The Effect of Acute Supplementation of Branched Chain Amino Acids on Serum Metabolites During Endurance Exercise in Healthy Young Males: An Integrative Metabolomics and Correlation Analysis Based on a Randomized Crossover Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
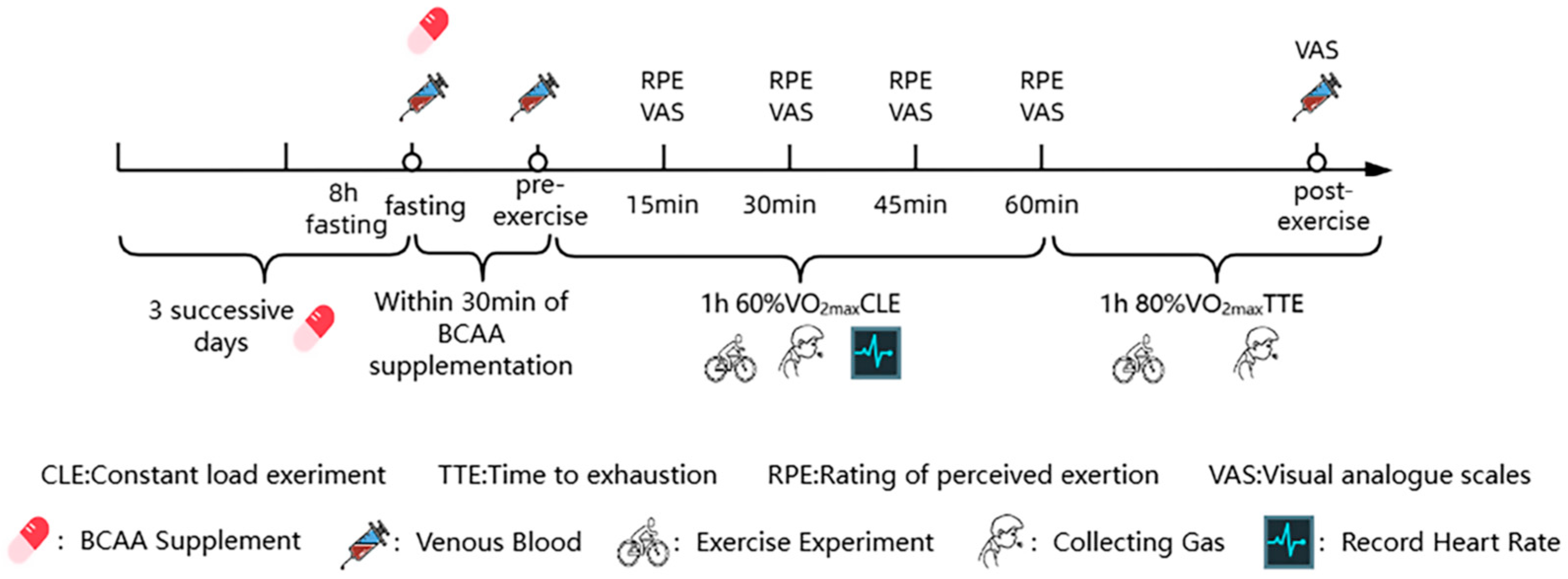
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Randomization and Supplementation Protocol
2.4. Dietary Control
2.5. Experimental Procedure
2.6. Blood Biochemical Analysis
2.7. Metabolite Profiling and Quantification
2.8. Quality Control and Differential Metabolites Screening
2.9. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Metabolomics Results
3.1.1. Data Quality Control
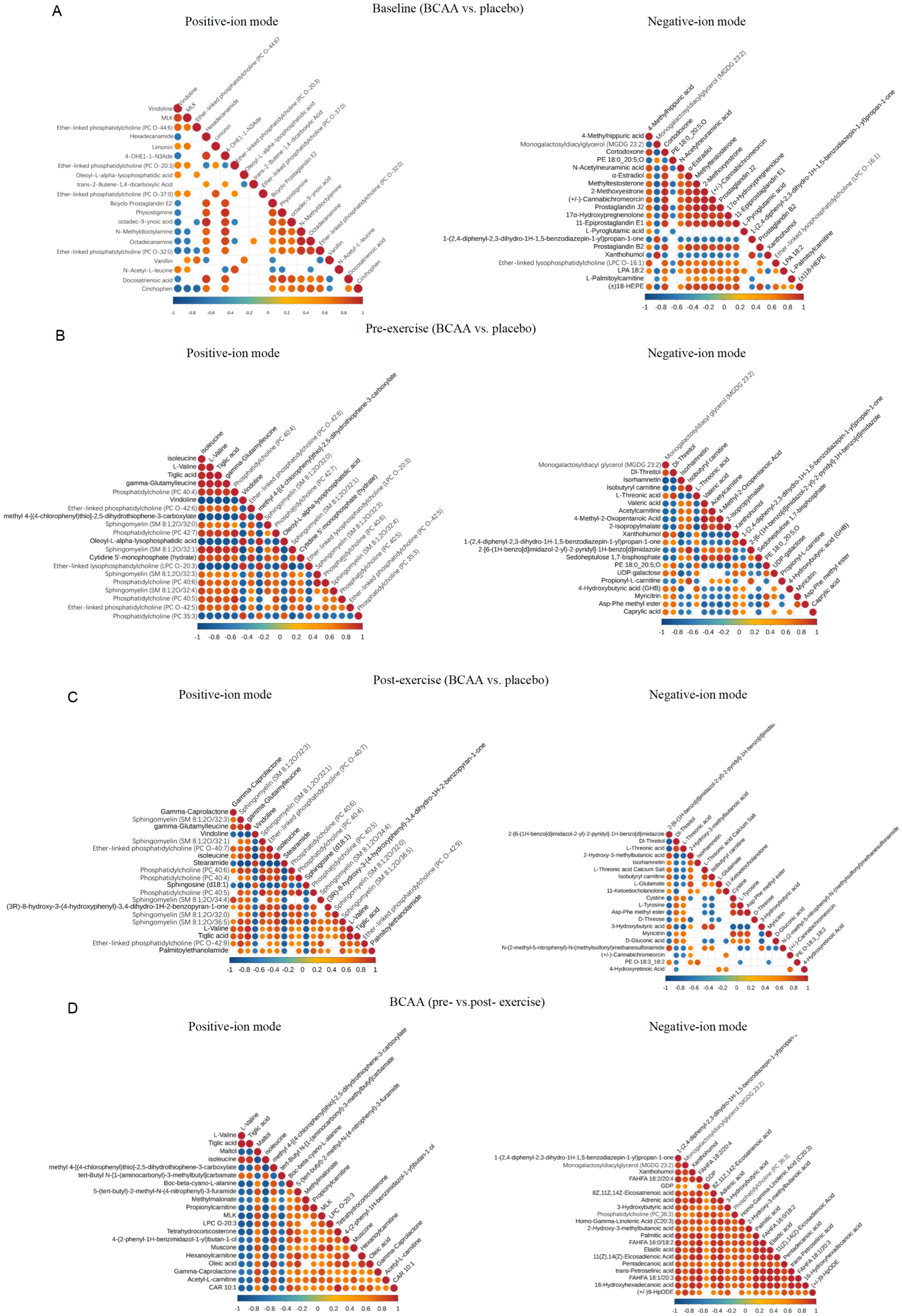
3.1.2. Characteristics of Differential Metabolite Between Supplementation Groups
3.1.3. Identification of Core Metabolites Altered by Exercise and BCAAs Supplementation
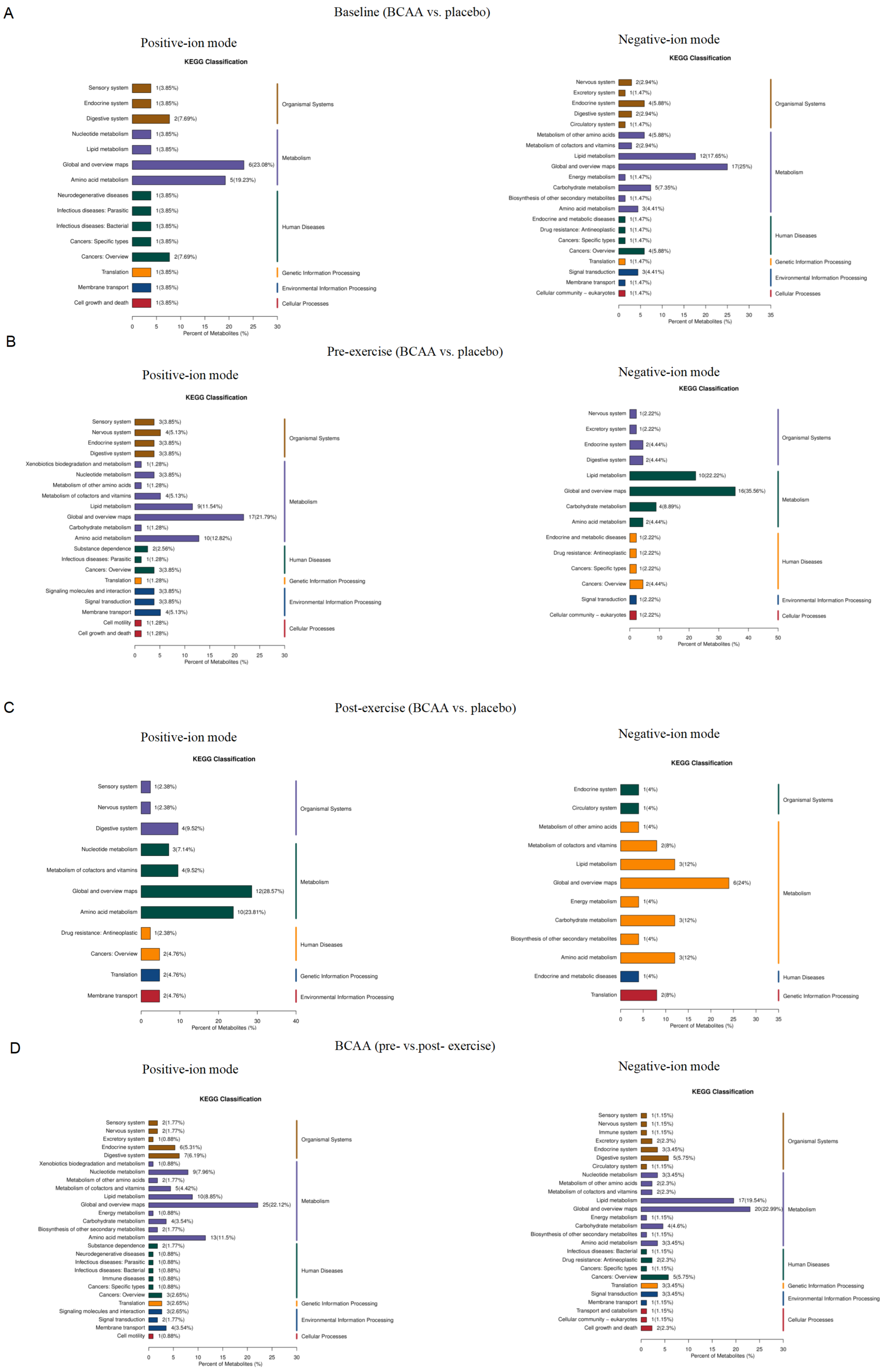
3.1.4. Pathway Enrichment Analysis
3.2. Integrative Correlation Analysis
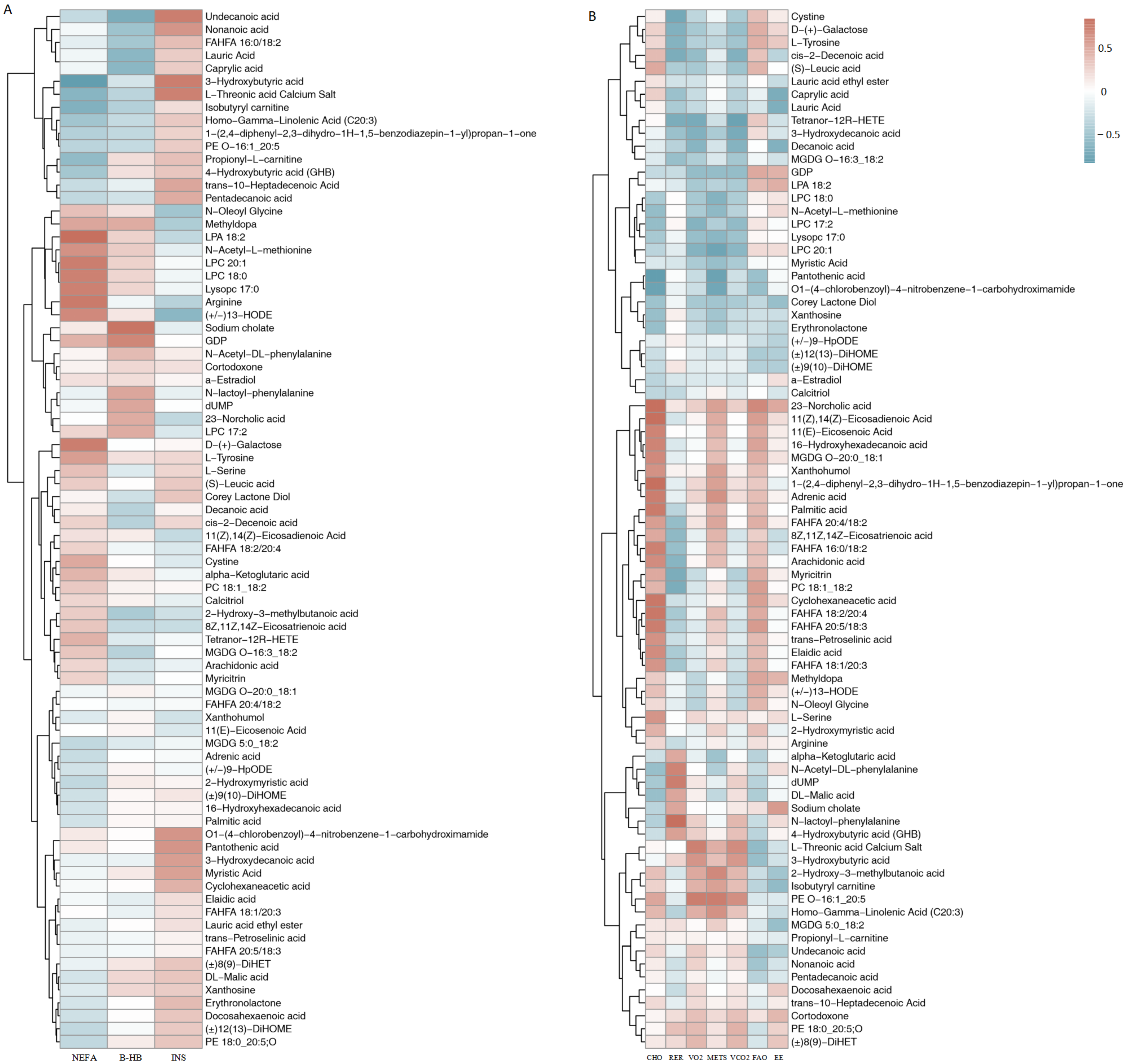
3.2.1. Correlation Between Blood Biochemical Markers and Metabolites
3.2.2. Correlation Between Respiratory Gas and Metabolites
3.3. Physiological and Biochemical Outcomes
4. Discussion
4.1. BCAA Supplementation Remodels Lipid and Energy Metabolism
4.2. Dual-Ion Mode Metabolic Regulation by BCAAs
4.3. Systemic Metabolic Coordination: Evidence from Correlation Analysis
4.4. Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Santos, C.d.S.; Nascimento, F.E.L. Isolated branched-chain amino acid intake and muscle protein synthesis in humans: A biochemical review. Einstein 2019, 17, eRB4898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, G.; Mora, S.; Madu, G.; Adegoke, O.A.J. Branched-chain Amino Acids: Catabolism in Skeletal Muscle and Implications for Muscle and Whole-body Metabolism. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 702826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaspy, M.S.; Hannaian, S.J.; Bell, Z.W.; Churchward-Venne, T.A. The effects of branched-chain amino acids on muscle protein synthesis, muscle protein breakdown and associated molecular signalling responses in humans: An update. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2023, 37, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedewa, M.V.; Spencer, S.O.; Williams, T.D.; Becker, Z.E.; Fuqua, C.A. Effect of branched-Chain Amino Acid Supplementation on Muscle Soreness following Exercise: A Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 2019, 89, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luan, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Zhou, N.; Song, G.; Ni, Z.; Xu, C.; Tang, C.; Fu, P.; Wang, X.; et al. Branched-Chain Amino Acid Supplementation Enhances Substrate Metabolism, Exercise Efficiency and Reduces Post-Exercise Fatigue in Active Young Males. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinho, D.V.; Nobari, H.; Faria, A.; Field, A.; Duarte, D.; Sarmento, H. Oral Branched-Chain Amino Acids Supplementation in Athletes: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salem, A.; Ben Maaoui, K.; Jahrami, H.; AlMarzooqi, M.A.; Boukhris, O.; Messai, B.; Clark, C.C.T.; Glenn, J.M.; Ghazzaoui, H.A.; Bragazzi, N.L.; et al. Attenuating Muscle Damage Biomarkers and Muscle Soreness After an Exercise-Induced Muscle Damage with Branched-Chain Amino Acid (BCAA) Supplementation: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis with Meta-regression. Sports Med.-Open 2024, 10, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondésert, E.; Bouchereau, J.; Schiff, M.; Benoist, J.-F.; Barcia, G.; Keren, B.; Mannes, I.; Pontoizeau, C.; Mansat, C.; Imbard, A. Branched-chain amino acid transferase type 2 (BCAT2) deficiency: Report of an eighth case and literature review. Mol. Genet. Metab. Rep. 2025, 43, 101213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hormoznejad, R.; Zare Javid, A.; Mansoori, A. Effect of BCAA supplementation on central fatigue, energy metabolism substrate and muscle damage to the exercise: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Sport Sci. Health 2019, 15, 265–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margolis, L.M.; Karl, J.P.; Wilson, M.A.; Coleman, J.L.; Whitney, C.C.; Pasiakos, S.M. Serum Branched-Chain Amino Acid Metabolites Increase in Males When Aerobic Exercise Is Initiated with Low Muscle Glycogen. Metabolites 2021, 11, 828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, M.G.; Dias, S.S.; de Angelis, T.R.; Fernandes, E.V.; Bernardes, A.G.; Milanez, V.F.; Jussiani, E.I.; de Paula Ramos, S. The use of BCAA to decrease delayed-onset muscle soreness after a single bout of exercise: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Amino Acids 2021, 53, 1663–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, R.S.; Kelly, M.P.; Kelly, P. Metabolomics, physical activity, exercise and health: A review of the current evidence. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Basis Dis. 2020, 1866, 165936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaguri, A.; Al Thani, A.A.; Elrayess, M.A. Exercise Metabolome: Insights for Health and Performance. Metabolites 2023, 13, 694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, M. Potential Role of Neuroactive Tryptophan Metabolites in Central Fatigue: Establishment of the Fatigue Circuit. Int. J. Tryptophan Res. 2020, 13, 1178646920936279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ra, S.-G.; Miyazaki, T.; Kojima, R.; Komine, S.; Ishikura, K.; Kawanaka, K.; Honda, A.; Matsuzaki, Y.; Ohmori, H. Effect of BCAA supplement timing on exercise-induced muscle soreness and damage: A pilot placebo-controlled double-blind study. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2018, 58, 1582–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez, M.C.; Herráiz, A.; Ciudad, M.J.; Arias, M.; Alonso, R.; Doblas, C.; Llama-Palacios, A.; Collado, L. Metabolomics and Biochemical Benefits of Multivitamin and Multimineral Supplementation in Healthy Individuals: A Pilot Study. Foods 2024, 13, 2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harshman, S.W.; Strayer, K.E.; Davidson, C.N.; Pitsch, R.L.; Narayanan, L.; Scott, A.M.; Schaeublin, N.M.; Wiens, T.L.; Phelps, M.S.; O’Connor, M.L.; et al. Rate normalization for sweat metabolomics biomarker discovery. Talanta 2021, 223, 121797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoramipour, K.; Sandbakk, Ø.; Keshteli, A.H.; Gaeini, A.A.; Wishart, D.S.; Chamari, K. Metabolomics in Exercise and Sports: A Systematic Review. Sports Med. 2021, 52, 547–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.; Long, Y.; Jiang, H.; Liao, Y.-J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J.-M.; Luo, Y.-H.; Feng, Z.; Yang, Y. Exercise-Induced Central Fatigue: Biomarkers, and Non-Medicinal Interventions. Aging Dis. 2024, 16, 1302–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Guo, Y.; Li, M.; Li, C.; Tan, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X.; Gao, F. Exercise Enhances Branched-Chain Amino Acid Catabolism and Decreases Cardiac Vulnerability to Myocardial Ischemic Injury. Cells 2022, 11, 1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoumacher, M.; Nguyen, J.; Brevers, E.; Cirillo, A.; Campas, M.; Grifnée, E.; Demeuse, J.; Huyghebaert, L.; Massonnet, P.; Dubrowski, T.; et al. Longitudinal NMR-based Metabolomics Analysis of Male Mountain Ultramarathon Runners: New Perspectives for Athletes Monitoring and Injury Prevention. Sports Med.-Open 2025, 11, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhao, C.; Hong, G.; Xiong, W.; Xia, J.; Dong, R.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, K.; Wang, B. Fatty acid oxidation contributed to NLRP3 inflammasome activation caused by N-nitrosamines co-exposure. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2025, 202, 115549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brun, J.F.; Myzia, J.; Varlet-Marie, E.; Raynaud de Mauverger, E.; Mercier, J. Beyond the Calorie Paradigm: Taking into Account in Practice the Balance of Fat and Carbohydrate Oxidation during Exercise? Nutrients 2022, 14, 1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Liu, Y.; Yan, T.; Zhang, B.; Zhou, L.; Zhu, W.; Wang, G.; Kang, J.; Peng, W.; Shi, L. Intermittent fasting, exercise, and dietary modification induce unique transcriptomic signatures of multiple tissues governing metabolic homeostasis during weight loss and rebound weight gain. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2024, 130, 109649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Luan, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Shan, W.; Ni, Z.; Xu, C.; Gong, L. The Effect of Acute Supplementation of Branched Chain Amino Acids on Serum Metabolites During Endurance Exercise in Healthy Young Males: An Integrative Metabolomics and Correlation Analysis Based on a Randomized Crossover Study. Metabolites 2026, 16, 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo16010041
Zhang X, Wang X, Luan C, Wang Y, Li J, Shan W, Ni Z, Xu C, Gong L. The Effect of Acute Supplementation of Branched Chain Amino Acids on Serum Metabolites During Endurance Exercise in Healthy Young Males: An Integrative Metabolomics and Correlation Analysis Based on a Randomized Crossover Study. Metabolites. 2026; 16(1):41. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo16010041
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xinxin, Xintang Wang, Chenglin Luan, Yizhang Wang, Junxi Li, Wei Shan, Zhen Ni, Chunyan Xu, and Lijing Gong. 2026. "The Effect of Acute Supplementation of Branched Chain Amino Acids on Serum Metabolites During Endurance Exercise in Healthy Young Males: An Integrative Metabolomics and Correlation Analysis Based on a Randomized Crossover Study" Metabolites 16, no. 1: 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo16010041
APA StyleZhang, X., Wang, X., Luan, C., Wang, Y., Li, J., Shan, W., Ni, Z., Xu, C., & Gong, L. (2026). The Effect of Acute Supplementation of Branched Chain Amino Acids on Serum Metabolites During Endurance Exercise in Healthy Young Males: An Integrative Metabolomics and Correlation Analysis Based on a Randomized Crossover Study. Metabolites, 16(1), 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo16010041






