Neuroprotective Effects of Quercetin in Alzheimer’s Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
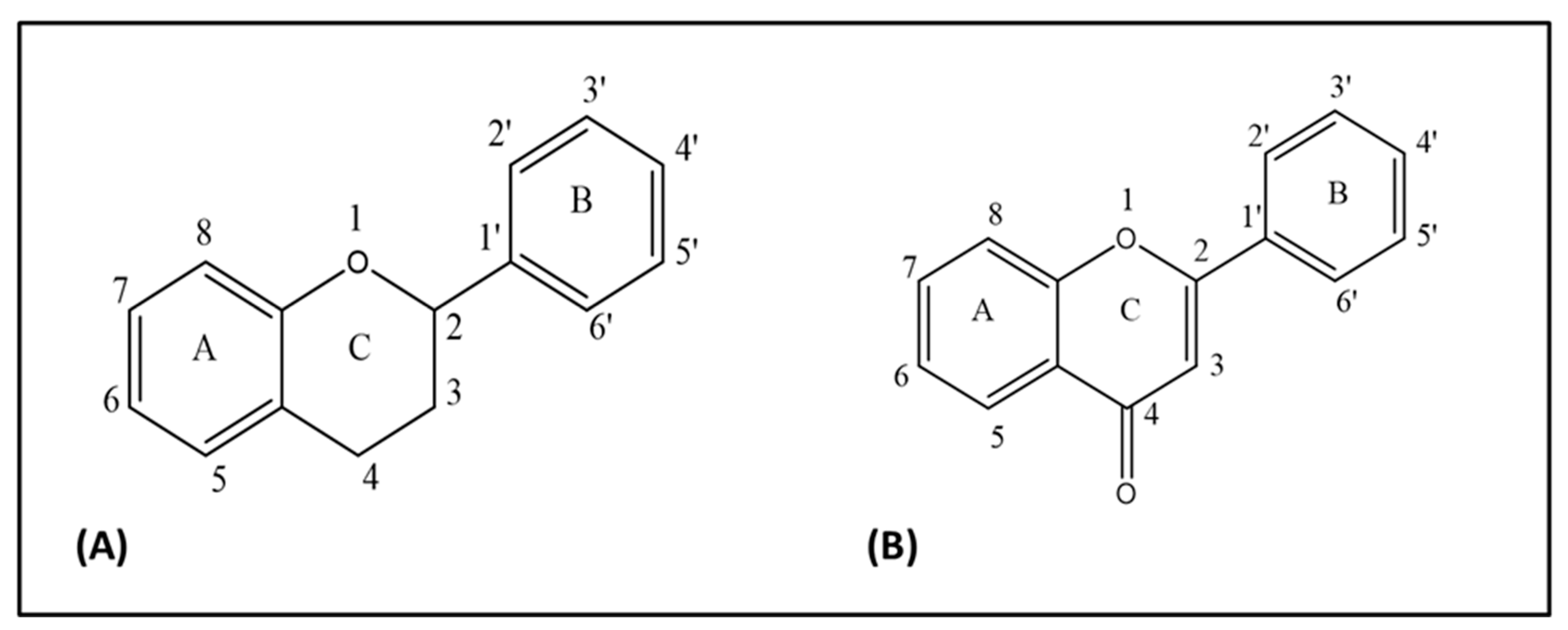
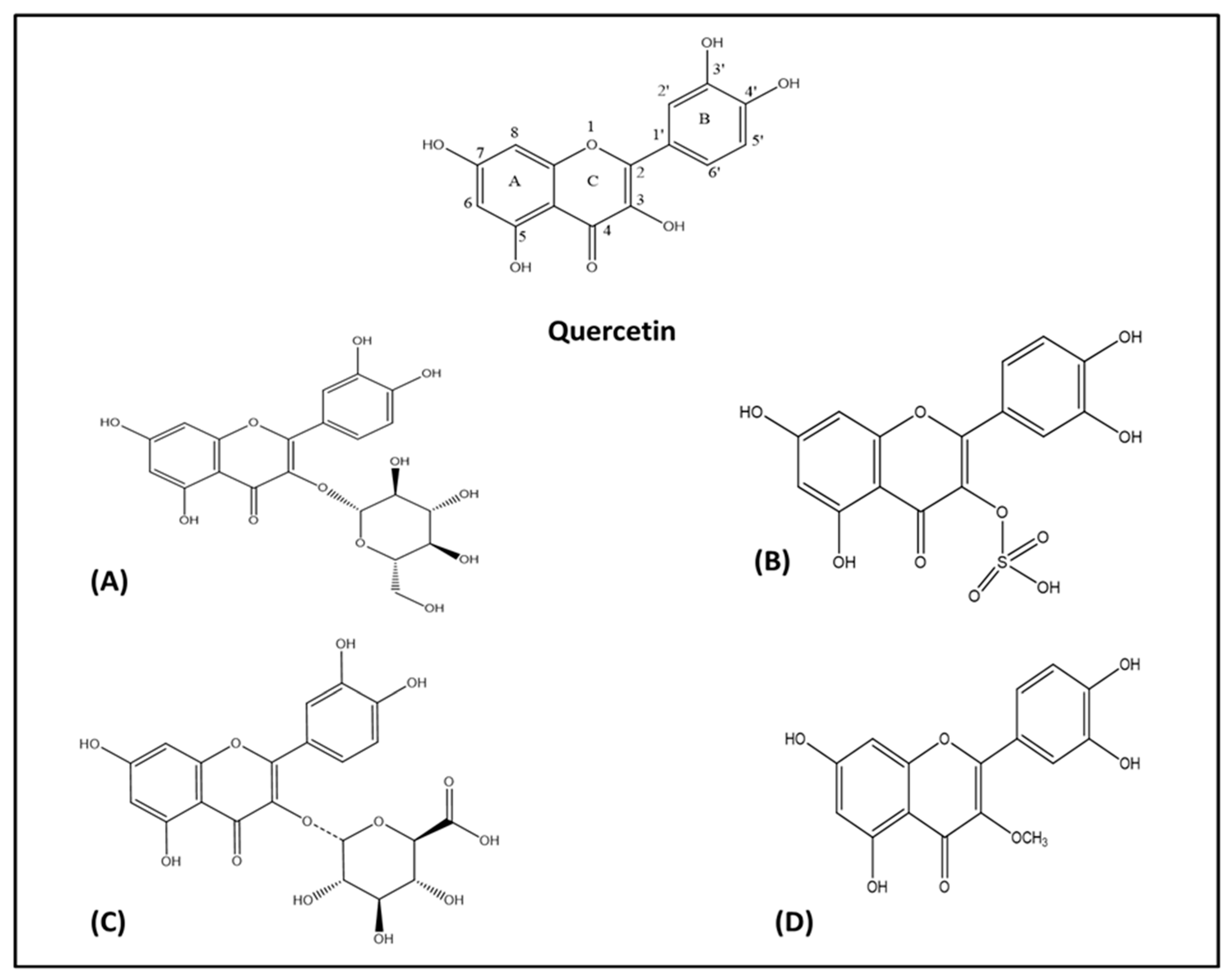
2. Chemistry of Quercetin
3. Sources
4. Pharmacokinetic Parameters of Quercetin
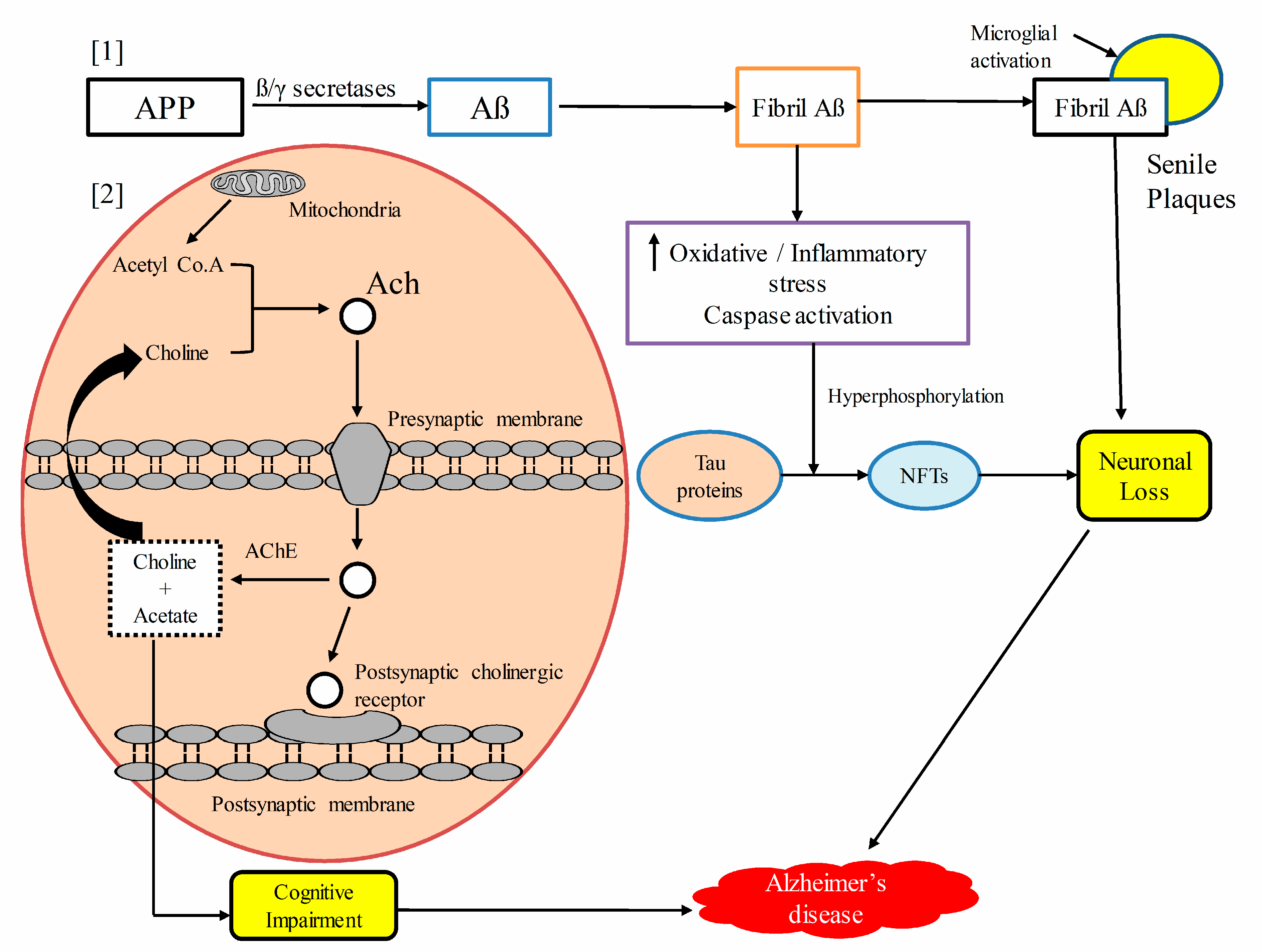
5. Pathophysiological Mechanisms of Alzheimer’s Disease
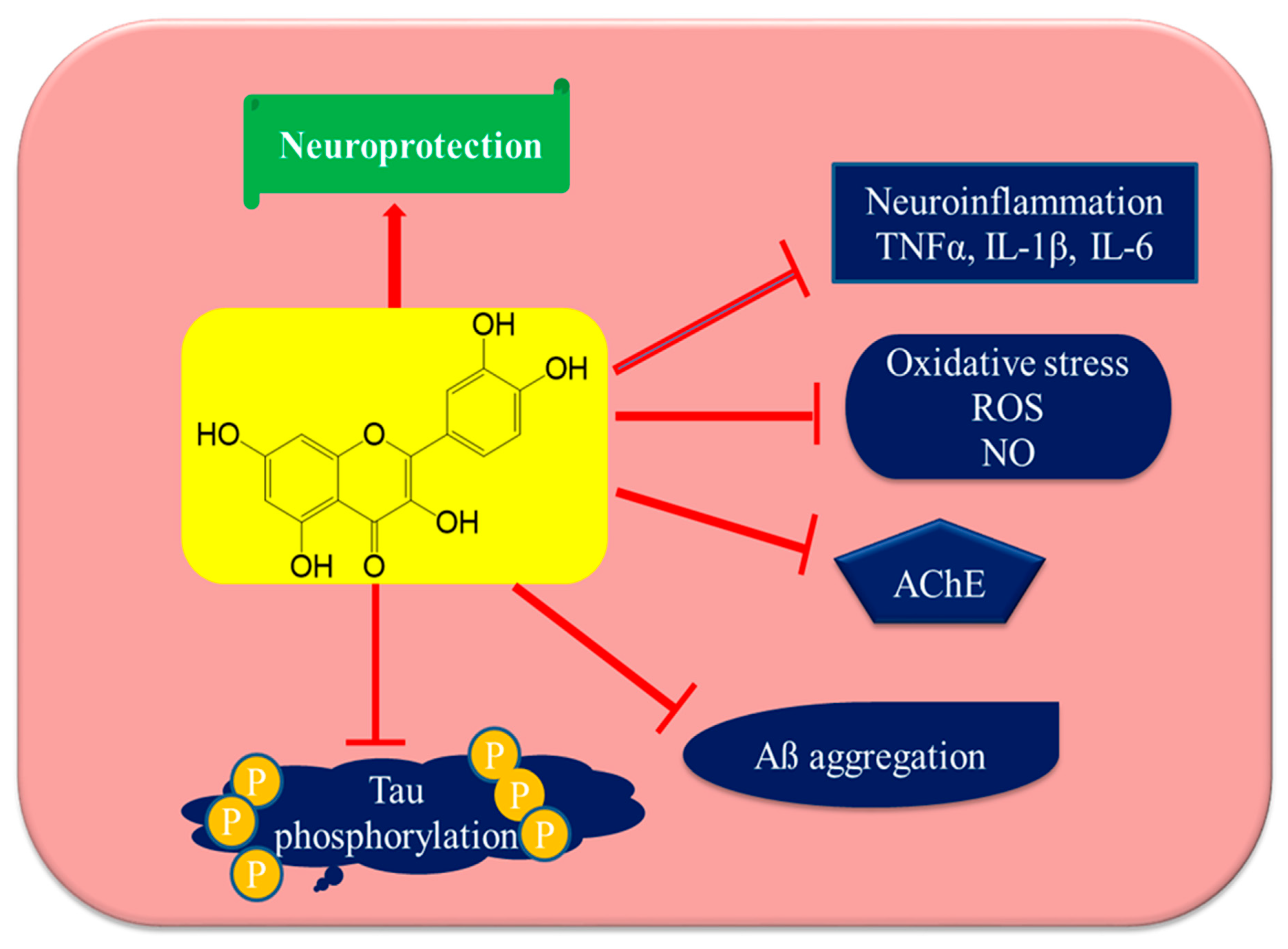
6. Neuroprotective Efficacy of Quercetin
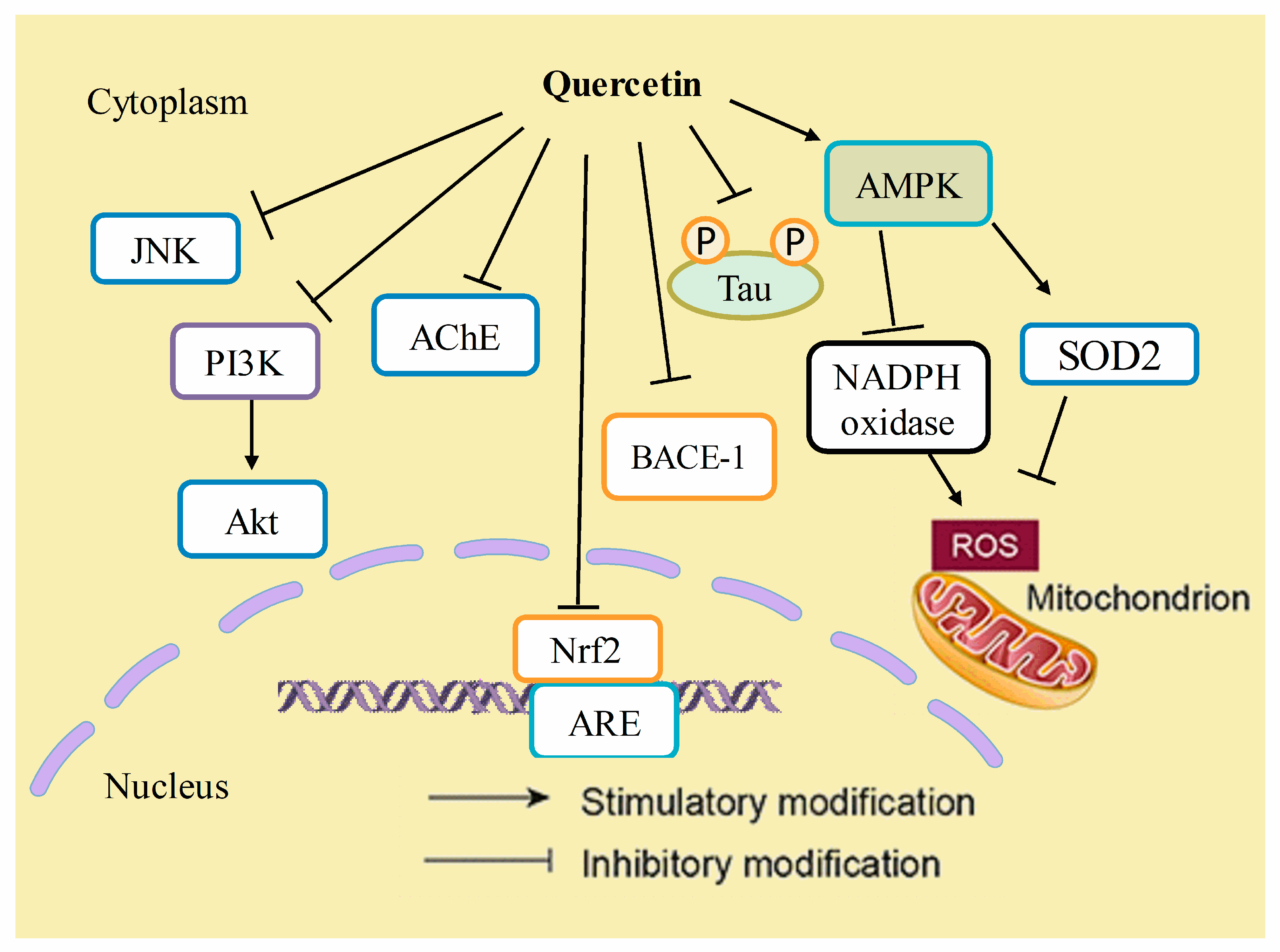
7. Anti-Alzheimer’s Disease Mechanisms of Quercetin
7.1. Inhibition of AβAggregation and Tau Phosphorylation
7.2. Acetylcholinesterase Inhibition
7.3. Attenuation of Oxidative Stress
7.4. Attenuation of Neuroinflammation by Quercetin
8. Anti-Alzheimer’s Disease Potential: In Vitro Studies on the Efficacy of Quercetin
9. Anti-Alzheimer’s Disease Potential: In Vivo Studies on the Efficacy of Quercetin
10. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- DeTure, M.A.; Dickson, D.W. The neuropathological diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2019, 14, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parent, M.J.; Zimmer, E.R.; Shin, M.; Kang, M.S.; Fonov, V.S.; Mathieu, A.; Aliaga, A.; Kostikov, A.; Do Carmo, S.; Dea, D. Multimodal imaging in rat model recapitulates Alzheimer’s Disease biomarkers abnormalities. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 12263–12271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kommaddi, R.P.; Das, D.; Karunakaran, S.; Nanguneri, S.; Bapat, D.; Ray, A.; Shaw, E.; Bennett, D.A.; Nair, D.; Ravindranath, V. Aβ mediates F-actin disassembly in dendritic spines leading to cognitive deficits in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurosci. 2018, 38, 1085–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, R.A.; Dalton, A.J. What can we learn from study of Alzheimer’s disease in patients with Down syndrome for early-onset Alzheimer’s disease in the general population? Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2011, 3, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hollingworth, P.; Harold, D.; Jones, L.; Owen, M.J.; Williams, J. Alzheimer’s disease genetics: Current knowledge and future challenges. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2011, 26, 793–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayeux, R.; Stern, Y. Epidemiology of Alzheimer disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2012, 2, a006239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliev, G.; Obrenovich, M.E.; Reddy, V.P.; Shenk, J.C.; Moreira, P.I.; Nunomura, A.; Zhu, X.; Smith, M.A.; Perry, G. Antioxidant therapy in Alzheimer’s disease: Theory and practice. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2008, 8, 1395–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rountree, S.D.; Chan, W.; Pavlik, V.N.; Darby, E.J.; Siddiqui, S.; Doody, R.S. Persistent treatment with cholinesterase inhibitors and/or memantine slows clinical progression of Alzheimer disease. Alzheimers Res. 2009, 1, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, K.W. Naturally occurring phytochemicals for the prevention of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurochem. 2010, 112, 1415–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farooq, U.; Khan, A.; Naz, S.; Rauf, A.; Khan, H.; Khan, A.; Ullah, I.; Bukhari, S.M. Sedative and antinociceptive activities of two new sesquiterpenes isolated from Ricinus communis. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2018, 16, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawad, M.; Khan, H.; Pervez, S.; Bawazeer, S.S.; Abu-Izneid, T.; Saeed, M.; Kamal, M.A. Pharmacological validation of the anxiolytic, muscle relaxant and sedative like activities of Capsicum annuum in animal model. Bangladesh J. Pharmacol. 2017, 12, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, N.; Khan, I.; Khan, H.; Ayub, B.; Abdel-Halim, H.; Gavande, N. Anxiolytic potential of natural flavonoids. Sm J. Steroids Horm. 2018, 1, 1001. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, H.; Marya; Amin, S.; Kamal, M.A.; Patel, S. Flavonoids as acetylcholinesterase inhibitors: Current therapeutic standing and future prospects. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 101, 860–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabavi, S.F.; Khan, H.; D’Onofrio, G.; Šamec, D.; Shirooie, S.; Dehpour, A.R.; Argüelles, S.; Habtemariam, S.; Sobarzo-Sanchez, E. Apigenin as neuroprotective agent: Of mice and men. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 128, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rengasamy, K.R.R.; Khan, H.; Gowrishankar, S.; Lagoa, R.J.L.; Mahomoodally, F.M.; Khan, Z.; Suroowan, S.; Tewari, D.; Zengin, G.; Hassan, S.T.S.; et al. The role of flavonoids in autoimmune diseases: Therapeutic updates. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 194, 107–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabavi, S.F.; Atanasov, A.G.; Khan, H.; Barreca, D.; Trombetta, D.; Testai, L.; Sureda, A.; Tejada, S.; Vacca, R.A.; Pittalà, V.; et al. Targeting ubiquitin-proteasome pathway by natural, in particular polyphenols, anticancer agents: Lessons learned from clinical trials. Cancer Lett. 2018, 434, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, H.; Ullah, H.; Martorell, M.; Valdes, S.E.; Belwal, T.; Tejada, S.; Sureda, A.; Kamal, M.A. Flavonoids nanoparticles in cancer: Treatment, prevention and clinical prospects. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2019, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solanki, I.; Parihar, P.; Mansuri, M.L.; Parihar, M.S. Flavonoid-based therapies in the early management of neurodegenerative diseases. Adv. Nutr. Int. Rev. J. 2015, 6, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devore, E.E.; Kang, J.H.; Breteler, M.; Grodstein, F. Dietary intakes of berries and flavonoids in relation to cognitive decline. Ann. Neurol. 2012, 72, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Cassidy, A.; Schwarzschild, M.; Rimm, E.; Ascherio, A. Habitual intake of dietary flavonoids and risk of Parkinson disease. Neurology 2012, 78, 1138–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, H.; Khan, H. Anti-Parkinson potential of silymarin: Mechanistic insight and therapeutic standing. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baptista, F.I.; Henriques, A.G.; Silva, A.M.; Wiltfang, J.; da Cruz e Silva, O.A. Flavonoids as therapeutic compounds targeting key proteins involved in Alzheimer’s disease. Acs Chem. Neurosci. 2014, 5, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.-H.; Wang, N.-N.; Zou, Z.-X.; Zhang, L.; Xu, K.-P.; Chen, A.F.; Cao, D.-S.; Tan, G.-S. Multi-Target Screening and Experimental Validation of Natural Products from Selaginella Plants against Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamaguchi, T.; Ono, K.; Murase, A.; Yamada, M. Phenolic compounds prevent Alzheimer’s pathology through different effects on the amyloid-β aggregation pathway. Am. J. Pathol. 2009, 175, 2557–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayaz, M.; Ullah, F.; Sadiq, A.; Kim, M.O.; Ali, T. Natural Products-Based Drugs: Potential Therapeutics against Alzheimer’s Disease and other Neurological Disorders. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, P. The potential of flavonoids for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouhestani, S.; Jafari, A.; Babaei, P. Kaempferol attenuates cognitive deficit via regulating oxidative stress and neuroinflammation in an ovariectomized rat model of sporadic dementia. Neural Regen. Res. 2018, 13, 1827. [Google Scholar]
- Brüll, V.; Burak, C.; Stoffel-Wagner, B.; Wolffram, S.; Nickenig, G.; Müller, C.; Langguth, P.; Alteheld, B.; Fimmers, R.; Naaf, S. Effects of a quercetin-rich onion skin extract on 24 h ambulatory blood pressure and endothelial function in overweight-to-obese patients with (pre-) hypertension: A randomised double-blinded placebo-controlled cross-over trial. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 114, 1263–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Khan, H.; Ullah, H.; Hassan, S.T.; Šmejkal, K.; Efferth, T.; Mahamoodally, M.F.; Xu, S.; Habtemariam, S.; Filosa, R. MicroRNA targeting by quercetin in cancer treatment and chemoprotection. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 104346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawabata, K.; Mukai, R.; Ishisaka, A. Quercetin and related polyphenols: New insights and implications for their bioactivity and bioavailability. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 1399–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harwood, M.; Danielewska-Nikiel, B.; Borzelleca, J.; Flamm, G.; Williams, G.; Lines, T. A critical review of the data related to the safety of quercetin and lack of evidence of in vivo toxicity, including lack of genotoxic/carcinogenic properties. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2007, 45, 2179–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Yao, J.; Han, C.; Yang, J.; Chaudhry, M.T.; Wang, S.; Liu, H.; Yin, Y. Quercetin, Inflammation and Immunity. Nutrients 2016, 8, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rishitha, N.; Muthuraman, A. Therapeutic evaluation of solid lipid nanoparticle of quercetin in pentylenetetrazole induced cognitive impairment of zebrafish. Life Sci. 2018, 199, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Wang, H.; Gao, Y.; Li, L.; Tang, C.; Wen, G.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, M.; Mao, L.; Fan, Y. Protective effects of quercetin on mitochondrial biogenesis in experimental traumatic brain injury via the Nrf2 signaling pathway. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0164237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Horany, H.E.; El-latif, R.N.A.; ElBatsh, M.M.; Emam, M.N. Ameliorative effect of quercetin on neurochemical and behavioral deficits in rotenone rat model of Parkinson’s disease: Modulating autophagy (quercetin on experimental Parkinson’s disease). J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2016, 30, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandhir, R.; Mehrotra, A. Quercetin supplementation is effective in improving mitochondrial dysfunctions induced by 3-nitropropionic acid: Implications in Huntington’s disease. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta 2013, 1832, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsao, R.; McCallum, J. Chemistry of flavonoids. In Fruit and Vegetable Phytochemicals; De la Rosa, L.A., Alvarez-Parrilla, E., Gonzalez-Aguilar, G.A., Eds.; Wiley-Blackwell: Ames, IA, USA, 2010; pp. 131–153. [Google Scholar]
- Aherne, S.A.; O’Brien, N.M. Dietary flavonols: Chemistry, food content, and metabolism. Nutrition 2002, 18, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Sharma, H.; Yadav, K. Quercetin and metabolic syndrome. EJPMR 2016, 3, 701–709. [Google Scholar]
- Dall’Acqua, S.; Miolo, G.; Innocenti, G.; Caffieri, S. The photodegradation of quercetin: Relation to oxidation. Molecules 2012, 17, 8898–8907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.P.; Son, K.H.; Chang, H.W.; Kang, S.S. Anti-inflammatory plant flavonoids and cellular action mechanisms. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2004, 96, 229–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganeshpurkar, A.; Saluja, A.K. The pharmacological potential of rutin. Saudi Pharm. J. 2017, 25, 149–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Z.H.; Li, N.G.; Tang, Y.P.; Shi, Q.P.; Tang, H.; Li, W.; Zhang, X.; Fu, H.A.; Duan, J.A. Biological Evaluation and SAR Analysis of O-Methylated Analogs of Quercetin as Inhibitors of Cancer Cell Proliferation. Drug Dev. Res. 2014, 75, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Z.-H.; Li, N.-G.; Tang, Y.-P.; Yang, J.-P.; Duan, J.-A. Metabolism-based synthesis, biologic evaluation and SARs analysis of O-methylated analogs of quercetin as thrombin inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 54, 210–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gliszczyńska-Świgło, A.; van der Woude, H.; de Haan, L.; Tyrakowska, B.; Aarts, J.M.; Rietjens, I.M. The role of quinone reductase (NQO1) and quinone chemistry in quercetin cytotoxicity. Toxicol. Vitr. 2003, 17, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biasutto, L.; Marotta, E.; De Marchi, U.; Zoratti, M.; Paradisi, C. Ester-based precursors to increase the bioavailability of quercetin. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echeverry, C.; Arredondo, F.; Abin-Carriquiry, J.A.; Midiwo, J.O.; Ochieng, C.; Kerubo, L.; Dajas, F. Pretreatment with natural flavones and neuronal cell survival after oxidative stress: A structure− activity relationship study. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 2111–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaimand, K.; Rezaee, M.B.; Behrad, Z.; Najafy-Ashtiany, A. Comparison of extraction and measurement of quercetin from stigma, style, sepals, petals and stamen of Crocus sativus by HPLC in combination with heat and ultrasonic. J. Med. Plants By-Prod. 2012, 1, 167–170. [Google Scholar]
- Alok, S.; Jain, S.K.; Verma, A.; Kumar, M.; Mahor, A.; Sabharwal, M. Herbal antioxidant in clinical practice: A review. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2014, 4, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, L.G.; Garrick, J.M.; Roquè, P.J.; Pellacani, C. Mechanisms of neuroprotection by quercetin: Counteracting oxidative stress and more. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, M.; Kumar, V.; Malhotra, H.; Singh, S. Medicinal plants with potential anti-arthritic activity. J. Intercult. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 4, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.-S.; Zhou, R.; Yu, Y.-B.; Xiao, Y.; Li, D.-H.; Xiao, B.; Yu, O.; Yang, Y.-J. Cloning and characterization of a flavonoid 3′-hydroxylase gene from tea plant (Camellia sinensis). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, D.; Das, S.; Sabhapondit, S.; Tamuly, P.; Deka, D. Antimicrobial Activities of Tocklai Vegetative Tea Clones. Indian J. Microbiol. 2011, 51, 450–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Henagan, T.; Cefalu, W.; Ribnicky, D.; Noland, R.; Dunville, K.; Campbell, W.; Stewart, L.; Forney, L.; Gettys, T.; Chang, J. In vivo effects of dietary quercetin and quercetin-rich red onion extract on skeletal muscle mitochondria, metabolism, and insulin sensitivity. Genes Nutr. 2015, 10, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, T.T.; Campos, K.M.; Cerqueira-Lima, A.T.; Carneiro, T.C.B.; da Silva Velozo, E.; Melo, I.C.A.R.; Figueiredo, E.A.; de Jesus Oliveira, E.; de Vasconcelos, D.F.S.A.; Pontes-de-Carvalho, L.C. Potential therapeutic effect of Allium cepa L. and quercetin in a murine model of Blomia tropicalis induced asthma. Daru J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 23, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gondi, M.; Rao, U.P. Ethanol extract of mango (Mangifera indica L.) peel inhibits α-amylase and α-glucosidase activities, and ameliorates diabetes related biochemical parameters in streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic rats. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 7883–7893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leone, A.; Spada, A.; Battezzati, A.; Schiraldi, A.; Aristil, J.; Bertoli, S. Cultivation, genetic, ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry and pharmacology of Moringa oleifera leaves: An overview. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 12791–12835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saini, R.K.; Sivanesan, I.; Keum, Y.-S. Phytochemicals of Moringa oleifera: A review of their nutritional, therapeutic and industrial significance. 3 Biotech. 2016, 6, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, A.P.; Costa, R.M.; Magalhães, A.S.; Pereira, J.A.; Carvalho, M.; Valentão, P.; Andrade, P.B.; Silva, B.M. Targeted metabolites and biological activities of Cydonia oblonga Miller leaves. Food Res. Int. 2012, 46, 496–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apati, P.; Szentmihályi, K.; Balázs, A.; Baumann, D.; Hamburger, M.; Kristó, T.S.; Szőke, É.; Kéry, Á. HPLC analysis of the flavonoids in pharmaceutical preparations from Canadian goldenrod (Solidago canadensis). Chromatographia 2002, 56, S65–S68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.-y.; Zhang, H.-c.; Liu, W.-x.; Li, C.-y. Survey of antioxidant capacity and phenolic composition of blueberry, blackberry, and strawberry in Nanjing. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2012, 13, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roopchand, D.E.; Kuhn, P.; Rojo, L.E.; Lila, M.A.; Raskin, I. Blueberry polyphenol-enriched soybean flour reduces hyperglycemia, body weight gain and serum cholesterol in mice. Pharmacol. Res. 2013, 68, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altaf, R.; Asmawi, M.Z.B.; Dewa, A.; Sadikun, A.; Umar, M.I. Phytochemistry and medicinal properties of Phaleria macrocarpa (Scheff.) Boerl. extracts. Pharmacogn. Rev. 2013, 7, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, T.; Hussain, K.; Koul, S.; Vishwakarma, R.; Vyas, D. Evaluation of nutritional and antioxidant status of Lepidium latifolium Linn.: A novel phytofood from Ladakh. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.M.; Singh, S.; Pandey, P.; Grover, A.; Ahmed, Z. Semi-quantitative analysis of transcript accumulation in response to drought stress by Lepidium latifolium seedlings. Plant. Signal. Behav. 2013, 8, e25388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Srivastava, M.; Hegde, M.; Chiruvella, K.K.; Koroth, J.; Bhattacharya, S.; Choudhary, B.; Raghavan, S.C. Sapodilla plum (Achras sapota) induces apoptosis in cancer cell lines and inhibits tumor progression in mice. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Street, R.A.; Sidana, J.; Prinsloo, G. Cichorium intybus: Traditional uses, phytochemistry, pharmacology, and toxicology. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bovy, A.; Schijlen, E.; Hall, R.D. Metabolic engineering of flavonoids in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum): The potential for metabolomics. Metabolomics 2007, 3, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newcomb, R.D.; Crowhurst, R.N.; Gleave, A.P.; Rikkerink, E.H.; Allan, A.C.; Beuning, L.L.; Bowen, J.H.; Gera, E.; Jamieson, K.R.; Janssen, B.J. Analyses of expressed sequence tags from apple. Plant. Physiol. 2006, 141, 147–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manela, N.; Oliva, M.; Ovadia, R.; Sikron-Persi, N.; Ayenew, B.; Fait, A.; Galili, G.; Perl, A.; Weiss, D.; Oren-Shamir, M. Phenylalanine and tyrosine levels are rate-limiting factors in production of health promoting metabolites in Vitis vinifera cv. Gamay Red cell suspension. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esatbeyoglu, T.; Ewald, P.; Yasui, Y.; Yokokawa, H.; Wagner, A.E.; Matsugo, S.; Winterhalter, P.; Rimbach, G. Chemical characterization, free radical scavenging, and cellular antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of a stilbenoid-rich root extract of Vitis vinifera. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 8591286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boussahel, S.; Speciale, A.; Dahamna, S.; Amar, Y.; Bonaccorsi, I.; Cacciola, F.; Cimino, F.; Donato, P.; Ferlazzo, G.; Harzallah, D. Flavonoid profile, antioxidant and cytotoxic activity of different extracts from Algerian Rhamnus alaternus L. bark. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2015, 11, S102. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aman, U.; Subhan, F.; Shahid, M.; Akbar, S.; Ahmad, N.; Ali, G.; Fawad, K.; Sewell, R.D. Passiflora incarnata attenuation of neuropathic allodynia and vulvodynia apropos GABA-ergic and opioidergic antinociceptive and behavioural mechanisms. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 16, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, H.; Saeed, M.; Khan, M.A.; Muhammad, N.; Ghaffar, R. Isolation of long-chain esters from the rhizome of Polygonatum verticillatum by potent tyrosinase inhibition. Med. Chem. Res. 2013, 22, 2088–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Król, E.; Jeszka-Skowron, M.; Krejpcio, Z.; Flaczyk, E.; Wójciak, R.W. The effects of supplementary Mulberry leaf (Morus alba) extracts on the trace element status (Fe, Zn and Cu) in relation to diabetes management and antioxidant indices in diabetic rats. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2016, 174, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shepperd, W.D. Ginkgo biloba L.: Ginkgo. In The Woody Plant Seed Manual; Agricultural Handbook No. 727; Bonner, F.T., Karrfalt, R.P., Eds.; Department of Agriculture, Forest Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2008; pp. 559–561. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, P.-C.; Xia, Q.; Fu, P.P. Ginkgo biloba leave extract: Biological, medicinal, and toxicological effects. J. Environ. Sci. Health C Environ. Carcinog. Ecotoxicol. Rev. 2007, 25, 211–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, A.I.; Pinho, C.; Sarmento, B.; Dias, A.C. Neuroprotective activity of Hypericum perforatum and its major components. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedek, B.; Kopp, B. Achillea millefolium L. sl revisited: Recent findings confirm the traditional use. Wien. Med. Wochenschr. 2007, 157, 312–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Fang, Z.; Dou, J.; Yu, A.; Zhai, G. Bioavailability of quercetin: Problems and promises. Curr. Med. Chem. 2013, 20, 2572–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ader, P.; Wessmann, A.; Wolffram, S. Bioavailability and metabolism of the flavonol quercetin in the pig. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2000, 28, 1056–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, Y.J.; Wang, L.; DiCenzo, R.; Morris, M.E. Quercetin pharmacokinetics in humans. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 2008, 29, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, A.J.; Mellon, F.; Barron, D.; Sarrazin, G.; Morgan, M.R.; Williamson, G. Human metabolism of dietary flavonoids: Identification of plasma metabolites of quercetin. Free Radic. Res. 2001, 35, 941–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youdim, K.A.; Qaiser, M.Z.; Begley, D.J.; Rice-Evans, C.A.; Abbott, N.J. Flavonoid permeability across an in situ model of the blood–brain barrier. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2004, 36, 592–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youdim, K.A.; Dobbie, M.S.; Kuhnle, G.; Proteggente, A.R.; Abbott, N.J.; Rice-Evans, C. Interaction between flavonoids and the blood–brain barrier: In vitro studies. J. Neurochem. 2003, 85, 180–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kroemer, H.K.; Klotz, U. Glucuronidation of drugs. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1992, 23, 292–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, Y.; Nishikawa, T.; Shiba, Y.; Saito, S.; Murota, K.; Shibata, N.; Kobayashi, M.; Kanayama, M.; Uchida, K.; Terao, J. Macrophage as a target of quercetin glucuronides in human atherosclerotic arteries implication in the anti-atherosclerotic mechanism of dietary flavonoids. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 9424–9434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, B.D.; Chakrabarty, P.; Levites, Y.; Kukar, T.L.; Baine, A.-M.; Moroni, T.; Ladd, T.B.; Das, P.; Dickson, D.W.; Golde, T.E. Overlapping profiles of Aβ peptides in the Alzheimer’s disease and pathological aging brains. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2012, 4, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swomley, A.M.; Förster, S.; Keeney, J.T.; Triplett, J.; Zhang, Z.; Sultana, R.; Butterfield, D.A. Abeta, oxidative stress in Alzheimer disease: Evidence based on proteomics studies. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta 2014, 1842, 1248–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revett, T.J.; Baker, G.B.; Jhamandas, J.; Kar, S. Glutamate system, amyloid β peptides and tau protein: Functional interrelationships and relevance to Alzheimer disease pathology. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 2013, 38, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawkins, E.; Small, D.H. Insights into the physiological function of the β-amyloid precursor protein: Beyond Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurochem. 2014, 129, 756–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teich, A.F.; Arancio, O. Is the amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease therapeutically relevant? Biochem. J. 2012, 446, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, V.W.; Mattson, M.P.; Wong, P.C.; Gleichmann, M. An overview of APP processing enzymes and products. Neuromolecular Med. 2010, 12, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šimić, G.; Babić Leko, M.; Wray, S.; Harrington, C.; Delalle, I.; Jovanov-Milošević, N.; Bažadona, D.; Buée, L.; De Silva, R.; Di Giovanni, G. Tau protein hyperphosphorylation and aggregation in Alzheimer’s disease and other tauopathies, and possible neuroprotective strategies. Biomolecules 2016, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piedrahita, D.; Hernández, I.; López-Tobón, A.; Fedorov, D.; Obara, B.; Manjunath, B.; Boudreau, R.L.; Davidson, B.; LaFerla, F.; Gallego-Gómez, J.C. Silencing of CDK5 reduces neurofibrillary tangles in transgenic alzheimer’s mice. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 13966–13976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, P.T.; Alafuzoff, I.; Bigio, E.H.; Bouras, C.; Braak, H.; Cairns, N.J.; Castellani, R.J.; Crain, B.J.; Davies, P.; Tredici, K.D. Correlation of Alzheimer disease neuropathologic changes with cognitive status: A review of the literature. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2012, 71, 362–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.-C.; Zhao, N.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Cirrito, J.R.; Kanekiyo, T.; Holtzman, D.M.; Bu, G. Neuronal heparan sulfates promote amyloid pathology by modulating brain amyloid-β clearance and aggregation in Alzheimer’s disease. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, ra44–ra332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butterfield, D.A.; Swomley, A.M.; Sultana, R. Amyloid β-peptide (1–42)-induced oxidative stress in Alzheimer disease: Importance in disease pathogenesis and progression. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2013, 19, 823–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butterfield, D.A.; Di Domenico, F.; Barone, E. Elevated risk of type 2 diabetes for development of Alzheimer disease: A key role for oxidative stress in brain. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta 2014, 1842, 1693–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, R.C.; Lopez, O.; Armstrong, M.J.; Getchius, T.S.; Ganguli, M.; Gloss, D.; Gronseth, G.S.; Marson, D.; Pringsheim, T.; Day, G.S. Practice guideline update summary: Mild cognitive impairment: Report of the Guideline Development, Dissemination, and Implementation Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology 2018, 90, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Escudero, V.; Martín-Maestro, P.; Perry, G.; Avila, J. Deconstructing mitochondrial dysfunction in Alzheimer disease. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardas, S.S.; Sultana, R.; Clark, A.M.; Beckett, T.L.; Szweda, L.I.; Murphy, M.P.; Butterfield, D.A. Oxidative modification of lipoic acid by HNE in Alzheimer disease brain. Redox Biol. 2013, 1, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.H.; Wang, X.; Zhu, X. Mitochondrial defects and oxidative stress in Alzheimer disease and Parkinson disease. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2013, 62, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heneka, M.T.; Carson, M.J.; El Khoury, J.; Landreth, G.E.; Brosseron, F.; Feinstein, D.L.; Jacobs, A.H.; Wyss-Coray, T.; Vitorica, J.; Ransohoff, R.M. Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet Neurol. 2015, 14, 388–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Strooper, B.; Karran, E. The cellular phase of Alzheimer’s disease. Cell 2016, 164, 603–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank-Cannon, T.C.; Alto, L.T.; McAlpine, F.E.; Tansey, M.G. Does neuroinflammation fan the flame in neurodegenerative diseases? Mol. Neurodegener. 2009, 4, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, R.; Juranek, J.K.; Rai, V. RAGE axis in neuroinflammation, neurodegeneration and its emerging role in the pathogenesis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2016, 62, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, T.; Zahid, S.; Mahboob, A.; Mehpara Farhat, S. Cholinergic system and post-translational modifications: An insight on the role in Alzheimer’s disease. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2017, 15, 480–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savonenko, A.V.; Melnikova, T.; Hiatt, A.; Li, T.; Worley, P.F.; Troncoso, J.C.; Wong, P.C.; Price, D.L. Alzheimer’s therapeutics: Translation of preclinical science to clinical drug development. Neuropsychopharmacology 2012, 37, 261–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruana, M.; Cauchi, R.; Vassallo, N. Putative role of red wine polyphenols against brain pathology in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease. Front. Nutr. 2016, 3, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jantan, I.; Ahmad, W.; Bukhari, S.N.A. Plant-derived immunomodulators: An insight on their preclinical evaluation and clinical trials. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueira, I.; Menezes, R.; Macedo, D.; Costa, I.; Nunes dos Santos, C. Polyphenols beyond barriers: A glimpse into the brain. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2017, 15, 562–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ay, M.; Luo, J.; Langley, M.; Jin, H.; Anantharam, V.; Kanthasamy, A.; Kanthasamy, A.G. Molecular mechanisms underlying protective effects of quercetin against mitochondrial dysfunction and progressive dopaminergic neurodegeneration in cell culture and MitoPark transgenic mouse models of Parkinson’s Disease. J. Neurochem. 2017, 141, 766–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, A.V.A.; Arulmoli, R.; Parasuraman, S. Overviews of biological importance of quercetin: A bioactive flavonoid. Pharmacogn. Rev. 2016, 10, 84. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.T.H.; Orhan, I.; Şenol, F.; Kartal, M.; Şener, B.; Dvorská, M.; Šmejkal, K.; Šlapetová, T. Cholinesterase inhibitory activities of some flavonoid derivatives and chosen xanthone and their molecular docking studies. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2009, 181, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimmyo, Y.; Kihara, T.; Akaike, A.; Niidome, T.; Sugimoto, H. Flavonols and flavones as BACE-1 inhibitors: Structure–activity relationship in cell-free, cell-based and in silico studies reveal novel pharmacophore features. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta 2008, 1780, 819–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabogal-Guáqueta, A.M.; Munoz-Manco, J.I.; Ramírez-Pineda, J.R.; Lamprea-Rodriguez, M.; Osorio, E.; Cardona-Gómez, G.P. The flavonoid quercetin ameliorates Alzheimer’s disease pathology and protects cognitive and emotional function in aged triple transgenic Alzheimer’s disease model mice. Neuropharmacology 2015, 93, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.-M.; Li, S.-Q.; Wu, W.-L.; Zhu, X.-Y.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, H.-Y. Effects of long-term treatment with quercetin on cognition and mitochondrial function in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurochem. Res. 2014, 39, 1533–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richetti, S.; Blank, M.; Capiotti, K.; Piato, A.; Bogo, M.; Vianna, M.; Bonan, C. Quercetin and rutin prevent scopolamine-induced memory impairment in zebrafish. Behav. Brain Res. 2011, 217, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regitz, C.; Marie Dußling, L.; Wenzel, U. Amyloid-beta (Aβ1–42)-induced paralysis in Caenorhabditis elegans is inhibited by the polyphenol quercetin through activation of protein degradation pathways. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2014, 58, 1931–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Aliaga, K.; Bermejo-Bescós, P.; Benedí, J.; Martín-Aragón, S. Quercetin and rutin exhibit antiamyloidogenic and fibril-disaggregating effects in vitro and potent antioxidant activity in APPswe cells. Life Sci. 2011, 89, 939–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porat, Y.; Abramowitz, A.; Gazit, E. Inhibition of amyloid fibril formation by polyphenols: Structural similarity and aromatic interactions as a common inhibition mechanism. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2006, 67, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, M.; Murakami, K.; Uno, M.; Nakagawa, Y.; Katayama, S.; Akagi, K.-i.; Masuda, Y.; Takegoshi, K.; Irie, K. Site-specific inhibitory mechanism for amyloid β42 aggregation by catechol-type flavonoids targeting the Lys residues. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 23212–23224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paris, D.; Mathura, V.; Ait-Ghezala, G.; Beaulieu-Abdelahad, D.; Patel, N.; Bachmeier, C.; Mullan, M. Flavonoids lower Alzheimer’s Aβ production via an NFκB dependent mechanism. Bioinformation 2011, 6, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.; Luo, T.; Li, S.; Zhou, Y.; Shen, X.-Y.; He, F.; Xu, J.; Wang, H.-Q. Quercetin protects against okadaic acid-induced injury via MAPK and PI3K/Akt/GSK3β signaling pathways in HT22 hippocampal neurons. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdalla, F.H.; Schmatz, R.; Cardoso, A.M.; Carvalho, F.B.; Baldissarelli, J.; de Oliveira, J.S.; Rosa, M.M.; Nunes, M.A.G.; Rubin, M.A.; da Cruz, I.B. Quercetin protects the impairment of memory and anxiogenic-like behavior in rats exposed to cadmium: Possible involvement of the acetylcholinesterase and Na+, K+-ATPase activities. Physiol. Behav. 2014, 135, 152–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalla, F.H.; Cardoso, A.M.; Pereira, L.B.; Schmatz, R.; Gonçalves, J.F.; Stefanello, N.; Fiorenza, A.M.; Gutierres, J.M.; da Silva Serres, J.D.; Zanini, D. Neuroprotective effect of quercetin in ectoenzymes and acetylcholinesterase activities in cerebral cortex synaptosomes of cadmium-exposed rats. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2013, 381, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ademosun, A.O.; Oboh, G.; Bello, F.; Ayeni, P.O. Antioxidative properties and effect of quercetin and its glycosylated form (Rutin) on acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase activities. J. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 21, NP11–NP17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldissarelli, J.; Santi, A.; Schmatz, R.; Abdalla, F.H.; Cardoso, A.M.; Martins, C.C.; Dias, G.R.M.; Calgaroto, N.S.; Pelinson, L.P.; Reichert, K.P. Hypothyroidism enhanced ectonucleotidases and acetylcholinesterase activities in rat synaptosomes can be prevented by the naturally occurring polyphenol quercetin. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 37, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, M.; Park, M. Acetylcholinesterase inhibition by flavonoids from Agrimonia pilosa. Molecules 2007, 12, 2130–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, M.A.; Moffat, T.C.; Gable, K.; Ganesan, S.; Niewola-Staszkowska, K.; Johnston, A.; Nislow, C.; Giaever, G.; Harris, L.J.; Loewith, R. A signaling lipid associated with Alzheimer’s disease promotes mitochondrial dysfunction. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Jo, D.-G.; Park, D.; Chung, H.Y.; Mattson, M.P. Adaptive cellular stress pathways as therapeutic targets of dietary phytochemicals: Focus on the nervous system. Pharmacol. Rev. 2014, 66, 815–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butterfield, D.A. The 2013 discovery award from the society for free radical biology and medicine: Selected discoveries from the Butterfield Laboratory of Oxidative Stress and its sequelae in brain in cognitive disorders exemplified by Alzheimer disease and chemotherapy induced cognitive impairment. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2014, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakhanpal, P.; Rai, D.K. Quercetin: A versatile flavonoid. Internet J. Med. Update 2007, 2, 22–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testa, G.; Gamba, P.; Badilli, U.; Gargiulo, S.; Maina, M.; Guina, T.; Calfapietra, S.; Biasi, F.; Cavalli, R.; Poli, G. Loading into nanoparticles improves quercetin’s efficacy in preventing neuroinflammation induced by oxysterols. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.-W.; Koppula, S.; Park, S.-Y.; Hwang, J.-W.; Park, P.-J.; Lim, J.-H.; Choi, D.-K. Attenuation of inflammatory-mediated neurotoxicity by Saururus chinensis extract in LPS-induced BV-2 microglia cells via regulation of NF-κB signaling and anti-oxidant properties. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 14, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qureshi, A.A.; Tan, X.; Reis, J.C.; Badr, M.Z.; Papasian, C.J.; Morrison, D.C.; Qureshi, N. Inhibition of nitric oxide in LPS-stimulated macrophages of young and senescent mice by δ-tocotrienol and quercetin. Lipids Health Dis. 2011, 10, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, J.M.; Murphy, E.A.; Carmichael, M.D. Effects of the dietary flavonoid quercetin upon performance and health. Curr. Sports Med. Rep. 2009, 8, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belo, D.; André, C.; Lucho, A.P.d.B.; Vinadé, L.; Rocha, L.; Seibert França, H.; Marangoni, S.; Rodrigues-Simioni, L. In vitro antiophidian mechanisms of Hypericum brasiliense choisy standardized extract: Quercetin-dependent neuroprotection. Biomed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 943520. [Google Scholar]
- Ansari, M.A.; Abdul, H.M.; Joshi, G.; Opii, W.O.; Butterfield, D.A. Protective effect of quercetin in primary neurons against Aβ (1–42): Relevance to Alzheimer’s disease. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2009, 20, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, S.; Bhugra, P. Emerging drug targets for Aβ and tau in Alzheimer’s disease: A systematic review. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2015, 80, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalingam, K.B.; Radhakrishnan, A.; Ramdas, P.; Haleagrahara, N. Quercetin glycosides induced neuroprotection by changes in the gene expression in a cellular model of Parkinson’s disease. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2015, 55, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.-s.; Wang, J.-l.; Feng, D.-y.; Qin, H.-z.; Wen, H.; Yin, Z.-m.; Gao, G.-d.; Li, C. Protective effect of quercetin against oxidative stress and brain edema in an experimental rat model of subarachnoid hemorrhage. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2014, 11, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Srivastav, S.; Yadav, A.K.; Srikrishna, S.; Perry, G. Overview of Alzheimer’s disease and some therapeutic approaches targeting Aβ by using several synthetic and herbal compounds. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 7361613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keddy, P.G.; Dunlop, K.; Warford, J.; Samson, M.L.; Jones, Q.R.; Rupasinghe, H.V.; Robertson, G.S. Neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory effects of the flavonoid-enriched fraction AF4 in a mouse model of hypoxic-ischemic brain injury. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tota, S.; Awasthi, H.; Kamat, P.K.; Nath, C.; Hanif, K. Protective effect of quercetin against intracerebral streptozotocin induced reduction in cerebral blood flow and impairment of memory in mice. Behav. Brain Res. 2010, 209, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ossola, B.; Kääriäinen, T.M.; Männistö, P.T. The multiple faces of quercetin in neuroprotection. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2009, 8, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| S.No. | Botanical Name | Family | Common Name | Active Parts | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 01 | Punica granatum | Lythraceae | Pomegranate | Fruits | [51] |
| 02 | Ruta graveolens | Rutaceae | Rue | Leaves | [51] |
| 03 | Camellia sinensis | Theaceae | Green tea | Leaves | [52,53] |
| 04 | Allium cepa | Amaryllidaceae | Red onion | Fruits | [54,55] |
| 05 | Mangifera indica | Anacardiaceae | Mango | Fruits | [56] |
| 06 | Moringa oleifera | Moringaceae | Drumstick tree | Leaves | [57,58] |
| 07 | Cydonia oblonga | Rosaceae | Quince | Fruits and leaves | [59] |
| 08 | Solidago canadensis L. | Compositae/ Asteraceae | Goldenrod | Flowering parts | [60] |
| 09 | Vaccinium angustifolium and Vaccinium corymbosum | Ericaceae | Blueberries | Fruits | [61,62] |
| 10 | Phaleria macrocarpa | Thymelaceae | Mahkotadewa | Seeds | [63] |
| 11 | Lepidium latifolium | Brassicaceae | Papperweed | Roots and leaves | [64,65] |
| 12 | Achras sapota (Manilkara zapota) | Sapotaceae | Sapodilla | Fruits | [66] |
| 13 | Cichorium intybus | Compositae/ Asteraceae | Chicory | Leaves | [67] |
| 14 | Solanum lycopersicum | Solanaceae | Tomato | Fruits | [68] |
| 15 | Malus domestica | Rosaceae | Apple | Fruits | [69] |
| 16 | Vitis vinifera | Vitaceae | Grapevines | Fruits | [70,71] |
| 17 | Rhamnus alaternus | Rhamnaceae | Buckthorn | Bark | [72] |
| 18 | Passiflora incarnate | Passifloraceae | Passion flower | Leaves | [73] |
| 19 | Morus alba | Moraceae | White mulberry or Tut | Leaves | [74,75] |
| 20 | Ginkgo biloba | Ginkgoaceae | Maidenhair tree | Leaves | [76,77] |
| 21 | Hypericum perforatum | Hypericaceae | St. John’s wort or hypericum | Aerial parts | [78] |
| 22 | Achillea millefolium L. | Compositae/ Asteraceae | Yarrow | Flowering tops | [79] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khan, H.; Ullah, H.; Aschner, M.; Cheang, W.S.; Akkol, E.K. Neuroprotective Effects of Quercetin in Alzheimer’s Disease. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10010059
Khan H, Ullah H, Aschner M, Cheang WS, Akkol EK. Neuroprotective Effects of Quercetin in Alzheimer’s Disease. Biomolecules. 2020; 10(1):59. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10010059
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhan, Haroon, Hammad Ullah, Michael Aschner, Wai San Cheang, and Esra Küpeli Akkol. 2020. "Neuroprotective Effects of Quercetin in Alzheimer’s Disease" Biomolecules 10, no. 1: 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10010059
APA StyleKhan, H., Ullah, H., Aschner, M., Cheang, W. S., & Akkol, E. K. (2020). Neuroprotective Effects of Quercetin in Alzheimer’s Disease. Biomolecules, 10(1), 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10010059









