Bone Formation in Zebrafish: The Significance of DAF-FM DA Staining for Nitric Oxide Detection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. NO Staining on Live Material
2.3. NO Staining on Fixed Material
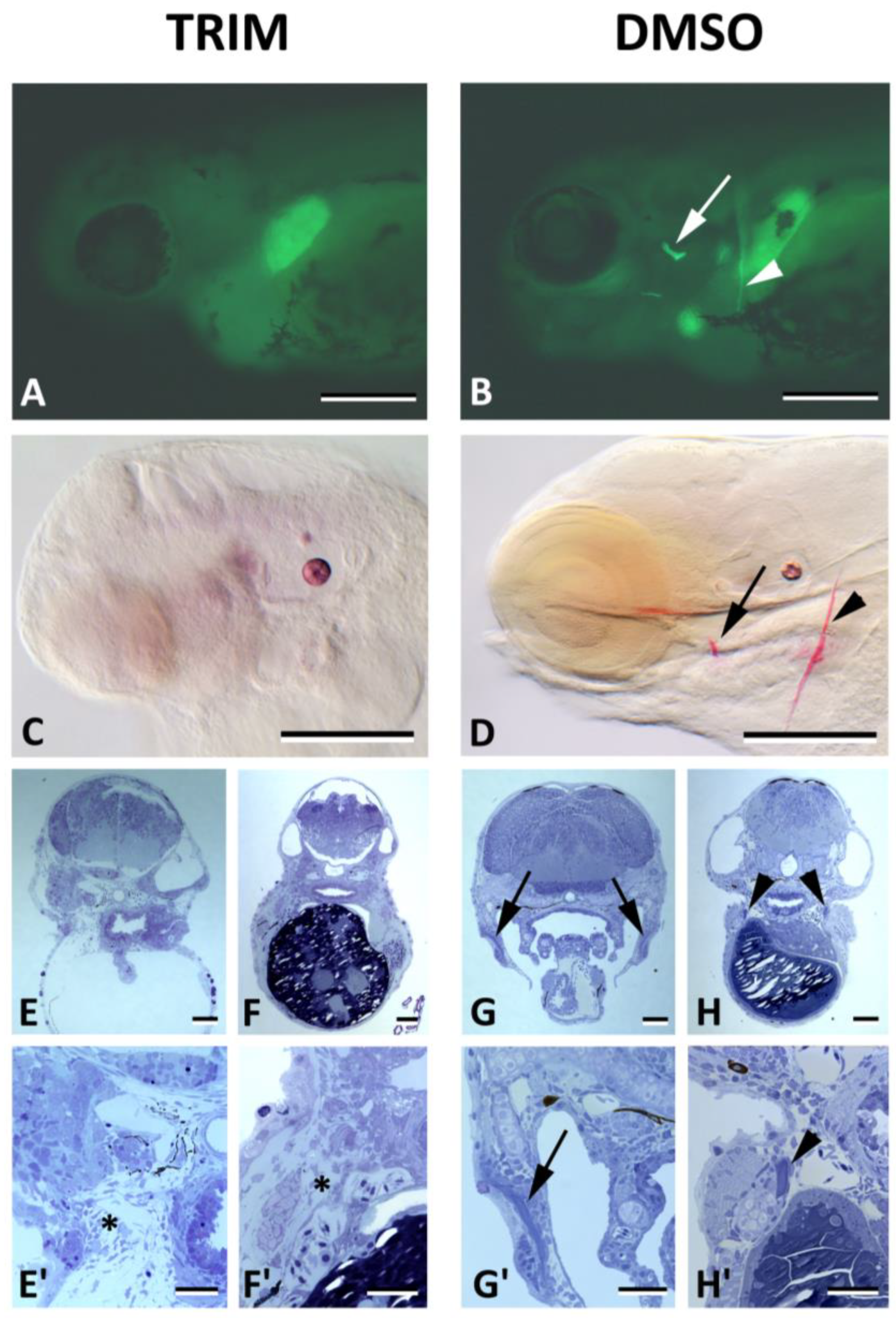
2.4. NO Staining after Inhibition of NOS
2.5. Processing for GMA Sections
2.6. Demonstration of Mineralized Tissues
2.7. Elastin Staining
2.8. Processing for Epon Sections and Transmission Electron Microscopy
2.9. Observations and Microphotography
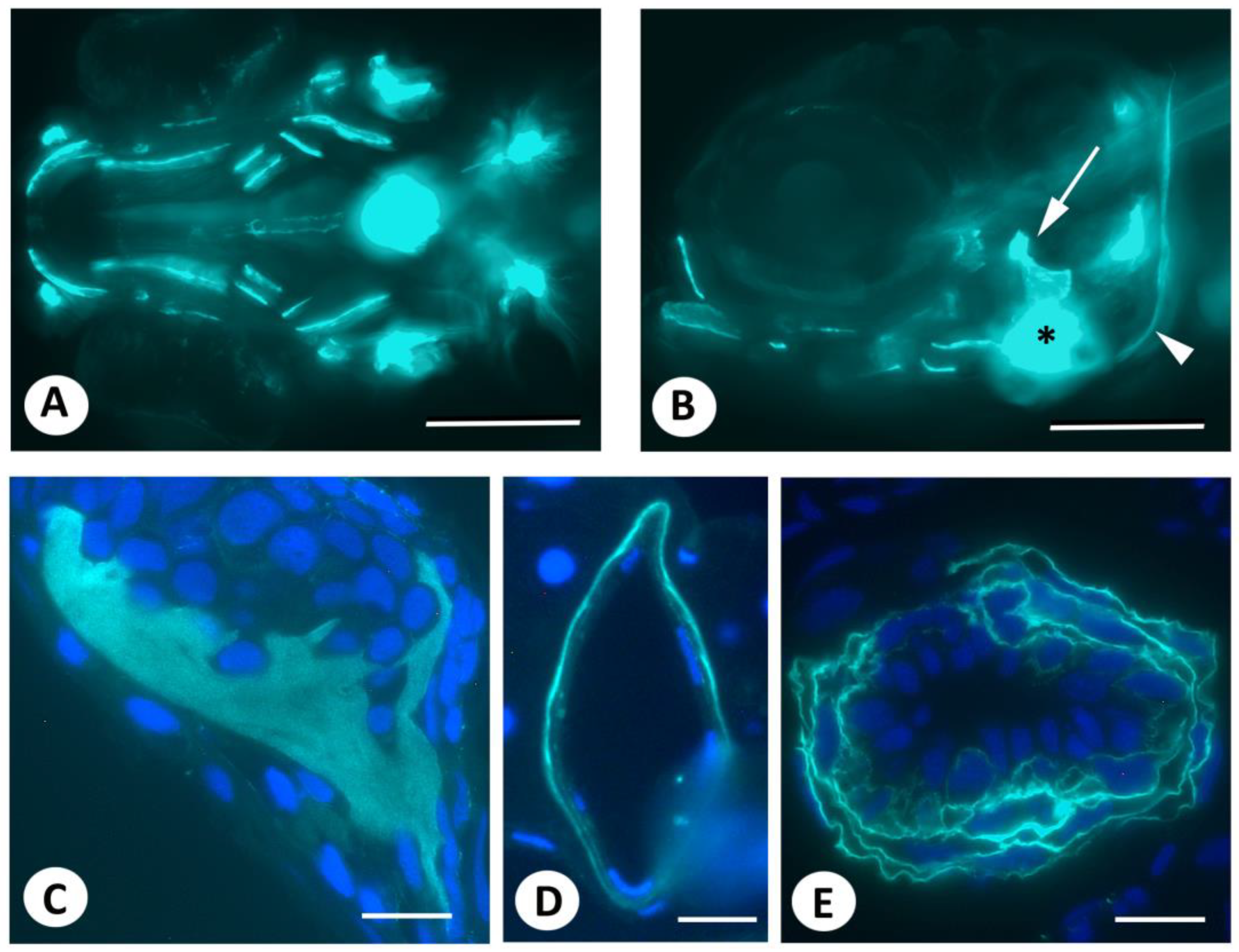
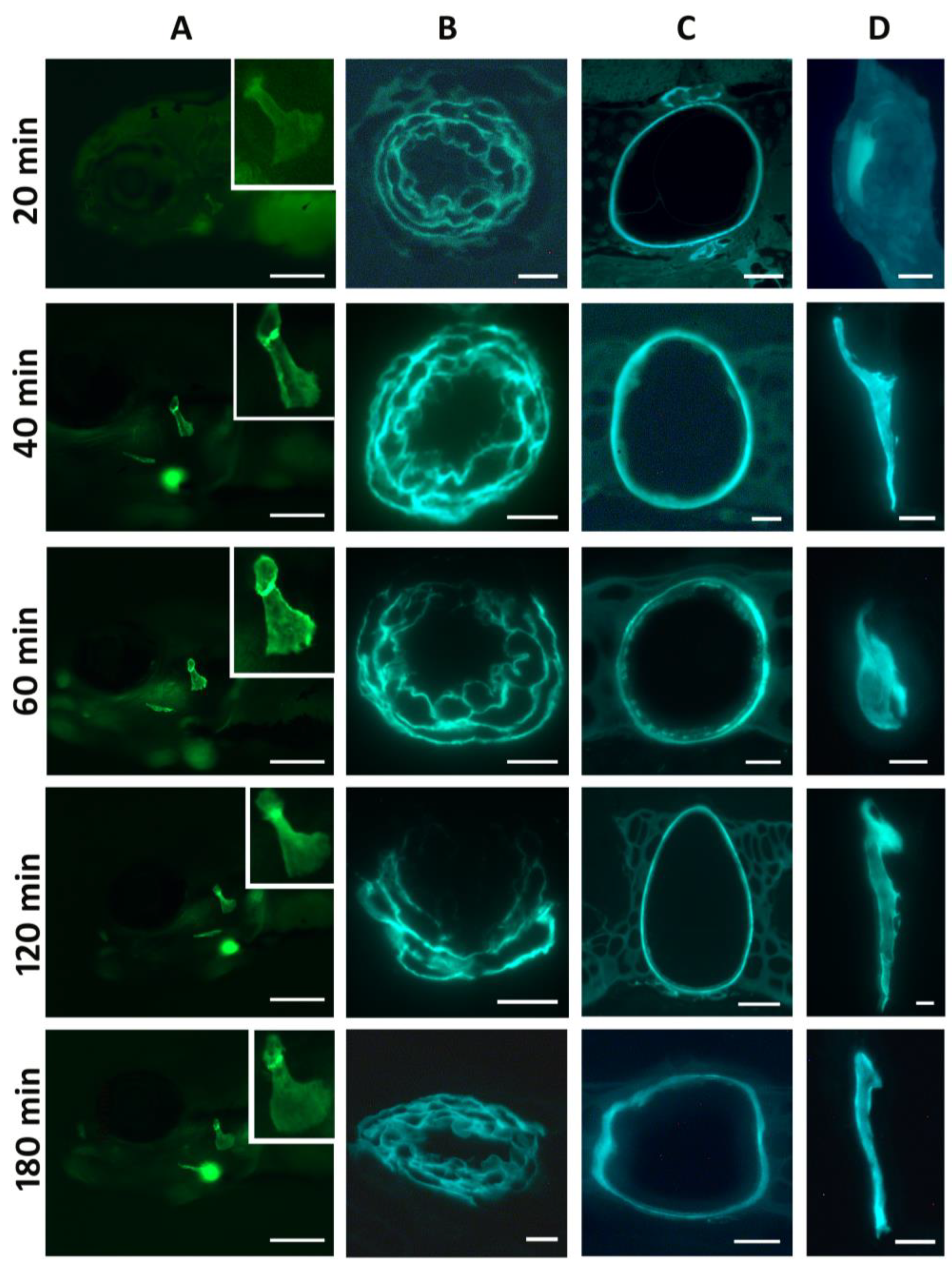
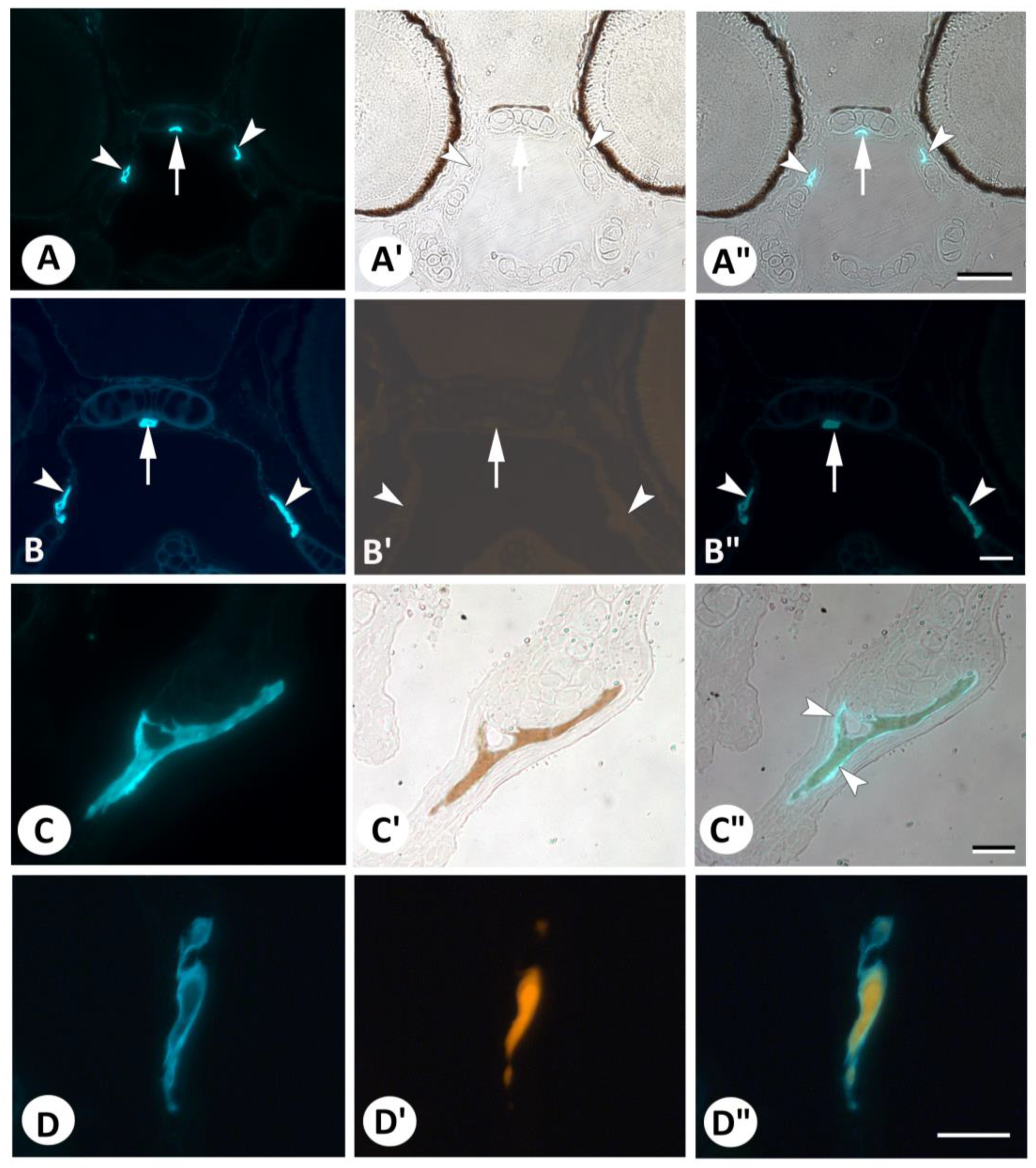
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lundberg, J.O.; Weitzberg, E. Nitric oxide signaling in health and disease. Cell 2022, 185, 2853–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piacenza, L.; Zeida, A.; Trujillo, M.; Radi, R. The superoxide radical switch in the biology of nitric oxide and peroxynitrite. Physiol. Rev. 2022, 102, 1881–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandi, M.L.; Hukkanen, M.; Umeda, T.; Moradi-Bidhendi, N.; Bianchi, S.; Gross, S.S.; Polak, J.M.; MacIntyre, I. Bidirectional regulation of osteoclast function by nitric oxide synthase isoforms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 2954–2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helfrich, M.H.; Evans, D.E.; Grabowski, P.S.; Pollock, J.S.; Ohshima, H.; Ralston, S.H. Expression of nitric oxide synthase isoforms in bone and bone cell cultures. J. Bone Miner. Res. 1997, 12, 1108–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, D.M.; Ralston, S.H. Nitric oxide and bone. J. Bone Miner. Res. 1996, 11, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burger, E.H.; Klein-Nulend, J.; Smit, T.H. Strain-derived canalicular fluid flow regulates osteoclast activity in a remodeling osteon—A proposal. J. Biomech. 2003, 36, 1453–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saura, M.; Tarin, C.; Zaragoza, C. Recent insights into the implication of nitric oxide in osteoblast differentiation and proliferation during bone development. Sci. World J. 2010, 10, 624–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moharrer, Y.; Boerckel, J.D. Tunnels in the rock: Dynamics of osteocyte morphogenesis. Bone 2021, 153, 116104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.; Xie, Y.; He, H.; Fan, W.; Huang, F. Role of nitric oxide in orthodontic tooth movement. Int. J. Molec. Med. 2021, 48, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, H.; Nakatsubo, N.; Kikuchi, K.; Kawahara, S.; Kirino, Y.; Nagoshi, H.; Hirata, Y.; Nagano, T. Detection and imaging of nitric oxide with novel fluorescent indicators: Diaminofluoresceins. Anal. Chem. 1998, 70, 2446–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, H.; Urano, Y.; Kikuchi, K.; Higuchi, T.; Hirata, Y.; Nagano, T. Fluorescent indicators for imaging nitric oxide production. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1999, 38, 3209–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepiller, S.; Laurens, V.; Bouchot, A.; Herbomel, P.; Solary, E.; Chlub, J. Imaging of nitric oxide in a living vertebrate using a diaminofluorescein probe. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2007, 43, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renn, J.; Pruvot, B.; Muller, M. Detection of nitric oxide by diaminofluorescein visualizes the skeleton in living zebrafish. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2014, 30, 701–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windhausen, T.; Squifflet, S.; Renn, J.; Muller, M. BMP signaling regulates bone morphogenesis in zebrafish through promoting osteoblast function as assessed by their nitric oxide production. Molecules 2015, 20, 7586–7601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westerfield, M. The Zebrafish Book. A Guide for the Laboratory Use of Zebrafish (Danio rerio), 4th ed.; University of Oregon Press: Eugene, ON, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Strähle, U.; Scholz, S.; Geisler, R.; Greiner, P.; Hollert, H.; Rastegar, S.; Schumacher, A.; Selderslaghs, I.; Weiss, C.; Witters, H.; et al. Zebrafish embryos as an alternative to animal experiments—A commentary on the definition of the onset of protected life stages in animal welfare regulations. Reprod. Toxicol. 2012, 33, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annona, G.; Sato, I.; Pascual-Anaya, J.; Osca, D.; Braasch, I.; Voss, R.; Stundl, J.; Soukup, V.; Ferrara, A.; Fontenot, Q.; et al. Evolution of the nitric oxide synthase family in vertebrates and novel insights in gill development. Proc. R. Soc. B 2022, 289, 20220667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oralová, V.; Rosa, J.T.; Soenens, M.; Bek, J.W.; Willaert, A.; Witten, P.E.; Huysseune, A. Beyond the whole-mount phenotype: High-resolution imaging in fluorescence-based applications on zebrafish. Biol. Open 2019, 8, bio042374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheehan, D.; Hrapchak, B. Theory and Practice of Histotechnology, 2nd ed.; Battelle Press: Columbus, OH, USA, 1987; p. 481. [Google Scholar]
- Presnell, J.K.; Schreibman, M.P. Humason’s Animal Tissue Techniques, 5th ed.; The Johns Hopkins University Press: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1997; p. 600. [Google Scholar]
- Huysseune, A.; Soenens, M.; Sire, J.-Y.; Witten, P.E. High resolution histology for craniofacial studies on zebrafish and other teleost models. Meth. Molec. Biol. 2022, 2403, 249–262. [Google Scholar]
- Hauschka, P.V.; Damoulis, P.D. Functions of nitric oxide in bone. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 1998, 26, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Tan, Y.; Yang, B.; Zhang, G.; Xiao, X.; Zheng, L. Effect of calcitonin gene-related peptide on nitric oxide production in osteoblasts: An experimental study. Cell Biol. Int. 2011, 35, 757–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, K.S.; Chon, S.; Choi, E.M. Limonene protects osteoblasts against methylglyoxal-derived adduct formation by regulating glyoxalase, oxidative stress, and mitochondrial function. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2017, 278, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Z.; Kho, J.; Dawson, B.; Jiang, M.-M.; Chen, Y.; Ali, S.; Burrage, L.C.; Grover, M.; Palmer, D.J.; Turner, D.L.; et al. Nitric oxide modulates bone anabolism through regulation of osteoblast glycolysis and differentiation. J Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, e138935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancaster, J.R. A tutorial on the diffusibility and reactivity of free nitric oxide. Nitric Oxide—Biol. Chem. 1997, 1, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilderbrand, S.A.; Lim, M.H.; Lippard, S.J. Fluorescence-based nitric oxide detection. In Topics in Fluorescence Spectroscopy; Geddes, C.D., Lakowicz, J.R., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2005; Volume 9, pp. 163–188. [Google Scholar]
- Silveira, A.; Kardjilov, N.; Markötte, H.; Longo, E.; Grevin, I.; Lasch, P.; Shahar, R.; Zaslansky, P. Water flow through bone: Neutron tomography reveals differences in water permeability between osteocytic and anosteocytic bone material. Mater. Des. 2022, 224, 111275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huysseune, A. Skeletal system. In The Laboratory Fish; Ostrander, G., Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2000; pp. 307–317. [Google Scholar]
- D’Alessandro, S.; Posocco, B.; Costa, A.; Zahariou, G.; Lo Schiavo, F.; Carbonera, D.; Zottini, M. Limits in the use of cPTIO as nitric oxide scavenger and EPR probe in plant cells and seedlings. Front. Plant Sci. 2013, 4, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arita, N.O.; Cohen, M.F.; Tokuda, G.; Yamasaki, H. Fluorometric detection of nitric oxide with diaminofluoresceins (DAFs): Applications and limitations for plant NO research. Plant Cell Monogr. 2006, 5, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardman, P. Fluorescent and luminescent probes for measurement of oxidative and nitrosative species in cells and tissues: Progress, pitfalls, and prospects. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2007, 43, 995–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.-S.; Ye, X.; Rubakhin, S.S.; Sweedler, J.V. Measuring nitric oxide in single neurons by capillary electrophoresis with laser-induced fluorescence: Use of ascorbate oxidase in diaminofluorescein measurements. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 1859–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balcerczyk, A.; Soszynski, M.; Bartosz, G. On the specificity of 4-amino-5-methylamino-2′,7′-difluorofluorescein as a probe for nitric oxide. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2005, 39, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamin, M.; Norman, D.; Santer, R.M.; Scarborough, D. Histological, histochemical and ultrastructural studies on the bulbus arteriosus of the sticklebacks, Gasterosteus aculeatus and Pungitius pungitius (Pisces: Teleostei). J. Zool. 1983, 200, 325–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Icardo, J.M. The teleost heart: A morphological approach. In Ontogeny and Phylogeny of the Vertebrate Heart; Sedmera, D., Wang, T., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 35–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, J.; Specian, V.; Maloney, R.; Jourd’heuil, D.; Feelisch, M. Performance of diamino fluorophores for the localization of sources and targets of nitric oxide. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2005, 38, 356–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, D.A. Fluorochromes and fluorescence. In Flow Cytometry: Principles and Applications; Macey, M.G., Ed.; Humana Press Inc.: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2007; pp. 59–112. [Google Scholar]
- Witten, P.E.; Hall, B.K. The Notochord. Development, Evolution and Contributions to the Vertebral Column; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2022; pp. 1–250. [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg, J.O.; Weitzberg, E.; Gladwin, M.T. The nitrate–nitrite–nitric oxide pathway in physiology and therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundberg, J.O.N.; Weitzberg, E.; Lundberg, J.M.; Alving, K. Intragastric nitric oxide production in humans: Measurements in expelled air. Gut 1994, 35, 1543–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Archer, S. Measurement of nitric oxide in biological models. FASEB J. 1993, 7, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Huang, H.; Ning, B.; Li, M.; He, L. A Highly sensitive and selective spectrofluorimetric method for the determination of nitrite in food products. Food Anal. Methods 2016, 9, 1293–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuman, M.W.; Neuman, W.F. On the measurement of water compartments, pH, and gradients in calvaria. Calcif. Tissue Int. 1980, 31, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huysseune, A.; Larsen, U.G.; Larionova, D.; Matthiesen, C.L.; Petersen, S.V.; Muller, M.; Witten, P.E. Bone Formation in Zebrafish: The Significance of DAF-FM DA Staining for Nitric Oxide Detection. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1780. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13121780
Huysseune A, Larsen UG, Larionova D, Matthiesen CL, Petersen SV, Muller M, Witten PE. Bone Formation in Zebrafish: The Significance of DAF-FM DA Staining for Nitric Oxide Detection. Biomolecules. 2023; 13(12):1780. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13121780
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuysseune, Ann, Ulrike G. Larsen, Daria Larionova, Cecilie L. Matthiesen, Steen V. Petersen, Marc Muller, and P. Eckhard Witten. 2023. "Bone Formation in Zebrafish: The Significance of DAF-FM DA Staining for Nitric Oxide Detection" Biomolecules 13, no. 12: 1780. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13121780
APA StyleHuysseune, A., Larsen, U. G., Larionova, D., Matthiesen, C. L., Petersen, S. V., Muller, M., & Witten, P. E. (2023). Bone Formation in Zebrafish: The Significance of DAF-FM DA Staining for Nitric Oxide Detection. Biomolecules, 13(12), 1780. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13121780






