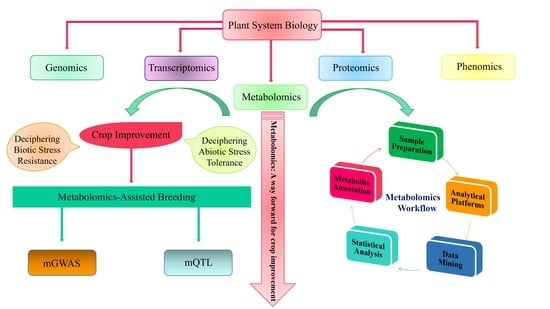
Metabolomics: A Way Forward for Crop Improvement
Abstract
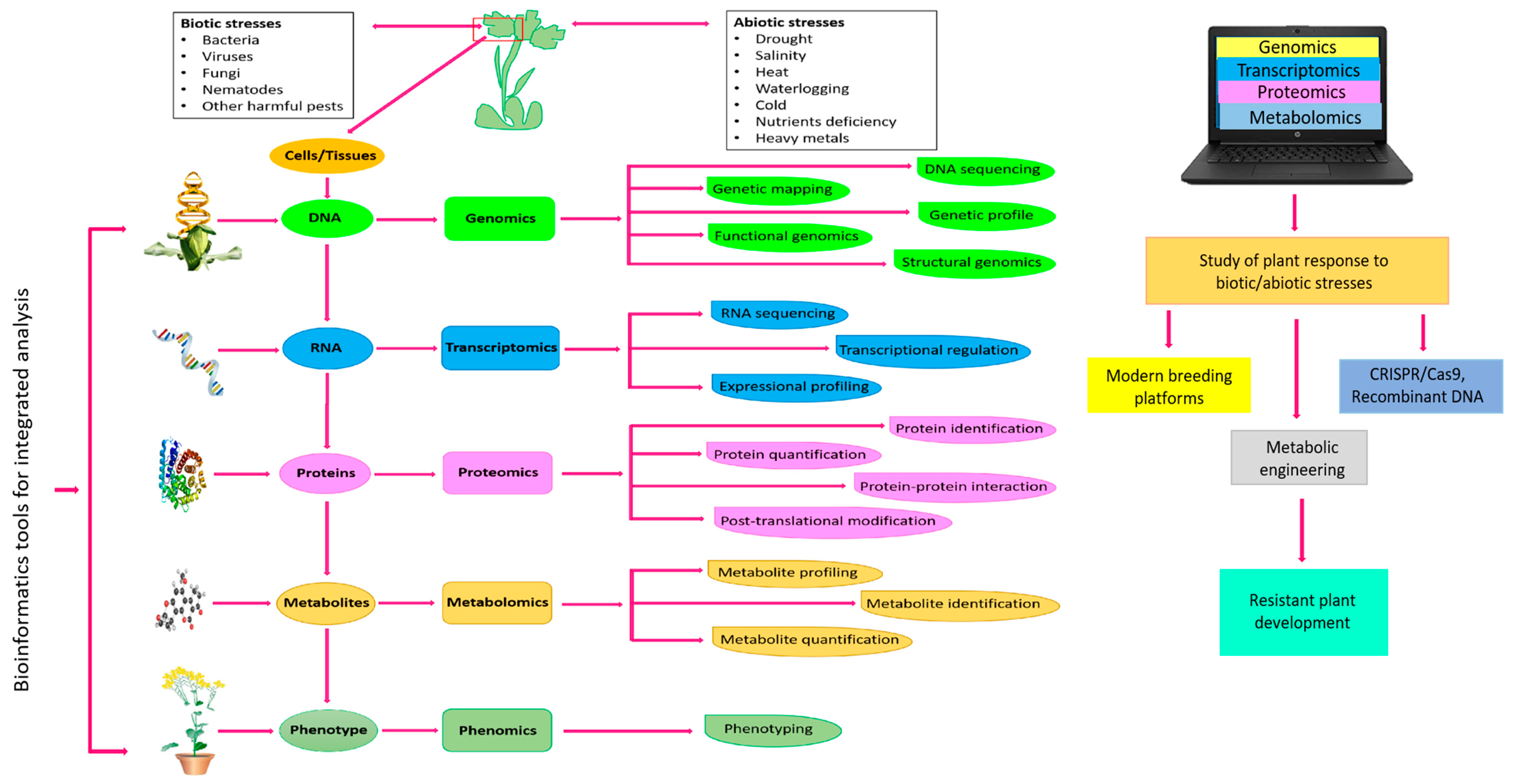
1. Metabolomics: Significance in Plant Biology
2. Advanced Tools for Analytical Research in Plant Metabolomics
3. The Workflow of Metabolomics Analysis
3.1. Sample Preparation
3.2. Data Mining, Annotation, and Processing in Metabolomics
3.3. Statistical Tools and Biomarker Identification
3.4. Bioinformatics Tools and Databases
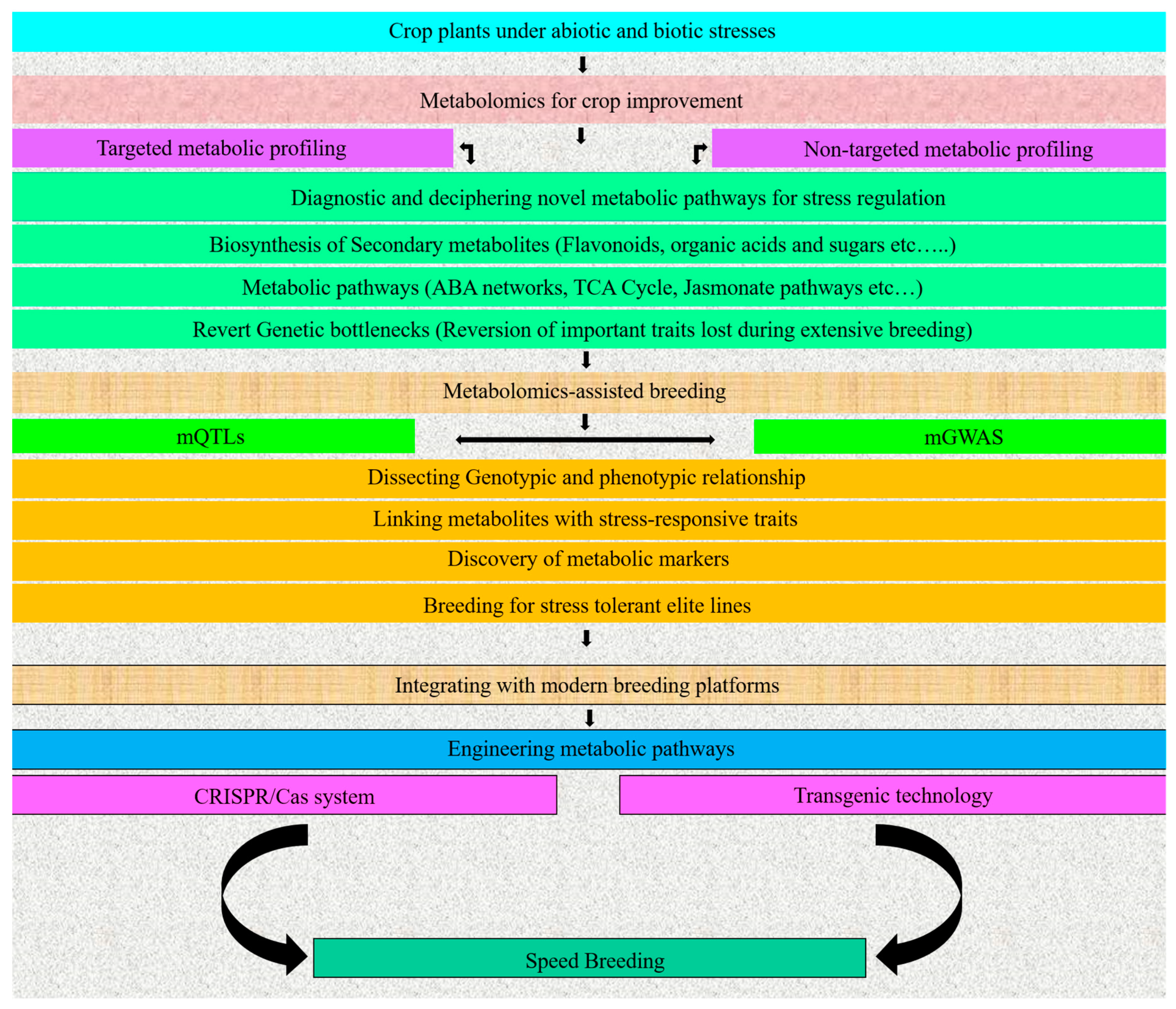
4. Metabolomics for Crop Improvement
4.1. Elucidation of Abiotic Stress Tolerance in Plants
4.1.1. Drought Stress Regulation
4.1.2. Salinity Stress Regulation
4.1.3. Waterlogging Stress Regulation
4.1.4. Temperature Stress Regulation
4.1.5. Metal-Induced Stress Regulation
4.1.6. Nutritional Deficiency Regulation
4.2. Elucidation of Biotic Stress Resistance in Plants
4.3. Soil Metabolomics
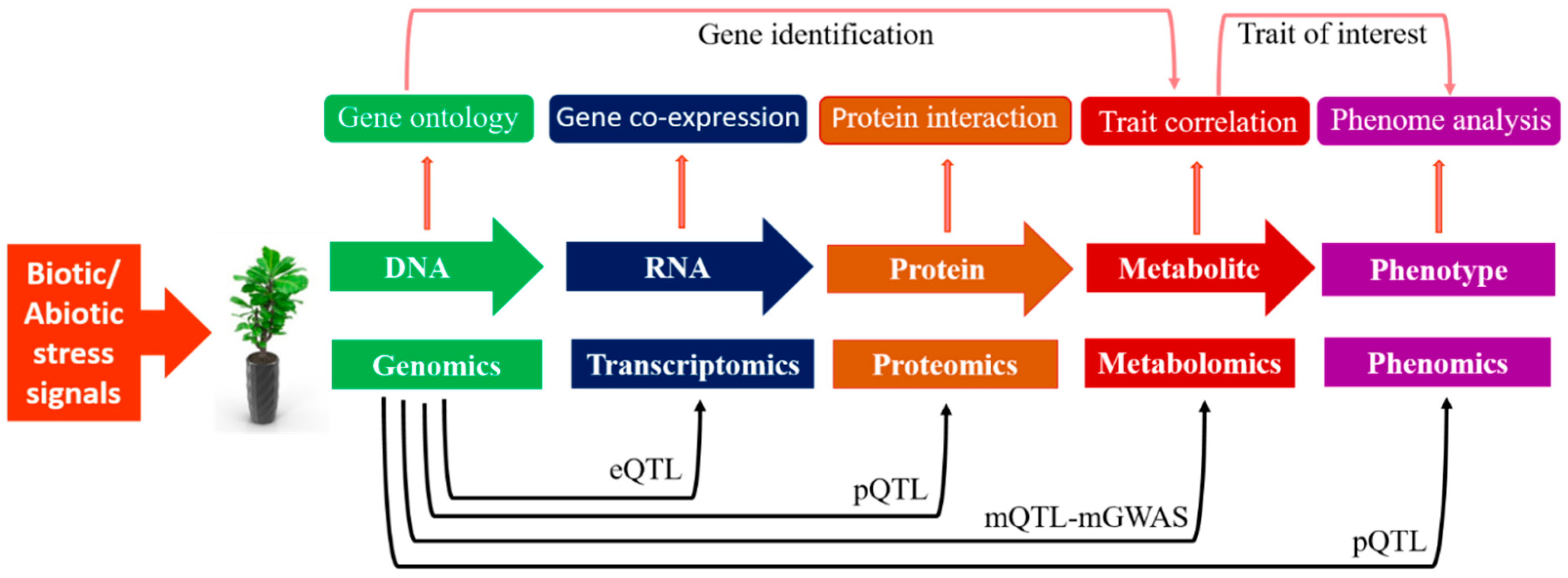
5. Metabolomics-Assisted Breeding
5.1. Metabolic QTLs (mQTLs)
5.2. Metabolic Genome-Wide Association Studies (mGWASs)
6. Bottlenecks Remain
7. Conclusions and Future Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shulaev, V.; Cortes, D.; Miller, G.; Mittler, R. Metabolomics for plant stress response. Physiol. Plant. 2008, 132, 199208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foito, A.; Stewart, D. Metabolomics: A high-throughput screen for biochemical and bioactivity diversity in plants and crops. Curr. Pharm. 2018, 24, 2043–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deborde, C.; Moing, A.; Roch, L.; Jacob, D.; Rolin, D.; Giraudeau, P. Plant metabolism as studied by NMR spectroscopy. Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc. 2017, 102, 61–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obata, T.; Witt, S.; Lisec, J.; Palacios-Rojas, N.; Florez-Sarasa, I.; Yousfi, S.; Araus, J.L.; Cairns, J.E.; Fernie, A.R. Metabolite profiles of maize leaves in drought, heat, and combined stress field trials reveal the relationship between metabolism and grain yield. Plant Physiol. 2015, 169, 2665–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.; Micallef, S.A. Environmental metabolomics of the tomato plant surface provides insights on Salmonella enterica colonization. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 3131–3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Cela, E.; Kiaitsi, E.; Medina, A.; Sulyok, M.; Krska, R.; Magan, N. Interacting environmental stress factors affects targeted metabolomic profiles in stored natural wheat and that inoculated with F. graminearum. Toxins 2018, 10, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piasecka, A.; Kachlicki, P.; Stobiecki, M. Analytical Methods for Detection of plant metabolomes changes in response to biotic and abiotic stresses. IJMS 2019, 20, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, J.; Lee, S.; Lee, Y.; Ha, S.; Song, B.; Kim, T.; Waters, B.M.; Krishnan, H.B. Metabolomic profiling from leaves and roots of tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) plants grown under nitrogen, phosphorus or potassium-deficient condition. Plant Sci. 2015, 241, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Che-Othman, M.H.; Jacoby, R.P.; Millar, A.H.; Taylor, N.L. Wheat mitochondrial respiration shifts from the tricarboxylic acid cycle to the GABA shunt under salt stress. New Phytol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawid, C.; Hille, K. Functional Metabolomics—A useful tool to characterize stress-induced metabolome alterations opening new avenues towards tailoring food crop quality. Agronomy 2018, 8, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.; Fuentes, D.; Threthowan, R.; Mohammad, F.; Ahmad, M. Comparative metabolite profiling of two wheat genotypes as affected by nitrogen stress at seedling stage. J. Anim. Plant Sci. 2019, 29, 260–268. [Google Scholar]
- Wishart, D.S. Advances in metabolite identification. Bioanalysis 2011, 3, 1769–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zivy, M.; Wienkoop, S.; Renaut, J.; Pinheiro, C.; Goulas, E.; Carpentier, S. The quest for tolerant varieties: The importance of integrating “omics” techniques to phenotyping. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Fountain, J.C.; Ji, P.; Ni, X.; Chen, S.; Lee, R.D.; Kemerait, R.C.; Guo, B. Deciphering drought-induced metabolic responses and regulation in developing maize kernels. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2018, 16, 1616–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gayen, D.; Barua, P.; Lande, N.V.; Varshney, S.; Sengupta, S.; Chakraborty, S.; Chakraborty, N. Dehydration-responsive alterations in the chloroplast proteome and cell metabolomic profile of rice reveals key stress adaptation responses. Environ. Exper. Bot. 2019, 160, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hein, J.A.; Sherrard, M.E.; Manfredi, K.P.; Abebe, T. The fifth leaf and spike organs of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) display different physiological and metabolic responses to drought stress. BMC Plant Biol. 2016, 16, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Z.; Babar, M.A.; Khan, N.; Guo, J.; Khan, J.; Islam, S.; Shrestha, S.; Shahi, D. Comparative metabolomic profiling in the roots and leaves in contrasting genotypes reveals complex mechanisms involved in post-anthesis drought tolerance in wheat. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0213502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, N.L.; Lah, W.A.C.; Kadir, N.A.; Mustaqim, M.; Rahmat, Z.; Ahmad, A.; Lam, S.D.; Ismail, M.R. Susceptibility and tolerance of rice crop to salt threat: Physiological and metabolic inspections. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribbenstedt, A.; Ziarrusta, H.; Benskin, J.P. Development, characterization and comparisons of targeted and non-targeted metabolomics methods. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0207082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.K.; Carroll, A.J.; Estavillo, G.M.; Rebetzke, G.J.; Pogson, B.J. Wheat drought tolerance in the field is predicted by amino acid responses to glasshouse-imposed drought. J. Exp. Bot. 2019, 70, 4931–4948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuperlovic-Culf, M.; Vaughan, M.M.; Vermillion, K.; Surendra, A.; Teresi, J.; McCormick, S.P. Effects of atmospheric CO2 level on the metabolic response of resistant and susceptible wheat to Fusarium graminearum infection. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2019, 32, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komatsu, S.; Nakamura, T.; Sugimoto, Y.; Sakamoto, K. Proteomic and metabolomic analyses of soybean root tips under flooding stress. Protein Pept. Lett. 2014, 21, 865–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.; Cheong, B.E.; Natera, S.; Roessner, U. Morphological and metabolic responses to salt stress of rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivars which differ in salinity tolerance. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 144, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Zhang, Y.K.; Kremling, K.A.; Ding, Y.; Bennett, J.S.; Bae, J.S.; Kim, D.K.; Ackerman, H.H.; Kolomiets, M.V.; Schmelz, E.A.; et al. Ethylene signaling regulates natural variation in the abundance of antifungal acetylated diferuloylsucroses and Fusarium graminearum resistance in maize seedling roots. New Phytol. 2019, 221, 2096–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomason, K.; Babar, M.A.; Erickson, J.E.; Mulvaney, M.; Beecher, C.; MacDonald, G. Comparative physiological and metabolomics analysis of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) following post-anthesis heat stress. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0197919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seybold, H.; Demetrowitsch, T.; Hassani, M.A.; Szymczak, S.; Reim, E.; Haueisen, J.; Rühlemann, M.; Franke, A.; Schwarz, K.; Stukenbrock, E.H. Hemibiotrophic fungal pathogen induces systemic susceptibility and systemic shifts in wheat metabolome and microbiome composition. bioRxiv 2019, 702373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boiteau, R.; Hoyt, D.; Nicora, C.; Kinmonth-Schultz, H.; Ward, J.; Bingol, K. Structure elucidation of unknown metabolites in metabolomics by combined NMR and MS/MS prediction. Metabolites 2018, 8, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, X.; Kirui, A.; Widanage, M.C.D.; Mentink-Vigier, F.; Cosgrove, D.J.; Wang, T. Lignin-polysaccharide interactions in plant secondary cell walls revealed by solid-state NMR. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Q.; Zhang, T.; Wang, Y.; Kong, W.; Guan, Q.; Yan, X.; Chen, S. Metabolomics of early stage plant cell-microbe interaction using stable isotope labeling. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas-Torres, C.; Wong, A. Current developments in µMAS NMR analysis for metabolomics. Metabolites 2019, 9, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verpoorte, R.; Choi, Y.H.; Kim, H.K. NMR-based metabolomics at work in phytochemistry. Phytochem. Rev. 2007, 6, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.K.; Choi, Y.H.; Verpoorte, R. NMR-based metabolomic analysis of plants. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.K.; Choi, Y.H.; Verpoorte, R. NMR-based plant metabolomics: Where do we stand, where do we go? Trends Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chikayama, E.; Sekiyama, Y.; Okamoto, M.; Nakanishi, Y.; Tsuboi, Y.; Akiyama, K.; Saito, K.; Shinozaki, K.; Kikuchi, J. Statistical indices for simultaneous large-scale metabolite detections for a single NMR spectrum. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 1653–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacs, H.; Moskau, D.; Spraul, M. Cryogenically cooled probes—A leap in NMR technology. Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc. 2005, 46, 131–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodoridis, G.; Gika, H.; Franceschi, P.; Caputi, L.; Arapitsas, P.; Scholz, M.; Masuero, D.; Wehrens, R.; Vrhovsek, U.; Mattivi, F. LC-MS based global metabolite profiling of grapes: Solvent extraction protocol optimisation. Metabolomics 2012, 8, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amelia, L.; Dell’Aversana, E.; Woodrow, P. Metabolomics for Crop Improvement Against Salinity Stress. In Salinity Responses and Tolerance in Plants, 2nd ed.; Kumar, V., Wani, S.H., Suprasanna, P., Tran, L.S.P., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 2, pp. 267–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorge, T.F.; Rodrigues, J.A.; Caldana, C.; Schmidt, R.; van Dongen, J.T.; Thomas-Oates, J.; António, C. Mass spectrometry-based plant metabolomics: Metabolite responses to abiotic stress. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2016, 35, 620–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Sun, X.; Weiszmann, J.; Weckwerth, W. System-level and granger network analysis of integrated proteomic and metabolomic dynamics identifies key points of grape berry development at the interface of primary and secondary metabolism. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enomoto, H.; Sensu, T.; Yumoto, E.; Yokota, T.; Yamane, H. Derivatization for detection of abscisic acid and 12- oxo-phytodienoic acid using matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization imaging mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2018, 32, 1565–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahbakhsh, F.; Hamzehzarghani, H.; Massah, A.; Tortosa, M.; Yasayee, M.; Rodriguez, V.M. Comparative metabolomics of temperature sensitive resistance to wheat streak mosaic virus (WSMV) in resistant and susceptible wheat cultivars. J. Plant Physiol. 2019, 237, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suharti, W.S.; Nose, A.; Zheng, S.H. Metabolomic study of two rice lines infected by Rhizoctonia solani in negative ion mode by CE/TOF-MS. J. Plant Physiol. 2016, 206, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Hu, C.; Hussain, S.; Tan, Q.; Wu, S.; Sun, X. Metabolomics analysis reveals potential mechanisms of tolerance to excess molybdenum in soybean seedlings. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2018, 164, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogbaga, C.C.; Stepien, P.; Dyson, B.C.; Rattray, N.J.; Ellis, D.I.; Goodacre, R.; Johnson, G.N. Biochemical analyses of sorghum varieties reveal differential responses to drought. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.K.; Verpoorte, R. Sample preparation for plant metabolomics. Phytochem. Anal. Int. J. Plant Chem. Biochem. Tech. 2010, 21, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Li, N.; Li, H.; Tang, H. An optimized method for NMR-based plant seed metabolomic analysis with maximized polar metabolite extraction efficiency, signal-to-noise ratio, and chemical shift consistency. Analyst 2014, 139, 1769–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; peng Song, Y.; Tang, H.; Wang, Y. Recent developments in sample preparation and data pre-treatment in metabonomics research. Arch. Biochem. Biophs. 2016, 589, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Causon, T.J.; Hann, S. Review of sample preparation strategies for MS-based metabolomic studies in industrial biotechnology. Anal. Chim. 2016, 938, 18–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harbourne, N.; Marete, E.; Jacquier, J.C.; O’Riordan, D. Effect of drying methods on the phenolic constituents of meadowsweet (Filipendula ulmaria) and willow (Salix alba). LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2009, 42, 1468–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuckovic, D. Current trends and challenges in sample preparation for global metabolomics using liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 403, 1523–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallardo, K.; Le Signor, C.; Vandekerckhove, J.; Thompson, R.D.; Burstin, J. Proteomics of Medicago truncatula seed development establishes the time frame of diverse metabolic processes related to reserve accumulation. Plant Physiol. 2003, 133, 664–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Garcés, N.; Gionfriddo, E. Recent developments and applications of solid phase microextraction as a sample preparation approach for mass-spectrometry-based metabolomics and lipidomics. Trac Trend. Anal Chem. 2019, 113, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Z.G.; Hu, J.; Wu, X.; Xu, Y.J. The recent developments in sample preparation for mass spectrometry-based metabolomics. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2017, 47, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pourmortazavi, S.M.; Hajimirsadeghi, S.S. Supercritical fluid extraction in plant essential and volatile oil analysis. J. Chromatogr. A 2007, 1163, 2–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altemimi, A.; Watson, D.G.; Choudhary, R.; Dasari, M.R.; Lightfoot, D.A. Ultrasound assisted extraction of phenolic compounds from peaches and pumpkins. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0148758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuorro, A.; Lavecchia, R.; Medici, F.; Piga, L. Enzyme-assisted production of tomato seed oil enriched with lycopene from tomato pomace. Food Bioprocess Tech. 2013, 6, 3499–3509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veličković, D.; Chu, R.K.; Myers, G.L.; Ahkami, A.H.; Anderton, C.R. An approach for visualizing the spatial metabolome of an entire plant root system inspired by the Swiss-rolling technique. J. Mass Spectrom. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki-Kinoshita, K.F. Overview of KEGG applications to omics-related research. J. Pest. Sci. 2006, 31, 296–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kuhn, S.; Egert, B.; Neumann, S.; Steinbeck, C. Building blocks for automated elucidation of metabolites: Machine learning methods for NMR prediction. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redestig, H.; Szymanski, J.; Hirai, M.Y.; Selbig, J.; Willmitzer, L.; Nikoloski, Z.; Saito, K. Data integration, metabolic networks and systems biology. Annu. Plant Rev. Online 2018, 261–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doerfler, H.; Lyon, D.; Nägele, T.; Sun, X.; Fragner, L.; Hadacek, F.; Egelhofer, V.; Weckwerth, W. Granger causality in integrated GC–MS and LC–MS metabolomics data reveals the interface of primary and secondary metabolism. Metabolomics 2013, 9, 564–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Weckwerth, W. COVAIN: A toolbox for uni-and multivariate statistics, time-series and correlation network analysis and inverse estimation of the differential Jacobian from metabolomics covariance data. Metabolomics 2012, 8, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liland, K.H. Multivariate methods in metabolomics–from pre-processing to dimension reduction and statistical analysis. Trends Anal. Chem. 2011, 30, 827–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Schreier, P.J.; Ramı’rez, D.; Hasija, T. Canonical correlation analysis of high-dimensional data with very small sample support. Signal Process. 2016, 128, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, O.; Urrutia, M.; Bernillon, S.; Giauffret, C.; Tardieu, F.; Le Gouis, J.; Langlade, N.; Charcosset, A.; Moing, A.; Gibon, Y. Fortune telling: Metabolic markers of plant performance. Metabolomics 2016, 12, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saccenti, E.; Hoefsloot, H.C.; Smilde, A.K.; Westerhuis, J.A.; Hendriks, M.M. Reflections on univariate and multivariate analysis of metabolomics data. Metabolomics 2014, 10, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiehn, O.; Barupal, D.K.; Kind, T. Extending biochemical databases by metabolomic surveys. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 23637–23643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Hinzman, A.A.; Kang, E.L.; Szczesniak, R.D.; Lu, L.J. Computational and statistical analysis of metabolomics data. Metabolomics 2015, 11, 1492–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weckwerth, W.; Morgenthal, K. Metabolomics: From pattern recognition to biological interpretation. Drug Discov. Today 2005, 10, 1551–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodacre, R.; Vaidyanathan, S.; Dunn, W.B.; Harrigan, G.G.; Kell, D.B. Metabolomics by numbers: Acquiring and understanding global metabolite data. Trends Biotechnol. 2004, 22, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Goodacre, R. Multiblock principal component analysis: An efficient tool for analyzing metabolomics data which contain two influential factors. Metabolomics 2012, 8, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, H.; Keleş, S. Sparse partial least squares regression for simultaneous dimension reduction and variable selection. J. R. Stat. Soc. Series B (Stat. Methodol.) 2010, 72, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trygg, J.; Wold, S. Orthogonal projections to latent structures (O-PLS). J. Chemom. A J. Chemom. Soc. 2002, 16, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggio, R.; VillasBôas, S.G.; Ruggiero, K. Metab: An R package for high-throughput analysis of metabolomics data generated by GC-MS. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2316–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, C.; Maraschin, M.; Rocha, M. An R package for the integrated analysis of metabolomics and spectral data. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2016, 129, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzpatrick, M.A.; McGrath, C.M.; Young, S.P. Pathomx: An interactive workflow-based tool for the analysis of metabolomic data. BMC Bioinform. 2014, 15, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.J.; Lin, Y.T.; Chen, C.W.; Lin, C.W.; Chao, K.M.; Pan, W.H.; Yang, H.C. SMART: Statistical Metabolomics Analysis An R Tool. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 6334–6341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spicer, R.; Salek, R.M.; Moreno, P.; Cañueto, D.; Steinbeck, C. Navigating freely-available software tools for metabolomics analysis. Metabolomics 2017, 13, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernest, B.; Gooding, J.R.; Campagna, S.R.; Saxton, A.M.; Voy, B.H. MetabR: An R script for linear model analysis of quantitative metabolomic data. BMC Res. Notes 2012, 5, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, J.; Xia, J. MetaboAnalystR: An R package for flexible and reproducible analysis of metabolomics data. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 4313–4314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Akwaa, F.M.; Yunits, B.; Huang, S.; Alhajaji, H.; Garmire, L.X. Lilikoi: An R package for personalized pathway-based classification modeling using metabolomics data. GigaScience 2018, 7, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mock, A.; Warta, R.; Dettling, S.; Brors, B.; Jäger, D.; Herold-Mende, C. MetaboDiff: An R package for differential metabolomic analysis. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 3417–3418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wishart, D.S. Current progress in computational metabolomics. Brief. Bioinform. 2007, 8, 279–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardinassi, L.G.; Xia, J.; Safo, S.E.; Li, S. Bioinformatics tools for the interpretation of metabolomics data. Curr. Pharmacol. Rep. 2017, 3, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tautenhahn, R.; Patti, G.J.; Rinehart, D.; Siuzdak, G. XCMS Online: A web-based platform to process untargeted metabolomic data. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 5035–5039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montenegro-Burke, J.R.; Aisporna, A.E.; Benton, H.P.; Rinehart, D.; Fang, M.; Huan, T.; Warth, B.; Forsberg, E.; Abe, B.T.; Ivanisevic, J. Data streaming for metabolomics: Accelerating data processing and analysis from days to minutes. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 1254–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forsberg, E.M.; Huan, T.; Rinehart, D.; Benton, H.P.; Warth, B.; Hilmers, B.; Siuzdak, G. Data processing, multi-omic pathway mapping, and metabolite activity analysis using XCMS Online. Nat. Protoc. 2018, 13, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaženović, I.; Kind, T.; Ji, J.; Fiehn, O. Software tools and approaches for compound identification of LC-MS/MS data in metabolomics. Metabolites 2018, 8, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.A.; O’Maille, G.; Want, E.J.; Qin, C.; Trauger, S.A.; Brandon, T.R.; Custodio, D.E.; Abagyan, R.; Siuzdak, G. METLIN: A metabolite mass spectral database. Ther. Drug Monit. 2005, 27, 747–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daub, C.O.; Kloska, S.; Selbig, J. MetaGeneAlyse: Analysis of integrated transcriptional and metabolite data. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 2332–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Wishart, D.S. MetPA: A web-based metabolomics tool for pathway analysis and visualization. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2342–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Wishart, D.S. MSEA: A web-based tool to identify biologically meaningful patterns in quantitative metabolomic data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, W71–W77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kessler, N.; Neuweger, H.; Bonte, A.; Langenkämper, G.; Niehaus, K.; Nattkemper, T.W.; Goesmann, A. MeltDB 2.0–advances of the metabolomics software system. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 2452–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, H.Y.; Chen, C.T.; Lih, T.M.; Lynn, K.S.; Juo, C.G.; Hsu, W.L.; Sung, T.Y. iMet-Q: A user-friendly tool for label-free metabolomics quantitation using dynamic peak-width determination. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0146112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lommen, A.; Kools, H.J. MetAlign 3.0: Performance enhancement by efficient use of advances in computer hardware. Metabolomics 2012, 8, 719–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsugawa, H.; Cajka, T.; Kind, T.; Ma, Y.; Higgins, B.; Ikeda, K.; Kanazawa, M.; VanderGheynst, J.; Fiehn, O.; Arita, M. MS-DIAL: Data-independent MS/MS deconvolution for comprehensive metabolome analysis. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draper, J.; Enot, D.P.; Parker, D.; Beckmann, M.; Snowdon, S.; Lin, W.; Zubair, H. Metabolite signal identification in accurate mass metabolomics data with MZedDB, an interactive m/z annotation tool utilising predicted ionisation behaviour ‘rules’. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, K.F.; Kanehisa, M. Using the KEGG database resource. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2005, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, R.L.; Weber, R.J.; Liu, H.; Sharma-Oates, A.; Viant, M.R. Galaxy-M: A Galaxy workflow for processing and analyzing direct infusion and liquid chromatography mass spectrometry-based metabolomics data. Gigascience 2016, 5, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanichthanarak, K.; Fan, S.; Grapov, D.; Barupal, D.K.; Fiehn, O. Metabox: A toolbox for metabolomic data analysis, interpretation and integrative exploration. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, R.; Salavert, F.; Garcia-Garcia, F.; Carbonell-Caballero, J.; Bleda, M.; Garcia-Alonso, L.; Sanchis-Juan, A.; Perez-Gil, D.; Marin-Garcia, P.; Sanchez, R. Babelomics 5.0: Functional interpretation for new generations of genomic data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W117–W121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich, M.; Liefeld, T.; Gould, J.; Lerner, J.; Tamayo, P.; Mesirov, J.P. GenePattern 2.0. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, J.; Psychogios, N.; Young, N.; Wishart, D.S. MetaboAnalyst: A web server for metabolomic data analysis and interpretation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, W652–W660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.; Wang, J.; Ressom, H.W. MetaboSearch: Tool for mass-based metabolite identification using multiple databases. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e40096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kastenmüller, G.; Römisch-Margl, W.; Wägele, B.; Altmaier, E.; Suhre, K. metaP-server: A web-based metabolomics data analysis tool. BioMed Res. Int. 2010, 2011, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cottret, L.; Wildridge, D.; Vinson, F.; Barrett, M.P.; Charles, H.; Sagot, M.F.; Jourdan, F. MetExplore: A web server to link metabolomic experiments and genome-scale metabolic networks. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, W132–W137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas-Chertó, M.; van Vliet, M.; Peironcely, J.E.; Van Doorn, R.; Kooyman, M.; Te Beek, T.; Van Driel, M.A.; Hankemeier, T.; Reijmers, T. MetiTree: A web application to organize and process high-resolution multi-stage mass spectrometry metabolomics data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 2707–2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruttkies, C.; Schymanski, E.L.; Wolf, S.; Hollender, J.; Neumann, S. MetFrag relaunched: Incorporating strategies beyond in silico fragmentation. J. Cheminform. 2016, 8, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, F.; Colmsee, C.; Czauderna, T.; Grafahrend-Belau, E.; Hartmann, A.; Junker, A.; Junker, B.H.; Klapperstück, M.; Scholz, U.; Weise, S. MetaCrop 2.0: Managing and exploring information about crop plant metabolism. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 40, D1173–D1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, R.; Rogers, S.; Wandy, J.; Jankevics, A.; Burgess, K.E.; Breitling, R. MetAssign: Probabilistic annotation of metabolites from LC–MS data using a Bayesian clustering approach. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2764–2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Chang, J.; Lei, Z.; Huhman, D.; Sumner, L.W.; Zhao, P.X. MET-COFEA: A liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry data processing platform for metabolite compound feature extraction and annotation. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 6245–6253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horai, H.; Arita, M.; Kanaya, S.; Nihei, Y.; Ikeda, T.; Suwa, K.; Ojima, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Tanaka, S.; Aoshima, K. MassBank: A public repository for sharing mass spectral data for life sciences. J. Mass Spectrom. 2010, 45, 703–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyanova, S.; Temu, T.; Cox, J. The MaxQuant computational platform for mass spectrometry-based shotgun proteomics. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 2301–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerlich, M.; Neumann, S. MetFusion: Integration of compound identification strategies. J. Mass Spectrom. 2013, 48, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clasquin, M.F.; Melamud, E.; Rabinowitz, J.D. LC-MS data processing with MAVEN: A metabolomic analysis and visualization engine. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2012, 37, 14.11.1–14.11.23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluskal, T.; Castillo, S.; Villar-Briones, A.; Orešič, M. MZmine 2: Modular framework for processing, visualizing, and analyzing mass spectrometry-based molecular profile data. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaever, A.; Landesfeind, M.; Feussner, K.; Mosblech, A.; Heilmann, I.; Morgenstern, B.; Feussner, I.; Meinicke, P. MarVis-Pathway: Integrative and exploratory pathway analysis of non-targeted metabolomics data. Metabolomics 2015, 11, 764–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Park, Y.; Duraisingham, S.; Strobel, F.H.; Khan, N.; Soltow, Q.A.; Jones, D.P.; Pulendran, B. Predicting network activity from high throughput metabolomics. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2013, 9, e1003123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Q.; Lewis, I.A.; Hegeman, A.D.; Anderson, M.E.; Li, J.; Schulte, C.F.; Westler, W.M.; Eghbalnia, H.R.; Sussman, M.R.; Markley, J.L. Metabolite identification via the madison metabolomics consortium database. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahieu, N.G.; Genenbacher, J.L.; Patti, G.J. A roadmap for the XCMS family of software solutions in metabolomics. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2016, 30, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willighagen, E.L.; Mayfield, J.W.; Alvarsson, J.; Berg, A.; Carlsson, L.; Jeliazkova, N.; Kuhn, S.; Pluskal, T.; Rojas-Chertó, M.; Spjuth, O. The Chemistry Development Kit (CDK) v2. 0: Atom typing, depiction, molecular formulas, and substructure searching. J. Cheminform. 2017, 9, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, F.; Pon, A.; Wilson, M.; Greiner, R.; Wishart, D. CFM-ID: A web server for annotation, spectrum prediction and metabolite identification from tandem mass spectra. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, W94–W99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.; Qiu, Y.; Ni, Y.; Su, M.; Jia, W.; Du, X. An Automated Data Analysis Pipeline for GC− TOF− MS Metabonomics Studies. J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 5974–5981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boutrot, F.; Zipfel, C. Function, discovery, and exploitation of plant pattern recognition receptors for broad-spectrum disease resistance. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2017, 55, 257–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang Han, Y.; Xiu Li, A.; Li, F.; Rong Zhao, M.; Wang, W. Characterization of a wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) expansin gene, TaEXPB23, involved in the abiotic stress response and phytohormone regulation. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 54, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Cristobal, J.; García-Villaraco, A.; Ramos, B.; Gutierrez-Mañero, J.; Lucas, J.A. Priming of pathogenesis related-proteins and enzymes related to oxidative stress by plant growth promoting rhizobacteria on rice plants upon abiotic and biotic stress challenge. J. Plant Physiol. 2015, 188, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, A.; Razzaq, A.; Mehmood, S.S.; Zou, X.; Zhang, X.; Lv, Y.; Xu, J. Impact of climate change on crops adaptation and strategies to tackle its outcome: A review. Plants 2019, 8, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Shi, L.; Jiao, Y.; Li, M.; Zhong, X.; Gu, F.; Liu, Q.; Xia, X.; Li, H. Metabolic responses to drought stress in the tissues of drought-tolerant and drought-sensitive wheat genotype seedlings. AoB Plants 2018, 10, ply016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouphael, Y.; Raimondi, G.; Lucini, L.; Carillo, P.; Kyriacou, M.C.; Colla, G.; Cirillo, V.; Pannico, A.; El-Nakhel, C.; De Pascale, S. Physiological and metabolic responses triggered by omeprazole improve tomato plant tolerance to NaCl stress. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, A. Osmotic adjustment is a prime drought stress adaptive engine in support of plant production. Plant Cell Envir. 2017, 40, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasensky, J.; Jonak, C. Drought, salt, and temperature stress-induced metabolic rearrangements and regulatory networks. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 1593–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves, M.; Oliveira, M. Mechanisms underlying plant resilience to water deficits: Prospects for water-saving agriculture. J. Exp. Bot. 2004, 55, 2365–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bitrián, M.; Zarza, X.; Altabella, T.; Tiburcio, A.F.; Alcázar, R. Polyamines under abiotic stress: Metabolic crossroads and hormonal crosstalks in plants. Metabolites 2012, 2, 516–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marček, T.; Hamow, K.Á.; Végh, B.; Janda, T.; Darko, E. Metabolic response to drought in six winter wheat genotypes. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0212411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michaletti, A.; Naghavi, M.R.; Toorchi, M.; Zolla, L.; Rinalducci, S. Metabolomics and proteomics reveal drought-stress responses of leaf tissues from spring-wheat. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.A.; Akond, M.; Babar, M.A.; Beecher, C.; Erickson, J.; Thomason, K.; De Jong, F.A.; Mason, R.E. LC-HRMS based non-targeted metabolomic profiling of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) under post-anthesis drought stress. AJPS 2017, 8, 3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skirycz, A.; Inzé, D. More from less: Plant growth under limited water. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2010, 21, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, K.H.; Kim, H.J.; Pack, I.S.; Kim, H.J.; Chung, Y.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, C.G. Global metabolite profiling based on GC–MS and LC–MS/MS analyses in ABF3-overexpressing soybean with enhanced drought tolerance. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2019, 62, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Xia, H.; Liu, Y.; Wei, H.; Zheng, X.; Song, C.; Chen, L.; Liu, H.; Luo, L. Transcriptomic and metabolomic studies disclose key metabolism pathways contributing to well-maintained photosynthesis under the drought and the consequent drought-tolerance in rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, P.T.; Degenkolbe, T.; Erban, A.; Heyer, A.G.; Kopka, J.; Köhl, K.I.; Hincha, D.K.; Zuther, E. Dissecting rice polyamine metabolism under controlled long-term drought stress. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e60325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witt, S.; Galicia, L.; Lisec, J.; Cairns, J.; Tiessen, A.; Araus, J.L.; Palacios-Rojas, N.; Fernie, A.R. Metabolic and phenotypic responses of greenhouse-grown maize hybrids to experimentally controlled drought stress. Mol. Plant 2012, 5, 401–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvente, S.; Sobolev, A.P.; Lara, M. Metabolite adjustments in drought tolerant and sensitive soybean genotypes in response to water stress. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degenkolbe, T.; Do, P.T.; Kopka, J.; Zuther, E.; Hincha, D.K.; Köhl, K.I. Identification of drought tolerance markers in a diverse population of rice cultivars by expression and metabolite profiling. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Yang, Z.; Li, F.; Yan, C.; Zhong, X.; Liu, Q.; Xia, X.; Li, H.; Zhao, L. Comparative metabolic responses and adaptive strategies of wheat (Triticum aestivum) to salt and alkali stress. BMC Plant Biol. 2015, 15, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Cai, S.; Chen, M.; Ye, L.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, H.; Dai, F.; Wu, F.; Zhang, G. Tissue metabolic responses to salt stress in wild and cultivated barley. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, P.; De, B. Metabolomics analysis of rice responses to salinity stress revealed elevation of serotonin, and gentisic acid levels in leaves of tolerant varieties. Plant Signal Behav. 2017, 12, e1335845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelden, M.C.; Dias, D.A.; Jayasinghe, N.S.; Bacic, A.; Roessner, U. Root spatial metabolite profiling of two genotypes of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) reveals differences in response to short-term salt stress. J. Exp. Bot. 2016, 67, 3731–3745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurotani, K.-i.; Hayashi, K.; Hatanaka, S.; Toda, Y.; Ogawa, D.; Ichikawa, H.; Ishimaru, Y.; Tashita, R.; Suzuki, T.; Ueda, M. Elevated levels of CYP94 family gene expression alleviate the jasmonate response and enhance salt tolerance in rice. Plant Cell Physiol. 2015, 56, 779–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrelli, G.M.; Fragasso, M.; Nigro, F.; Platani, C.; Papa, R.; Beleggia, R.; Trono, D. Analysis of metabolic and mineral changes in response to salt stress in durum wheat (Triticum turgidum ssp. durum) genotypes, which differ in salinity tolerance. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 133, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zörb, C.; Geilfus, C.-M.; Mühling, K.H.; Ludwig-Müller, J. The influence of salt stress on ABA and auxin concentrations in two maize cultivars differing in salt resistance. J. Plant Physiol. 2013, 170, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barding, G.A., Jr.; Béni, S.; Fukao, T.; Bailey-Serres, J.; Larive, C.K. Comparison of GC-MS and NMR for metabolite profiling of rice subjected to submergence stress. J. Proteome Res. 2012, 12, 898–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutinho, I.D.; Henning, L.M.M.; Döpp, S.A.; Nepomuceno, A.; Moraes, L.A.C.; Marcolino-Gomes, J.; Richter, C.; Schwalbe, H.; Colnago, L.A. Flooded soybean metabolomic analysis reveals important primary and secondary metabolites involved in the hypoxia stress response and tolerance. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2018, 153, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzog, M.; Fukao, T.; Winkel, A.; Konnerup, D.; Lamichhane, S.; Alpuerto, J.B.; Hasler-Sheetal, H.; Pedersen, O. Physiology, gene expression, and metabolome of two wheat cultivars with contrasting submergence tolerance. Plant Cell Environ. 2018, 41, 1632–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locke, A.M.; Barding, G.A., Jr.; Sathnur, S.; Larive, C.K.; Bailey-Serres, J. Rice SUB1A constrains remodelling of the transcriptome and metabolome during submergence to facilitate post-submergence recovery. Plant Cell Environ. 2018, 41, 721–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luengwilai, K.; Saltveit, M.; Beckles, D.M. Metabolite content of harvested Micro-Tom tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) fruit is altered by chilling and protective heat-shock treatments as shown by GC–MS metabolic profiling. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2012, 63, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Hou, L.; Lu, Y.; Wu, B.; Gong, X.; Liu, M.; Wang, J.; Sun, Q.; Vierling, E.; Xu, S. Metabolic adaptation of wheat grain contributes to a stable filling rate under heat stress. J. Exp. Bot. 2018, 69, 5531–5545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chebrolu, K.K.; Fritschi, F.B.; Ye, S.; Krishnan, H.B.; Smith, J.R.; Gillman, J.D. Impact of heat stress during seed development on soybean seed metabolome. Metabolomics 2016, 12, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Xu, W.; Zhang, J.; Guo, R.; Zhao, M.; Hu, L.; Wang, H.; Dong, H.; Li, Y. Physiological characteristics and metabolomics of transgenic wheat containing the maize C 4 phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase (PEPC) gene under high temperature stress. Protoplasma 2017, 254, 1017–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paupière, M.J.; Müller, F.; Li, H.; Rieu, I.; Tikunov, Y.M.; Visser, R.G.; Bovy, A.G. Untargeted metabolomic analysis of tomato pollen development and heat stress response. Plant Reprod. 2017, 30, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Gao, X.; Li, M.; Fu, J.; Zhang, Y. Plastic responses in the metabolome and functional traits of maize plants to temperature variations. Plant Biol. 2016, 18, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibarra, A.A.G.; Wrobel, K.; Barrientos, E.Y.; Escobosa, A.R.C.; Corona, J.F.G.; Donis, I.E.; Wrobel, K. Impact of Cr (VI) on the oxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids in Helianthus annuus roots studied by metabolomic tools. Chemosphere 2019, 220, 442–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manivasagaperumal, R.; Balamurugan, S.; Thiyagarajan, G.; Sekar, J. Effect of zinc on germination, seedling growth and biochemical content of cluster bean (Cyamopsis tetragonoloba (L.) Taub). Curr. Bot. 2011, 2, 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Jahangir, M.; Abdel-Farid, I.B.; Choi, Y.H.; Verpoorte, R. Metal ion-inducing metabolite accumulation in Brassica rapa. J. Plant Physiol. 2008, 165, 1429–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foito, A.; Byrne, S.L.; Hackett, C.A.; Hancock, R.D.; Stewart, D.; Barth, S. Short-term response in leaf metabolism of perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne) to alterations in nitrogen supply. Metabolomics 2013, 9, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comadira, G.; Rasool, B.; Karpinska, B.; Morris, J.; Verrall, S.R.; Hedley, P.E.; Foyer, C.H.; Hancock, R.D. Nitrogen deficiency in barley (Hordeum vulgare) seedlings induces molecular and metabolic adjustments that trigger aphid resistance. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 3639–3655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyneke, E.; Watanabe, M.; Erban, A.; Duan, G.; Buchner, P.; Walther, D.; Kopka, J.; Hawkesford, M.J.; Hoefgen, R. Characterization of the wheat leaf metabolome during grain filling and under varied N-supply. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoefgen, R.; Nikiforova, V.J. Metabolomics integrated with transcriptomics: Assessing systems response to sulfur-deficiency stress. Physiol. Plant. 2008, 132, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosson, H.; Schwarzenberg, A.; Jamois, F.; Yvin, J.C. Simultaneous untargeted and targeted metabolomics profiling of underivatized primary metabolites in sulfur-deficient barley by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole/time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Plant Pethods 2018, 14, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodorou, M.E.; Plaxton, W.C. Metabolic adaptations of plant respiration to nutritional phosphate deprivation. Plant Physiol. 1993, 101, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.Y.; Roessner, U.; Eickmeier, I.; Genc, Y.; Callahan, D.L.; Shirley, N.; Langridge, P.; Bacic, A. Metabolite profiling reveals distinct changes in carbon and nitrogen metabolism in phosphate-deficient barley plants (Hordeum vulgare L.). Plant Cell Physiol. 2008, 49, 691–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, G.; Valdés-López, O.; Ramírez, M.; Goffard, N.; Weiller, G.; Aparicio-Fabre, R.; Fuentes, S.I.; Erban, A.; Kopka, J.; Udvardi, M.K. Global changes in the transcript and metabolic profiles during symbiotic nitrogen fixation in phosphorus-stressed common bean plants. Plant Physiol. 2009, 151, 1221–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ma, X.M.; Wang, X.C.; Liu, J.H.; Huang, B.Y.; Guo, X.Y.; Xiong, S.P.; La, G.X. UPLC-QTOF analysis reveals metabolomic changes in the flag leaf of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) under low-nitrogen stress. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 111, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allwood, J.W.; Ellis, D.I.; Goodacre, R. Metabolomic technologies and their application to the study of plants and plant–host interactions. Physiol. Plant. 2008, 132, 117–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tenenboim, H.; Brotman, Y. Omic relief for the biotically stressed: Metabolomics of plant biotic interactions. Trends Plant Sci. 2016, 21, 781–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balmer, D.; Flors, V.; Glauser, G.; Mauch-Mani, B. Metabolomics of cereals under biotic stress: Current knowledge and techniques. Front. Plant Sci. 2013, 4, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niculaes, C.; Abramov, A.; Hannemann, L.; Frey, M. Plant protection by benzoxazinoids—Recent insights into biosynthesis and function. Agronomy 2018, 8, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenk, M.; Wenig, M.; Mengel, F.; Häußler, F.; Vlot, A. Arabidopsis thaliana immunity-related compounds modulate disease susceptibility in barley. Agronomy 2018, 8, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Gresa, M.P.; Maltese, F.; Bellés, J.M.; Conejero, V.; Kim, H.K.; Choi, Y.H.; Verpoorte, R. Metabolic response of tomato leaves upon different plant–pathogen interactions. Phytochem. Anal. Int. J. Plant Chem. Biochem. Tech. 2010, 21, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunnaiah, R.; Kushalappa, A.C.; Duggavathi, R.; Fox, S.; Somers, D.J. Integrated metabolo-proteomic approach to decipher the mechanisms by which wheat QTL (Fhb1) contributes to resistance against Fusarium graminearum. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e40695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuperlovic-Culf, M.; Wang, L.; Forseille, L.; Boyle, K.; Merkley, N.; Burton, I.; Fobert, P.R. Metabolic biomarker panels of response to fusarium head blight infection in different wheat varieties. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarrwal, R.; Bentur, J.S.; Nair, S. Gas chromatography mass spectrometry based metabolic profiling reveals biomarkers involved in rice-gall midge interactions. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2014, 56, 837–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sana, T.R.; Fischer, S.; Wohlgemuth, G.; Katrekar, A.; Jung, K.H.; Ronald, P.C.; Fiehn, O. Metabolomic and transcriptomic analysis of the rice response to the bacterial blight pathogen Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Metabolomics 2010, 6, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, O.A.; Maguire, M.L.; Griffin, J.L.; Jung, Y.-H.; Shibato, J.; Rakwal, R.; Agrawal, G.K.; Jwa, N.-S. Using metabolic profiling to assess plant-pathogen interactions: An example using rice (Oryza sativa) and the blast pathogen Magnaporthe grisea. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2011, 129, 539–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasmatkar, P.; Kaur, K.; Pannu, P.P.S.; Kaur, G.; Kaur, H. Unraveling the metabolite signatures of maize genotypes showing differential response towards southern corn leaf blight by 1H-NMR and FTIR spectroscopy. Physiolol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2019, 108, 101441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Qi, J.; He, K.; Wu, J.; Bai, S.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Z. The Asian corn borer Ostrinia furnacalis feeding increases the direct and indirect defence of mid-whorl stage commercial maize in the field. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2019, 17, 88–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, L.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Song, C.; Shangguan, X.; Zhu, L.; He, G. Comparative metabolomics of the interaction between rice and the brown planthopper. Metabolomics 2016, 12, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, X.; Tzin, V.; Romeis, J.; Peng, Y.; Li, Y. Combined transcriptome and metabolome analyses to understand the dynamic responses of rice plants to attack by the rice stem borer Chilo suppressalis (Lepidoptera: Crambidae). BMC Plant Biol. 2016, 16, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shavit, R.; Batyrshina, Z.S.; Dotan, N.; Tzin, V. Cereal aphids differently affect benzoxazinoid levels in durum wheat. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0208103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asaduzzaman, M.; Pratley, J.E.; An, M.; Luckett, D.J.; Lemerle, D. Metabolomics differentiation of canola genotypes: Toward an understanding of canola allelochemicals. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 5, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwendwa, J.M.; Weston, P.A.; Fomsgaard, I.; Laursen, B.B.; Brown, W.B.; Wu, H.; Rebetzke, G.; Quinn, J.C.; Weston, L.A. Metabolic Profiling for Benzoxazinoids in Weed-Suppressive and Early Vigour Wheat Genotypes. In Proceedings of the 20th Australasian weeds Conference, Perth, Western Australia, 11–15 September 2016; Volume 11, pp. 353–357. [Google Scholar]
- Mwendwa, J.M.; Brown, W.; Haque, K.S.; Heath, G.; Weston, L. Mechanisms of Weed Suppression by Wheat Genotypes. In GRDC Grains Research Update; Grain Research and Development Cooporation: Canberra, Australia, 2016; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Latif, S.; Gurusinghe, S.; Weston, P.A.; Quinn, J.C.; Piltz, J.W.; Weston, L.A. Metabolomic approaches for the identification of flavonoids associated with weed suppression in selected Hardseeded annual pasture legumes. Plant Soil 2019, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johns, C.W.; Lee, A.B.; Springer, T.I.; Rosskopf, E.N.; Hong, J.C.; Turechek, W.; Kokalis-Burelle, N.; Finley, N.L. Using NMR-based metabolomics to monitor the biochemical composition of agricultural soils: A pilot study. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2017, 83, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monreal, C.M.; Schnitzer, M.I. Labile organic matter in soil solution: II. Separation and identification of metabolites from plant–microbial communication in soil solutions of wheat rhizospheres. Labile Org. Matter SSSA. SPEC. PUB. 2015, 62, 173–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, H.L.; Rochfort, S.J.; Ezernieks, V.; Savin, K.W.; Mele, P.M. Metabolomics approaches for the discrimination of disease suppressive soils for Rhizoctonia solani AG8 in cereal crops using 1H NMR and LC-MS. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 1627–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochfort, S.; Ezernieks, V.; Mele, P.; Kitching, M. NMR metabolomics for soil analysis provide complementary, orthogonal data to MIR and traditional soil chemistry approaches—A land use study. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2015, 53, 719–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guijas, C.; Montenegro-Burke, J.R.; Warth, B.; Spilker, M.E.; Siuzdak, G. Metabolomics activity screening for identifying metabolites that modulate phenotype. Nat. Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernie, A.R.; Schauer, N. Metabolomics-assisted breeding: A viable option for crop improvement? Trends Genet. 2009, 25, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Gao, Y.; Xie, W.; Gong, L.; Lu, K.; Wang, W.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, H.; Dong, H. Genome-wide association analyses provide genetic and biochemical insights into natural variation in rice metabolism. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, L.; Chen, W.; Gao, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, H.; Xu, C.; Yu, S.; Zhang, Q.; Luo, J. Genetic analysis of the metabolome exemplified using a rice population. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 20320–20325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, W.; Li, K.; Alseekh, S.; Omranian, N.; Zhao, L.; Zhou, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Jin, M.; Yang, N.; Liu, H.; et al. Genetic determinants of the network of primary metabolism and their relationships to plant performance in a maize recombinant inbred line population. Plant Cell 2015, 27, 1839–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, W.; Liu, H.; Zhou, Y.; Jin, M.; Yang, N.; Li, D.; Luo, J.; Xiao, Y.; Pan, Q.; Tohge, T.; et al. Combining quantitative genetics approaches with regulatory network analysis to dissect the complex metabolism of the maize kernel. Plant Physiol. 2016, 170, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scossa, F.; Brotman, Y.; e Lima, F.d.A.; Willmitzer, L.; Nikoloski, Z.; Tohge, T.; Fernie, A.R. Genomics-based strategies for the use of natural variation in the improvement of crop metabolism. Plant Sci. 2016, 242, 47–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beleggia, R.; Rau, D.; Laidò, G.; Platani, C.; Nigro, F.; Fragasso, M.; De Vita, P.; Scossa, F.; Fernie, A.R.; Nikoloski, Z. Evolutionary metabolomics reveals domestication-associated changes in tetraploid wheat kernels. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1740–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toubiana, D.; Semel, Y.; Tohge, T.; Beleggia, R.; Cattivelli, L.; Rosental, L.; Nikoloski, Z.; Zamir, D.; Fernie, A.R.; Fait, A. Metabolic profiling of a mapping population exposes new insights in the regulation of seed metabolism and seed, fruit, and plant relations. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carreno-Quintero, N.; Acharjee, A.; Maliepaard, C.; Bachem, C.W.; Mumm, R.; Bouwmeester, H.; Visser, R.G.; Keurentjes, J.J. Untargeted metabolic quantitative trait loci analyses reveal a relationship between primary metabolism and potato tuber quality. Plant Physiol. 2012, 158, 1306–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuda, F.; Okazaki, Y.; Oikawa, A.; Kusano, M.; Nakabayashi, R.; Kikuchi, J.; Yonemaru, J.I.; Ebana, K.; Yano, M.; Saito, K. Dissection of genotype–phenotype associations in rice grains using metabolome quantitative trait loci analysis. Plant J. 2012, 70, 624–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piasecka, A.; Sawikowska, A.; Kuczynska, A.; Ogrodowicz, P.; Mikolajczak, K.; Krystkowiak, K.; Gudys, K.; Guzy-Wrobel-ska, J.; Krajewski, P.; Kachlicki, P. Drought-related econdary metabolites of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) leaves and their metabolomic quantitative trait loci. Plant J. 2017, 89, 898–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Templer, S.E.; Ammon, A.; Pscheidt, D.; Ciobotea, O.; Schuy, C.; McCollum, C.; Sonnewald, U.; Hanemann, A.; Förster, J.; Ordon, F.; et al. Metabolite profiling of barley flag leaves under drought and combined heat and drought stress reveals metabolic QTLs for metabolites associated with antioxidant defense. J. Exp. Bot. 2017, 68, 1697–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Long, Y.; Shi, L.; Shi, J.; Barker, G.; Meng, J. Characterization of metabolite quantitative trait loci and metabolic networks that control glucosinolate concentration in the seeds and leaves of Brassica napus. New Phytol. 2012, 193, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alseekh, S.; Tohge, T.; Wendenberg, R.; Scossa, F.; Omranian, N.; Li, J.; Kleessen, S.; Giavalisco, P.; Pleban, T.; Mueller-Roeber, B. Identification and mode of inheritance of quantitative trait loci for secondary metabolite abundance in tomato. Plant Cell 2015, 27, 485–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alseekh, S.; Tong, H.; Scossa, F.; Brotman, Y.; Vigroux, F.; Tohge, T.; Ofner, I.; Zamir, D.; Nikoloski, Z.; Fernie, A.R. Canalization of tomato fruit metabolism. Plant Cell 2017, 29, 2753–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, C.B.; Taylor, J.D.; Edwards, J.; Mather, D.; Langridge, P.; Bacic, A.; Roessner, U. Detection of QTL for metabolic and agronomic traits in wheat with adjustments for variation at genetic loci that affect plant phenology. Plant Sci. 2015, 233, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazmi, R.H.; Willems, L.A.; Joosen, R.V.; Khan, N.; Ligterink, W.; Hilhorst, H.W. Metabolomic analysis of tomato seed germination. Metabolomics 2017, 13, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, F.; Bradbury, P.J.; Brown, P.J.; Hung, H.; Sun, Q.; Flint-Garcia, S.; Rocheford, T.R.; McMullen, M.D.; Holland, J.B.; Buckler, E.S. Genome-wide association study of leaf architecture in the maize nested association mapping population. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, W.; Li, D.; Li, X.; Gao, Y.; Li, W.; Li, H.; Liu, J.; Liu, H.; Chen, W.; Luo, J. Metabolome-based genome-wide association study of maize kernel leads to novel biochemical insights. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.; Gao, Y.; Chen, W.; Wang, W.; Gong, L.; Liu, X.; Luo, J. Spatiotemporal distribution of phenolamides and the genetics of natural variation of hydroxycinnamoyl spermidine in rice. Mol. Plant. 2015, 8, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sotelo, T.; Soengas, P.; Velasco, P.; Rodríguez, V.M.; Cartea, M.E. Identification of metabolic QTLs and candidate genes for glucosinolate synthesis in Brassica oleracea leaves, seeds and flower buds. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Wang, W.; Peng, M.; Gong, L.; Gao, Y.; Wan, J.; Wang, S.; Shi, L.; Zhou, B.; Li, Z. Comparative and parallel genome-wide association studies for metabolic and agronomic traits in cereals. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, M.; Shahzad, R.; Gul, A.; Subthain, H.; Shen, S.; Lei, L.; Zheng, Z.; Zhou, J.; Lu, D.; Wang, S. Differentially evolved glucosyltransferases determine natural variation of rice flavone accumulation and UV-tolerance. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, F.; Nakabayashi, R.; Yang, Z.; Okazaki, Y.; Yonemaru, J.; Ebana, K.; Yano, M.; Saito, K. Metabolome-genome-wide association study (mGWAS) dissects genetic architecture for generating natural variation in rice secondary metabolism. Plant J. 2014, 81, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedelsheimer, C.; Lisec, J.; Czedik-Eysenberg, A.; Sulpice, R.; Flis, A.; Grieder, C.; Altmann, T.; Stitt, M.; Willmitzer, L.; Melchinger, A.E. Genome-wide association mapping of leaf metabolic profiles for dissecting complex traits in maize. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 8872–8877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Peng, Z.; Yang, X.; Wang, W.; Fu, J.; Wang, J.; Han, Y.; Chai, Y.; Guo, T.; Yang, N.; et al. Genome-wide association study dissects the genetic architecture of oil biosynthesis in maize kernels. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matros, A.; Liu, G.; Hartmann, A.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, H.; Ebmeyer, E.; Korzun, V.; Schachschneider, R.; Kazman, E.; et al. Genome–metabolite associations revealed low heritability, high genetic complexity, and causal relations for leaf metabolites in winter wheat (Triticum aestivum). J. Exp. Bot. 2016, 68, 415–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipka, A.E.; Gore, M.A.; Magallanes-Lundback, M.; Mesberg, A.; Lin, H.; Tiede, T.; Chen, C.; Buell, C.R.; Buckler, E.S.; Rocheford, T.; et al. Genome-wide association study and pathway-level analysis of tocochromanol levels in maize grain. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2013, 3, 1287–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owens, B.F.; Lipka, A.E.; Magallanes-Lundback, M.; Tiede, T.; Diepenbrock, C.H.; Kandianis, C.B.; Kim, E.; Cepela, J.; Mateos-Hernandez, M.; Buell, C.R.; et al. A foundation for provitamin A biofortification of maize: Genome-wide association and genomic prediction models of carotenoid levels. Genetics 2014, 198, 1699–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauvage, C.; Segura, V.; Bauchet, G.; Stevens, R.; Do, P.T.; Nikoloski, Z.; Fernie, A.R.; Causse, M. Genome-wide association in tomato reveals 44 candidate loci for fruit metabolic traits. Plant Physiol. 2014, 165, 1120–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razzaq, A.; Saleem, F.; Kanwal, M.; Mustafa, G.; Yousaf, S.; Imran Arshad, H.M.; Hameed, M.K.; Khan, M.S.; Joyia, F.A. Modern Trends in Plant Genome Editing: An Inclusive Review of the CRISPR/Cas9 Toolbox. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Analytical Tool | Applications | Advantages | Disadvantages | Properties |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (NMR) | Non-destructive; examination of metabolites; Comparative analysis of samples | Quantitative; Highly reproducible; Accurate quantification; Robust analysis; Ease of sample preparation; Provide rich information about metabolite structure; Separation not needed; Compatible with solids and liquids | High cost of instrument; Low sensitivity; Lack of bioinformatics platform; Large volume of sample is required; Spectral analysis hectic and time-consuming | Mass range: <~50 kDa; Sensitivity: Low (10−6 M) |
| Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS) | Good for detection of polar compounds; Suitable for secondary metabolite analysis like vitamins, glucosinolates; flavonoids and carotenoids; Ionization method: Atmospheric pressure chemical ionization (APCI) and electrospray ionization (ESI) | High sensitivity; Good selectivity; Less volume of sample required; Derivatization not needed; Minimal sample preparation; Covers a large portion of the metabolome | Destructive; Low separation of LC column; Reduced quantification; Ion suppression; Suitable for targeted profiling; Laborious sample preparation | Mass range: <1500 Da; Accuracy: 50–100 ppm; Sensitivity: High (10−15 M) |
| Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS) | Good for hydrophobic and polar compounds such as vitamins, organic acids, sugars, hydrocarbons and essential oils having a low molecular weight Ionization method: Electron impact (EI) | More accurate; High resolving power; Suitable for volatile compound analysis; Good sensitivity; Economical than NMR and LC-MS; Supported by bioinformatics and databases; Reproducible | Derivatization required; Destructive; Unsuitable for non-volatile compounds; Possible loss of pseudomolecular ion | Mass range: <350 Da; Accuracy: <50 ppm; Sensitivity: High (10−12 M) |
| Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR) | Detection of unknown metabolites analysis conducted based on mass to charge ratio (m/z) ion chemistry high-resolution MALDI | High-throughput analysis; Cost-effective; Direct characterization and separation in mixed samples; Provide more information about data | Not feasible for wet samples; Less specificity; Limited dynamic range; Isomer-related issues | Mass range: <1500 Da; Accuracy: <1 ppm; Sensitivity: High (10−18 M) |
| Crop | Stress Condition | Analytical Platform | Specific Tissue | Key Metabolites Produced | Data Analysis | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abiotic Stress Tolerance | ||||||
| Maize | Drought stress | RP/UPLC-MS/MS | Immature kernels | Metabolism of lipids, carbohydrates and glutathione cycle | PLS-DA KEGG | [14] |
| Maize | Drought stress | GC-TOF-MS | Multiple tissues | Adenine, phenylalanine, isoleucine, succinic acid, pyruvic acid, alanine, proline and xylose | ANOVA and PCA | [141] |
| Maize | Drought stress | GC/MS | Leaf blades | Myoinositol and glycine | ANOVA and PCA | [4] |
| Barley | Drought stress | MS-EI | Fifth leaf and Palea | Aromatic amino acids, proline, glutamine, threonine, aspartate, glycine and serine | PROC UNIVARIATE, SAS v. 9.4 | [16] |
| Wheat | Drought stress | GC-MS | Roots and leaves | Malic acid, fumaric acid, citric acid, valine and tryptophan | PLS-DA, KEEG | [17] |
| Wheat | Drought stress | GC/MS | Flag leaves | Glutamine, serine, methionine, lysine and asparagine | MetabolomeExpress | [20] |
| Wheat | Drought stress | GC-TOF-MS | Shoots | Malic acid, mannose, fructose, sucrose and proline | SIMCA 14.0, PCA, KEGG, MetaboAnalyst | [128] |
| Rice | Drought stress | GC-MS | Leaves | 4-hydroxycinnamic acid, ferulic acid, stearic acid and xylitol | PCA, PLS-DA | [139] |
| Rice | Drought stress | GC/EI-TOF-MS | Leaf | Glutamate, proline, GABA, arginine and spermidine | TagFinder and NIST | [140] |
| Rice | Drought stress | GC/MS | Leaf blades | Serine, threonine and asparagine | PCA | [143] |
| Soybean | Drought Stress | H-NMR | Leaf | Glutamine, GABA, allantoin, pinitol and myoinositol | PCA | [142] |
| Sorghum | Drought stress | FT-IR and GC/MS | Leaf | Sugars and sugar alcohols | PC-DFA | [44] |
| Rice | Salt stress | GC/MS | Leaf | Mannitol and sucrose | ANOVA and MassHunter MS | [23] |
| Rice | Salt stress | GC-MS | Seedling | Leucine, isoleucine, valine, proline and GABA | ANOVA and DMRT | [15] |
| Rice | Salt stress | NMR | Leaf and root | Acetic acid, GABA, sucrose and non-polar metabolites | PLS-DA | [18] |
| Rice | Salt stress | GC-MS | Leaf | Vanillic acid, 4-hydroxybenzoic acid, palmitic acid, stearic acid, raffinose, L-tryptophan and pyruvic acid | PCA, PLS-DA and MetaboAnalyst 3.0 | [146] |
| Wheat | Salt stress | GC/MS | Leaf | Proline, lysine, alanine and GABA | METABOLOMEEXPRESS | [9] |
| Wheat | Salt stress | HPLC | Roots and Shoots | Malic acid, proline, fructose, mannose, glycine, Glutamic acid | ANOVA, PCA, | [149] |
| Wheat | Salt stress | GC-TOF/MS | Leaf | Lysine, proline, sorbitol, lyxose and sucrose | PCA, OPLS-DA, KEGG and MetaboAnalyst | [144] |
| Maize | Salt stress | GC-MS | Leaf | Auxin, ABA | PCA, PLS-DA and SIMCA | [150] |
| Barley | Salt stress | GC/MS | Roots | Proline, sucrose, xylose and maltose | MetaboAnalyst | [147] |
| Tomato | Salt stress | UHPLC-ESI/QTOF-MS | Terminal leaflet | Sesquiterpene lactones, alkaloids and poluamines | ANNOVA, PCA, PLS-DA | [129] |
| Soybean | Waterlogging | CE/MS | Leaf | Phosphoenol pyruvate, NADH2, glycine and gammaaminobutyric acid | ANOVA | [22] |
| Soybean | Waterlogging | NMR | Roots and leaves | Isoflavones and kaempfero | ANOVA, PCA and MATLAB | [152] |
| Wheat | Waterlogging | GC/MS and LC/MS | Shoot | Lysine, proline, methionine and tryptophan | ANOVA and PCA | [153] |
| Rice | Waterlogging | GC/MS | Leaf | Glycine, alanine and GABA | PCA and MarkerLynx XS | [151] |
| Rice | Waterlogging | GC/MS and NMR | Leaf | 6-phosphogluconate, phenylalanine and lactate | ANOVA and PCA | [154] |
| Wheat | Heat stress | LC-HRMS | Flag leaves | Pipecolate and L-tryptophan | PLS-DA, KEGG | [25] |
| Wheat | Heat stress | LC-MS/MS HPLC | Filling grains | G1p and sucrose | Metaboanalyst 2.0 and KEGG | [156] |
| Wheat | Heat stress | GC-MS | Leaves | Melibiose, serine, lysine, glycine, malic acid, mannitol, xylitol, inositol, fructose, proline, glutamic acid and alanine | LSD | [158] |
| Tomato | Heat stress | GC-MS | Fruit pericarp | Rhamnose, putrescine, myoinositol, allantoin and alanine | PCA | [155] |
| Tomato | Heat stress | LC-QTOF-MS | Pollens | Flavonoids | MetAlign, METLIN, PCA and ANNOVA | [159] |
| Soybean | Heat stress | LC-MS, GC-MS | Seed | Ferulate, naringenin-7-O-glucoside, genistein, glycitein and apigenin | PCA | [157] |
| Maize | Heat stress | NMR | Leaf | Sucrose, fructose, GABA, aspartate, asparagine, valine, inositol, analine and proline | PCA and SIMCA | [160] |
| Canola | Metal stress | NMR | Roots and leaves | Hydroxycinnamic acids and glucosinolates | PCA, ANOVA and MultiExperiment Viewer | [163] |
| Sunflower | Metal stress (Cr) | capHPLC-ESI(−)-QTOF-MS | Roots and leaves | Fatty acids | PLS and MetaboScape | [161] |
| Soybean | Metal stress (Mo) | UPLC | Roots and leaves | Citric acid, D-glucarate, gluconic, L-nicotine, and flavonoids/isoflavone | PCA, KEGG, Metlin | [43] |
| Wheat | Nitrogen stress | GC-MS and LC-MS | Leaf | Tyrosine, lysine, allo-inositol and L-ascorbic acid | MS-excel package | [11] |
| Wheat | Nitrogen stress | GC-TOF-MS | Leaf | Fucose, ribulose, lyxose, galactinol and erythritol | PCA | [166] |
| Wheat | Low-nitrogen stress | UPLC-QTOF | Flag leaf | Methylisoorientin-2″-O-rhamnoside, iso-orientin and iso-vitexin | PCA, OPLS-DA, Markerlynx XS™, SIMCA-P | [172] |
| Barley | Sulfur stress | UPLC | Roots and leaves | sulfur metabolites, organic acids and amino acids | PCA, ANOVA, MassLynx and Progenesis QI | [168] |
| Biotic stress tolerance | ||||||
| Wheat | Zymoseptoria tritici | FT-ICR-MS | Leaf | Flavonoids, hydroxycinnamic acid amides and cinnamyl alcohols | MetaboScape 4.0, DataAnalysis 5.0 and KEGG | [26] |
| Wheat | Fusarium graminearum | NMR | Leaf | Trehalose, asparagine, phenylalanine, myoinositol, 3-hydroxybutarate and L-alanine | PCA, MestReNova 9.1.0 and Matlab | [21] |
| Wheat | Fusarium graminearum | NMR | Spikelet | Spermine, putrescine, GABA, inositols, galactose and lactic acid | PCA, MestReNova 9.1.0 and Matlab | [180] |
| Wheat | Wheat streak mosaic virus | UPLC-QTOF/MS | Leaf | Reduction in some amino acids such as L-tyrosine, tryptophan, isoleucine and phenylalanine | PCA, KEGG, METLIN, MetFrag and MetaboAnalyst | [41] |
| Wheat | Fusarium graminearum | LC-LTQ-Orbitrap | Rachis and spikelet | Fatty acids, terpenoid, phenolic glycosides, flavonoid and phenylpropanoids | MetaXCMS | [179] |
| Wheat | Triticum turgidum | LC/MS | Leaf | benzoxazinoids | PCA, XCMS and CAMERA | [188] |
| Rice | Orseolia royzae | GC/MS | Leaf | Heneicosanoic acid, threonic acid, palmitoleic acid, palmitic acid, nonadecanoic acid and linoleic acid | ANOVA | [181] |
| Rice | Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae | GC/TOF and LC/TOF | Leaf | Phenylalanine and tyrosine | KEGG, MassHunter, GeneSpring-MS 1.2 and METLIN | [182] |
| Rice | Magnaporthe grisea | NMR, GC/MS and LC/MS | Leaf | Cinnamate, proline, glutamine and malate | PCA and MATLAB | [183] |
| Rice | Rhizoctonia solani | CE/TOF-MS | Leaf | Jasmonic acid, mucic acid and glyceric acid | MPP software | [42] |
| Rice | Nilaparvata lugens | GC/MS | Leaf sheath | GABA and glyoxylate | PCA and PLS-DA | [186] |
| Rice | Chilo suppressalis | UHPLC-MS and GC-MS | Leaf | Terpenoids and phenylpropanoids | KEGG | [187] |
| Maize | Fusarium graminearum | LC/MS | Roots | metabolites smiglaside and smilaside A | ANOVA and SAS software | [24] |
| Maize | Bipolaris maydis | FT-IR and NMR | Leaf | lignin, flavonoids and polyphenols | PCA | [184] |
| Maize | Ostrinia furnacalis | HPLC-MS/MS | Leaf | Phtohormones and benzoxzinoids | KEGG, PLS-DA | [185] |
| Tomato | Pseudomonas syringae pv | NMR and LC/MS | Leaf | Flavonoid and phenylpropanoids | PCA, PLS-DA | [178] |
| Rice | Lolium perenne | LC-QTOF-MS | Root and shoot extracts | 3,5,6,7,8-pentahydroxy flavones, p-hydroxybenzoic acid and sinapyl alcohol | ANOVA and LSD | [189] |
| Wheat | Weeds | LC-MS/MS Q Trap | Root and shoot extracts | Benzooxazinoids | Analyst software | [190] |
| Wheat | Lolium rigidum Urochloa panicoides | LC-MS/MS Q Trap | Root and shoot extracts | Hydroxamic acids and Benzoxazinoids | Analyst software | [191] |
| Legumes | Weeds | UHPLC QTOF-MS | Root and shoot extracts | Flavonoids | METLIN | [192] |
| Wheat | Pathogen resistance | Py-FIMS | Soil rhizosphere | Glutarimide, consabatine, methylpyrrole, arachidonic acid, gibberellic acid and diacetyllycopsamine | PCA | [194] |
| Cereals | Rhizoctonia solani | LC/MS and 1H NMR | Soil rhizosphere | macrocarpal | PCA, PLS-DA, ANOVA and Matlab | [195] |
| Crop plants | Bacillus subtilis | NMR | Soil rhizosphere | Antimicrobial compounds | PCA | [196] |
| Crop | Analytical Tool | Sample Tissue | Population | Metabolic Traits | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mQTL | |||||
| Rice | LC-EI-MS | Flag leaf and seed | RILs | Metabolome | [200] |
| Rice | LC-Q-TOF-MS | Seed | BILs | Metabolome | [207] |
| Barley | LC/MS | Flag leaf | RILs | Metabolome | [208] |
| Barley | IC-MS, HPLC | Flag leaf | Landrace accessions | Metabolome | [209] |
| Maize | LC-MS | Kernel | RILs | Metabolome | [216] |
| Maize | LC-MS | Kernel | ILs and RILs | Metabolome | [202] |
| Maize | GC-TOF-MS | Kernel, leaf and seedling | RILs | Primary metabolism | [201] |
| Canola | HPLC | Seed and leaf | DH lines | Glucosinolates | [210] |
| Tomato | UPLC | Fruit | ILs | Secondary Metabolites | [211] |
| Tomato | UPL C-MS | Fruit | ILs | Secondary Metabolites | [212] |
| Tomato | GC/MS | Fruit | ILs | Metabolome | [205] |
| Wheat | LC-ESI-MS | Flag leaf | DH lines | Metabolome | [213] |
| Tomato | GC-TOF-MS | Germinating seed | RILs | Metabolome | [214] |
| mGWAS | |||||
| Rice | LC-E SI-MS | Grains | Landrace accessions | Metabolome | [219] |
| Rice | LC-QTOF-MS | Leaf | Landrace accessions | Secodary metabolites | [221] |
| Rice | LC/MS | Leaf | Landrace accessions | Phenolamides | [217] |
| Rice | LC/MS | Leaf | Landrace accessions | Metabolome | [199] |
| Maize | GC-MS | Leaf | ILs | Metabolome | [222] |
| Maize | UPLC | Kernel | ILs | Oil components | [223] |
| Maize | HPLC | Grain | ILs | Tocochromanol | [225] |
| Maize | HPLC | Grain | ILs | Carotenoid | [226] |
| Wheat | GC-MS | Leaf | Elite lines | Metabolome | [224] |
| Tomato | GC-MS | Fruit | Landrace accessions | Metabolome | [227] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Razzaq, A.; Sadia, B.; Raza, A.; Khalid Hameed, M.; Saleem, F. Metabolomics: A Way Forward for Crop Improvement. Metabolites 2019, 9, 303. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo9120303
Razzaq A, Sadia B, Raza A, Khalid Hameed M, Saleem F. Metabolomics: A Way Forward for Crop Improvement. Metabolites. 2019; 9(12):303. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo9120303
Chicago/Turabian StyleRazzaq, Ali, Bushra Sadia, Ali Raza, Muhammad Khalid Hameed, and Fozia Saleem. 2019. "Metabolomics: A Way Forward for Crop Improvement" Metabolites 9, no. 12: 303. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo9120303
APA StyleRazzaq, A., Sadia, B., Raza, A., Khalid Hameed, M., & Saleem, F. (2019). Metabolomics: A Way Forward for Crop Improvement. Metabolites, 9(12), 303. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo9120303