Role of Intestinal Microbiota in Metabolism of Gastrodin In Vitro and In Vivo
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Method Development and Validation
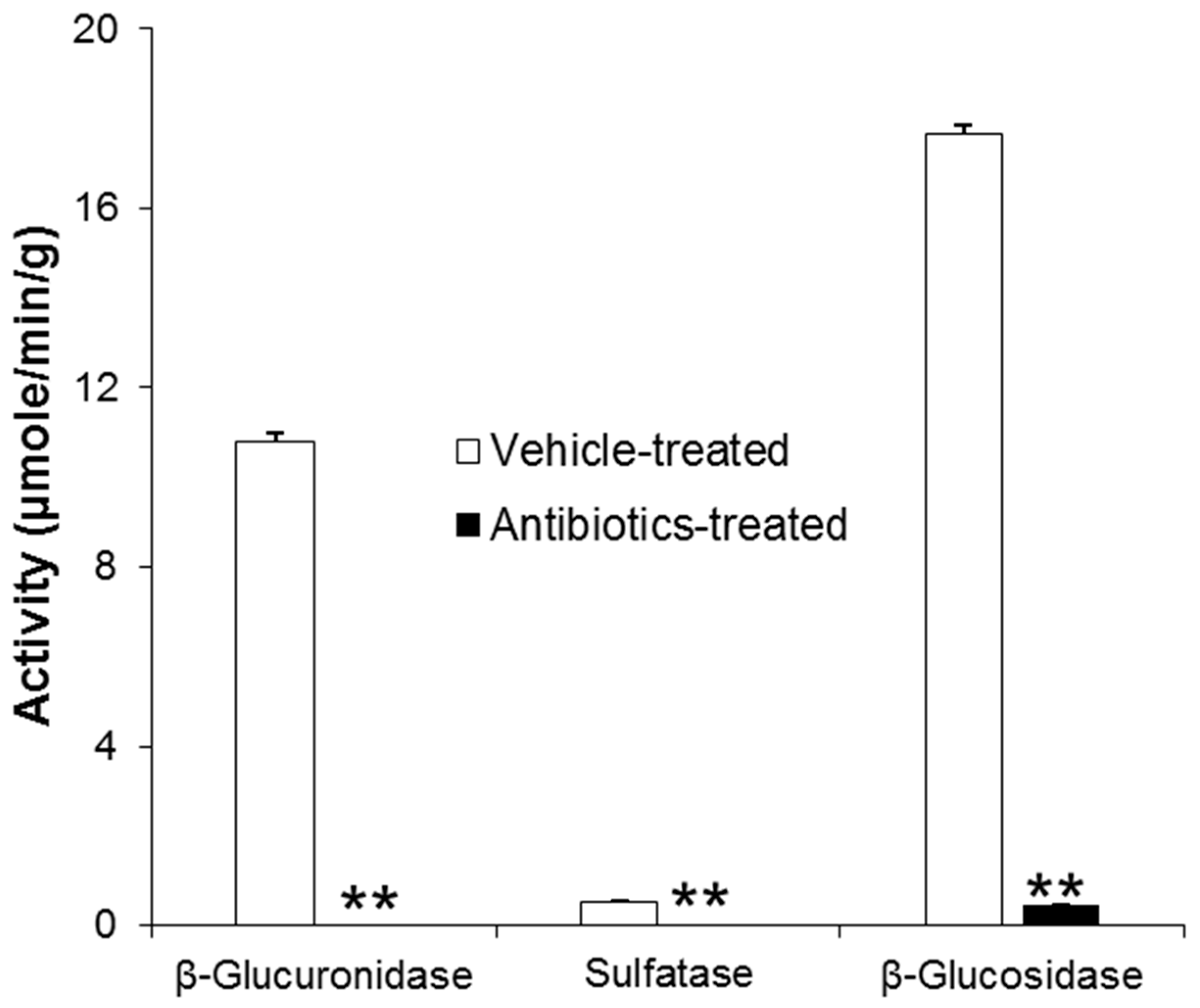
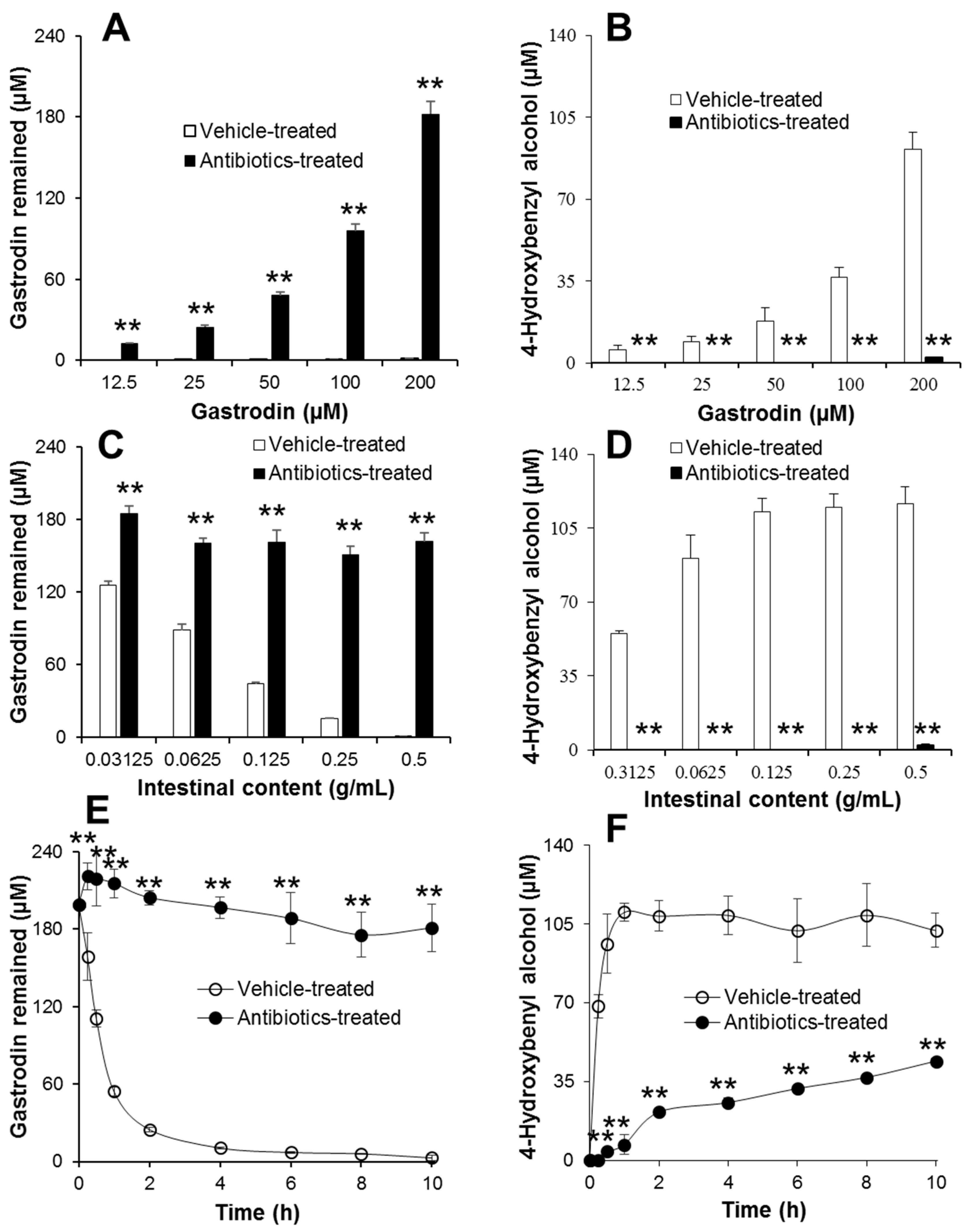
2.2. In Vitro Metabolism of Gastrodin in Vehicle- and Antibiotics-Treated Rats
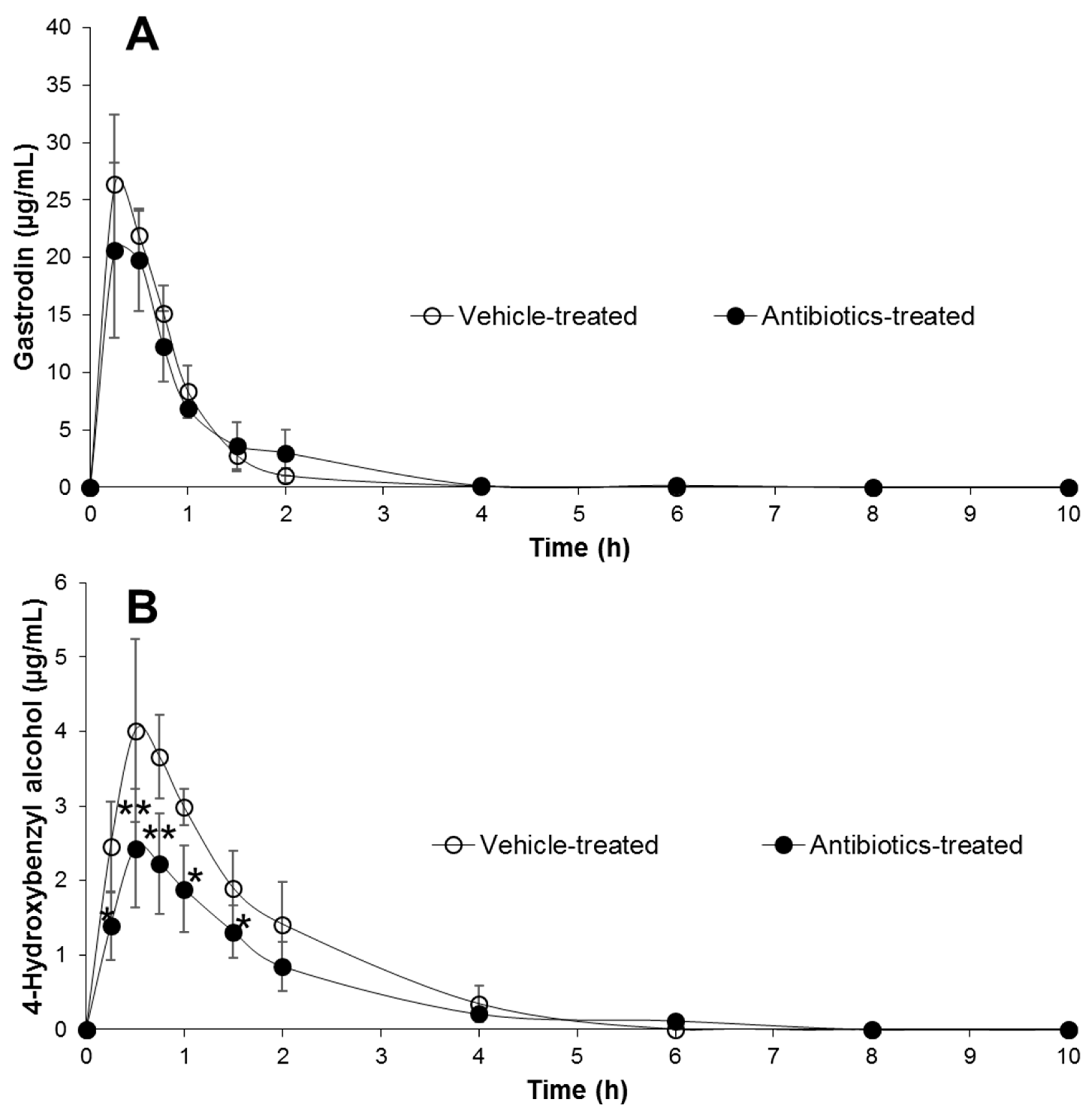
2.3. Pharmacokinetics of Gastrodin in Rats
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Animals
4.3. Animal Treatment
4.4. Analytical Conditions
4.5. Analytical Validation
4.6. Assays of β-Glucuronidase, Sulfatase, and β-Glucosidase Activities
4.7. In Vitro Metabolism of Gastrodin
4.8. Pharmacokinetic Study of Gastrodin
4.9. Pharmacokinetic Parameters and Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cummings, J.H.; Macfarlane, G.T. Role of intestinal bacteria in nutrient metabolism. J. Parenter. Enteral Nutr. 1997, 21, 357–365. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, L.; Zhang, J. Role of intestinal microbiota and metabolites on gut homeostasis and human diseases. BMC Immunol. 2017, 18, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, I.D.; Nicholson, J.K. Gut microbiome interactions with drug metabolism, efficacy, and toxicity. Transl. Res. 2017, 179, 204–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Gao, J.; Peng, M.; Meng, H.; Ma, H.; Cai, P.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Si, G. A review on central nervous system effects of gastrodin. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, L.C.; Chen, Y.F.; Tsai, T.R.; Tsai, T.H. Analysis of brain distribution and biliary excretion of a nutrient supplement, gastrodin, in rat. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 590, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, M.T.; Wu, C.R.; Chen, C.F. Gastrodin and p-hydroxybenzyl alcohol facilitate memory consolidation and retrieval, but not acquisition, on the passive avoidance task in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1997, 56, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.G.; Kang, M.J.; Kim, H.G.; Oh, D.G.; Kim, J.S.; Lee, S.K.; Jeong, T.C. Role of intestinal microflora in xenobiotic-induced toxicity. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2013, 57, 84–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Y.; Li, X.; Xie, H.; Shen, J.; Luo, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, K.D.; Liu, Q.; Kong, L. Analysis and pharmacokinetics studies of gastrodin and p-hydroxybenzyl alcohol in dogs using ultra fast liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2014, 99, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.C.; Chen, Y.F.; Lee, W.C.; Wu, Y.T.; Tsai, T.H. Pharmacokinetics of gastrodin and its metabolite p-hydroxybenzyl alcohol in rat blood, brain and bile by microdialysis coupled to LC-MS/MS. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2008, 48, 909–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Chen, G.; Zeng, S. Distribution and metabolism of gastrodin in rat brain. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2008, 46, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.J.; Ko, G.S.; Oh, D.G.; Kim, J.S.; Noh, K.; Kang, W.; Yoon, W.K.; Kim, H.C.; Jeong, H.G.; Jeong, T.C. Role of metabolism by intestinal microbiota in pharmacokinetics of oral baicalin. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2014, 37, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.; Wang, L.; Li, J.; Liu, X.; Cheng, M.; Xiao, H. Analysis of the metabolic profile of parishin by ultra-performance liquid chromatography/quadrupole-time of flight mass spectrometry. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2015, 29, 1913–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, E.S.; Heng, M.Y.; Tan, S.N.; Hong Yong, J.W.; Koh, H.; Teo, C.C.; Hew, C.S. Determination of gastrodin and vanillyl alcohol in Gastrodia elata Blume by pressurized liquid extraction at room temperature. J. Sep. Sci. 2007, 30, 2130–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Ma, P.; Xu, Y.; Zhan, M.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, S.; Zhang, S. Preventive effect of gastrodin on cognitive decline after cardiac surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass: A double-blind, randomized controlled study. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technolog. Med. Sci. 2011, 31, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, F.; Wang, X.; Shang, B.; Fang, J.; Xi, Y.; Li, A.; Diao, Y. Gastrodin ameliorates spinal cord injury via antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2016, 63, 589–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.L.; Xing, G.H.; Hong, B.; Li, X.M.; Zou, Y.; Zhang, X.J.; Dong, M.X. Gastrodin prevents motor deficits and oxidative stress in the MPTP mouse model of Parkinson’s disease: Involvement of ERK1/2-Nrf2 signaling pathway. Life Sci. 2014, 114, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, H.; Kim, I.S.; More, S.V.; Kim, B.W.; Bahk, Y.Y.; Choi, D.K. Gastrodin protects apoptotic dopaminergic neurons in a toxin-induced Parkinson’s disease model. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2013, 2013, 514095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kren, V.; Rezanka, T. Sweet antibiotics—The role of glycosidic residues in antibiotic and antitumor activity and their randomization. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2008, 32, 858–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appelt, H.R.; Oliveira, J.S.; Santos, R.C.V.; Rodrigues, O.E.D.; Santos, M.Z.; Heck, E.F.; Rosa, L.C. Synthesis and antimicrobial activity of carbohydrate based schiff bases: Importance of sugar moiety. Int. J. Carbohydr. Chem. 2013, 2013, 320892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utzschneider, K.M.; Kratz, M.; Damman, C.J.; Hullarg, M. Mechanisms linking the gut microbiome and glucose metabolism. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 101, 1445–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hertz, F.B.; Løbner-Olesen, A.; Frimodt-Møller, N. Antibiotic selection of Escherichia coli sequence type 131 in a mouse intestinal colonization model. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 6139–6144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Yoo, D.H.; Kim, I.S.; Van Le, T.K.; Jung, I.H.; Yoo, H.H.; Kim, D.H. Gut microbiota-mediated drug interactions between lovastatin and antibiotics. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2014, 42, 1508–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Wu, B.; Tang, C.; Zhao, J. Analytical techniques and pharmacokinetics of Gastrodia elata Blume and its constituents. Molecules 2017, 22, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Z.; Huang, J.; Luo, H.; Lei, X.; Yang, Z.; Mai, Y.; Liu, Z. Role of glucose transporters in the intestinal absorption of gastrodin, a highly water-soluble drug with good oral bioavailability. J. Drug Target. 2013, 21, 574–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.J.; Khanal, T.; Kim, H.G.; Lee, D.H.; Yeo, H.K.; Lee, Y.S.; Ahn, Y.T.; Kim, D.H.; Jeong, H.G.; Jeong, T.C. Role of metabolism by human intestinal microflora in geniposide-induced toxicity in HepG2 cells. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2012, 35, 733–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Ko, G. Effect of metformin on metabolic improvement and gut microbiota. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 5935–5943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; He, J.; Jia, W. The influence of gut microbiota on drug metabolism and toxicity. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2016, 12, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanca, A.; Palomba, A.; Pisanu, S.; Addis, M.F.; Uzzau, S. A human gut metaproteomic dataset from stool samples pretreated or not by differential centrifugation. Data Brief. 2015, 4, 559–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USFDA. Guidance for Industry on Bioanalytical Method Validation. Available online: https:// www.fda.gov/ucm/groups/fdagov-public/@fdagov-drugs-gen/documents/document/ucm368107.pdf (accessed on 7 April 2019).
- Jin, M.J.; Kim, U.; Kim, I.S.; Kim, Y.; Kim, D.-H.; Han, S.B.; Kim, D.-H.; Kwon, O.-S.; Yoo, H.H. Effects of gut microflora on pharmacokinetics of hesperidin: A study on non-antibiotic and pseudo-germ-free rats. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 2010, 73, 1441–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, K.; Nepal, M.R.; Jeong, K.S.; Kim, S.A.; Um, Y.J.; Seo, C.S.; Kang, M.J.; Park, P.H.; Kang, W.; Jeong, H.G. Effects of baicalin on oral pharmacokinetics of caffeine in rats. Biomol. Ther. 2015, 23, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

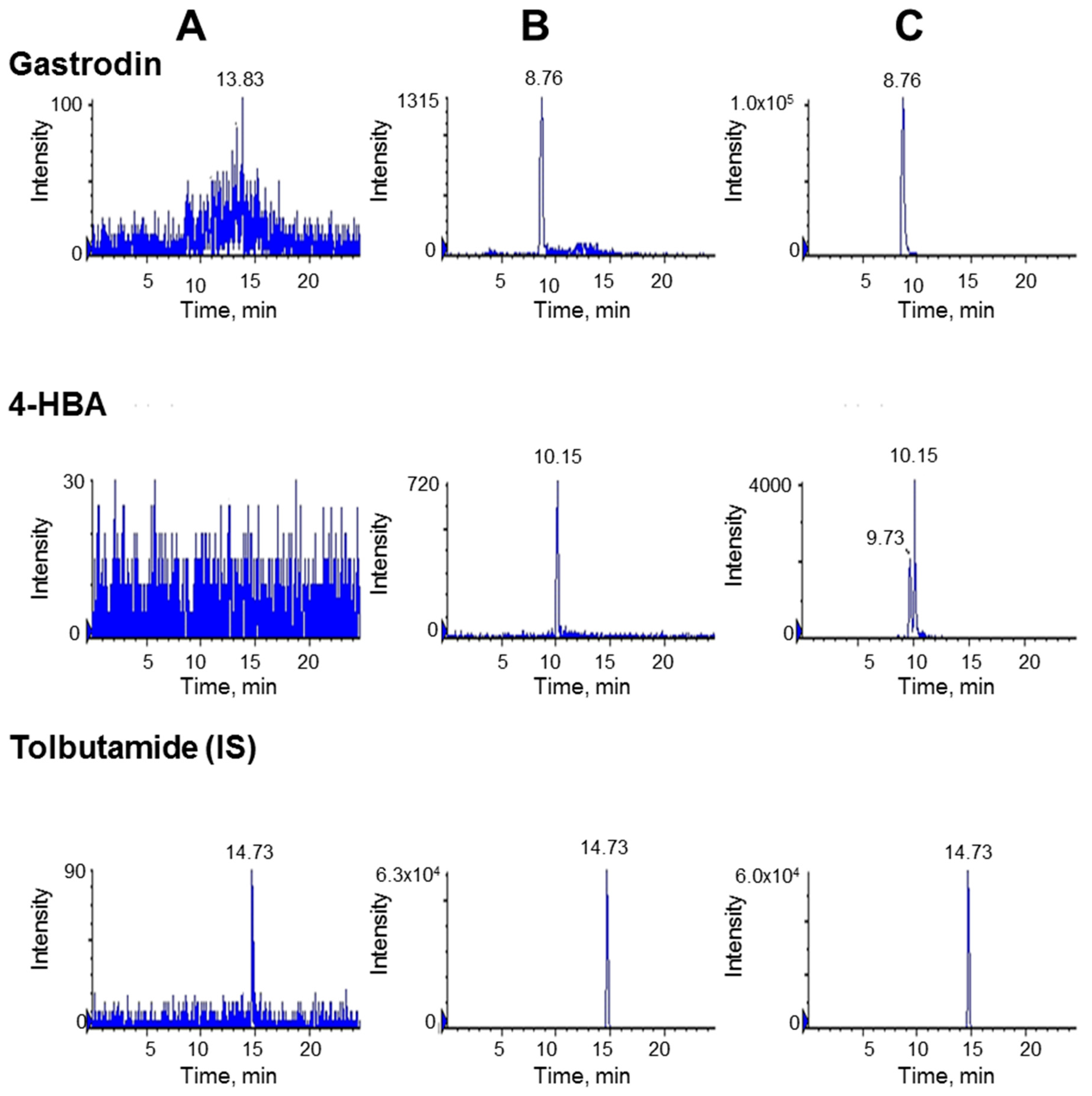
| Spiked Concentrations (µg/mL) | Intra-day (n = 5) | Inter-day (n = 5) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy % | CV % | Accuracy % | CV % | ||
| Gastrodin | 0.01 | 97.0 ± 10.5 | 10.8 | 106.6 ± 13.2 | 12.4 |
| 0.1 | 94.3 ± 4.5 | 4.8 | 93.4 ± 6.1 | 6.6 | |
| 1 | 101.6 ± 4.8 | 4.7 | 98.5 ± 3.8 | 3.9 | |
| 20 | 93.5 ± 5.8 | 6.2 | 94.6 ± 3.1 | 3.3 | |
| 4-HBA | 0.1 | 106.0 ± 7.8 | 7.4 | 115.0 ± 2.8 | 2.5 |
| 1 | 102.7 ± 1.5 | 1.5 | 99.0 ± 4.2 | 4.3 | |
| 5 | 105.0 ± 8.3 | 7.9 | 94.1 ± 4.4 | 4.6 | |
| 10 | 109.7 ± 8.4 | 7.6 | 112.2 ± 3.3 | 3.0 | |
| Measured Concentrations (% of control) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gastrodin (µg/mL) | 4-HBA (µg/mL) | |||||
| 0.01 | 1 | 20 | 0.1 | 1 | 10 | |
| Short-term at 25 °C | 100.2 ± 4.0 | 102 ± 0.0 | 101 ± 2.8 | 111 ± 5.7 | 101 ± 0.0 | 105 ± 5.7 |
| Short-term at +4 °C | 94.5 ± 4.7 | 102.5 ± 3.5 | 98.5 ± 1.4 | 111 ± 7.1 | 103 ± 1.4 | 112 ± 8.5 |
| Long-term at −20 °C | 102.2 ± 6.8 | 99.7 ± 0.5 | 100 ± 1.4 | 110.5 ± 3.5 | 102 ± 0.0 | 102 ± 0.0 |
| Freeze−thaw (−20 °C to 25 °C) | 93.8 ± 2.1 | 99.7 ± 0.5 | 98.3 ± 1.1 | 102.5 ± 0.7 | 97.3 ± 2.7 | 100.2 ± 12.4 |
| Parameters | Gastrodin | 4-HBA | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vehicle-treated | Antibiotics-treated | Vehicle-treated | Antibiotics-treated | |
| Tmax (h) | 0.3 ± 0.1 | 0.3 ± 0.1 | 0.7 ± 0.2 | 0.6 ± 0.1 |
| Cmax (µg/mL) | 26.9 ± 5.3 | 22.9 ± 5.5 | 4.2 ± 1.0 | 2.5 ± 0.8* |
| t1/2 (h) | 0.6 ± 0.0 | 0.6 ± 0.2 | 0.9 ± 0.3 | 1.1 ± 0.3 |
| AUC (µg·h/mL) | 21.8 ± 2.3 | 21.9 ± 1.4 | 7 ± 1.4 | 4.6 ± 1.0* |
| Vd (L/kg) | 1.1 ± 0.2 | 1.6 ± 0.4 | 7.4 ± 1.0 | 14.8 ± 6.6* |
| CL (L/h/kg) | 1.9 ± 0.2 | 1.8 ± 0.1 | 5.8 ± 1.4 | 9.0 ± 2.0* |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nepal, M.R.; Jeong, K.S.; Kim, G.H.; Cha, D.H.; Kang, M.J.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, J.-H.; Jeong, T.C. Role of Intestinal Microbiota in Metabolism of Gastrodin In Vitro and In Vivo. Metabolites 2019, 9, 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo9040069
Nepal MR, Jeong KS, Kim GH, Cha DH, Kang MJ, Kim JS, Kim J-H, Jeong TC. Role of Intestinal Microbiota in Metabolism of Gastrodin In Vitro and In Vivo. Metabolites. 2019; 9(4):69. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo9040069
Chicago/Turabian StyleNepal, Mahesh Raj, Ki Sun Jeong, Geon Ho Kim, Dong Ho Cha, Mi Jeong Kang, Jin Sung Kim, Ju-Hyun Kim, and Tae Cheon Jeong. 2019. "Role of Intestinal Microbiota in Metabolism of Gastrodin In Vitro and In Vivo" Metabolites 9, no. 4: 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo9040069
APA StyleNepal, M. R., Jeong, K. S., Kim, G. H., Cha, D. H., Kang, M. J., Kim, J. S., Kim, J.-H., & Jeong, T. C. (2019). Role of Intestinal Microbiota in Metabolism of Gastrodin In Vitro and In Vivo. Metabolites, 9(4), 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo9040069





