Monte Carlo FLUKA Simulation of Gamma Backscattering for Rebar Detection in Reinforced Concrete with Basaltic Aggregates
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Physical Basis of Compton Scattering
3. Materials and Methods
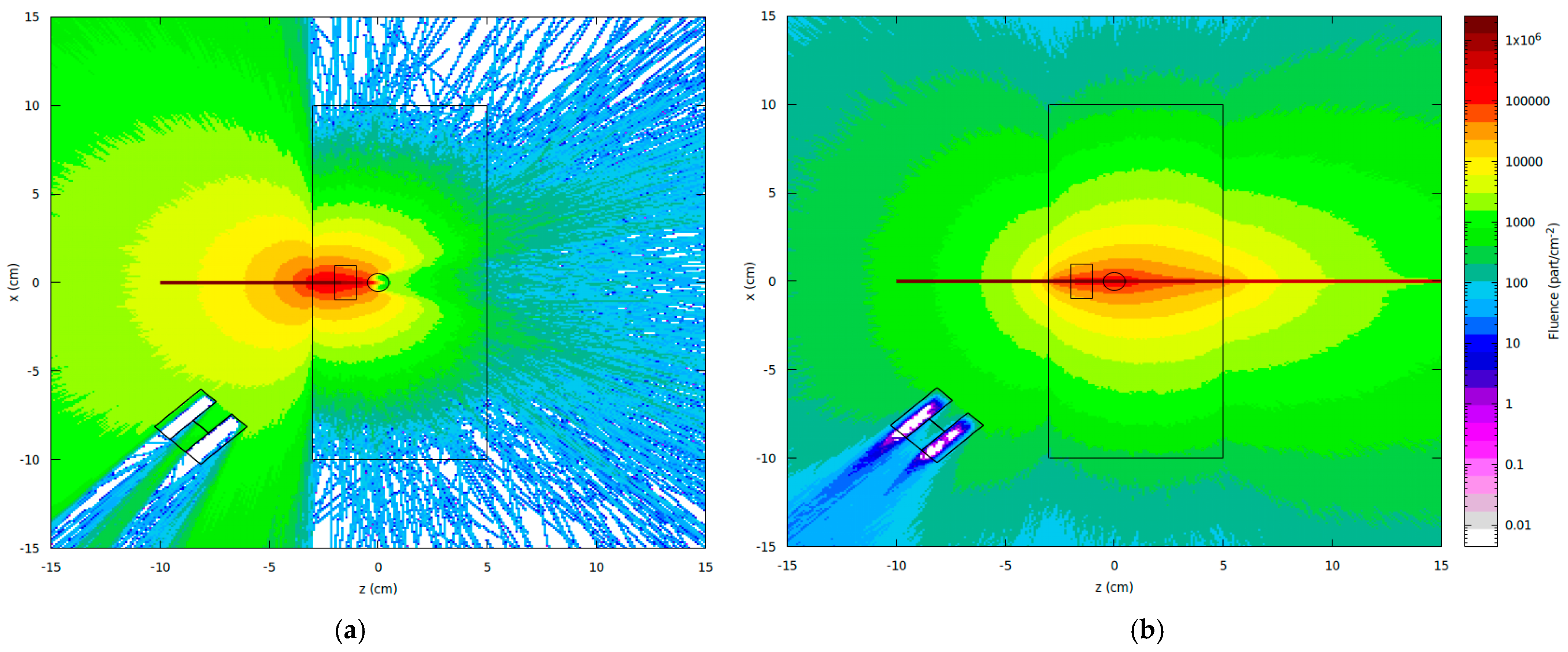
3.1. Monte Carlo Simulation
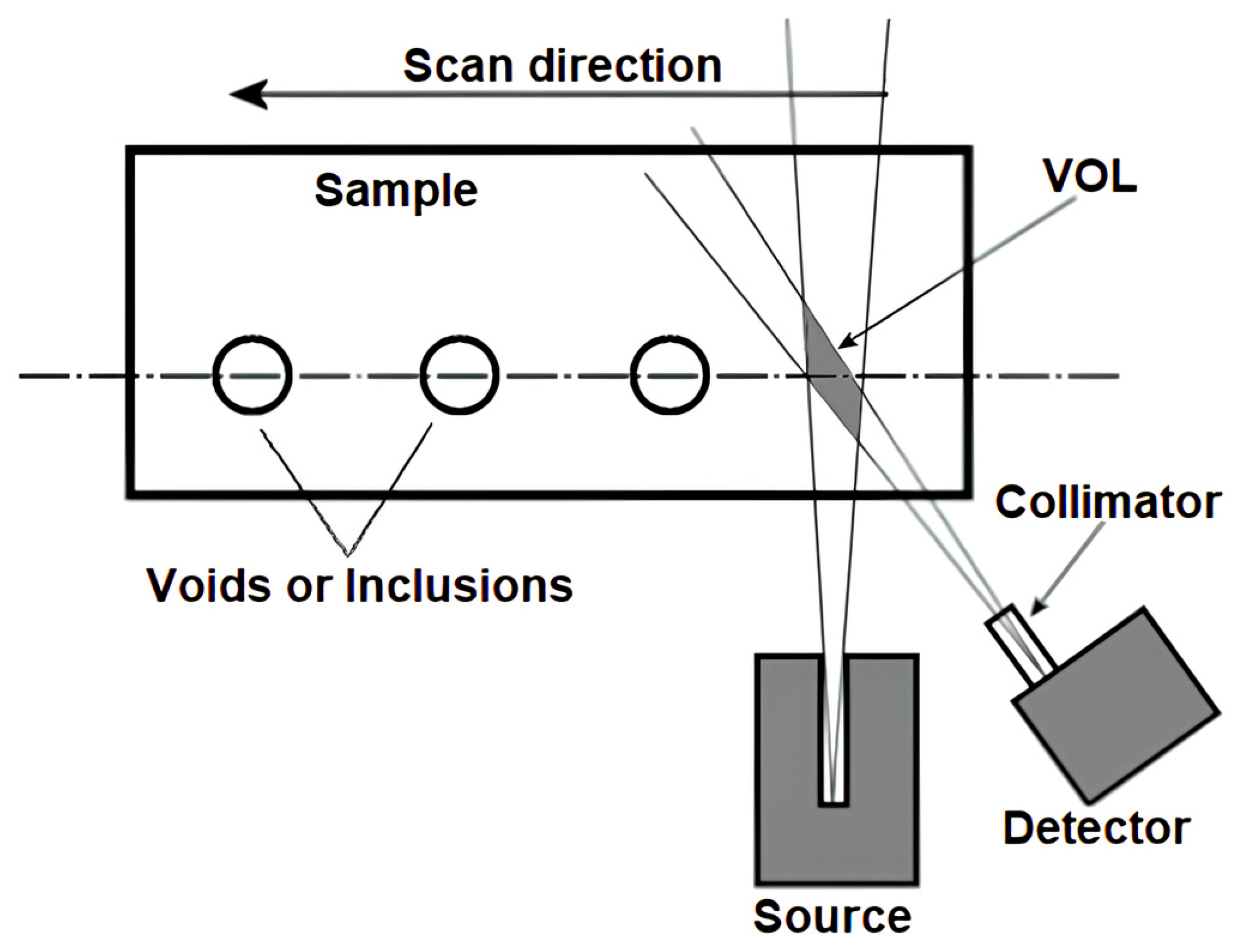
3.2. Study Case
3.3. Beam Energies and Scanning Positions
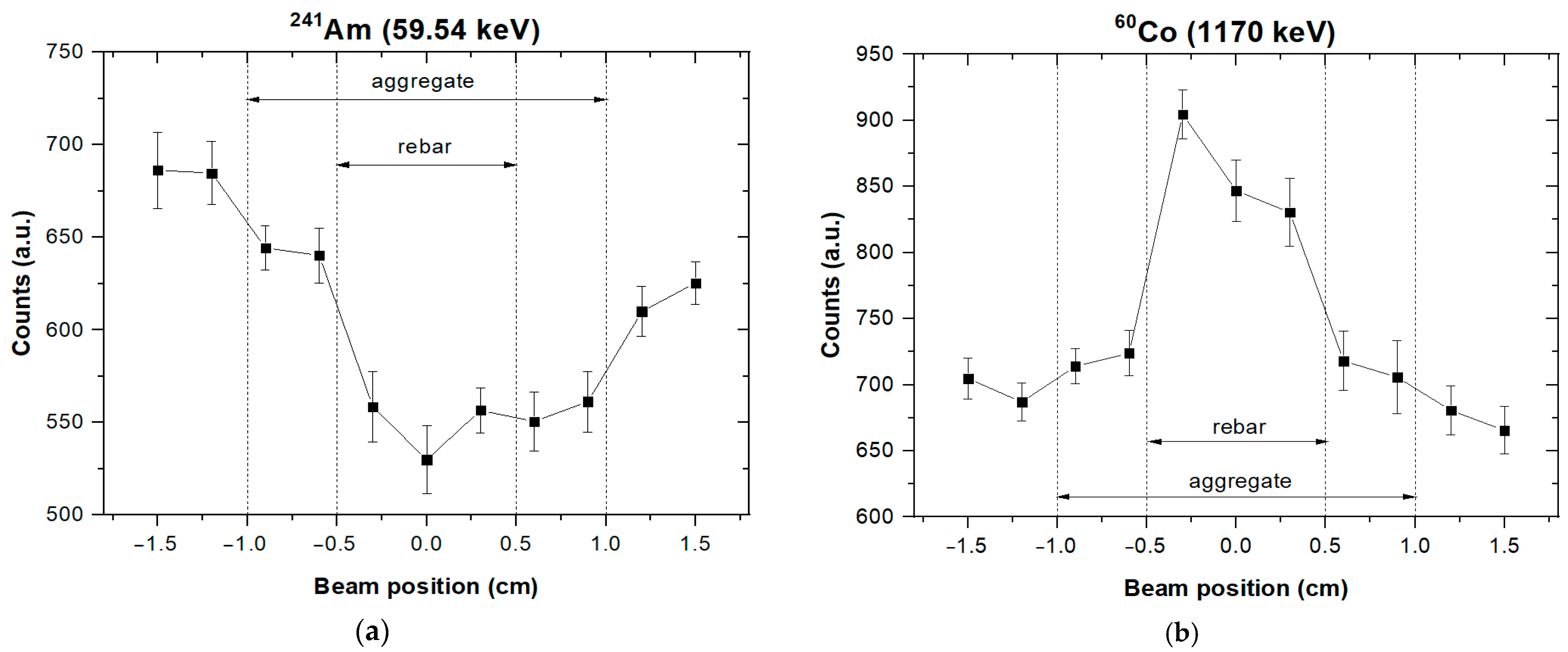
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| VOL | inspection volume |
References
- Rodrigues, R.; Gaboreau, S.; Gance, J.; Ignatiadis, I.; Betelu, S. Reinforced concrete structures: A review of corrosion mechanisms and advances in electrical methods for corrosion monitoring. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 269, 121240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsener, B.; Angst, U. Corrosion of steel in concrete: New challenges. In Encyclopedia of Interfacial Chemistry Surface Science and Electrochemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamasemani, N.F.; Kelishadi, M.; Mostafaei, H.; Najvani, M.A.D.; Mashayekhi, M. Environmental impacts of reinforced concrete buildings: Comparing common and sustainable materials: A case study. Constr. Mater. 2024, 4, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wu, X.; Nie, Q.; Yu, J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Q.; Gao, Q. Lifetime prediction of damaged or cracked concrete structures: A review. Structures 2025, 71, 108095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, B.S.; Castela, A.S.; Silva, M.A.; Duarte, R.G.; Ferreira, M.G.S.; Montemor, M.F. Influence of GFRP confinement of reinforced concrete columns on the corrosion of reinforcing steel in a salt water environment. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2014, 27, 04014107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bichsel, H.; Schindler, H. The interaction of radiation with matter. In Particle Physics Reference Library: Detectors for Particles and Radiation; Fabjan, C.W., Schopper, H., Eds.; Springer: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 2, pp. 5–44. [Google Scholar]
- Sharaf, J.M. Practical aspects of Compton scatter densitometry. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2001, 54, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, G.; Harding, E. Compton scatter imaging: A tool for historical exploration. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2010, 68, 993–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuzi, S.; Sato, O. Determination of positions of reinforcing bars in reinforced concrete by backscattered gamma rays—II. Experimental and Monte Carlo results. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 1993, 44, 1279–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, E.M.; Whynot, T.M. A Compton scattering method for inspecting concrete structures. Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 1989, 283, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Sandhu, B.S.; Singh, B. A gamma ray tomographic densitometer system for the investigation of concrete structures. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 2011, 59, 2880–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyada, P.; Ramar, R. Application of gamma ray scattering technique for non-destructive evaluation of voids in concrete. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2013, 74, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boldo, E.M.; Appoloni, C.R. Inspection of reinforced concrete samples by Compton backscattering technique. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2014, 95, 392–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Villaverde, E.R.; Vul, S.N.; Nguyen, M.K.; Noumowé, A. A new Compton Scattered Tomography Modality and Its Application to Material Non-Destructive Evaluation. Int. Refer. J. Eng. Sci. 2015, 4, 13–19. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, M.; Shams, M.A.; Bheel, N.; Almaliki, A.H.; Mahmoud, A.S.; Dodo, Y.A.; Benjeddou, O. A review on chloride induced corrosion in reinforced concrete structures: Lab and in situ investigation. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 37252–37271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margret, M.; Menaka, M.; Venkatraman, B.; Chandrasekaran, S. Compton back scatter imaging for mild steel rebar detection and depth characterization embedded in concrete. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. B 2015, 343, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, M.; Mijnarends, P.; Shiotani, N.; Sakai, N.; Bansil, A. X-Ray Compton Scattering, 1st ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2004; pp. 5–10. [Google Scholar]
- Ball, A.J.; Solomon, C.J.; Zarnecki, J.C. The response of gamma backscatter density gauges to spatial inhomogeneity—An extension of the single scattering model. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. B 1998, 140, 449–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knoll, G.F. Radiation Detection and Measurement, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Salgado, C.M.; Salgado, W.L.; de Freitas Dam, R.S.; Conti, C.C. Calculation of scales in oil pipeline using gamma-ray scattering and artificial intelligence. Measurement 2021, 179, 109455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Singh, G.; Sandhu, B.S.; Singh, B. Effect of detector collimator and sample thickness on 0.662 MeV multiply Compton-scattered gamma rays. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2006, 64, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Xiao, Y.; Dong, M.; Ouyang, X.; Shen, M.; Lan, D.; Ma, P. Multiple scattering correction with Monte Carlo simulations for Compton backscatter tomography. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 2025, 1075, 170411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wart, J.A.; Hussein, E.M.; Waller, E.J. Detection and localization of money bills concealed behind wooden walls using Compton scattering. Nucl. Technol. 2005, 150, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasso, A.; Ferrari, A.; Ranft, J.; Sala, P.R. FLUKA: A Multi-Particle Transport Code. CERN-2005-10 2005, SLAC-R-773, 24–28. Available online: https://www.slac.stanford.edu/pubs/slacreports/reports16/slac-r-773.pdf (accessed on 1 March 2025).
- Ahdida, C.; Bozzato, D.; Calzolari, D.; Cerutti, F.; Charitonidis, N.; Cimmino, A.; Coronetti, A.; D’aLessandro, G.L.; Servelle, A.D.; Esposito, L.S.; et al. New capabilities of the FLUKA multi-purpose code. Front. Phys. 2022, 9, 788253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battistoni, G.; Boehlen, T.; Cerutti, F.; Chin, P.W.; Esposito, L.S.; Fassò, A.; Ferrari, A.; Lechner, A.; Empl, A.; Mairani, A.; et al. Overview of the FLUKA code. Ann. Nucl. Energy 2015, 82, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malano, F.; Mattea, F.; Geser, F.A.; Pérez, P.; Barraco, D.; Santibáñez, M.; Figueroa, R.; Valente, M. Assessment of FLUKA, PENELOPE and MCNP6 Monte Carlo codes for estimating gold fluorescence applied to the detection of gold-infused tumoral volumes. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2019, 151, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oranj, L.M.; Bakhtiari, M.; Kye, Y.U.; Jung, N.S.; Lee, A.; Lee, H.S. Benchmarking FLUKA, PHITS, MCNPX, and MARS15 codes with product yields of 209Bi (p, x) reactions. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. B 2020, 462, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugo, G.; Ahdida, C.; Bozzato, D.; Calzolari, D.; Cerutti, F.; Ciccotelli, A.; Cimmino, A.; Devienne, A.; Servelle, A.D.; Dyrcz, P.K.; et al. Latest FLUKA developments. EPJ Nucl. Sci. Technol. 2024, 10, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donadon, A.; Hugo, G.; Theis, C.; Vlachoudis, V. FLAIR3–recasting simulation experiences with the Advanced Interface for FLUKA and other Monte Carlo codes. EPJ Web Conf. 2024, 302, 11005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NBR 7211; Aggregates for Concrete—Specification. Brazilian Association of Technical Standards (ABNT): Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2005; 12p.
- Sunny, J.E.; Varghese, R.A.; Sagar, S.; John, S.; Kassim, R. Application of basalt and its products in civil engineering. Int. J. Eng. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, M.P.B.; Gomes, L.D.S.S.; Silva, A.R.; Tamashiro, J.R.; Paiva, F.F.G.; Silva, L.H.P.; Kinoshita, A. Basalt Rock Powder in Cementitious Materials: A Systematic Review. Resources 2025, 14, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babievskaya, I.Z.; Drobot, N.F.; Fomichev, S.V.; Krenev, V.A. Calculation of the mineral composition of basaltic rocks. Inorg. Mater. 2009, 45, 916–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomaz, W.D.A. Contribuição ao Estudo do Módulo de Elasticidade Estático e Dinâmico de Concretos Contendo Agregados Basálticos: Análise Experimental e Proposta de Modelo de Correlação. Master’s Thesis, Universidade Federal da Integração Latino-Americana, Foz do Iguaçu, Brazil, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Hubbell, J.H. Photon mass attenuation and energy-absorption coefficients. Int. J. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 1982, 33, 1269–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iori, A.O.G.; Kassahara, L.N.; Boldo, E.M. Non-destructive evaluation of reinforced concrete using the Compton backscattering technique. In Proceedings of the 71ª Reunião Anual da SBPC, Campo Grande, Brazil, 21–27 July 2019; Available online: http://reunioessbpc.org.br/campogrande/inscritos/resumos/5085_144336c66f38804c3c225795c3be9c503.pdf (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- Scannavino, F.; Cruvinel, P. A graphical tool for an analytical approach of scattering photons by the Compton effect. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 2012, 674, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obaid, S.S.; Sayyed, M.I.; Gaikwad, D.K.; Pawar, P.P. Attenuation coefficients and exposure buildup factor of some rocks for gamma ray shielding applications. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2018, 148, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salisu, A.M.; Abaleni, J.I.; Aisha, A.S. Determination of shielding effectiveness of concretes with different aggregate and cement composition. Phys. Access 2023, 2, 78–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Oxid. | SiO2 | Fe2O3 | Al2O3 | CaO | MgO | Na2O3 | TiO2 | K2O | P2O5 | MnO | SrO | ZnO | ZrO2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % | 50.5 | 15.5 | 14.2 | 10.0 | 4.1 | 2.5 | 1.3 | 1.0 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| Density Contrast (%) | ||
|---|---|---|
| 241Am | 60Co | |
| Cement/Aggregate | 6.31 | 3.31 |
| Aggregate/Steel Rebar | 20.02 | 20.13 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iori, A.O.G.; Boldo, E.M. Monte Carlo FLUKA Simulation of Gamma Backscattering for Rebar Detection in Reinforced Concrete with Basaltic Aggregates. Atoms 2025, 13, 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/atoms13070067
Iori AOG, Boldo EM. Monte Carlo FLUKA Simulation of Gamma Backscattering for Rebar Detection in Reinforced Concrete with Basaltic Aggregates. Atoms. 2025; 13(7):67. https://doi.org/10.3390/atoms13070067
Chicago/Turabian StyleIori, Alexandre Osni Gral, and Emerson Mario Boldo. 2025. "Monte Carlo FLUKA Simulation of Gamma Backscattering for Rebar Detection in Reinforced Concrete with Basaltic Aggregates" Atoms 13, no. 7: 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/atoms13070067
APA StyleIori, A. O. G., & Boldo, E. M. (2025). Monte Carlo FLUKA Simulation of Gamma Backscattering for Rebar Detection in Reinforced Concrete with Basaltic Aggregates. Atoms, 13(7), 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/atoms13070067






