Optimization of Intra-Arterial Administration of Chemotherapeutic Agents for Glioblastoma in the F98-Fischer Glioma-Bearing Rat Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Cell Line and Culture Conditions
2.3. Animals
2.4. Drugs Administration
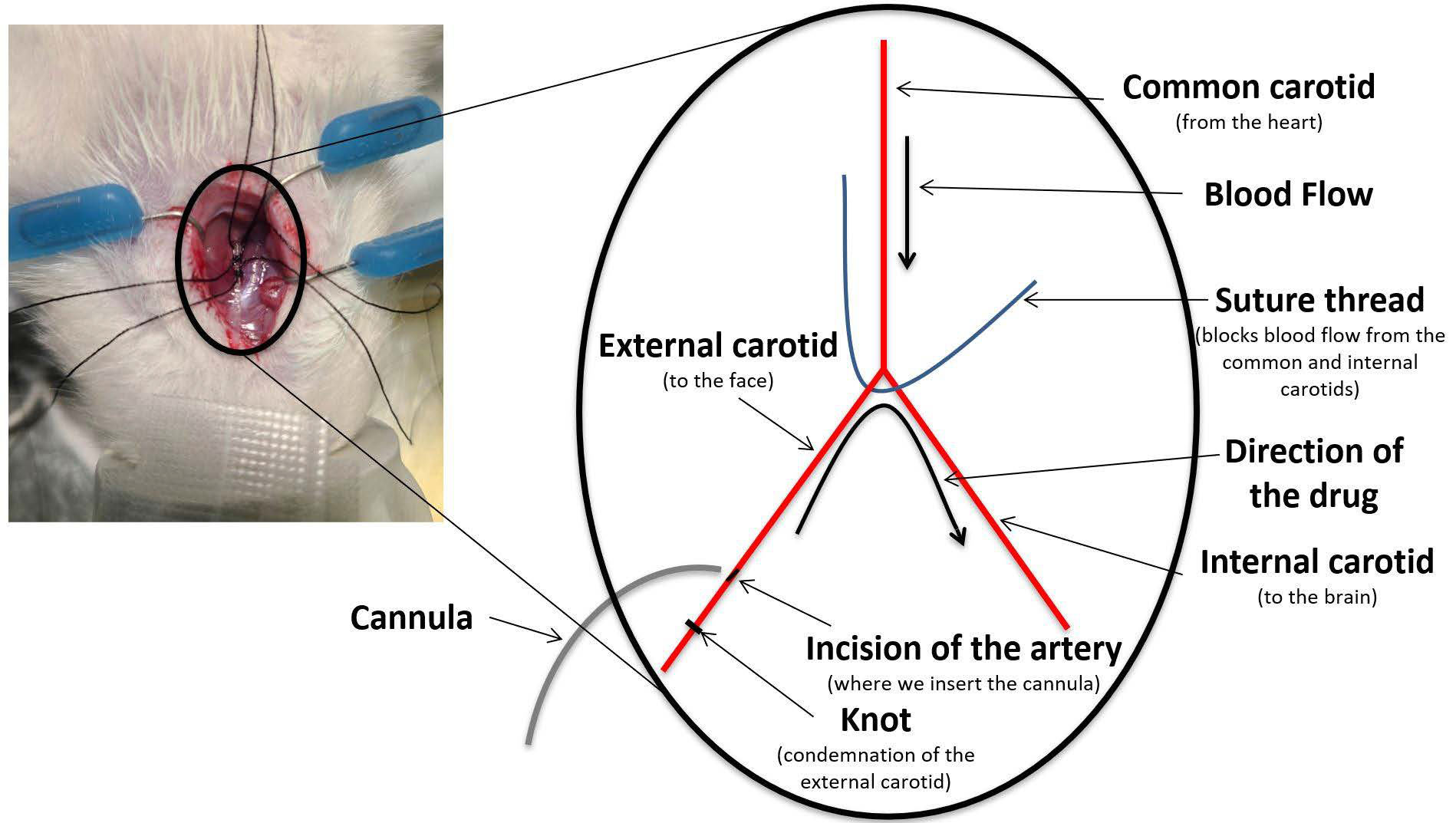
2.5. Treatment Groups
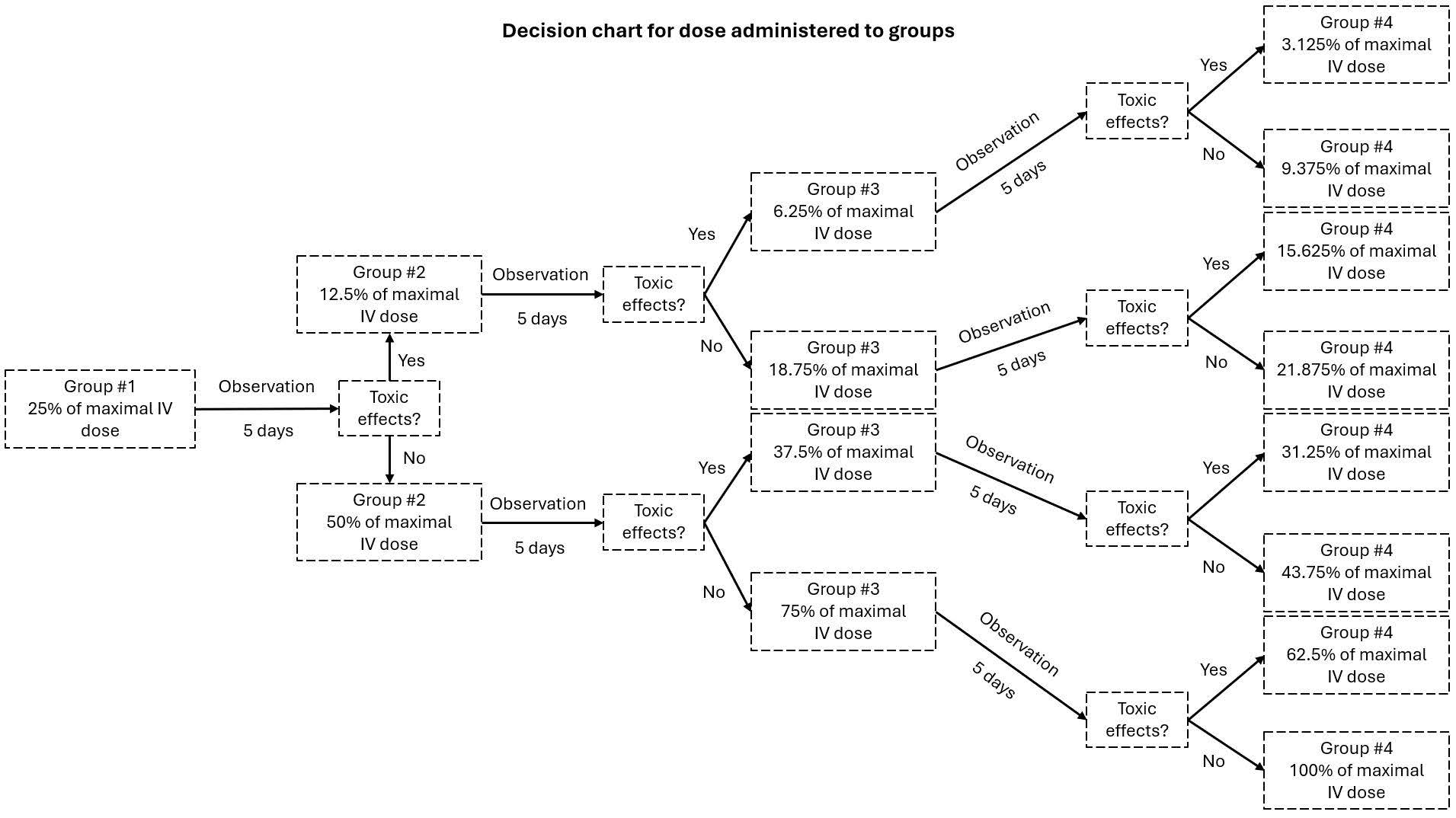
2.6. MTD Evaluation
2.7. Implantation
2.8. Evaluation of Mean Survival Time
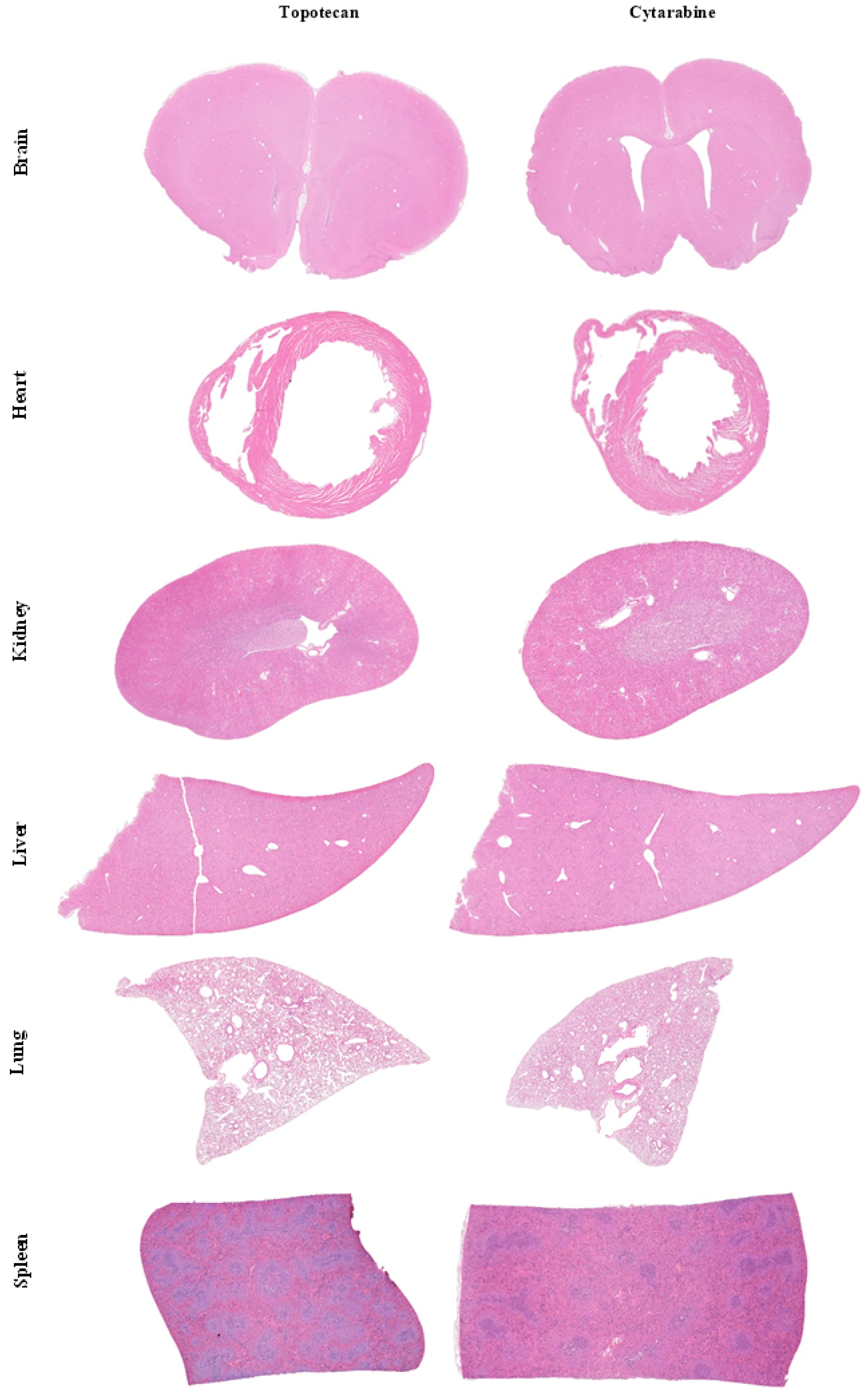
2.9. Histology
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. MTD Study
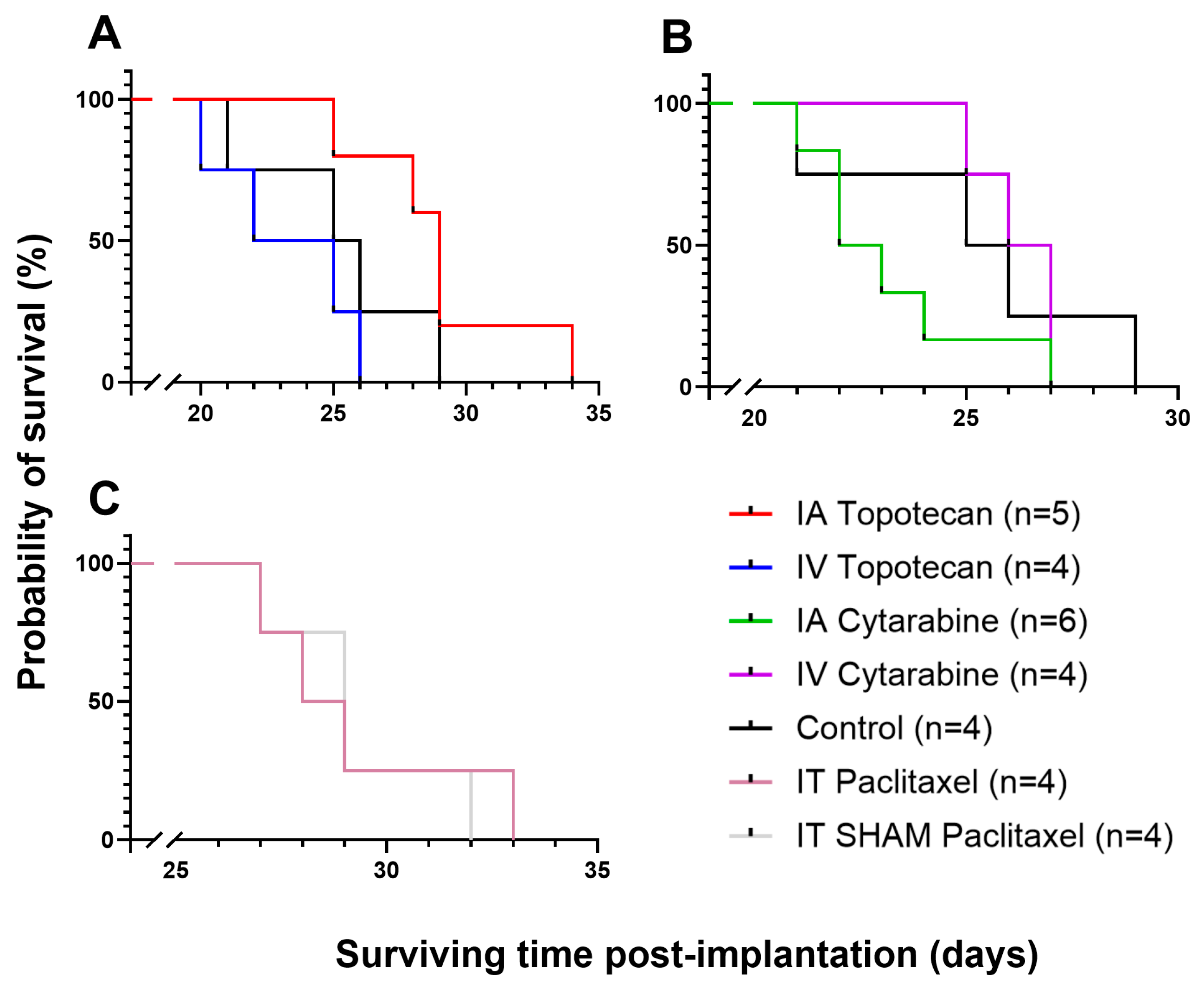
3.2. Efficacy/Survival Study
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BBB | Blood–brain barrier |
| CED | Convection-enhanced delivery |
| CHUS | Centre Hospitalier de l’Université de Sherbrooke |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| CTA | Chemotherapy agent |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s modified eagle medium |
| GBM | Glioblastoma multiform |
| H&E | Hematoxylin and eosin |
| IA | Intra-arterial/intra-arterially |
| IT | Intratumoral |
| IV | Intravenous |
| MTD | Maximal tolerable dose |
| BBBD | Blood–brain barrier disruption |
| PFA | Paraformaldehyde |
References
- Stupp, R.; Mason, W.P.; van den Bent, M.J.; Weller, M.; Fisher, B.; Taphoorn, M.J.B.; Belanger, K.; Brandes, A.A.; Marosi, C.; Bogdahn, U.; et al. Radiotherapy plus Concomitant and Adjuvant Temozolomide for Glioblastoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchette, M.; Tremblay, L.; Lepage, M.; Fortin, D. Impact of Drug Size on Brain Tumor and Brain Parenchyma Delivery after a Blood–Brain Barrier Disruption. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab 2014, 34, 820–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Chen, Q.; Chen, X.; Han, F.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Y. The Blood-Brain Barrier: Structure, Regulation, and Drug Delivery. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alifieris, C.; Trafalis, D.T. Glioblastoma multiforme: Pathogenesis and treatment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 152, 63–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Solinge, T.S.; Nieland, L.; Chiocca, E.A.; Broekman, M.L.D. Advances in local therapy for glioblastoma—Taking the fight to the tumour. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2022, 18, 221–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’amico, R.S.; Khatri, D.; Reichman, N.; Patel, N.V.; Wong, T.; Fralin, S.R.; Li, M.; Ellis, J.A.; Ortiz, R.; Langer, D.J.; et al. Super selective intra-arterial cerebral infusion of modern chemotherapeutics after blood–brain barrier disruption: Where are we now, and where we are going. J. Neuro-Oncology 2020, 147, 261–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinkiewicz, M.; Pinkiewicz, M.; Walecki, J.; Zawadzki, M. A systematic review on intra-arterial cerebral infusions of chemotherapeutics in the treatment of glioblastoma multiforme: The state-of-the-art. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 950167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortin, D. Drug Delivery Technology to the CNS in the Treatment of Brain Tumors: The Sherbrooke Experience. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boockvar, J.A.; Tsiouris, A.J.; Hofstetter, C.P.; Kovanlikaya, I.; Fralin, S.; Kesavabhotla, K.; Seedial, S.M.; Pannullo, S.C.; Schwartz, T.H.; Stieg, P.; et al. Safety and maximum tolerated dose of superselective intraarterial cerebral infusion of bevacizumab after osmotic blood-brain barrier disruption for recurrent malignant glioma. J. Neurosurg. 2011, 114, 624–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, J.; Shi, Y.; Luo, P.; Li, L.; Huang, J.; Chen, J.; Yang, H. Safety and feasibility of intra-arterial delivery of teniposide to high grade gliomas after blood–brain barrier disruption: A case series. J. NeuroInterventional Surg. 2023, 16, 1152–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uluc, K.; Ambady, P.; McIntyre, M.K.; Tabb, J.P.; Kersch, C.N.; Nerison, C.S.; Huddleston, A.; Liu, J.J.; Dogan, A.; Priest, R.; et al. Safety of intra-arterial chemotherapy with or without osmotic blood–brain barrier disruption for the treatment of patients with brain tumors. Neuro-Oncology Adv. 2022, 4, vdac104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drapeau, A.; Fortin, D. Chemotherapy Delivery Strategies to the Central Nervous System: Neither Optional nor Superfluous. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2015, 15, 752–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spinazzi, E.F.; Argenziano, M.G.; Upadhyayula, P.S.; Banu, M.A.; Neira, J.O.; Higgins, D.M.; Wu, P.B.; Pereira, B.; Mahajan, A.; Humala, N.; et al. Chronic convection-enhanced delivery of topotecan for patients with recurrent glioblastoma: A first-in-patient, single-centre, single-arm, phase 1b trial. Lancet Oncol. 2022, 23, 1409–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollmannsberger, C.; Mross, K.; Jakob, A.; Kanz, L.; Bokemeyer, C. Topotecan—A Novel Topoisomerase I Inhibitor: Pharmacology and Clinical Experience. Oncology 1999, 56, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, W.J.; Royer, G.L., Jr.; Weiss, R.B. Cytarabine and neurologic toxicity. J. Clin. Oncol. 1991, 9, 679–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dréan, A.; Lemaire, N.; Bouchoux, G.; Goldwirt, L.; Canney, M.; Goli, L.; Bouzidi, A.; Schmitt, C.; Guehennec, J.; Verreault, M.; et al. Temporary blood–brain barrier disruption by low intensity pulsed ultrasound increases carboplatin delivery and efficacy in preclinical models of glioblastoma. J. Neuro-Oncology 2019, 144, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpentier, A.; Stupp, R.; Sonabend, A.M.; Dufour, H.; Chinot, O.; Mathon, B.; Ducray, F.; Guyotat, J.; Baize, N.; Menei, P.; et al. Repeated Blood-Brain Barrier Opening with a Nine-Emitter Implantable Ultrasound Device in Combination with Car-boplatin in Recurrent Glioblastoma: A Phase I/II Clinical Trial. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqahtani, F.Y.; Aleanizy, F.S.; El Tahir, E.; Alkahtani, H.M.; Alquadeib, B. Paclitaxel. In Profiles of Drug Substances, Excipients and Related Methodology; Elsevier BV: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; Volume 44, pp. 205–238. [Google Scholar]
- Ranganath, S.H.; Kee, I.; Krantz, W.B.; Chow, P.K.-H.; Wang, C.-H. Hydrogel Matrix Entrapping PLGA-Paclitaxel Microspheres: Drug Delivery with Near Zero-Order Release and Implantability Advantages for Malignant Brain Tumour Chemotherapy. Pharm. Res. 2009, 26, 2101–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.W.; Dang, W.; Tyler, B.M.; Troiano, G.; Tihan, T.; Brem, H.; Walter, K.A. Polilactofate Microspheres for Paclitaxel De-livery to Central Nervous System Malignancies. Clin. Cancer Res. 2003, 9, 3441–3447. [Google Scholar]
- Blanchard, J.; Mathieu, D.; Patenaude, Y.; Fortin, D. MR-Pathological Comparison in F98-Fischer Glioma Model Using a Human Gantry. Can. J. Neurol. Sci. / J. Can. des Sci. Neurol. 2006, 33, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charest, G.; Sanche, L.; Fortin, D.; Mathieu, D.; Paquette, B. Glioblastoma Treatment: Bypassing the Toxicity of Platinum Compounds by Using Liposomal Formulation and Increasing Treatment Efficiency With Concomitant Radiotherapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2012, 84, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortin, D.; Adams, R.; Gallez, A. A blood-brain barrier disruption model eliminating the hemodynamic effect of ketamine. Can. J. Neurol. Sci. / J. Can. des Sci. Neurol. 2004, 31, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.-H.; Jang, J.-H.; Lee, Y.-B. Pharmacokinetic Comparison of Three Different Administration Routes for Topotecan Hydrochloride in Rats. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groothuis, D.R.; Benalcazar, H.; Allen, C.V.; Wise, R.M.; Dills, C.; Dobrescu, C.; Rothholtz, V.; Levy, R.M. Comparison of cytosine arabinoside delivery to rat brain by intravenous, intrathecal, intraventricular and intraparenchymal routes of administration. Brain Res. 2000, 856, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdes, J.; Gagné-Sansfaçon, J.; Reyes, V.; Armas, A.; Marrero, G.; Moyo-Muamba, M.; Ramanathan, S.; Perreault, N.; Ilangumaran, S.; Rivard, N.; et al. Defects in the expression of colonic host defense factors associate with barrier dysfunction induced by a high-fat/high-cholesterol diet. Anat. Rec. 2022, 306, 1165–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charest, G.; Sanche, L.; Fortin, D.; Mathieu, D.; Paquette, B. Optimization of the route of platinum drugs administration to optimize the concomitant treatment with radiotherapy for glioblastoma implanted in the Fischer rat brain. J. Neuro-Oncology 2013, 115, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathieu, D.; Lecomte, R.; Tsanaclis, A.M.; Larouche, A.; Fortin, D. Standardization and Detailed Characterization of the Syngeneic Fischer/F98 Glioma Model. Can. J. Neurol. Sci. / J. Can. des Sci. Neurol. 2007, 34, 296–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Côté, J.; Savard, M.; Neugebauer, W.; Fortin, D.; Lepage, M.; Gobeil, F. Dual kinin B1 and B2 receptor activation provides enhanced blood–brain barrier permeability and anticancer drug delivery into brain tumors. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2013, 14, 806–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinchon-Petit, S.; Jarnet, D.; Paillard, A.; Benoit, J.-P.; Garcion, E.; Menei, P. In vivo evaluation of intracellular drug-nanocarriers infused into intracranial tumours by convection-enhanced delivery: Distribution and radiosensitisation efficacy. J. Neuro-Oncology 2009, 97, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dashti, S.R.; Kadner, R.J.; Folley, B.S.; Sheehan, J.P.; Han, D.Y.; Kryscio, R.J.; Carter, M.B.; Shields, L.B.E.; Plato, B.M.; La Rocca, R.V.; et al. Single low-dose targeted bevacizumab infusion in adult patients with steroid-refractory radiation necrosis of the brain: A phase II open-label prospective clinical trial. J. Neurosurg. 2022, 137, 1676–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gahide, G.; Vendrell, J.-F.; Massicotte-Tisluck, K.; Caux, S.; Deschamps, S.; Noël-Lamy, M.; Belzile, F.; Roy, L.-O.; Fortin, D. Safety of Cerebral Intra-Arterial Chemotherapy for the Treatment of Malignant Brain Tumours. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCrea, H.J.; Ivanidze, J.; O’connor, A.; Hersh, E.H.; Boockvar, J.A.; Gobin, Y.P.; Knopman, J.; Greenfield, J.P. Intraarterial delivery of bevacizumab and cetuximab utilizing blood-brain barrier disruption in children with high-grade glioma and diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma: Results of a phase I trial. J. Neurosurgery Pediatr. 2021, 28, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upadhyayula, P.S.; Spinazzi, E.F.; Argenziano, M.G.; Canoll, P.; Bruce, J.N. Convection Enhanced Delivery of Topotecan for Gliomas: A Single-Center Experience. Pharmaceutics 2020, 13, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| CTA | 1st Dosage | 4th Dosage | % of the IV Dosage | Dosage Used for Survival Studies |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Topotecan | 1 mg/kg | 4 mg/kg | 100% | 4 mg/kg |
| Cytarabine | 10 mg/kg | 8.75 mg/kg | 21.88% | 8.75 mg/kg |
| Paclitaxel | 3.3 mg/kg | 0.825 mg/kg | - | Too toxic |
| Chemotherapy Agent and Administration Route | Median Survival (Days) |
|---|---|
| Topotecan—IA | 29.0 |
| Topotecan—IV | 23.5 |
| Cytarabine—IA | 22.5 |
| Cytarabine—IV | 26.5 |
| Control | 25.5 |
| Carboplatin (Ingenew‘s formulation)—IA | 37.5 |
| Paclitaxel (Ingenew’s formulation)—IT | 28.5 |
| Paclitaxel (Ingenew’s formulation) SHAM—IT | 29.0 |
| Study | Côté et al. (2013) [29] | Charest et al. (2013) [27] | Present Study |
|---|---|---|---|
| Drug | Carboplatin (saline) | Carboplatin (5% dextrose) | Carboplatin (Ingenew’s formulation) |
| Median survival (days) | 26.0 *** | 30.0 ** | 37.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Latulippe, J.; Roy, L.-O.; Gobeil, F.; Fortin, D. Optimization of Intra-Arterial Administration of Chemotherapeutic Agents for Glioblastoma in the F98-Fischer Glioma-Bearing Rat Model. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 421. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15030421
Latulippe J, Roy L-O, Gobeil F, Fortin D. Optimization of Intra-Arterial Administration of Chemotherapeutic Agents for Glioblastoma in the F98-Fischer Glioma-Bearing Rat Model. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(3):421. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15030421
Chicago/Turabian StyleLatulippe, Juliette, Laurent-Olivier Roy, Fernand Gobeil, and David Fortin. 2025. "Optimization of Intra-Arterial Administration of Chemotherapeutic Agents for Glioblastoma in the F98-Fischer Glioma-Bearing Rat Model" Biomolecules 15, no. 3: 421. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15030421
APA StyleLatulippe, J., Roy, L.-O., Gobeil, F., & Fortin, D. (2025). Optimization of Intra-Arterial Administration of Chemotherapeutic Agents for Glioblastoma in the F98-Fischer Glioma-Bearing Rat Model. Biomolecules, 15(3), 421. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15030421







