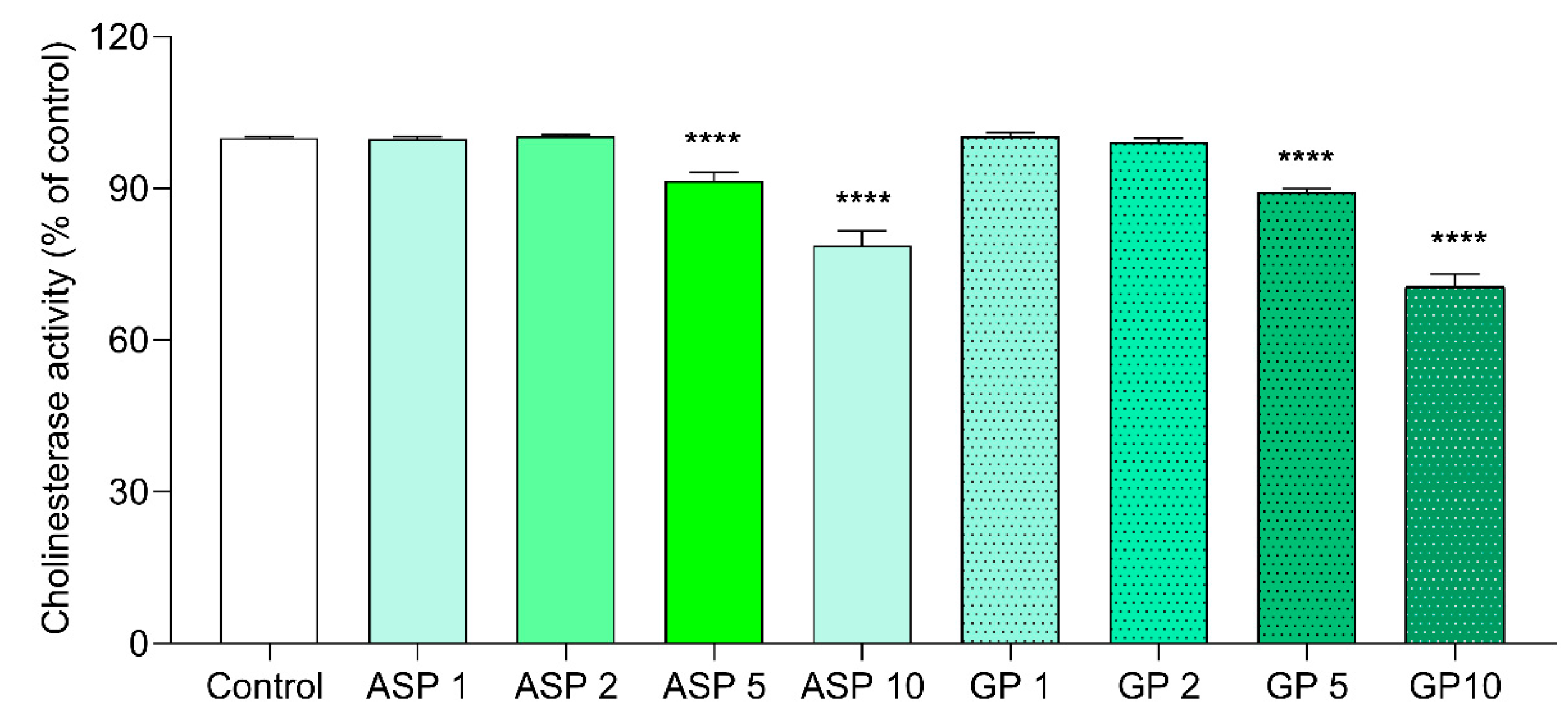
3.2.4. Anticholinesterase Activity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GP | Geniposide |
| ASP | Asperuloside |
| CNS | Central Nervous system |
| AChE | Acetylcholinesterase |
| BChE | Butyrylcholinesterase |
References
- Agnello, L.; Ciaccio, M. Neurodegenerative Diseases: From Molecular Basis to Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodryzlova, Y.; Mehrabi, F.; Bosson, A.; Maïano, C.; André, C.; Bélanger, E.; Moullec, G. The Potential of Social Policies in Preventing Dementia: An Ecological Study Using Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Aging Soc. Policy 2023, 36, 1004–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cummings, J.L.; Morstorf, T.; Zhong, K. Alzheimer’s Disease Drug-Development Pipeline: Few Candidates, Frequent Failures. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2014, 6, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joe, E.; Ringman, J.M. Cognitive Symptoms of Alzheimer’s Disease: Clinical Management and Prevention. BMJ 2019, 367, l6217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, P.N.H.; Baltos, J.A.; Hellyer, S.D.; May, L.T.; Gregory, K.J. Adenosine Receptor Signalling in Alzheimer’s Disease. Purinergic Signal 2022, 18, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, J.; Haider, N.; Khan, M.A.; Md, S.; Alhakamy, N.A.; Ghoneim, M.M.; Alshehri, S.; Sarim Imam, S.; Ahmad, M.Z.; Mishra, A. Novel Therapeutic Interventions for Combating Parkinson’s Disease and Prospects of Nose-to-Brain Drug Delivery. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2022, 195, 114849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalia, L.V.; Lang, A.E. Parkinson’s Disease. Lancet 2015, 386, 896–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schapira, A.H.V.; Chaudhuri, K.R.; Jenner, P. Non-Motor Features of Parkinson Disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2017, 18, 435–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schapira, A.H.V.; Bezard, E.; Brotchie, J.; Calon, F.; Collingridge, G.L.; Ferger, B.; Hengerer, B.; Hirsch, E.; Jenner, P.; Novère, N.L.; et al. Novel Pharmacological Targets for the Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2006, 5, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, K.; Yamafuji, M.; Nakabeppu, Y.; Noda, M. Therapeutic Approach to Neurodegenerative Diseases by Medical Gases: Focusing on Redox Signaling and Related Antioxidant Enzymes. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2012, 324256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhou, L.; An, D.; Xu, W.; Wu, C.; Sha, S.; Li, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, A.; Du, Y.; et al. TRPV4-Induced Inflammatory Response Is Involved in Neuronal Death in Pilocarpine Model of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy in Mice. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.X.; Zhang, R.Q.; Rahman, K.; Cao, Z.X.; Zhang, H.; Peng, C. Diverse Pharmacological Activities and Potential Medicinal Benefits of Geniposide. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 4925682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Huang, C.; Zong, G.; Zha, D.; Meng, X.; Li, J.; Tang, W. Hepatoprotective Effects of Geniposide in a Rat Model of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2011, 63, 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.Q.; Chang, G.L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, D.Y.; Cao, L.; Liu, J. Geniposide Prevents Hypoxia/Reoxygenation-Induced Apoptosis in H9c2 Cells: Improvement of Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Activation of GLP-1R and the PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 39, 407–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Duan, G.; He, J.; Meng, Q.; Liu, Y.; Chen, W.; Meng, Y. Geniposide Attenuates Epilepsy Symptoms in a Mouse Model through the PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β Signaling Pathway. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 15, 1136–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.; Lee, J.; Choi, S.Y.; Lee, S.E.; Lee, S.; Son, D. Geniposide from Gardenia Jasminoides Attenuates Neuronal Cell Death in Oxygen and Glucose Deprivation-Exposed Rat Hippocampal Slice Culture. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2006, 29, 174–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, L.; Hölscher, C. Neuroprotective Effects of Geniposide in the MPTP Mouse Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 768, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Zhang, H.; Li, H.; Lv, C.; Liu, X.; Li, Z.; Xin, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, W. Geniposide Ameliorates Cognitive Deficits by Attenuating the Cholinergic Defect and Amyloidosis in Middle-Aged Alzheimer Model Mice. Neuropharmacology 2017, 116, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, C.; Liu, X.; Liu, H.; Chen, T.; Zhang, W. Geniposide Attenuates Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Memory Deficits in APP/PS1 Transgenic Mice. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2014, 11, 580–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirata, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Wada, A.; Ueda, T.; Fujikawa, T.; Miyashita, H.; Ikeda, T.; Tsukamoto, S.; Nohara, T. Anti-Obesity Compounds in Green Leaves of Eucommia Ulmoides. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 1786–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Lu, X.; Wei, T.; Dong, Y.; Cai, Z.; Tang, L.; Liu, M. Asperuloside and Asperulosidic Acid Exert an Anti-Inflammatory Effect via Suppression of the NF-ΚB and MAPK Signaling Pathways in LPS-Induced RAW 264.7 Macrophages. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, L.; Lv, M.; Pei, R.; Li, P.; Pei, Z.; Wang, Y.; Su, W.; Xie, X.Q. AlzPlatform: An Alzheimer’s Disease Domain-Specific Chemogenomics Knowledgebase for Polypharmacology and Target Identification Research. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2014, 54, 1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vendruscolo, M.H.; das Neves, G.M.; Kagami, L.P.; Rodrigues Junior, L.C.; Nunes Diehl, M.L.; Gnoatto, S.C.B.; de Loreto Bordignon, S.A.; Romão, P.R.T.; Eifler-Lima, V.L.; von Poser, G.L. In Vitro and in Silico Activity of Iridoids Against Leishmania Amazonensis. Curr. Drug Discov. Technol. 2018, 16, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Amrouche, A.T.; Huang, W.; Lu, B. Asperuloside, the Bioactive Compound in the Edible Eucommia Ulmoides Male Flower, Delays Muscle Aging by Daf-16 Mediated Improvement in Mitochondrial Dysfunction. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 5562–5575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, B.; Li, M.; Liu, J.P.; Yang, H.L.; Shi, Y.H. Baicalin and Geniposide Inhibit Polarization and Inflammatory Injury of OGD/R-Treated Microglia by Suppressing the 5-LOX/LTB4 Pathway. Neurochem. Res. 2021, 46, 1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Dai, Y.; Gu, R.; Jiang, R. Geniposide Protects PC12 Cells from Lipopolysaccharide-Evoked Inflammatory Injury via up-Regulation of MiR-145-5p. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 2875–2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umar, M.; Hussain, M.; Maloney, S.K. Assessment of Cholinesterase Inhibition Activity of Birds Inhabiting Pesticide Exposed Croplands and Protected Area in Hot Semi-Arid Region of Pakistan. Braz. J. Biol. 2021, 83, e248842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, R.A. Levodopa: Past, Present, and Future. Eur. Neurol. 2009, 62, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, N.J.; Patabendige, A.A.K.; Dolman, D.E.M.; Yusof, S.R.; Begley, D.J. Structure and Function of the Blood-Brain Barrier. Neurobiol. Dis. 2010, 37, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohtsuki, S.; Terasaki, T. Contribution of Carrier-Mediated Transport Systems to the Blood-Brain Barrier as a Supporting and Protecting Interface for the Brain; Importance for CNS Drug Discovery and Development. Pharm. Res. 2007, 24, 1745–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoni, E.; Daniele, S.; Bottegoni, G.; Pizzirani, D.; Trincavelli, M.L.; Goldoni, L.; Tarozzo, G.; Reggiani, A.; Martini, C.; Piomelli, D.; et al. Combining Galantamine and Memantine in Multitargeted, New Chemical Entities Potentially Useful in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 9708–9721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansch, C.; Björkroth, J.P.; Leo, A. Hydrophobicity and Central Nervous System Agents: On the Principle of Minimal Hydrophobicity in Drug Design. J. Pharm. Sci. 1987, 76, 663–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osterberg, T.; Norinder, U. Theoretical calculation and prediction of P-glycoprotein-interacting drugs using MolSurf parametrization and PLS statistics. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2000, 10, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benet, L.Z.; Hosey, C.M.; Ursu, O.; Oprea, T.I. BDDCS, the Rule of 5 and Drugability. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 101, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pajouhesh, H.; Lenz, G.R. Medicinal Chemical Properties of Successful Central Nervous System Drugs. NeuroRx 2005, 2, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leeson, P.D.; Davis, A.M. Time-Related Differences in the Physical Property Profiles of Oral Drugs. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 6338–6348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Chi, G.; Wu, Q.; Ren, Y.; Chen, C.; Feng, H.; Chan, Y.; Ng, S.W.; Xin Tan, J.Z.; Gupta, G.; et al. Pretreatment with the Compound Asperuloside Decreases Acute Lung Injury via Inhibiting MAPK and NF-ΚB Signaling in a Murine Model. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2018, 19, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, K.; Zhao, L.; Luo, X.; Zhang, C.; Hou, P.; Bi, K.; Chen, X. An LC-MS Method for Simultaneous Determination of Five Iridoids from Zhi-Zi-Chi Decoction in Rat Brain Microdialysates and Tissue Homogenates: Towards an in Depth Study for Its Antidepressive Activity. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2014, 965, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, Y.; Li, Z.; Yang, T.; Shen, X.; Wang, X.; Li, H.; Zhou, K.; Li, L.; Xia, Z.; Zheng, X.; et al. Therapeutic Potential of Plant Iridoids in Depression: A Review. Pharm. Biol. 2022, 60, 2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, C.; Nieto, O.; Fontenla, J.A.; Rivas, E.; De Ceballos, M.L.; Fernandez-Mayoralas, A. Synthesis of Glycosyl Derivatives as Dopamine Prodrugs: Interaction with Glucose Carrier GLUT-1. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2003, 1, 767–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temizyürek, A.; Yılmaz, C.U.; Emik, S.; Akcan, U.; Atış, M.; Orhan, N.; Arıcan, N.; Ahishali, B.; Tüzün, E.; Küçük, M.; et al. Blood-Brain Barrier Targeted Delivery of Lacosamide-Conjugated Gold Nanoparticles: Improving Outcomes in Absence Seizures. Epilepsy Res. 2022, 184, 106939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rankovic, Z. CNS Drug Design: Balancing Physicochemical Properties for Optimal Brain Exposure. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 58, 2584–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Chen, P.; Huang, L.; Li, S.; Zhu, R.; Sheng, T.; Yu, W.; Chen, Z.; Wang, T. Geniposide Attenuates Post-Ischaemic Neurovascular Damage via GluN2A/AKT/ ERK-Dependent Mechanism. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 43, 705–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Chen, B.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Y.; He, Z.; Cai, X.; Qin, Y.; Ye, J.; Yang, Y.; Shen, J.; et al. Geniposide Protects against Neurotoxicity in Mouse Models of Rotenone-Induced Parkinson’s Disease Involving the MTOR and Nrf2 Pathways. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 318, 116914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Tan, L.; Yu, S.; Song, J.; Li, Z.; Peng, X.; Wei, Q.; He, Z.; Zhang, W.; Yang, X. Geniposide Reduced Oxidative Stress-Induced Apoptosis in HK-2 Cell through PI3K/AKT3/FOXO1 by M6A Modification. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 131, 111820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D. Molecular Toxicology in Caenorhabditis Elegans; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 1–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejeda-Benitez, L.; Olivero-Verbel, J. Caenorhabditis elegans, a Biological Model for Research in Toxicology. In Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; Volume 237, pp. 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
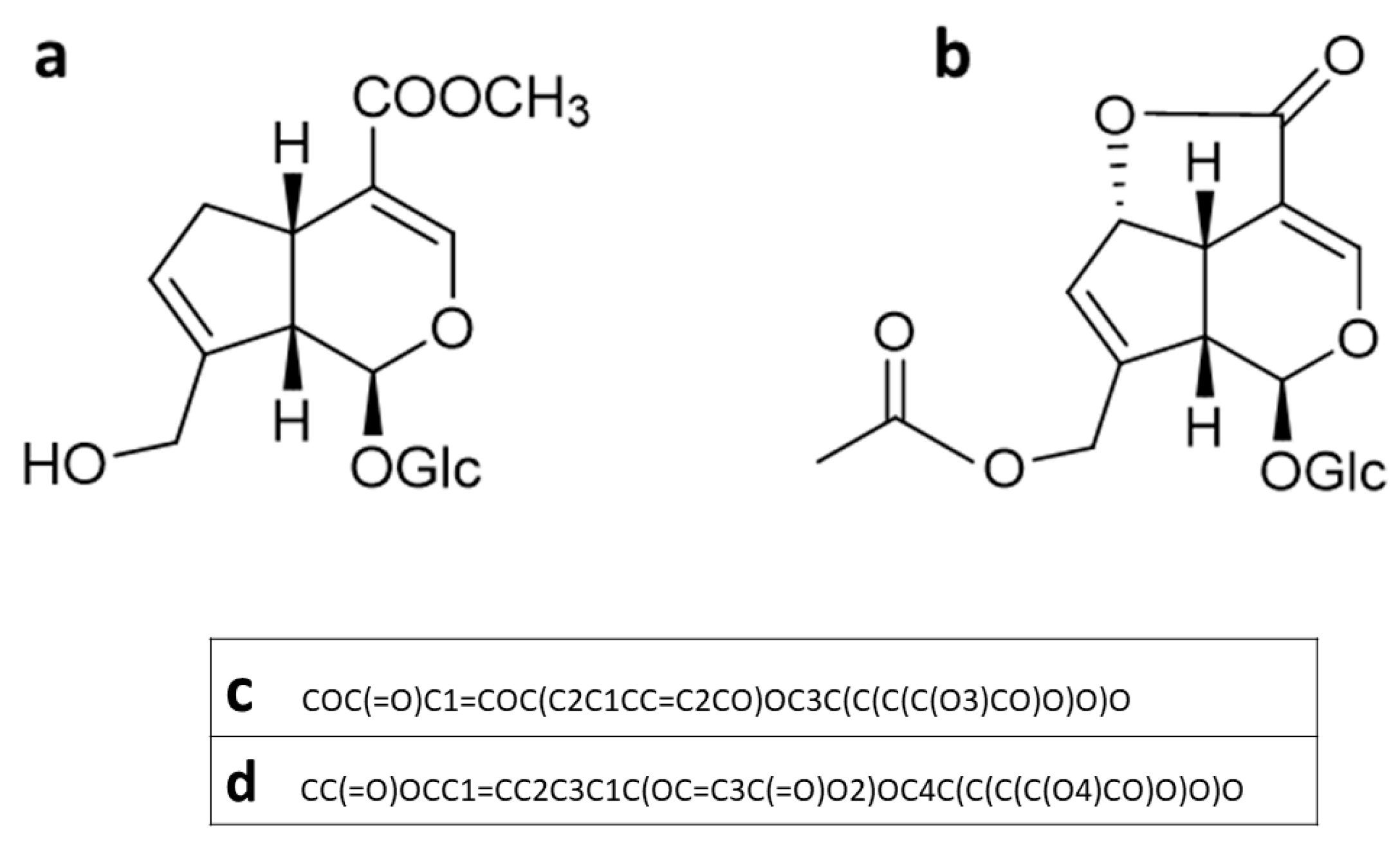
| miLogP | MW | nON | nOHNH | NV | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Geniposide | −1.53 | 388.37 | 10 | 5 | 0 |
| Asperuloside | −2.65 | 414.36 | 11 | 4 | 1 |
| Galantamine | 1.54 | 287.36 | 4 | 1 | 0 |
| Donepezil | 4.10 | 379.50 | 4 | 0 | 0 |
| L-Dopa | −2.20 | 197.19 | 5 | 5 | 0 |
| Apomorphine | 2.89 | 267.33 | 3 | 2 | 0 |
| TPSA | Nrotb | MV | Water Solubility (log mol/L) | Caco2 Permeability | Unbound % | VDss | Ctot | Abs (% Absorbed) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Geniposide | 155.15 | 6 | 331.54 | −2.81 | 0.35 | 0.66 | −0.22 | 1.40 | 41.63 |
| Asperuloside | 161.22 | 6 | 340.68 | −3.27 | 0.38 | 0.58 | −0.19 | 1.21 | 51.52 |
| Galantamine | 41.93 | 1 | 268.19 | −2.64 | 0.89 | 0.36 | 0.89 | 0.99 | 94.99 |
| Donepezil | 38.78 | 6 | 367.89 | −4.97 | 1.10 | 0.03 | 1.25 | 1.01 | 93.76 |
| L-Dopa | 103.78 | 3 | 172.00 | −2.89 | −0.28 | 0.60 | −0.10 | 0.43 | 47.74 |
| Apomorphine | 43.69 | 0 | 246.38 | −3.94 | 1.18 | 0.16 | 1.18 | 0.98 | 94.22 |
| AdaBust | SVM | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug | MACCS | Open Babel | MolPrint | PubChem | MACCS | Open Babel | MolPrint | PubChem | |
| Geniposide | −0.850 | 1.488 | −2.174 | 7.957 | −0.031 | −0.096 | 0.136 | −0.284 | |
| Asperuloside | 0.786 | −3.390 | −3.198 | 6.057 | −0.053 | −0.140 | 0.033 | −0.280 | |
| AD | Galantamine | 7.509 | 7.849 | 11.736 | 14.128 | 0.154 | 0.091 | 0.649 | 0.346 |
| Donepezil | 5.214 | 6.608 | 10.430 | 19.401 | 0.135 | 0.086 | 0.433 | 0.380 | |
| PD | L-Dopa | −2.057 | −1.150 | −173.760 | −1.221 | −0.032 | −0.084 | 0.681 | −0.112 |
| Apomorphine | 2.326 | 4.772 | 1.996 | 7.093 | 0.071 | 0.063 | 0.288 | 0.222 | |
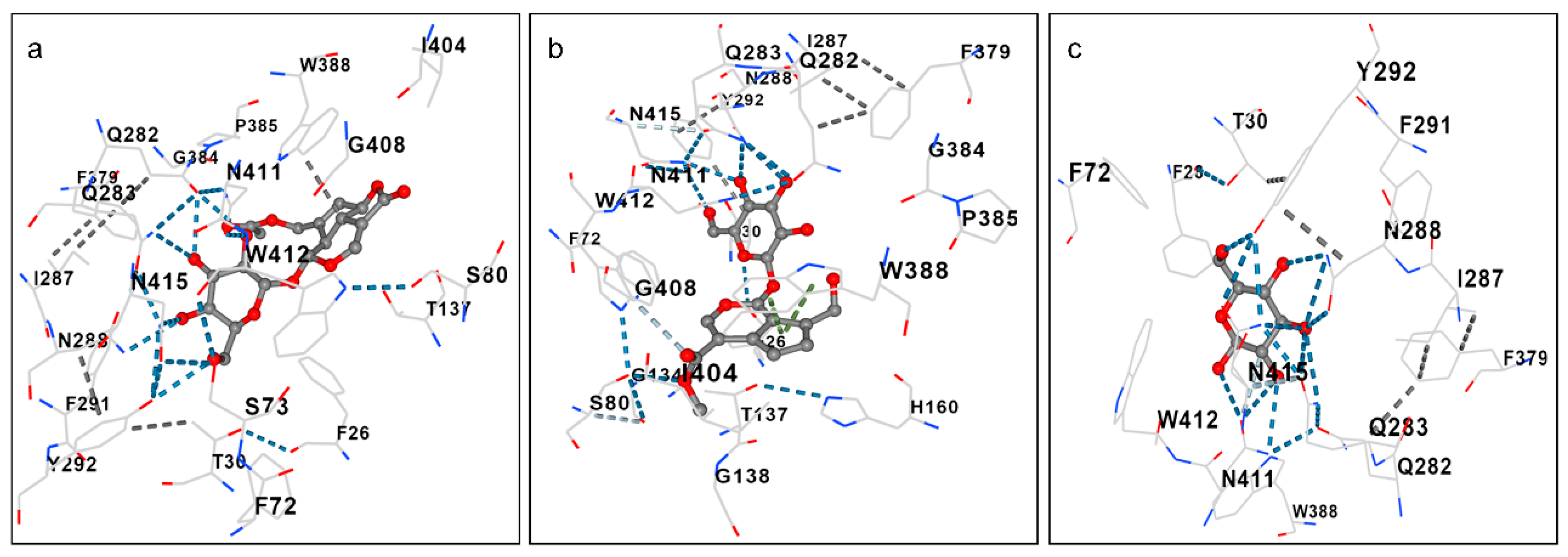
| GLUT-1 (kcal/mol) | Interactions | |
|---|---|---|
| GP | −8.3 | PHE26 THR30 PHE72 ILE164 VAL165 ILE168 GLN279 GLN282 GLN283 ASN288PHE291 TYR292 ASN317 THR321 PHE379 GLU380 PRO383 GLY384 PRO385 TRP388ASN411 TRP412 ASN415 |
| ASP | −7.4 | PHE26 THR30 PHE72 SER73 SER80 THR137 GLN282 GLN283ILE287 ASN288 TYR292 PHE379 GLY384 PRO385 TRP388 ILE404 GLY408 ASN411 TRP412 ASN415 |
| D-glucose | −5.1 | ILE164 ILE168 GLN282 GLN283 ILE287 ASN288 PHE291 TYR292 PHE379 GLY384 TRP388 ASN411 ASN415 |
| P-gp Substrate | P-gp Inhibitor | |
|---|---|---|
| Geniposide | Yes | No |
| Asperuloside | Yes | No |
| Galantamine | No | No |
| Donepezil | Yes | Yes |
| L-dopa | Yes | No |
| Apomorphine | Yes | No |
| AChE (Ki) | BChE (Ki) | AChE (Ki)/BChE (Ki) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| GP | 9.3 | 9.2 | 1.0109 |
| ASP | 9.5 | 9.4 | 1.0106 |
| Galantamine | 10 | 8 | 1.2500 |
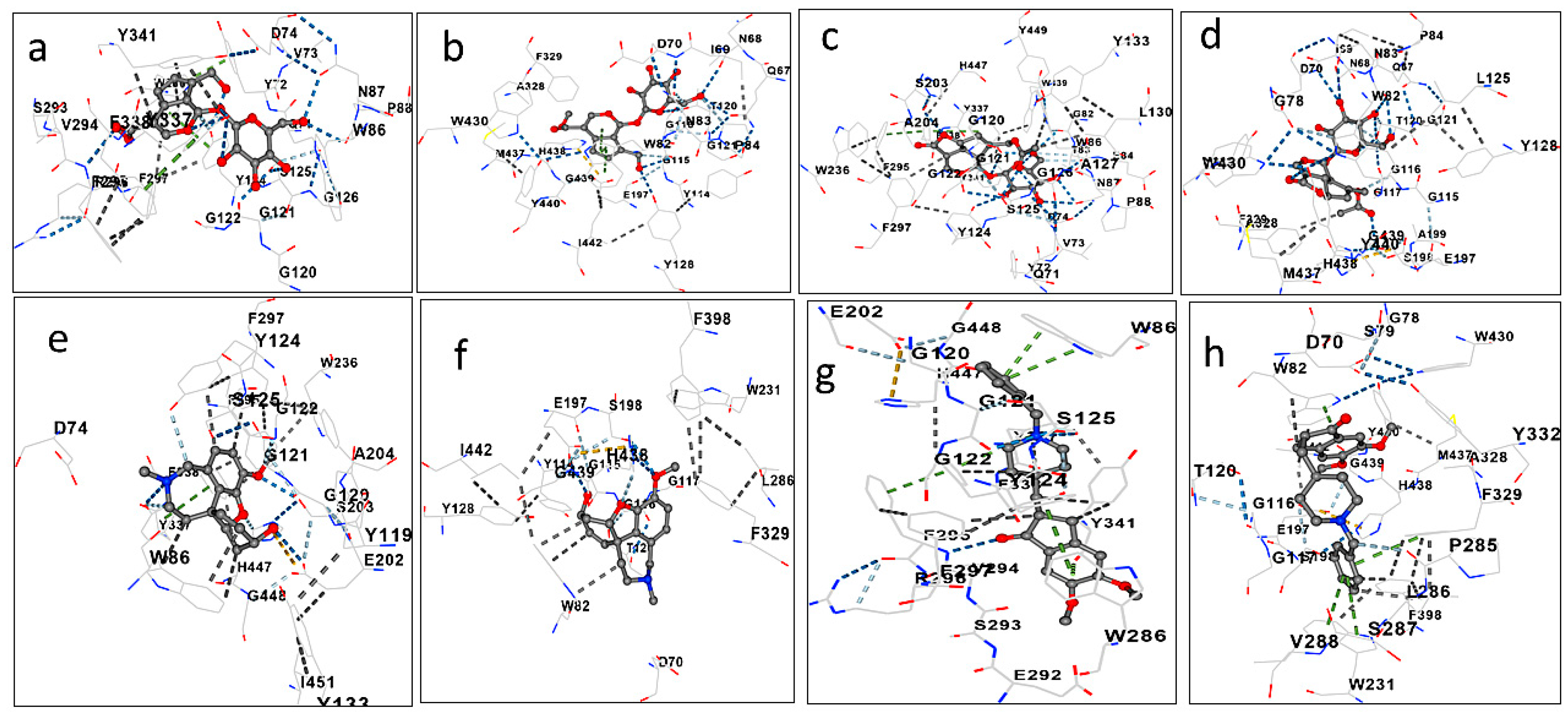
| AChE (PDB: 4EY6) | BChE (PDB: 4TPK) | |
|---|---|---|
| Geniposide | −8.8 | −9.1 |
| Asperuloside | −8.0 | −8.7 |
| Galantamine | −10.3 | −8.6 |
| Donepezil | −10.3 | −9.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Uczay, M.; Santos, P.A.; Pflüger, P.; von Poser, G.; Brea, J.; Loza, M.I.; Pereira, P.; Fontenla, J.A. In Silico and In Vivo Pharmacological Evaluation of Iridoid Compounds: Geniposide and Asperuloside Profile Study Through Molecular Docking Assay and in the Caenorhabditis elegans Model. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 1105. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15081105
Uczay M, Santos PA, Pflüger P, von Poser G, Brea J, Loza MI, Pereira P, Fontenla JA. In Silico and In Vivo Pharmacological Evaluation of Iridoid Compounds: Geniposide and Asperuloside Profile Study Through Molecular Docking Assay and in the Caenorhabditis elegans Model. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(8):1105. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15081105
Chicago/Turabian StyleUczay, Mariana, Péterson Alves Santos, Pricila Pflüger, Gilsane von Poser, José Brea, Maria Isabel Loza, Patrícia Pereira, and José Angel Fontenla. 2025. "In Silico and In Vivo Pharmacological Evaluation of Iridoid Compounds: Geniposide and Asperuloside Profile Study Through Molecular Docking Assay and in the Caenorhabditis elegans Model" Biomolecules 15, no. 8: 1105. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15081105
APA StyleUczay, M., Santos, P. A., Pflüger, P., von Poser, G., Brea, J., Loza, M. I., Pereira, P., & Fontenla, J. A. (2025). In Silico and In Vivo Pharmacological Evaluation of Iridoid Compounds: Geniposide and Asperuloside Profile Study Through Molecular Docking Assay and in the Caenorhabditis elegans Model. Biomolecules, 15(8), 1105. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15081105








