Epidemiological and Liver Biomarkers Profile of Epstein-Barr Virus Infection and Its Coinfection with Cytomegalovirus in Patients with Hematological Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Serological Analysis
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Prevalence of EBV Infection and EBV/CMV Coinfection
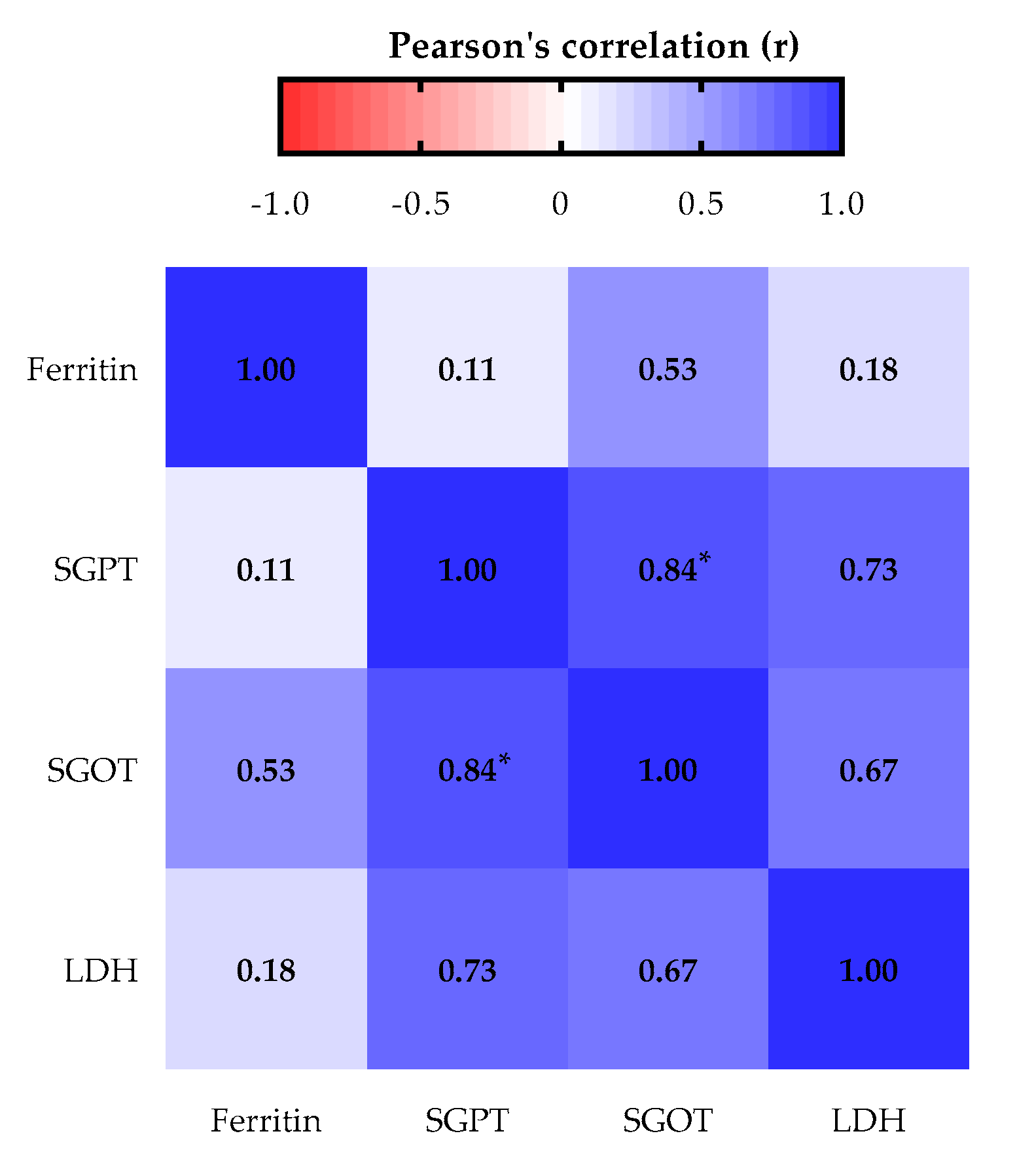
3.2. Liver Biomarkers Profile
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ambinder, R.F. Epstein-barr virus and hodgkin lymphoma. Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program 2007, 2007, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolis, V.; Karadedos, C.; Chiotis, I.; Chaliasos, N.; Tsabouri, S. Atypical manifestations of Epstein-Barr virus in children: A diagnostic challenge. J. Pediatr. Rio. J. 2016, 92, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, H.; Balicer, R.D.; Rozhavski, V.; Halperin, T.; Shreberk, M.; Davidovitch, N.; Huerta-Hartal, M.; Ankol, O.E. Seroepidemiology of Epstein-Barr virus and cytomegalovirus among Israeli male young adults. Ann. Epidemiol. 2012, 22, 783–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balfour, H.H.; Sifakis, F.; Sliman, J.A.; Knight, J.A.; Schmeling, D.O.; Thomas, W. Age-Specific prevalence of epstein-barr virus infection among individuals aged 6-19 years in the United States and factors affecting its acquisition. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 208, 1286–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueira-Silva, C.M.; Pereira, F.E. Prevalence of Epstein-Barr virus antibodies in healthy children and adolescents in Vitoria, State of Espirito Santo, Brazil. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2004, 37, 409–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamora, M.R. DNA viruses (CMV, EBV, and the herpesviruses). Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 32, 454–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mecadon, K.; Jandovitz, N.; Salerno, D.; Martinez, M.; Kato, T. Treatment of Epstein-Barr Virus Viremia in Pediatric Intestinal and Liver Transplant Recipients. Transplantation 2017, 39, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salter, B.; Sehmi, R. Epstein-Barr Virus—Induced Gene 2 and Leukocyte Airway Recruitment in Response to Allergen Challenge When Innate Responses Matter: ILC2s Loom Large in Allergic Airway In fl ammation. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 195, 1543–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, T.A.F.; Costa, I.B.; Costa, I.B.; dos Corrêa, T.L.S.; Coelho, B.M.R.; Silva, A.E.S.; de Ramos, F.L.P.; Filho, A.J.M.; Monteiro, J.L.F.; Siqueira, J.A.M.; et al. Genotypes of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV1/EBV2) in individuals with infectious mononucleosis in the metropolitan area of Belém, Brazil, between 2005 and 2016. Brazilian J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 24, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dematapitiya, C.; Perera, C.; Chinthaka, W.; Senanayaka, S.; Tennakoon, D.; Ameer, A.; Ranasinghe, D.; Warriyapperuma, U.; Weerarathna, S.; Satharasinghe, R. Cold type autoimmune hemolytic anemia- a rare manifestation of infectious mononucleosis; Serum ferritin as an important biomarker. BMC Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, M.A.; Barr, Y.M.; Achong, B.G. Virus particles in cultured lymphoblasts from Burkitt’s lymphoma. Lancet 1964, 15, 702–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.A.; Wang, R.C.; Yang, Y.; Chuang, S.S. Epstein-Barr virus-positive diffuse large B cell lymphoma arising from a chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Overlapping features with classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Pathol. Int. 2016, 66, 393–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarwari, N.M.; Khoury, J.D.; Hernandez, C.M.R. Chronic Epstein Barr virus infection leading to classical Hodgkin lymphoma. BMC Hematol. 2016, 16, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, A.; Suzuki, R. Epstein-barr virus-associated post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorders after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: Pathogenesis, risk factors and clinical outcomes. Cancers 2020, 12, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuhair, M.; Smit, G.S.A.; Wallis, G.; Jabbar, F.; Smith, C.; Devleesschauwer, B.; Griffiths, P. Estimation of the worldwide seroprevalence of cytomegalovirus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Rev. Med. Virol. 2019, 29, e2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smatti, M.K.; Al-Sadeq, D.W.; Ali, N.H.; Pintus, G.; Abou-Saleh, H.; Nasrallah, G.K. Epstein-barr virus epidemiology, serology, and genetic variability of LMP-1 oncogene among healthy population: An update. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiguman, G.M.B.; Poll, L.B.; de Castro Alves, C.E.; Pontes, G.S.; Silva, M.T.; Galvao, T.F. Seroprevalence of cytomegalovirus and its coinfection with epstein-barr virus in adult residents from manaus: A population-based study. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2020, 53, e20190363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuri, A.; Jacobs, B.M.; Vickaryous, N.; Pakpoor, J.; Middeldorp, J.; Giovannoni, G.; Dobson, R. Epidemiology of Epstein-Barr Virus infection and Infectious Mononucleosis in the United Kingdom. BMC Public Health 2020, 20, 912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winter, J.R.; Taylor, G.S.; Thomas, O.G.; Jackson, C.; Lewis, J.E.A.; Stagg, H.R. Factors associated with cytomegalovirus serostatus in young people in England: A cross-sectional study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowd, J.B.; Palermo, T.; Brite, J.; McDade, T.W.; Aiello, A. Seroprevalence of Epstein-Barr Virus Infection in U.S. Children Ages 6–19, 2003–2010. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourahamad, M.; Hooshmand, F.; Olyaee Nezhad, S.; Sepidkar, A. EBV seroepidemiology in married and unmarried women and men in Iran. Reports Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 2, 94–947. [Google Scholar]
- de Melo Silva, J.; Pinheiro-Silva, R.; Dhyani, A.; Pontes, G.S. Cytomegalovirus and Epstein-Barr infections: Prevalence and impact on patients with hematological diseases. Biomed Res. Int. 2020, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.; Zhou, J.; Wei, X.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Peng, B.; Niu, T.; Niu, T. The role of epstein-barr virus (EBV) and cytomegalovirus (CMV) in immune thrombocytopenia. Hematology 2013, 18, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, C.C. Epstein-Barr virus associated with immune thrombocytopenic purpura in childhood: A retrospective study. J. Paediatr. Child Health 2000, 36, 445–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kogawa, K.; Sato, H.; Asano, T.; Ohga, S.; Kudo, K.; Morimoto, A.; Ohta, S.; Wakiguchi, H.; Kanegane, H.; Oda, M.; et al. Prognostic Factors of Epstein-Barr Virus-Associated Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis in Children: Report of the Japan Histiocytosis Study Group. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2014, 61, 1257–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirkol, D.; Kavgacl, U.; Babaoǧlu, B.; Tanju, S.; Oflaz Sözmen, B.; Tekin, S. Cytomegalovirus reactivation in a critically ill patient: A case report. J. Med. Case Rep. 2018, 12, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Atim-Oluk, M. Cytomegalovirus associated haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in the immunocompetent adult managed according to HLH-2004 diagnostic using clinical and sero logical means only. Eur. J. Microbiol. Immunol. 2013, 3, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnecaze, A.; Willeford, W.G.; Lichstein, P.; Ohar, J. Acute Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Infection Associated with Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) in an Immunocompetent Host Meeting All Eight HLH 2004 Diagnostic Criteria. Cureus 2017, 9, e1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harley, J.B.; Chen, X.; Pujato, M.; Miller, D.; Maddox, A.; Forney, C.; Magnusen, A.F.; Lynch, A.; Chetal, K.; Yukawa, M.; et al. Transcription factors operate across disease loci, with EBNA2 implicated in autoimmunity. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 699–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enok Bonong, P.R.; Buteau, C.; Delage, G.; Tanner, J.E.; Lacroix, J.; Duval, M.; Laporte, L.; Tucci, M.; Robitaille, N.; Spinella, P.C.; et al. Transfusion-related Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection: A multicenter prospective cohort study among pediatric recipients of hematopoietic stem cell transplants (TREASuRE study). Transfusion 2021, 61, 144–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sociodemographic Characteristics | N (%) | EBV IgG Positive (%) | EBV PR (95% CI) | p-Value a | Coinfection EBV/CMV Positive (%) | Coinfection PR (95% CI) | p-Value a |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | |||||||
| Male | 112 (49.12) | 92 (82.14) | 0.93 (0.83–1.04) | 0.149 | 84 (75.00) | 0.92 (0.79–1.05) | 0.134 |
| Female | 116 (50.88) | 102 (87.93) | 1.00 (ref.) | 95 (81.90) | 1.00 (ref.) | ||
| Age | |||||||
| 1–10 | 64 (28.07) | 46 (71.88) | 0.80 (0.66–0.91) | 0.001 * | 37 (57.81) | 0.67 (0.52–0.81) | <0.0001 * |
| 11–20 | 52 (22.81) | 45 (86.54) | 1.00 (ref.) | 41 (78.85) | 1.00 (ref.) | ||
| 21–30 | 28 (12.28) | 26 (92.86) | 1.11 (0.92–1.22) | 0.171 | 25 (89.29) | 1.16 (0.94–1.31) | 0.108 |
| 31–40 | 29 (12.72) | 28 (96.55) | 1.16 (0.99–1.26) | 0.058 | 28 (96.55) | 1.27 (1.08–1.40) | 0.011 * |
| 41–50 | 20 (8.77) | 15 (75.00) | 0.87 (0.62–1.05) | 0.159 | 15 (75.00) | 0.95 (0.67–1.15) | 0.454 |
| 51–60 | 20 (8.77) | 19 (95.00) | 1.13 (0.90–1.23) | 0.165 | 18 (90.00) | 1.16 (0.90–1.31) | 0.153 |
| >60 | 15 (6.58) | 15 (100.00) | 15 (100.00) | ||||
| Ethnicity | |||||||
| White | 64 (28.07) | 54 (84.38) | 0.99 (0.85–1.10) | 0.493 | 49 (76.56) | 0.97 (0.81–1.11) | 0.395 |
| Brown | 146 (64.04) | 125 (85.62) | 1.00 (ref.) | 115 (78.77) | 1.00 (ref.) | ||
| Black | 18 (7.89) | 15 (83.33) | 0.98 (0.71–1.13) | 0.450 | 15 (83.33) | 1.07 (0.77–1.24) | 0.413 |
| Marital status | |||||||
| Single | 168 (73.68) | 137 (81.55) | 1.00 (ref.) | 124 (73.81) | 1.00 (ref.) | ||
| Married | 60 (26.32) | 57 (95.00) | 1.17 (1.04–1.28) | 0.011 * | 55 (91.67) | 1.24 (1.09–1.40) | 0.003 * |
| Income | |||||||
| Up to a minimum wage | 115 (50.44) | 98 (85.22) | 1.02 (0.90–1.12) | 0.448 | 90 (78.26) | 0.99 (0.86–1.14) | 0.472 |
| 2–5 minimum wages | 102 (44.74) | 85 (83.33) | 1.00 (ref.) | 78 (76.47) | 1.00 (ref.) | ||
| Above 6 minimum wages | 11 (4.82) | 11 (100.00) | 11 (100.00) | ||||
| Level of schooling | |||||||
| Illiterate ** | 36 (15.79) | 25 (69.44) | 0.79 (0.60–0.94) | 0.004 * | 22 (61.11) | 0.75 (0.55–0.93) | 0.005 * |
| Literate *** | 53 (23.25) | 42 (79.25) | 0.91 (0.76–1.04) | 0.127 | 36 (67.92) | 0.83 (0.66–0.99) | 0.026 * |
| Complete middle school | 57 (25.00) | 52 (91.23) | 1.10 (0.96–1.21) | 0.099 | 49 (85.96) | 1.13 (0.97–1.28) | 0.081 |
| Complete high school | 49 (21.49) | 45 (91.84) | 1.10 (0.96–1.22) | 0.102 | 43 (87.76) | 1.16 (0.98–1.31) | 0.057 |
| Undergraduate | 23 (10.09) | 21 (91.30) | 1.00 (ref.) | 21 (91.30) | 1.00 (ref.) |
| Hematological Disease/Transfusion | N (%) | EBV IgG Positive (%) | EBV PR (95% CI) | p-Value a | Coinfection Positives (%) | Coinfection PR (95% CI) | p-Value a |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hematological disease | |||||||
| Anemia | 72 (31.58) | 61 (84.72) | 0.99 (0.87–1.11) | 0.462 | 56 (77.78) | 0.99 (0.84–1.13) | 0.496 |
| ITP | 20 (8.77) | 18 (90.00) | 1.06 (0.82–1.19) | 0.376 | 16 (80.00) | 1.02 (0.74–1.21) | 0.454 |
| Leukemia | 117 (51.32) | 98 (83.76) | 0.97 (0.86–1.08) | 0.348 | 92 (78.63) | 1.00 (0.87–1.16) | 0.454 |
| ALL | 83 (70.94) | 68 (81.93) | 0.93 (0.80–1.14) | 0.286 | 65 (78.31) | 0.99 (0.82–1.26) | 0.454 |
| AML | 22 (18.80) | 19 (86.36) | 1.00 (ref.) | 17 (77.27) | 1.00 (ref.) | ||
| CLL | 1 (0.86) | 1 (100.00) | 1 (100.00) | ||||
| CML | 11 (9.40) | 10 (90.91) | 1.10 (0.75–1.26) | 0.403 | 9 (81.82) | 1.05 (0.66–1.28) | 0.454 |
| Lymphoma | 19 (8.33) | 17 (89.47) | 1.00 (ref.) | 15 (78.95) | 1.00 (ref.) | ||
| Type of transfusion | 143 (62.72) | 119 (83.22) | 0.94 (0.85–1.06) | 0.202 | 111 (77.62) | 0.97 (0.85–1.13) | 0.399 |
| Complete | 101 (70.63) | 82 (57.34) | 0.92 (0.80–1.10) | 0.223 | 76 (75.25) | 0.90 (0.76–1.11) | 0.202 |
| Erythrocytes | 30 (20.98) | 28 (19.58) | 1.16 (0.96–1.31) | 0.082 | 26 (86.67) | 1.15 (0.92–1.35) | 0.138 |
| Erythrocytes/Platelets | 2 (1.40) | 2 (1.40) | 2 (100.00) | ||||
| Plasma | 1 (0.70) | 0 (0.00) | |||||
| Platelets | 9 (6.29) | 7 (4.90) | 0.93 (0.54–1.15) | 0.496 | 7 (77.78) | 1.00 (0.58–1.25) | 0.344 |
| No transfusion | 85 (37.28) | 75 (88.24) | 1.00 (ref.) | 68 (80.00) | 1.00 (ref.) | 0.399 |
| Liver Biomarkers | N (%) | EBV IgG Positive (%) | EBV PR (95% CI) | p-Value a | Coinfection EBV/CMV Positive (%) | Coinfection PR (95% CI) | p-Value a |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ferritin | |||||||
| Altered | 28 (38.89) | 27 (96.43) | 1.25 (1.03–1.54) | 0.031 * | 25 (89.29) | 1.31 (1.02–1.70) | 0.038 * |
| Normal | 44 (61.11) | 34 (77.27) | 1.00 (ref.) | 30 (68.18) | 1.00 (ref.) | ||
| SGPT | |||||||
| Altered | 7 (20.59) | 6 (85.71) | 1.16 (0.64–1.63) | 0.442 | 5 (71.43) | 1.02 (0.49–1.56) | 0.341 |
| Normal | 27 (79.41) | 20 (74.07) | 1.00 (ref.) | 19 (70.37) | 1.00 (ref.) | ||
| SGOT | |||||||
| Altered | 13 (34.21) | 10 (76.92) | 1.07 (0.66–1.56) | 0.476 | 10 (76.92) | 1.20 (0.73–1.84) | 0.328 |
| Normal | 25 (65.79) | 18 (72.00) | 1.00 (ref.) | 16 (64.00) | 1.00 (ref.) | ||
| LDH | |||||||
| Altered | 20 (55.56) | 18 (90.00) | 12.00 (0.88–1.81) | 0.227 | 17 (85.00) | 1.24 (0.86–1.96) | 0.223 |
| Normal | 16 (44.44) | 12 (75.00) | 1.00 (ref.) | 11 (68.75) | 1.00 (ref.) | ||
| Creatinine | |||||||
| Altered | 24 (64.86) | 18 (75.00) | 17 (70.83) | ||||
| Normal | 13 (35.14) | 13 (100.00) | 13 (100.00) | ||||
| Liver function | |||||||
| Altered | 40 (69.00) | 34 (85.00) | 1.16 (0.93–1.41) | 0.126 | 32 (80.00) | 1.18 (0.93–1.49) | 0.123 |
| Normal | 68 (31.00) | 50 (73.53) | 1.00 (ref.) | 46 (67.65) | 1.00 (ref.) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ferrari de Freitas, L.; de Melo Silva, J.; Nogueira Barbosa, A.; Miranda Santos, E.; Pinheiro-Silva, R.; Soares Pontes, G. Epidemiological and Liver Biomarkers Profile of Epstein-Barr Virus Infection and Its Coinfection with Cytomegalovirus in Patients with Hematological Diseases. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1151. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11081151
Ferrari de Freitas L, de Melo Silva J, Nogueira Barbosa A, Miranda Santos E, Pinheiro-Silva R, Soares Pontes G. Epidemiological and Liver Biomarkers Profile of Epstein-Barr Virus Infection and Its Coinfection with Cytomegalovirus in Patients with Hematological Diseases. Biomolecules. 2021; 11(8):1151. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11081151
Chicago/Turabian StyleFerrari de Freitas, Lilian, Jean de Melo Silva, Anderson Nogueira Barbosa, Enzo Miranda Santos, Renato Pinheiro-Silva, and Gemilson Soares Pontes. 2021. "Epidemiological and Liver Biomarkers Profile of Epstein-Barr Virus Infection and Its Coinfection with Cytomegalovirus in Patients with Hematological Diseases" Biomolecules 11, no. 8: 1151. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11081151
APA StyleFerrari de Freitas, L., de Melo Silva, J., Nogueira Barbosa, A., Miranda Santos, E., Pinheiro-Silva, R., & Soares Pontes, G. (2021). Epidemiological and Liver Biomarkers Profile of Epstein-Barr Virus Infection and Its Coinfection with Cytomegalovirus in Patients with Hematological Diseases. Biomolecules, 11(8), 1151. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11081151







