Urinary 1H-NMR Metabolomics Highlights MIIA (Microbiota–Immune–Inflammation Axis) Activation by Organic Mediterranean Diet
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
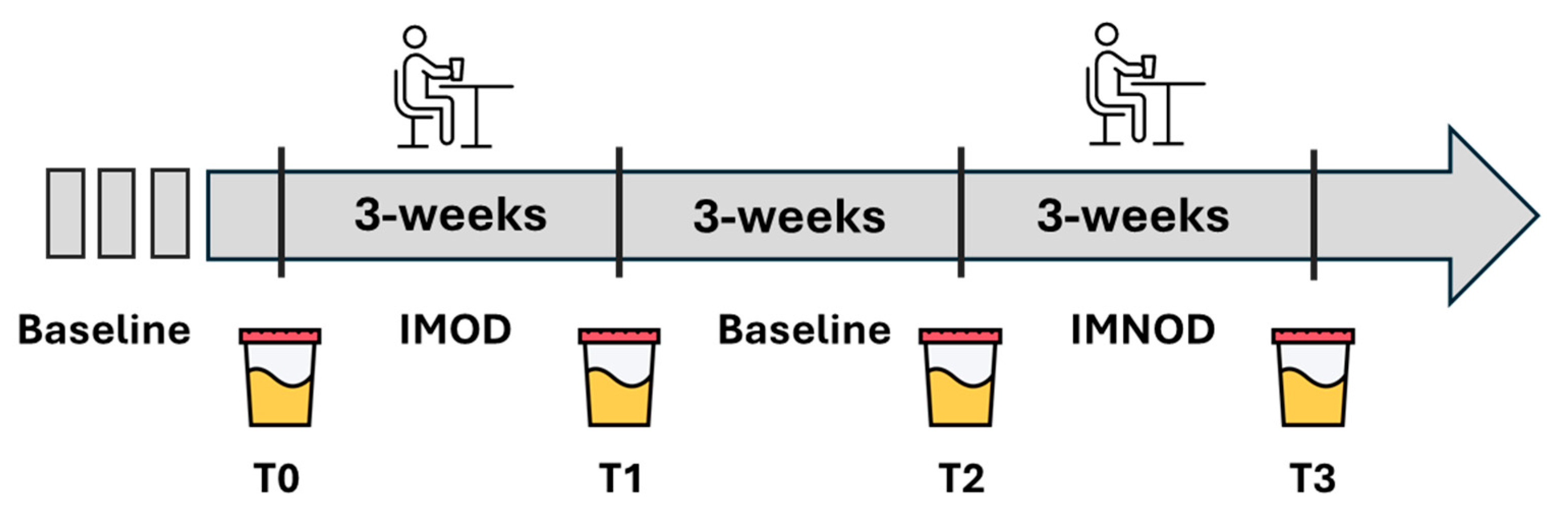
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Intervention Diets
2.3. Sample Preparation
2.4. 1H-NMR Spectral Acquisition
2.5. Spectral Deconvolution
2.6. Data Processing
2.6.1. Delta Calculation
2.6.2. Data Scaling and Multivariate Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Subject Enrollment
3.2. NMR Profiling Applied to Nutrition
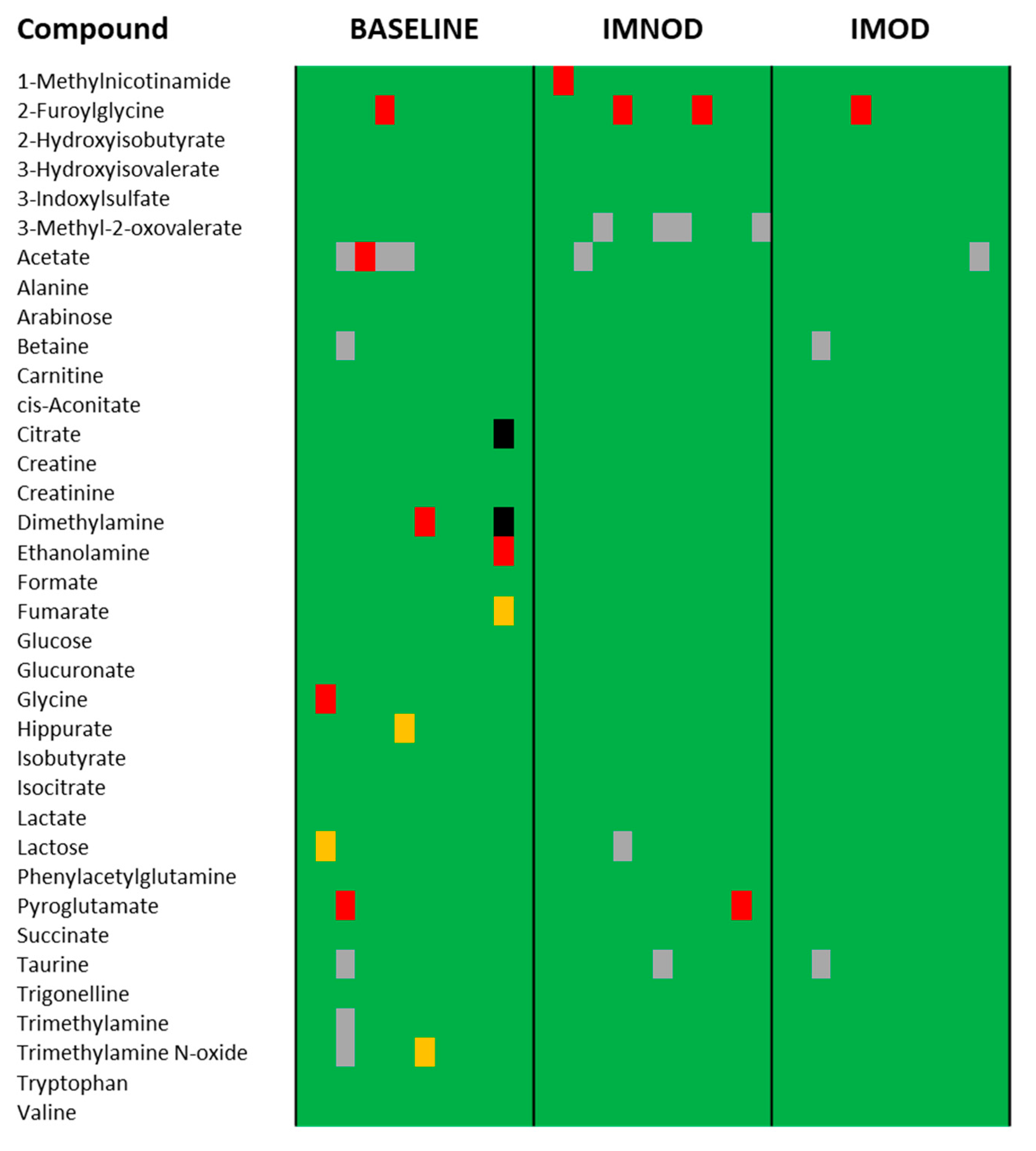
3.3. Subsection Comparison to Physiological Reference Ranges Suggests Metabolic Stabilization Following Mediterranean Diet Intervention
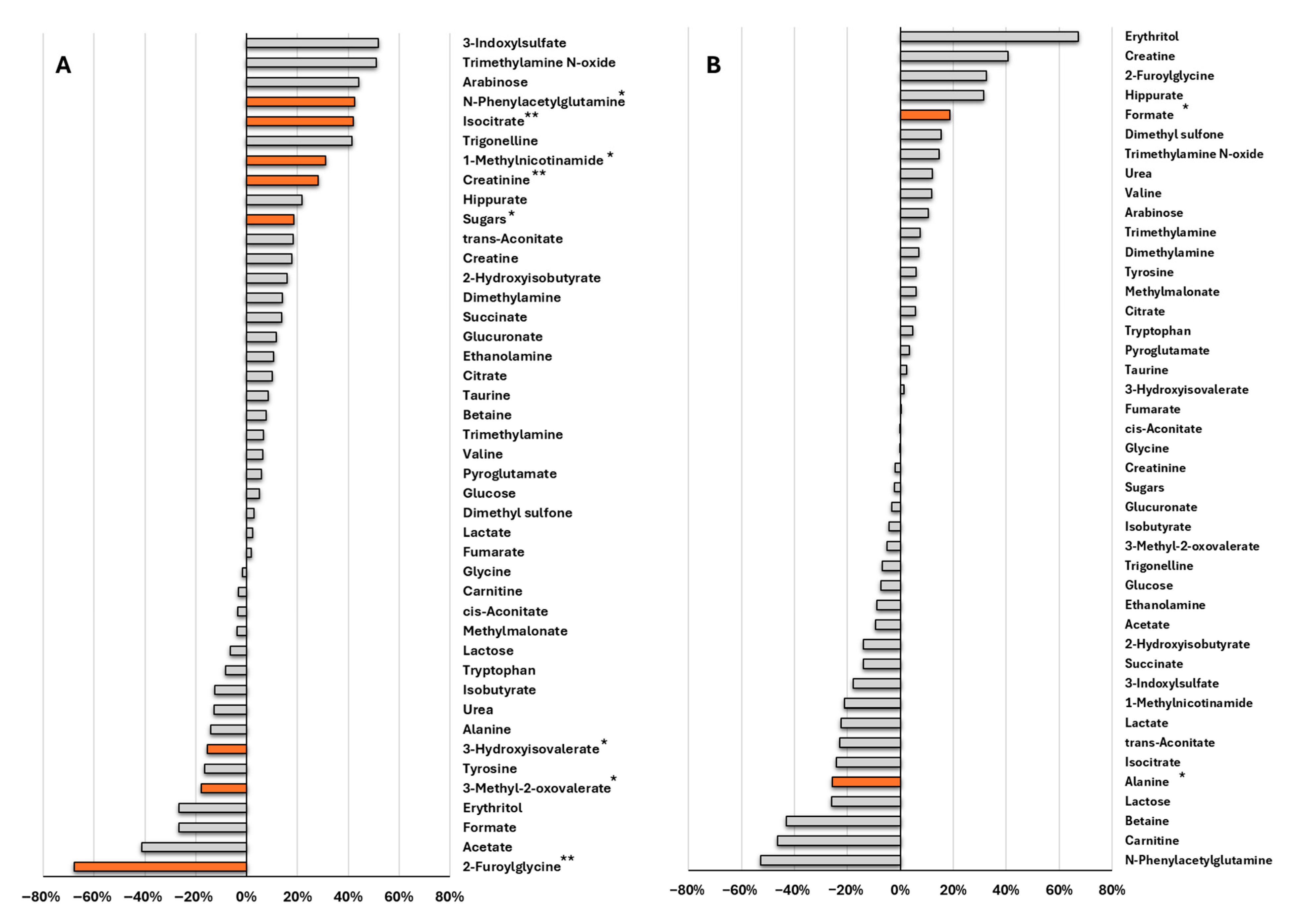
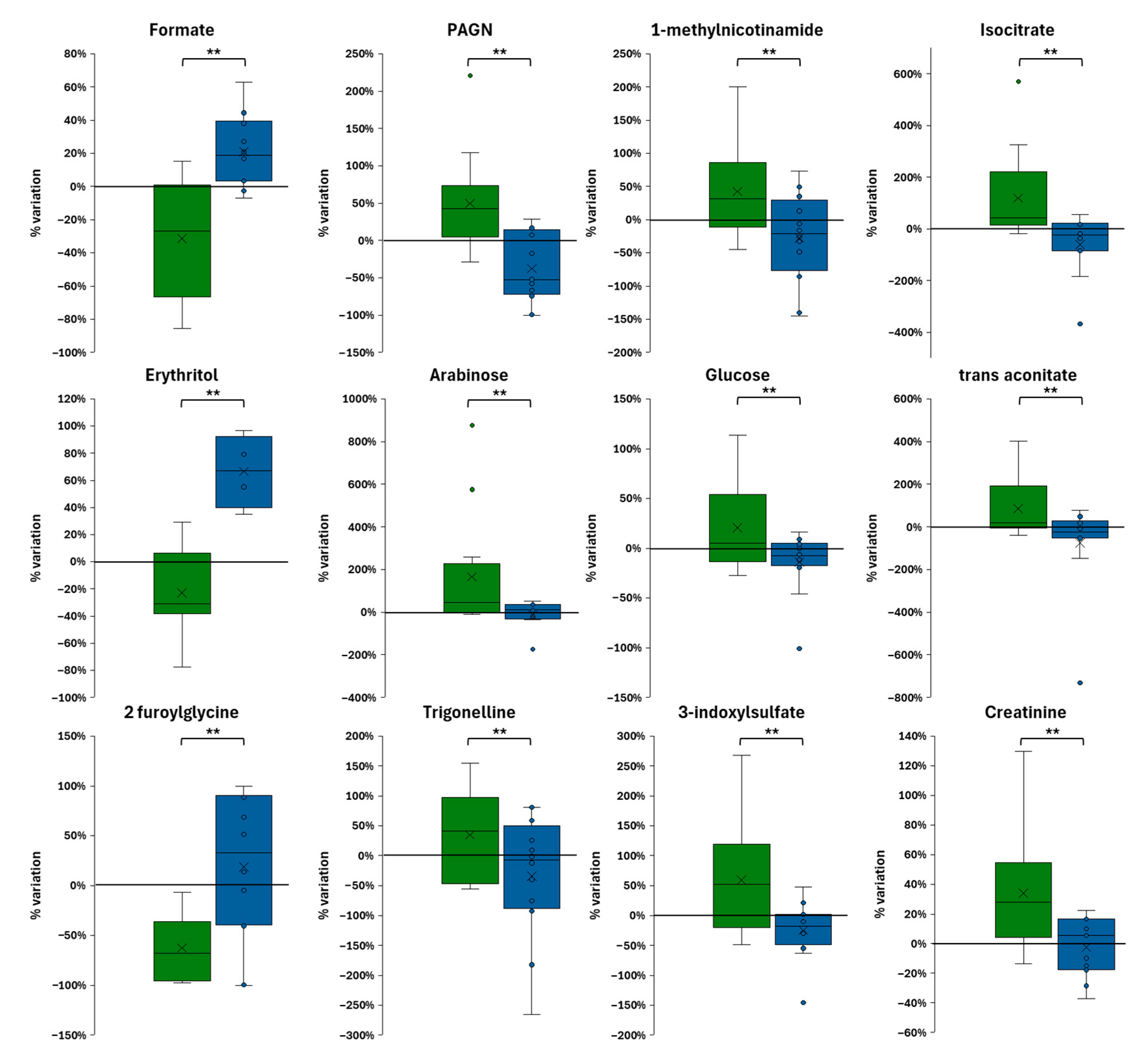
3.4. Subsection Organic Foods Alter a Broader Range of Urinary Metabolites Compared to Non-Organic Foods
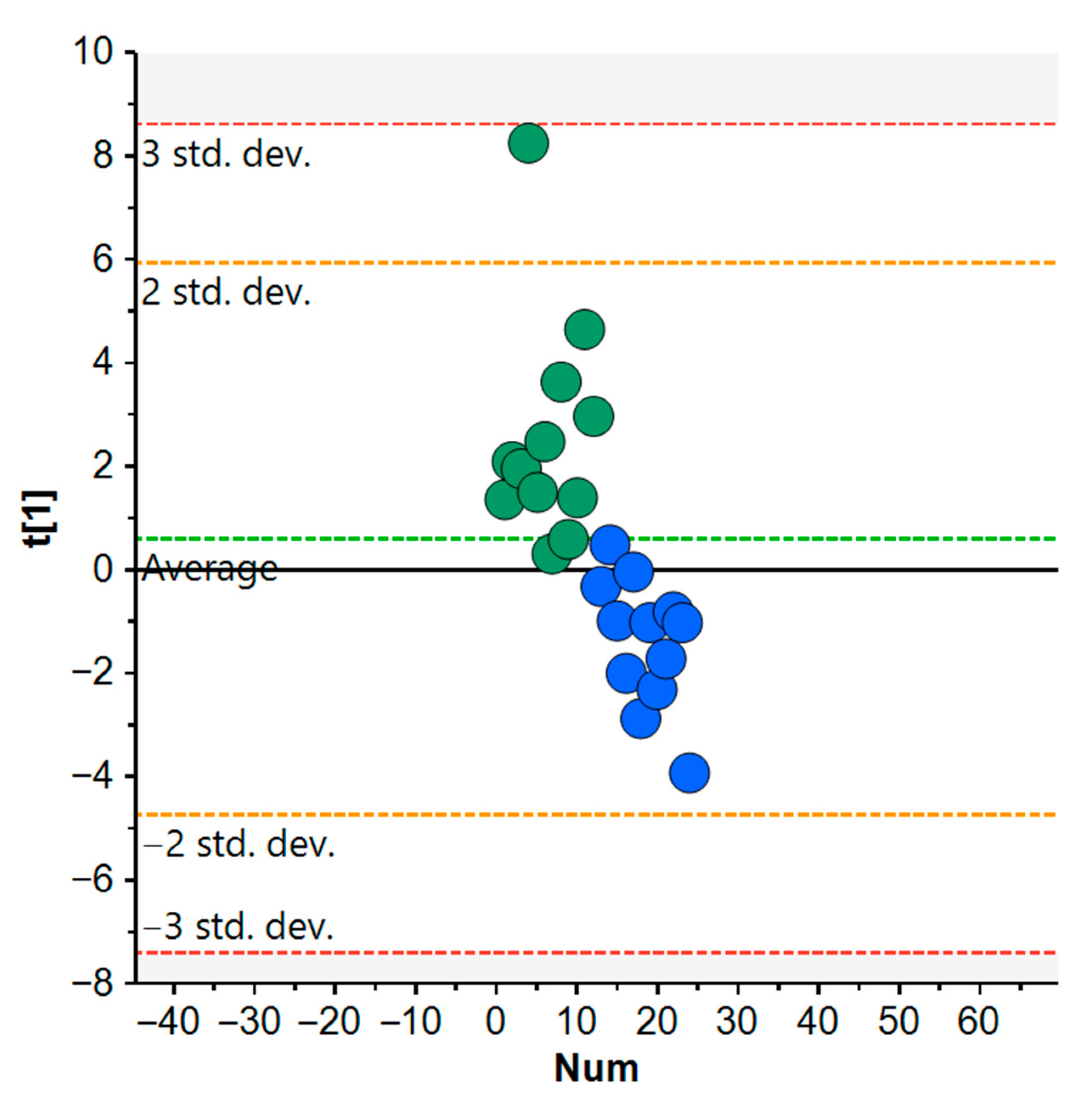
3.5. Comparative Effects of Organic vs. Non-Organic Diets on Metabolism
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 3-week | 3 weeks |
| FID | Free Induction Decay |
| IMNOD | Italian Mediterranean Non Organic Diet |
| IMOD | Italian Mediterranean Organic Diet |
| MIIA | Microbiota–Immune–Inflammation Axis |
| PCA | Principal Component Analysis |
| SCFAs | Short-Chain Fatty Acids |
| TCA | Tricarboxylic Acid |
References
- Tosti, V.; Bertozzi, B.; Fontana, L. Health Benefits of the Mediterranean Diet: Metabolic and Molecular Mechanisms. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2017, 73, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, G.; Pala, B.; Gualtieri, P.; Tocci, G.; La Placa, G.; Di Renzo, L. Adherence to Mediterranean Diet and Implications for Cardiovascular Risk Prevention. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasti, A.N.; Katsas, K.; Petsis, K.; Lambrinou, S.; Synodinou, K.D.; Kapetani, A.; Smart, K.L.; Nikolaki, M.D.; Halvatsiotis, P.; Triantafyllou, K.; et al. Is the Mediterranean Low Fodmap Diet Effective in Managing Irritable Bowel Syndrome Symptoms and Gut Microbiota? An Innovative Research Protocol. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aron-Wisnewsky, J.; Warmbrunn, M.V.; Nieuwdorp, M.; Clément, K. Metabolism and Metabolic Disorders and the Microbiome: The Intestinal Microbiota Associated With Obesity, Lipid Metabolism, and Metabolic Health—Pathophysiology and Therapeutic Strategies. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 573–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vineis, P.; Robinson, O.; Chadeau-Hyam, M.; Dehghan, A.; Mudway, I.; Dagnino, S. What Is New in the Exposome? Environ. Int. 2020, 143, 105887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Zhao, J. A Review on the Health Effects of Pesticides Based on Host Gut Microbiome and Metabolomics. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 632955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Yan, H.; Di, S.; Guo, C.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, S.; Gold, A.; Wang, Y.; Hu, M.; Wu, D.; et al. Mapping Pesticide-Induced Metabolic Alterations in Human Gut Bacteria. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 4355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuzaki, R.; Gunnigle, E.; Geissen, V.; Clarke, G.; Nagpal, J.; Cryan, J.F. Pesticide Exposure and the Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis. ISME J. 2023, 17, 1153–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueyama, J.; Hayashi, M.; Hirayama, M.; Nishiwaki, H.; Ito, M.; Saito, I.; Tsuboi, Y.; Isobe, T.; Ohno, K. Effects of Pesticide Intake on Gut Microbiota and Metabolites in Healthy Adults. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2023, 20, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poulia, K.A.; Bakaloudi, D.R.; Alevizou, M.; Papakonstantinou, E.; Zampelas, A.; Chourdakis, M. Impact of Organic Foods on Chronic Diseases and Health Perception: A Systematic Review of the Evidence. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2025, 79, 90–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barański, M.; Średnicka-Tober, D.; Rempelos, L.; Hasanaliyeva, G.; Gromadzka-Ostrowska, J.; Skwarło-Sońta, K.; Królikowski, T.; Rembiałkowska, E.; Hajslova, J.; Schulzova, V.; et al. Feed Composition Differences Resulting from Organic and Conventional Farming Practices Affect Physiological Parameters in Wistar Rats-Results from a Factorial, Two-Generation Dietary Intervention Trial. Nutrients 2021, 13, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigar, V.; Myers, S.; Oliver, C.; Arellano, J.; Robinson, S.; Leifert, C. A Systematic Review of Organic versus Conventional Food Consumption: Is There a Measurable Benefit on Human Health? Nutrients 2020, 12, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkaid, Y.; Hand, T.W. Role of the Microbiota in Immunity and Inflammation. Cell 2014, 157, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, D.; Liwinski, T.; Elinav, E. Interaction between Microbiota and Immunity in Health and Disease. Cell Res. 2020, 30, 492–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, A.; Hussain, F.H.N.; Nadeem Hussain, T.H.; Al Dweik, R.; Raza, A. Therapeutic Targeting of the Host-Microbiota-Immune Axis: Implications for Precision Health. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1570233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Renzo, L.; Frank, G.; Pala, B.; Cianci, R.; La Placa, G.; Raffaelli, G.; Palma, R.; Peluso, D.; De Lorenzo, A.; Gualtieri, P.; et al. Effects of Italian Mediterranean Organic Diet on the Gut Microbiota: A Pilot Comparative Study with Conventional Products and Free Diet. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbons, H.; O’Gorman, A.; Brennan, L. Metabolomics as a Tool in Nutritional Research. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2015, 26, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Lorenzo, A.; Noce, A.; Bigioni, M.; Calabrese, V.; Della Rocca, D.G.; Di Daniele, N.; Tozzo, C.; Di Renzo, L. The Effects of Italian Mediterranean Organic Diet (IMOD) on Health Status. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2010, 16, 814–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, A.; Kumar, R.; Kumar, V.; Yadav, M. Homocysteine, Vitamin B12 and Folate Level: Possible Risk Factors in the Progression of Chronic Heart and Kidney Disorders. Curr. Cardiol. Rev. 2023, 19, e090223213539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowda, G.A.N.; Raftery, D. (Eds.) NMR-Based Metabolomics: Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2019; Volume 2037, ISBN 978-1-4939-9689-6. [Google Scholar]
- Ansone, L.; Rovite, V.; Brīvība, M.; Jagare, L.; Pelcmane, L.; Borisova, D.; Thews, A.; Leiminger, R.; Kloviņš, J. Longitudinal NMR-Based Metabolomics Study Reveals How Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients Recover: Evidence of Dyslipidemia and Energy Metabolism Dysregulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobolev, A.P.; Ingallina, C.; Spano, M.; Di Matteo, G.; Mannina, L. NMR-Based Approaches in the Study of Foods. Molecules 2022, 27, 7906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wishart, D.S.; Guo, A.; Oler, E.; Wang, F.; Anjum, A.; Peters, H.; Dizon, R.; Sayeeda, Z.; Tian, S.; Lee, B.L.; et al. HMDB 5.0: The Human Metabolome Database for 2022. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D622–D631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurtado-Barroso, S.; Tresserra-Rimbau, A.; Vallverdú-Queralt, A.; Lamuela-Raventós, R.M. Organic Food and the Impact on Human Health. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 704–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barański, M.; Średnicka-Tober, D.; Volakakis, N.; Seal, C.; Sanderson, R.; Stewart, G.B.; Benbrook, C.; Biavati, B.; Markellou, E.; Giotis, C.; et al. Higher Antioxidant and Lower Cadmium Concentrations and Lower Incidence of Pesticide Residues in Organically Grown Crops: A Systematic Literature Review and Meta-Analyses. Br. J. Nutr. 2014, 112, 794–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bezabeh, T.; Capati, A.; Ijare, O.B. NMR-Based Urinary Metabolomics Applications. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 2037, 215–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudry, J.; Assmann, K.E.; Touvier, M.; Allès, B.; Seconda, L.; Latino-Martel, P.; Ezzedine, K.; Galan, P.; Hercberg, S.; Lairon, D.; et al. Association of Frequency of Organic Food Consumption With Cancer Risk: Findings From the NutriNet-Santé Prospective Cohort Study. JAMA Intern. Med. 2018, 178, 1597–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesse-Guyot, E.; Péneau, S.; Méjean, C.; Szabo de Edelenyi, F.; Galan, P.; Hercberg, S.; Lairon, D. Profiles of Organic Food Consumers in a Large Sample of French Adults: Results from the Nutrinet-Santé Cohort Study. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.; Baharlouei, P.; Koh, E.H.Y.; Pirvu, D.G.; Rehmani, R.; Arcos, M.; Puri, S. A Comprehensive Analysis of Organic Food: Evaluating Nutritional Value and Impact on Human Health. Foods 2024, 13, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-González, M.A.; Gea, A.; Ruiz-Canela, M. The Mediterranean Diet and Cardiovascular Health: A Critical Review. Circ Res 2019, 124, 779–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Remón, A.; Casas, R.; Tressserra-Rimbau, A.; Ros, E.; Martínez-González, M.A.; Fitó, M.; Corella, D.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Lamuela-Raventos, R.M.; Estruch, R. Polyphenol Intake from a Mediterranean Diet Decreases Inflammatory Biomarkers Related to Atherosclerosis: A Substudy of the PREDIMED Trial. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2017, 83, 114–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofi, F.; Martini, D.; Angelino, D.; Cairella, G.; Campanozzi, A.; Danesi, F.; Dinu, M.; Erba, D.; Iacoviello, L.; Pellegrini, N.; et al. Mediterranean Diet: Why a New Pyramid? An Updated Representation of the Traditional Mediterranean Diet by the Italian Society of Human Nutrition (SINU). Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2025, 35, 103919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardamone, E.; Iacoponi, F.; Di Benedetto, R.; Lorenzoni, G.; Di Nucci, A.; Zobec, F.; Gregori, D.; Silano, M. Adherence to Mediterranean Diet and Its Main Determinants in a Sample of Italian Adults: Results from the ARIANNA Cross-Sectional Survey. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1346455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, I.; Son, H.; Baek, J.H. Tricarboxylic Acid (TCA) Cycle Intermediates: Regulators of Immune Responses. Life 2021, 11, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Dwivedi, M.; Mahdi, A.A.; Khetrapal, C.L.; Bhandari, M. Broad Identification of Bacterial Type in Urinary Tract Infection Using 1H NMR Spectroscopy. J. Proteome Res. 2012, 11, 1844–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyles, L.; Fernández-Real, J.M.; Federici, M.; Serino, M.; Abbott, J.; Charpentier, J.; Heymes, C.; Luque, J.L.; Anthony, E.; Barton, R.H.; et al. Molecular Phenomics and Metagenomics of Hepatic Steatosis in Non-Diabetic Obese Women. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1070–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalbert, A.; Huybrechts, I.; Gunter, M.J. The Food Exposome. In Unraveling the Exposome: A Practical View; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 217–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jyoti; Dey, P. Mechanisms and Implications of the Gut Microbial Modulation of Intestinal Metabolic Processes. Npj Metab. Health Dis. 2025, 3, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreou, E.; Papaneophytou, C. Boosting Immunity Through Nutrition and Gut Health: A Narrative Review on Managing Allergies and Multimorbidity. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Di Renzo, L.; Cesaroni, S.; Frank, G.; Pala, B.; Cicero, D.O.; Gualtieri, P.; Petrella, G. Urinary 1H-NMR Metabolomics Highlights MIIA (Microbiota–Immune–Inflammation Axis) Activation by Organic Mediterranean Diet. Metabolites 2025, 15, 571. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15090571
Di Renzo L, Cesaroni S, Frank G, Pala B, Cicero DO, Gualtieri P, Petrella G. Urinary 1H-NMR Metabolomics Highlights MIIA (Microbiota–Immune–Inflammation Axis) Activation by Organic Mediterranean Diet. Metabolites. 2025; 15(9):571. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15090571
Chicago/Turabian StyleDi Renzo, Laura, Simona Cesaroni, Giulia Frank, Barbara Pala, Daniel Oscar Cicero, Paola Gualtieri, and Greta Petrella. 2025. "Urinary 1H-NMR Metabolomics Highlights MIIA (Microbiota–Immune–Inflammation Axis) Activation by Organic Mediterranean Diet" Metabolites 15, no. 9: 571. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15090571
APA StyleDi Renzo, L., Cesaroni, S., Frank, G., Pala, B., Cicero, D. O., Gualtieri, P., & Petrella, G. (2025). Urinary 1H-NMR Metabolomics Highlights MIIA (Microbiota–Immune–Inflammation Axis) Activation by Organic Mediterranean Diet. Metabolites, 15(9), 571. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15090571












