Effects of Macrococcus caseolyticus on the Volatile Flavor Substances of Chinese-Style Sausage
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Starter Cultures
2.2. Sausage Preparation
2.3. Determination of Aw, pH Value, Total Plate Counts and Total Cocci Counts
2.4. Determination of Total Volatile Basic Nitrogen (TVB-N) Content
2.5. Determination of Malondialdehyde Content, Carbonyl Content, and Sulfhydryl Content
2.6. Gas Chromatography–Ion Mobility Spectrometry (GC-IMS) Analysis
2.7. Calculation of Relative Odor Activity Values (ROAVs)
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Subsection Physical and Chemical Evaluation
3.1.1. Aw and pH Analysis
3.1.2. Microbiological Analysis
3.1.3. TVB-N Content Analysis
3.1.4. Antioxidant Capacity Analysis
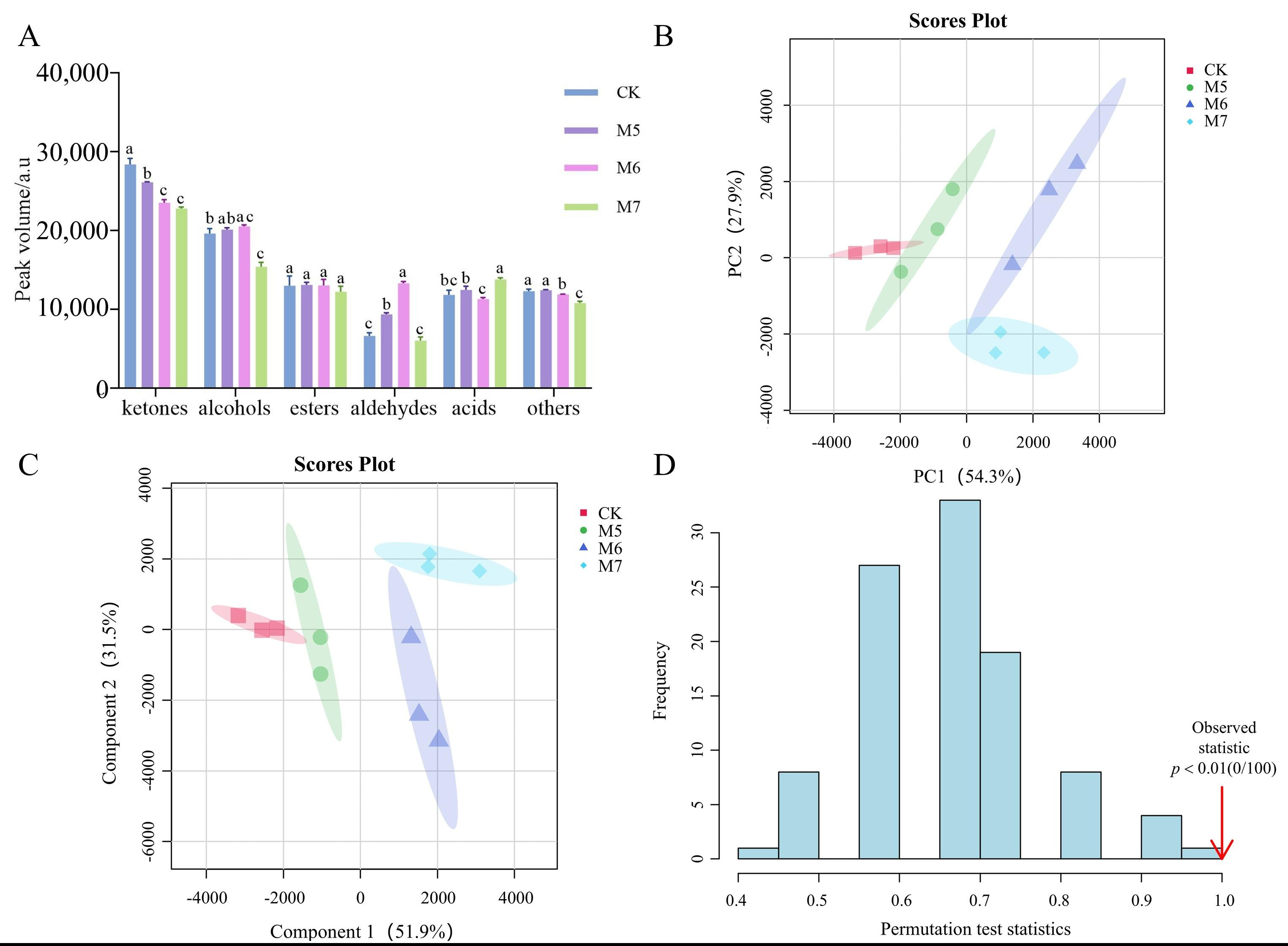
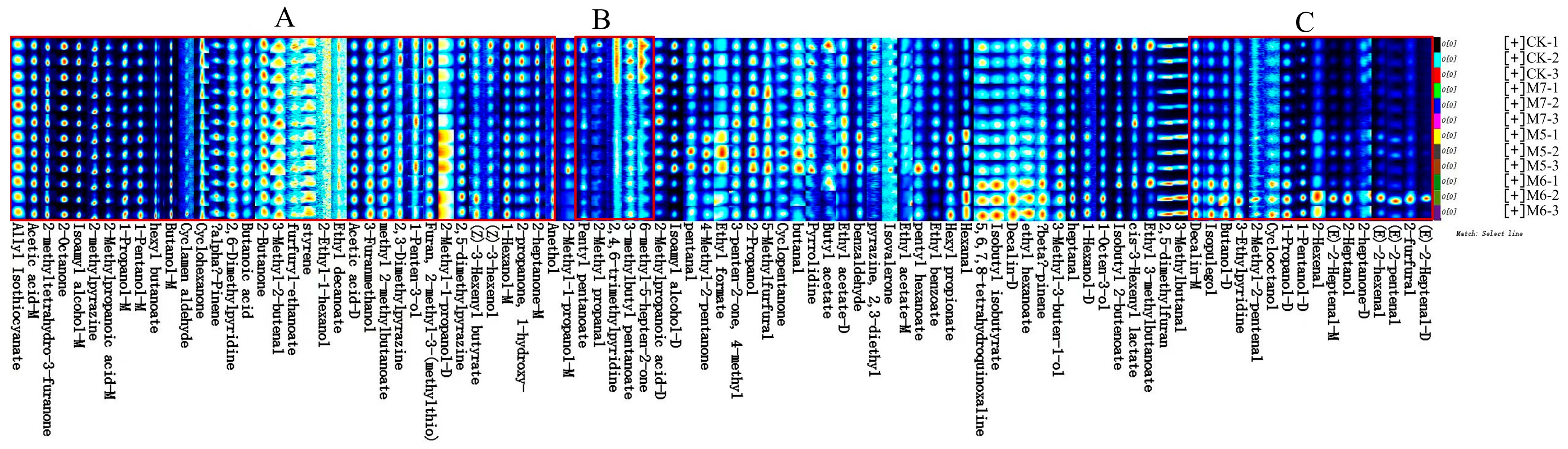
3.2. GC-IMS Analysis of the VOCs in Sausages
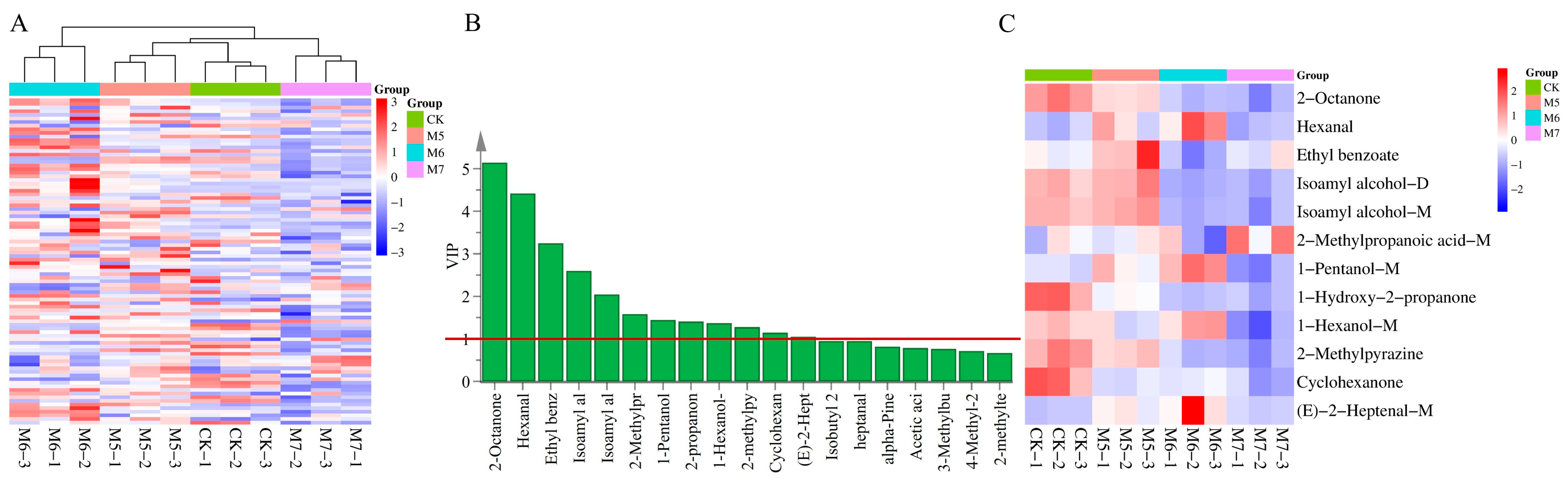
3.3. Multivariate Statistical Analysis of VOCs
3.4. Analysis of the Differential VOCs in Sausages
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, Y.; Gao, Y.F.; Xu, Y.J.; Zhou, H.; Zhou, K.; Li, C.; Xu, B.C. Microbiota dynamics and volatile metabolite generation during sausage fermentation. Food Chem. 2023, 423, 136297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuping, W.; Pengfei, Z.; Jingrong, C.; Huaigu, Y.; Jinhao, Z.; Xueming, L. The role of endogenous enzyme from straw mushroom (Volvariella volvacea) in improving taste and volatile flavor characteristics of Cantonese sausage. LWT 2022, 154, 112627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Gu, Y.; Zhang, K.P.; Tian, J.J.; Jin, Y. Effects of compound fermentation of lactic acid bacteria IMAUJBP3 and IMAUJBR3 on the characteristic flavors and metabolites of mutton fermented sausages. LWT 2024, 212, 116995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, M.; Gil, H.; YoungSu, S.; Inmyoung, P. Evolution of food fermentation processes and the use of multi-omics in deciphering the roles of the microbiota. Foods 2021, 10, 2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kai, S.; Yuanyue, Y.; Jingyi, W.; Tianming, Z.; Xianming, Z.; Miao, Z.; Weixin, K.; Hui, H.; Chunbao, L. Effect of probiotic Bacillus cereus DM423 on the flavor formation of fermented sausage. Food Res. Int. 2023, 172, 113210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, X.; Wang, H.; Song, X.; Xu, N.; Cai, L.; Sun, J.; Xu, X. Decoding the flavor regulation mechanism of fermented sausages inoculated with indigenous strains via metagenomic and GC-MS analysis. LWT 2024, 206, 116604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, M. Understanding the implications of current health trends on the aroma of wet and dry cured meat products. Meat Sci. 2018, 144, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingyan, X.; Min, Q.; Feng, C.; Yi, W.; Jun, H.; Ye, X.; Kaiping, Z.; Jianjun, T.; Ye, J. The effect of lactic acid bacteria on lipid metabolism and flavor of fermented sausages. Food Biosci. 2023, 56, 103172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruifang, M.; Xi, C.; Suyue, X.; Biao, Q.; Jiapeng, L.; Xiaoling, Q.; Wenhua, C.; Chao, Q.; Shouwei, W. Predominant yeasts in Chinese Dong fermented pork (Nanx Wudl) and their aroma-producing properties in fermented sausage condition. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2021, 10, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ángeles, S.M.; Estefanía, S.N.; Julia, R.M.; Paola, S.L.; Virginia, Z.M.; Manuel, L.J.; Lisandro, S.M.; Sebastián, F.L. Effects of lactic acid bacteria and coagulase-negative staphylococci on dry-fermented sausage quality and safety: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Meat Sci. 2023, 206, 109337. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, F.; Zhang, K.; Wang, D.; Xia, L.; Gu, Y.; Tian, J.; Jin, Y. Effect of Lactobacillus helveticus IMAUJBH1 on fat and volatile flavor substances in fermented mutton sausages. Food Chem. X 2024, 21, 101205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, Y.; Zhang, B.; Liu, J.; Zhu, J.; Ren, J.; Qin, L.; Chen, Q. Screening and evaluating yeast strains with antioxidant potential from the traditional dry sausage of northern China. LWT 2024, 203, 116395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.F.; Zhou, C.Y.; Ning, J.W.; Wang, S.; Nie, Q.; Wang, W.; Zhang, J.M.; Ji, L.L. Effect of fermentation by Pediococcus pentosaceus and Staphylococcus carnosus on the metabolite profile of sausages. Food Res. Int. 2022, 162, 112096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiramatsu, K.; Katayama, Y.; Matsuo, M.; Sasaki, T.; Morimoto, Y.; Sekiguchi, A.; Baba, T. Multi-drug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and future chemotherapy. J. Infect. Chemother. 2014, 20, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacFadyen, A.C.; Fisher, E.A.; Costa, B.; Cullen, C.; Paterson, G.K. Genome analysis of methicillin resistance in Macrococcus caseolyticus from dairy cattle in England and Wales. Microb. Genom. 2018, 4, e000191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazhar, S.; Kilcawley, K.N.; Hill, C.; McAuliffe, O. A Systems-Wide Analysis of proteolytic and lipolytic pathways uncovers the flavor-forming potential of the gram-positive bacterium Macrococcus caseolyticus subsp. caseolyticus. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrkonjić, F.M.; Stefanie, W.; Marion, E.; Gerhard, W.; Jasmina, H.; Michael, S. Dynamics of bacterial communities during the ripening process of different Croatian cheese types derived from raw ewe’s milk cheeses. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80734. [Google Scholar]
- Standard’s National Food Safety Standard of the People’s Republic of China (GB 5009.228-2016); Determination of total volatile basic nitrogen in food. China National Standardization Administration: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Standard’s National Food Safety Standard of the People’s Republic of China (GB 5009.181-2016); Determination of malondialdehyde in food. China National Standardization Administration: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Hongfan, C.; Xin, N.; Tao, P.; Lu, X.; Dayu, L.; Huailiang, L.; Zhiping, Z. Effects of Low-Temperature and Low-Salt fermentation on the physicochemical properties and volatile flavor substances of Chinese Kohlrabi using gas chromatography–ion mobility spectrometry. Fermentation 2023, 9, 146. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.; Wang, Q.; Hu, S.; Jiang, J.; Wu, J.; Li, P.; Gu, Q.; Xiao, H. Comparative analysis of the microbiota succession and flavor formation in spontaneously fermented fish sauces made with silvery pomfret (Pampus argenteus) and little yellow croaker (Larimichthys polyactis). LWT 2024, 208, 116747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Li, H.; Wu, H.; Liu, S.; He, Z. Staphylococcus inoculation enhances the sensorial attributes of Chinese bacon by coordinating the composition of flavor compounds through amino acid metabolism. Food Res. Int. 2024, 178, 113936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rongxin, W.; Fangda, S.; Yan, W.; Qian, C.; Baohua, K. Evaluation the potential of lactic acid bacteria isolates from traditional beef jerky as starter cultures and their effects on flavor formation during fermentation. LWT 2021, 142, 110982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Luo, H.; Xiao, Q.; Chen, C.; Xu, B.; Li, P. Effect of Latilactobacillus sakei and Staphylococcus xylosus on the textural characteristics of dry fermented sausages. Food Biosci. 2024, 59, 103972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekhit, A.E.-D.A.; Holman, B.W.; Giteru, S.G.; Hopkins, D.L. Total volatile basic nitrogen (TVB-N) and its role in meat spoilage: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 109, 280–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debao, W.; Guanhua, H.; Huiting, W.; Limei, W.; Yuanyuan, Z.; Yufu, Z.; Lihua, Z.; Fang, L.; Ye, J. Effect of mixed starters on proteolysis and formation of biogenic amines in dry fermented mutton sausages. Foods 2021, 10, 2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores, M.; Toldrá, F. Microbial enzymatic activities for improved fermented meats. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 22, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Kong, B.; Han, Q.; Liu, Q.; Xu, L. The role of bacterial fermentation in the hydrolysis and oxidation of sarcoplasmic and myofibrillar proteins in Harbin dry sausages. Meat Sci. 2016, 121, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, X.; Zhang, R.; Jiang, S.; Song, Z.; Du, M.; Liu, A. Volatile flavor profiles of douchis from different origins and varieties based on GC-IMS and GC-O-QTOF/MS analysis. Food Chem. 2024, 460, 140717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Zeng, Y.; Zhu, K.; Peng, Y.; Xv, P.; Dong, P.; Qiao, M.; Fan, W. Characterization of the quality and flavor in Chinese sausage: Comparison between Cantonese, Five-Spice, and Mala sausages. Foods 2025, 14, 1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroy, F.; Verluyten, J.; De Vuyst, L. Functional meat starter cultures for improved sausage fermentation. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2006, 106, 270–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspardo, B.; Procida, G.; Toso, B.; Stefanon, B. Determination of volatile compounds in San Daniele ham using headspace GC–MS. Meat Sci. 2008, 80, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuobing, X.; Longxue, L.; Yunwei, N.; Jing, Z.; Daoying, W.; Cunshan, Z. Mushroom alcohol(1-octen-3-ol)and other 7 aroma compounds selected from Chinese dry-cured hams can enhance saltiness perception. Meat Sci. 2024, 208, 109398. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Cao, Z.; Yu, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Zhao, K. Effect of inoculating mixed starter cultures of Lactobacillus and Staphylococcus on bacterial communities and volatile flavor in fermented sausages. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2023, 12, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natteewan, U.; Sureelak, R.; Somboon, T.; Jirawat, Y. Improvement of fish sauce quality by strain CMC5-3-1: A novel species of Staphylococcus sp. J. Food Sci. 2015, 80, M2015–M2022. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Hou, J.N.; Zhang, X.; Hu, J.R.; Yu, Z.H.; Zhu, Y.C. Improving the flavor of fermented sausage by increasing its bacterial quality via inoculation with Lactobacillus plantarum MSZ2 and Staphylococcus xylosus YCC3. Foods 2022, 11, 736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariutti, L.R.B.; Bragagnolo, N. Influence of salt on lipid oxidation in meat and seafood products: A review. Food Res. Int. 2017, 94, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Liu, Y.; He, N.; Li, X.; Zhu, Y. Comprehensive analysis of the effect of Staphylococcus xylosus YCC3 fermentation on bacterial community, flavor and lipid metabolism of fermented sausages. Food Biosci. 2025, 69, 106920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
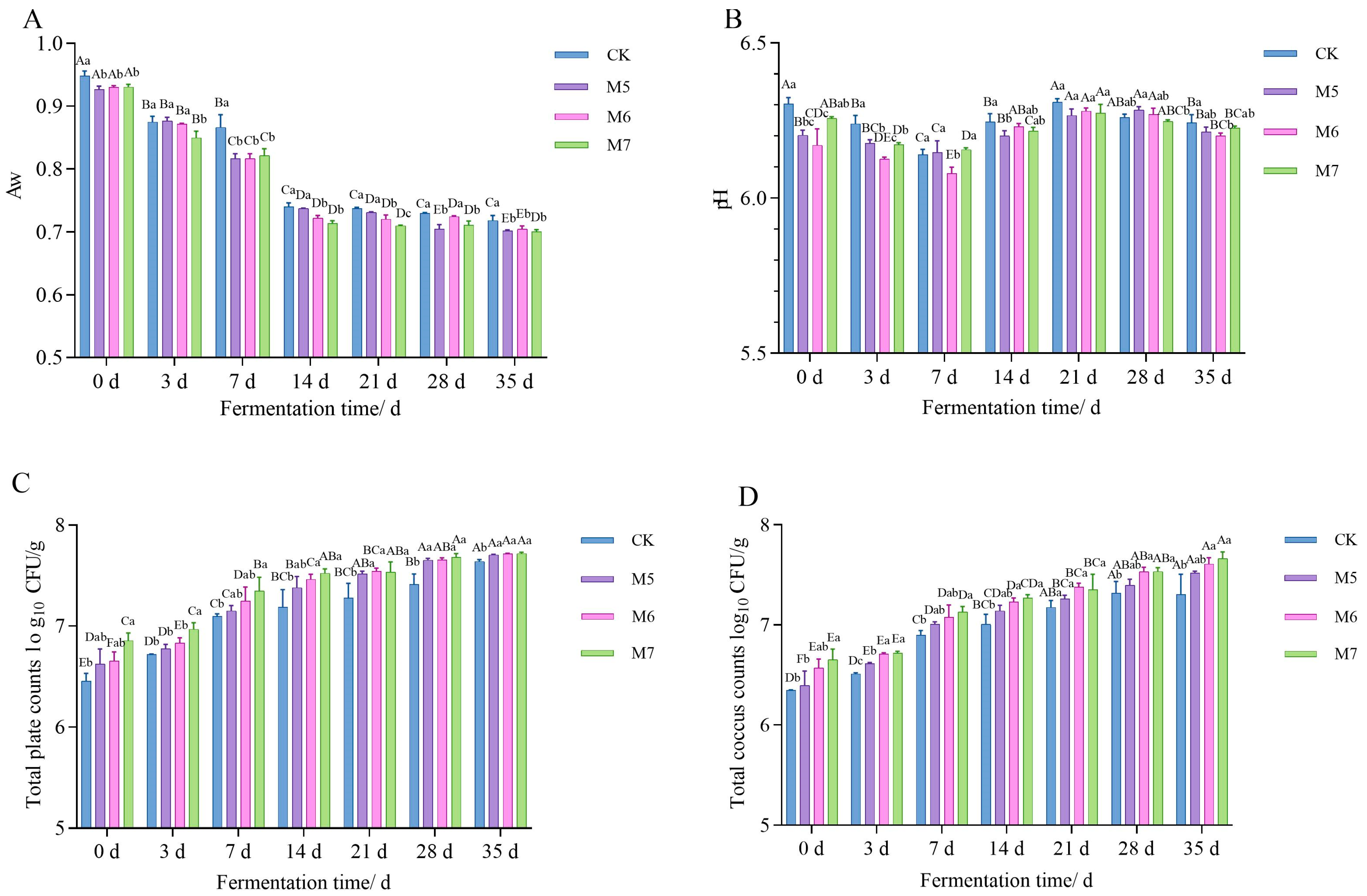
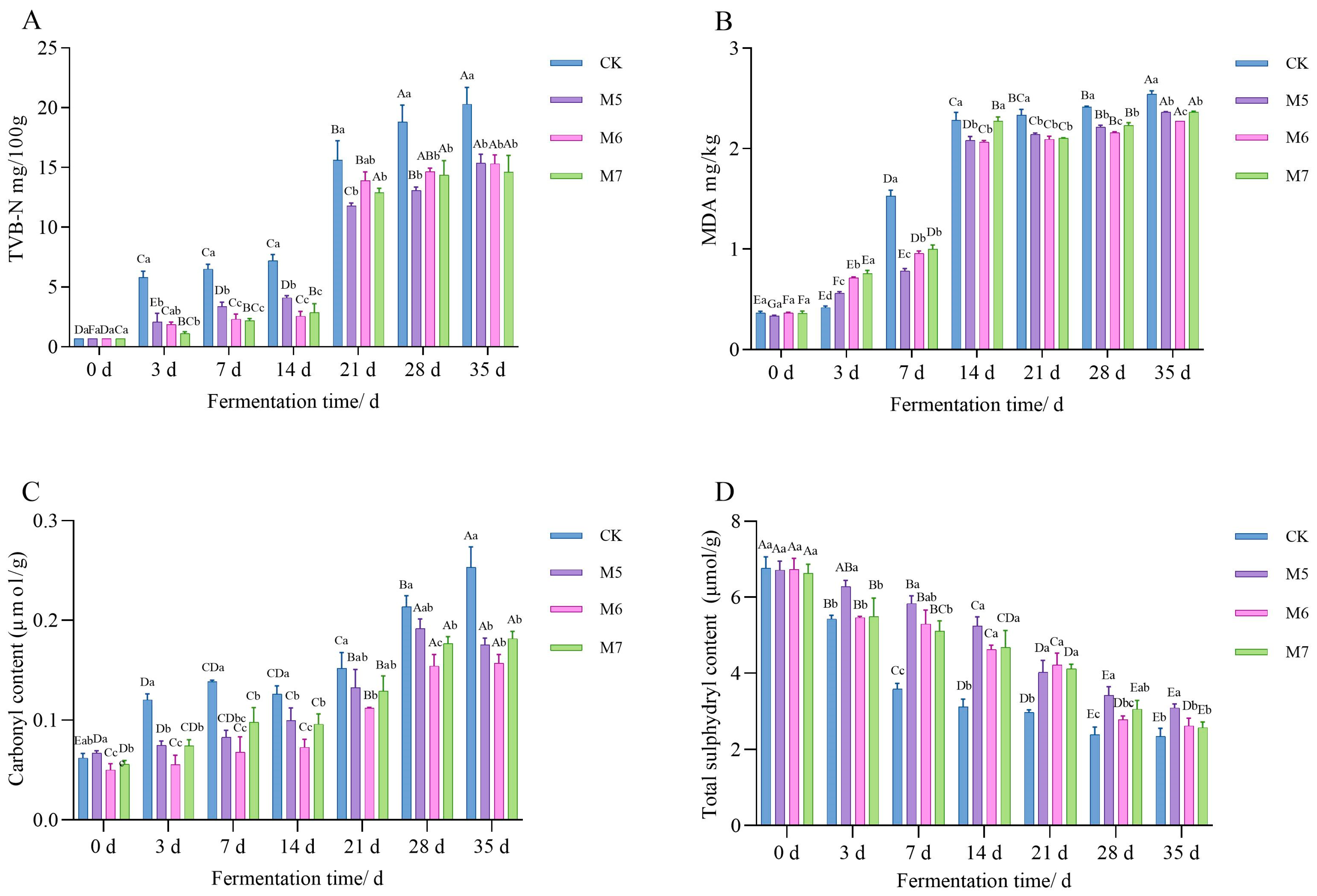

| Experimental Factor and Interaction of Experimental Factors | Aw | pH | TPC | Coccus Count | TVB-N | MDA | Carbonyl | Sulfhydryl |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fermentation time | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 |
| Concentrations | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 |
| Fermentation time × Concentrations | <0.05 | <0.05 | 0.121 | 0.917 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 |
| Parameter trend | ↓ | ↓ | ↑ | ↑ | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ | ↑ |
| CAS | Flavor Substances | VIP | Aroma Descriptions | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | C111137 | 2-Octanone | 5.14186 | Cheese, flower |
| 2 | C66251 | Hexanal | 4.41696 | Fruit, vegetable |
| 3 | C93890 | Ethyl benzoate | 3.24763 | Flower, fruit |
| 4 | C123513 | Isoamyl alcohol-D | 2.59784 | |
| 5 | C123513 | Isoamyl alcohol-M | 2.04378 | Bitter, grease |
| 6 | C79312 | 2-Methylpropanoic acid-M | 1.58308 | Cream, cheese |
| 7 | C71410 | 1-Pentanol-M | 1.44508 | Camphor |
| 8 | C109944 | 1-Hydroxy-2-propanone | 1.40796 | Fruit |
| 9 | C111273 | 1-Hexanol-M | 1.37159 | Fruit |
| 10 | C109080 | 2-Methylpyrazine | 1.27721 | Roasted nuts |
| 11 | C108941 | Cyclohexanone | 1.14571 | Mint |
| 12 | C18829555 | (E)-2-Heptenal-M | 1.05179 | Grease, fruit |
| Compounds | CAS | Retention Time/s | Threshold (μg/kg) | ROAV | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | M5 | M6 | M7 | ||||
| 1-Octen-3-ol | C3391864 | 1,138,229 | 1.50 | 1.02 | 1.33 | 1.20 | 1.04 |
| Isoamyl alcohol | C123513 | 486,655 | 4.00 | 1.42 | 2.26 | 0.68 | 1.01 |
| Heptanal | C111717 | 461,602 | 2.80 | 0.70 | 1.35 | 1.07 | 0.82 |
| Hexanal | C66251 | 348,385 | 5.00 | 0.77 | 2.00 | 1.92 | 1.01 |
| Methyl 2-methylbutyrate | C868575 | 311,674 | 0.25 | 2.63 | 4.43 | 3.13 | 3.74 |
| Ethyl 3-methylbutanoate | C108645 | 252,942 | 0.01 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| Alpha-Pinene | C80568 | 29,052 | 4.60 | 0.61 | 1.16 | 0.83 | 0.92 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gu, Y.; Chen, X.; Mao, J.; Nie, X.; Zhu, C.; Zou, Q.; Luo, Q.; Zeng, Y.; Laghi, L.; Picone, G.; et al. Effects of Macrococcus caseolyticus on the Volatile Flavor Substances of Chinese-Style Sausage. Metabolites 2025, 15, 570. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15090570
Gu Y, Chen X, Mao J, Nie X, Zhu C, Zou Q, Luo Q, Zeng Y, Laghi L, Picone G, et al. Effects of Macrococcus caseolyticus on the Volatile Flavor Substances of Chinese-Style Sausage. Metabolites. 2025; 15(9):570. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15090570
Chicago/Turabian StyleGu, Yuanqing, Xinya Chen, Jingjing Mao, Xin Nie, Chenglin Zhu, Qin Zou, Qiqi Luo, Yudi Zeng, Luca Laghi, Gianfranco Picone, and et al. 2025. "Effects of Macrococcus caseolyticus on the Volatile Flavor Substances of Chinese-Style Sausage" Metabolites 15, no. 9: 570. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15090570
APA StyleGu, Y., Chen, X., Mao, J., Nie, X., Zhu, C., Zou, Q., Luo, Q., Zeng, Y., Laghi, L., Picone, G., & Zhao, Z. (2025). Effects of Macrococcus caseolyticus on the Volatile Flavor Substances of Chinese-Style Sausage. Metabolites, 15(9), 570. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15090570





