Local Insulin for Local Needs? Insights into Retinal Insulin Signaling and RPE Metabolism
Abstract
1. Introduction
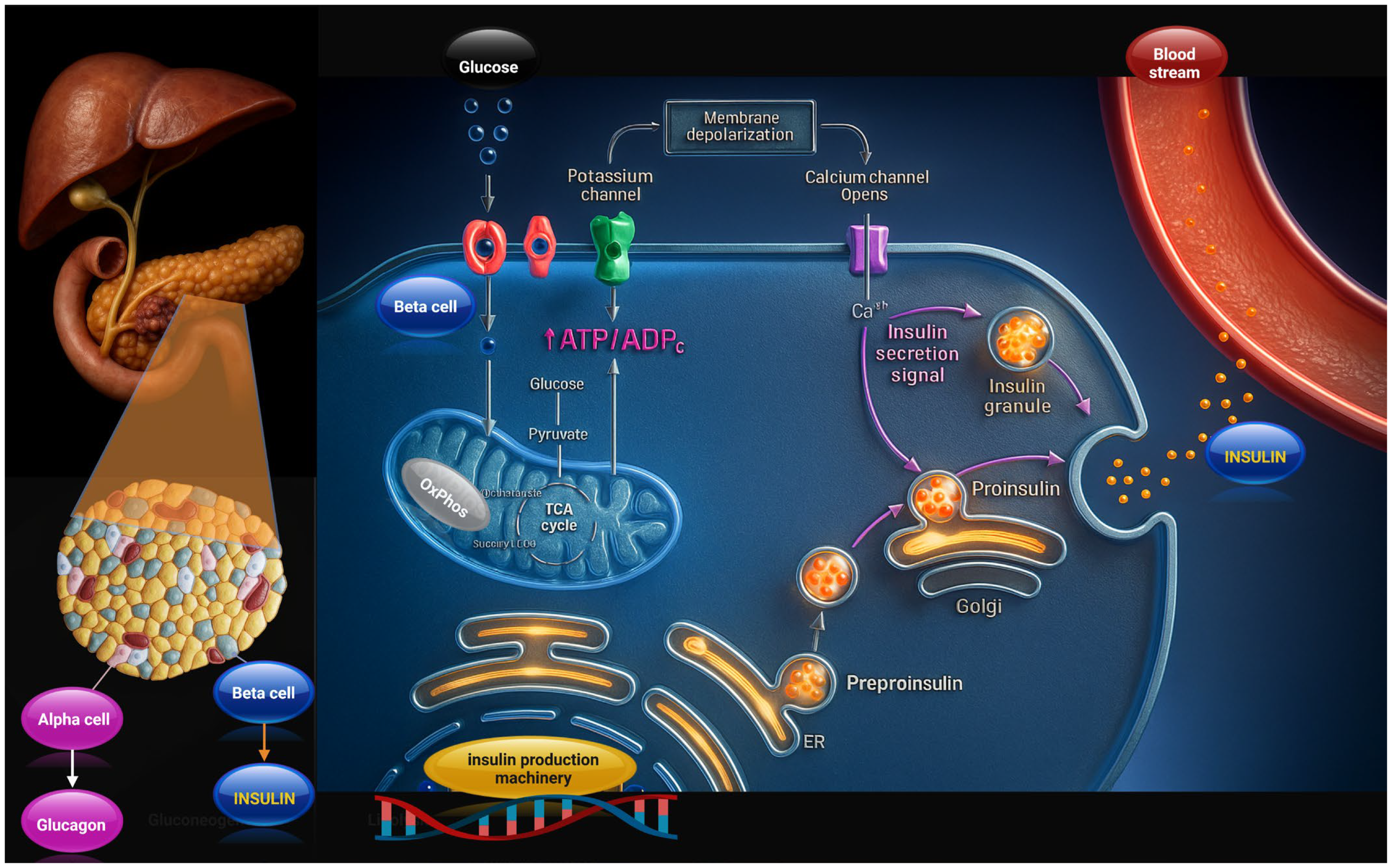
2. Insulin and Its Pancreatic Production: Molecular Mechanisms and Physiological and Pathological Implications
2.1. Pancreatic Insulin Production and Release
2.2. Molecular Mechanisms of Insulin Action
2.3. Insulin Systemic Metabolic Effects
| Cell Type | Insulin Receptor (IR) Relative Expression/Function | Major Downstream Pathways Activated | Key Metabolic and Functional Outcomes | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pancreatic β-cell | Moderate IR expression; autocrine/paracrine roles—IR influences β-cell function and survival. | PI3K → Akt (survival, proliferation, transcriptional effects) and MAPK/ERK (growth/secretion modulation). | Regulation of insulin secretion (modulatory/autocrine), β-cell growth and survival, gene expression related to secretory machinery. | [69,70] |
| Skeletal muscle (myocytes) | High functional IR at the surface of insulin-responsive fibers; key peripheral glucose sink. | PI3K → Akt → AS160/TBC1D4 cascade and also MAPK/ERK. The PI3K pathway is required for GLUT4 translocation. | Rapid GLUT4 translocation → ↑ glucose uptake; glycogen synthesis (via GSK3 inhibition); protein synthesis (mTOR). | [71,72] |
| Adipocyte (white adipose tissue) | High IR expression; insulin controls adipocyte differentiation and lipogenesis. | PI3K → Akt → mTORC1 and SREBP-1c induction; MAPK/ERK involved in proliferation/differentiation. | ↑ GLUT4 translocation and glucose uptake, ↑ lipogenesis (SREBP-1c → lipogenic genes), inhibition of lipolysis (via PDE3B/cAMP pathways). | [73,74] |
| Hepatocyte (liver) | High expression of IR; the liver is a major insulin target. | PI3K → Akt (dominant) and MAPK/ERK. PI3K/Akt → mTORC1, inhibition of GSK3, regulation of FOXO1. | ↑ glycogen synthesis (via GSK3 inhibition & GCK), ↓ gluconeogenesis (via FOXO1 inactivation), ↑ lipogenesis (SREBP-1c via mTORC1). | [75] |
| Endothelial cell (vascular endothelium) | Moderate IR expression; endothelial insulin signaling is physiologically important but can be selectively impaired in insulin resistance. | PI3K → Akt → eNOS activation (NO production); MAPK/ERK mainly mediates mitogenic responses. | Vasodilation via eNOS/NO, regulation of capillary recruitment and hemodynamic–metabolic coupling; effects on vascular tone and substrate delivery. | [76,77] |
| Neurons / Retina (neuronal cells, photoreceptors, retinal ganglion cells) | Variable/moderate IR expression—retina and many CNS neurons express IR and are insulin-sensitive. | PI3K → Akt (survival, metabolism) and MAPK/ERK (growth/plasticity). | Neuronal survival, synaptic maintenance, metabolic support; in the retina, insulin signaling supports photoreceptor and ganglion cell function. Dysregulation linked to retinal disease. | [19,78] |
3. Insulin and Retina: State of the Art
3.1. Insulin Signaling Effect on Retina in Physiological and Pathological Conditions
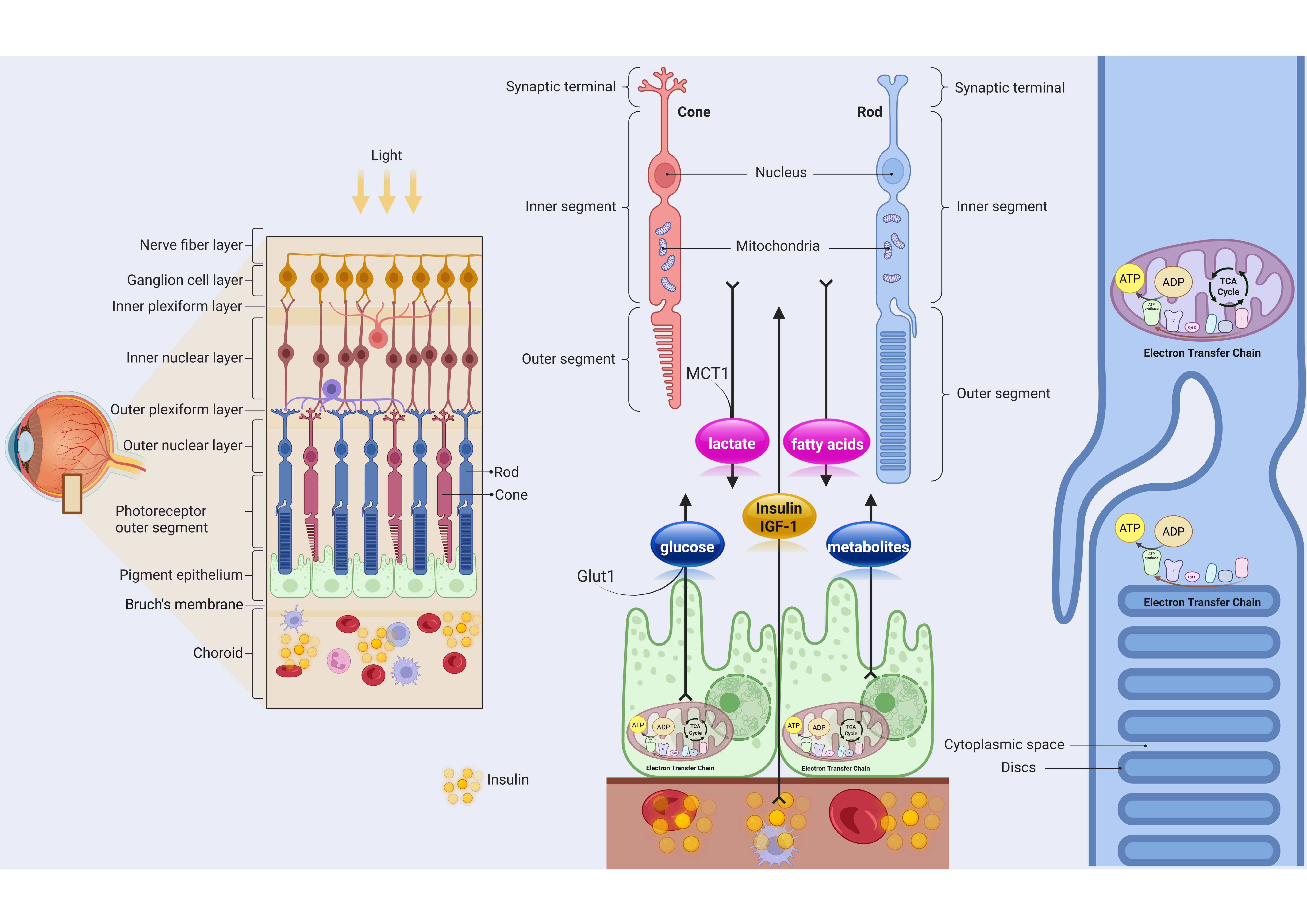
3.2. Interaction Between Photoreceptors and RPE
3.3. Metabolic Crosstalk Between Photoreceptors and RPE and Insulin Role in This Link
4. Insulin and Retina: New Perspectives
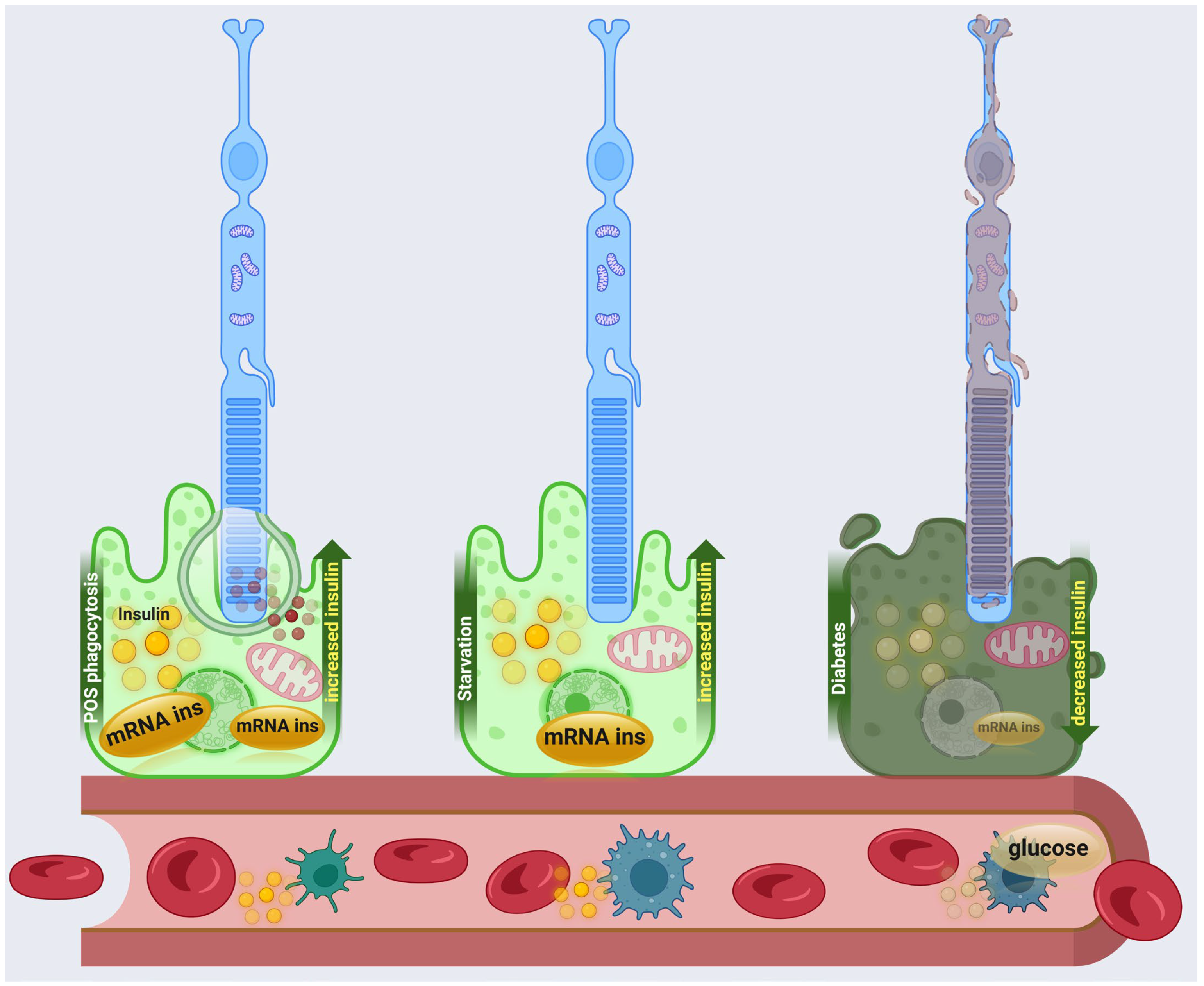
4.1. Local Insulin Production in RPE
4.2. Perspective on RPE Insulin Production on Retinal Diseases
4.3. Study Limitations
4.4. Future Research Priorities
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Etchegaray, J.I.; Kelley, S.; Penberthy, K.; Karvelyte, L.; Nagasaka, Y.; Gasperino, S.; Paul, S.; Seshadri, V.; Raymond, M.; Marco, A.R.; et al. Phagocytosis in the Retina Promotes Local Insulin Production in the Eye. Nat. Metab. 2023, 5, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarchick, M.J.; Cutler, A.H.; Trobenter, T.D.; Kozlowski, M.R.; Makowski, E.R.; Holoman, N.; Shao, J.; Shen, B.; Anand-Apte, B.; Samuels, I.S. Endogenous Insulin Signaling in the RPE Contributes to the Maintenance of Rod Photoreceptor Function in Diabetes. Exp. Eye Res. 2019, 180, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.S.; Hossain, K.S.; Das, S.; Kundu, S.; Adegoke, E.O.; Rahman, M.A.; Hannan, M.A.; Uddin, M.J.; Pang, M.G. Role of Insulin in Health and Disease: An Update. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norton, L.; Shannon, C.; Gastaldelli, A.; DeFronzo, R.A. Insulin: The Master Regulator of Glucose Metabolism. Metabolism 2022, 129, 155142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rorsman, P.; Ashcroft, F.M. Pancreatic β-Cell Electrical Activity and Insulin Secretion: Of Mice and Men. Physiol. Rev. 2017, 98, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honka, M.J.; Latva-Rasku, A.; Bucci, M.; Virtanen, K.A.; Hannukainen, J.C.; Kalliokoski, K.K.; Nuutila, P. Insulin-Stimulated Glucose Uptake in Skeletal Muscle, Adipose Tissue and Liver: A Positron Emission Tomography Study. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 178, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrannini, E.; Iozzo, P.; Virtanen, K.A.; Honka, M.J.; Bucci, M.; Nuutila, P. Adipose Tissue and Skeletal Muscle Insulin-Mediated Glucose Uptake in Insulin Resistance: Role of Blood Flow and Diabetes. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 108, 749–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gastaldelli, A.; Toschi, E.; Pettiti, M.; Frascerra, S.; Quiñones-Galvan, A.; Sironi, A.M.; Natali, A.; Ferrannini, E. Effect of Physiological Hyperinsulinemia on Gluconeogenesis in Nondiabetic Subjects and in Type 2 Diabetic Patients. Diabetes 2001, 50, 1807–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatting, M.; Tavares, C.D.J.; Sharabi, K.; Rines, A.K.; Puigserver, P. Insulin Regulation of Gluconeogenesis. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2017, 1411, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, L. Energy Metabolism in the Liver. Compr. Physiol. 2014, 4, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessari, P. Stepwise Discovery of Insulin Effects on Amino Acid and Protein Metabolism. Nutrients 2023, 16, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riachi, R.; Khalife, E.; Kędzia, A.; Niechciał, E. Understanding Insulin Actions Beyond Glycemic Control: A Narrative Review. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 5039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Yu, M.G.; Li, Q.; Park, K.; King, G.L. Insulin’s Actions on Vascular Tissues: Physiological Effects and Pathophysiological Contributions to Vascular Complications of Diabetes. Mol. Metab. 2021, 52, 101236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straus, D.S. Effects of Insulin on Cellular Growth and Proliferation. Life Sci. 1981, 29, 2131–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, R.M.; Streeper, R.S.; Ayala, J.E.; Stadelmaier, B.T.; Hornbuckle, L.A. Insulin-Regulated Gene Expression. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2001, 29, 552–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, W.B.; Barrett, E.J. Microvascular Dysfunction in Diabetes Mellitus and Cardiometabolic Disease. Endocr. Rev. 2020, 42, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathy, D.; Chavez, A.O. Defects in Insulin Secretion and Action in the Pathogenesis of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Curr. Diab. Rep. 2010, 10, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, K.; Islam, R.; Nguyen, I.; Malik, H.; Pirzadah, H.; Shrestha, B.; Lentz, I.B.; Shekoohi, S.; Kaye, A.D. Diabetes Mellitus and Associated Vascular Disease: Pathogenesis, Complications, and Evolving Treatments. Adv. Ther. 2025, 42, 2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.; Yu, X. Insulin Resistance in the Retina: Possible Implications for Certain Ocular Diseases. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1415521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, G.D.S. The Cells of the Islets of Langerhans. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, P.E.; Joseph, J.W.; Rorsman, P. Glucose-Sensing Mechanisms in Pancreatic β-Cells. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2005, 360, 2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerf, M.E. Beta Cell Dysfunction and Insulin Resistance. Front. Endocrinol. 2013, 4, 43179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Weiss, M.A.; Arunagiri, A.; Yong, J.; Rege, N.; Sun, J.; Haataja, L.; Kaufman, R.J.; Arvan, P. Biosynthesis, Structure, and Folding of the Insulin Precursor Protein. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2018, 20, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Huang, Y.; Xu, X.; Li, X.; Alam, M.; Arunagiri, A.; Haataja, L.; Ding, L.; Wang, S.; Itkin-Ansari, P.; et al. Normal and Defective Pathways in Biogenesis and Maintenance of the Insulin Storage Pool. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, 142240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarmiento, B.E.; Felipe, L.; Menezes, S.; Schwartz, E.F.; Gomes, P.A.C.; Galdiero, S.; Teixeira, C. Insulin Release Mechanism Modulated by Toxins Isolated from Animal Venoms: From Basic Research to Drug Development Prospects. Molecules 2019, 24, 1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilcox, G. Insulin and Insulin Resistance. Clin. Biochem. Rev. 2005, 26, 19. [Google Scholar]
- Berger, C.; Zdzieblo, D. Glucose Transporters in Pancreatic Islets. Pflügers Arch.-Eur. J. Physiol. 2020, 472, 1249–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, M.; Takei, M.; Ishii, H.; Sato, Y. Glucose—Stimulated Insulin Secretion: A Newer Perspective. J. Diabetes Investig. 2013, 4, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Wei, M.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, Z.; Song, M.; Mi, J.; Yang, X.; Tian, G. Regulation of Insulin Secretion by the Post-Translational Modifications. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 1217189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newsholme, P.; Krause, M. Nutritional Regulation of Insulin Secretion: Implications for Diabetes. Clin. Biochem. Rev. 2012, 33, 35. [Google Scholar]
- Itoh, Y.; Kawamata, Y.; Harada, M.; Kobayashi, M.; Fujii, R.; Fukusumi, S.; Ogi, K.; Hosoya, M.; Tanaka, Y.; Uejima, H.; et al. Free Fatty Acids Regulate Insulin Secretion from Pancreatic Beta Cells through GPR40. Nature 2003, 422, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seino, Y.; Fukushima, M.; Yabe, D. GIP and GLP-1, the Two Incretin Hormones: Similarities and Differences. J. Diabetes Investig. 2010, 1, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayendraraj, A.; Rosenkilde, M.M.; Gasbjerg, L.S. GLP-1 and GIP Receptor Signaling in Beta Cells—A Review of Receptor Interactions and Co-Stimulation. Peptides 2022, 151, 170749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chon, S.; Gautier, J.F. An Update on the Effect of Incretin-Based Therapies on β-Cell Function and Mass. Diabetes Metab. J. 2016, 40, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.-H.; Lee, M.-K. The Incretins and Pancreatic β-Cells: Use of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 and Glucose-Dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide to Cure Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Korean Diabetes J. 2010, 34, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prates, K.V.; de Oliveira, J.C.; Malta, A.; Matiusso, C.C.I.; Miranda, R.A.; Ribeiro, T.A.; Francisco, F.A.; Franco, C.C.S.; Moreira, V.M.; Alves, V.S.; et al. Sympathetic Innervation Is Essential for Metabolic Homeostasis and Pancreatic Beta Cell Function in Adult Rats. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2018, 462, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, J.; Rodriguez-Diaz, R.; Fachado, A.; Jacques-Silva, M.C.; Berggren, P.O.; Caicedo, A. Control of Insulin Secretion by Cholinergic Signaling in the Human Pancreatic Islet. Diabetes 2014, 63, 2714–2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tengholm, A.; Gylfe, E. CAMP Signalling in Insulin and Glucagon Secretion. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2017, 19, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merabet, N.; Lucassen, P.J.; Crielaard, L.; Stronks, K.; Quax, R.; Sloot, P.M.A.; la Fleur, S.E.; Nicolaou, M. How Exposure to Chronic Stress Contributes to the Development of Type 2 Diabetes: A Complexity Science Approach. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2022, 65, 100972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, M.C.; Shulman, G.I. Mechanisms of Insulin Action and Insulin Resistance. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbard, S.R. The Insulin Receptor: Both a Prototypical and Atypical Receptor Tyrosine Kinase. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a008946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saltiel, A.R. Insulin Signaling in Health and Disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, 142241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, B.J.; Bittner-Kowalczyk, A.; White, M.F.; Harbeck, M. Tyrosine Dephosphorylation and Deactivation of Insulin Receptor Substrate-1 by Protein-Tyrosine Phosphatase 1B: Possible Facilitation by the Formation of a Ternary Complex with the GRB2 Adaptor Protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 4283–4289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanke, S.; Mann, M. The Phosphotyrosine Interactome of the Insulin Receptor Family and Its Substrates IRS-1 and IRS-2. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2009, 8, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Meyts, P. The Insulin Receptor and Its Signal Transduction Network. Endotext 2016. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK378978/ (accessed on 5 November 2025).
- Yunn, N.O.; Kim, J.; Ryu, S.H.; Cho, Y. A Stepwise Activation Model for the Insulin Receptor. Exp. Mol. Med. 2023, 55, 2147–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Świderska, E.; Strycharz, J.; Wróblewski, A.; Szemraj, J.; Drzewoski, J.; Śliwińska, A.; Świderska, E.; Strycharz, J.; Wróblewski, A.; Szemraj, J.; et al. Role of PI3K/AKT Pathway in Insulin-Mediated Glucose Uptake. Blood Glucose Levels 2018, 37, 80402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirago, G.; Picca, A.; Calvani, R.; Coelho-Júnior, H.J.; Marzetti, E. Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (MTOR) Signaling at the Crossroad of Muscle Fiber Fate in Sarcopenia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, M.J.; Sul, H.S. Insulin Regulation of Fatty Acid Synthase Gene Transcription: Roles of USF and SREBP-1c. IUBMB Life 2004, 56, 595–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, C.; Tsujita, T.; Okuda, H. Antilipolytic Actions of Insulin on Basal and Hormone-Induced Lipolysis in Rat Adipocytes. J. Lipid Res. 1998, 39, 957–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, C.A.; Ribon, V.; Kanzaki, M.; Thurmond, D.C.; Mora, S.; Shigematsu, S.; Bickel, P.E.; Pessin, J.E.; Saltiel, A.R. CAP Defines a Second Signalling Pathway Required for Insulin-Stimulated Glucose Transport. Nature 2000, 407, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, B.J. Protein-Tyrosine Phosphatases: Emerging Targets for Therapeutic Intervention in Type 2 Diabetes and Related States of Insulin Resistance. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 87, 2474–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fisslthaler, B.; Benzing, T.; Busse, R.; Fleming, I. Insulin Enhances the Expression of the Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase in Native Endothelial Cells: A Dual Role for Akt and AP-1. Nitric. Oxide 2003, 8, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.R.; Wang, M.Y.; Zhang, C.L.; Wang, Y. Endothelial Dysfunction in Vascular Complications of Diabetes: A Comprehensive Review of Mechanisms and Implications. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1359255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, B. Pathophysiological Mechanisms of Diabetes-Induced Macrovascular and Microvascular Complications: The Role of Oxidative Stress. Med. Sci. 2025, 13, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, A.; Thool, A.R.; Daigavane, S. Understanding the Clinical Relationship Between Diabetic Retinopathy, Nephropathy, and Neuropathy: A Comprehensive Review. Cureus 2024, 16, e56674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Heide, L.P.; Ramakers, G.M.J.; Smidt, M.P. Insulin Signaling in the Central Nervous System: Learning to Survive. Prog. Neurobiol. 2006, 79, 205–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, E.; Carrillo Sepulveda, M.A. Biochemistry, Insulin, Metabolic Effects; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2018. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK525983/ (accessed on 5 November 2025).
- Merz, K.E.; Thurmond, D.C. Role of Skeletal Muscle in Insulin Resistance and Glucose Uptake. Compr. Physiol. 2020, 10, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J. Enhanced Skeletal Muscle for Effective Glucose Homeostasis. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2014, 121, 133–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, A.; McGraw, T.E.; Kahn, B.B. Insulin Action in Adipocytes, Adipose Remodeling, and Systemic Effects. Cell Metab. 2021, 33, 748–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titchenell, P.M.; Lazar, M.A.; Birnbaum, M.J. Unraveling the Regulation of Hepatic Metabolism by Insulin. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 28, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, H.A.; O’Neill, B.T.; Nair, K.S. Insulin Regulation of Proteostasis and Clinical Implications. Cell Metab 2017, 26, 310–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, D.Y.; Park, S.H.; Marquez, J.; Kwak, H.B.; Kim, T.N.; Bae, J.H.; Koh, J.H.; Han, J. Hepatokines as a Molecular Transducer of Exercise. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafontan, M.; Viguerie, N. Role of Adipokines in the Control of Energy Metabolism: Focus on Adiponectin. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2006, 6, 580–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ormazabal, V.; Nair, S.; Elfeky, O.; Aguayo, C.; Salomon, C.; Zuñiga, F.A. Association between Insulin Resistance and the Development of Cardiovascular Disease. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2018, 17, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjornstad, P.; Eckel, R.H. Pathogenesis of Lipid Disorders in Insulin Resistance: A Brief Review. Curr. Diab. Rep. 2018, 18, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parhofer, K.G. Interaction between Glucose and Lipid Metabolism: More than Diabetic Dyslipidemia. Diabetes Metab. J. 2015, 39, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leibiger, B.; Leibiger, I.B.; Moede, T.; Kemper, S.; Kulkarni, R.N.; Kahn, C.R.; De Vargas, L.M.; Berggren, P.O. Selective Insulin Signaling through A and B Insulin Receptors Regulates Transcription of Insulin and Glucokinase Genes in Pancreatic Beta Cells. Mol. Cell 2001, 7, 559–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, C.J.; White, M.F.; Leahy, J.L.; Kahn, S.E. Direct Autocrine Action of Insulin on β-Cells: Does It Make Physiological Sense? Diabetes 2013, 62, 2157–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ijuin, T.; Hatano, N.; Hosooka, T.; Takenawa, T. Regulation of Insulin Signaling in Skeletal Muscle by PIP3 Phosphatase, SKIP, and Endoplasmic Reticulum Molecular Chaperone Glucose-Regulated Protein 78. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Cell Res. 2015, 1853, 3192–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Gerwen, J.; Shun-Shion, A.S.; Fazakerley, D.J. Insulin Signalling and GLUT4 Trafficking in Insulin Resistance. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2023, 51, 1057–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cignarelli, A.; Genchi, V.A.; Perrini, S.; Natalicchio, A.; Laviola, L.; Giorgino, F. Insulin and Insulin Receptors in Adipose Tissue Development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crewe, C.; Zhu, Y.; Paschoal, V.A.; Joffin, N.; Ghaben, A.L.; Gordillo, R.; Oh, D.Y.; Liang, G.; Horton, J.D.; Scherer, P.E. SREBP-Regulated Adipocyte Lipogenesis Is Dependent on Substrate Availability and Redox Modulation of MTORC1. JCI Insight 2019, 4, e129397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.H.; Najjar, S.M.; Kahn, C.R.; Hinds, T.D. Hepatic Insulin Receptor: New Views on the Mechanisms of Liver Disease. Metabolism 2023, 145, 155607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muniyappa, R.; Iantorno, M.; Quon, M.J. An Integrated View of Insulin Resistance and Endothelial Dysfunction. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2008, 37, 685–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, G.; Nystrom, F.H.; Ravichandran, L.V.; Cong, L.N.; Kirby, M.; Mostowski, H.; Quon, M.J. Roles for Insulin Receptor, PI3-Kinase, and Akt in Insulin-Signaling Pathways Related to Production of Nitric Oxide in Human Vascular Endothelial Cells. Circulation 2000, 101, 1539–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiter, C.E.N.; Gardner, T.W. Functions of Insulin and Insulin Receptor Signaling in Retina: Possible Implications for Diabetic Retinopathy. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2003, 22, 545–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Awamlh, S.A.H.; Wareham, L.K.; Risner, M.L.; Calkins, D.J. Insulin Signaling as a Therapeutic Target in Glaucomatous Neurodegeneration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Lee, S.R.; Mathai, A.E.; Zhang, R.; Du, J.; Yam, M.X.; Pye, V.; Barnett, N.L.; Rayner, C.L.; Zhu, L.; et al. Effect of Selectively Knocking down Key Metabolic Genes in Müller Glia on Photoreceptor Health. Glia 2021, 69, 1966–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajala, A.; Dighe, R.; Agbaga, M.P.; Anderson, R.E.; Rajala, R.V.S. Insulin Receptor Signaling in Cones. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 19503–19515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajala, A.; Wang, Y.; Brush, R.S.; Tsantilas, K.; Jankowski, C.S.R.; Lindsay, K.J.; Linton, J.D.; Hurley, J.B.; Anderson, R.E.; Rajala, R.V.S. Pyruvate Kinase M2 Regulates Photoreceptor Structure, Function, and Viability. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocrant, I.; Fay, C.T.; Parmelee, J.T. Expression of Insulin and Insulin-like Growth Factor Receptors and Binding Proteins by Retinal Pigment Epithelium. Exp. Eye Res. 1991, 52, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Hajji, S.; Shiga, Y.; Belforte, N.; Solorio, Y.C.; Tastet, O.; D’Onofrio, P.; Dotigny, F.; Prat, A.; Arbour, N.; Fortune, B.; et al. Insulin Restores Retinal Ganglion Cell Functional Connectivity and Promotes Visual Recovery in Glaucoma. Sci. Adv. 2024, 10, 5722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivaprasad, S.; Wong, T.Y.; Gardner, T.W.; Sun, J.K.; Bressler, N.M. Diabetic Retinal Disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2025, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rask-Madsen, C.; King, G.L. Vascular Complications of Diabetes: Mechanisms of Injury and Protective Factors. Cell Metab. 2013, 17, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padovani-Claudio, D.A.; Ramos, C.J.; Capozzi, M.E.; Penn, J.S. Elucidating Glial Responses to Products of Diabetes-Associated Systemic Dyshomeostasis. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2023, 94, 101151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Sun, X.; Fan, C.; Li, R.; Zhou, S.; Yu, H. The Pathophysiological Mechanisms Underlying Diabetic Retinopathy. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 963615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiemer, N.G.M.; Eekhoff, E.M.W.; Simsek, S.; Heine, R.J.; Ringens, P.J.; Polak, B.C.P.; Dubbelman, M. The Effect of Acute Hyperglycemia on Retinal Thickness and Ocular Refraction in Healthy Subjects. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2008, 246, 703–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Cruz, A.; Hernández-Pinto, A.; Lillo, C.; Isiegas, C.; Marchena, M.; Lizasoain, I.; Bosch, F.; de la Villa, P.; Hernández-Sánchez, C.; de la Rosa, E.J. Insulin Receptor Activation by Proinsulin Preserves Synapses and Vision in Retinitis Pigmentosa. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovács-Valasek, A.; Rák, T.; Pöstyéni, E.; Csutak, A.; Gábriel, R. Three Major Causes of Metabolic Retinal Degenerations and Three Ways to Avoid Them. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, S.S.R.; Radhakrishnan, N.S.; Roohipourmoallai, R.; Guerin, C.M.; Maylath, J.S.; Garson, N. Chronic Ocular Small Vessel Disease: An Overview of Diabetic Retinopathy and Its Relationship with Cardiovascular Health. Am. Heart Hournal Plus Cardiol. Res. Pract. 2023, 29, 100270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, M.; Petroianu, G.; Adem, A. Advanced Glycation End Products and Diabetes Mellitus: Mechanisms and Perspectives. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, E.; Alam, N.M.; Prusky, G.T.; Sagdullaev, B.T. Blood-Retina Barrier Failure and Vision Loss in Neuron-Specific Degeneration. JCI Insight 2019, 4, e126747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Zhou, M.; Cai, X.; Zhou, Y.; Jiang, X.; Luo, Y.; Hu, Y.; Qiu, R.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; et al. VEGF Promotes Diabetic Retinopathy by Upregulating the PKC/ET/NF-ΚB/ICAM-1 Signaling Pathway. Eur. J. Histochem. 2022, 66, 3522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callan, A.; Heckman, J.; Tah, G.; Lopez, S.; Valdez, L.; Tsin, A. VEGF in Diabetic Retinopathy and Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurley, J.B. Retina Metabolism and Metabolism in the Pigmented Epithelium: A Busy Intersection. Annu. Rev. Vis. Sci. 2021, 7, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, W.; Chen, M.; Cao, Y.; Lu, W.; Li, X. The Retinal Pigment Epithelium: Functions and Roles in Ocular Diseases. Fundam. Res. 2023, 4, 1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansman, D.S.; Ma, Y.; Thomas, D.; Smith, J.R.; Casson, R.J.; Peet, D.J. Metabolic Reprogramming of the Retinal Pigment Epithelium by Cytokines Associated with Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Biosci. Rep. 2024, 44, BSR20231904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieffrig, S.A.; Gyimesi, G.; Mao, Y.; Finnemann, S.C. Clearance Phagocytosis by the Retinal Pigment Epithelium during Photoreceptor Outer Segment Renewal: Molecular Mechanisms and Relation to Retinal Inflammation. Immunol. Rev. 2023, 319, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen-Legros, J.; Hicks, D. Renewal of Photoreceptor Outer Segments and Their Phagocytosis by the Retinal Pigment Epithelium. Int. Rev. Cytol. 2000, 196, 245–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milićević, N.; Hakkari, O.A.-H.; Bagchi, U.; Sandu, C.; Jongejan, A.; Moerland, P.D.; ten Brink, J.B.; Hicks, D.; Bergen, A.A.; Felder-Schmittbuhl, M.P. Core Circadian Clock Genes Per1 and Per2 Regulate the Rhythm in Photoreceptor Outer Segment Phagocytosis. FASEB J. 2021, 35, e21722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baba, K.; Goyal, V.; Tosini, G. Circadian Regulation of Retinal Pigment Epithelium Function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.Y.; Kim, I.S. Engulfment Signals and the Phagocytic Machinery for Apoptotic Cell Clearance. Exp. Mol. Med. 2017, 49, e331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Audo, I.; Mohand-Said, S.; Boulanger-Scemama, E.; Zanlonghi, X.; Condroyer, C.; Démontant, V.; Boyard, F.; Antonio, A.; Méjécase, C.; Shamieh, S.E.; et al. MERTK Mutation Update in Inherited Retinal Diseases. Hum. Mutat. 2018, 39, 887–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Lu, Q.; Wei, Y.; Han, L.; Ji, R.; Li, Q.; Lu, Q. Mertk Deficiency Alters Expression of MicroRNAs in the Retinal Pigment Epithelium Cells. Metab. Brain Dis. 2015, 30, 943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejos, C.; Kuny, S.; Han, W.H.; Capel, H.; Lemieux, H.; Sauvé, Y. Photoreceptor-Induced RPE Phagolysosomal Maturation Defects in Stargardt-like Maculopathy (STGD3). Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, W.; Freeman, S.A. Phagocytosis by the Retinal Pigment Epithelium: Recognition, Resolution, Recycling. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 604205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dontsov, A.; Ostrovsky, M. Retinal Pigment Epithelium Pigment Granules: Norms, Age Relations and Pathology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewandowski, D.; Sander, C.L.; Tworak, A.; Gao, F.; Xu, Q.; Skowronska-Krawczyk, D. Dynamic Lipid Turnover in Photoreceptors and Retinal Pigment Epithelium throughout Life. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2021, 89, 101037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, A.L.; Fehilly, J.D.; Jones, D.F.; Collery, R.; Kennedy, B.N. Regulation of the Rhythmic Diversity of Daily Photoreceptor Outer Segment Phagocytosis in Vivo. FASEB J. 2022, 36, e22556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piskova, T.; Kozyrina, A.N.; Russo, J. Di Mechanobiological Implications of Age-Related Remodelling in the Outer Retina. Biomater. Adv. 2023, 147, 213343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abokyi, S.; Tse, D.Y.Y. Age-Related Driving Mechanisms of Retinal Diseases and Neuroprotection by Transcription Factor EB-Targeted Therapy. Neural Regen. Res. 2024, 20, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sparrrow, J.R.; Hicks, D.; Hamel, C.P. The Retinal Pigment Epithelium in Health and Disease. Curr. Mol. Med. 2010, 10, 802–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.W.; Wubben, T.J.; Besirli, C.G. Photoreceptor Metabolic Reprogramming: Current Understanding and Therapeutic Implications. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hass, D.T.; Bisbach, C.M.; Sadilek, M.; Sweet, I.R.; Hurley, J.B. Aerobic Glycolysis in Photoreceptors Supports Energy Demand in the Absence of Mitochondrial Coupling. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2023, 1415, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linton, J.D.; Holzhausen, L.C.; Babai, N.; Song, H.; Miyagishima, K.J.; Stearns, G.W.; Lindsay, K.; Wei, J.; Chertov, A.O.; Peters, T.A.; et al. Flow of Energy in the Outer Retina in Darkness and in Light. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 8599–8604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Rountree, A.; Cleghorn, W.M.; Contreras, L.; Lindsay, K.J.; Sadilek, M.; Gu, H.; Djukovic, D.; Raftery, D.; Satrústegui, J.; et al. Phototransduction Influences Metabolic Flux and Nucleotide Metabolism in Mouse Retina. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 4698–4710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panfoli, I.; Calzia, D.; Bruschi, M.; Oneto, M.; Bianchini, P.; Ravera, S.; Petretto, A.; Diaspro, A.; Candiano, G. Functional Expression of Oxidative Phosphorylation Proteins in the Rod Outer Segment Disc. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2013, 31, 2943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panfoli, I.; Calzia, D.; Bianchini, P.; Ravera, S.; Diaspro, A.; Candiano, G.; Bachi, A.; Monticone, M.; Aluigi, M.G.; Barabino, S.; et al. Evidence for Aerobic Metabolism in Retinal Rod Outer Segment Disks. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2009, 41, 2555–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panfoli, I.; Calzia, D.; Ravera, S.; Bruschi, M.; Tacchetti, C.; Candiani, S.; Morelli, A.; Candiano, G. Extramitochondrial Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle in Retinal Rod Outer Segments. Biochimie 2011, 93, 1565–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panfoli, I.; Musante, L.; Bachi, A.; Ravera, S.; Calzia, D.; Cattaneo, A.; Bruschi, M.; Bianchini, P.; Diaspro, A.; Morelli, A.; et al. Proteomic Analysis of the Retinal Rod Outer Segment Disks. J. Proteome Res. 2008, 7, 2654–2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calzia, D.; Panfoli, I.; Heinig, N.; Schumann, U.; Ader, M.; Traverso, C.E.; Funk, R.H.W.; Roehlecke, C. Impairment of Extramitochondrial Oxidative Phosphorylation in Mouse Rod Outer Segments by Blue Light Irradiation. Biochimie 2016, 125, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Kern, T.S.; Hellström, A.; Smith, L.E.H. Fatty Acid Oxidation and Photoreceptor Metabolic Needs. J. Lipid Res. 2021, 62, 100035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajala, R.V.S.; Anderson, R.E. Rhodopsin-Regulated Insulin Receptor Signaling Pathway in Rod Photoreceptor Neurons. Mol. Neurobiol. 2010, 42, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Punzo, C.; Kornacker, K.; Cepko, C.L. Stimulation of the Insulin/MTOR Pathway Delays Cone Death in a Mouse Model of Retinitis Pigmentosa. Nat. Neurosci. 2008, 12, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natalini, P.M.; Mateos, M.V.; de Boschero, M.G.I.; Giusto, N.M. Insulin-Related Signaling Pathways Elicited by Light in Photoreceptor Nuclei from Bovine Retina. Exp. Eye Res. 2016, 145, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanna, J.; David, L.A.; Touahri, Y.; Fleming, T.; Screaton, R.A.; Schuurmans, C. Beyond Genetics: The Role of Metabolism in Photoreceptor Survival, Development and Repair. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 887764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, S.; Carroll, L.S.; Vinberg, F. Diabetic Photoreceptors: Mechanisms Underlying Changes in Structure and Function. Vis. Neurosci. 2020, 37, E008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Wu, W.; Hara, M.; Zhou, J.; Panzarin, C.; Schafer, C.M.; Griffin, C.T.; Cai, J.; Ma, J.X.; Takahashi, Y. Deficient RPE Mitochondrial Energetics Leads to Subretinal Fibrosis in Age-Related Neovascular Macular Degeneration. Commun. Biol. 2024, 7, 1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhang, T.; Liu, W.; Wang, Y.; Xu, R.; Zeng, S.; Zhang, R.; Zhu, S.; Gillies, M.C.; Zhu, L.; et al. Metabolic Features of Mouse and Human Retinas: Rods versus Cones, Macula versus Periphery, Retina versus RPE. iScience 2020, 23, 101672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravera, S.; Puddu, A.; Bertola, N.; Verzola, D.; Russo, E.; Maggi, D.; Panfoli, I. IGF-1 Signaling Modulates Oxidative Metabolism and Stress Resistance in ARPE-19 Cells Through PKM2 Function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 13640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coffe, V.; Carbajal, R.C.; Salceda, R. Glucose Metabolism in Rat Retinal Pigment Epithelium. Neurochem. Res. 2006, 31, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swarup, A.; Samuels, I.S.; Bell, B.A.; Han, J.Y.S.; Du, J.; Massenzio, E.; Abel, E.D.; Boesze-Battaglia, K.; Peachey, N.S.; Philp, N.J. Modulating GLUT1 Expression in Retinal Pigment Epithelium Decreases Glucose Levels in the Retina: Impact on Photoreceptors and Müller Glial Cells. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2018, 316, C121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, J.R.; Knight, K.; Engel, A.L.; Jankowski, C.; Wang, Y.; Manson, M.A.; Gu, H.; Djukovic, D.; Raftery, D.; Hurley, J.B.; et al. Human Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells Prefer Proline as a Nutrient and Transport Metabolic Intermediates to the Retinal Side. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 12895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Ritz, B.K.; Wang, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhao, C.; Gong, K.; Liu, X.; Du, J. The Retina and Retinal Pigment Epithelium Differ in Nitrogen Metabolism and Are Metabolically Connected. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 2324–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Q.; Yang, F.; Zhu, X.; Zou, H.; Xu, W. Hyperglycemia and Insulin Treatment Promote the Proliferation of Retinal Pigment Epithelium Cells in Early Diabetes: An in Vitro and in Vivo Study. J. Histotechnol. 2025, 48, 2503520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salceda, R. Insulin-Stimulated Taurine Uptake in Rat Retina and Retinal Pigment Epithelium. Neurochem. Int. 1999, 35, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanie-Jahromi, F.; Khosravi, A.; Hadianfard, H.; Nowroozzadeh, M.H. Effects of Regular, Glulisine, and Aspart Insulin on Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor and Angiotensinogen Expression in Hyperglycemic Retinal Pigment Epithelial (RPE) and Human Retinal Endothelial Cells (HRECs). Front. Ophthalmol. 2025, 5, 1570232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daley, R.; Maddipatla, V.; Ghosh, S.; Chowdhury, O.; Hose, S.; Zigler, J.S.; Sinha, D.; Liu, H. Aberrant Akt2 Signaling in the RPE May Contribute to Retinal Fibrosis Process in Diabetic Retinopathy. Cell Death Discov. 2023, 9, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurihara, T.; Westenskow, P.D.; Gantner, M.L.; Usui, Y.; Schultz, A.; Bravo, S.; Aguilar, E.; Wittgrove, C.; Friedlander, M.S.H.; Paris, L.P.; et al. Hypoxia-Induced Metabolic Stress in Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells Is Sufficient to Induce Photoreceptor Degeneration. Elife 2016, 5, e14319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Go, Y.M.; Zhang, J.; Fernandes, J.; Litwin, C.; Chen, R.; Wensel, T.G.; Jones, D.P.; Cai, J.; Chen, Y. MTOR-Initiated Metabolic Switch and Degeneration in the Retinal Pigment Epithelium. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 12502–12520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rains, J.L.; Jain, S.K. Oxidative Stress, Insulin Signaling, and Diabetes. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2011, 50, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Liao, X.; Li, N.; Zhou, H.; Li, H.; Zhang, Q.; Hu, K.; Yang, P.; Hou, S. A Single-Cell Transcriptome Atlas of the Human Retinal Pigment Epithelium. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 802457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adijanto, J.; Du, J.; Moffat, C.; Seifert, E.L.; Hurley, J.B.; Philp, N.J. The Retinal Pigment Epithelium Utilizes Fatty Acids for Ketogenesis: Implications for Metabolic Coupling with the Outer Retina. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 20570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- deS Senanayake, P.; Calabro, A.; Hu, J.G.; Bonilha, V.L.; Darr, A.; Bok, D.; Hollyfield, J.G. Glucose Utilization by the Retinal Pigment Epithelium: Evidence for Rapid Uptake and Storage in Glycogen, Followed by Glycogen Utilization. Exp. Eye Res. 2006, 83, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansman, D.S.; Du, J.; Casson, R.J.; Peet, D.J. Eye on the Horizon: The Metabolic Landscape of the RPE in Aging and Disease. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2025, 104, 101306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustafi, D.; Engel, A.H.; Palczewski, K. Structure of Cone Photoreceptors. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2009, 28, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trachsel-Moncho, L.; Benlloch-Navarro, S.; Fernández-Carbonell, Á.; Ramírez-Lamelas, D.T.; Olivar, T.; Silvestre, D.; Poch, E.; Miranda, M. Oxidative Stress and Autophagy-Related Changes during Retinal Degeneration and Development. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Organisciak, D.T.; Vaughan, D.K. Retinal Light Damage: Mechanisms and Protection. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2009, 29, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonade, D.; Kern, T.S. Photoreceptor Cells and RPE Contribute to the Development of Diabetic Retinopathy. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2020, 83, 100919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravera, S.; Bertola, N.; Puddu, A.; Bruno, S.; Maggi, D.; Panfoli, I. Crosstalk between the Rod Outer Segments and Retinal Pigmented Epithelium in the Generation of Oxidative Stress in an In Vitro Model. Cells 2023, 12, 2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.A.; Jadeja, R.N.; Flandrin, O.; Abdelrahman, A.A.; Thounojam, M.C.; Thomas, S.; Dai, C.; Xiao, H.; Chen, J.K.; Smith, S.B.; et al. Autonomous Regulation of Retinal Insulin Biosynthesis in Diabetes. Neuropeptides 2022, 94, 102258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jian, H.J.; Anand, A.; Lai, J.Y.; Huang, C.C.; Ma, D.H.K.; Lai, C.C.; Chang, H.T. Ultrahigh-Efficacy VEGF Neutralization Using Carbonized Nanodonuts: Implications for Intraocular Anti-Angiogenic Therapy. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2024, 13, 202302881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, D.M.; Kaiser, P.K.; Michels, M.; Soubrane, G.; Heier, J.S.; Kim, R.Y.; Sy, J.P.; Schneider, S. Ranibizumab versus Verteporfin for Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 355, 1432–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koksaldi, S.; Karti, O.; Saatci, A.O. Anti-Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Therapies in Ophthalmology. Med. Hypothesis Discov. Innov. Ophthalmol. 2025, 14, 107–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Balbi, M.; Puddu, A.; Amaroli, A.; Maggi, D.; Panfoli, I.; Ravera, S. Local Insulin for Local Needs? Insights into Retinal Insulin Signaling and RPE Metabolism. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 1570. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15111570
Balbi M, Puddu A, Amaroli A, Maggi D, Panfoli I, Ravera S. Local Insulin for Local Needs? Insights into Retinal Insulin Signaling and RPE Metabolism. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(11):1570. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15111570
Chicago/Turabian StyleBalbi, Matilde, Alessandra Puddu, Andrea Amaroli, Davide Maggi, Isabella Panfoli, and Silvia Ravera. 2025. "Local Insulin for Local Needs? Insights into Retinal Insulin Signaling and RPE Metabolism" Biomolecules 15, no. 11: 1570. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15111570
APA StyleBalbi, M., Puddu, A., Amaroli, A., Maggi, D., Panfoli, I., & Ravera, S. (2025). Local Insulin for Local Needs? Insights into Retinal Insulin Signaling and RPE Metabolism. Biomolecules, 15(11), 1570. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15111570








