Composition and Function of Telomerase—A Polymerase Associated with the Origin of Eukaryotes
Abstract
:1. Telomerase Activity
2. The Origin of Telomerase
3. RNA Subunit of Telomerase
4. TERT Subunit of Telomerase
5. Telomerase Regulation
6. Composition of Enzymatically Active Telomerase
7. Conclusions
Abreviations
| h | human |
| AAA+ | ATPases associated with diverse cellular activities |
| ALT | alternative mechanisms of lengthening of telomeres |
| ARM | armadillo/β-catenin-like repeat-containing protein |
| At | Arabidopsis thaliana |
| CAB-box | Cajal body-box |
| CBF5 | centromere-binding factor |
| CR4/5 | conserved region 4/5 |
| CRM1 | chromosome region maintenance 1 protein homolog |
| CRuMs | collodictyonids, Rigifilida, Mantamonas |
| CTE | C-terminal extension |
| DDR | DNA damage response |
| DNA Pol α | DNA polymerase alpha |
| DNA Pol δ | DNA polymerase delta |
| DNA Pol ε | DNA polymerase epsilon |
| eToL | Tree of Life |
| FHC | fetal human colon |
| FL | full-length |
| GAR1,2 | Glycine Arginine Rich 1, 2 |
| H/ACA | H/ACA (H-box (consensus ANANNA) and ACA-box (ACA)) |
| HR | homologous recombination |
| Hsp70 | heat shock protein 70 |
| Hsp90 | heat shock protein 90 |
| HT-29 | adenocarcinoma colon |
| CHIP | carboxyl-terminus of Hsp70 Interacting Protein |
| CHR19 | chromatin remodeling 19 |
| Imp | importin |
| LECA | last eukaryote common ancestor |
| LUCA | last universal common ancestor |
| MCRS2 | microspherule protein 2 |
| MKRN1 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase makorin-1 |
| MMG | monomethylguanosine |
| mRNA | messenger RNA |
| mtDNA | mitochondrial DNA |
| n.p. | nuclear pores |
| NAF1 | nuclear assembly factor 1 |
| NCL | nucleolin |
| NF- κB | nuclear factor κB |
| NF-κB | nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells |
| NHP2 | non-histone protein 2 |
| NLS | nucleus localization-like signal |
| non-LTR-retrotransposons | non-long-terminal-repeat retrotransposons |
| NOP10 | nucleolar protein 10 |
| NPM | nucleophosmin |
| NUC-L1 | nucleolin-like1 |
| P | phosphorylation |
| p23 | co-chaperone |
| PINX1 | PIN2/TERF1—interacting telomerase inhibitor 1 |
| poly (A) tail | polyadenylate tail |
| POT1 | protection of telomeres protein 1 |
| POT1a | protection of telomeres protein 1a |
| RAP1 | repressor/activator site binding protein |
| RID1 | RNA interaction domain 1 |
| RNA Pol II | RNA polymerase II |
| RNA Pol III | RNA polymerase III |
| RNPs | ribonucleoproteins |
| RT | reverse transcriptase |
| RT domain | reverse transcriptase motifs domain |
| RT-qPCR | reverse transcription-quantitative PCR |
| RuvBL1 | RuvB-like 1 AAA+ ATPases (pontin) |
| RuvBL2 | RuvB-like 2 AAA+ ATPases (reptin) |
| scaRNA | small Cajal body RNA |
| SHQ1 | snRNA of the box H/ACA family quantitative accumulation 1 |
| SMN | survival motor neuron protein |
| snoRNA | small nucleolar RNA |
| SP1/3 | specificity protein 1/3 |
| STAT3 | signal transducer and activator of Transcription 3 |
| t/PK | template/pseudoknot |
| TAC1 | telomerase activator 1 |
| TBE | template boundary element |
| TCAB1 | telomere cajal body protein 1 |
| TEN | telomerase essential N-terminal domain |
| TERT | catalytic telomerase reverse transcriptase |
| TIN2 | TRF1-interacting nuclear factor 2 |
| TMG | N2, 2, 7 trimethylguanosine |
| TPP1 | TIN2- and POT1-organizing protein |
| TR, TER, TERC | telomerase RNA component |
| TRBD | RNA-binding domain |
| TRF1/2 | telomeric-repeat binding factor 1/2 |
| TSAR | telonemids, stramenopiles, alveolates, and Rhizaria |
| Ubq | ubiquitin |
| USE | upstream sequence element |
| Wnt/β-catenin | wnt/beta-catenin |
| - α TERT | minus alpha TERT |
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Olovnikov, A.M. Principle of marginotomy in template synthesis of polynucleotides. Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR 1971, 201, 1496–1499. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Greider, C.W. Telomeres and senescence: The history, the experiment, the future. Curr. Biol. 1998, 8, R178–R181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aubert, G.; Lansdorp, P.M. Telomeres and Aging. Physiol. Rev. 2008, 88, 557–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leman, A.; Noguchi, E. The Replication Fork: Understanding the Eukaryotic Replication Machinery and the Challenges to Genome Duplication. Genes 2013, 4, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gilson, E.; Géli, V. How telomeres are replicated. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 825–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diede, S.J.; Gottschling, D.E. Telomerase-Mediated Telomere Addition In Vivo Requires DNA Primase and DNA Polymerases α and δ. Cell 1999, 99, 723–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Procházková Schrumpfová, P.; Fojtová, M.; Fajkus, J. Telomeres in Plants and Humans: Not So Different, Not So Similar. Cells 2019, 8, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shay, J.W.; Wright, W.E. Senescence and immortalization: Role of telomeres and telomerase. Carcinogenesis 2005, 26, 867–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fajkus, J.; Kovařík, A.; Královics, R. Telomerase activity in plant cells. FEBS Lett. 1996, 391, 307–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jurečková, J.F.; Sýkorová, E.; Hafidh, S.; Honys, D.; Fajkus, J.; Fojtová, M. Tissue-specific expression of telomerase reverse transcriptase gene variants in Nicotiana tabacum. Planta 2017, 245, 549–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogrocká, A.; Sýkorová, E.; Fajkus, J.; Fojtová, M. Developmental silencing of the AtTERT gene is associated with increased H3K27me3 loading and maintenance of its euchromatic environment. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 4233–4241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riha, K.; Fajkus, J.; Siroky, J.; Vyskot, B. Developmental Control of Telomere Lengths and Telomerase Activity in Plants. Plant Cell 1998, 10, 1691–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zachová, D.; Fojtová, M.; Dvořáčková, M.; Mozgová, I.; Lermontova, I.; Peška, V.; Schubert, I.; Fajkus, J.; Sýkorová, E. Structure-function relationships during transgenic telomerase expression in Arabidopsis. Physiol. Plant. 2013, 149, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shay, J.W.; Wright, W.E. Telomeres and telomerase: Three decades of progress. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2019, 20, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, Y.-S.; Wright, W.E.; Shay, J.W. Human Telomerase and Its Regulation. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2002, 66, 407–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Avilion, A.A.; Piatyszek, M.A.; Gupta, J.; Shay, J.W.; Bacchetti, S.; Greider, C.W. Human Telomerase RNA and Telomerase Activity in Immortal Cell Lines and Tumor Tissues. Cancer Res. 1996, 1996, 645–650. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, K.; Hodes, R.J.; Weng, N. Cutting Edge: Telomerase Activation in Human T Lymphocytes Does Not Require Increase in Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase (hTERT) Protein but Is Associated with hTERT Phosphorylation and Nuclear Translocation. J. Immunol. 2001, 166, 4826–4830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weng, N.; Levine, B.L.; June, C.H.; Hodes, R.J. Regulation of telomerase RNA template expression in human T lymphocyte development and activation. J. Immunol. 1997, 158, 3215–3220. [Google Scholar]
- Fajkus, P.; Peška, V.; Závodník, M.; Fojtová, M.; Fulnečková, J.; Dobias, Š.; Kilar, A.; Dvořáčková, M.; Zachová, D.; Nečasová, I.; et al. Telomerase RNAs in land plants. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 9842–9856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, J.; Okada, T.; Fukushima, T.; Tsudzuki, T.; Sugiura, M.; Yukawa, Y. A novel hypoxic stress-responsive long non-coding RNA transcribed by RNA polymerase III in Arabidopsis. RNA Biol. 2012, 9, 302–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Greider, C.W.; Blackburn, E.H. The telomere terminal transferase of Tetrahymena is a ribonucleoprotein enzyme with two kinds of primer specificity. Cell 1987, 51, 887–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Procházková Schrumpfová, P.; Schořová, Š.; Fajkus, J. Telomere- and Telomerase-Associated Proteins and Their Functions in the Plant Cell. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.; Parrinello, S.; Kim, J.; Campisi, J. Mus musculus and Mus spretus homologues of the human telomere-associated protein TIN2. Genomics 2003, 81, 422–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burki, F.; Roger, A.J.; Brown, M.W.; Simpson, A.G.B. The New Tree of Eukaryotes. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2020, 35, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aksenova, A.Y.; Mirkin, S.M. At the Beginning of the End and in the Middle of the Beginning: Structure and Maintenance of Telomeric DNA Repeats and Interstitial Telomeric Sequences. Genes 2019, 10, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sepsiova, R.; Necasova, I.; Willcox, S.; Prochazkova, K.; Gorilak, P.; Nosek, J.; Hofr, C.; Griffith, J.D.; Tomaska, L. Evolution of Telomeres in Schizosaccharomyces pombe and Its Possible Relationship to the Diversification of Telomere Binding Proteins. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuznetsova, V.; Grozeva, S.; Gokhman, V. Telomere structure in insects: A review. J. Zool. Syst. Evol. Res. 2020, 58, 127–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vítková, M.; Král, J.; Traut, W.; Zrzavý, J.; Marec, F. The evolutionary origin of insect telomeric repeats, (TTAGG) N. Chromosome Res. 2005, 13, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wicky, C.; Villeneuve, A.M.; Lauper, N.; Codourey, L.; Tobler, H.; Muller, F. Telomeric repeats (TTAGGC)n are sufficient for chromosome capping function in Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 8983–8988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Červenák, F.; Juríková, K.; Sepšiová, R.; Neboháčová, M.; Nosek, J.; Tomáška, L. Double-stranded telomeric DNA binding proteins: Diversity matters. Cell Cycle 2017, 16, 1568–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fujiwara, H.; Osanai, M.; Matsumoto, T.; Kojima, K.K. Telomere-specific non-LTR retrotransposons and telomere maintenance in the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Chromosome Res. 2005, 13, 455–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casacuberta, E. Drosophila: Retrotransposons Making up Telomeres. Viruses 2017, 9, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Servant, G.; Deininger, P.L. Insertion of Retrotransposons at Chromosome Ends: Adaptive Response to Chromosome Maintenance. Front. Genet. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sasaki, T.; Fujiwara, H. Detection and distribution patterns of telomerase activity in insects: Telomerase activity in insects. Eur. J. Biochem. 2000, 267, 3025–3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, H.; Okazaki, S.; Fujiwara, H. A New Family of Site-Specific Retrotransposons, SART1, Is Inserted into Telomeric Repeats of the Silkworm, Bombyx Mori. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 1578–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mason, J.M.; Randall, T.A.; Capkova Frydrychova, R. Telomerase lost? Chromosoma 2016, 125, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koonin, E.V. The origin of introns and their role in eukaryogenesis: a compromise solution to the introns-early versus introns-late debate? Biol. Direct 2006, 1, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fulnečková, J.; Ševčíková, T.; Fajkus, J.; Lukešová, A.; Lukeš, M.; Vlček, Č.; Lang, B.F.; Kim, E.; Eliáš, M.; Sýkorová, E. A Broad Phylogenetic Survey Unveils the Diversity and Evolution of Telomeres in Eukaryotes. Genome Biol. Evol. 2013, 5, 468–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adl, S.M.; Simpson, A.G.B.; Lane, C.E.; Lukeš, J.; Bass, D.; Bowser, S.S.; Brown, M.W.; Burki, F.; Dunthorn, M.; Hampl, V.; et al. The Revised Classification of Eukaryotes. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2012, 59, 429–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Richards, E.J.; Ausubel, F.M. Isolation of a higher eukaryotic telomere from Arabidopsis thaliana. Cell 1988, 53, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sýkorová, E.; Lim, K.Y.; Kunická, Z.; Chase, M.W.; Bennett, M.D.; Fajkus, J.; Leitch, A.R. Telomere variability in the monocotyledonous plant order Asparagales. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 2003, 270, 1893–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sýkorová, E.; Leitch, A.R.; Fajkus, J. Asparagales Telomerases which Synthesize the Human Type of Telomeres. Plant Mol. Biol. 2006, 60, 633–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fajkus, P.; Peška, V.; Sitová, Z.; Fulnečková, J.; Dvořáčková, M.; Gogela, R.; Sýkorová, E.; Hapala, J.; Fajkus, J. Allium telomeres unmasked: The unusual telomeric sequence (CTCGGTTATGGG) n is synthesized by telomerase. Plant J. 2016, 85, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peška, V.; Fajkus, P.; Fojtová, M.; Dvořáčková, M.; Hapala, J.; Dvořáček, V.; Polanská, P.; Leitch, A.R.; Sýkorová, E.; Fajkus, J. Characterisation of an unusual telomere motif (TTTTTTAGGG) n in the plant Cestrum elegans (Solanaceae), a species with a large genome. Plant J. 2015, 82, 644–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, T.D.; Cao, H.X.; Jovtchev, G.; Neumann, P.; Novák, P.; Fojtová, M.; Vu, G.T.H.; Macas, J.; Fajkus, J.; Schubert, I.; et al. Centromere and telomere sequence alterations reflect the rapid genome evolution within the carnivorous plant genus Genlisea. Plant J. 2015, 84, 1087–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fulnečková, J.; Ševčíková, T.; Lukešová, A.; Sýkorová, E. Transitions between the Arabidopsis-type and the human-type telomere sequence in green algae (clade Caudivolvoxa, Chlamydomonadales). Chromosoma 2016, 125, 437–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peska, V.; Garcia, S. Origin, Diversity, and Evolution of Telomere Sequences in Plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Lange, T. A loopy view of telomere evolution. Front. Genet. 2015, 6, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lambowitz, A.M.; Zimmerly, S. Group II Introns: Mobile Ribozymes that Invade DNA. Cold Spring Harbor Perspect. Biol. 2011, 3, a003616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, T.M. Telomerase Catalytic Subunit Homologs from Fission Yeast and Human. Science 1997, 277, 955–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingner, J. Reverse Transcriptase Motifs in the Catalytic Subunit of Telomerase. Science 1997, 276, 561–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boeke, J.D. The Unusual Phylogenetic Distribution of Retrotransposons: A Hypothesis. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 1975–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dreesen, O. Telomere structure and shortening in telomerase-deficient Trypanosoma brucei. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, 4536–4543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giardini, M.A.; Lira, C.B.B.; Conte, F.F.; Camillo, L.R.; de Siqueira Neto, J.L.; Ramos, C.H.I.; Cano, M.I.N. The putative telomerase reverse transcriptase component of Leishmania amazonensis: Gene cloning and characterization. Parasitol. Res. 2006, 98, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podlevsky, J.D.; Chen, J.J.-L. Evolutionary perspectives of telomerase RNA structure and function. RNA Biol. 2016, 13, 720–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dey, A.; Chakrabarti, K. Current Perspectives of Telomerase Structure and Function in Eukaryotes with Emerging Views on Telomerase in Human Parasites. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fragnet, L.; Blasco, M.A.; Klapper, W.; Rasschaert, D. The RNA Subunit of Telomerase Is Encoded by Marek’s Disease Virus. JVI 2003, 77, 5985–5996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trapp-Fragnet, L.; Marie-Egyptienne, D.; Fakhoury, J.; Rasschaert, D.; Autexier, C. The human telomerase catalytic subunit and viral telomerase RNA reconstitute a functional telomerase complex in a cell-free system, but not in human cells. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2012, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bryan, T.M.; Englezou, A.; Gupta, J.; Bacchetti, S.; Reddel, R.R. Telomere elongation in immortal human cells without detectable telomerase activity. EMBO J. 1995, 14, 4240–4248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunham, M.A.; Neumann, A.A.; Fasching, C.L.; Reddel, R.R. Telomere maintenance by recombination in human cells. Nat. Genet. 2000, 26, 447–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundblad, V.; Blackburn, E.H. An alternative pathway for yeast telomere maintenance rescues est1− senescence. Cell 1993, 73, 347–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Růčková, E.; Friml, J.; Procházková Schrumpfová, P.; Fajkus, J. Role of alternative telomere lengthening unmasked in telomerase knock-out mutant plants. Plant Mol. Biol. 2008, 66, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kachouri-Lafond, R.; Dujon, B.; Gilson, E.; Westhof, E.; Fairhead, C.; Teixeira, M.T. Large telomerase RNA, telomere length heterogeneity and escape from senescence in Candida glabrata. FEBS Lett. 2009, 583, 3605–3610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egan, E.D.; Collins, K. Biogenesis of telomerase ribonucleoproteins. RNA 2012, 18, 1747–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Collins, K. The biogenesis and regulation of telomerase holoenzymes. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006, 7, 484–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Feng, J.; Funk, W.; Wang, S.; Weinrich, S.; Avilion, A.; Chiu, C.; Adams, R.; Chang, E.; Allsopp, R.; Yu, J.; et al. The RNA component of human telomerase. Science 1995, 269, 1236–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dew-Budd, K.; Cheung, J.; Palos, K.; Forsythe, E.S.; Beilstein, M.A. Evolutionary and biochemical analyses reveal conservation of the Brassicaceae telomerase ribonucleoprotein complex. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0222687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cifuentes-Rojas, C.; Kannan, K.; Tseng, L.; Shippen, D.E. Two RNA subunits and POT1a are components of Arabidopsis telomerase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cifuentes-Rojas, C.; Kannan, K.; Tseng, L.; Shippen, D.E. Retraction for Cifuentes-Rojas et al., Two RNA subunits and POT1a are components of Arabidopsis telomerase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 24908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, R.A.; Upton, H.E.; Vogan, J.M.; Collins, K. Telomerase Mechanism of Telomere Synthesis. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2017, 86, 439–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, J.; Logeswaran, D.; Castillo-González, C.; Li, Y.; Bose, S.; Aklilu, B.B.; Ma, Z.; Polkhovskiy, A.; Chen, J.J.-L.; Shippen, D.E. The conserved structure of plant telomerase RNA provides the missing link for an evolutionary pathway from ciliates to humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 24542–24550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Chan, H.; Cash, D.D.; Miracco, E.J.; Ogorzalek Loo, R.R.; Upton, H.E.; Cascio, D.; O’Brien Johnson, R.; Collins, K.; Loo, J.A.; et al. Structure of Tetrahymena telomerase reveals previously unknown subunits, functions, and interactions. Science 2015, 350, aab4070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, M.; Podlevsky, J.D.; Qi, X.; Bley, C.J.; Chen, J.J.-L. A novel motif in telomerase reverse transcriptase regulates telomere repeat addition rate and processivity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, 1982–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chan, H.; Wang, Y.; Feigon, J. Progress in Human and Tetrahymena Telomerase Structure Determination. Annu. Rev. Biophys. 2017, 46, 199–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sýkorová, E.; Fajkus, J. Structure-function relationships in telomerase genes. Biol. Cell 2009, 101, 375–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukowiak, A.A.; Narayanan, A.; Li, Z.H.; Terns, R.M.; Terns, M.P. The snoRNA domain of vertebrate telomerase RNA functions to localize the RNA within the nucleus. RNA 2001, 7, 1833–1844. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Tomlinson, R.L.; Lukowiak, A.A.; Terns, R.M.; Terns, M.P. Telomerase RNA Accumulates in Cajal Bodies in Human Cancer Cells. Mol. Biol. Cell 2004, 15, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasco, M.; Funk, W.; Villeponteau, B.; Greider, C. Functional characterization and developmental regulation of mouse telomerase RNA. Science 1995, 269, 1267–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kiss, T.; Filipowicz, W. Exonucleolytic processing of small nucleolar RNAs from pre-mRNA introns. Genes Dev. 1995, 9, 1411–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kiss, T.; Fayet-Lebaron, E.; Jády, B.E. Box H/ACA Small Ribonucleoproteins. Mol. Cell 2010, 37, 597–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, A.; Cowling, V.H. mRNA cap regulation in mammalian cell function and fate. Biochim. Biophys. Acta -Gene Regul. Mech. 2019, 1862, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Roake, C.M.; Galati, A.; Bavasso, F.; Micheli, E.; Saggio, I.; Schoeftner, S.; Cacchione, S.; Gatti, M.; Artandi, S.E.; et al. Loss of Human TGS1 Hypermethylase Promotes Increased Telomerase RNA and Telomere Elongation. Cell Rep. 2020, 30, 1358–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jády, B.E.; Bertrand, E.; Kiss, T. Human telomerase RNA and box H/ACA scaRNAs share a common Cajal body–specific localization signal. J. Cell Biol. 2004, 164, 647–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacNeil, D.; Bensoussan, H.; Autexier, C. Telomerase Regulation from Beginning to the End. Genes 2016, 7, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubtsova, M.; Dontsova, O. Human Telomerase RNA: Telomerase Component or More? Biomolecules 2020, 10, 873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robart, A.R.; Collins, K. Investigation of Human Telomerase Holoenzyme Assembly, Activity, and Processivity Using Disease-linked Subunit Variants. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 4375–4386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, J.; Brown, A.F.; Wu, J.; Xue, J.; Bley, C.J.; Rand, D.P.; Wu, L.; Zhang, R.; Chen, J.J.-L.; Lei, M. Structural basis for protein-RNA recognition in telomerase. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2014, 21, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Podlevsky, J.D.; Logeswaran, D.; Chen, J.J. A single nucleotide incorporation step limits human telomerase repeat addition activity. EMBO J. 2018, 37, e97953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, K.; Greider, C.W. Tetrahymena telomerase catalyzes nucleolytic cleavage and nonprocessive elongation. Genes Dev. 1993, 7, 1364–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lue, N.F. A Physical and Functional Constituent of Telomerase Anchor Site. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 26586–26591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akiyama, B.M.; Parks, J.W.; Stone, M.D. The telomerase essential N-terminal domain promotes DNA synthesis by stabilizing short RNA-DNA hybrids. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 5537–5549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Patrick, E.M.; Slivka, J.D.; Payne, B.; Comstock, M.J.; Schmidt, J.C. Observation of processive telomerase catalysis using high-resolution optical tweezers. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2020, 16, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriarty, T.J.; Marie-Egyptienne, D.T.; Autexier, C. Functional Organization of Repeat Addition Processivity and DNA Synthesis Determinants in the Human Telomerase Multimer. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 24, 3720–3733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sauerwald, A.; Sandin, S.; Cristofari, G.; Scheres, S.H.W.; Lingner, J.; Rhodes, D. Structure of active dimeric human telomerase. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2013, 20, 454–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandin, S.; Rhodes, D. Telomerase structure. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2014, 25, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, T.H.D.; Tam, J.; Wu, R.A.; Greber, B.J.; Toso, D.; Nogales, E.; Collins, K. Cryo-EM structure of substrate-bound human telomerase holoenzyme. Nature 2018, 557, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Miracco, E.J.; Hong, K.; Eckert, B.; Chan, H.; Cash, D.D.; Min, B.; Zhou, Z.H.; Collins, K.; Feigon, J. The architecture of Tetrahymena telomerase holoenzyme. Nature 2013, 496, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Majerská, J.; Procházková Schrumpfová, P.; Dokládal, L.; Schořová, Š.; Stejskal, K.; Obořil, M.; Honys, D.; Kozáková, L.; Polanská, P.S.; Sýkorová, E. Tandem affinity purification of AtTERT reveals putative interaction partners of plant telomerase in vivo. Protoplasma 2017, 254, 1547–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dergai, O.; Hernandez, N. How to Recruit the Correct RNA Polymerase? Lessons from snRNA Genes. Trends Genet. 2019, 35, 457–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, D.D.; Collins, K. Biological and Biochemical Functions of RNA in the Tetrahymena Telomerase Holoenzyme. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 25, 4442–4454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roake, C.M.; Artandi, S.E. Regulation of human telomerase in homeostasis and disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 384–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, H.S.; Burke, W.D.; Eickbush, T.H. Putative telomerase catalytic subunits from Giardia lamblia and Caenorhabditis elegans. Gene 2000, 251, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, A.G.; Pouchkina-Stantcheva, N.; Di Donfrancesco, A.; Kildisiute, G.; Sahu, S.; Aboobaker, A.A. The protein subunit of telomerase displays patterns of dynamic evolution and conservation across different metazoan taxa. BMC Evol. Biol. 2017, 17, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chung, J.; Khadka, P.; Chung, I.K. Nuclear import of hTERT requires a bipartite nuclear localization signal and Akt-mediated phosphorylation. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125, 2684–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoffman, H.; Rice, C.; Skordalakes, E. Structural Analysis Reveals the Deleterious Effects of Telomerase Mutations in Bone Marrow Failure Syndromes. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 4593–4601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Autexier, C.; Lue, N.F. The Structure and Function of Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2006, 75, 493–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilian, A.; Bowtell, D.D.L.; Abud, H.E.; Hime, G.R.; Venter, D.J.; Keese, P.K.; Duncan, E.L.; Reddel, R.R.; Jefferson, R.A. Isolation of a Candidate Human Telomerase Catalytic Subunit Gene, Which Reveals Complex Splicing Patterns in Different Cell Types. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1997, 6, 2011–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrington, L.; Zhou, W.; McPhail, T.; Oulton, R.; Yeung, D.S.K.; Mar, V.; Bass, M.B.; Robinson, M.O. Human telomerase contains evolutionarily conserved catalytic and structural subunits. Genes Dev. 1997, 11, 3109–3115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meyerson, M.; Counter, C.M.; Eaton, E.N.; Ellisen, L.W.; Steiner, P.; Caddle, S.D.; Ziaugra, L.; Beijersbergen, R.L.; Davidoff, M.J.; Liu, Q.; et al. hEST2, the Putative Human Telomerase Catalytic Subunit Gene, Is Up-Regulated in Tumor Cells and during Immortalization. Cell 1997, 90, 785–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sýkorová, E.; Fulnečková, J.; Mokroš, P.; Fajkus, J.; Fojtová, M.; Peška, V. Three TERT genes in Nicotiana tabacum. Chromosome Res. 2012, 20, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khattar, E.; Tergaonkar, V. Transcriptional Regulation of Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase (TERT) by MYC. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2017, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jie, M.-M.; Chang, X.; Zeng, S.; Liu, C.; Liao, G.-B.; Wu, Y.-R.; Liu, C.-H.; Hu, C.-J.; Yang, S.-M.; Li, X.-Z. Diverse regulatory manners of human telomerase reverse transcriptase. Cell Commun. Signal 2019, 17, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ramlee, M.; Wang, J.; Toh, W.; Li, S. Transcription Regulation of the Human Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase (hTERT) Gene. Genes 2016, 7, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flavin, P.; Redmond, A.; McBryan, J.; Cocchiglia, S.; Tibbitts, P.; Fahy-Browne, P.; Kay, E.; Treumann, A.; Perrem, K.; McIlroy, M.; et al. RuvBl2 cooperates with Ets2 to transcriptionally regulate hTERT in colon cancer. FEBS Lett. 2011, 585, 2537–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takakura, M.; Kyo, S.; Kanaya, T.; Hirano, H.; Takeda, J.; Yutsudo, M.; Inoue, M. Cloning of Human Telomerase Catalytic Subunit (hTERT) Gene Promoter and Identification of Proximal Core Promoter Sequences Essential for Transcriptional Activation in Immortalized and Cancer Cells. Cancer Research 1999, 59, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Horikawa, I.; Cable, P.L.; Afshari, C.; Barrett, J.C. Cloning and Characterization of the Promoter Region of Human Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase Gene. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 826–830. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Crhák, T.; Zachová, D.; Fojtová, M.; Sýkorová, E. The region upstream of the telomerase reverse transcriptase gene is essential for in planta telomerase complementation. Plant Sci. 2019, 281, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, J.L.; Theodorescu, D.; Vogelstein, B.; Papadopoulos, N.; Cech, T.R. Mutation of the TERT promoter, switch to active chromatin, and monoallelic TERT expression in multiple cancers. Genes Dev. 2015, 29, 2219–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akıncılar, S.C.; Khattar, E.; Boon, P.L.S.; Unal, B.; Fullwood, M.J.; Tergaonkar, V. Long-Range Chromatin Interactions Drive Mutant TERT Promoter Activation. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, 1276–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fajkus, J.; Fulnečková, J.; Hulánová, M.; Berková, K.; Říha, K.; Matyášek, R. Plant cells express telomerase activity upon transfer to callus culture, without extensively changing telomere lengths. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1998, 260, 470–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, Y.; Wen, J.; Bacchetti, S. The human telomerase catalytic subunit hTERT: Organization of the gene and characterization of the promoter. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1999, 8, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antosz, W.; Pfab, A.; Ehrnsberger, H.F.; Holzinger, P.; Köllen, K.; Mortensen, S.A.; Bruckmann, A.; Schubert, T.; Längst, G.; Griesenbeck, J.; et al. The Composition of the Arabidopsis RNA Polymerase II Transcript Elongation Complex Reveals the Interplay between Elongation and mRNA Processing Factors. Plant Cell 2017, 29, 854–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stern, J.L.; Paucek, R.D.; Huang, F.W.; Ghandi, M.; Nwumeh, R.; Costello, J.C.; Cech, T.R. Allele-Specific DNA Methylation and Its Interplay with Repressive Histone Marks at Promoter-Mutant TERT Genes. Cell Rep. 2017, 21, 3700–3707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bodnar, A.G. Extension of Life-Span by Introduction of Telomerase into Normal Human Cells. Science 1998, 279, 349–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hrdlickova, R.; Nehyba, J.; Bose, H.R. Alternatively Spliced Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase Variants Lacking Telomerase Activity Stimulate Cell Proliferation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2012, 32, 4283–4296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, S.S.; Kwon, T.; Kwon, D.Y.; Do, S.I. Akt Protein Kinase Enhances Human Telomerase Activity through Phosphorylation of Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase Subunit. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 13085–13090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.H. Ubiquitin ligase MKRN1 modulates telomere length homeostasis through a proteolysis of hTERT. Genes Dev. 2005, 19, 776–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oguchi, K.; Tamura, K.; Takahashi, H. Characterization of Oryza sativa telomerase reverse transcriptase and possible role of its phosphorylation in the control of telomerase activity. Gene 2004, 342, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.W.; Jin, E.; Chung, I.K.; Kim, W.T. Cell cycle-dependent regulation of telomerase activity by auxin, abscisic acid and protein phosphorylation in tobacco BY-2 suspension culture cells. Plant J. 2002, 29, 617–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.A.; Kim, K.; Lee, J.H.; Cha, J.S.; Khadka, P.; Cho, H.-S.; Chung, I.K. Akt-mediated phosphorylation increases the binding affinity of hTERT for importin to promote nuclear translocation. J. Cell Sci. 2015, 128, 2287–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fitzgerald, M.S.; Riha, K.; Gao, F.; Ren, S.; McKnight, T.D.; Shippen, D.E. Disruption of the telomerase catalytic subunit gene from Arabidopsis inactivates telomerase and leads to a slow loss of telomeric DNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 14813–14818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Atkinson, S.P.; Hoare, S.F.; Glasspool, R.M.; Keith, W.N. Lack of Telomerase Gene Expression in Alternative Lengthening of Telomere Cells Is Associated with Chromatin Remodeling of the hTR and hTERT Gene Promoters. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 7585–7590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cairney, C.J.; Hoare, S.F.; Daidone, M.-G.; Zaffaroni, N.; Keith, W.N. High level of telomerase RNA gene expression is associated with chromatin modification, the ALT phenotype and poor prognosis in liposarcoma. Br. J. Cancer 2008, 98, 1467–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schořová, Š.; Fajkus, J.; Záveská Drábková, L.; Honys, D.; Procházková Schrumpfová, P. The plant Pontin and Reptin homologues, Ruv BL 1 and Ruv BL 2a, colocalize with TERT and TRB proteins in vivo, and participate in telomerase biogenesis. Plant J. 2019, 98, 195–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pendle, A.F.; Clark, G.P.; Boon, R.; Lewandowska, D.; Lam, Y.W.; Andersen, J.; Mann, M.; Lamond, A.I.; Brown, J.W.S.; Shaw, P.J. Proteomic Analysis of the Arabidopsis Nucleolus Suggests Novel Nucleolar Functions. Mol. Biol. Cell 2005, 16, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lermontova, I.; Schubert, V.; Börnke, F.; Macas, J.; Schubert, I. Arabidopsis CBF5 interacts with the H/ACA snoRNP assembly factor NAF1. Plant Mol. Biol. 2007, 65, 615–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khurts, S.; Masutomi, K.; Delgermaa, L.; Arai, K.; Oishi, N.; Mizuno, H.; Hayashi, N.; Hahn, W.C.; Murakami, S. Nucleolin Interacts with Telomerase. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 51508–51515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pontvianne, F.; Carpentier, M.-C.; Durut, N.; Pavlištová, V.; Jaške, K.; Schořová, Š.; Parrinello, H.; Rohmer, M.; Pikaard, C.S.; Fojtová, M.; et al. Identification of Nucleolus-Associated Chromatin Domains Reveals a Role for the Nucleolus in 3D Organization of the A. thaliana Genome. Cell Rep. 2016, 16, 1574–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pontvianne, F.; Abou-Ellail, M.; Douet, J.; Comella, P.; Matia, I.; Chandrasekhara, C.; DeBures, A.; Blevins, T.; Cooke, R.; Medina, F.J.; et al. Nucleolin Is Required for DNA Methylation State and the Expression of rRNA Gene Variants in Arabidopsis thaliana. PLoS Genet. 2010, 6, e1001225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Venteicher, A.S.; Meng, Z.; Mason, P.J.; Veenstra, T.D.; Artandi, S.E. Identification of ATPases Pontin and Reptin as Telomerase Components Essential for Holoenzyme Assembly. Cell 2008, 132, 945–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poole, A.R.; Hebert, M.D. SMN and coilin negatively regulate dyskerin association with telomerase RNA. Biol. Open 2016, 5, 726–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hebert, M.D.; Shpargel, K.B.; Ospina, J.K.; Tucker, K.E.; Matera, A.G. Coilin Methylation Regulates Nuclear Body Formation. Dev. Cell 2002, 3, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvorackova, M. Analysis of Arabidopsis Telomere-Associated Proteins in Vivo. Ph.D. Thesis, Masaryk University, Brno, Czech Republic, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, F.L.; Batista, L.F.Z.; Freund, A.; Pech, M.F.; Venteicher, A.S.; Artandi, S.E. TPP1 OB-Fold Domain Controls Telomere Maintenance by Recruiting Telomerase to Chromosome Ends. Cell 2012, 150, 481–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Procházková Schrumpfová, P.; Vychodilová, I.; Dvořáčková, M.; Majerská, J.; Dokládal, L.; Schořová, Š.; Fajkus, J. Telomere repeat binding proteins are functional components of Arabidopsis telomeres and interact with telomerase. Plant J. 2014, 77, 770–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ulaner, G.A.; Hu, J.F.; Vu, T.H.; Giudice, L.C.; Hoffman, A.R. Telomerase Activity in Human Development Is Regulated by Human Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase (hTERT) Transcription and by Alternate Splicing of hTERT Transcripts. Cancer Res. 1998, 58, 4168–4172. [Google Scholar]
- Nehyba, J.; Hrdlickova, R.; Bose, H.R. The Regulation of Telomerase by Alternative Splicing of TERT. In Reviews on Selected Topics of Telomere Biology; Li, B., Ed.; InTech: London, UK, 2012; ISBN 978-953-51-0849-8. [Google Scholar]
- Ulaner, G.A.; Hu, J.F.; Vu, T.H.; Giudice, L.C.; Hoffman, A.R. Tissue-specific alternate splicing of human telomerase reverse transcriptase (hTERT) influences telomere lengths during human development. Int. J. Cancer 2001, 91, 644–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, C.A.; Wolny, Y.M.; Adler, R.R.; Cohen, J. Alternative splicing of the telomerase catalytic subunit in human oocytes and embryos. MHR Basic Sci. Reprod. Med. 1999, 5, 845–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, R.; Esumi, S.; Yagi, T.; Hirabayashi, T. Predominant Expression of rTERTb, an Inactive TERT Variant, in the Adult Rat Brain. Protein Pept. Lett. 2006, 13, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludlow, A.T.; Slusher, A.L.; Sayed, M.E. Insights into Telomerase/hTERT Alternative Splicing Regulation Using Bioinformatics and Network Analysis in Cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wong, M.S.; Wright, W.E.; Shay, J.W. Alternative splicing regulation of telomerase: A new paradigm? Trends Genet. 2014, 30, 430–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Colgin, L.M.; Wilkinso, C.; Englezou, A.; Kilian, A.; Robinson, M.O.; Reddel, R.R. The hTERTα Splice Variant is a Dominant Negative Inhibitor of Telomerase Activity. Neoplasia 2000, 2, 426–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kunická, Z.; Mucha, I.; Fajkus, J. Telomerase activity in head and neck cancer. Anticancer Res. 2008, 28, 3125–3129. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Listerman, I.; Sun, J.; Gazzaniga, F.S.; Lukas, J.L.; Blackburn, E.H. The Major Reverse Transcriptase-Incompetent Splice Variant of the Human Telomerase Protein Inhibits Telomerase Activity but Protects from Apoptosis. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 2817–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rossignol, P.; Collier, S.; Bush, M.; Shaw, P.; Doonan, J.H. Arabidopsis POT1A interacts with TERT-V(I8), an N-terminal splicing variant of telomerase. J. Cell Sci. 2007, 120, 3678–3687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rotková, G.; Sýkorová, E.; Fajkus, J. Protect and regulate: Recent findings on plant POT1-like proteins. Biol. Plant. 2009, 53, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Liu, H.; Takahashi, H. Auxin Induction of Cell Cycle Regulated Activity of Tobacco Telomerase. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 20997–21002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ren, S.; Johnston, J.S.; Shippen, D.E.; McKnight, T.D. TELOMERASE ACTIVATOR1 Induces Telomerase Activity and Potentiates Responses to Auxin in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2004, 16, 2910–2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ren, S.; Mandadi, K.K.; Boedeker, A.L.; Rathore, K.S.; McKnight, T.D. Regulation of Telomerase in Arabidopsis by BT2, an Apparent Target of TELOMERASE ACTIVATOR1. Plant Cell 2007, 19, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, D.; Grenier St-Sauveur, V.; Bergeron, D.; Dupuis-Sandoval, F.; Scott, M.S.; Bachand, F. A Polyadenylation-Dependent 3′ End Maturation Pathway Is Required for the Synthesis of the Human Telomerase RNA. Cell Rep. 2015, 13, 2244–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tseng, C.-K.; Wang, H.-F.; Burns, A.M.; Schroeder, M.R.; Gaspari, M.; Baumann, P. Human Telomerase RNA Processing and Quality Control. Cell Rep. 2015, 13, 2232–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Majerská, J.; Sýkorová, E.; Fajkus, J. Non-telomeric activities of telomerase. Mol. BioSyst. 2011, 7, 1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blasco, M.A.; Rizen, M.; Greider, C.W.; Hanahan, D. Differential regulation of telomerase activity and telomerase RNA during multi-stage tumorigenesis. Nat. Genet. 1996, 12, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kedde, M.; le Sage, C.; Duursma, A.; Zlotorynski, E.; van Leeuwen, B.; Nijkamp, W.; Beijersbergen, R.; Agami, R. Telomerase-independent Regulation of ATR by Human Telomerase RNA. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 40503–40514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ségal-Bendirdjian, E.; Geli, V. Non-canonical Roles of Telomerase: Unraveling the Imbroglio. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 7, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dokládal, L.; Benková, E.; Honys, D.; Dupľáková, N.; Lee, L.-Y.; Gelvin, S.B.; Sýkorová, E. An armadillo-domain protein participates in a telomerase interaction network. Plant Mol. Biol. 2018, 97, 407–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, J.-I.; Venteicher, A.S.; Hong, J.Y.; Choi, J.; Jun, S.; Shkreli, M.; Chang, W.; Meng, Z.; Cheung, P.; Ji, H.; et al. Telomerase modulates Wnt signalling by association with target gene chromatin. Nature 2009, 460, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, Y.-T.; Meier, U.T. RNA-guided isomerization of uridine to pseudouridine—Pseudouridylation. RNA Biol. 2014, 11, 1483–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.H.; Lee, Y.S.; Jeong, S.A.; Khadka, P.; Roth, J.; Chung, I.K. Catalytically active telomerase holoenzyme is assembled in the dense fibrillar component of the nucleolus during S phase. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2014, 141, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, D.H.-C.; Ho, S.-T.; Lau, K.-F.; Jin, R.; Wang, Y.-N.; Kung, H.-F.; Huang, J.-J.; Shaw, P.-C. Nucleophosmin Interacts with PIN2/TERF1-interacting Telomerase Inhibitor 1 (PinX1) and Attenuates the PinX1 Inhibition on Telomerase Activity. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, K.T.T.T.; Wong, J.M.Y. Telomerase Biogenesis and Activities from the Perspective of Its Direct Interacting Partners. Cancers 2020, 12, 1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broome, H.J.; Carrero, Z.I.; Douglas, H.E.; Hebert, M.D. Phosphorylation regulates coilin activity and RNA association. Biol. Open 2013, 2, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Broome, H.J.; Hebert, M.D. Coilin Displays Differential Affinity for Specific RNAs In Vivo and Is Linked to Telomerase RNA Biogenesis. J. Mol. Biol. 2013, 425, 713–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mahmoudi, S.; Henriksson, S.; Weibrecht, I.; Smith, S.; Söderberg, O.; Strömblad, S.; Wiman, K.G.; Farnebo, M. WRAP53 Is Essential for Cajal Body Formation and for Targeting the Survival of Motor Neuron Complex to Cajal Bodies. PLoS Biol. 2010, 8, e1000521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Venteicher, A.S.; Abreu, E.B.; Meng, Z.; McCann, K.E.; Terns, R.M.; Veenstra, T.D.; Terns, M.P.; Artandi, S.E. A Human Telomerase Holoenzyme Protein Required for Cajal Body Localization and Telomere Synthesis. Science 2009, 323, 644–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sweetlove, L.; Gutierrez, C. The journey to the end of the chromosome: Delivering active telomerase to telomeres in plants. Plant J. 2019, 98, 193–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Love, A.J.; Yu, C.; Petukhova, N.V.; Kalinina, N.O.; Chen, J.; Taliansky, M.E. Cajal bodies and their role in plant stress and disease responses. RNA Biol. 2017, 14, 779–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrumpfová, P.; Kuchař, M.; Miková, G.; Skříovská, L.; Kubičárová, T.; Fajkus, J. Characterization of two Arabidopsis thaliana myb-like proteins showing affinity to telomeric DNA sequence. Genome 2004, 47, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mozgová, I.; Procházková Schrumpfová, P.; Hofr, C.; Fajkus, J. Functional characterization of domains in AtTRB1, a putative telomere-binding protein in Arabidopsis thaliana. Phytochemistry 2008, 69, 1814–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peska, V.; Procházková Schrumpfová, P.; Fajkus, J. Using the Telobox to Search for Plant Telomere Binding Proteins. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2011, 12, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
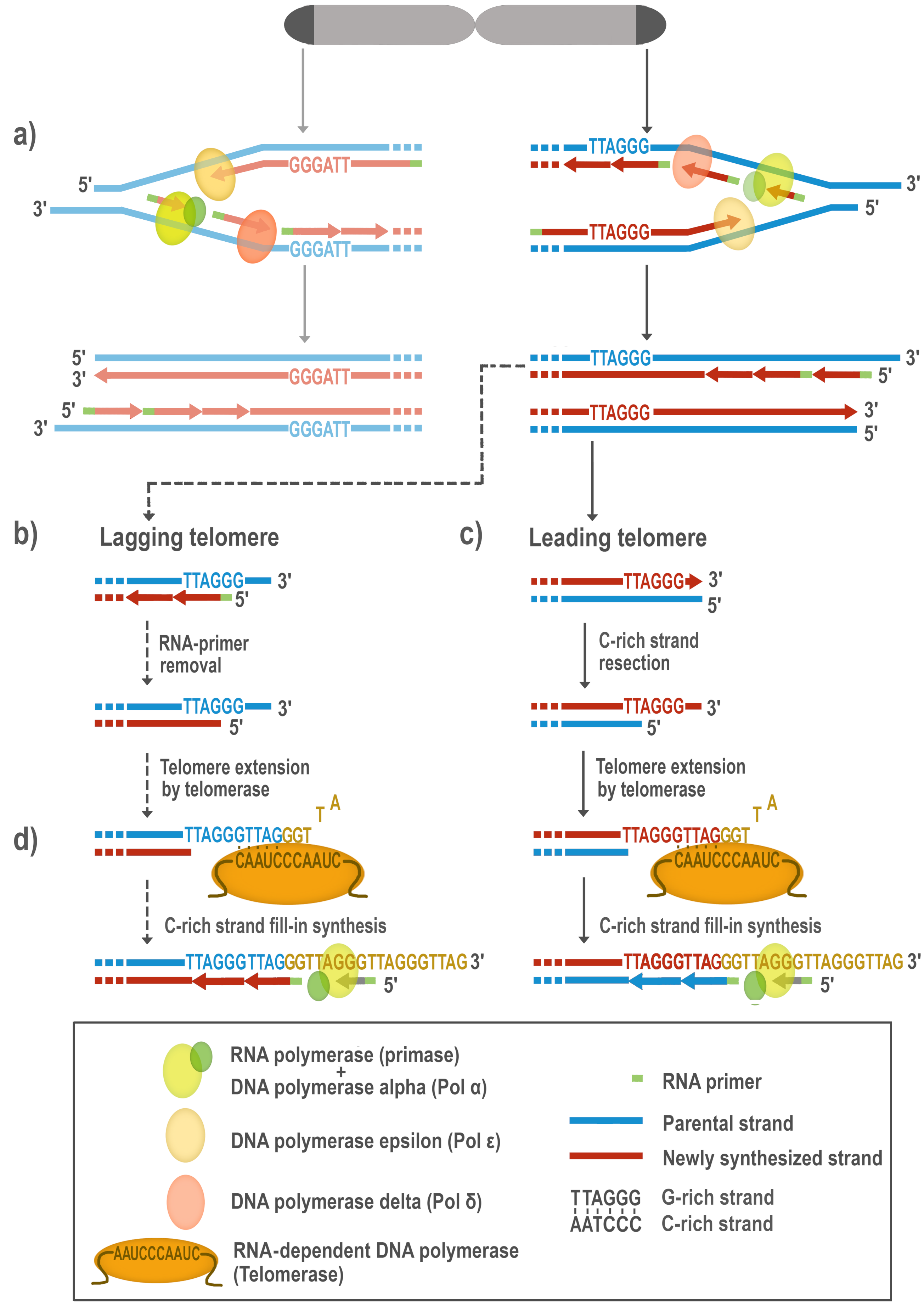
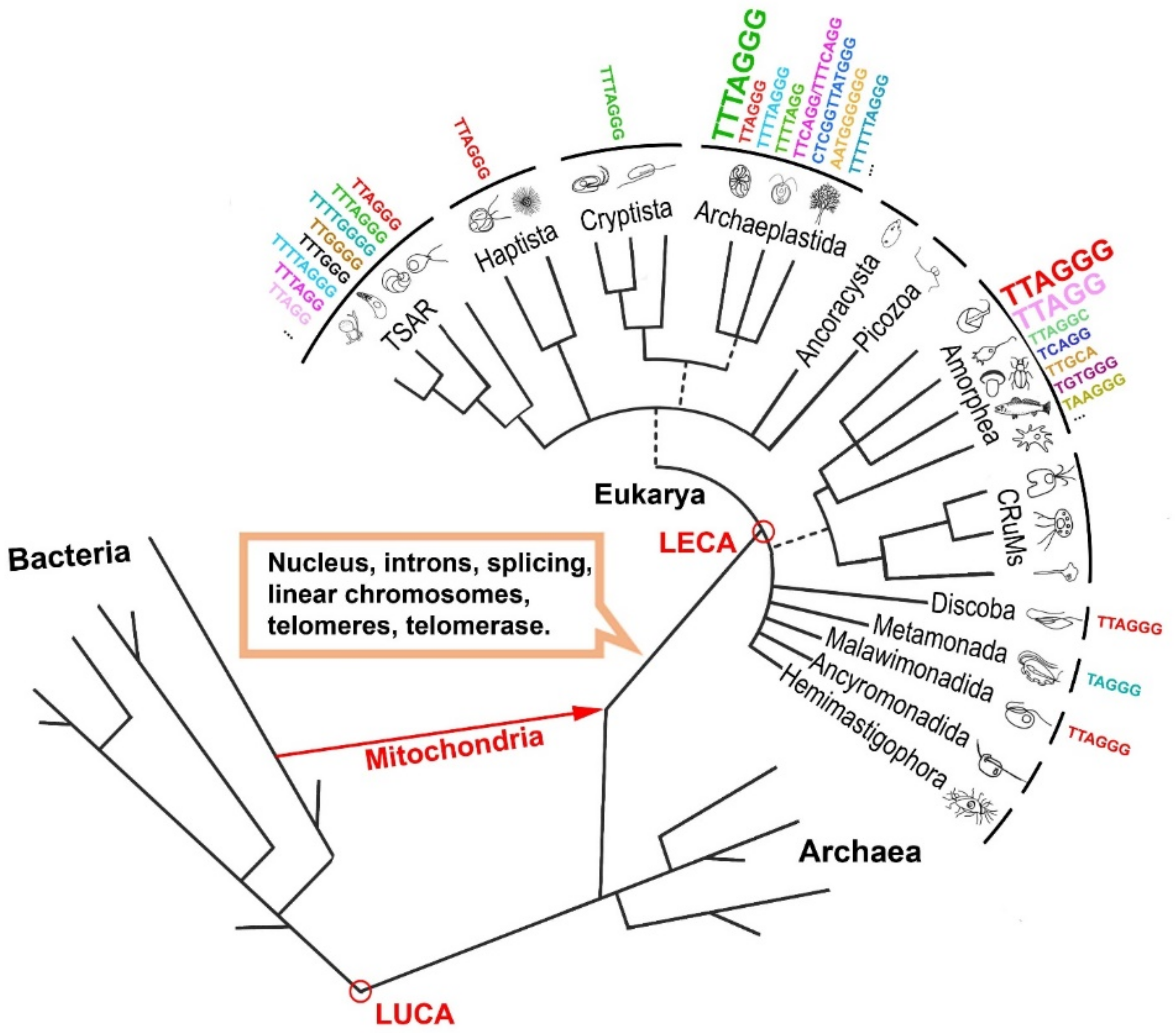
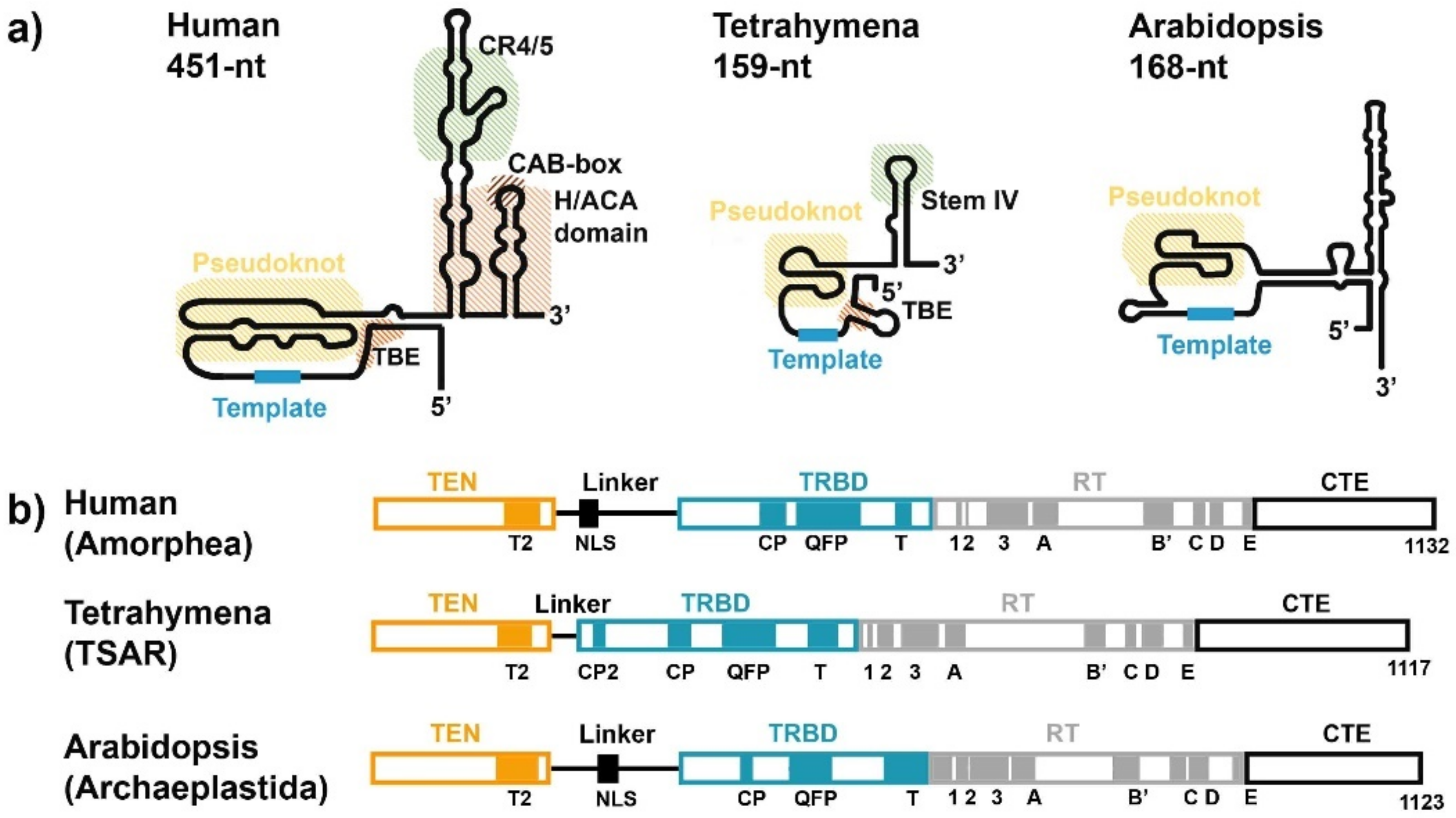
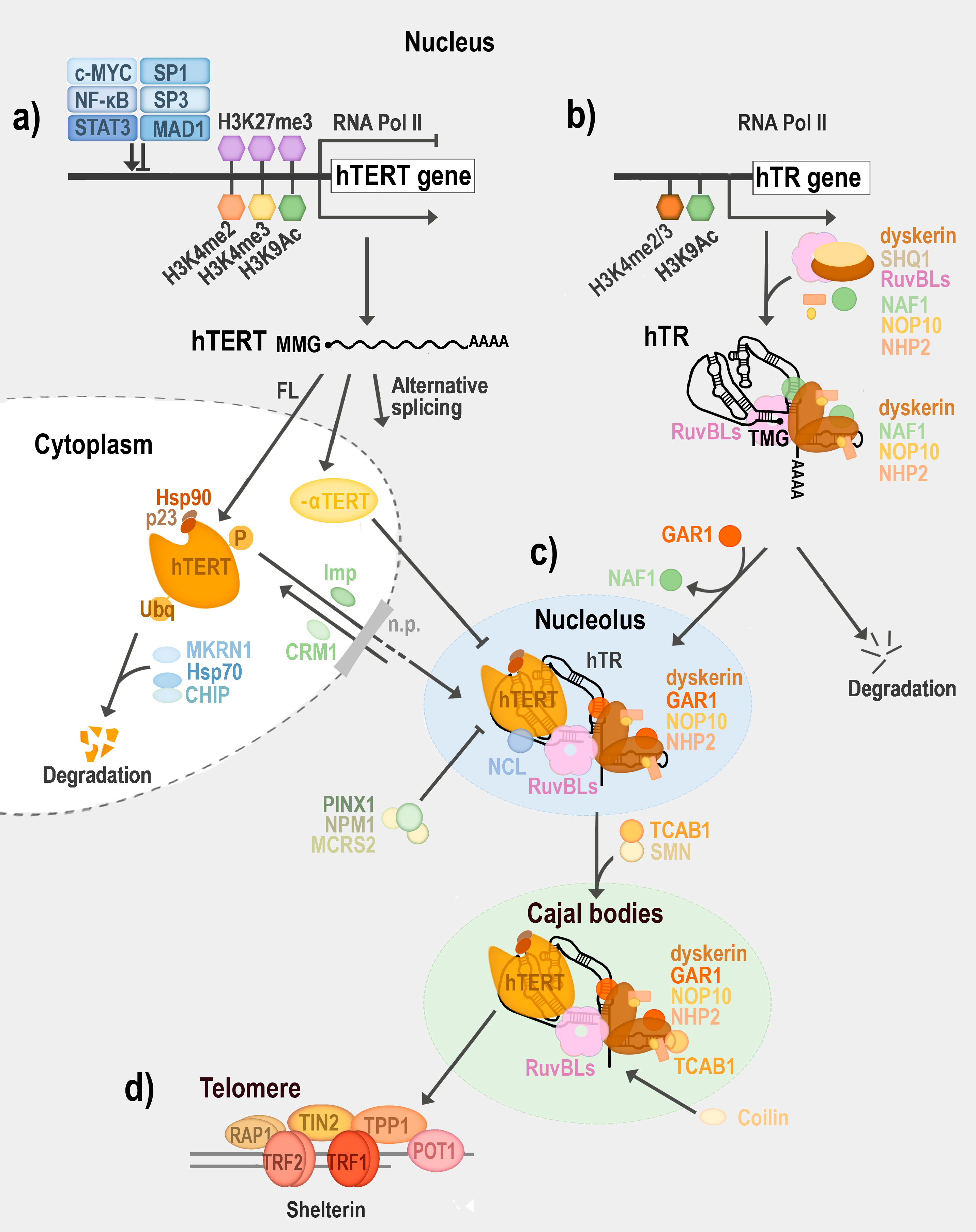
| Mammals (Human) | Reference(s) | Plants (Arabidopsis thaliana) | Reference(s) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (a) TERT | Minimal promoter | 330 bp upstream of the translation start site to 228 bp downstream. | [115,116,121] | 336 bp long promoter region of the translation start site with plausible regulatory intron 1. | [13,117] |
| RNA Polymerase | RNA Pol II | [115] | RNA Pol II | [122] | |
| Histone modifications of promoter | Telomerase-negative tissues: H3K27me3; telomerase-positive tissues (mutated TERT allele): H3K4me2, H3K4me3 and H3K9ac. | [118,119,123] | Telomerase-negative tissues: H3K27me3, H3K4me3, H3K9Ac; telomerase-positive tissues: H3K4me3, H3K9Ac. | [11] | |
| TERT expression in organism | TERT expression is strictly controlled at the transcript level. | [15,124] | The dynamics of TERT transcripts correlates with telomerase activity observed in plant tissues. | [7,11] | |
| Number of exons | 16 exons | [75,121] | 12 exons | [75] | |
| Alternative splicing of mRNA | TERT pre-mRNA can be spliced into at least 22 isoforms. | [125] | TERT pre-mRNA can be spliced into 3 isoforms. | [75] | |
| Post-translational modifications | Phosphorylation or ubiquitination. | [126,127] | No putative phosphorylation site in A. thaliana TERT (but predicted in rice or tabacum TERT ). | [128,129] | |
| Import to the cell nucleus | Importin α promotes nuclear import of the TERT. | [130] | Importin subunit alpha-4 is associated with TERT. | [98] | |
| Protein domains | TEN, TRBD, RT, CTE. | [75,108] | TEN, TRBD, RT, CTE. | [75] | |
| Protein length | 1132 aa | [108] | 1123 aa | [131] | |
| (b) TR | Histone modifications | TR expression in telomerase-positive cell lines is associated with H3K4me2/3, H3K9Ac and hyperacetylation of H4. | [132,133] | Not known yet. | |
| RNA Polymerase | RNA Pol II | [66] | RNA Pol III | [19,20] | |
| Modifications | 5′ end cap, internally modified, poly (A) tail | [83] | Not known yet. | ||
| Template region | 11 nt long template region (synthesizes 6 nt telomeric repeats GGTTAG). | [66,88] | 9 nt long template region (synthesizes 7 nt telomeric repeat GGTTAG). | [19] | |
| TR gene length | 451 nt long transcript | [66] | 268 nt long transcript | [19,20,71] | |
| TR expression in organism | In most tissues TR is ubiquitously expressed regardless of telomerase activity. | [16,17] | The dynamics of TR transcripts correlates with telomerase activity observed in plant tissues. | [7,11] | |
| (c) Nucleolus and CBs | TR scaffold proteins | Dyskerin, NOP10, NHP2, NAF1/GAR1. | [84,96] | Not known yet. Dyskerin (CBF5), NOP10, NHP2, NAF1, and GAR1 are localized in the nucleolus. Telomerase activity can be immunoprecipitated with dyskerin (CBF5) in plants. Dyskerin associates with TRB proteins. | [19,134,135,136] |
| Nucleolin | NCL involves nucleolar localization of TERT. | [137] | NUC-L1 has a role in telomere maintenance and telomere clustering. | [138,139] | |
| RuvBLs | RuvBLs (pontin and reptin) interact with TERT and dyskerin. | [140] | Interactions between TERT and RuvBL proteins are mediated by TRB proteins. | [134] | |
| coilin | Interacts with TR. | [141,142] | Colocalizes with TRB1 in the CBs adjacent to the nucleolus. | [143] | |
| (d) Association with telomere | The TPP1 protein interacts with TERT and facilitates the recruitment of the mature telomerase complex to the telomeres. | [144] | The TRB proteins interact with TERT and may help to recruit telomerase to the plant telomeres. | [145] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schrumpfová, P.P.; Fajkus, J. Composition and Function of Telomerase—A Polymerase Associated with the Origin of Eukaryotes. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1425. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10101425
Schrumpfová PP, Fajkus J. Composition and Function of Telomerase—A Polymerase Associated with the Origin of Eukaryotes. Biomolecules. 2020; 10(10):1425. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10101425
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchrumpfová, Petra Procházková, and Jiří Fajkus. 2020. "Composition and Function of Telomerase—A Polymerase Associated with the Origin of Eukaryotes" Biomolecules 10, no. 10: 1425. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10101425
APA StyleSchrumpfová, P. P., & Fajkus, J. (2020). Composition and Function of Telomerase—A Polymerase Associated with the Origin of Eukaryotes. Biomolecules, 10(10), 1425. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10101425





