Abstract
Testosterone is a hormone that plays a crucial role in men, maintaining muscle mass and bone density and regulating sexual function. This hormone is associated with the inhibition of obesity and the prevention of obesity-related diseases, such as type 2 diabetes, impaired glucose tolerance, dyslipidemia, hypertension, coronary artery disease, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Obesity has a complex effect on testosterone production and metabolism. Chronic inflammation and hormones associated with obesity cause dysfunction of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis, leading to reduced testosterone production. Studies have demonstrated that blood testosterone levels decrease in obese men, suggesting a reciprocal interaction between decreased testosterone and obesity. Additionally, decreased testosterone levels are closely associated with aging. The natural decline in testosterone levels with age can lead to visceral obesity, thus increasing the risk of type 2 diabetes and other chronic metabolic diseases. In many countries, the population is aging, and the importance of testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) for aging men with low testosterone is increasing. Recent studies have expanded our understanding of TRT, highlighting its potential benefits in obese individuals, its interaction with gut microbiota, and the influence of racial differences and genetic polymorphisms on treatment efficacy. This review provides a comprehensive overview of the physiological mechanisms linking obesity and testosterone, current therapeutic approaches including TRT, and emerging research directions that may inform personalized treatment strategies.
1. Introduction
Obesity is recognized as a major global public health concern [1,2,3]. Metabolic changes associated with obesity have been shown to increase the risk of chronic diseases, including cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, fatty liver, and sleep apnea [4,5,6,7]. Obesity also affects the endocrine system and is increasingly recognized as a factor contributing to hormonal imbalances [8,9,10,11,12,13,14]. The relationship between obesity and testosterone has been discussed in several clinical and epidemiological studies [15,16].
Testosterone plays essential roles in men, including maintaining muscle mass, bone density, and sexual function. It also helps reduce adiposity and mitigate the risk of related metabolic diseases, including type 2 diabetes, dyslipidemia, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease [16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25]. On the one hand, obesity has a complex effect on testosterone production and metabolism [16,17,18]. Specifically, chronic inflammation associated with obesity causes dysfunction of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal (HPG) axis, leading to suppressed testosterone production. Consequently, blood testosterone levels are often reduced in obese men. Thus, there is an interaction between testosterone reduction and obesity [16,17,19].
Testosterone decline is also closely related to aging [15,16,17,18]. Age-related testosterone deficiency, referred to as late-onset hypogonadism, is characterized by low serum testosterone (total or free) and clinical symptoms, including low sexual desire, erectile dysfunction, and reduced capacity for vigorous activity [20]. This condition may also contribute to visceral obesity, further increasing the risk of type 2 diabetes and other chronic metabolic diseases. In this review, we examine the mechanisms underlying age-related testosterone decline. We summarize recent findings on commonly used testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) formulations and evaluate their efficacy and safety, highlighting both potential benefits and concerns, particularly those related to cardiovascular and prostate risks [21,22,23,24,25].
Additionally, emerging evidence indicates that testosterone metabolism may be influenced by the gut microbiota, forming a gut–testis axis, a bidirectional communication pathway between the gut microbiota and testicular function that modulates hormonal balance. Racial differences and genetic polymorphisms may also affect testosterone levels and the efficacy of TRT, highlighting the importance of personalized treatment approaches. This review further discusses recent findings on the roles of gut microbiota and genetic factors in regulating testosterone levels and treatment outcomes. Finally, we present our perspective on future research directions that may contribute to the development of improved clinical strategies.
Overall, this comprehensive review aims to provide insights into the complex relationship between obesity and testosterone, current therapeutic strategies, and emerging topics that may inform individualized care for men with metabolic and hormonal disorders.
For this review, we conducted a literature search using an AI-based search tool in combination with conventional databases, including PubMed and Google Scholar. Keywords included “testosterone,” “obesity,” “hypogonadism,” and “testosterone replacement therapy (TRT),” as well as related terms. The initial search results were screened by the authors, who individually reviewed abstracts and full texts. Inclusion criteria were: (1) human studies or high-quality systematic reviews/meta-analyses, (2) studies published in English, and (3) relevance to testosterone physiology, obesity, or TRT. Exclusion criteria included case reports, non-peer-reviewed articles, conference abstracts, and studies not directly related to the scope of this review. Through this process, inappropriate articles were excluded, resulting in the final set of references.
2. Obesity and Testosterone
2.1. Obesity Caused by Low Testosterone
2.1.1. Increased Fat Mass
Several studies have investigated the specific mechanisms by which testosterone directly inhibits fat accumulation in adipocytes. Lipoprotein lipase (LPL) promotes fat accumulation in adipocytes by hydrolyzing triglycerides into free fatty acids. Testosterone reduces the LPL activity in adipocytes and regulates fat accumulation, particularly in the visceral fat [26]. In addition, testosterone upregulates beta-adrenergic receptor expression and promotes lipolysis via noradrenaline [27,28]. However, when testosterone levels decrease, this response also decreases, thereby promoting obesity. Additionally, several mechanisms have been reported to suppress fat accumulation through androgen receptors (AR), including the regulation of ELOVL3 [29], Retinol Binding Protein 4 [30], and the modulation of Wnt signaling pathways [31]. Furthermore, indirect effects on adipocytes have been reported. Animal studies suggest that testosterone stimulates physical activity through dopamine pathways and estrogen receptor α (ERα) signaling in the hypothalamus [32,33]. In addition, testosterone differentiates macrophages into the M2 type via the inhibitory regulatory G protein rather than AR. As a result, it has been shown to inhibit the differentiation of preadipocytes [34]. Thus, testosterone inhibits adipose tissue expansion through multiple mechanisms, including reduced adipocyte differentiation and fat formation, as well as enhanced physical activity. Conversely, low testosterone impairs these functions, promoting obesity. Clinical studies consistently demonstrate that low testosterone levels are positively correlated with obesity, particularly with increased visceral fat, which elevates the risk of obesity-related diseases [35,36,37,38,39,40].
2.1.2. Loss of Skeletal Muscle Mass and Decrease in Basal Metabolic Rate
Testosterone plays a pivotal role in maintaining skeletal muscle mass [41,42,43]. It promotes protein synthesis in skeletal muscle [44,45,46], and clinical studies confirm that exogenous testosterone administration exerts anabolic effects on muscle tissue [44,47,48]. In murine models, 5α-dihydrotestosterone (5α-DHT), a potent androgen, has been suggested to act via a putative membrane androgen receptor, GPR133, leading to increased cyclic AMP (cAMP) production and augmented contractile force [49]. Moreover, it stimulates muscle satellite cell proliferation and their differentiation into myoblasts, contributing to muscle regeneration and growth [50,51]. Declines in testosterone impair these processes, leading to muscle atrophy and loss of skeletal muscle mass [52,53]. This reduction in muscle mass lowers the basal metabolic rate, thereby increasing the risk of obesity and related metabolic disorders [54,55,56]. Maintaining adequate testosterone levels is therefore essential for preserving muscle mass, sustaining metabolic rate, and preventing obesity-related complications.
2.1.3. Metabolic Inflammation Caused by Low Testosterone
Obesity is characterized by excessive adipose tissue accumulation, which induces a chronic low-grade inflammatory state known as “metabolic inflammation” [57,58,59]. This condition increases the risk of insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and certain cancers [57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64]. These health problems are particularly pronounced in visceral obesity [59,60,61,62]. Low testosterone contributes to visceral obesity and subsequent metabolic inflammation through several mechanisms. As visceral adiposity progresses, the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6) increases [62,63]. Evidence suggests that testosterone deficiency may be associated with elevated inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6) in clinical meta-analyses and basic studies [16,17]. TRT has also been shown to reduce the levels of inflammatory cytokines [65,66,67]. These findings suggest that testosterone’s anti-inflammatory effects could contribute to reduced atherosclerosis risk, partly by reducing obesity-related metabolic inflammation [63,64,68,69,70].
During obesity, hypertrophy of adipocytes and alterations in the gut microbiota lead to the excessive production of specific inflammatory ligands, including saturated fatty acids (SFAs), lipopolysaccharides (LPS), and Resistin [71,72,73]. These ligands bind to Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) on the surface of cells including macrophages and adipocytes, activating the NF-κB signaling pathway and triggering inflammation [71]. Upon activation of TLR4, inhibitor of κB (IκB) is phosphorylated and ubiquitinated, leading to its degradation by the proteasome. This allows NF-κB to translocate into the nucleus, where it binds to specific DNA sequences and promotes the transcription of pro-inflammatory cytokines. These cytokines, in turn, activate NF-κB through their respective receptors, creating a vicious cycle of inflammation [71,72,73].
Some preclinical studies suggest that testosterone may reduce TLR4 expression and inhibit NF-κB signaling. In orchiectomized mice, TLR4 expression is increased, while testosterone administration reduces TLR4 expression in macrophage cell lines [74,75]. Additionally, testosterone has been reported to inhibit NF-κB signaling in multiple organs [66,76].
Taken together, these findings suggest that testosterone not only indirectly suppresses metabolic inflammation induced by obesity but may also directly regulate inflammatory processes. Elucidating the molecular mechanisms by which testosterone downregulates TLR4 expression and inhibits NF-κB signaling is crucial for developing therapeutic strategies targeting inflammation associated with obesity and metabolic disorders (Figure 1), Figure S1.
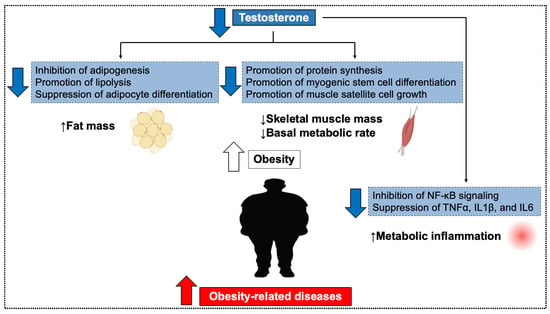
Figure 1.
Obesity caused by low testosterone. Decreased testosterone action results in increased fat mass, loss of skeletal muscle mass, and a decrease in basal metabolic rate. Additionally, it increases metabolic inflammation. As a result, the risk of obesity-related diseases is elevated.
2.1.4. The Relationship Between Testosterone and Gut Microbiota
Recent studies have revealed a close association between the gut microbiome and obesity [77,78,79,80,81]. Animal experiments have demonstrated that testosterone influences the composition of the gut microbiota. For example, orchiectomized mice show changes in their gut microbial profile, including an increased Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio and a higher abundance of Lactobacillus, which are commonly associated with obesity [81,82,83]. These microbial shifts have been hypothesized to influence energy absorption and lipid metabolism [82,83].
Although human studies remain limited, systematic reviews have shown that increased testosterone levels are positively correlated with the abundance of Ruminococcus and Acinetobacter species, as well as with greater microbial diversity [84]. Clinical studies suggest that in elderly men, higher testosterone levels are associated with increased abundance of Firmicutes phylum bacteria [85].
A decline in circulating testosterone can alter gut microbiota composition, and conversely, microbiota changes are closely linked to testicular function. This bidirectional relationship, termed the gut–testis axis, is an emerging research focus [77,81,82,86]. Short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), produced through bacterial fermentation of dietary fiber, may enter the systemic circulation and potentially enhance testosterone synthesis [87,88,89]. One proposed mechanism involves SCFA-induced upregulation of luteinizing hormone receptor (LHR) protein expression and activation of the cAMP/PKA signaling pathway in Leydig cells, which has been shown to stimulate testosterone production [89]. Additionally, certain microbial strains (e.g., Butyricicoccus desmolans, Clostridium scindens) express key steroid-metabolizing enzymes, such as steroid 17,20-desmolase [90,91], and are capable of converting pregnenolone and progesterone into androgenic precursors. These findings suggest that the gut microbiota may function as an extra-gonadal androgen-producing system. On the other hand, the presence of Pseudomonas nitroreducens, a bacterium that degrades testosterone and expresses 3β and 17β hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (3β and 17β HSD), has been identified. Its potential association with testosterone-induced hyperlipidemia has been suggested [92].
Obesity and the associated metabolic inflammation are associated with gut microbiota alterations [93,94]. This increases intestinal permeability, allowing microbial components such as lipopolysaccharide to enter the bloodstream, which further aggravates metabolic inflammation [95,96]. These inflammatory and metabolic disturbances may also affect the HPG axis and the testes, impairing testosterone production [78,80,97,98,99,100].
Therapeutic strategies that target the gut microbiota, such as probiotics, prebiotics, dietary interventions, and fecal microbiota transplantation, have shown promise in improving testosterone levels and metabolic health in men with functional hypogonadism by ameliorating inflammation caused by harmful gut microbiota [78,80,81,82]. However, the current quality of human evidence remains limited. Most clinical data are observational or derived from studies with small sample sizes and heterogeneous populations. While the effects of TRT on the gut microbiome have been explored in transgender individuals [101], robust interventional trials in hypogonadal men are lacking. A deeper understanding of the gut–testis axis may lead to personalized treatments for metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes, and age-related androgen decline. To achieve this, future research must address translational challenges, including the variability in microbiota composition across individuals, the complexity of host–microbe interactions, and the need for standardized protocols.
2.2. Testosterone Decline Caused by Obesity
2.2.1. Leptin Resistance
Leptin is a peptide hormone secreted primarily by adipocytes. It acts on hypothalamic kisspeptin neurons to stimulate gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) secretion [102,103,104,105,106,107,108]. Specifically, leptin binds to receptors (LEPR) on kisspeptin neurons, enhancing kisspeptin release. However, in obesity, leptin resistance develops, LEPR activity decreases, and kisspeptin secretion declines. Consequently, GnRH neuron signaling via the KiSS-1 receptor (Kiss1R) diminishes, reducing GnRH output [103,104,106]. Additionally, some studies have shown that high levels of leptin reduce testosterone production in the testis [109]. LEPRs are expressed in Leydig cells, and elevated leptin reduces expression of steroidogenic acute regulatory protein (StAR), impairing testosterone synthesis [109]. Thus, obesity-induced leptin resistance and hyperleptinemia decrease testosterone production through central and peripheral mechanisms.
2.2.2. Metabolic Inflammation Associated with Obesity
Obesity is associated with low-grade inflammation characterized by elevated inflammatory cytokine production, particularly from visceral adipose tissue [7,93]. Overproduction of cytokines (e.g., TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6) not only contributes to metabolic complications but is also linked to reduced testosterone levels [93,97,110,111].
Pro-inflammatory cytokines impair the HPG axis. Long-term TNF-α exposure suppresses Kiss1R gene expression, disrupts kisspeptin signaling, and reduces GnRH secretion in hypothalamic cells [99]. Similarly, IL-1β interferes with GnRH mRNA translation and inhibits luteinizing hormone (LH) release [100]. In addition, cytokines directly impair Leydig cell steroidogenesis: cultured Leydig cells exposed to TNF-α, IL-1β, or IL-6 produce less testosterone [110,112]. Obesity also increases reactive oxygen species (ROS) production [113]. ROS induce mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in Leydig cells, inhibiting StAR activity [114,115,116]. Reduced StAR function decreases cholesterol-to-testosterone conversion, further lowering testosterone levels.
2.2.3. Increased Estradiol Production
The relationship between obesity, estradiol, and hypothalamic function in men is complex. Early studies reported higher circulating estradiol levels in obese men compared with lean controls [117], attributed to increased aromatization of testosterone to estradiol in adipose tissue. Elevated estradiol then suppresses GnRH secretion via negative feedback on the HPG axis, reducing LH and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) secretion and thereby decreasing testicular testosterone production [16]. However, subsequent studies have challenged the universality of this mechanism. Some reports indicate that estradiol levels are not consistently elevated in obese hypogonadal men and may even be lower than in non-obese men [118]. Moreover, weight loss interventions have not always resulted in significant reductions in plasma estradiol levels [119]. Elevated estradiol levels may also contribute to HPG suppression in some obese men, as some guidelines mention the use of aromatase inhibitors as a potential option in specific cases [120]. However, leptin resistance and inflammation are likely to represent more dominant and consistent mechanisms [17].
2.2.4. Reduction in Sex Hormone-Binding Globulin (SHBG)
SHBG is a glycoprotein that binds and transports sex hormones, including testosterone and estrogen, in the circulation [121]. Obesity is associated with marked reductions in SHBG levels, which directly affect testosterone bioavailability [122,123]. Specifically, SHBG decreases by approximately 1.26 nmol/L for every one-unit increase in body mass index (BMI) [124]. Obese men exhibit significantly lower serum testosterone and SHBG compared with non-obese men, suggesting that obesity exerts direct effects on androgen status [125]. SHBG is synthesized in the liver, and its production is reduced by factors linked to obesity, including insulin resistance and inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6) [121]. Therefore, decreased SHBG is considered one of the major contributors to obesity-associated hypogonadism [15,16,17] (Figure 2).
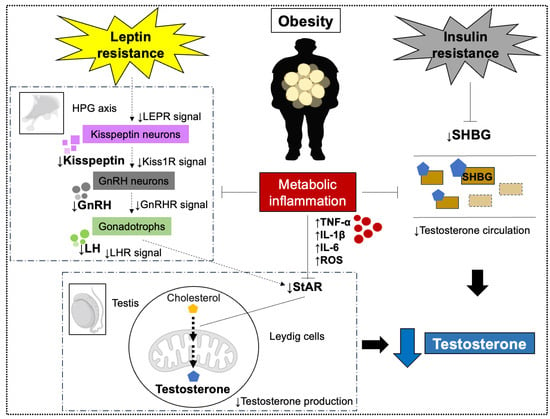
Figure 2.
Testosterone decline caused by obesity. Obesity-induced increases in Leptin resistance and insulin resistance, metabolic inflammation, inhibit various mechanisms related to testosterone synthesis in the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal (HPG) axis and testes. As a result, the amount of testosterone produced is decreased. Abbreviations: Leptin receptor (LEPR); KiSS-1 receptor (Kiss1R); Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH); GnRH receptor (GnRHR); Luteinizing hormone (LH); LH receptor (LHR); reactive oxygen species (ROS); steroidogenic acute regulatory protein (StAR); sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG).
3. Aging and Testosterone
3.1. Age-Related Testosterone Decline and Its Mechanisms
3.1.1. Testicular Dysfunction
Leydig cells, which produce testosterone in the testes, gradually lose function with aging [126,127,128,129]. Testosterone synthesis in Leydig cells involves LH, StAR, translocation protein (TSPO), and a series of steroid hormone synthases (CYP11A1, 3β-HSD, CYP17A1, and 17β-HSD). When LH acts on Leydig cells, it activates the cAMP pathway. This activation promotes the function of StAR protein and transports cholesterol into the mitochondrial membrane. TSPO is also involved in cholesterol transport to the mitochondrial membrane. Within mitochondria, cholesterol is progressively converted by various steroid hormone synthase to produce pregnenolone and eventually testosterone. In aging men, a reduced responsiveness to LH stimulation has been reported to impair the steroidogenic pathway in Leydig cells [129,130,131]. Furthermore, decreased cAMP production [130,131,132], reduced StAR expression [133,134], lower TSPO levels, and diminished activity of steroidogenic enzymes [135,136,137,138,139] have all been observed. In addition, studies have demonstrated a decline in the number of Leydig cells in older men [140], further contributing to reduced testosterone production capacity.
3.1.2. Dysfunction of the HPG Axis
GnRH secreted by the hypothalamus stimulates LH secretion from the pituitary gland, which in turn promotes testosterone production in the testes. In aging men, GnRH is secreted in an irregular pattern with reduced mean amplitude, resulting in lower overall secretion [15,141]. Consequently, LH secretion becomes irregular and decreases. This reduction in LH secretion is attributed to age-related changes in the hypothalamus and pituitary gland, particularly a decline in the number and function of GnRH neurons and degeneration of kisspeptin neurons. These combined factors reduce LH secretion [15]. However, pituitary responsiveness to GnRH is not affected by age, suggesting that hypothalamic changes are the primary cause [142,143]. These mechanisms are further complicated by the involvement of obesity and comorbidities in addition to the effects of aging (Figure 3).
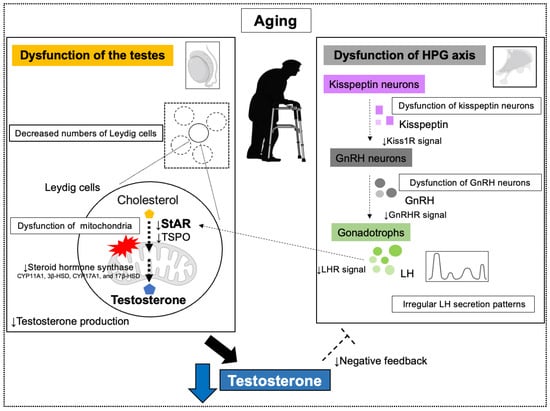
Figure 3.
Age-induced testosterone decline and its mechanism. Age-related dysfunction of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal (HPG) axis and dysfunction of the testes reduce testosterone synthesis. Abbreviations: steroidogenic acute regulatory protein (StAR); translocation protein (TSPO); Kisspeptin Receptor (Kiss 1R); Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH); Luteinizing hormone (LH); LH receptor (LHR).
3.2. “Primary Hypogonadism” and “Secondary Hypogonadism”
Low testosterone with aging is classified into “Primary hypogonadism,” mainly caused by testicular dysfunction, and “Secondary hypogonadism,” caused by hypothalamic dysfunction [15]. Primary hypogonadism refers to a condition in which blood testosterone levels are low and serum LH levels are elevated simultaneously [144,145,146]. This is primarily due to age-related testicular dysfunction. The increase in LH levels in this pathology is thought to be due to a decrease in negative feedback to the HPG axis by testosterone and estradiol, which is converted from testosterone by aromatase [15]. AR and estrogen receptor-α (ERα) are present in kisspeptin neurons in the hypothalamus [15,147]. Some studies have reported absent AR-mediated negative feedback of testosterone at the pituitary level [148,149]. Collectively, these findings suggest that testosterone and estrogen suppress kisspeptin neurons in the hypothalamus, thereby exerting negative feedback on the HPG axis. Some studies have shown increased kisspeptin signaling in the hypothalamus of aging men, possibly due to reduced negative feedback from testosterone [150,151]. Therefore, it is thought that low testosterone levels due to decreased testicular function reduce this feedback mechanism and increase the blood LH levels. Primary hypogonadism has been observed to increase in men aged 65–70 years and older, and TRT for them may exert similar effects on primary hypogonadism in younger men [15].
In contrast, secondary hypogonadism refers to a condition in which serum testosterone levels are low, but serum LH levels are not elevated [15]. Its primary pathology lies in dysfunction of the HPG axis, and it is frequently associated with obesity [152]. In such cases, clinicians should prioritize lifestyle interventions targeting weight reduction and overall health improvement [153]. It is also necessary to consider the possibility that age-related decline in hypothalamic function may be the cause. Changes in LH levels in aging men vary depending on the individual case. If the LH level is low in low testosterone aging men, secondary hypogonadism is suspected. If it is high, primary hypogonadism is suspected. However, it is important to note that it is difficult to distinguish between these states clearly. As all aging men have age-related changes in the testis and hypothalamus, this classification only indicates which factor is more pronounced. Therefore, aging men should be considered to have both primary and secondary hypogonadism [154,155,156]. Careful clinical assessment and comprehensive diagnosis are required.
3.3. Differences Between TRT for Obesity and TRT for Age-Related Testosterone Decline
Currently, evidence on the efficacy and safety of TRT in obese men with low testosterone is insufficient [157,158,159]. Many studies have demonstrated that achieving weight reduction to an appropriate level can improve endogenous testosterone concentrations. For example, weight loss induced by calorie restriction has been shown to significantly increase testosterone levels in obese men [160,161,162]. Similarly, aerobic exercise and resistance training may contribute to the restoration of endogenous testosterone secretion by reducing body fat [163,164]. Accordingly, current guidelines do not recommend TRT as a treatment for obesity per se, and its use requires careful consideration [158,165,166]. However, some recent studies have advocated differently. TRT has been reported to reduce obesity through fat loss and skeletal muscle mass gain, and to have beneficial effects on the reduction of cardiovascular risk factors [165,166,167]. Thus, some obese men may benefit from TRT as part of a broader health strategy. Further well-designed randomized controlled trials and mechanistic studies are warranted to clarify the risks and benefits of TRT in obese men. Until such data are available, healthcare professionals should reserve TRT for men with confirmed hypogonadism (symptoms plus consistently low testosterone levels), ensure ongoing monitoring, and strongly encourage lifestyle modifications as the primary approach to weight management.
In contrast, the approach differs for age-related testosterone decline. After approximately age 65–70, Leydig cell function progressively decreases, leading to a higher prevalence of primary hypogonadism, characterized by low serum testosterone and elevated LH. As age-related primary hypogonadism is typically irreversible, TRT may be an effective treatment [22,168]. Similarly, even in secondary hypogonadism without elevated LH, if hypothalamic decline with aging is irreversible, TRT may be required. However, in some aging men, hypothalamic and/or testis functions may be preserved. Improving obesity may improve low testosterone status in these men. Thus, in obese older men with low testosterone, lifestyle intervention should be the first-line strategy.
The indication for TRT in older men requires careful consideration. TRT should be considered for those with irreversible primary hypogonadism (low testosterone and elevated LH) who are symptomatic. Even in secondary hypogonadism without elevated LH, TRT may be appropriate if due to an irreversible hypothalamic decline. Before starting TRT, clinicians must rule out reversible causes such as systemic illness, medication, or pituitary disorders. In addition, obese men should not be completely excluded from TRT indications. It is also recommended to consider TRT for obese men if the benefits for improving symptoms are greater than the risk of treatment, while managing obesity at the same time. However, although some studies suggest potential benefits of TRT in obese men [165,166,167,168], the overall evidence remains insufficient to draw firm conclusions regarding efficacy and safety.
In conclusion, treatment decisions should be individualized and focused on symptom improvement. Additionally, in obese men, it is desirable to encourage lifestyle improvements and implement interventions. In addition, it is recommended to consider TRT when the benefits outweigh the risks.
4. Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT)
4.1. Current Formulations for TRT
A variety of TRT formulations are currently available [157,159,169]. Each formulation has its unique advantages and disadvantages, and the right choice must be made based on the patient’s lifestyle, treatment goals, risk of side effects, and economic factors.
Intranasal gels are noninvasive, easy to use, and allow the maintenance of a relatively stable level of testosterone in the blood [170,171,172]. They also avoid the first-pass effect in the liver. However, frequent doses are required, and this may affect patient adherence. In addition, local side effects, such as irritation of the nasal mucosa, have been reported.
Transdermal testosterone gels are self-administered, flexible in dosing, and generally well accepted by patients [173,174,175]. However, there is a risk of secondary exposure by touching another person with the hand where the drug was applied, and there is a possibility of skin irritation. It has also been suggested that the blood testosterone levels may fluctuate [157,169]. Transdermal testosterone ointment, like a gel, is a noninvasive and convenient method of administration [176,177]. The texture is easy to apply and blend into the skin, making it suitable for individualized treatment. However, as with gels, the risk of secondary exposure to others, rough skin, and blood testosterone levels may fluctuate.
Oral testosterone tablets are convenient to carry and store [178]. However, they undergo first-pass hepatic metabolism, leading to fluctuations in serum levels and potential systemic side effects such as hepatotoxicity, polycythemia, hypertension, and acne [157,179].
Intramuscular injections are relatively inexpensive, long-acting, and maintain stable serum testosterone levels [157,179,180]. In addition, because frequent dosing is not required, it can be expected that patients’ medication adherence will improve [180]. However, they are associated with pain at the injection site, injection-site reactions, and systemic side effects, including polycythemia, hypertension, and acne, as well as potential impairment of fertility [179,181].
Subcutaneous injections are a relatively new option [180,182,183]. It has been suggested that this treatment has a stable and predictable concentration of the drug during treatment. Additionally, it is better accepted by patients, easier to self-administer than intramuscular injection. In addition, local side effects that occur at the injection site are mild and most likely transient. However, they require patients to master self-injection techniques, which may reduce adherence [157,179]. Long-term studies with larger populations are still needed to evaluate their safety and efficacy.
Testosterone pellets provide prolonged testosterone release, requiring infrequent administration and improving adherence [184,185,186,187]. However, implantation is invasive, carries a risk of infection or local inflammation, and may negatively impact fertility [179].
To choose the best treatment among these options, a thorough consultation between the clinician and patient is essential (Table 1).

Table 1.
The Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT) formulations currently in use and their advantages and disadvantages.
4.2. Short-Acting and Long-Acting TRT Drugs
TRT drugs may be classified into short -acting and long-acting drugs, depending on the difference in the action time of the formulation and the characteristics of the side effects [188,189,190]. Short- and long-acting testosterone drugs have different characteristics and are considered important factors in the choice of treatment [190].
Short-acting formulations require multiple daily doses but mimic physiological testosterone secretion [172,188]. Therefore, it has a low impact on male fertility and minimizes the suppression of spermatogenesis and LH [188]. This property may allow for the treatment of hypogonadism while maintaining fertility. They may also reduce the risk of secondary erythrocytosis [171]. However, owing to the need for frequent dosing, patient adherence can be challenging. Medications include intranasal gels, transdermal testosterone gels, transdermal testosterone ointments, and oral testosterone tablets [189,190].
On the other hand, Long-acting formulations require less frequent dosing, improve adherence, and maintain more stable testosterone levels [189,190]. However, this formulation may suppress spermatogenesis by suppressing the HPG axis, thereby increasing the risk of infertility [188,191,192]. In addition, the risk of polycythemia has been noted [157,179]. Medications include intramuscular injections, subcutaneous injections, and testosterone pellets.
Clinicians should balance efficacy, safety, and patient preference when selecting an appropriate formulation.
4.3. Recent Perspectives on the Side Effects of TRT
4.3.1. Cardiovascular Disease
In the past, there have been concerns that TRT increases the risk of cardiovascular disease, but recent large-scale studies are challenging the previously assumed link [25,193,194]. There are many reports that TRT within the physiological range does not increase the risk of cardiovascular events, and its safety is supported [25,194]. The Testosterone Replacement Therapy for Assessment of Long-term Vascular Events and Efficacy Response in Hypogonadal Men (TRAVERSE) study evaluated the cardiovascular safety of TRT in men with hypogonadism or high-risk and cardiovascular disease [25]. The results showed that TRT was non-inferior to placebo in the incidence of major adverse cardiac events. On the other hand, the study reported an increased incidence of non-fatal arrhythmias requiring intervention, including atrial fibrillation. However, meta-analyses in several other studies have shown that the risk of atrial fibrillation with TRT was non-inferior compared to placebo [194]. This result suggests that there is a poor association between TRT and an increased risk of atrial fibrillation. In addition, TRT for type 2 diabetes mellitus and metabolic syndrome men has been shown to reduce triglycerides (TG) and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and improve high-density lipoprotein (HDL) and may reduce cardiovascular risk [195,196,197,198,199].
From these recent studies, the epidemiological evidence supporting that TRT does not increase cardiovascular risk is strong. These findings are likely attributable to improvements in obesity associated with TRT, and TRT in obese patients may exert a protective effect against cardiovascular disease risk. However, lifestyle-based weight reduction remains the first-line intervention for obese men with low testosterone, and TRT should be considered when hypogonadal symptoms persist despite such measures. For patients outside of these categories, such as non-obese older men, a different interpretation is required. Moreover, evidence regarding patients with underlying medical conditions is insufficient and warrants further investigation. Caution is particularly needed in non-obese older men with multiple comorbidities. A recent report has shown that the prevalence of erectile dysfunction (ED) in men with coronary artery disease reaches 90%, which may increase the demand for TRT [200]. Further large-scale studies are required to verify the safety and effectiveness of TRT in such patients.
4.3.2. Prostate Disease
The association between TRT and prostate cancer has been extensively debated. Recent evidence suggests that TRT does not increase the risk of prostate cancer [201,202,203]. A randomized controlled trial in middle-aged and older hypogonadal men found no significant difference in high-grade prostate cancer or other prostate-related events between TRT and placebo [203]. However, careful judgment is required when applying TRT in patients with a history of prostate cancer [201,204]. Specifically, TRT is not recommended for the presence of unassessed prostate nodules or induration, or for PSA levels greater than 4 ng/mL (greater than 3 ng/mL for African Americans and men with a family history of high-risk prostate cancer).
Furthermore, recent studies have shown that TRT does not significantly increase the risk of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), especially in men with hypogonadism. For example, a study by Bhasin et al. and a study by Rastrelli et al. suggested that TRT may not cause worsening of lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) or an increase in prostate size in men who have been adequately screened for prostate cancer risk [201,205]. However, some studies suggest that testosterone may contribute to prostate growth, and individual responses to TRT can vary greatly [206,207]. These findings show a complex relationship between testosterone levels and prostate health.
Although numerous studies have investigated the cardiovascular and prostate effects of TRT, the evidence remains heterogeneous [25,193,202,203,208]. Clinical trials and observational studies differ substantially in study design, sample size, population characteristics, and follow-up duration. For example, while some randomized controlled trials have suggested neutral or even beneficial effects of TRT on cardiovascular outcomes, others have reported potential risks, particularly in older men with preexisting cardiovascular disease [193,209]. Similarly, findings regarding prostate safety are inconsistent, partly due to variations in baseline risk profiles, inclusion criteria, and outcome definitions. These discrepancies highlight the importance of recognizing methodological limitations, potential biases, and population heterogeneity when interpreting the literature. Further large-scale, long-term trials with standardized endpoints are warranted to establish a clearer understanding of TRT safety in these areas of controversy.
4.3.3. Other Adverse Effects
TRT has traditionally been considered beneficial for improving bone mineral density. However, a recent sub-study of the TRAVERSE trial, which included 5204 participants, reported an unexpected increase in the incidence of clinical fractures, particularly traumatic fractures involving the ribs, wrists, and ankles [210]. This finding challenges previous assumptions and warrants closer examination. Importantly, the TRAVERSE trial was not originally designed to investigate fracture risk or elucidate the underlying biological mechanisms. As such, the causal relationship between TRT and increased fracture risk remains unclear. Several speculative mechanisms have been proposed. One possibility is that TRT-induced improvements in mood and energy levels may lead to increased physical activity [211,212], inadvertently raising the risk of trauma-related fractures. Another consideration is the effect of testosterone on bone turnover. Changes in the balance between bone formation and resorption could influence bone strength in ways that are not yet fully understood [213,214]. It is also possible that this observation was coincidental and not directly related to TRT [215]. Further research is needed to clarify these possibilities.
Beyond fracture risk, other adverse effects of TRT have been reported, including polycythemia, sleep apnea, fluid retention, peripheral edema, and, in some cases, heart failure [157,201,216]. Due to individual variability, TRT should be tailored to each patient’s comorbidities and genetic profile. Personalized approaches may help minimize risks while maximizing therapeutic benefits.
4.4. Comparison of the Guidelines for Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT)
Currently, official guidelines for TRT are provided by organizations: the Endocrine Society [179], the American Urological Association (AUA) [120], the International Society for the Study of the Aging Male (ISSAM) [217], and the European Menopause and Andropause Society (EMAS) [159]. These guidelines are periodically updated. In this section, we summarize their commonalities, differences, and distinctive features based on the latest information (Table 2).

Table 2.
Comparison of Key Recommendations from Major Guidelines on Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT).
A common issue among all guidelines is that TRT can suppress spermatogenesis and reduce fertility. Therefore, young men with hypogonadism should receive counseling regarding potential fertility concerns prior to treatment. In addition, regular monitoring of serum testosterone levels, hematocrit (Ht), and prostate-specific antigen (PSA) is recommended both before and after initiating TRT.
A major difference among the guidelines lies in the diagnostic cut-off criteria for total testosterone levels. The Endocrine Society emphasizes the presence of compatible clinical symptoms together with consistently low morning total testosterone levels confirmed on repeated testing, rather than defining a strict numerical threshold. Harmonized reference ranges from population studies suggest a lower limit of approximately 264 ng/dL (9.2 nmol/L) in healthy young men. The AUA recommends a total testosterone level <300 ng/dL (10.4 nmol/L) as a reasonable cut-off to support the diagnosis of hypogonadism. ISSAM suggests considering TRT when morning values (between 7 a.m. and 11 a.m.) are below approximately 350 ng/dL (12.1 nmol/L). EMAS considers values <8 nmol/L (≈231 ng/dL) as indicative of a high probability of hypogonadism, whereas values between 8–12 nmol/L (≈231–345 ng/dL) are considered borderline, warranting further assessment of free testosterone levels. Regarding free testosterone, the Endocrine Society recommends measurement using equilibrium dialysis or calculated values based on total testosterone, SHBG, and albumin concentrations. ISSAM refers to a lower limit of approximately 220–347 pmol/L (≈63.5–100 pg/mL). EMAS considers a free testosterone level <225 pmol/L (≈65 pg/mL) as supportive evidence of hypogonadism when total testosterone is borderline. Because reference values differ depending on assay and calculation methods, results should be interpreted using standardized methods and consistent units.
In their characteristic statements, the Endocrine Society highlights the potential role of TRT in specific secondary hypogonadal conditions, including men with HIV-associated hypogonadism and those with opioid-induced hypogonadism. The AUA emphasizes the importance of counseling both before and during TRT, particularly in men concerned with fertility, and suggests alternative treatment options such as selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs), human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), and aromatase inhibitors. EMAS places special emphasis on bone health, addressing osteoporosis and fracture risk, and explicitly incorporates bone density assessment into its recommended monitoring schedules. ISSAM particularly discusses the use of long-acting injectable testosterone undecanoate and transdermal testosterone gel, while expressing a negative view of oral testosterone formulations due to safety and pharmacokinetic concerns. ISSAM also notes that androgen receptor CAG repeat polymorphisms may modulate individual responses to TRT. As outlined above, each guideline presents both similarities and distinctive perspectives, providing recommendations on TRT from its respective viewpoint.
4.5. Racial Differences in Response to TRT
Racial and ethnic backgrounds may influence baseline testosterone levels and clinical responses to TRT. Several studies have reported significant interethnic differences in circulating testosterone. African men and women generally have higher testosterone levels than their White counterparts, even after adjusting for age and BMI [218]. Hispanic men also show elevated levels compared to White men, though the difference is less pronounced [218]. In comparisons between American and Chinese men, total testosterone is higher in Americans, while free and bioavailable testosterone levels show no significant differences [219]. Lifestyle and cultural factors such as diet, physical activity, alcohol intake, and sleep patterns also vary across populations and may interact with endocrine and metabolic pathways relevant to obesity and testosterone regulation [220,221,222,223,224,225].
SHBG concentrations, which affect testosterone bioavailability, differ by race and may influence free testosterone levels and TRT outcomes. For example, White men have lower age-adjusted SHBG levels than African men [226]. The CAG repeat length in the AR gene is a determinant of androgen sensitivity. Shorter repeats are associated with higher receptor activity [227,228,229,230]. African American men typically have shorter repeats (18–20), suggesting greater AR activity, while Caucasian men average 21–22 repeats. East Asian men tend to have longer repeats (23–24), which may indicate reduced AR activity. Hispanic men show similar lengths to Caucasians, around 21 [231,232]. These genetic differences may contribute to variable responses to TRT across populations.
Despite these findings, there is a paucity of comparative studies directly assessing the efficacy and safety of TRT across diverse racial and ethnic populations. Large-scale, multi-ethnic cohort studies and randomized controlled trials are needed to elucidate how racial and ethnic backgrounds influence the relationship between testosterone and obesity, thereby informing more personalized treatment strategies.
5. Discussion and Future Research Topics
5.1. Elucidation of the Causal Relationship Between Obesity and Low Testosterone
A detailed genetic-level analysis is required to better understand the relationship between obesity and low testosterone. Previous studies have shown that testosterone inhibits fat accumulation and promotes lipolysis in adipocytes [26,28,31,34]. However, the direct roles of AR target genes remain poorly understood. In addition, the transcriptional activity of AR is strongly influenced by transcription factors [233,234], and research on transcriptional factors involved in AR action in adipocytes has been insufficient. Recent studies have also indicated that AR functions not only as a nuclear receptor but also as a membrane receptor, and the role of membrane AR in adipocytes warrants further investigation [49]. In addition, mouse models with adipocyte-specific AR knockout (ARKO) mice have been provided at the individual level; however, adipocyte ARKO mouse models did not show an increase in fat mass [235]. The reason for this is thought to be the influence of organs other than adipocytes, such as the immune effect of blood cells derived from the bone marrow [236,237]. Therefore, a proper understanding of AR function in adipocytes and obesity requires careful distinction between cellular- and organism-level mechanisms. Moreover, CAG repeat polymorphisms in the AR gene have been shown to correlate with reduced AR transcriptional activity [227,238,239]. The impact of CAG repeat number on AR activity in adipocytes, and its association with obesity and visceral fat accumulation in humans, is not yet fully understood. To clarify this, further studies using animal and cell models are necessary.
5.2. Search for TRT Protocols That Maintain Reproductive Function
Fertility is an important component of men’s quality of life, especially in countries with declining birthrates. Reduced reproductive function is a major concern with TRT, as men with low testosterone must choose between the benefits of TRT (e.g., improved mental health) and the preservation of fertility. Thus, there is a need to develop TRT strategies that minimize adverse effects on fertility. Short-acting TRT formulations may help preserve fertility [172,176,188,190]. Intranasal gels, although supported by less evidence than other formulations, have been proposed as a newer option that may preserve reproductive function [189]. In addition, certain agents traditionally used to treat azoospermia have been considered for use alongside TRT. Specifically, aromatase inhibitors, combination therapy with human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) and testosterone, and selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) may be effective [240,241]. These approaches may help improve patient quality of life while preserving future fertility potential.
5.3. The Need for Revalidation of Guidelines for TRT in Aging Men
An unexpected finding of the TRAVERSE study was an increased risk of fractures, despite previous evidence that TRT improves bone density [210]. One possibility is that the mood-enhancing effects of TRT increased activity levels, but the causal relationship between TRT and fracture risk requires further investigation. Thus, TRT in aging men may involve unanticipated adverse effects, particularly those influenced by age-specific factors such as comorbidities and concurrent medications. To promptly detect and address such risks, careful and extensive data collection is required. In addition, the current TRT uses only testosterone concentration (blood testosterone level) as an indicator; however, this may not be sufficient. Age is associated with higher SHBG levels, and total testosterone binding to SHBG in blood levels is insufficient to assess biologically active testosterone in the elderly [242,243,244]. Free testosterone levels, which reflect biologically active testosterone rather than total testosterone levels, have been used; however, the credibility of clinically convenient immunoassay methods is questionable [245,246]. Furthermore, some patients experience persistent symptoms despite reaching target testosterone levels during replacement therapy [247,248]. These issues suggest the need for new evaluation methods that assess not only testosterone levels but also biological effects.
Emerging digital health technologies offer promising solutions for monitoring TRT efficacy and safety. Wearable devices can track physical activity, sleep patterns, heart rate variability, and other physiological parameters in real time, providing valuable insights into treatment responses and potential adverse effects [249]. Additionally, advanced biomarkers such as metabolomic and proteomic profiles may help assess tissue-level androgen activity and identify early signs of treatment-related complications [250,251]. Integrating these tools into clinical practice could enable more personalized and adaptive TRT monitoring and strategies, particularly for aging populations with complex health needs.
Addressing these challenges will support the development of safer and more effective TRT protocols. Such progress may contribute to improved management of obesity and age-related hormonal imbalances. Future advancements will depend on translational research and well-designed randomized clinical trials with clearly defined endpoints.
6. Conclusions
Obesity and testosterone deficiency are major challenges in modern medicine, and elucidating their interaction may lead to the development of novel therapeutic strategies. In aging societies, addressing these issues may contribute to maintaining both individual and public health. To deepen our understanding in this field, continued research and discussion are essential. Future studies should prioritize long-term randomized controlled trials of TRT in obese men, interventional approaches targeting the gut microbiome, and the integration of genetic and metabolomic data into personalized clinical practice, which may pave the way for more effective and individualized treatments.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/biom15111521/s1, Figure S1: Suppression of Metabolic Inflammation by Testosterone.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, writing—original draft preparation, T.T.; supervision, K.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| HPG | Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Gonadal |
| TRT | Testosterone Replacement Therapy |
| LPL | Lipoprotein lipase |
| AR | Androgen receptor |
| GnRH | Gonadotropin-releasing hormone |
| LEPR | Leptin receptors |
| Kiss1R | KiSS-1 receptor |
| StAR | Steroidogenic acute regulatory protein |
| LH | Luteinizing hormone |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| FSH | Follicle-stimulating hormone |
| SHBG | Sex hormone-binding globulin |
| TSPO | Translocation protein |
| ERα | Estrogen receptor-α |
| 5α-DHT | 5α-dihydrotestosterone |
| cAMP | cyclic AMP |
| SFA | Saturated fatty acids |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| IκB | Inhibitor of κB |
| TNFR | TNF receptor |
| IL-1RI | Interleukin-1 receptor type I |
| TG | Triglycerides |
| LDL | Low-density lipoprotein |
| HDL | High-density lipoprotein |
| ES | Endocrine Society |
| AUA | American Urological Association |
| ISSAM | International Society for the Study of the Aging Male |
| EMAS | European Menopause and Andropause Society |
| TT | Total Testosterone |
| Free T | Free Testosterone |
| PSA | Prostate-Specific Antigen |
| Ht | Hematocrit |
| SERMs | Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators |
| hCG | Human Chorionic Gonadotropin |
References
- Bray, G.A.; Heisel, W.E.; Afshin, A.; Jensen, M.D.; Dietz, W.H.; Long, M.; Kushner, R.F.; Daniels, S.R.; Wadden, T.A.; Tsai, A.G.; et al. The Science of Obesity Management: An Endocrine Society Scientific Statement. Endocr. Rev. 2018, 39, 79–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blüher, M. Obesity: Global Epidemiology and Pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apovian, C.M. Obesity: Definition, Comorbidities, Causes, and Burden. Am. J. Manag. Care 2016, 22, s176–s185. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bonsignore, M.R. Obesity and Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2022, 274, 181–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Nguyen, T.T.; Zhang, Y.; Ryu, D.; Gariani, K. Sarcopenic Obesity: Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, Cardiovascular Disease, Mortality, and Management. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1185221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell-Wiley, T.M.; Poirier, P.; Burke, L.E.; Després, J.-P.; Gordon-Larsen, P.; Lavie, C.J.; Lear, S.A.; Ndumele, C.E.; Neeland, I.J.; Sanders, P.; et al. Obesity and Cardiovascular Disease: A Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2021, 143, e984–e1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varra, F.-N.; Varras, M.; Varra, V.-K.; Theodosis-Nobelos, P. Molecular and Pathophysiological Relationship between Obesity and Chronic Inflammation in the Manifestation of Metabolic Dysfunctions and Their Inflammation-mediating Treatment Options (Review). Mol. Med. Rep. 2024, 29, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, K.J.; Hewitt, S.C.; Arao, Y.; Korach, K.S. Estrogen Hormone Biology. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 2017, 125, 109–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Jiang, W.; Liao, W.; Yan, H.; Ai, W.; Pan, Q.; Brashear, W.A.; Xu, Y.; He, L.; Guo, S. An Estrogen Receptor α-Derived Peptide Improves Glucose Homeostasis during Obesity. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 3410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achari, A.E.; Jain, S.K. Adiponectin, a Therapeutic Target for Obesity, Diabetes, and Endothelial Dysfunction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engin, A. Adiponectin Resistance in Obesity: Adiponectin Leptin/Insulin Interaction. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2024, 1460, 431–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genchi, V.A.; D’Oria, R.; Palma, G.; Caccioppoli, C.; Cignarelli, A.; Natalicchio, A.; Laviola, L.; Giorgino, F.; Perrini, S. Impaired Leptin Signalling in Obesity: Is Leptin a New Thermolipokine? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, H.; López, M.; Rahmouni, K. The Cellular and Molecular Bases of Leptin and Ghrelin Resistance in Obesity. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2017, 13, 338–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obradovic, M.; Sudar-Milovanovic, E.; Soskic, S.; Essack, M.; Arya, S.; Stewart, A.J.; Gojobori, T.; Isenovic, E.R. Leptin and Obesity: Role and Clinical Implication. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 585887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anawalt, B.D.; Matsumoto, A.M. Aging and androgens: Physiology and clinical implications. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2022, 23, 1123–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, D.M.; Jones, T.H. Testosterone and Obesity. Obes. Rev. 2015, 16, 581–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genchi, V.A.; Rossi, E.; Lauriola, C.; D’Oria, R.; Palma, G.; Borrelli, A.; Caccioppoli, C.; Giorgino, F.; Cignarelli, A. Adipose Tissue Dysfunction and Obesity-Related Male Hypogonadism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.C.W.; Tajar, A.; Pye, S.R.; Silman, A.J.; Finn, J.D.; O’Neill, T.W.; Bartfai, G.; Casanueva, F.; Forti, G.; Giwercman, A.; et al. Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Testicular Axis Disruptions in Older Men Are Differentially Linked to Age and Modifiable Risk Factors: The European Male Aging Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 93, 2737–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, J.; Haring, R.; Grarup, N.; Vandenput, L.; Wallaschofski, H.; Lorentzen, E.; Hansen, T.; Mellström, D.; Pedersen, O.; Nauck, M.; et al. Causal Relationship between Obesity and Serum Testosterone Status in Men: A Bi-Directional Mendelian Randomization Analysis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.C.W.; Tajar, A.; Beynon, J.M.; Pye, S.R.; Silman, A.J.; Finn, J.D.; O’Neill, T.W.; Bartfai, G.; Casanueva, F.F.; Forti, G.; et al. Identification of Late-Onset Hypogonadism in Middle-Aged and Elderly Men. New Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barone, B.; Napolitano, L.; Abate, M.; Cirillo, L.; Reccia, P.; Passaro, F.; Turco, C.; Morra, S.; Mastrangelo, F.; Scarpato, A.; et al. The Role of Testosterone in the Elderly: What Do We Know? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orwoll, E. Safety of Testosterone-Replacement Therapy in Older Men. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 177–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagliano-Jucá, T.; Basaria, S. Testosterone Replacement Therapy and Cardiovascular Risk. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2019, 16, 555–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidelbaugh, J.J.; Belakovskiy, A. Testosterone Replacement Therapy for Male Hypogonadism. Am. Fam. Physician 2024, 109, 543–549. [Google Scholar]
- Lincoff, A.M.; Bhasin, S.; Flevaris, P.; Mitchell, L.M.; Basaria, S.; Boden, W.E.; Cunningham, G.R.; Granger, C.B.; Khera, M.; Thompson, I.M.; et al. Cardiovascular Safety of Testosterone-Replacement Therapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santosa, S.; Bush, N.C.; Jensen, M.D. Acute Testosterone Deficiency Alters Adipose Tissue Fatty Acid Storage. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 102, 3056–3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; De Pergola, G.; Eriksson, P.S.; Fu, L.; Carlsson, B.; Yang, S.; Edén, S.; Björntorp, P. Postreceptor Events Involved in the Up-Regulation of Beta-Adrenergic Receptor Mediated Lipolysis by Testosterone in Rat White Adipocytes. Endocrinology 1993, 132, 1651–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.F.; De Pergola, G.; Björntorp, P. Testosterone Increases Lipolysis and the Number of Beta-Adrenoceptors in Male Rat Adipocytes. Endocrinology 1991, 128, 379–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.; Wang, Y.; Chan, S.; Zheng, M.; Xue, M.; Yang, X.; Luo, Y.; Fang, M. Testosterone Inhibits Lipid Accumulation in Porcine Preadipocytes by Regulating ELOVL3. Animals 2024, 14, 2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McInnes, K.J.; Smith, L.B.; Hunger, N.I.; Saunders, P.T.K.; Andrew, R.; Walker, B.R. Deletion of the Androgen Receptor in Adipose Tissue in Male Mice Elevates Retinol Binding Protein 4 and Reveals Independent Effects on Visceral Fat Mass and on Glucose Homeostasis. Diabetes 2012, 61, 1072–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Artaza, J.N.; Taylor, W.E.; Braga, M.; Yuan, X.; Gonzalez-Cadavid, N.F.; Bhasin, S. Testosterone Inhibits Adipogenic Differentiation in 3T3-L1 Cells: Nuclear Translocation of Androgen Receptor Complex with Beta-Catenin and T-Cell Factor 4 May Bypass Canonical Wnt Signaling to down-Regulate Adipogenic Transcription Factors. Endocrinology 2006, 147, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jardí, F.; Laurent, M.R.; Kim, N.; Khalil, R.; De Bundel, D.; Van Eeckhaut, A.; Van Helleputte, L.; Deboel, L.; Dubois, V.; Schollaert, D.; et al. Testosterone Boosts Physical Activity in Male Mice via Dopaminergic Pathways. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, N.R.; David, K.; Corbeels, K.; Khalil, R.; Antonio, L.; Schollaert, D.; Deboel, L.; Ohlsson, C.; Gustafsson, J.-Å.; Vangoitsenhoven, R.; et al. Testosterone Reduces Body Fat in Male Mice by Stimulation of Physical Activity Via Extrahypothalamic ERα Signaling. Endocrinology 2021, 162, bqab045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, X.; Fu, X.; Zhang, X.; Chen, S.; Huang, S.; Yao, L.; Liu, G. Testosterone Regulates 3T3-L1 Pre-Adipocyte Differentiation and Epididymal Fat Accumulation in Mice through Modulating Macrophage Polarization. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2017, 140, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolduc, C.; Yoshioka, M.; St-Amand, J. Transcriptomic Characterization of the Long-Term Dihydrotestosterone Effects in Adipose Tissue. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2007, 15, 1107–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santosa, S.; Jensen, M.D. Effects of Male Hypogonadism on Regional Adipose Tissue Fatty Acid Storage and Lipogenic Proteins. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchernof, A.; Brochu, D.; Maltais-Payette, I.; Mansour, M.F.; Marchand, G.B.; Carreau, A.-M.; Kapeluto, J. Androgens and the Regulation of Adiposity and Body Fat Distribution in Humans. Compr. Physiol. 2018, 8, 1253–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caesar, R.; Manieri, M.; Kelder, T.; Boekschoten, M.; Evelo, C.; Müller, M.; Kooistra, T.; Cinti, S.; Kleemann, R.; Drevon, C.A. A Combined Transcriptomics and Lipidomics Analysis of Subcutaneous, Epididymal and Mesenteric Adipose Tissue Reveals Marked Functional Differences. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muir, C.A.; Wittert, G.A.; Handelsman, D.J. Approach to the Patient: Low Testosterone Concentrations in Men with Obesity. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2025, 110, e3125–e3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fui, M.N.T.; Dupuis, P.; Grossmann, M. Lowered Testosterone in Male Obesity: Mechanisms, Morbidity and Management. Asian J. Androl. 2014, 16, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbst, K.L.; Bhasin, S. Testosterone Action on Skeletal Muscle. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2004, 7, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serra, C.; Tangherlini, F.; Rudy, S.; Lee, D.; Toraldo, G.; Sandor, N.L.; Zhang, A.; Jasuja, R.; Bhasin, S. Testosterone Improves the Regeneration of Old and Young Mouse Skeletal Muscle. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2013, 68, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powers, M.L.; Florini, J.R. A Direct Effect of Testosterone on Muscle Cells in Tissue Culture. Endocrinology 1975, 97, 1043–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urban, R.J.; Bodenburg, Y.H.; Gilkison, C.; Foxworth, J.; Coggan, A.R.; Wolfe, R.R.; Ferrando, A. Testosterone Administration to Elderly Men Increases Skeletal Muscle Strength and Protein Synthesis. Am. J. Physiol. 1995, 269, E820–E826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florini, J.R. Effects of Testosterone on Qualitative Pattern of Protein Synthesis in Skeletal Muscle. Biochemistry 1970, 9, 909–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigsby, J.S.; Bergen, W.G.; Merkel, R.A. The Effect of Testosterone on Skeletal Muscle Development and Protein Synthesis in Rabbits. Growth 1976, 40, 303–316. [Google Scholar]
- Skinner, J.W.; Otzel, D.M.; Bowser, A.; Nargi, D.; Agarwal, S.; Peterson, M.D.; Zou, B.; Borst, S.E.; Yarrow, J.F. Muscular Responses to Testosterone Replacement Vary by Administration Route: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2018, 9, 465–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.-W.; Kao, P.-Y.; Chen, Y.-C.; Wang, S.-T. Effects of Testosterone Replacement Therapy on Muscle Strength in Older Men with Low to Low-Normal Testosterone Levels: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Gerontology 2023, 69, 1157–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Ping, Y.-Q.; Wang, M.-W.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, S.-H.; Xi, Y.-T.; Zhu, K.-K.; Ding, W.; Zhang, Q.-Y.; Song, Z.-C.; et al. Identification, Structure, and Agonist Design of an Androgen Membrane Receptor. Cell 2025, 188, 1589–1604.e24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha-Hikim, I.; Cornford, M.; Gaytan, H.; Lee, M.L.; Bhasin, S. Effects of Testosterone Supplementation on Skeletal Muscle Fiber Hypertrophy and Satellite Cells in Community-Dwelling Older Men. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 91, 3024–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha-Hikim, I.; Roth, S.M.; Lee, M.I.; Bhasin, S. Testosterone-Induced Muscle Hypertrophy Is Associated with an Increase in Satellite Cell Number in Healthy, Young Men. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 285, E197–E205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivas-Shankar, U.; Wu, F. Frailty and Muscle Function: Role for Testosterone? Front. Horm. Res. 2009, 37, 133–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, A.S.; Gray, H.; Schache, A.G.; Hoermann, R.; Lim Joon, D.; Zajac, J.D.; Pandy, M.G.; Grossmann, M. Androgen Deprivation Causes Selective Deficits in the Biomechanical Leg Muscle Function of Men during Walking: A Prospective Case-Control Study. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2017, 8, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, D.M.; Jones, T.H. Testosterone: A Metabolic Hormone in Health and Disease. J. Endocrinol. 2013, 217, R25–R45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deepika, F.N.U.; Ballato, E.; Colleluori, G.; Aguirre, L.; Chen, R.; Qualls, C.; Villareal, D.T.; Armamento-Villareal, R. Baseline Testosterone Predicts Body Composition and Metabolic Response to Testosterone Therapy. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 915309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welle, S.; Jozefowicz, R.; Forbes, G.; Griggs, R.C. Effect of Testosterone on Metabolic Rate and Body Composition in Normal Men and Men with Muscular Dystrophy. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1992, 74, 332–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Gao, L.; Meng, H.; Zhang, A.; Liang, Y.; Lu, J. Obesity Alters Immunopathology in Cancers and Inflammatory Diseases. Obes. Rev. 2023, 24, e13638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruppert, Z.; Neuperger, P.; Rákóczi, B.; Gémes, N.; Dukay, B.; Hajdu, P.; Péter, M.; Balogh, G.; Tiszlavicz, L.; Vígh, L.; et al. Characterization of Obesity-Related Diseases and Inflammation Using Single Cell Immunophenotyping in Two Different Diet-Induced Obesity Models. Int. J. Obes. 2024, 48, 1568–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schleh, M.W.; Caslin, H.L.; Garcia, J.N.; Mashayekhi, M.; Srivastava, G.; Bradley, A.B.; Hasty, A.H. Metaflammation in Obesity and Its Therapeutic Targeting. Sci. Transl. Med. 2023, 15, eadf9382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, H. Obese Visceral Fat Tissue Inflammation: From Protective to Detrimental? BMC Med. 2022, 20, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, H.F.; Corrêa-Giannella, M.L.; Consolim-Colombo, F.M.; Egan, B.M. Visceral Adiposity Syndrome. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2016, 8, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khafagy, R.; Dash, S. Obesity and Cardiovascular Disease: The Emerging Role of Inflammation. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 768119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battineni, G.; Sagaro, G.G.; Chintalapudi, N.; Amenta, F.; Tomassoni, D.; Tayebati, S.K. Impact of Obesity-Induced Inflammation on Cardiovascular Diseases (Cvd). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oussaada, S.M.; Kilicarslan, M.; de Weijer, B.A.; Gilijamse, P.W.; Şekercan, A.; Virtue, S.; Janssen, I.M.C.; van de Laar, A.; Demirkiran, A.; van Wagensveld, B.A.; et al. Tissue-Specific Inflammation and Insulin Sensitivity in Subjects with Obesity. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2024, 211, 111663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhindsa, S.; Ghanim, H.; Batra, M.; Kuhadiya, N.D.; Abuaysheh, S.; Sandhu, S.; Green, K.; Makdissi, A.; Hejna, J.; Chaudhuri, A.; et al. Insulin Resistance and Inflammation in Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism and Their Reduction after Testosterone Replacement in Men with Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhou, R.; Tong, Y.; Chen, P.; Shen, Y.; Miao, S.; Liu, X. Neuroprotection by Dihydrotestosterone in LPS-Induced Neuroinflammation. Neurobiol. Dis. 2020, 140, 104814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelegrin, Á.F.; de Paiva Gonçalves, V.; Carvalho, J.d.S.; Spolidorio, D.M.P.; Spolidorio, L.C. Testosterone Replacement Relieves Ligature-Induced Periodontitis by Mitigating Inflammation, Increasing pro-Resolving Markers and Promoting Angiogenesis in Rats: A Preclinical Study. Arch. Oral Biol. 2023, 146, 105605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeap, B.B.; Alfonso, H.; Paul Chubb, S.A.; Handelsman, D.J.; Hankey, G.J.; Almeida, O.P.; Golledge, J.; Norman, P.E.; Flicker, L. In Older Men an Optimal Plasma Testosterone Is Associated with Reduced All-Cause Mortality and Higher Dihydrotestosterone with Reduced Ischemic Heart Disease Mortality, While Estradiol Levels Do Not Predict Mortality. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, E9–E18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeap, B.B.; Marriott, R.J.; Antonio, L.; Chan, Y.X.; Raj, S.; Dwivedi, G.; Reid, C.M.; Anawalt, B.D.; Bhasin, S.; Dobs, A.S.; et al. Serum Testosterone Is Inversely and Sex Hormone-Binding Globulin Is Directly Associated with All-Cause Mortality in Men. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 106, E625–E637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeap, B.B.; Marriott, R.J.; Dwivedi, G.; Adams, R.J.; Antonio, L.; Ballantyne, C.M.; Bauer, D.C.; Bhasin, S.; Biggs, M.L.; Cawthon, P.M.; et al. Associations of Testosterone and Related Hormones With All-Cause and Cardiovascular Mortality and Incident Cardiovascular Disease in Men: Individual Participant Data Meta-Analyses. Ann. Intern. Med. 2024, 177, 768–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Jin, Y.; Chen, X.; Ye, X.; Shen, X.; Lin, M.; Zeng, C.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, J. NF-ΚB in Biology and Targeted Therapy: New Insights and Translational Implications. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poma, P. Nf-Κb and Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, S.; Vargas, J.; Hoffmann, A. Signaling via the NFκB System. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Syst. Biol. Med. 2016, 8, 227–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vancolen, S.; Sébire, G.; Robaire, B. Influence of Androgens on the Innate Immune System. Andrology 2023, 11, 1237–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rettew, J.A.; Huet-Hudson, Y.M.; Marriott, I. Testosterone Reduces Macrophage Expression in the Mouse of Toll-like Receptor 4, a Trigger for Inflammation and Innate Immunity. Biol. Reprod. 2008, 78, 432–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Tong, Y.; Chen, P.-F.; Miao, S.; Zhou, R.-Y. Neuroprotection of Dihydrotestosterone via Suppression of the Toll-like Receptor 4/Nuclear Factor-Kappa B Signaling Pathway in High Glucose-Induced BV-2 Microglia Inflammatory Responses. Neuroreport 2020, 31, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cheng, W.; Shang, H.; Wei, H.; Deng, C. The Interplay between Androgen and Gut Microbiota: Is There a Microbiota-Gut-Testis Axis. Reprod. Sci. 2022, 29, 1674–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xie, Z. Exploring the Role of Gut Microbiome in Male Reproduction. Andrology 2022, 10, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, K.; Kim, N. Roles of Sex Hormones and Gender in the Gut Microbiota. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2021, 27, 314–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, N.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.D.; Jing, J.; Liu, S.S.; Mu, Y.P.; Peng, L.L.; Yan, Y.J.; Xiao, G.M.; Bi, X.Y.; et al. Impairment of Spermatogenesis and Sperm Motility by the High-Fat Diet-Induced Dysbiosis of Gut Microbes. Gut 2020, 69, 1608–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, N.; Hanaoka, R.; Hanada, K.; Izawa, T.; Inui, H.; Yamaji, R. Hypogonadism Alters Cecal and Fecal Microbiota in Male Mice. Gut Microbes 2016, 7, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moadi, L.; Turjeman, S.; Asulin, N.; Koren, O. The Effect of Testosterone on the Gut Microbiome in Mice. Commun. Biol. 2024, 7, 880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Xie, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhong, Y.; Liu, L.; Liu, J.; Zhang, W.; Pi, Y.; Tang, F.; Liu, Z.; et al. Androgen Deficiency-Induced Loss of Lactobacillus Salivarius Extracellular Vesicles Is Associated with the Pathogenesis of Osteoporosis. Microbiol. Res. 2025, 293, 128047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- d’Afflitto, M.; Upadhyaya, A.; Green, A.; Peiris, M. Association Between Sex Hormone Levels and Gut Microbiota Composition and Diversity-A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2022, 56, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushita, M.; Fujita, K.; Motooka, D.; Hatano, K.; Hata, J.; Nishimoto, M.; Banno, E.; Takezawa, K.; Fukuhara, S.; Kiuchi, H.; et al. Firmicutes in Gut Microbiota Correlate with Blood Testosterone Levels in Elderly Men. World J. Men’s Health 2022, 40, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaltsas, A.; Giannakodimos, I.; Markou, E.; Stavropoulos, M.; Deligiannis, D.; Kratiras, Z.; Chrisofos, M. The Androbactome and the Gut Microbiota-Testis Axis: A Narrative Review of Emerging Insights into Male Fertility. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Feng, Y.; Hao, Y.; Zhong, R.; Jiang, Y.; Tang, X.; Lu, D.; Fang, H.; Agarwal, M.; Chen, L.; et al. Gut-Testis Axis: Microbiota Prime Metabolome To Increase Sperm Quality in Young Type 2 Diabetes. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0142322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wei, Z.; Tan, J.; Sun, H.; Jiang, H.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Schroyen, M. Alginate Oligosaccharide Extends the Service Lifespan by Improving the Sperm Metabolome and Gut Microbiota in an Aging Duroc Boars Model. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1308484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Sun, Y.; Chen, Z.; Gao, R.; Song, M.; Zou, T.; Gong, X.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, C.; et al. Sodium Butyrate Promotes Synthesis of Testosterone and Meiosis of Hyperuricemic Male Mice. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 14757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devendran, S.; Mythen, S.M.; Ridlon, J.M. The DesA and DesB Genes from Clostridium Scindens ATCC 35704 Encode Steroid-17,20-Desmolase. J. Lipid Res. 2018, 59, 1005–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devendran, S.; Méndez-García, C.; Ridlon, J.M. Identification and Characterization of a 20β-HSDH from the Anaerobic Gut Bacterium Butyricicoccus Desmolans ATCC 43058. J. Lipid Res. 2017, 58, 916–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, J.; Dai, W.; Lyu, Y.; Liu, H.; Le, J.; Sun, T.; Yao, Q.; Zhao, Z.; Jiang, X.; Li, Y. Role of Intestinal Testosterone-Degrading Bacteria and 3/17β-HSD in the Pathogenesis of Testosterone Deficiency-Induced Hyperlipidemia in Males. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2024, 10, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, R.; Cheng, D.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, J.; Chen, S.; Xia, Y. Immune Microenvironment Dysregulation: A Contributing Factor to Obesity-Associated Male Infertility. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Zhang, L.; Yang, L.; Chu, H. The Critical Role of Gut Microbiota in Obesity. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1025706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakaroun, R.M.; Massier, L.; Kovacs, P. Gut Microbiome, Intestinal Permeability, and Tissue Bacteria in Metabolic Disease: Perpetrators or Bystanders? Nutrients 2020, 12, 1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergheim, I.; Moreno-Navarrete, J.M. The Relevance of Intestinal Barrier Dysfunction, Antimicrobial Proteins and Bacterial Endotoxin in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2024, 54, e14224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelton Tremellen, X.; Mcphee, N.; Pearce, K.; Benson, S.; Schedlowski, M.; Engler, H. Endotoxin-Initiated Inflammation Reduces Testosterone Production in Men of Reproductive Age. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 314, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamad, N.V.; Wong, S.K.; Wan Hasan, W.N.; Jolly, J.J.; Nur-Farhana, M.F.; Ima-Nirwana, S.; Chin, K.Y. The Relationship between Circulating Testosterone and Inflammatory Cytokines in Men. Aging Male 2019, 22, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarchielli, E.; Comeglio, P.; Squecco, R.; Ballerini, L.; Mello, T.; Guarnieri, G.; Idrizaj, E.; Mazzanti, B.; Vignozzi, L.; Gallina, P.; et al. Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Impairs Kisspeptin Signaling in Human Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone Primary Neurons. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 102, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, A.P.; Misztal, T.; Romanowicz, K.; Tomaszewska-Zaremba, D. Central Injection of Exogenous IL-1β in the Control Activities of Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Gonadal Axis in Anestrous Ewes. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2012, 47, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, R.M.; Pace, F.; Kuntz, T.M.; Morgan, X.C.; Hyland, P.; Summers, K.; McDermott, E.; Blumen, K.; Watnick, P.I. Testosterone Treatment Impacts the Intestinal Microbiome of Transgender Individuals. mSphere 2024, 9, e0055724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, L.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Niu, W.; Liu, C.; Wang, Y. Downregulation of Leptin Receptor and Kisspeptin/GPR54 in the Murine Hypothalamus Contributes to Male Hypogonadism Caused by High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity. Endocrine 2018, 62, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, B.; Song, C.; Gao, H.; Ma, T.; Li, T.; Ma, Q.; Yao, T.; Wang, M.; Li, J.; Yi, X.; et al. Leptin and Inflammatory Factors Play a Synergistic Role in the Regulation of Reproduction in Male Mice through Hypothalamic Kisspeptin-Mediated Energy Balance. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2021, 19, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Q.; Li, W.; Li, M.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H. Leptin/LeptinR-Kisspeptin/Kiss1r-GnRH Pathway Reacting to Regulate Puberty Onset during Negative Energy Balance. Life Sci. 2016, 153, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rønnekleiv, O.K.; Qiu, J.; Kelly, M.J. Hypothalamic Kisspeptin Neurons and the Control of Homeostasis. Endocrinology 2022, 163, bqab253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaderpour, S.; Ghiasi, R.; Heydari, H.; Keyhanmanesh, R. The Relation between Obesity, Kisspeptin, Leptin, and Male Fertility. Horm. Mol. Biol. Clin. Investig. 2021, 43, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perakakis, N.; Mantzoros, C.S. Evidence from Clinical Studies of Leptin: Current and Future Clinical Applications in Humans. Metabolism 2024, 161, 156053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perakakis, N.; Farr, O.M.; Mantzoros, C.S. Leptin in Leanness and Obesity: JACC State-of-the-Art Review. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2021, 77, 745–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landry, D.A.; Sormany, F.; Haché, J.; Roumaud, P.; Martin, L.J. Steroidogenic Genes Expressions Are Repressed by High Levels of Leptin and the JAK/STAT Signaling Pathway in MA-10 Leydig Cells. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2017, 433, 79–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’bryan, M.K.; Schlatt, S.; Phillips, D.J.; De Kretser, D.M.; Hedger, M.P. Bacterial Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammation Compromises Testicular Function at Multiple Levels in Vivo. Endocrinology 2000, 141, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, H.; Bhushan, S.; Fijak, M.; Meinhardt, A. Mechanism of Inflammatory Associated Impairment of Sperm Function, Spermatogenesis and Steroidogenesis. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 897029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leisegang, K.; Henkel, R. The in Vitro Modulation of Steroidogenesis by Inflammatory Cytokines and Insulin in TM3 Leydig Cells. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2018, 16, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Mello, A.H.; Costa, A.B.; Engel, J.D.G.; Rezin, G.T. Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Obesity. Life Sci. 2018, 192, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Tang, Y.; Chen, B.; Zhao, Y.; Aguilar, Z.P.; Tao, X.; Xu, H. Inhibition of Testosterone Synthesis Induced by Oral TiO2NPs Is Associated with ROS-MAPK(ERK1/2)-StAR Signaling Pathway in SD Rat. Toxicol. Res. 2021, 10, 937–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Zhang, J.; Miao, C.; Ying, H.; Zhang, X.; Song, M.; Cui, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Cheng, P. Aflatoxin B1-Induced Testosterone Biosynthesis Disorder via the ROS/AMPK Signaling Pathway in Male Mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 5955–5965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sam, A.D.; Sharma, A.C.; Lee, L.Y.; Hales, D.B.; Law, W.R.; Ferguson, J.L.; Bosmann, H.B. Sepsis Produces Depression of Testosterone and Steroidogenic Acute Regulatory (StAR) Protein. Shock 1999, 11, 298–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Schneider, G.; Kirschner, M.A.; Berkowitz, R.; Ertel, N.H. Increased estrogen production in obese men. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1979, 48, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhindsa, S.; Batra, M.; Kuhadiya, N.; Dandona, P. Oestradiol Concentrations Are Not Elevated in Obesity-Associated Hypogonadotrophic Hypogonadism. Clin. Endocrinol. 2014, 80, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strain, G.W.; Zumoff, B.; Miller, L.K.; Rosner, W.; Levit, C.; Kalin, M.; Hershcopf, R.J.; Rosenfeld, R.S. Effect of Massive Weight Loss on Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Gonadal Function in Obese Men. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1988, 66, 1019–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulhall, J.P.; Trost, L.W.; Brannigan, R.E.; Kurtz, E.G.; Redmon, J.B.; Chiles, K.A.; Lightner, D.J.; Miner, M.M.; Murad, M.H.; Nelson, C.J.; et al. Evaluation and Management of Testosterone Deficiency: AUA Guideline. J. Urol. 2018, 200, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simó, R.; Sáez-López, C.; Barbosa-Desongles, A.; Hernández, C.; Selva, D.M. Novel Insights in SHBG Regulation and Clinical Implications. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 26, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hautanen, A. Synthesis and Regulation of Sex Hormone-Binding Globulin in Obesity. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2000, 24 (Suppl. S2), S64–S70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, B.; Ma, N.; Zhou, Z.; Lv, C. Putative Causal Inference for the Relationship between Obesity and Sex Hormones in Males: A Bidirectional Mendelian Randomization Study. PeerJ 2023, 11, e15760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, L.A.; Page, S.T.; Amory, J.K.; Anawalt, B.D.; Matsumoto, A.M. The Association of Obesity with Sex Hormone-Binding Globulin Is Stronger than the Association with Ageing--Implications for the Interpretation of Total Testosterone Measurements. Clin. Endocrinol. 2015, 83, 828–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souteiro, P.; Belo, S.; Oliveira, S.C.; Neves, J.S.; Magalhães, D.; Pedro, J.; Bettencourt-Silva, R.; Costa, M.M.; Varela, A.; Queirós, J.; et al. Insulin Resistance and Sex Hormone-Binding Globulin Are Independently Correlated with Low Free Testosterone Levels in Obese Males. Andrologia 2018, 50, e13035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.; Wang, J.; Wen, X.; Xie, J.; Huang, F.; Guan, X.; Hao, X.; Duan, P.; Chen, C.; Chen, H. Effects of Aging and Macrophages on Mice Stem Leydig Cell Proliferation and Differentiation in Vitro. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1139281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, K.; Yu, J.; Liu, G.; Chen, H.; Ge, R.; Deng, C. Editorial: Aging and Male Hypogonadism. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1207907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beattie, M.C.; Adekola, L.; Papadopoulos, V.; Chen, H.; Zirkin, B.R. Leydig Cell Aging and Hypogonadism. Exp. Gerontol. 2015, 68, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Peng, H.; Yu, J.; Luo, P.; Xiong, C.; Chen, H.; Fan, H.; Ma, Y.; Ou, W.; Zhang, S.; et al. Impaired Ketogenesis in Leydig Cells Drives Testicular Aging. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 4224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santiago, J.; Silva, J.V.; Alves, M.G.; Oliveira, P.F.; Fardilha, M. Testicular Aging: An Overview of Ultrastructural, Cellular, and Molecular Alterations. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2019, 74, 860–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Liu, J.; Luo, L.; Zirkin, B.R. Dibutyryl Cyclic Adenosine Monophosphate Restores the Ability of Aged Leydig Cells to Produce Testosterone at the High Levels Characteristic of Young Cells. Endocrinology 2004, 145, 4441–4446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, L.; Chen, H.; Zirkin, B.R. Temporal Relationships among Testosterone Production, Steroidogenic Acute Regulatory Protein (StAR), and P450 Side-Chain Cleavage Enzyme (P450scc) during Leydig Cell Aging. J. Androl. 2005, 26, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.; Wei, W.; Xie, F.; Zhu, X.; Zheng, L.; Lv, Z. Steroidogenesis Decline Accompanied with Reduced Antioxidation and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Mice Testes during Ageing. Andrologia 2018, 50, e12816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Yu, H.; Fan, Y.; Wu, L.; Fang, Y.; Wei, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Cao, Y. Integrated Stress Response Mediates HSP70 to Inhibit Testosterone Synthesis in Aging Testicular Leydig Cells. Reprod. Biol. 2024, 24, 100954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, F.; Ye, L.; Zirkin, B.; Chen, H. Steroidogenesis in Leydig Cells: Effects of Aging and Environmental Factors. Reproduction 2017, 154, R111–R122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Chen, H.; Zirkin, B.R. Leydig Cell Aging: Steroidogenic Acute Regulatory Protein (StAR) and Cholesterol Side-Chain Cleavage Enzyme. J. Androl. 2001, 22, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zirkin, B.R.; Chen, H. Regulation of Leydig Cell Steroidogenic Function during Aging. Biol. Reprod. 2000, 63, 977–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.Y.; Chen, H.; Midzak, A.; Burnett, A.L.; Papadopoulos, V.; Zirkin, B.R. Drug Ligand-Induced Activation of Translocator Protein (TSPO) Stimulates Steroid Production by Aged Brown Norway Rat Leydig Cells. Endocrinology 2013, 154, 2156–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garza, S.; Chen, L.; Galano, M.; Cheung, G.; Sottas, C.; Li, L.; Li, Y.; Zirkin, B.R.; Papadopoulos, V. Mitochondrial Dynamics, Leydig Cell Function, and Age-Related Testosterone Deficiency. FASEB J. 2022, 36, e22637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mularoni, V.; Esposito, V.; Di Persio, S.; Vicini, E.; Spadetta, G.; Berloco, P.; Fanelli, F.; Mezzullo, M.; Pagotto, U.; Pelusi, C.; et al. Age-Related Changes in Human Leydig Cell Status. Hum. Reprod. 2020, 35, 2663–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veldhuis, J.D.; Zwart, A.; Mulligan, T.; Iranmanesh, A. Muting of Androgen Negative Feedback Unveils Impoverished Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone/Luteinizing Hormone Secretory Reactivity in Healthy Older Men. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 529–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Gruenewald, D.A.; Naai, M.A.; Marck, B.T.; Matsumoto, A.M. Age-Related Decrease in Hypothalamic Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone (GnRH) Gene Expression, but Not Pituitary Responsiveness to GnRH, in the Male Brown Norway Rat. J. Androl. 2000, 21, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iranmanesh, A.; Mulligan, T.; Veldhuis, J.D. Age in Men Does Not Determine Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone’s Dose-Dependent Stimulation of Luteinizing Hormone Secretion under an Exogenous Testosterone Clamp. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 95, 2877–2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufman, J.-M.; Lapauw, B.; Mahmoud, A.; T’Sjoen, G.; Huhtaniemi, I.T. Aging and the Male Reproductive System. Endocr. Rev. 2019, 40, 906–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapauw, B.; Goemaere, S.; Zmierczak, H.; Van Pottelbergh, I.; Mahmoud, A.; Taes, Y.; De Bacquer, D.; Vansteelandt, S.; Kaufman, J.M. The Decline of Serum Testosterone Levels in Community-Dwelling Men over 70 Years of Age: Descriptive Data and Predictors of Longitudinal Changes. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2008, 159, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morley, J.E.; Kaiser, F.E.; Perry, H.M.; Patrick, P.; Morley, P.M.; Stauber, P.M.; Vellas, B.; Baumgartner, R.N.; Garry, P.J. Longitudinal Changes in Testosterone, Luteinizing Hormone, and Follicle-Stimulating Hormone in Healthy Older Men. Metabolism 1997, 46, 410–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oride, A.; Kanasaki, H. The Role of KNDy Neurons in Human Reproductive Health. Endocr. J. 2024, 71, 733–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, G.E.; Bohaczuk, S.C.; Cassin, J.; Witham, E.A.; Shojaei, S.; Ho, E.V.; Thackray, V.G.; Mellon, P.L. Androgen Receptor Positively Regulates Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone Receptor in Pituitary Gonadotropes. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2021, 530, 111286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Chen, Y.; Fajobi, T.; DiVall, S.A.; Chang, C.; Yeh, S.; Wolfe, A. Conditional Knockout of the Androgen Receptor in Gonadotropes Reveals Crucial Roles for Androgen in Gonadotropin Synthesis and Surge in Female Mice. Mol. Endocrinol. 2014, 28, 1670–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnár, C.S.; Vida, B.; Sipos, M.T.; Ciofi, P.; Borsay, B.Á.; Rácz, K.; Herczeg, L.; Bloom, S.R.; Ghatei, M.A.; Dhillo, W.S.; et al. Morphological Evidence for Enhanced Kisspeptin and Neurokinin B Signaling in the Infundibular Nucleus of the Aging Man. Endocrinology 2012, 153, 5428–5439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hrabovszky, E.; Takács, S.; Göcz, B.; Skrapits, K. New Perspectives for Anatomical and Molecular Studies of Kisspeptin Neurons in the Aging Human Brain. Neuroendocrinology 2019, 109, 230–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rastrelli, G.; Carter, E.L.; Ahern, T.; Finn, J.D.; Antonio, L.; O’Neill, T.W.; Bartfai, G.; Casanueva, F.F.; Forti, G.; Keevil, B.; et al. Development of and Recovery from Secondary Hypogonadism in Aging Men: Prospective Results from the EMAS. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, 3172–3182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeap, B.B.; Almeida, O.P.; Hyde, Z.; Norman, P.E.; Chubb, S.A.P.; Jamrozik, K.; Hankey, G.J.; Flicker, L. Healthier Lifestyle Predicts Higher Circulating Testosterone in Older Men: The Health in Men Study. Clin. Endocrinol. 2009, 70, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banica, T.; Verroken, C.; Reyns, T.; Mahmoud, A.; T’Sjoen, G.; Fiers, T.; Kaufman, J.-M.; Lapauw, B. Early Decline of Androgen Levels in Healthy Adult Men: An Effect of Aging Per Se? A Prospective Cohort Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 106, 1074–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeap, B.B.; Manning, L.; Chubb, S.A.P.; Handelsman, D.J.; Almeida, O.P.; Hankey, G.J.; Flicker, L. Progressive Impairment of Testicular Endocrine Function in Ageing Men: Testosterone and Dihydrotestosterone Decrease, and Luteinizing Hormone Increases, in Men Transitioning from the 8th to 9th Decades of Life. Clin. Endocrinol. 2018, 88, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajar, A.; Forti, G.; O’Neill, T.W.; Lee, D.M.; Silman, A.J.; Finn, J.D.; Bartfai, G.; Boonen, S.; Casanueva, F.F.; Giwercman, A.; et al. Characteristics of Secondary, Primary, and Compensated Hypogonadism in Aging Men: Evidence from the European Male Ageing Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 95, 1810–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbonetti, A.; D’Andrea, S.; Francavilla, S. Testosterone Replacement Therapy. Andrology 2020, 8, 1551–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapauw, B.; Kaufman, J.-M. MANAGEMENT OF ENDOCRINE DISEASE: Rationale and Current Evidence for Testosterone Therapy in the Management of Obesity and Its Complications. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2020, 183, R167–R183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanakis, G.A.; Pofi, R.; Goulis, D.G.; Isidori, A.M.; Armeni, E.; Erel, C.T.; Fistonić, I.; Hillard, T.; Hirschberg, A.L.; Meczekalski, B.; et al. EMAS Position Statement: Testosterone Replacement Therapy in Older Men. Maturitas 2023, 178, 107854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mongioì, L.M.; Cimino, L.; Condorelli, R.A.; Magagnini, M.C.; Barbagallo, F.; Cannarella, R.; La Vignera, S.; Calogero, A.E. Effectiveness of a Very Low Calorie Ketogenic Diet on Testicular Function in Overweight/Obese Men. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulte, D.M.; Hahn, M.; Oberhäuser, F.; Malchau, G.; Schubert, M.; Heppner, C.; Müller, N.; Güdelhöfer, H.; Faust, M.; Krone, W.; et al. Caloric Restriction Increases Serum Testosterone Concentrations in Obese Male Subjects by Two Distinct Mechanisms. Horm. Metab. Res. 2014, 46, 283–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corona, G.; Rastrelli, G.; Monami, M.; Saad, F.; Luconi, M.; Lucchese, M.; Facchiano, E.; Sforza, A.; Forti, G.; Mannucci, E.; et al. Body Weight Loss Reverts Obesity-Associated Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2013, 168, 829–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, D.J.; Chasland, L.C.; Yeap, B.B.; Naylor, L.H. Comparing the Impacts of Testosterone and Exercise on Lean Body Mass, Strength and Aerobic Fitness in Aging Men. Sports Med. Open 2024, 10, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chasland, L.C.; Yeap, B.B.; Maiorana, A.J.; Chan, Y.X.; Maslen, B.A.; Cooke, B.R.; Dembo, L.; Naylor, L.H.; Green, D.J. Testosterone and Exercise: Effects on Fitness, Body Composition, and Strength in Middle-to-Older Aged Men with Low-Normal Serum Testosterone Levels. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2021, 320, H1985–H1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossmann, M.; Ng Tang Fui, M.; Cheung, A.S. Late-Onset Hypogonadism: Metabolic Impact. Andrology 2020, 8, 1519–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corona, G.; Vignozzi, L.; Sforza, A.; Mannucci, E.; Maggi, M. Obesity and Late-Onset Hypogonadism. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2015, 418 Pt 2, 120–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangolim, A.S.; Brito, L.d.A.R.; Nunes-Nogueira, V.D.S. Effectiveness of Testosterone Replacement in Men with Obesity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2021, 186, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, R.K.; Bhattacharya, S.B. Late-Onset Hypogonadism and Testosterone Replacement in Older Men. Clin. Geriatr. Med. 2015, 31, 631–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoskes, J.J.; Wilson, M.K.; Spinner, M.L. Pharmacology of Testosterone Replacement Therapy Preparations. Transl. Androl. Urol. 2016, 5, 834–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogol, A.D.; Tkachenko, N.; Bryson, N. NatestoTM, a Novel Testosterone Nasal Gel, Normalizes Androgen Levels in Hypogonadal Men. Andrology 2016, 4, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, R.; Diaz, P.; Blachman-Braun, R.; Loloi, J.; Rahman, F.; Ory, J.; Dullea, A.; Zucker, I.; Gonzalez, D.C.; Kresch, E.; et al. Prevalence of Secondary Erythrocytosis in Men Receiving Testosterone Therapy A Matched-Cohort Analysis of Intranasal Gel, Injections, and Pellets. Can. Urol. Assoc. J. 2023, 17, E202–E207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masterson, T.A.; Turner, D.; Vo, D.; Blachman-Braun, R.; Best, J.C.; Westfield, G.; Bryson, N.; Ramasamy, R. The Effect of Longer-Acting vs Shorter-Acting Testosterone Therapy on Follicle Stimulating Hormone and Luteinizing Hormone. Sex Med. Rev. 2021, 9, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirby, M.; Kalhan, A.; Hackett, G. New Testosterone 2% Gel Using Ferring Advanced Skin Technology (FAST), for the Treatment of Testosterone Deficiency in Men, with a Novel Applicator. Expert. Rev. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 15, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iannone, M.; Palermo, A.; de la Torre, X.; Romanelli, F.; Sansone, A.; Sansone, M.; Lenzi, A.; Botrè, F. Effects of Transdermal Administration of Testosterone Gel on the Urinary Steroid Profile in Hypogonadal Men: Implications in Antidoping Analysis. Steroids 2019, 152, 108491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sansone, A.; Sansone, M.; Selleri, R.; Schiavo, A.; Gianfrilli, D.; Pozza, C.; Zitzmann, M.; Lenzi, A.; Romanelli, F. Monitoring Testosterone Replacement Therapy with Transdermal Gel: When and How? J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2019, 42, 1491–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amano, T.; Iwamoto, T.; Sato, Y.; Imao, T.; Earle, C. The Efficacy and Safety of Short-Acting Testosterone Ointment (Glowmin) for Late-Onset Hypogonadism in Accordance with Testosterone Circadian Rhythm. Aging Male 2018, 21, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narukawa, T.; Soh, J.; Kanemitsu, N.; Harikai, S.; Ukimura, O. Efficacy of Combined Treatment of Intramuscular Testosterone Injection and Testosterone Ointment Application for Late-Onset Hypogonadism: An Open-Labeled, Randomized, Crossover Study. Aging Male 2021, 23, 1059–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.W.; Molfetto, G.; Montoya, D.; Camero, A. Is Oral Testosterone the New Frontier of Testosterone Replacement Therapy? Cureus 2022, 14, e27796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhasin, S.; Brito, J.P.; Cunningham, G.R.; Hayes, F.J.; Hodis, H.N.; Matsumoto, A.M.; Snyder, P.J.; Swerdloff, R.S.; Wu, F.C.; Yialamas, M.A. Testosterone Therapy in Men with Hypogonadism: An Endocrine Society. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 103, 1715–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, M.G.; Gagliano-Jucá, T.; Basaria, S. Testosterone Therapy with Subcutaneous Injections: A Safe, Practical, and Reasonable Option. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 107, 614–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anawalt, B.D.; Bremner, W.J. Reproductive Endocrinology: Are Intramuscular Testosterone Injections Harmful? Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2015, 11, 510–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McFarland, J.; Craig, W.; Clarke, N.J.; Spratt, D.I. Serum Testosterone Concentrations Remain Stable between Injections in Patients Receiving Subcutaneous Testosterone. J. Endocr. Soc. 2017, 1, 1095–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Choi, E.J.; Xu, P.; Barham, D.; El-Khatib, F.M.; Yafi, F.A.; Kavoussi, P.K. Comparison of Outcomes for Hypogonadal Men Treated with Intramuscular Testosterone Cypionate versus Subcutaneous Testosterone Enanthate. J. Urol. 2022, 207, 677–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCullough, A. A Review of Testosterone Pellets in the Treatment of Hypogonadism. Curr. Sex. Health Rep. 2014, 6, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCullough, A.R.; Khera, M.; Goldstein, I.; Hellstrom, W.J.G.; Morgentaler, A.; Levine, L.A. A Multi-Institutional Observational Study of Testosterone Levels after Testosterone Pellet (Testopel(®)) Insertion. J. Sex. Med. 2012, 9, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavender, R.K.; Fairall, M. Subcutaneous Testosterone Pellet Implant (Testopel) Therapy for Men with Testosterone Deficiency Syndrome: A Single-Site Retrospective Safety Analysis. J. Sex. Med. 2009, 6, 3177–3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresch, E.; Lima, T.F.N.; Molina, M.; Deebel, N.A.; Reddy, R.; Patel, M.; Loloi, J.; Carto, C.; Nackeeran, S.; Gonzalez, D.C.; et al. Efficacy and Safety Outcomes of a Compounded Testosterone Pellet versus a Branded Testosterone Pellet in Men with Testosterone Deficiency: A Single-Center, Open-Label, Randomized Trial. Sex. Med. 2023, 11, qfad007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, K.Y.; Kulandavelu, S.; Masterson, T.A.; Ibrahim, E.; Arora, H.; Ramasamy, R. Short-Acting Testosterone Appears to Have Lesser Effect on Male Reproductive Potential Compared to Long-Acting Testosterone in Mice. F&S Sci. 2020, 1, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavoussi, P.K.; Machen, G.L.; Chen, S.H.; Gilkey, M.S.; Chen, J.; Hamzeh, Y.; Aston, K.I.; Kavoussi, S.K. Direct Conversion from Long-Acting Testosterone Replacement Therapy to Natesto Allows for Spermatogenesis Resumption: Proof of Concept. Andrologia 2022, 54, e14453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurayah, A.A.; Dullea, A.; Weber, A.; Masterson, J.M.; Khodamoradi, K.; Mohamed, A.I.; Ramasamy, R. Long vs Short Acting Testosterone Treatments: A Look at the Risks. Urology 2023, 172, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockie, A.W.C.; Grice, P.; Mathur, R.; Pearce, I.; Modgil, V. Diagnosis and Treatment of Hypogonadism in Men Seeking to Preserve Fertility—What Are the Options? Int. J. Impot. Res. 2025, 37, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, K.Y.; Achua, J.K.; Ramasamy, R. Strategies to Increase Testosterone in Men Seeking Fertility. Urol. Res. Pract. 2023, 49, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auerbach, J.M.; Khera, M. Testosterone Replacement Therapy and Cardiovascular Disease. Int. J. Impot. Res. 2022, 34, 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corona, G.; Rastrelli, G.; Sparano, C.; Carinci, V.; Casella, G.; Vignozzi, L.; Sforza, A.; Maggi, M. Cardiovascular Safety of Testosterone Replacement Therapy in Men: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Expert. Opin. Drug Saf. 2024, 23, 565–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.Y.; Zhao, Y.L.; Yang, Y.F.; Wang, X.; Nie, M.; Wu, X.Y.; Mao, J.F. Metabolic Effects of Testosterone Replacement Therapy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus or Metabolic Syndrome: A Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2020, 2020, 4732021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Park, J.J.; Kim, K.H.; Yang, H.J.; Kim, D.S.; Lee, C.H.; Jeon, Y.S.; Shim, S.R.; Kim, J.H. Efficacy of Testosterone Replacement Therapy for Treating Metabolic Disturbances in Late-Onset Hypogonadism: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2021, 53, 1733–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlynarz, N.; Miedziaszczyk, M.; Wieckowska, B.; Szalek, E.; Lacka, K. Effects of Testosterone Replacement Therapy on Metabolic Syndrome in Male Patients-Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Khatri, M.; Memon, R.A.; Velastegui, J.L.; Podaneva, K.Z.; Gutierrez, D.B.; Nadeem, B.; Anumolu, A.R.; Azhar, M.; Zain, A. Effects of Testosterone Therapy in Adult Males with Hypogonadism and T2DM: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2022, 16, 102588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, K.; Kumar, R.; Memon, A.; Kumari, B.; Tehrim, M.; Kumari, P.; Shehryar, M.; Islam, H.; Islam, R.; Khatri, M.; et al. Treatment with Testosterone Therapy in Type 2 Diabetic Hypogonadal Adult Males: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Pract. 2023, 13, 454–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biernikiewicz, M.; Sobieszczańska, M.; Szuster, E.; Pawlikowska-Gorzelańczyk, A.; Janocha, A.; Rożek-Piechura, K.; Rusiecka, A.; Gebala, J.; Okrzymowska, P.; Kałka, D. Erectile Dysfunction as an Obesity-Related Condition in Elderly Men with Coronary Artery Disease. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhasin, S.; Thompson, I.M. Prostate Risk and Monitoring during Testosterone Replacement Therapy. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 109, 1975–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, B.; Qiu, S.; Xiong, X.; Su, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wei, Q.; Yang, L. The Effect of Different Administrations of Testosterone Therapy on Adverse Prostate Events: A Bayesian Network Meta-Analysis. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1009900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhasin, S.; Travison, T.G.; Pencina, K.M.; O’Leary, M.; Cunningham, G.R.; Lincoff, A.M.; Nissen, S.E.; Lucia, M.S.; Preston, M.A.; Khera, M.; et al. Prostate Safety Events during Testosterone Replacement Therapy in Men with Hypogonadism: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, E2348692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daza, J.; Ahmad, A.; Shabir, U.; Jing, Z.; Shiekh, M.; Kauffman, E.; Guru, K.A.; Hussein, A.A. Does Testosterone Replacement Therapy Increase the Risk of Conversion to Treatment in Patients with Prostate Cancer on Active Surveillance? Urol. Oncol. 2023, 41, 429.e1–429.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastrelli, G.; Vignozzi, L.; Corona, G.; Maggi, M. Testosterone and Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. Sex. Med. Rev. 2019, 7, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fendereski, K.; Horns, J.J.; Dehghanbanadaki, H.; Watkins, C.M.; Hotaling, J.M. The Impact of Testosterone Therapy on Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia in Hypogonadal Males. Urology 2024, 196, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Naim, A.B.; Neamatallah, T.; Eid, B.G.; Esmat, A.; Alamoudi, A.J.; Abd El-Aziz, G.S.; Ashour, O.M. 2-Methoxyestradiol Attenuates Testosterone-Induced Benign Prostate Hyperplasia in Rats through Inhibition of HIF-1 α /TGF-β/Smad2 Axis. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2018, 2018, 4389484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackwell, K.; Blackwell, M.; Blackwell, T. Testosterone Replacement Therapy and Cardiovascular Disease: Balancing Safety and Risks in Hypogonadal Men. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2023, 25, 1157–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, S.; Aldana-Bitar, J.; Golub, I.; Ichikawa, K.; Shabir, A.; Bagheri, M.; Hamidi, H.; Benzing, T.; Kianoush, S.; Budoff, M.J. Testosterone Therapy and the Risk of Cardiovascular Disease in Older, Hypogonadal Men. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2024, 84, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snyder, P.J.; Bauer, D.C.; Ellenberg, S.S.; Cauley, J.A.; Buhr, K.A.; Bhasin, S.; Miller, M.G.; Khan, N.S.; Li, X.; Nissen, S.E. Testosterone Treatment and Fractures in Men with Hypogonadism. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handelsman, D.J.; Wittert, G.A. Testosterone and Depression Symptoms in Aging Men. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 109, e1798–e1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pope, H.G.; Kouri, E.M.; Hudson, J.I. Effects of Supraphysiologic Doses of Testosterone on Mood and Aggression in Normal Men: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2000, 57, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, M.; Daher, M.; Diebo, B.G.; Daniels, A.H.; Arcand, M.A. Testosterone Replacement Therapy Is Associated with Increased Incidence Rate of Vertebral Fractures: A Matched Retrospective Analysis. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. Glob. Res. Rev. 2025, 9, e24.00248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Mukaddam, M.; Rajapakse, C.S.; Bhagat, Y.A.; Wehrli, F.W.; Guo, W.; Peachey, H.; LeBeau, S.O.; Zemel, B.S.; Wang, C.; Swerdloff, R.S.; et al. Effects of Testosterone and Growth Hormone on the Structural and Mechanical Properties of Bone by Micro-MRI in the Distal Tibia of Men with Hypopituitarism. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, 1236–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenuta, M.; Hasenmajer, V.; Gianfrilli, D.; Isidori, A.M. Testosterone and Male Bone Health: A Puzzle of Interactions. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2025, 110, e2121–e2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Swerdloff, R.S. Testosterone Replacement Therapy in Hypogonadal Men. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2022, 51, 77–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunenfeld, B.; Mskhalaya, G.; Zitzmann, M.; Corona, G.; Arver, S.; Kalinchenko, S.; Tishova, Y.; Morgentaler, A. Recommendations on the Diagnosis, Treatment and Monitoring of Testosterone Deficiency in Men. Aging Male 2021, 24, 119–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Joseph Auchus, R.; McDonald, J.; Rege, J.; Rainey, W.E.; Turcu, A.F. 7212 Racial/Ethnical Differences in Classic and 11-Oxygenated Androgens. J. Endocr. Soc. 2024, 8, bvae163.277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Au Yeung, S.L.; Kavikondala, S.; Leung, G.M.; Schooling, C.M. Testosterone Concentrations in Young Healthy US versus Chinese Men. Am. J. Hum. Biol. 2014, 26, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moosazadeh, M.; Heydari, K.; Rasouli, K.; Azari, S.; Afshari, M.; Barzegari, S.; Nikaeen, R.; Kardan-Souraki, M.; Khani, S.; Motafeghi, F.; et al. Association of the Effect of Alcohol Consumption on Luteinizing Hormone (LH), Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH), and Testosterone Hormones in Men: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2024, 15, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, P.; Shiff, B.; Kohn, T.P.; Ramasamy, R. Impaired Sleep Is Associated with Low Testosterone in US Adult Males: Results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. World J. Urol. 2019, 37, 1449–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genchi, V.A.; Cignarelli, A.; Sansone, A.; Yannas, D.; Dalla Valentina, L.; Renda Livraghi, D.; Spaggiari, G.; Santi, D. Understanding the Role of Alcohol in Metabolic Dysfunction and Male Infertility. Metabolites 2024, 14, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riachy, R.; McKinney, K.; Tuvdendorj, D.R. Various Factors May Modulate the Effect of Exercise on Testosterone Levels in Men. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2020, 5, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steeves, J.A.; Fitzhugh, E.C.; Bradwin, G.; McGlynn, K.A.; Platz, E.A.; Joshu, C.E. Cross-Sectional Association between Physical Activity and Serum Testosterone Levels in US Men: Results from NHANES 1999–2004. Andrology 2016, 4, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurniawan, A.L.; Hsu, C.-Y.; Chao, J.C.-J.; Lin, L.-Y.; Paramastri, R.; Lee, H.-A.; Hsieh, N.-C.; Wu, S.-F.V. Interactive Effects of Unhealthy Lifestyle Behaviors on Testicular Function among Healthy Adult Men: A Cross-Sectional Study in Taiwan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 4925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghanbanadaki, H.; Kim, B.; Fendereski, K.; Horns, J.J.; Ramsay, J.M.; Jimbo, M.; Gross, K.X.; Pastuszak, A.W.; Hotaling, J.M. Racial/Ethnic Differences in Male Reproductive Health: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Semen Parameters and Hormonal Profiles in the United States. Int. J. Impot. Res. 2025, 21, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, K.A.; Witte, J.S. Androgen Receptor CAG Repeats and Prostate Cancer. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2002, 155, 883–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milatiner, D.; Halle, D.; Huerta, M.; Margalioth, E.J.; Cohen, Y.; Ben-Chetrit, A.; Gal, M.; Mimoni, T.; Eldar-Geva, T. Associations between Androgen Receptor CAG Repeat Length and Sperm Morphology. Hum. Reprod. 2004, 19, 1426–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zitzmann, M. The Role of the CAG Repeat Androgen Receptor Polymorphism in Andrology. Front. Horm. Res. 2009, 37, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferro, P.; Catalano, M.G.; Dell’Eva, R.; Fortunati, N.; Pfeffer, U. The Androgen Receptor CAG Repeat: A Modifier of Carcinogenesis? Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2002, 193, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajpert-De Meyts, E.; Leffers, H.; Daugaard, G.; Andersen, C.B.; Petersen, P.M.; Hinrichsen, J.; Pedersen, L.G.; Skakkebaek, N.E. Analysis of the Polymorphic CAG Repeat Length in the Androgen Receptor Gene in Patients with Testicular Germ Cell Cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2002, 102, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malavige, L.S.; Jayawickrama, S.; Ranasinghe, P.; Levy, J.C. Androgen Receptor CAG Repeat Polymorphism Is Not Associated with Insulin Resistance and Diabetes among South Asian Males. BMC Res. Notes 2017, 10, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, R.C.; Leach, D.A.; Bevan, C.L. Epigenetic Coregulation of Androgen Receptor Signaling. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2022, 1390, 277–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Biswas, M.; Massah, S.; Lee, J.; Lingadahalli, S.; Wong, S.; Wells, C.; Foo, J.; Khan, N.; Morin, H.; et al. Dynamic Phase Separation of the Androgen Receptor and Its Coactivators Key to Regulate Gene Expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, 99–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, I.-C.; Lin, H.-Y.; Liu, N.-C.; Wang, R.-S.; Sparks, J.D.; Yeh, S.; Chang, C. Hyperleptinemia without Obesity in Male Mice Lacking Androgen Receptor in Adipose Tissue. Endocrinology 2008, 149, 2361–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubinow, K.B.; Wang, S.; den Hartigh, L.J.; Subramanian, S.; Morton, G.J.; Buaas, F.W.; Lamont, D.; Gray, N.; Braun, R.E.; Page, S.T. Hematopoietic Androgen Receptor Deficiency Promotes Visceral Fat Deposition in Male Mice without Impairing Glucose Homeostasis. Andrology 2015, 3, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-K.; Lai, K.-P.; Luo, J.; Tsai, M.-Y.; Kang, H.-Y.; Chen, Y.; Lee, S.O.; Chang, C. Loss of Androgen Receptor Promotes Adipogenesis but Suppresses Osteogenesis in Bone Marrow Stromal Cells. Stem Cell Res. 2013, 11, 938–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bhasin, S. Biologic Significance of the Short Tandem Trinucleotide Repeats in the Androgen Receptor Gene. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2025, 110, e1276–e1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovannucci, E.; Stampfer, M.J.; Krithivas, K.; Brown, M.; Dahl, D.; Brufsky, A.; Talcott, J.; Hennekens, C.H.; Kantoff, P.W. The CAG Repeat within the Androgen Receptor Gene and Its Relationship to Prostate Cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 3320–3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Hashimi, M.; Pinggera, G.-M.; Shah, R.; Agarwal, A. Clinician’s Guide to the Management of Azoospermia Induced by Exogenous Testosterone or Anabolic-Androgenic Steroids. Asian J. Androl. 2025, 27, 330–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, J.; Ide, H.; Horie, S. Management of Male Fertility in Hypogonadal Patients on Testosterone Replacement Therapy. Medicina 2024, 60, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decaroli, M.C.; Rochira, V. Aging and Sex Hormones in Males. Virulence 2017, 8, 545–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krakowsky, Y.; Conners, W.; Morgentaler, A. Serum Concentrations of Sex Hormone-Binding Globulin Vary Widely in Younger and Older Men: Clinical Data from a Men’s Health Practice. Eur. Urol. Focus. 2019, 5, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rastrelli, G.; Corona, G.; Cipriani, S.; Mannucci, E.; Maggi, M. Sex Hormone-Binding Globulin Is Associated with Androgen Deficiency Features Independently of Total Testosterone. Clin. Endocrinol. 2018, 88, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, B.; Natale, C.; Hellstrom, W.J.G. Testosterone Assays. Urol. Clin. N. Am. 2022, 49, 665–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keevil, B.G.; Adaway, J. Assessment of Free Testosterone Concentration. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019, 190, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farber, N.J.; Vij, S.C.; Shoskes, D.A. Failure of Testosterone Replacement Therapy to Improve Symptoms Correlates with Burden of Systemic Conditions. Transl. Androl. Urol. 2020, 9, 1108–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Shi, Q. Testosterone Treatment: Who Will Benefit the Most? Lancet Healthy Longev. 2023, 4, e524–e525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.; Aziz, S.; Abd-Alrazaq, A.; Farooq, F.; Househ, M.; Sheikh, J. The Effectiveness of Wearable Devices Using Artificial Intelligence for Blood Glucose Level Forecasting or Prediction: Systematic Review. J. Med. Internet. Res. 2023, 25, e40259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haring, R. Perspectives for Metabolomics in Testosterone Replacement Therapy. J. Endocrinol. 2012, 215, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wörheide, M.A.; Krumsiek, J.; Kastenmüller, G.; Arnold, M. Multi-Omics Integration in Biomedical Research—A Metabolomics-Centric Review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1141, 144–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).



