Whey Proteins and Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease Features: Evolving the Current Knowledge and Future Trends
Abstract
1. Introduction
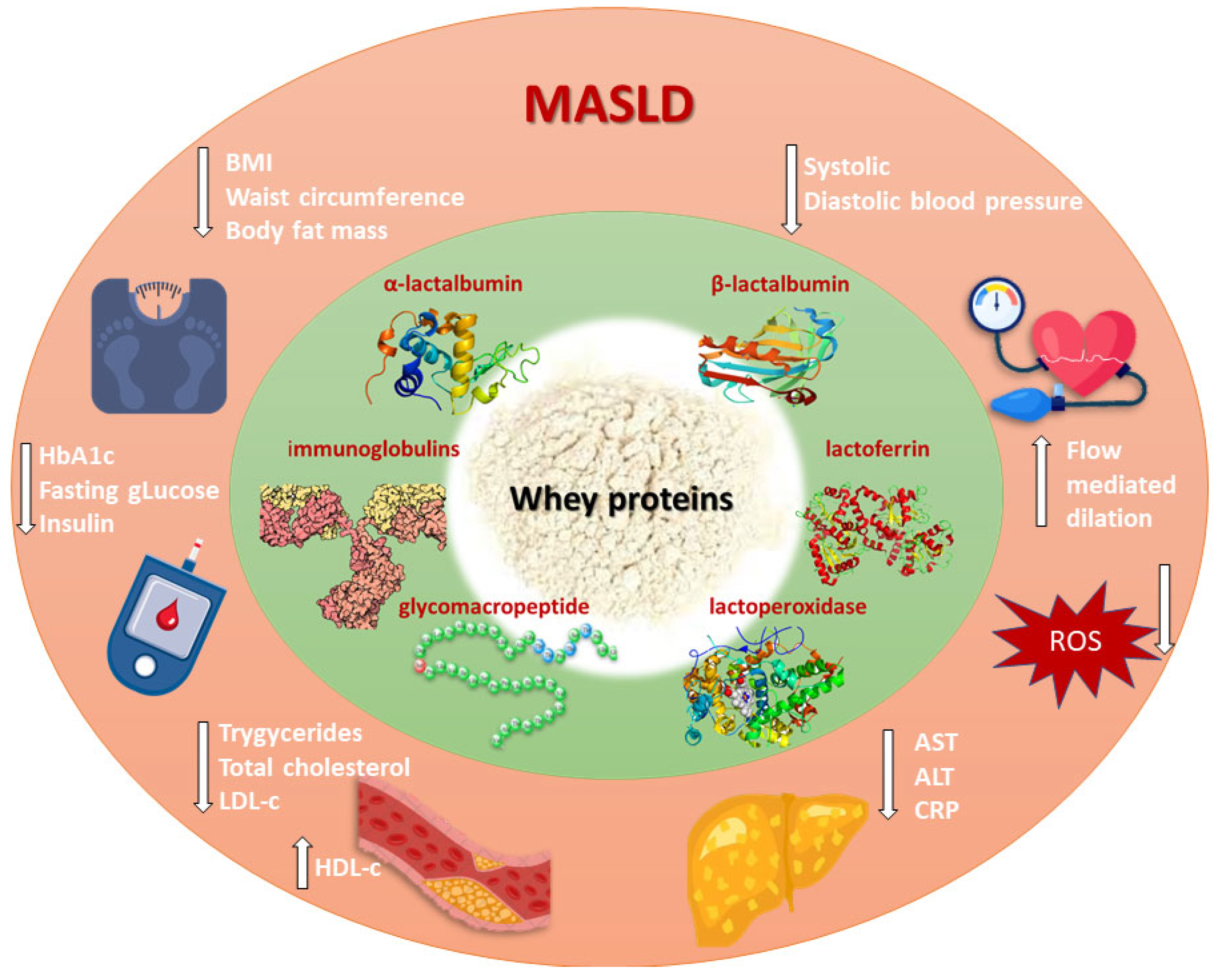
2. MASLD
3. Whey Proteins
4. Whey Proteins and Obesity
5. Whey Proteins and Hypertension
6. Whey Proteins and Glucose Metabolism
7. Whey Proteins and Lipid Metabolism
8. Whey Proteins and Liver Health
9. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feng, G.; Targher, G.; Byrne, C.D.; Yilmaz, Y.; Wong, V.W.-S.; Lesmana, C.R.A.; Adams, L.A.; Boursier, J.; Papatheodoridis, G.; El-Kassas, M.; et al. Global burden of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease, 2010 to 2021. JHEP Rep. 2024, 7, 101271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huttasch, M.; Roden, M.; Kahl, S. Obesity and MASLD: Is weight loss the (only) key to treat metabolic liver disease? Metabolism 2024, 157, 155937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gangireddy, V.G.R.; Pilkerton, C.; Xiang, J.; Tinajero, R.; Ashcraft, A.M. Hepatic Fibrosis and Ste-atosis in Metabolic Syndrome. J. Obes. Metab. Syndr. 2022, 31, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, L.; Targher, G.; Byrne, C.D.; Cao, Y.Y.; Zheng, M.H. Current status and future trends of the global burden of MASLD. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 35, 697–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, F.; Liu, J.; She, B.; Yang, H.; Ji, F.; Zhang, L. Global Trends and Inequalities of Liver Compli-cations Related to Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: An Analysis From 1990 to 2021. Liver Int. 2025, 45, e16120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, D.; Fan, J. Drug treatment for metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: Progress and direction. Chin. Med. J. 2024, 137, 2687–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Lau, H.C.; Yu, J. Pharmacological treatment for metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease and related disorders: Current and emerging therapeutic options. Pharmacol. Rev. 2025, 77, 100018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelhameed, F.; Mustafa, A.; Kite, C.; Lagojda, L.; Dallaway, A.; Than, N.N.; Kassi, E.; Kyrou, I.; Randeva, H.S. Gut Microbiota and Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD): Emerging Pathogenic Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications. Livers 2025, 5, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmukh, N.; Rao, P.S.; Sharma, H.; Kumar, M. Waste to nutrition: The evolution of whey, a byproduct to galactooligosaccharides production. Food Chem. Adv. 2024, 4, 100642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yiğit, A.; Bielska, P.; Cais-Sokolińska, D.; Samur, G. Whey proteins as a functional food: Health effects, functional properties, and applications in food. J. Am. Nutr. Assoc. 2023, 42, 758–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinella, M.E.; Lazarus, J.V.; Ratziu, V.; Francque, S.M.; Sanyal, A.J.; Kanwal, F.; Romero, D.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Anstee, Q.M.; Arab, P.; et al. A multisociety Delphi consensus statement on new fatty liver disease nomenclature. J. Hepatol. 2023, 79, 1542–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boccatonda, A.; Andreetto, L.; D’Ardes, D.; Cocco, G.; Rossi, I.; Vicari, S.; Schiavone, C.; Cipollone, F.; Guagnano, M.T. From NAFLD to MAFLD: Definition, Pathophysiological Basis and Cardiovascular Implications. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefan, N.; Yki-Järvinen, H.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A. Metabolic dysfunction-associated ste-atotic liver disease: Heterogeneous pathomechanisms and effectiveness of metabolism-based treatment. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2025, 13, 134–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Corey, K.E.; Lim, J.K. AGA Clinical Practice Update on Lifestyle Modification Using Diet and Exercise to Achieve Weight Loss in the Management of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Expert Review. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 912–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, M.T.; Noureddin, M.; Lim, J.K. AGA Clinical Practice Update: Diagnosis and Manage-ment of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Lean Individuals: Expert Review. Gastroenterology 2022, 163, 764–774.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minj, S.; Anand, S. Whey Proteins and Its Derivatives: Bioactivity, Functionality, and Cur-rent Applications. Dairy 2020, 1, 233–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luparelli, A.; Trisciuzzi, D.; Schirinzi, W.M.; Caputo, L.; Smiriglia, L.; Quintieri, L.; Nico-lotti, O.; Monaci, L. Whey Proteins and Bioactive Peptides: Advances in Production, Selection and Bioactivity Profiling. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchanan, D.; Martindale, W.; Romeih, E.; Hebishy, E. Recent advances in whey processing and valorisation: Technological and environmental perspectives. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2023, 76, 291–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- León-López, A.; Pérez-Marroquín, X.A.; Estrada-Fernández, A.G.; Campos-Lozada, G.; Morales-Peñaloza, A.; Campos-Montiel, R.G.; Aguirre-Álvarez, G. Milk Whey Hydrolysates as High Value-Added Natural Polymers: Functional Properties and Applications. Polymers 2022, 14, 1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smithers, G.W. Whey and whey proteins—From ‘gutter-to-gold’. Int. Dairy J. 2008, 18, 695–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Macuil, R.J.; Perez-Armendariz, B.; Cardoso-Ugarte, G.A.; Tolibia, S.E.M.; Benítez-Rojas, A.C. Recent Biotechnological Applications of Whey: Review and Perspectives. Fermentation 2025, 11, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solak, B.B.; Akin, N. Health benefits of whey protein: A review. J. Food Sci. Eng. 2012, 2, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Ma, Y.; Qi, X.; Tian, J.; Ma, Y.; Niu, T. α-Lactalbumin Peptide Asp-Gln-Trp Ameliorates Hepatic Steatosis and Oxidative Stress in Free Fatty Acids-Treated HepG2 Cells and High-Fat Diet-Induced NAFLD Mice by Activating the PPARα Pathway. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2023, 67, e2200499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zandona, E.; Blažić, M.; Režek Jambrak, A. Whey Utilization: Sustainable Uses and Environmental Approach. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2021, 59, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cava, E.; Padua, E.; Campaci, D.; Bernardi, M.; Muthanna, F.M.S.; Caprio, M.; Lombardo, M. Investigating the Health Implications of Whey Protein Consumption: A Narrative Review of Risks, Adverse Effects, and Associated Health Issues. Healthcare 2024, 12, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mykhalevych, A.; Buniowska-Olejnik, M.; Polishchuk, G.; Puchalski, C.; Kamińska-Dwórznicka, A.; Berthold-Pluta, A. The Influence of Whey Protein Isolate on the Quality Indicators of Acidophilic Ice Cream Based on Liquid Concentrates of Demineralized Whey. Foods 2024, 13, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhar, H.; Verma, S.; Dogra, S.; Katoch, S.; Vij, R.; Singh, G.; Sharma, M. Functional attributes of bioactive peptides of bovine milk origin and application of in silico approaches for peptide prediction and functional annotations. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 64, 9432–9454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abadía-García, L.; Castaño-Tostado, E.; Cardador-Martínez, A.; Martín-del-Campo, S.T.; Amaya-Llano, S.L. Production of ACE Inhibitory Peptides from Whey Proteins Modified by High Intensity Ultrasound Using Bromelain. Foods 2021, 10, 2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamad, E.M.; Taha, S.H.; Abou Dawood, A.G.; Sitohy, M.Z.; Abdel-Hamid, M. Protective effect of whey proteins against nonalcoholic fatty liver in rats. Lipids Health Dis. 2011, 10, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuda, K.; Nagano, N.; Nakazaki, K.; Katayama, D.; Tokunaga, W.; Okuda, K.; Shimizu, S.; Aoki, R.; Fuwa, K.; Shirai, K.; et al. Amelioration of Insulin Resistance by Whey Protein in a High-Fat Diet-Induced Pediatric Obesity Male Mouse Model. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansinhbhai, C.H.; Sakure, A.; Maurya, R.; Bishnoi, M.; Kondepudi, K.K.; Das, S.; Hati, S. Significance of whey protein hydrolysate on anti-oxidative, ACE-inhibitory and anti-inflammatory activities and release of peptides with biofunctionality: An in vitro and in silico approach. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 59, 2629–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydın, B.; Oğuz, A.; Şekeroğlu, V.; Şekeroğlu, Z.A. Whey protein protects liver mitochondrial function against oxidative stress in rats exposed to acrolein. Arch. Ind. Hyg. Toxicol. 2022, 73, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Fu, Z.; Li, X.; Hong, H.; Zhan, X.; Guo, X.; Luo, Y.; Tan, Y. Whey protein hydrolysate alleviated atherosclerosis and hepatic steatosis by regulating lipid metabolism in apoE-/- mice fed a Western diet. Food Res. Int. 2022, 157, 111419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakazaki, K.; Nagano, N.; Katayama, D.; Shimizu, S.; Matsuda, K.; Tokunaga, W.; Aoki, R.; Fuwa, K.; Morioka, I. Body Fat-Reducing Effects of Whey Protein Diet in Male Mice. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morifuji, M.; Sakai, K.; Sanbongi, C.; Sugiura, K. Dietary whey protein downregulates fatty acid synthesis in the liver, but upregulates it in skeletal muscle of exercise-trained rats. Nutrition 2005, 21, 1052–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregersen, S.; Bystrup, S.; Overgaard, A.; Jeppesen, P.B.; Sønderstgaard Thorup, A.C.; Jensen, E.; Hermansen, K. Effects of whey proteins on glucose metabolism in normal Wistar rats and Zucker diabetic fatty (ZDF) rats. Rev. Diabet. Stud. 2013, 10, 252–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shertzer, H.G.; Woods, S.E.; Krishan, M.; Genter, M.B.; Pearson, K.J. Dietary whey protein lowers the risk for metabolic disease in mice fed a high-fat diet. J. Nutr. 2011, 141, 582–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomovska, J.; Dimitrovska, G.; Presilski, S.; Velkova, K. Whey and its inhibition of liver enzymes. Biotechnol. Anim. Husb. 2016, 32, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nii, A.; Utsunomiya, T.; Shimada, M.; Ikegami, T.; Ishibashi, H.; Imura, S.; Morine, Y.; Ikemoto, T.; Sasaki, H.; Kawashima, A. Hydrolyzed whey peptide-based diet ameliorates hepatic is-chemia-reperfusion injury in the rat nonalcoholic fatty liver. Surg. Today 2014, 44, 2354–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Kriti, M.; Catanzaro, R.; Marotta, F.; Malvi, M.; Jain, A.; Verma, V.; Nagpal, R.; Tiwari, R.; Kumar, M. Deciphering the Gut–Liver Axis: A Comprehensive Scientific Review of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Livers 2024, 4, 435–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallianou, N.G.; Kounatidis, D.; Psallida, S.; Vythoulkas-Biotis, N.; Adamou, A.; Zachariadou, T.; Kargioti, S.; Karampela, I.; Dalamaga, M. NAFLD/MASLD and the Gut–Liver Axis: From Pathogenesis to Treatment Options. Metabolites 2024, 14, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnabl, B.; Damman, C.J.; Carr, R.M. Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease and the gut microbiome: Pathogenic insights and therapeutic innovations. J. Clin. Investig. 2025, 135, e186423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boscaini, S.; Skuse, P.; Nilaweera, K.N.; Cryan, J.F.; Cotter, P.D. The ‘Whey’to good health: Whey protein and its beneficial effect on metabolism, gut microbiota and mental health. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 133, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loomba, R.; Friedman, S.L.; Shulman, G.I. Mechanisms and disease consequences of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Cell 2021, 184, 2537–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambert, J.E.; Ramos-Roman, M.A.; Valdez, M.J.; Browning, J.D.; Rogers, T.; Parks, E.J. Weight loss in MASLD restores the balance of liver fatty acid sources. J. Clin. Investig. 2025, 135, e174233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koutoukidis, D.A.; Koshiaris, C.; Henry, J.A.; Noreik, M.; Morris, E.; Manoharan, I.; Tudor, K.; Bodenham, E.; Dunnigan, A.; Jebb, S.A.; et al. The effect of the magnitude of weight loss on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Metabolism 2021, 115, 154455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sepandi, M.; Samadi, M.; Shirvani, H.; Alimohamadi, Y.; Taghdir, M.; Goudarzi, F.; Akbarzadeh, I. Effect of whey protein supplementation on weight and body composition indicators: A meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2022, 50, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, P.E.; Alexander, D.D.; Perez, V. Effects of whey protein and resistance exercise on body composition: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2014, 33, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wirunsawanya, K.; Upala, S.; Jaruvongvanich, V.; Sanguankeo, A. Whey Protein Supplementation Improves Body Composition and Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Overweight and Obese Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2018, 37, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergia, R.E., 3rd; Hudson, J.L.; Campbell, W.W. Effect of whey protein supplementation on body composition changes in women: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutr. Rev. 2018, 76, 539–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frestedt, J.L.; Zenk, J.L.; Kuskowski, M.A.; Ward, L.S.; Bastian, E.D. A whey-protein supplement increases fat loss and spares lean muscle in obese subjects: A randomized human clinical study. Nutr. Metab. 2008, 5, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, M.; Imai, T.; Yamada, T.; Muramae, N.; Yoshimura, K.; Mitomo, Y.; Bando, H.; Sugawara, K.; Asahara, S.-I.; Hirota, Y.; et al. Effects of soy or whey protein on weight reduction in patients with obesity: An exploratory, three-arm, placebo-controlled, double-blind, randomized clinical trial. Clin. Nutr. Open Sci. 2024, 55, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badely, M.; Sepandi, M.; Samadi, M.; Parastouei, K.; Taghdir, M. The effect of whey protein on the components of metabolic syndrome in overweight and obese individuals; a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2019, 13, 3121–3131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flaim, C.; Kob, M.; Di Pierro, A.M.; Herrmann, M.; Lucchin, L. Effects of a whey protein supplementation on oxidative stress, body composition and glucose metabolism among over-weight people affected by diabetes mellitus or impaired fasting glucose: A pilot study. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2017, 50, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Wang, H.P.; Tong, X.; Li, Z.N.; Xu, J.Y.; Zhou, L.; Zhou, B.Y.; Qin, L.Q. Effect of whey protein on blood pressure in pre- and mildly hypertensive adults: A randomized controlled study. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 7, 1857–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Ling, C.; Liu, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Tong, X.; Hidayat, K.; Chen, M.; Chen, X.; Zhou, H.; et al. Effects of Whey Protein or Its Hydrolysate Supplements Combined with an Energy-Restricted Diet on Weight Loss: A Randomized Controlled Trial in Older Women. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabuco, H.C.G.; Tomeleri, C.M.; Sugihara Junior, P.; Fernandes, R.R.; Cavalcante, E.F.; Venturini, D.; Barbosa, D.S.; Silva, A.M.; Sardinha, L.B.; Cyrino, E.S. Effects of pre- or post-exercise whey protein supplementation on body fat and metabolic and inflammatory profile in pre-conditioned older women: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2019, 29, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakubowicz, D.; Froy, O. Biochemical and metabolic mechanisms by which dietary whey protein may combat obesity and Type 2 diabetes. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2013, 24, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Hypertension. 2023. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hypertension (accessed on 3 May 2025).
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Hypertension Cascade: Hypertension Prevalence, Treatment and Control Estimates Among US Adults Aged 18 Years and Older Applying the Criteria from the American College of Cardiology and American Heart Association’s 2017 Hypertension Guideline—NHANES 2017–March 2020. 2023. Available online: https://millionhearts.hhs.gov/data-reports/hypertension-prevalence.html (accessed on 3 May 2025).
- Gao, Z.; Deng, H.; Qin, B.; Bai, L.; Li, J.; Zhang, J. Impact of hypertension on liver fibrosis in pa-tients with metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease. Front. Med. 2025, 12, 1539283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirovski, G.; Schacherer, D.; Wobser, H.; Huber, H.; Niessen, C.; Beer, K.; Schoelmerich, J.; Hellerbrand, C. Prevalence of ultrasound-diagnosed non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in a hospital cohort and its association with anthropometric, biochemical and sonographic characteristics. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2010, 48, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golabi, P.; Stepanova, M.; Pham, H.T.; Cable, R.; Rafiq, N.; Bush, H.; Gogoll, T.; Younossi, Z.M. Non-alcoholic Steatofibrosis (Nasf) can independently predict mortality in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (Nafld). BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2018, 5, e000198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniele, A.; Lucas, S.J.E.; Rendeiro, C. Variability of flow-mediated dilation across lower and upper limb conduit arteries. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2024, 124, 3265–3278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fekete, Á.A.; Giromini, C.; Chatzidiakou, Y.; Givens, D.I.; Lovegrove, J.A. Whey protein lowers blood pressure and improves endothelial function and lipid biomarkers in adults with prehypertension and mild hypertension: Results from the chronic Whey2Go randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 104, 1534–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Son, K.C.; Te Nijenhuis-Noort, L.C.; Boone, S.C.; Mook-Kanamori, D.O.; Holleboom, A.G.; Roos, P.R.; Lamb, H.J.; Alblas, G.; Coenraad, M.J.; Rosendaal, F.R.; et al. Prevalence of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) in a middle-aged population with overweight and normal liver enzymes, and diagnostic accuracy of noninvasive proxies. Medicine 2024, 103, e34934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahavorgar, A.; Vafa, M.; Shidfar, F.; Gohari, M.; Heydari, I. Beneficial effects of whey protein preloads on some cardiovascular diseases risk factors of overweight and obese men are stronger than soy protein preloads–A randomized clinical trial. J. Nutr. Intermed. Metab. 2015, 2, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vajdi, M.; Musazadeh, V.; Zareei, M.; Adeli, S.; Karimi, A.; Hojjati, A.; Darzi, M.; Shoorei, H.; Abbasalizad Farhangi, M. The effects of whey protein on blood pressure: A systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2023, 33, 1633–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Cheng, F.; He, J.; Xu, T.; Zhang, X.; Wan, S.; Qi, J.; He, J.; Chen, F.; Luo, J.; et al. Effects of high-quality protein supplementation on cardiovascular risk factors in individuals with metabolic diseases: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Clin. Nutr. 2024, 43, 1740–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, B.; Athira, S.; Sharma, R.; Kumar, R.; Sarkar, P. Bioactive Peptides from Whey Proteins. In Whey Proteins; Deeth, H.C., Bansal, N., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 519–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messerli, F.H.; Bangalore, S.; Bavishi, C.; Rimoldi, S.F. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors in Hypertension: To Use or Not to Use? J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 71, 1474–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leith, D.; Lin, Y.Y.; Brennan, P. Metabolic Dysfunction-associated Steatotic Liver Disease and Type 2 Diabetes: A Deadly Synergy. TouchREVIEWS Endocrinol. 2024, 20, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrera, F.; Uribe, J.; Olvares, N.; Huerta, P.; Cabrera, D.; Romero-Gómez, M. The Janus of a disease: Diabetes and metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease. Ann. Hepatol. 2024, 29, 101501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogueira, J.P.; Cusi, K. Role of Insulin Resistance in the Development of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in People With Type 2 Diabetes: From Bench to Patient Care. Diabetes Spectr. 2024, 37, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gancheva, S.; Roden, M.; Castera, L. Diabetes as a risk factor for MASH progression. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2024, 217, 111846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amirani, E.; Milajerdi, A.; Reiner, Ž.; Mirzaei, H.; Mansournia, M.A.; Asemi, Z. Effects of whey protein intake on glycemic control and serum lipoproteins in patients with metabolic syndrome and related conditions: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled clinical trials. Lipids Health Dis. 2020, 19, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salimi, Z.; Asadi, M.; Mansoori, A. The Effect of Whey Protein Consumption on Postprandial Glucose, Insulin and Incretin Responses in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Acute-Term Controlled Clinical Trials. J. Nutr. Food Secur. 2025, 10, 178–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zumbro, E.L.; Rao, M.; Balcom-Luker, S.; Broughton, K.S.; LeMieux, M.J. Whey Protein Supple-mentation Improves the Glycemic Response and May Reduce Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Related Biomarkers in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS). Nutrients 2021, 13, 2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, G.T.; Lira, F.S.; Rosa, J.C.; de Oliveira, E.P.; Oyama, L.M.; Santos, R.V.; Pimentel, G.D. Dietary whey protein lessens several risk factors for metabolic diseases: A review. Lipids Health Dis. 2012, 11, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ang, T.; Mason, S.A.; Dao, G.M.; Bruce, C.R.; Kowalski, G.M. The impact of a single dose of whey protein on glucose flux and metabolite profiles in normoglycemic males: Insights into glucagon and insulin biology. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 325, E688–E699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carli, F.; Della Pepa, G.; Sabatini, S.; Vidal Puig, A.; Gastaldelli, A. Lipid metabolism in MASLD and MASH: From mechanism to the clinic. JHEP Rep. 2024, 6, 101185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bril, F.; Berg, G.; Barchuk, M.; Nogueira, J.P. Practical Approaches to Managing Dyslipidemia in Patients With Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease. J. Lipid Atheroscler. 2025, 14, 5–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Liu, Y.; Ma, X.; Guo, X. The association between non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio and hepatic steatosis and liver fibrosis among US adults based on NHANES. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 6527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurevitz, C.; Chen, L.; Muntner, P.; Rosenson, R. Hypertriglyceridemia and multi-organ disease among US adults. JACC Adv. 2024, 3, 100932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pustjens, J.; van Kleef, L.A.; Janssen, H.L.A.; de Knegt, R.J.; Brouwer, W.P. Differential prevalence and prognostic value of metabolic syndrome components among patients with MASLD. JHEP Rep. 2024, 6, 101193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurevitz, C.; Rosenson, R.S. Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease, Hypertriglyceridemia and Cardiovascular Risk. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gataa, I.S.; Abdullah, Z.; González Cabrera, M.V.; RenukaJyothi, S.; Verma, S.; Arora, I.; Monsi, M.; Muzammil, K.; Zainul, R. Impact of whey protein on lipid profiles: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2025, 35, 103858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prokopidis, K.; Morgan, P.T.; Veronese, N.; Morwani-Mangnani, J.; Triantafyllidis, K.K.; Kechagias, K.S.; Roberts, J.; Hurst, C.; Stevenson, E.; Vlachopoulos, D.; et al. The effects of whey protein supplementation on indices of cardiometabolic health: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Clin. Nutr. 2025, 44, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.W.; Tong, X.; Wan, Z.; Wang, Y.; Qin, L.Q.; Szeto, I.M. Effect of whey protein on blood lipid profiles: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 70, 879–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bortolotti, M.; Maiolo, E.; Corazza, M.; Van Dijke, E.; Schneiter, P.; Boss, A.; Carrel, G.; Giusti, V.; Lê, K.A.; Quo Chong, D.G.; et al. Effects of a whey protein supplementation on intrahepatocellular lipids in obese female patients. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 30, 494–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.T.; Chen, T.I.; Yin, S.C.; Huang, C.W.; Huang, J.F.; Lu, S.N.; Yeh, M.L.; Huang, C.F.; Dai, C.Y.; Chen, Y.W.; et al. Prevalence, proportions of elevated liver enzyme levels, and long-term cardiometabolic mortality of patients with metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 39, 1939–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.; Sechi, L.A.; Navarese, E.P.; Casu, G.; Vidili, G. Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease and cardiovascular risk: A comprehensive review. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2024, 23, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.J.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, Y. Association of Hematological Biomarkers of Inflammation with 10-Year Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events and All-Cause Mortality in Patients with Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: The ARIC Study. J. Inflamm. Res. 2024, 17, 4247–4256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, S.U.; Yoon, J.H. High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein Levels in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD), Metabolic Alcohol-Associated Liver Disease (MetALD), and Alcoholic Liver Disease (ALD) with Metabolic Dysfunction. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Lee, H.S.; Ahn, S.B.; Kwon, Y.J. Dairy protein intake is inversely related to development of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 5252–5260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarcella, M.; Scarpellini, E.; Ascani, A.; Commissari, R.; Scorcella, C.; Zanetti, M.; Parisi, A.; Monti, R.; Milic, N.; Donati, A.; et al. Effect of Whey Proteins on Malnutrition and Extubating Time of Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients. Nutrients 2022, 14, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.B.; Park, H.S.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, H.S.; Park, J.J. Does whey protein supplementation during resistance exercise have additional benefits for decreasing hepatic fat content? J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2023, 20, 217783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chitapanarux, T.; Tienboon, P.; Pojchamarnwiputh, S.; Leelarungrayub, D. Open-labeled pilot study of cysteine-rich whey protein isolate supplementation for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis patients. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2009, 24, 1045–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyssy, L.A.; Mui, R.; Kisaka, J. Hepatotoxic Effects of Whey Protein Supplementation. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 117, S1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gürgen, S.G.; Yücel, A.T.; Karakuş, A.Ç.; Çeçen, D.; Özen, G.; Koçtürk, S. Usage of whey protein may cause liver damage via inflammatory and apoptotic responses. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2015, 34, 769–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deminice, R.; Comparotto, H.; Jordao, A.A. Whey protein supplementation increases methionine intake but not homocysteine plasma concentration in rats. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2015, 40, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunes, R.; Silva, P.; Alves, J.; Stefani, G.; Petry, M.; Rhoden, C.; Dal Lago, P.; Schneider, C.D. Effects of resistance training associated with whey protein supplementation on liver and kidney biomarkers in rats. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2013, 38, 1166–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, J.M.; Mikušová, L.; Verlaan, S.; Bautmans, I.; Brandt, K.; Donini, L.M.; Maggio, M.; Mets, T.; Wijers, S.L.J.; Garthoff, J.A.; et al. Safety and tolerability of 6-month supplementation with a vitamin D, calcium and leucine-enriched whey protein medical nutrition drink in sarcopenic older adults. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2020, 32, 1501–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hattori, C.M.; Tiselius, H.G.; Heilberg, I.P. Whey protein and albumin effects upon urinary risk factors for stone formation. Urolithiasis 2017, 45, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Phenotype | Clinical Characteristics |
|---|---|
| MASLD with a strong hepatic genetic component | − or + Insulin resistance 1 |
| − Adiposity | |
| − Dyslipidemia | |
| + Type 2 diabetes | |
| − or +Cardiovascular disease 2 | |
| + or ++ MASH | |
| + or ++ Fibrosis | |
| MASLD with a strong metabolic component related to hepatic de novo lipogenesis | ++ Insulin resistance |
| ++ Adiposity | |
| +++ Dyslipidemia | |
| ++ Type 2 diabetes | |
| ++ Cardiovascular disease | |
| + MASH | |
| + Fibrosis | |
| MASLD with a strong metabolic component related to adipose tissue dysfunction | ++ Insulin resistance |
| − Adiposity | |
| + Dyslipidemia | |
| ++ Type 2 diabetes | |
| ++ Cardiovascular disease | |
| + MASH | |
| + Fibrosis |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Milanović, M.; Milošević, N.; Ružić, M.; Abenavoli, L.; Milić, N. Whey Proteins and Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease Features: Evolving the Current Knowledge and Future Trends. Metabolites 2025, 15, 516. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15080516
Milanović M, Milošević N, Ružić M, Abenavoli L, Milić N. Whey Proteins and Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease Features: Evolving the Current Knowledge and Future Trends. Metabolites. 2025; 15(8):516. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15080516
Chicago/Turabian StyleMilanović, Maja, Nataša Milošević, Maja Ružić, Ludovico Abenavoli, and Nataša Milić. 2025. "Whey Proteins and Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease Features: Evolving the Current Knowledge and Future Trends" Metabolites 15, no. 8: 516. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15080516
APA StyleMilanović, M., Milošević, N., Ružić, M., Abenavoli, L., & Milić, N. (2025). Whey Proteins and Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease Features: Evolving the Current Knowledge and Future Trends. Metabolites, 15(8), 516. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15080516








