Sphaerostilbellins, New Antimicrobial Aminolipopeptide Peptaibiotics from Sphaerostilbella toxica
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fermentation of Strains
2.2. Zone of Inhibition Assays
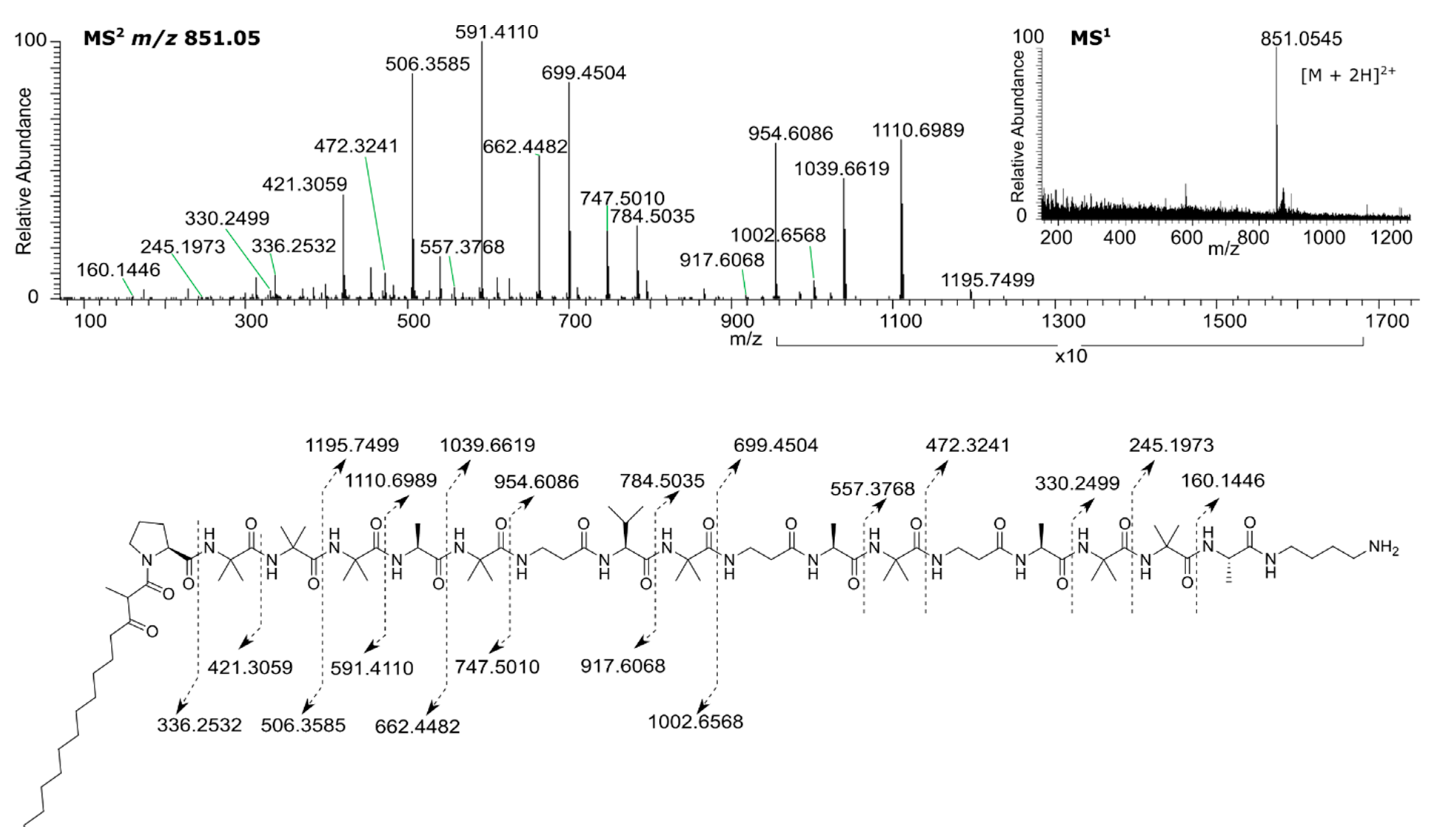
2.3. Isolation and Characterization of Active Compounds from Strain TTI-0467
2.4. Determination of Absolute Configuration of Amino Acids
2.5. Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) Assays
2.6. Macrophage-Fungal Co-Incubation and Macrophage Cytotoxicity Assays
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Benedict, K.; Jackson, B.R.; Chiller, T.; Beer, K.D. Estimation of direct healthcare costs of fungal diseases in the United States. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 68, 1791–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rajasingham, R.; Smith, R.M.; Park, B.J.; Jarvis, J.N.; Govender, N.P.; Chiller, T.M.; Denning, D.W.; Loyse, A.; Boulware, D.R. Global burden of disease of HIV-associated cryptococcal meningitis: An updated analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 873–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brown, G.D.; Denning, D.W.; Gow, N.A.R.; Levitz, S.M.; Netea, M.G.; White, T.C. Hidden killers: Human fungal infections. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4, 165rv113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Perfect, J.R. The antifungal pipeline: A reality check. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 603–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Daele, R.; Spriet, I.; Wauters, J.; Maertens, J.; Mercier, T.; Van Hecke, S.; Bruggemann, R. Antifungal drugs: What brings the future? Med. Mycol. 2019, 57, S328–S343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, L.; Li, Y.; Biggins, J.B.; Bowman, B.R.; Verdine, G.L.; Gloer, J.B.; Alspaugh, J.A.; Bills, G.F. Identification of cyclosporin C from Amphichorda felina using a Cryptococcus neoformans differential temperature sensitivity assay. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 2337–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Yue, Q.; Jayanetti, D.R.; Swenson, D.C.; Bartholomeusz, G.A.; An, Z.; Gloer, J.B.; Bills, G.F. Anti-cryptococcus phenalenones and cyclic tetrapeptides from Auxarthron pseudauxarthron. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 2101–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Põldmaa, K.; Bills, G.; Lewis, D.P.; Tamm, H. Taxonomy of the Sphaerostilbella broomeana-group (Hypocreales, Ascomycota). Mycol. Prog. 2019, 18, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gams, W.; Diederich, P.; Põldmaa, K. Chapter 17 - Fungicolous fungi. In Biodiversity of Fungi; Mueller, G.M., Bills, G.F., Foster, M.S., Eds.; Academic Press: Burlington, MA, USA, 2004; pp. 343–392. [Google Scholar]
- Rossman, A.Y.; Samuels, G.J.; Rogerson, C.T.; Lowen, R. Genera of Bionectriaceae, Hypocreaceae and Nectriaceae (Hypocreales, Ascomycetes). Stud. Mycol. 1999, 42, 1–248. [Google Scholar]
- Kredics, L.; Hatvani, L.; Naeimi, S.; Körmöczi, P.; Manczinger, L.; Vágvölgyi, C.; Druzhinina, I. Chapter 1 - Biodiversity of the genus Hypocrea/Trichoderma in different habitats. In Biotechnology and Biology of Trichoderma; Gupta, V.K., Schmoll, M., Herrera-Estrella, A., Upadhyay, R.S., Druzhinina, I., Tuohy, M.G., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 3–24. [Google Scholar]
- Dhodary, B.; Schilg, M.; Wirth, R.; Spiteller, D. Secondary metabolites from Escovopsis weberi and their role in attacking the garden fungus of leaf-cutting ants. Chem. Eur. J. 2018, 24, 4445–4452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nair, M.S.R.; Carey, S.T.; James, J.C. Metabolites of pyrenomycetes. XIV. Structure and partial stereochemistry of the antibiotic macrolides hypothemycin and dihydrohypothemycin. Tetrahedron 1981, 37, 2445–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Röhrich, C.R.; Jaklitsch, W.M.; Voglmayr, H.; Iversen, A.; Vilcinskas, A.; Nielsen, K.F.; Thrane, U.; von Döhren, H.; Brückner, H.; Degenkolb, T. Front line defenders of the ecological niche! Screening the structural diversity of peptaibiotics from saprotrophic and fungicolous Trichoderma/Hypocrea species. Fungal Divers. 2014, 69, 117–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Sossah, F.L.; Sun, L.; Fu, Y.; Li, Y. Genome analysis of Hypomyces perniciosus, the causal agent of wet bubble disease of button mushroom (Agaricus bisporus). Genes 2019, 10, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Degenkolb, T.; Kirschbaum, J.; Brückner, H. New sequences, constituents, and producers of peptaibiotics: An updated review. Chem. Biodivers. 2007, 4, 1052–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neumann, N.K.N.; Stoppacher, N.; Zeilinger, S.; Degenkolb, T.; Brückner, H.; Schuhmacher, R. The peptaibiotics database—A comprehensive online resource. Chem. Biodivers. 2015, 12, 743–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degenkolb, T.; von Döhren, H.; Fog Nielsen, K.; Samuels, G.J.; Brückner, H. Recent advances and future prospects in peptaibiotics, hydrophobin, and mycotoxin sesearch, and their importance for chemotaxonomy of Trichoderma and Hypocrea. Chem. Biodivers. 2008, 5, 671–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degenkolb, T.; Berg, A.; Gams, W.; Schlegel, B.; Grafe, U. The occurrence of peptaibols and structurally related peptaibiotics in fungi and their mass spectrometric identification via diagnostic fragment ions. J. Pept. Sci. 2003, 9, 666–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bills, G.F.; Dombrowski, A.W.; Goetz, M.A. The "FERMEX" method for metabolite-enriched fungal extracts. Meth. Mol. Biol. 2012, 944, 79–96. [Google Scholar]
- Ayers, S.; Ehrmann, B.M.; Adcock, A.F.; Kroll, D.J.; Carcache de Blanco, E.J.; Shen, Q.; Swanson, S.M.; Falkinham III, J.O.; Wani, M.C.; Mitchell, S.M.; et al. Peptaibols from two unidentified fungi of the order Hypocreales with cytotoxic, antibiotic, and anthelmintic activities. J. Pept. Sci. 2012, 18, 500–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alexander, B.D. Reference Method for Broth Dilution Antifungal Susceptibility Testing of Yeasts. Approved Standard M27–A4, 4th ed.; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Samantaray, S.; Correia, J.N.; Garelnabi, M.; Voelz, K.; May, R.C.; Hall, R.A. Novel cell-based in vitro screen to identify small-molecule inhibitors against intracellular replication of Cryptococcus neoformans in macrophages. Int. J. Antimicrobiol. Agents 2016, 48, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flissi, A.; Ricart, E.; Campart, C.; Chevalier, M.; Dufresne, Y.; Michalik, J.; Jacques, P.; Flahaut, C.; Lisacek, F.; Leclère, V.; et al. Norine: Update of the nonribosomal peptide resource. Nucl. Acid. Res. 2019, 48, D465–D469. [Google Scholar]
- Whitmore, L.; Wallace, B.A. The peptaibol database: A database for sequences and structures of naturally occurring peptaibols. Nucl. Acid. Res. 2004, 32, D593–D594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hegde, V.R.; Silver, J.; Patel, M.; Gullo, V.P.; Yarborough, R.; Huang, E.; Das, P.R.; Puar, M.S.; DiDomenico, B.J.; Loebenberg, D. Novel fungal metabolites as cell wall active antifungals: Fermentation, isolation, physico-chemical properties, structure and biological activity. J. Antibiotics 2001, 54, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krasnoff, S.B.; Reátegui, R.F.; Wagenaar, M.M.; Gloer, J.B.; Gibson, D.M. Cicadapeptins I and II: New Aib-containing peptides from the entomopathogenic fungus Cordyceps heteropoda. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brückner, H.; Fox, S.; Degenkolb, T. Sequences of acretocins, peptaibiotics containing the rare 1-aminocyclopropanecarboxylic Aacid, from Acremonium crotocinigenum CBS 217.70. Chem. Biodivers. 2019, 16, e1900276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, L.; Risinger, A.L.; Mitchell, C.A.; You, J.; Stamps, B.W.; Pan, N.; King, J.B.; Bopassa, J.C.; Judge, S.I.V.; Yang, Z.; et al. Unique amalgamation of primary and secondary structural elements transform peptaibols into potent bioactive cell-penetrating peptides. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E8957–E8966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vemula, H.; Kitase, Y.; Ayon, N.J.; Bonewald, L.; Gutheil, W.G. Gaussian and linear deconvolution of LC-MS/MS chromatograms of the eight aminobutyric acid isomers. Anal. Biochem. 2017, 516, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ayon, N.J.; Sharma, A.D.; Gutheil, W.G. LC-MS/MS-based separation and quantification of Marfey’s reagent derivatized proteinogenic amino acid DL-stereoisomers. J. Amer. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2019, 30, 448–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikuina, Y.; Bando, C.; Yoshida, M.; Yano, H.; Saitoh, Y. MS-681a, b, c and d, new inhibitors of myosin light chain kinase from Myrothecium sp. II. Physico-chemical properties and structure elucidation. J. Antibiotics 1997, 50, 998–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Christner, C.; Zerlin, M.; Gräfe, U.; Heinze, S.; Küllertz, G.; Fischer, G. Lipohexin, a new inhibitor of prolyl endopeptidase from Moeszia lindtneri (HKI-0054) and Paecilomyces sp. (HKI-0055; HKI-0096). II. Inhibitory activities and specificity. J. Antibiotics 1997, 50, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heinze, S.; Ritzau, M.; Ihn, W.; Hülsmann, H.; Schlegel, B.; Dornberger, K.; Fleck, W.F.; Zerlin, M.; Christner, C.; Gräfe, U.; et al. Lipohexin, a new inhibitor of prolyl endopeptidase from Moeszia lindtneri (HKI-0054) and Paecilomyces sp. (HKI-0055; HKI-0096). I. Screening, isolation and structure elucidation. J. Antibiotics 1997, 50, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hegde, V.R.; Silver, J.; Patel, M.; Gullo, V.P.; Puar, M.S.; Das, P.R.; Loebenberg, D. Novel fungal metabolites as cell wall active antifungals: Fermentation, isolation, physico-chemical properties, structure and biological activity. J. Antibiotics 2003, 56, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stump, H.; Stahl, W.; Wink, J.; Markus, A.; Kogler, H.; Backhaus, J. Antifungal Peptides from Scleroderma Texense. U.S. Patent 6,221,844, 2 June 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Pierson, N.A.; Chen, L.; Russell, D.H.; Clemmer, D.E. Cis–Trans isomerizations of proline residues are key to bradykinin conformations. J. Amer. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 3186–3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Glover, M.S.; Shi, L.; Fuller, D.R.; Arnold, R.J.; Radivojac, P.; Clemmer, D.E. On the split personality of penultimate proline. J. Amer. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2015, 26, 444–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Siebler, C.; Maryasin, B.; Kuemin, M.; Erdmann, R.S.; Rigling, C.; Grünenfelder, C.; Ochsenfeld, C.; Wennemers, H. Importance of dipole moments and ambient polarity for the conformation of Xaa–Pro moieties—A combined experimental and theoretical study. Chem. Sci. 2015, 6, 6725–6730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loureiro, A.; Pais, C.; Sampaio, P. Relevance of macrophage extracellular traps in C. albicans killing. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.-Y.; Xie, B.-B.; Chen, X.-L.; Zhang, Y.-Z. Biosynthesis and molecular genetics of peptaibiotics—Fungal peptides containing alpha, alpha-dialkyl amino acids. In Biosynthesis and Molecular Genetics of Fungal Secondary Metabolites; Zeilinger, S., Martín, J.-F., García-Estrada, C., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015; Volume 2, pp. 235–252. [Google Scholar]
- Toniolo, C.; Crisma, M.; Formaggio, F.; Peggion, C.; Epand, R.F.; Epand, R.M. Lipopeptaibols, a novel family of membrane active, antimicrobial peptides. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2001, 58, 1179–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdés-Santiago, L.; Ruiz-Herrera, J. Stress and polyamine metabolism in fungi. Front. Chem. 2014, 1, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




| Residue. | Position | δC | δH, mult (J in Hz) | Residue | Position | δC | δH, mult (J in Hz) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MOTDA | 1 | 169.40 | Aib9 | NH | 8.02, s | ||
| 2 | 50.83 | 3.80, q (6.9) | α | 55.85 | |||
| 2’ | 12.45 | 1.15, d (6.9) | β-1 | 23.13 | 1.39, m a | ||
| 3 | 206.39 | β-2 | 24.30 | 1.33, m a | |||
| 4 | 40.42 | 2.47, m | C=O | 174.08 | |||
| 5 | 22.84 | 1.40, m | β-Ala10 | NH | 7.44, t (5.5) | ||
| 6 | 22.04 | 1.22, m | α | 35.81 | a: 3.32, m; b: 3.14, m | ||
| 7 | 28.69 | 1.16, m | β | 35.09 | 2.29, m | ||
| 8 | 28.89 | 1.20, m | C=O | 171.18 | |||
| 9 | 28.95 | 1.21, m | L-Ala11 | NH | 8.12, d (4.8) | ||
| 10 | 28.82 | 1.24, m | α | 49.19 | 4.10, q (6.6) | ||
| 11 | 28.99 | 1.25, m | β | 17.09 | 1.18, m | ||
| 12 | 28.64 | 1.36, m | C=O | 172.20 | |||
| 13 | 31.23 | 1.23, m | Aib12 | NH | 8.04, s | ||
| 14 | 13.91 | 0.85, m | α | 56.06 | |||
| L-Pro1 | α | 60.13 | 4.26, dd (5.8, 7.8) | β-1 | 23.38 | 1.27, m a | |
| β | 28.45 | a: 2.16, m; b: 1.93, m | β-2 | 25.75 | 1.37, m a | ||
| γ | 24.57 | a: 2.02, m; b: 1.92, m | C=O | 174.09 | |||
| δ | 47.57 | 3.64, t (6.6) | β-Ala13 | NH | 7.50, t (5.6) | ||
| C=O | 172.43 | α | 35.83 | a: 3.30, m; b: 3.21, m | |||
| Aib2 | NH | 8.55, s | β | 35.06 | 2.31, m | ||
| α | 55.96 | C=O | 171.54 | ||||
| β1 | 23.90 | 1.34, m a | L-Ala14 | NH | 8.19, d (4.7) | ||
| β2 | 25.50 | 1.32, m a | α | 49.94 | 4.03, m d | ||
| C=O | 175.38 | β | 16.63 | 1.24, m | |||
| Aib3 | NH | 7.95, s | C=O | 174.01 | |||
| α | 55.84 | Aib15 | NH | 8.40, s | |||
| β-1 | 24.58 | 1.39, m a | α | 55.99 | |||
| β-2 | 25.74 | 1.36, m a | β-1 | 24.10 | 1.37, m a | ||
| C=O | 175.19 | β-2 | 24.96 | 1.36, m a | |||
| Aib4 | NH | 7.70, s b | C=O | 175.34 | |||
| α | 55.88 | Aib16 | NH | 7.80, s | |||
| β-1 | 24.92 | 1.34, m a | α | 55.69 | |||
| β-2 | 26.46 | 1.30, m a | β-1 | 22.93 | 1.29, m a | ||
| C=O | 175.14 | β-2 | 25.80 | 1.32, m a | |||
| L-Ala5 | NH | 7.71, d b | C=O | 175.26 | |||
| α | 50.02 | 3.93, m c | Aib17 | NH | 7.67, s | ||
| β | 16.47 | 1.28, m | α | 55.95 | |||
| C=O | 172.00 | β-1 | 21.99 | 1.33, m a | |||
| Aib6 | NH | 7.34, s | β-2 | 26.64 | 1.35, m a | ||
| α | 56.01 | C=O | 173.37 | ||||
| β-1 | 24.67 | 1.36, m a | L-Ala18 | NH | 7.56, d (7.8) | ||
| β-2 | 24.70 | 1.36, m a | α | 48.96 | 4.04, m d | ||
| C=O | 174.02 | β | 17.11 | 1.31, m | |||
| β-Ala7 | NH | 7.13, t (5.4) | C=O | 172.05 | |||
| α | 35.60 | a: 3.28, m; b: 3.18, m | Put | NH | 7.39, t (5.6) | ||
| β | 35.20 | 2.35, m | α | 37.90 | a: 3.10, m; b: 3.02, m | ||
| C=O | 171.04 | β | 25.88 | 1.50, m e | |||
| L-Val8 | NH | 8.00, d (7.0) | γ | 24.26 | 1.53, m e | ||
| α | 58.93 | 3.92, m c | δ | 38.53 | 2.78, m | ||
| β | 29.58 | 1.93, m | NH2 | 7.69, m b | |||
| γ-1 | 19.08 | 0.86, m | |||||
| γ-2 | 18.68 | 0.87, m | |||||
| C=O | 170.78 |
| Residue | Position | δC | δH, mult (J in Hz) | Residue | Position | δC | δH, mult (J in Hz) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MOTDA | 1 | 169.40 | Aib9 | NH | 8.02, s | ||
| 2 | 50.83 | 3.80, q (6.9) | α | 55.85 | |||
| 2’ | 12.45 | 1.15, d (6.9) | β-1 | 23.13 | 1.39, m a | ||
| 3 | 206.39 | β-2 | 24.30 | 1.33, m a | |||
| 4 | 40.42 | 2.47, m | C=O | 174.08 | |||
| 5 | 22.84 | 1.40, m a | β-Ala10 | NH | 7.44, m d | ||
| 6 | 22.04 | 1.24, m f | α | 35.81 | a: 3.32, m; b: 3.14, m | ||
| 7 | 28.69 | 1.16, m f | β | 35.09 | 2.29, m | ||
| 8 | 28.89 | 1.20, m f | C=O | 171.18 | |||
| 9 | 28.95 | 1.21, m f | L-Ala11 | NH | 8.10, d (4.8) | ||
| 10 | 28.82 | 1.24, m f | α | 49.19 | 4.10, q (6.6) | ||
| 11 | 28.99 | 1.25, m f | β | 17.15 | 1.18, m | ||
| 12 | 28.64 | 1.36, m a | C=O | 172.20 | |||
| 13 | 31.23 | 1.23, m f | Aib12 | NH | 8.04, s | ||
| 14 | 13.91 | 0.85, m | α | 56.06 | |||
| L-Pro1 | α | 60.13 | 4.26, dd (5.8, 7.8) | β-1 | 23.38 | 1.27, m a | |
| β | 28.45 | a: 2.16, m; b: 1.93, m | β-2 | 25.75 | 1.37, m a | ||
| γ | 24.57 | a: 2.02, m; b: 1.92, m | C=O | 174.03 | |||
| δ | 47.57 | 3.64, t (6.4) m | β-Ala13 | NH | 7.50, m e | ||
| C=O | 172.43 | α | 35.83 | a: 3.30, m; b: 3.21, m | |||
| Aib2 | NH | 8.55, s | β | 35.06 | 2.31, m | ||
| α | 55.96 | C=O | 171.54 | ||||
| β1 | 23.90 | 1.34, m a | L-Ala14 | NH | 8.14, d (4.7) | ||
| β2 | 25.50 | 1.32, m a | α | 49.70 | 4.03, m g | ||
| C=O | 175.38 | β | 16.74 | 1.24, m | |||
| Aib3 | NH | 7.95, s | C=O | 173.97 | |||
| α | 55.84 | Aib15 | NH | 8.41, s | |||
| β-1 | 24.58 | 1.39, m a | α | 55.99 | |||
| β-2 | 25.74 | 1.36, m a | β-1 | 23.90 | 1.37, m a | ||
| C=O | 175.19 | β-2 | 25.27 | 1.36, m a | |||
| Aib4 | NH | 7.70, s b | C=O | 175.00 | |||
| α | 55.88 | Aib16 | NH | 7.71, s | |||
| β-1 | 24.92 | 1.34, m a | α | 55.86 | |||
| β-2 | 26.46 | 1.30, m a | β-1 | 21.99 | 1.33, m a | ||
| C=O | 175.14 | β-2 | 26.47 | 1.35, m a | |||
| L-Ala5 | NH | 7.71, db | C=O | 173.49 | |||
| α | 50.02 | 3.93, m c | L-Ala17 | NH | 7.49, m e | ||
| β | 16.47 | 1.28, m | α | 48.96 | 4.04, m g | ||
| C=O | 172.00 | β | 17.27 | 1.31, m | |||
| Aib6 | NH | 7.34, s | C=O | 172.05 | |||
| α | 56.01 | Put | NH | 7.45, m d | |||
| β-1 | 24.67 | 1.36, m a | α | 37.9 | a: 3.10, m; b: 3.02, m | ||
| β-2 | 24.70 | 1.36, m a | β | 25.88 | 1.50, m h | ||
| C=O | 174.02 | γ | 24.26 | 1.53, m h | |||
| β-Ala7 | NH | 7.13, t (5.4) | δ | 38.49 | 2.78, m | ||
| α | 35.60 | a: 3.28, m; b: 3.18, m | NH2 | 7.69, m b | |||
| β | 35.20 | 2.35, m | |||||
| C=O | 171.04 | ||||||
| L-Val8 | NH | 8.00, d (7.0) | |||||
| α | 58.93 | 3.92, m c | |||||
| β | 29.58 | 1.93, m | |||||
| γ-1 | 19.08 | 0.86, m | |||||
| γ-2 | 18.68 | 0.87, m | |||||
| C=O | 170.78 |
| Pathogen or Cell Line | Compound (μM) | |
|---|---|---|
| Sphaerostilbellin A (1) | Sphaerostilbellin B (2) | |
| C. neoformans H99 37 °C | 2 | 2 |
| C. neoformans H99 30 °C | 2 | 2 |
| C. albicans ATCC 10231 | 4 | 2 |
| A. fumigatus FGSC A1240 | 1 | 1 |
| S. aureus ATCC 43300 | 8 | 32 |
| Murine macrophage J774A.1 | >32 | 32 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Perlatti, B.; Nichols, C.B.; Alspaugh, J.A.; Gloer, J.B.; Bills, G.F. Sphaerostilbellins, New Antimicrobial Aminolipopeptide Peptaibiotics from Sphaerostilbella toxica. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1371. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10101371
Perlatti B, Nichols CB, Alspaugh JA, Gloer JB, Bills GF. Sphaerostilbellins, New Antimicrobial Aminolipopeptide Peptaibiotics from Sphaerostilbella toxica. Biomolecules. 2020; 10(10):1371. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10101371
Chicago/Turabian StylePerlatti, Bruno, Connie B. Nichols, J. Andrew Alspaugh, James B. Gloer, and Gerald F. Bills. 2020. "Sphaerostilbellins, New Antimicrobial Aminolipopeptide Peptaibiotics from Sphaerostilbella toxica" Biomolecules 10, no. 10: 1371. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10101371
APA StylePerlatti, B., Nichols, C. B., Alspaugh, J. A., Gloer, J. B., & Bills, G. F. (2020). Sphaerostilbellins, New Antimicrobial Aminolipopeptide Peptaibiotics from Sphaerostilbella toxica. Biomolecules, 10(10), 1371. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10101371






