A Natural Polyphenol, Chlorogenic Acid, Attenuates Obesity-Related Metabolic Disorders in Male Rats via miR-146a-IRAK1-TRAF6 and NRF2-Mediated Antioxidant Pathways
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
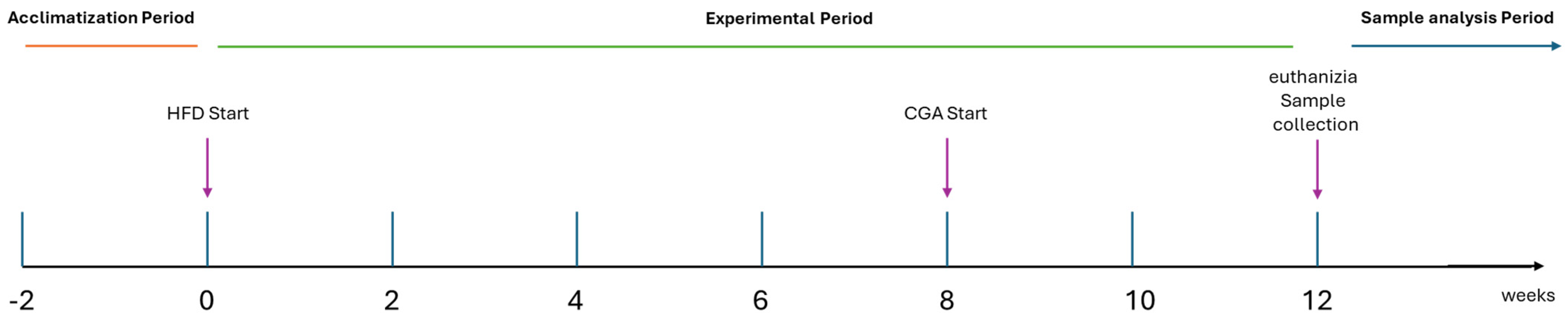
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Tissue and Blood Sampling
2.4. Biochemical Analysis
2.5. Real-Time PCR Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Metabolic and Anthropometric Effects of HFD and CGA Administration
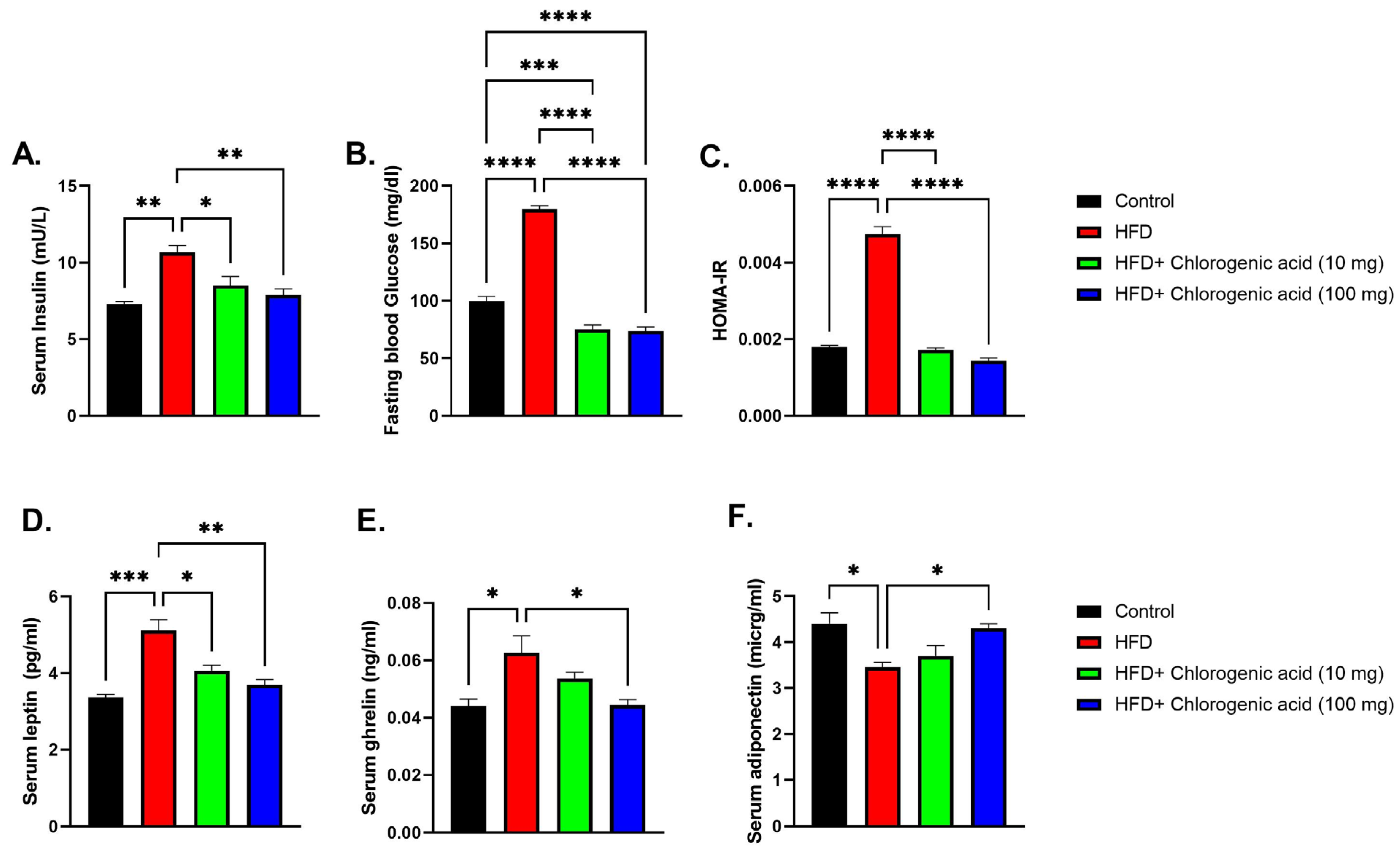
3.2. Effects of HFD and CGA on Metabolic Hormones
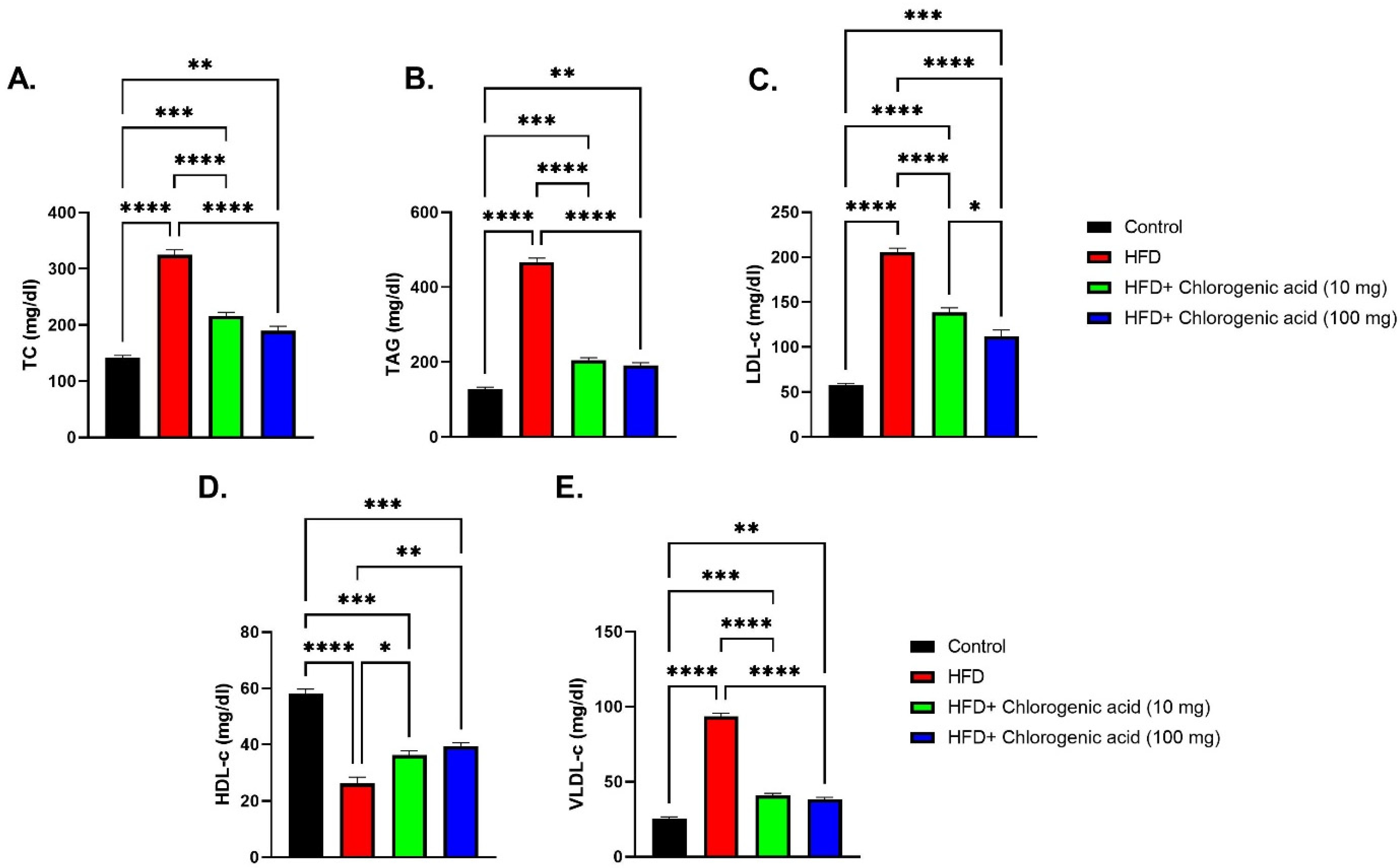
3.3. Effects of HFD and CGA on Lipid Profile
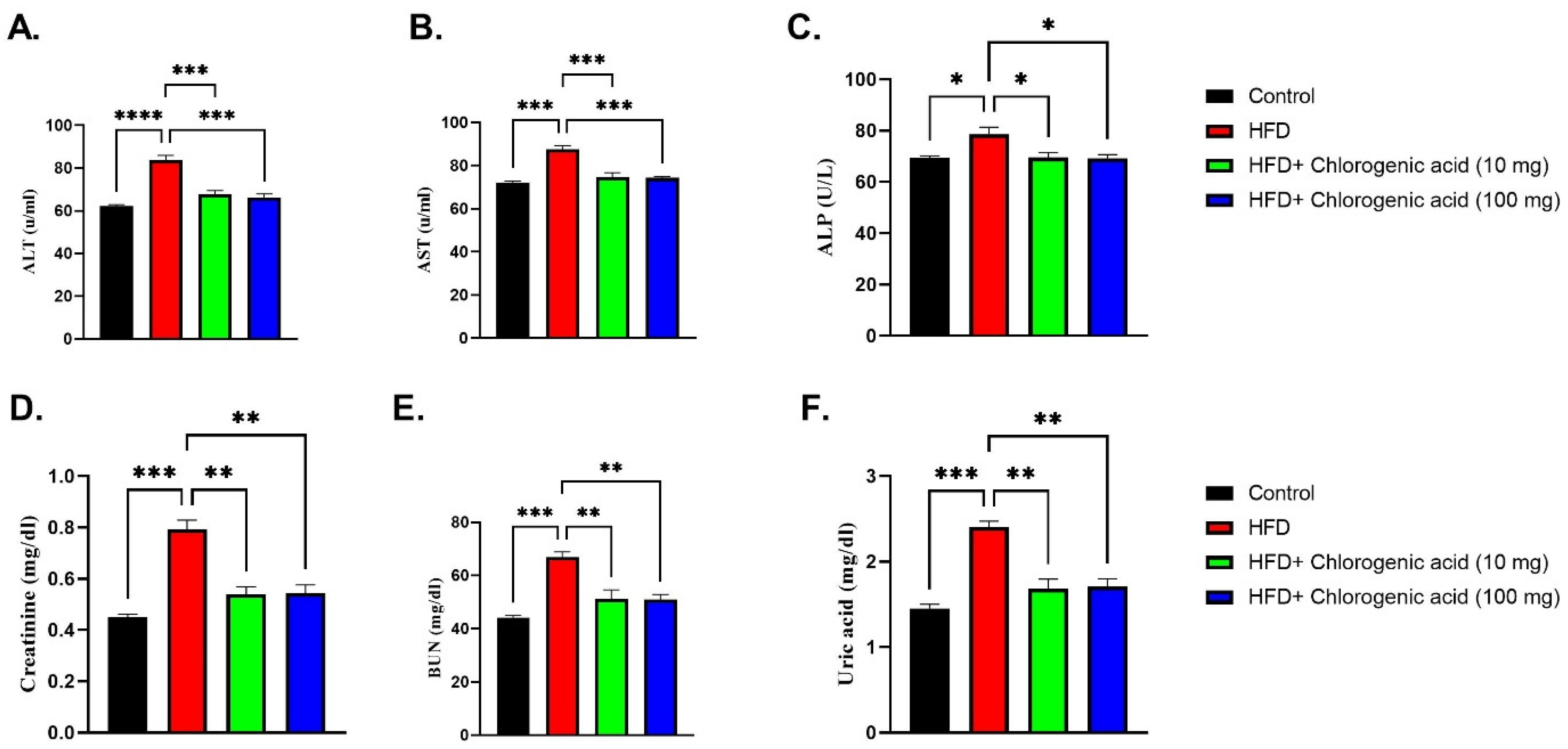
3.4. Effects of HFD and CGA on Hepatic and Renal Function Biomarkers
3.5. Effects of HFD and CGA on Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Cytokines
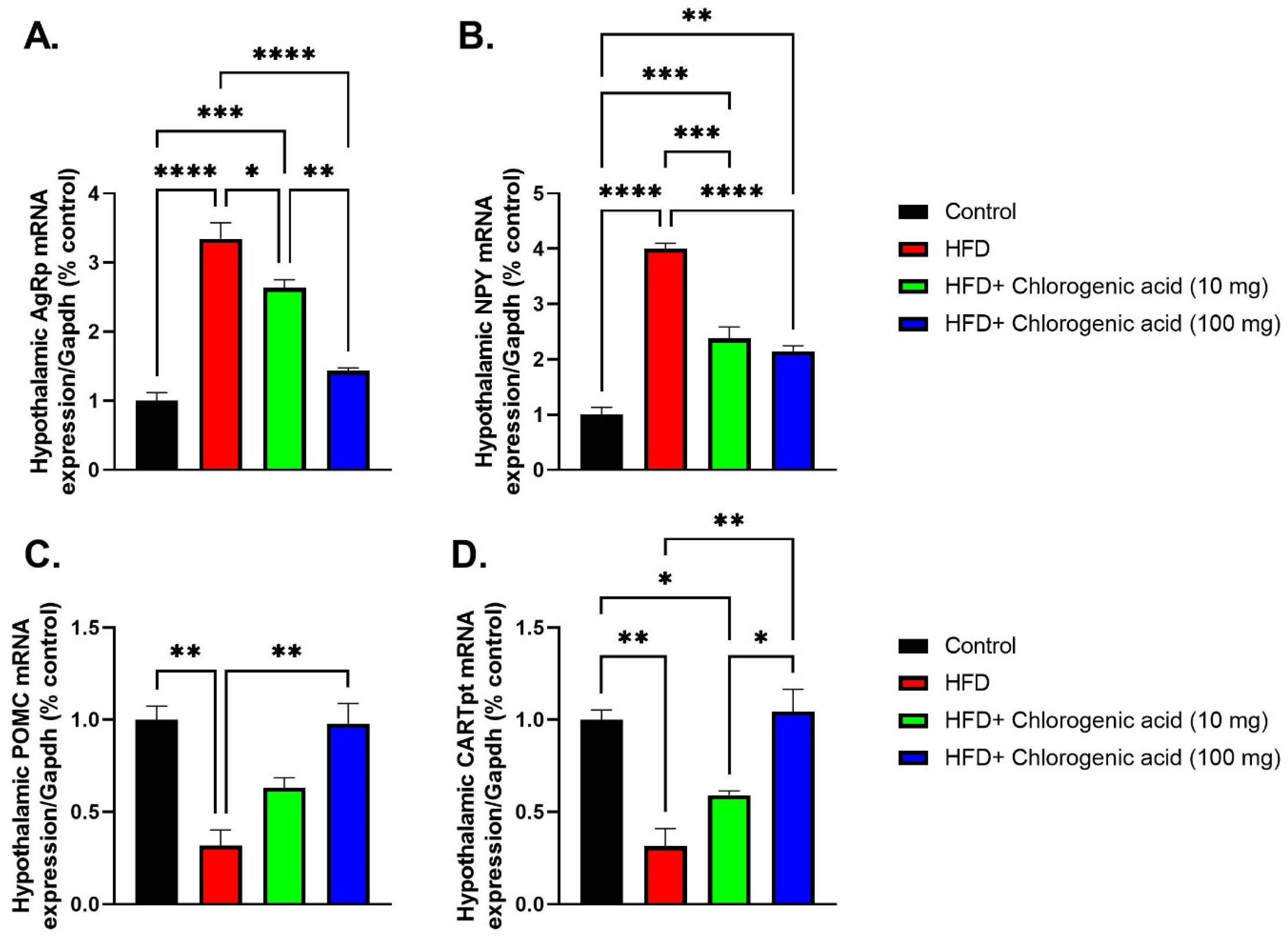
3.6. Effects of HFD and CGA on Hypothalamic Appetite-Regulating Gene Expression
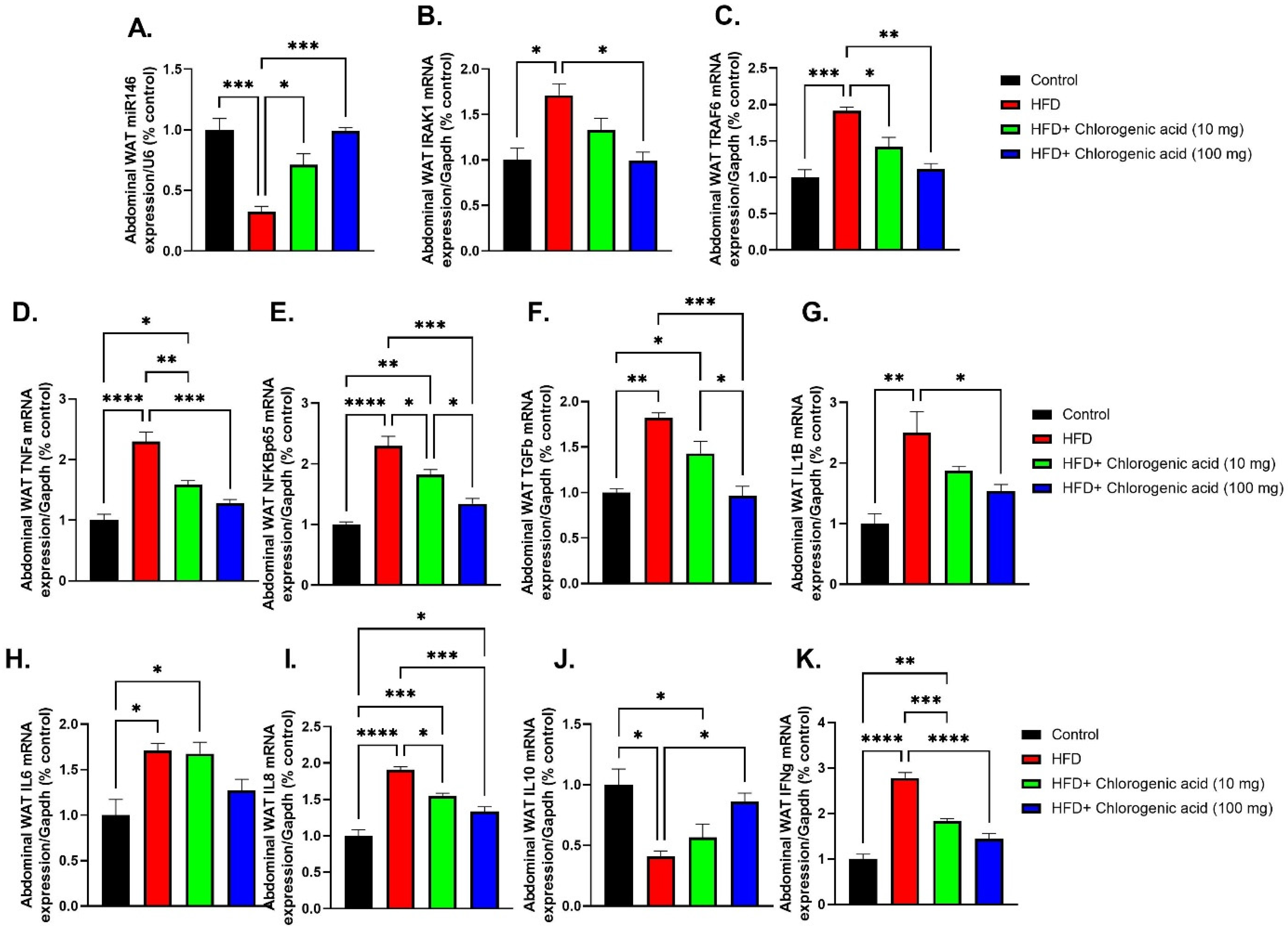
3.7. Effects of HFD and CGA on Abdominal WAT Inflammatory Gene Expression and miR-146a Regulation
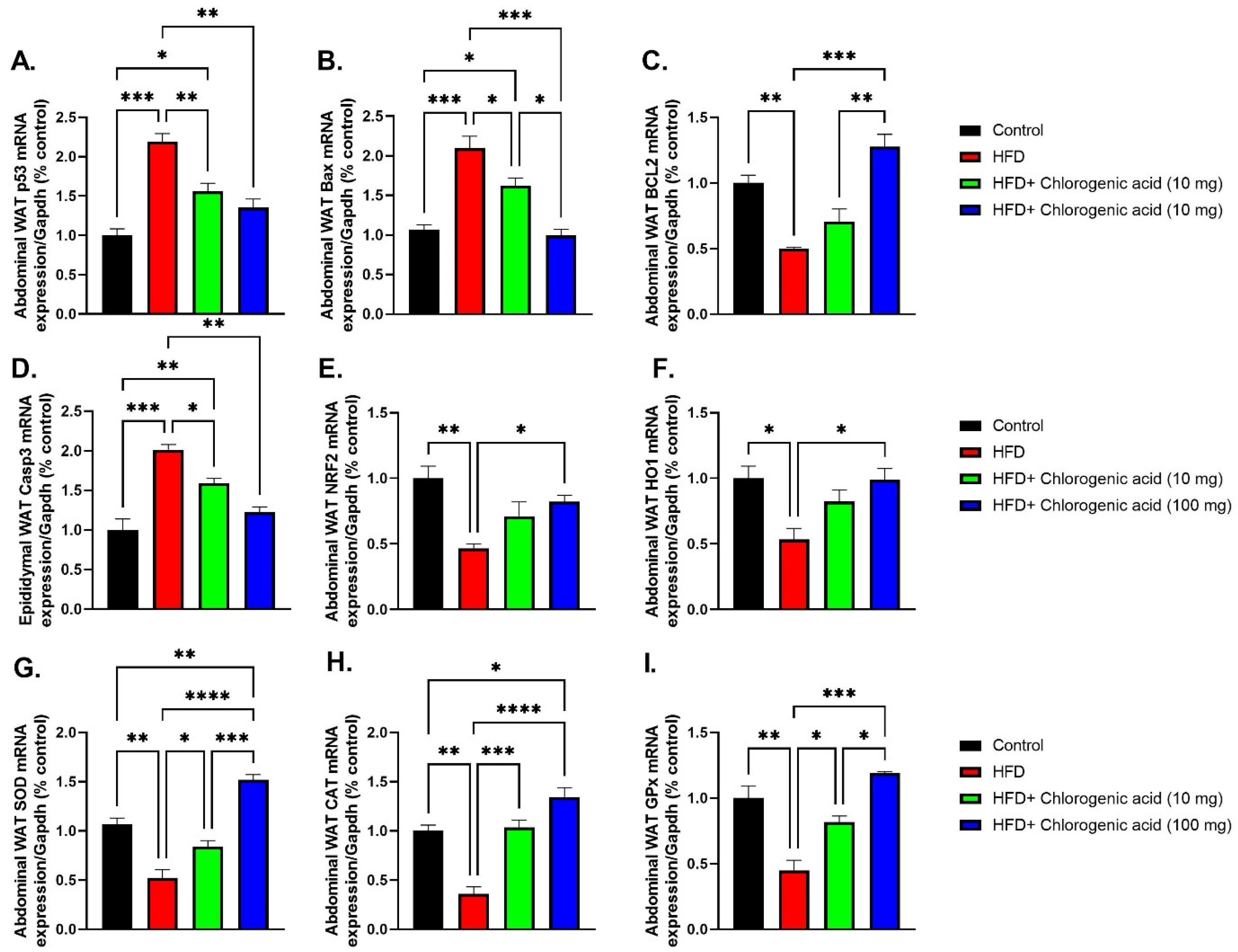
3.8. Effects of HFD and CGA on Apoptosis and Oxidative Stress Pathways in Abdominal White Adipose Tissue
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Westbury, S.; Oyebode, O.; van Rens, T.; Barber, T.M. Obesity Stigma: Causes, Consequences, and Potential Solutions. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2023, 12, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blüher, M. Obesity: Global epidemiology and pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregor, M.F.; Hotamisligil, G.S. Inflammatory Mechanisms in Obesity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 29, 415–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, V.; Sundaresan, A.; Shishodia, S. Overnutrition and Lipotoxicity: Impaired Efferocytosis and Chronic Inflammation as Precursors to Multifaceted Disease Pathogenesis. Biology 2024, 13, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, U.J.; Choi, M.-S. Obesity and Its Metabolic Complications: The Role of Adipokines and the Relationship between Obesity, Inflammation, Insulin Resistance, Dyslipidemia and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 6184–6223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wali, J.A.; Jarzebska, N.; Raubenheimer, D.; Simpson, S.J.; Rodionov, R.N.; O’Sullivan, J.F. Cardio-Metabolic Effects of High-Fat Diets and Their Underlying Mechanisms—A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, S.; Fujita, T.; Shimabukuro, M.; Iwaki, M.; Yamada, Y.; Nakajima, Y.; Nakayama, O.; Makishima, M.; Matsuda, M.; Shimomura, I. Increased oxidative stress in obesity and its impact on metabolic syndrome. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 114, 1752–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingappan, K. NF-κB in Oxidative Stress. Curr. Opin. Toxicol. 2018, 7, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olefsky, J.M.; Glass, C.K. Macrophages, inflammation, and insulin resistance. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2010, 72, 219–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abizaid, A.; Horvath, T.L. Brain circuits regulating energy homeostasis. Regul. Pept. 2008, 149, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madamanchi, N.R.; Vendrov, A.; Runge, M.S. Oxidative stress and vascular disease. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2005, 25, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canali, R.; Comitato, R.; Ambra, R.; Virgili, F. Red wine metabolites modulate NF-kappaB, activator protein-1 and cAMP response element-binding proteins in human endothelial cells. Br. J. Nutr. 2010, 103, 807–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzino, G.; Irrera, N.; Cucinotta, M.; Pallio, G.; Mannino, F.; Arcoraci, V.; Squadrito, F.; Altavilla, D.; Bitto, A. Oxidative Stress: Harms and Benefits for Human Health. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 8416763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalbert, A.; Claudine, M.; Christine, M.; Christian, R.; Jiménez, L. Dietary Polyphenols and the Prevention of Diseases. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2005, 45, 287–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, S.S.-C.; Nelson, M.A.; Bedner, M.; Lang, B.E.; Phinney, K.W.; Sander, L.C.; Yen, J.H.; Betz, J.M.; Sempos, C.T.; Wise, S.A. Development of Standard Reference Material (SRM) 2973 Vitamin D Metabolites in Frozen Human Serum (High Level). J. AOAC Int. 2019, 100, 1294–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, H.; Ouyang, H.; Guo, Q.; Wei, M.; Lu, B.; Kai, G.; Ji, L. Chlorogenic acid alleviated liver fibrosis in methionine and choline deficient diet-induced nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in mice and its mechanism. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2022, 106, 109020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farah, A.; Monteiro, M.; Donangelo, C.M.; Lafay, S. Chlorogenic acids from green coffee extract are highly bioavailable in humans. J. Nutr. 2008, 138, 2309–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joensen, L.E.; Almdal, T.P.; Willaing, I. Type 1 diabetes and living without a partner: Psychological and social aspects, self-management behaviour, and glycaemic control. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2013, 101, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.; Taine, E.G.; Meng, D.; Cui, T.; Tan, W. Chlorogenic Acid: A Systematic Review on the Biological Functions, Mechanistic Actions, and Therapeutic Potentials. Nutrients 2024, 16, 924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, K.; Dai, S.; Zhang, Y.; Gong, J.; Wang, C.; Yao, C.; Zhang, S.; Peng, C.; Li, Y. Natural product chlorogenic acid achieves pharmacological activity and health protection via regulating gut microbiota: A review. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2025, 14, 9250153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Lam, K.L.; Hu, J.; Ge, S.; Zhou, A.; Zheng, B.; Zeng, S.; Lin, S. Chlorogenic acid alleviates obesity and modulates gut microbiota in high-fat-fed mice. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 7, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.Y.; Jin, J.; Jin, L.W.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, Z.H.; Li, Z.Y. Chlorogenic Acid Attenuates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Kidney Injury by Inhibiting TLR4/NF-κB Signal Pathway. Inflammation 2017, 40, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javidan, A.; Jiang, W.; Okuyama, M.; Thiagarajan, D.; Yang, L.; Moorleghen, J.J.; Muniappan, L.; Subramanian, V. miR-146a Deficiency Accelerates Hepatic Inflammation Without Influencing Diet-induced Obesity in Mice. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taganov, K.D.; Boldin, M.P.; Chang, K.-J.; Baltimore, D. NF-κB-dependent induction of microRNA miR-146, an inhibitor targeted to signaling proteins of innate immune responses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 12481–12486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suraweera, T.L.; Rupasinghe, H.P.V.; Dellaire, G.; Xu, Z. Regulation of Nrf2/ARE Pathway by Dietary Flavonoids: A Friend or Foe for Cancer Management? Antioxidants 2020, 9, 973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Tian, M.; Lu, S.; Qin, Y.; Zhao, T.; Shi, H.; Li, Z.; Qin, D. The antioxidant role of aromatic plant extracts in managing neurodegenerative diseases: A comprehensive review. Brain Res. Bull. 2025, 222, 111253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortez, N.; Villegas, C.; Burgos, V.; Ortiz, L.; Cabrera-Pardo, J.R.; Paz, C. Therapeutic Potential of Chlorogenic Acid in Chemoresistance and Chemoprotection in Cancer Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubant, R.; Poon, A.N.; Sánchez-Hernández, D.; Domenichiello, A.F.; Huot, P.S.P.; Pannia, E.; Cho, C.E.; Hunschede, S.; Bazinet, R.P.; Anderson, G.H. A comparison of effects of lard and hydrogenated vegetable shortening on the development of high-fat diet-induced obesity in rats. Nutr. Diabetes 2015, 5, e188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furnes, M.W.; Zhao, C.M.; Chen, D. Development of obesity is associated with increased calories per meal rather than per day. A study of high-fat diet-induced obesity in young rats. Obes. Surg. 2009, 19, 1430–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrea, D.R.; Malkey, R.; Florian, T.L.; Filip, A.; Clichici, S.; Bidian, C.; Moldovan, R.; Hoteiuc, O.A.; Toader, A.M.; Baldea, I. Daily oral administration of chlorogenic acid prevents the experimental carrageenan-induced oxidative stress. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. Off. J. Pol. Physiol. Soc. 2020, 71, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana-Gálvez, J.; Cisneros-Zevallos, L.; Jacobo-Velázquez, D.A. Chlorogenic Acid: Recent Advances on Its Dual Role as a Food Additive and a Nutraceutical against Metabolic Syndrome. Molecules 2017, 22, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novelli, E.L.; Diniz, Y.S.; Galhardi, C.M.; Ebaid, G.M.; Rodrigues, H.G.; Mani, F.; Fernandes, A.A.; Cicogna, A.C.; Novelli Filho, J.L. Anthropometrical parameters and markers of obesity in rats. Lab. Anim. 2007, 41, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christoper, A.; Herman, H.; Abdulah, R.; Zulhendri, F.; Lesmana, R. Short communication: The effect of Propolis extract treatment on the Lee index and brain-body weight ratio in diet-induced obesity rats. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2025, 42, 102039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arisha, A.H.; Moustafa, A. Potential inhibitory effect of swimming exercise on the Kisspeptin–GnRH signaling pathway in male rats. Theriogenology 2019, 133, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glowinski, J.; Iversen, L.L. REGIONAL STUDIES OF CATECHOLAMINES IN THE RAT BRAIN-I. J. Neurochem. 1966, 13, 655–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arisha, A.H.; Ahmed, M.M.; Kamel, M.A.; Attia, Y.A.; Hussein, M.M.A. Morin ameliorates the testicular apoptosis, oxidative stress, and impact on blood–testis barrier induced by photo-extracellularly synthesized silver nanoparticles. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 28749–28762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, M.M.; Ali, H.A.; Ahmed, M.M. Ameliorative effects of phycocyanin against gibberellic acid induced hepatotoxicity. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2015, 119, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, M.M.; Ali, H.A.; Saadeldin, I.M.; Ahmed, M.M. Querectin Alleviates Zinc Oxide Nanoreprotoxicity in Male Albino Rats. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2016, 30, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czimmerer, Z.; Hulvely, J.; Simandi, Z.; Varallyay, E.; Havelda, Z.; Szabo, E.; Varga, A.; Dezso, B.; Balogh, M.; Horvath, A.; et al. A versatile method to design stem-loop primer-based quantitative PCR assays for detecting small regulatory RNA molecules. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Ridzon, D.A.; Broomer, A.J.; Zhou, Z.; Lee, D.H.; Nguyen, J.T.; Barbisin, M.; Xu, N.L.; Mahuvakar, V.R.; Andersen, M.R.; et al. Real-time quantification of microRNAs by stem-loop RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, e179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Li, Q.; Shen, L.; Guo, K.; Zhou, X. Chlorogenic acid improves glucose tolerance, lipid metabolism, inflammation and microbiota composition in diabetic db/db mice. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1042044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahn, S.E.; Hull, R.L.; Utzschneider, K.M. Mechanisms linking obesity to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Nature 2006, 444, 840–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotamisligil, G.S. Inflammation and metabolic disorders. Nature 2006, 444, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, J.M.; Halaas, J.L. Leptin and the regulation of body weight in mammals. Nature 1998, 395, 763–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, M.G., Jr.; Leibel, R.L.; Seeley, R.J.; Schwartz, M.W. Obesity and leptin resistance: Distinguishing cause from effect. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. TEM 2010, 21, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, S.; Cao, J.; Feng, Q.; Peng, J.; Hu, Y. Roles of chlorogenic Acid on regulating glucose and lipids metabolism: A review. Evid. -Based Complement. Altern. Med. Ecam 2013, 2013, 801457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kojima, M.; Kangawa, K. Ghrelin: Structure and Function. Physiol. Rev. 2005, 85, 495–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tschöp, M.; Smiley, D.L.; Heiman, M.L. Ghrelin induces adiposity in rodents. Nature 2000, 407, 908–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Gao, M.; Liu, D. Chlorogenic acid improves high fat diet-induced hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance in mice. Pharm. Res. 2015, 32, 1200–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamauchi, T.; Kamon, J.; Waki, H.; Terauchi, Y.; Kubota, N.; Hara, K.; Mori, Y.; Ide, T.; Murakami, K.; Tsuboyama-Kasaoka, N.; et al. The fat-derived hormone adiponectin reverses insulin resistance associated with both lipoatrophy and obesity. Nat. Med. 2001, 7, 941–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arita, Y.; Kihara, S.; Ouchi, N.; Takahashi, M.; Maeda, K.; Miyagawa, J.-i.; Hotta, K.; Shimomura, I.; Nakamura, T.; Miyaoka, K.; et al. Paradoxical Decrease of an Adipose-Specific Protein, Adiponectin, in Obesity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1999, 257, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ge, H.; Xu, Y.; Xie, J.; Karim, N.; Yan, F.; Mo, J.; Chen, W. Chlorogenic acid alleviates oxidative damage in hepatocytes by regulating miR-199a-5p/GRP78 axis. Food Biosci. 2023, 53, 102595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.; Niu, J.; Zhang, J.; Qiao, Y.; Dong, G.; Guo, R.; Zheng, X.; Song, Z.; Huang, J.; Wang, J.; et al. Hepatoprotective effects of chlorogenic acid on mice exposed to aflatoxin B1: Modulation of oxidative stress and inflammation. Toxicon 2023, 231, 107177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panickar, K.S. Effects of dietary polyphenols on neuroregulatory factors and pathways that mediate food intake and energy regulation in obesity. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2013, 57, 34–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Li, L.; Chen, B.; Fang, Y.; Lin, W.; Zhang, T.; Feng, X.; Tao, X.; Wu, Y.; Fu, X.; et al. Chlorogenic acid exerts neuroprotective effect against hypoxia-ischemia brain injury in neonatal rats by activating Sirt1 to regulate the Nrf2-NF-κB signaling pathway. Cell Commun. Signal. CCS 2022, 20, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trius-Soler, M.; Moreno, J.J. Bitter taste receptors: Key target to understand the effects of polyphenols on glucose and body weight homeostasis. Pathophysiological and pharmacological implications. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2024, 228, 116192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Pan, X.; Jiang, L.; Chu, Y.; Gao, S.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Luo, S.; Peng, C. The Biological Activity Mechanism of Chlorogenic Acid and Its Applications in Food Industry: A Review. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 943911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, L.; Li, J.; Zha, D.; Zhang, L.; Gao, P.; Yao, T.; Wu, X. Chlorogenic acid prevents diabetic nephropathy by inhibiting oxidative stress and inflammation through modulation of the Nrf2/HO-1 and NF-ĸB pathways. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2018, 54, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Barnes, G.T.; Yang, Q.; Tan, G.; Yang, D.; Chou, C.J.; Sole, J.; Nichols, A.; Ross, J.S.; Tartaglia, L.A.; et al. Chronic inflammation in fat plays a crucial role in the development of obesity-related insulin resistance. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 1821–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donath, M.Y.; Shoelson, S.E. Type 2 diabetes as an inflammatory disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhar-e-Alam Kulyar, M.; Yao, W.; Ding, Y.; Du, H.; Mo, Q.; Pan, H.; Shahzad, M.; Mehmood, K.; Iqbal, M.; Akhtar, M.; et al. Chlorogenic acid suppresses mitochondrial apoptotic effectors Bax/Bak to counteract Nod-like receptor pyrin domain 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome in thiram exposed chondrocytes. Phytomedicine 2022, 95, 153865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, T.; Autieri, M.V.; Scalia, R. Adipose tissue inflammation and metabolic dysfunction in obesity. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2021, 320, C375–C391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Xie, M.; He, L.; Song, X.; Cao, T. Chlorogenic acid: A review on its mechanisms of anti-inflammation, disease treatment, and related delivery systems. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1218015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, L.A.; Sheedy, F.J.; McCoy, C.E. MicroRNAs: The fine-tuners of Toll-like receptor signalling. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runtsch, M.C.; Nelson, M.C.; Lee, S.H.; Voth, W.; Alexander, M.; Hu, R.; Wallace, J.; Petersen, C.; Panic, V.; Villanueva, C.J.; et al. Anti-inflammatory microRNA-146a protects mice from diet-induced metabolic disease. PLoS Genet. 2019, 15, e1007970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanada, T.; Sano, T.; Sotomaru, Y.; Alshargabi, R.; Yamawaki, Y.; Yamashita, A.; Matsunaga, H.; Iwashita, M.; Shinjo, T.; Kanematsu, T.; et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of miRNA-146a induced in adipose and periodontal tissues. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2020, 22, 100757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinisch, I.; Enzenhofer, S.; Prokesch, A. Mechanisms of Lipid-Associated Macrophage Accrual in Metabolically Stressed Adipose Tissue. BioEssays 2025, 47, e202400203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masenga, S.K.; Kabwe, L.S.; Chakulya, M.; Kirabo, A. Mechanisms of Oxidative Stress in Metabolic Syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunes, A.D.C.; Weigl, M.; Schneider, A.; Noureddine, S.; Yu, L.; Lahde, C.; Saccon, T.D.; Mitra, K.; Beltran, E.; Grillari, J.; et al. miR-146a-5p modulates cellular senescence and apoptosis in visceral adipose tissue of long-lived Ames dwarf mice and in cultured pre-adipocytes. GeroScience 2022, 44, 503–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, H.; Lei, D. microRNA-146a Promotes Growth of Acute Leukemia Cells by Downregulating Ciliary Neurotrophic Factor Receptor and Activating JAK2/STAT3 Signaling. Yonsei Med. J. 2019, 60, 924–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwafor, E.-O.; Lu, P.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, R.; Peng, H.; Xing, B.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Chlorogenic acid: Potential source of natural drugs for the therapeutics of fibrosis and cancer. Transl. Oncol. 2022, 15, 101294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhou, Z.; Yu, S.; Ma, Y.; Wang, G.; Han, X.; Jiao, C.; Luan, J.; Liu, Z.; Xu, Y.; et al. Nrf2 protects against renal fibrosis induced by chronic cadmium exposure in mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2023, 178, 113875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Ingredient | HFD (g/kg Diet (kcal/kg)) |
|---|---|
| Casein | 200 (716) |
| L-Cystine | 3 (12) |
| Sucrose | 100 (400) |
| Cornstarch | 173.1 (623) |
| Dyetrose | 58 (220.4) |
| Lard | 350 (3150) |
| Cellulose | 50 (0) |
| Mineral Mix (#210025) | 49.3 (43.4) |
| Vitamin Mix (#310025) | 14.1 (54.6) |
| Choline Bitartrate | 2.5 (0) |
| Total | 1000 (5219.4) |
| Group | Diet | Treatment Duration | Chlorogenic Acid Dose |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control Group | Standard chow diet (10% kcal from fat) | 12 weeks | Vehicle only (distilled water, orally, last 4 weeks) |
| HFD Group | High-fat diet (60% kcal from fat) | 12 weeks | Vehicle only (distilled water, orally, last 4 weeks) |
| HFD + Low-Dose CGA Group | High-fat diet (60% kcal from fat) | First 8 weeks: HFD only Last 4 weeks: HFD + CGA | 10 mg/kg/day, oral gavage |
| HFD + High-Dose CGA Group | High-fat diet (60% kcal from fat) | First 8 weeks: HFD only Last 4 weeks: HFD + CGA | 100 mg/kg/day, oral gavage |
| Gene | Forward Primer (5′-3′) | Reverse Primer (5′-3′) | Accession Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| AGRP | AAGCTTTGGCAGAGGTGCTA | GACTCGTGCAGCCTTACACA | NM_033650.1 |
| NPY | TACTCCGCTCTGCGACACTA | TGTCTCAGGGCTGGATCTCT | NM_012614.2 |
| CART-pt | CCCTACTGCTGCTGCTACCT | CACGGCAGAGTAGATGTCCA | NM_017110.1 |
| POMC | GCTTCATGACCTCCGAGAAG | TCTTGATGATGGCGTTCTTG | NM_139326.3 |
| IRAK1 | GCTGTGGACACCGAT | GCTACACCCATCCACA | NM_001127555.1 |
| TRAF6 | CAGTCCCCTGCACATT | GAGGAGGCATCGCAT | M_001107754.2 |
| TNF-α | AGGGTCTGGGCCATAGAAC | CCACCACGCTCTTCTGTCTAC | NM_012675.3 |
| NF-κB | CAGGACCAGGAACAGTTCGAA | CCAGGTTCTGGAAGCTATGGAT | NM_199267.2 |
| TGFβ1 | CTGAACCAAGGAGACGGAAT | GGTTCATGTCATGGATGGTG | NM_021578.2 |
| IL1β | CACCTCTCAAGCAGAGCACAGA | ACGGGTTCCATGGTGAAGTC | NM_031512.2 |
| IL6 | ATATGTTCTCAGGGAGATCTTGGAA | GTGCATCATCGCTGTTCATACA | NM_012589.2 |
| IL8 | CATTAATATTTAACGATGTGGATGCGTTTCA | GCCTACCATCTTTAAACTGCACAAT | NM_030845.1 |
| IL10 | GTAGAAGTGATGCCCCAGGC | AGAAATCGATGACAGCGTCG | NM_012854.2 |
| IFNg | GTGAACAACCCACAGATCCA | GAATCAGCACCGACTCCTTT | NM_138880.3 |
| P53 | CATGAGCGTTGCTCTGATGGT | GATTTCCTTCCACCCGGATAA | NM_030989.3 |
| Bax | CGAATTGGCGATGAACTGGA | CAAACATGTCAGCTGCCACAC | NM_017059.2 |
| Bcl-2 | GACTGAGTACCTGAACCGGCATC | CTGAGCAGCGTCTTCAGAGACA | NM_016993.1 |
| Casp-3 | GAGACAGACAGTGGAACTGACGATG | GGCGCAAAGTGACTGGATGA | NM_012922.2 |
| NRF2 | CACATCCAGACAGACACCAGT | CTACAAATGGGAATGTCTCTGC | NM_031789 |
| HO1 | GTAAATGCAGTGTTGGCCCC | ATGTGCCAGGCATCTCCTTC | NM_012580.2 |
| CAT | TCCATCCTTTATCCATAGCC | TTAACCAGCTTGAAGGTGTG | NM_012520.2 |
| SOD | TGTGATCTCACTCTCAGGAG | CTCAGACCACATAGGGAATG | NM_017050.1 |
| GPx | GCGTCCCTCTGAGGCACCAC | AAGTTGGGCTCGAACCCACC | NM_030826.4 |
| Gapdh | GTGCCAGCCTCGTCTCATAG | CGTTGATGGCAACAATGTCCA | NM_017008.4 |
| U6 | GCTCGCTTCGGCAGCACA | GAGGTATTCGCACCAGAGGA | |
| miR146a | GTTTGGTGAGAACTGAATTCCA | GTGCAGGGTCCGAGGT | |
| U6 stem-Loop primer | AACGCTTCACGAATTTGCGTG | ||
| miR14 stem-Loop primer | GTTGGCTCTGGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACCAGAGCCAACAACCCA | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alenezi, R.F.; Abdelkhalek, A.; El-Sayed, G.; Pet, I.; Ahmadi, M.; Sherbini, E.S.E.; Pușcașiu, D.; Arisha, A.H. A Natural Polyphenol, Chlorogenic Acid, Attenuates Obesity-Related Metabolic Disorders in Male Rats via miR-146a-IRAK1-TRAF6 and NRF2-Mediated Antioxidant Pathways. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 1086. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15081086
Alenezi RF, Abdelkhalek A, El-Sayed G, Pet I, Ahmadi M, Sherbini ESE, Pușcașiu D, Arisha AH. A Natural Polyphenol, Chlorogenic Acid, Attenuates Obesity-Related Metabolic Disorders in Male Rats via miR-146a-IRAK1-TRAF6 and NRF2-Mediated Antioxidant Pathways. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(8):1086. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15081086
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlenezi, Rashid Fahed, Adel Abdelkhalek, Gehad El-Sayed, Ioan Pet, Mirela Ahmadi, El Said El Sherbini, Daniela Pușcașiu, and Ahmed Hamed Arisha. 2025. "A Natural Polyphenol, Chlorogenic Acid, Attenuates Obesity-Related Metabolic Disorders in Male Rats via miR-146a-IRAK1-TRAF6 and NRF2-Mediated Antioxidant Pathways" Biomolecules 15, no. 8: 1086. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15081086
APA StyleAlenezi, R. F., Abdelkhalek, A., El-Sayed, G., Pet, I., Ahmadi, M., Sherbini, E. S. E., Pușcașiu, D., & Arisha, A. H. (2025). A Natural Polyphenol, Chlorogenic Acid, Attenuates Obesity-Related Metabolic Disorders in Male Rats via miR-146a-IRAK1-TRAF6 and NRF2-Mediated Antioxidant Pathways. Biomolecules, 15(8), 1086. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15081086







